Abstract
Thorectandra choanoides (CMB-01889) was prioritized as a source of promising new chemistry from a library of 960 southern Australian marine sponge extracts, using a global natural products social (GNPS) molecular networking approach. The sponge was collected at a depth of 45 m. Chemical fractionation followed by detailed spectroscopic analysis led to the discovery of a new tryptophan-derived alkaloid, thorectandrin A (1), with the GNPS cluster revealing a halo of related alkaloids 1a–1n. In considering biosynthetic origins, we propose that Thorectandra choanoides (CMB-01889) produces four well-known alkaloids, 6-bromo-1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin (2), 6-bromoaplysinopsin (3), aplysinopsin (4), and 1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin (10), all of which are susceptible to processing by a putative indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-like (IDO) enzyme to 1a–1n. Where the 1′,8-dihydroalkaloids 2 and 10 are fully transformed to stable ring-opened thorectandrins 1 and 1a–1b, and 1h–1j, respectively, the conjugated precursors 3 and 4 are transformed to highly reactive Michael acceptors that during extraction and handling undergo complete transformation to artifacts 1c–1g, and 1k–1n, respectively. Knowledge of the susceptibility of aplysinopsins as substrates for IDOs, and the relative reactivity of Michael acceptor transformation products, informs our understanding of the pharmaceutical potential of this vintage marine pharmacophore. For example, the cancer tissue specificity of IDOs could be exploited for an immunotherapeutic response, with aplysinopsins transforming in situ to Michael acceptor thorectandrins, which covalently bind and inhibit the enzyme.
1. Introduction
Marine sponges of the genus Thorectandra are a rich source of structurally diverse metabolites with novel scaffolds. Examples include, the 1988 report of the sesterterpenes manoalide 25-monoacetate and thorectolide 25-monoacetate from Thorectandra excavates collected near Darwin, Australia [1]; the 1995 report of a furanoditerpene from a Southern Australian Thorectandra choanoides [2]; and the 2001 and 2002 reports of sesterterpenes thorectandoles A–E from a Palauan Thorectandra sp. [3,4]. In addition to terpenes, many alkaloids were also reported from Thorectandra sp., including β-carboline alkaloids (i.e., thorectandramine [5], 1-deoxysecofascaplysin A, and fascaplysin [6]), tryptophan alkaloids (i.e., 1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin and (1H-indole-3-yl)acetic acid [7]), and brominated tryptophan alkaloids (i.e., 6-bromo-1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin, 6-bromo-1′-hydroxy-1′,8-dihydro-aplysinopsin, 6-bromo-1′-methoxy-1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin, (–)-5-bromo-N,N-dimethyl-tryptophan, and (+)-5-bromohypaphorine [7]).
Recently, a GNPS molecular networking analysis was employed on 960 Southern Australian marine sponges, to map the chemical space of natural products, which resulted in the isolation of rare indolo-imidazole alkaloids, trachycladindoles H–M [8], new sesterterpene butenolides, cacolides A–L and cacolic acids A–C [9], and new sesquiterpenes, dysidealactams A–F, and dysidealactones A–B [10]. In this report, we present the discovery of a new class of tryptophan-derived alkaloid, thorectandrin A (1) (Figure 1), from a Great Australian Bight specimen of Thorectandra choanoides, prioritized for chemical investigation, based on GNPS molecular networking analysis of the same library of Southern Australian sponges.
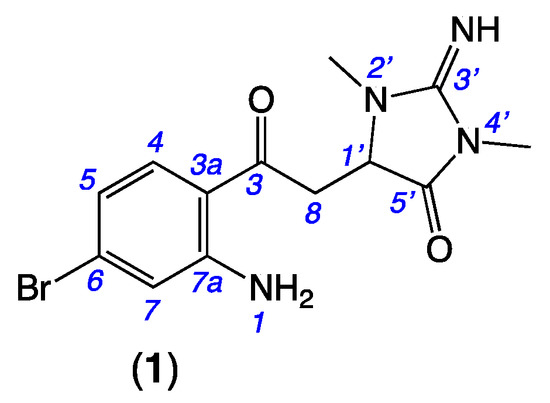
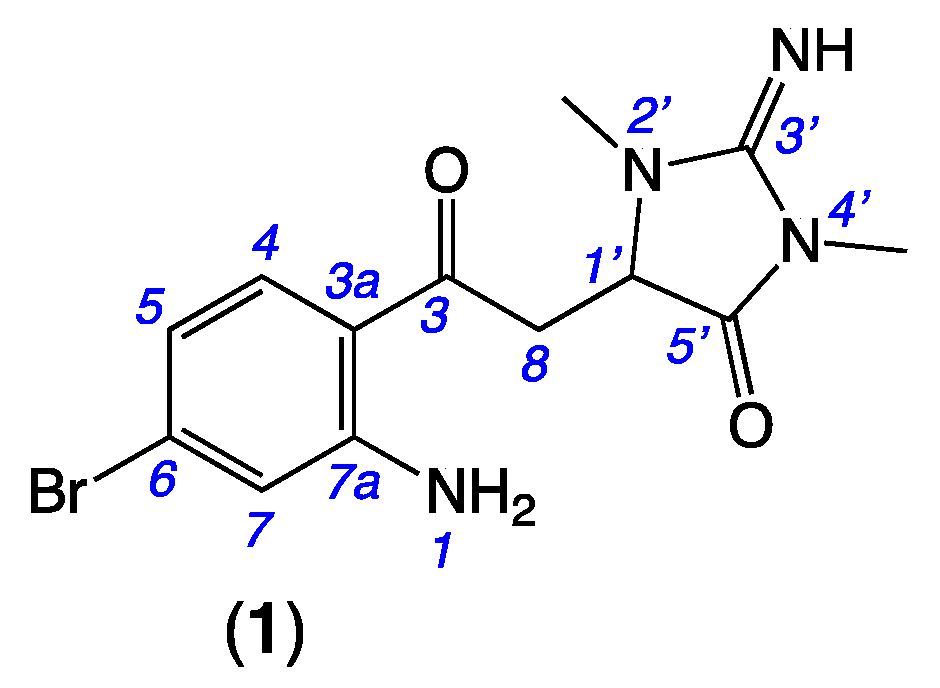
Figure 1.
Thorectandrin A (1).
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. GNPS Molecular Networking to Explore New Chemistry
To search for new marine natural products, 960 n-BuOH soluble partitions from the EtOH extracts of a library of Southern Australian marine sponges and 95 authentic standards (previously isolated from marine sponges) from the Capon lab were assembled and subjected to UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS analysis. The resulting data were used to create a consolidated GNPS molecular network (Figure S1). In this molecular network, we found a specific molecular cluster (Figure S2) associated with Thorectandra choanoides (CMB-01889) (collected in 1995 during deep water scientific trawling in the Great Australian Bight), which did not co-correlate with any metabolites found in the other 959 sponge extracts, or any of our authentic marine natural products. Following isolation, detailed spectroscopic analysis identified a new alkaloid scaffold, thorectandrin A (1) (Figure 1), while mass spectrometry (MS) data revealed molecular formulae for a host of structurally related analogues (1a–1n) in the same GNPS cluster. Note: All Thorectandra choanoides (CMB-01889) chemistry in this report are displayed as free bases, although all were isolated, and where appropriate, characterised as the trifluoroacetic acid salts.
2.2. Thorectandrin A (1)
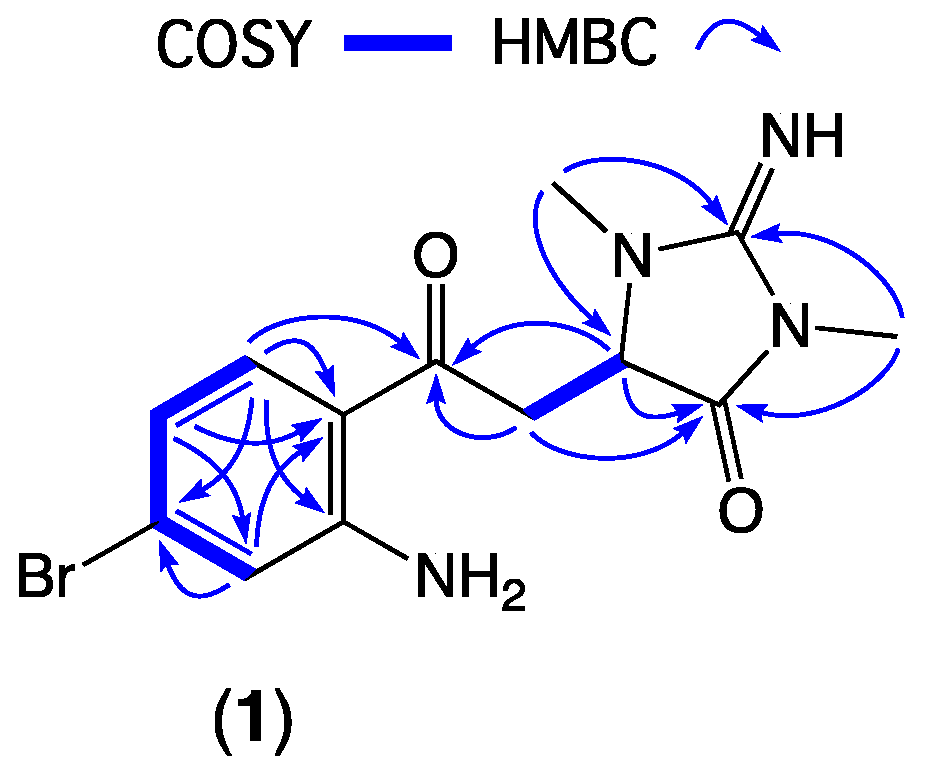
HRESI (+) MS analysis of 1 returned a molecular formula (C13H15BrN4O2, Δmmu +2.6) incorporating eight double-bond equivalents (DBE). The NMR (methanol-d4) data for 1 (Table 1, Figures S5–S10) revealed resonances attributed to a ketone (δC 197.8, C-3), two sp2 amido/imino carbonyl carbons (δC 160.3, C-3′ and 173.8, C-5′), and a 1,2,4-trisubstituted aromatic ring (δC 154.1, C-7a; 133.9, C-4, 131.1, C-6; 120.7, C-7; 119.4, C-5; 116.1, C-3a; δH 7.67, d, J = 8.7 Hz, H-4; 6.73, br d, J = 8.7 Hz, H-5 and 6.97, br s, H-7), accounting for seven DBE, and requiring that 1 incorporate an additional ring system. Further analysis of NMR data revealed resonances for two N-methyls (δH 3.09, s, 2′N-Me and 3.26, s, 4′N-Me) and a deshielded diastereotopic methylene-methine spin system (δH 3.94, dd, J = 19.0 and 3.5 Hz, H-8a; 3.67, dd, J = 19.0 and 3.9 Hz, H-8b; and 4.56, dd, J = 3.9 and 3.5 Hz, H-1′). HMBC correlations from 2′N-Me and 4′N-Me to a common C-3′ guanidino carbon; from 4′N-Me and H-1′ to a common carbonyl C-5′ and from 2′N-Me to C-1′ (δC 60.8) suggested the presence of a 2-imino-1,3-dimethylimidazolidin-4-one ring system, similar to that observed in the well-known Thorectandra metabolite aplysinopsin [11]. HMBC correlations from H-4, H-8a, H-8b, and H-1′ to C-3 confirmed that the aromatic ring was connected to the imidazolidinone ring, through a common carbon C-3, establishing the structure of thorectandrin A (1), as shown (Figure 2). Comparison of 1D and 2D NMR data of 1 with that of the known sponge metabolite 6-bromo-1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin (2) [7] (Figure 2) revealed the main differences as the disappearance of resonances for H-2/C-2 (δH 7.09, δC 124.8) in 2 and replacement of the resonance of an sp2 carbon C-3 (δC 106.5) in 2 with an α,β-unsaturated ketone (δC 197.8) in 1, consistent with a ring-opened analogue of 2.

Table 1.
NMR (600 MHz) data for thorectandrin A (1) in methanol-d4.
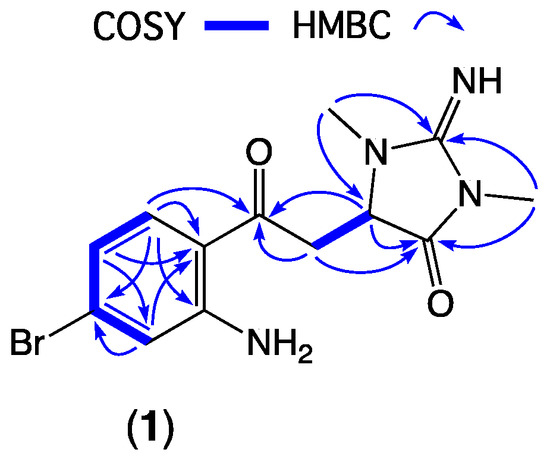
Figure 2.
Diagnostic 2D NMR correlations for thorectandrin A (1).
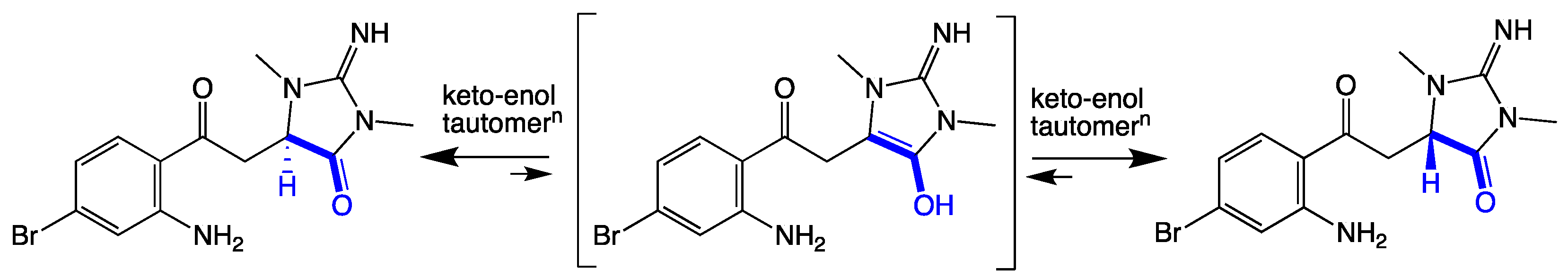
As thorectandrin A (1) did not exhibit a measurable [α]D or ECD spectrum (Figure S12), we propose it exists as a racemate, induced by a slow keto-enol tautomerization during long-term storage (~25 years) in EtOH (Scheme 1). That the proposed racemization is slow was evident when 1 did not incorporate deuterium, when stored in deuterated methanol for several days.
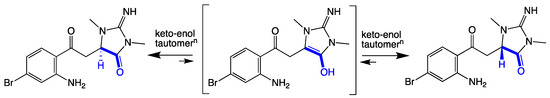
Scheme 1.
Keto-enol tautomerization of thorectandrin A (1).
Thorectandrin A (1) did not exhibit growth inhibitory activity against the Gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis (ATCC 6051), the Gram-negative Escherichia coli (ATCC 11775), the fungus Candida albicans (ATCC 10231), or human colorectal (SW620) and lung (NCI-H460) carcinoma cells, at concentrations up to 30 μM (Figures S13 and S14).
2.3. Plausible Biosynthetic Pathway
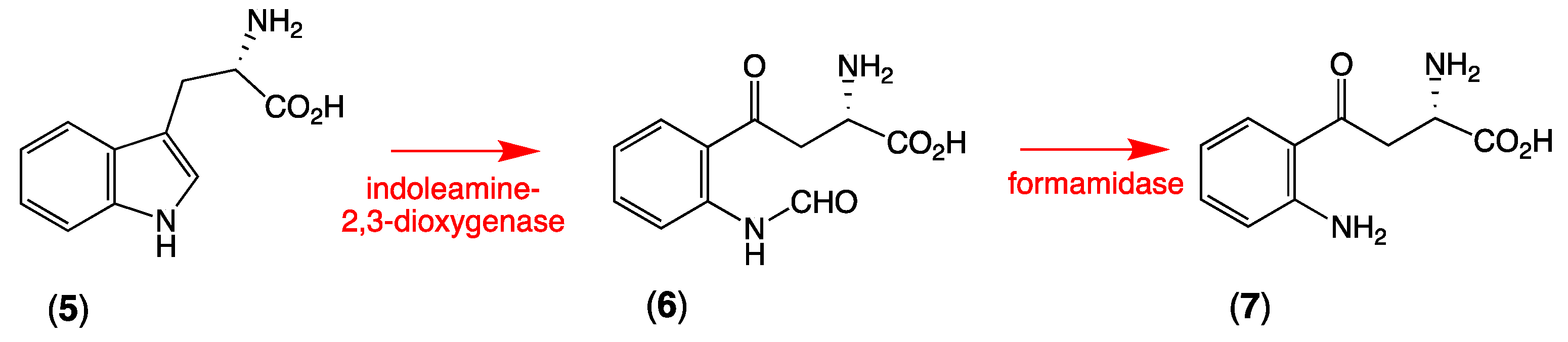
Aplysinopsins are tryptophan-derived marine natural products, which were isolated from many genera of sponges and scleractinian corals, as well as from one sea anemone and one nudibranch [11], the latter most likely a dietary input from nudibranches feeding on sponges. Typical exemplars include 6-bromoaplysinopsin (3) and aplysinopsin (4). In turning our attention to the likely biosynthesis of thorectandrin A (1), we considered the metabolic relationship between L-tryptophan (5), N-formyl-L-kynurenine (6), and L-kynurenine (7), and the fact that indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is known to convert 5 to 6, which undergoes facile hydrolysis by a formamidase to 7 (Scheme 2) [12].
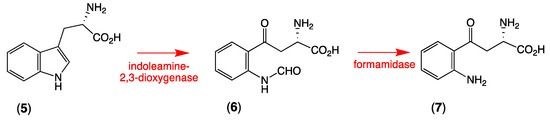
Scheme 2.
Biosynthetic conversion of L-tryptophan (5) to N-formyl-L-kynurenine (6) to L-kynurenine (7).
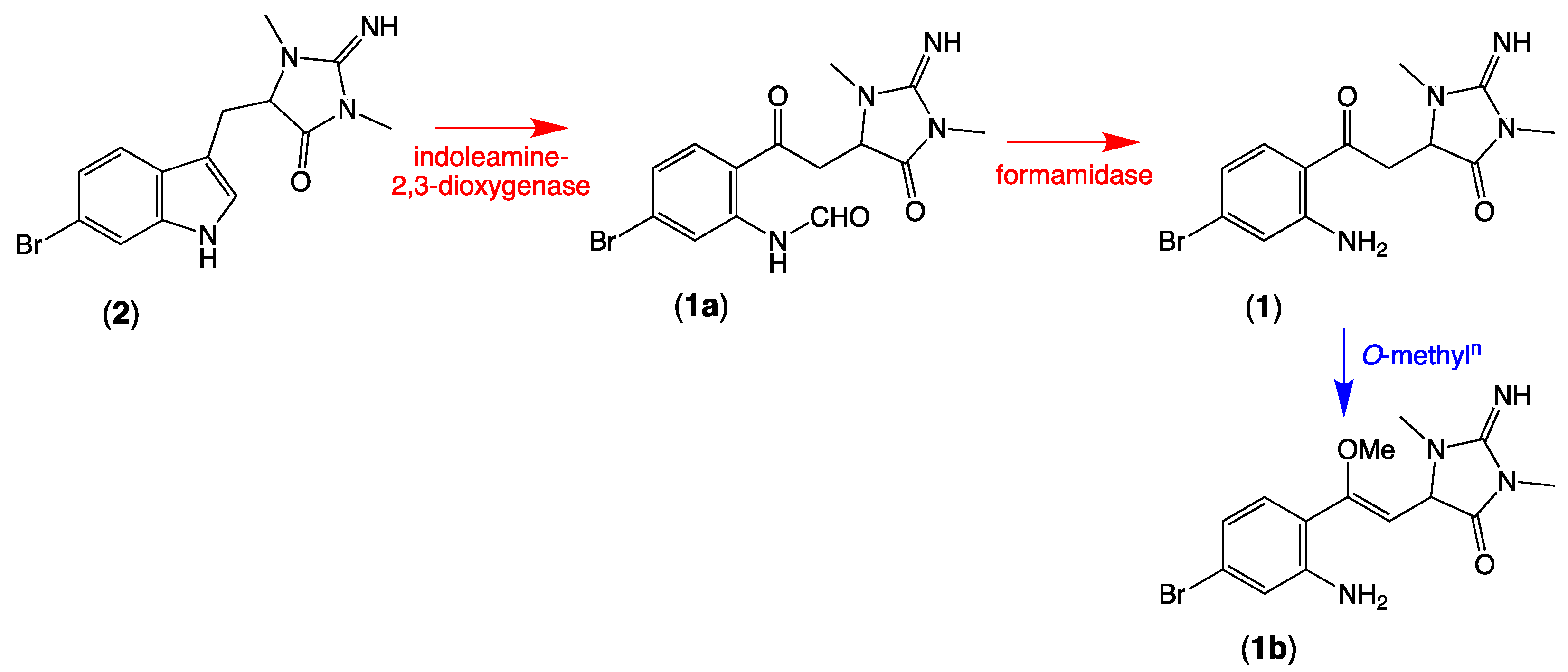
Inspired by this sequence of transformations, we hypothesised that a comparable indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-like enzyme in Thorectandra choanoides (CMB-01889) converts 6-bromo-1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin (2) to its ring-opened N-formyl derivative (1a), which is then rapidly hydrolyzed to thorectandrin A (1) (Scheme 3). Although 2 is reported as a sponge natural product [7], its absolute configuration (even enantiopurity) remains unassigned. Based on our experience, a possible challenge to assigning an absolute configuration to 2 might be enantiopurity, due to a propensity for keto-enol mediated epimerisation/racemisation.
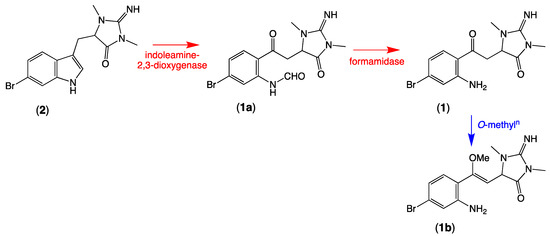
Scheme 3.
Possible biosynthetic link between 6-bromo-1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin (2), N-formyl thorectandrin A (1a), O-methylthorectandrin A (1b), and thorectandrin A (1).
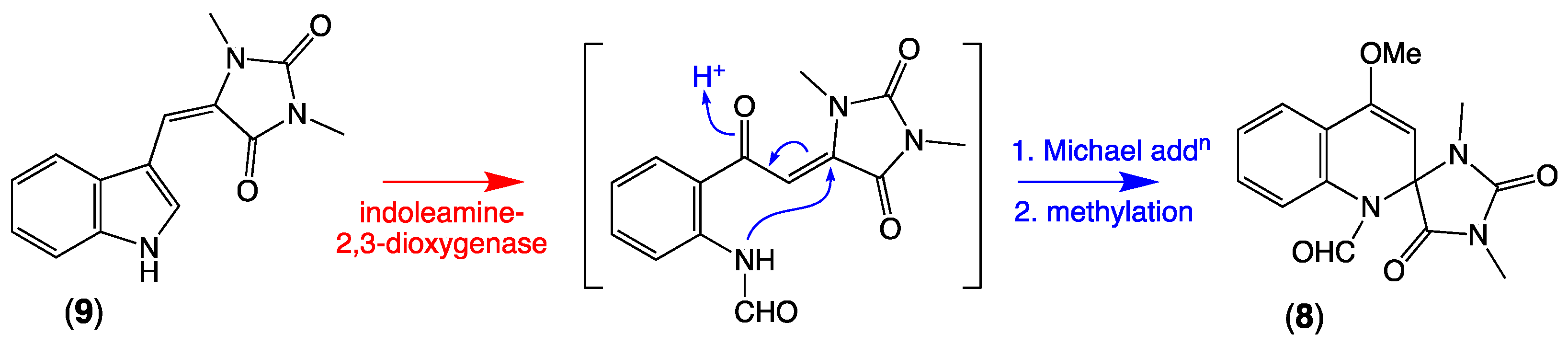
Armed with knowledge of the new thorectandrin scaffold and its likely biosynthetic relationship to the vintage aplysinopsin scaffold, we turned our attention to the literature and noted a 2015 report of racemic spiroreticulatine (8) from the South China Sea marine sponge Fascaplysinopsis reticulata [13], and a subsequent 2019 report from the same source of the known sponge alkaloid (Z)-3′-deimino-3′-oxoaplysinopsin (9), as a co-metabolite with 1b [14]. Although 8 was initially ascribed a plausible biosynthesis involving condensation of indole-3-carboxaldehyde and 1,3-dimethylhydantoin, this hypothesis seems highly improbable. A far more likely pathway would see ring opening of the indole heterocycle in the cometabolite 9, delivering a reactive Michael acceptor intermediate that undergoes non-stereoselective (enzyme or non-enzyme mediated) intramolecular Michael addition to racemic 8 (see Scheme 4).
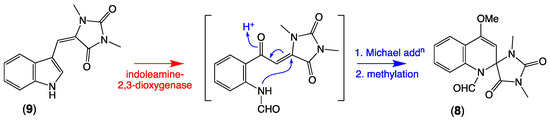
Scheme 4.
Possible biosynthetic link between (Z)-3′-deimino-3′-oxoaplysinopsin (9) and spiroreticulatine (8).
2.4. Other Thorectandrin Co-Metabolites
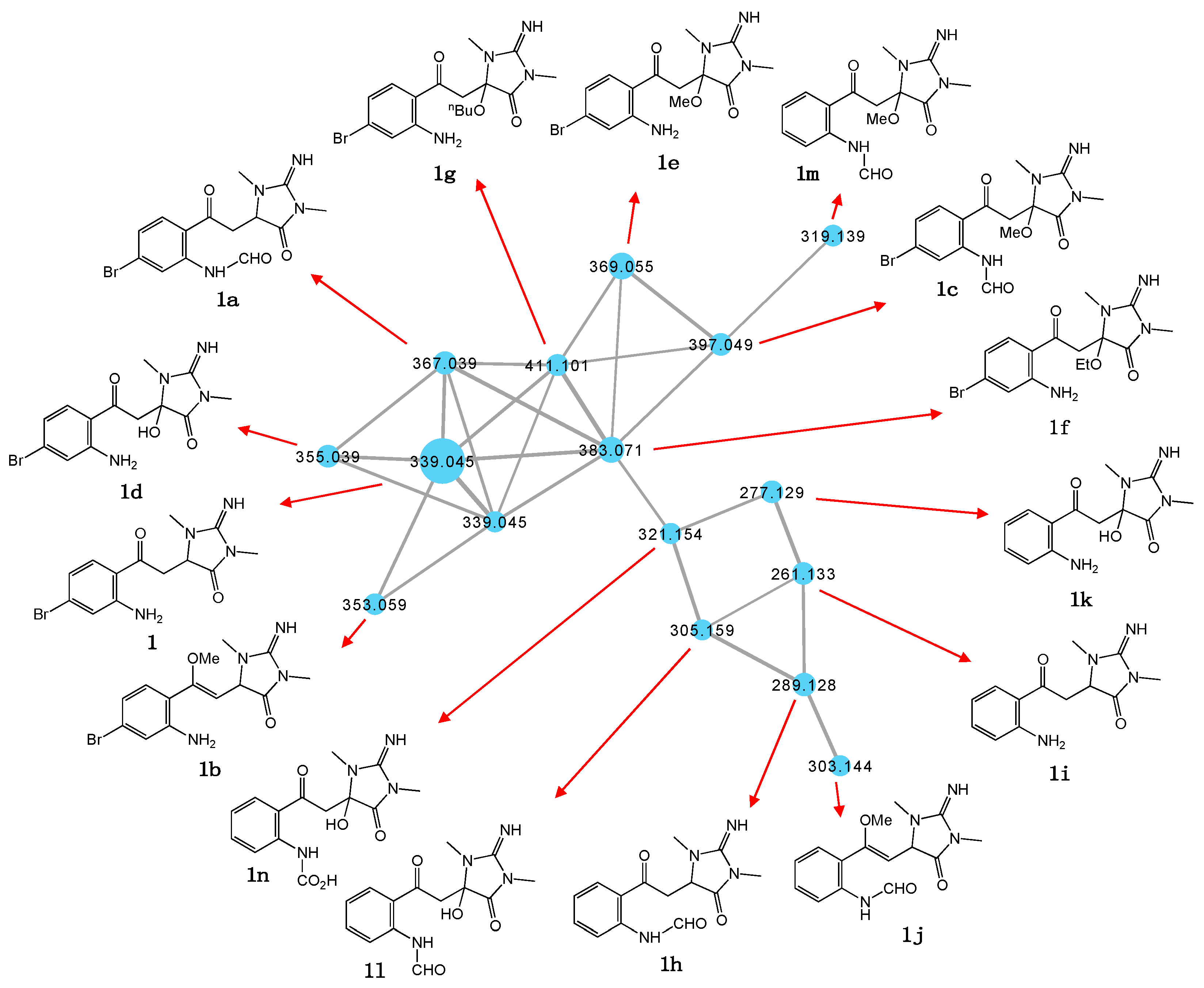
While the thorectandrin GNPS cluster revealed a number of related metabolites, due to low abundance and a lack of sponge biomass, it was not possible to isolate and acquire definitive spectroscopic data to secure unambiguous structure assignments. Notwithstanding, we did acquire molecular formulae for many minor compounds, and on the basis of these measurements and biosynthetic considerations we tentatively propose structures, as shown in Table 2 and Figure 3. For example, based on differences in MW and elemental composition with 1, we detected a node attributed to the hypothesized N-formyl 1a (M + H m/z 367, C14H15BrN4O3) and O-methyl 1b (M + H m/z 353, C14H17BrN4O2) (Scheme 3).

Table 2.
Molecular formulae of compounds within the thorectandrin GNPS cluster.
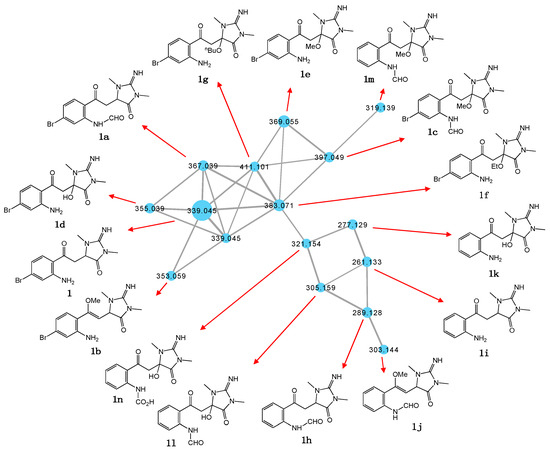
Figure 3.
Structures attributed to nodes in the thorectandrin GNPS cluster.
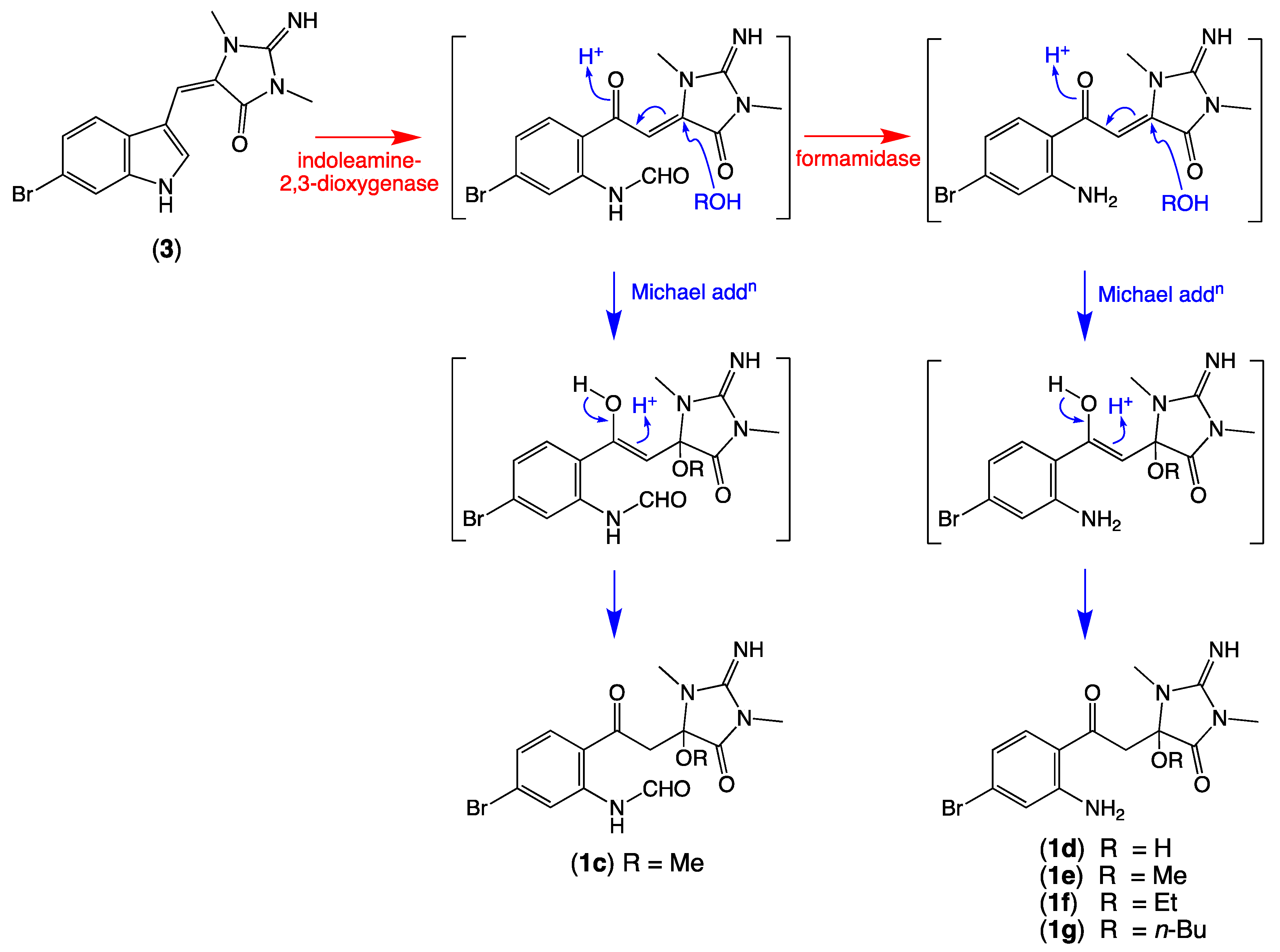
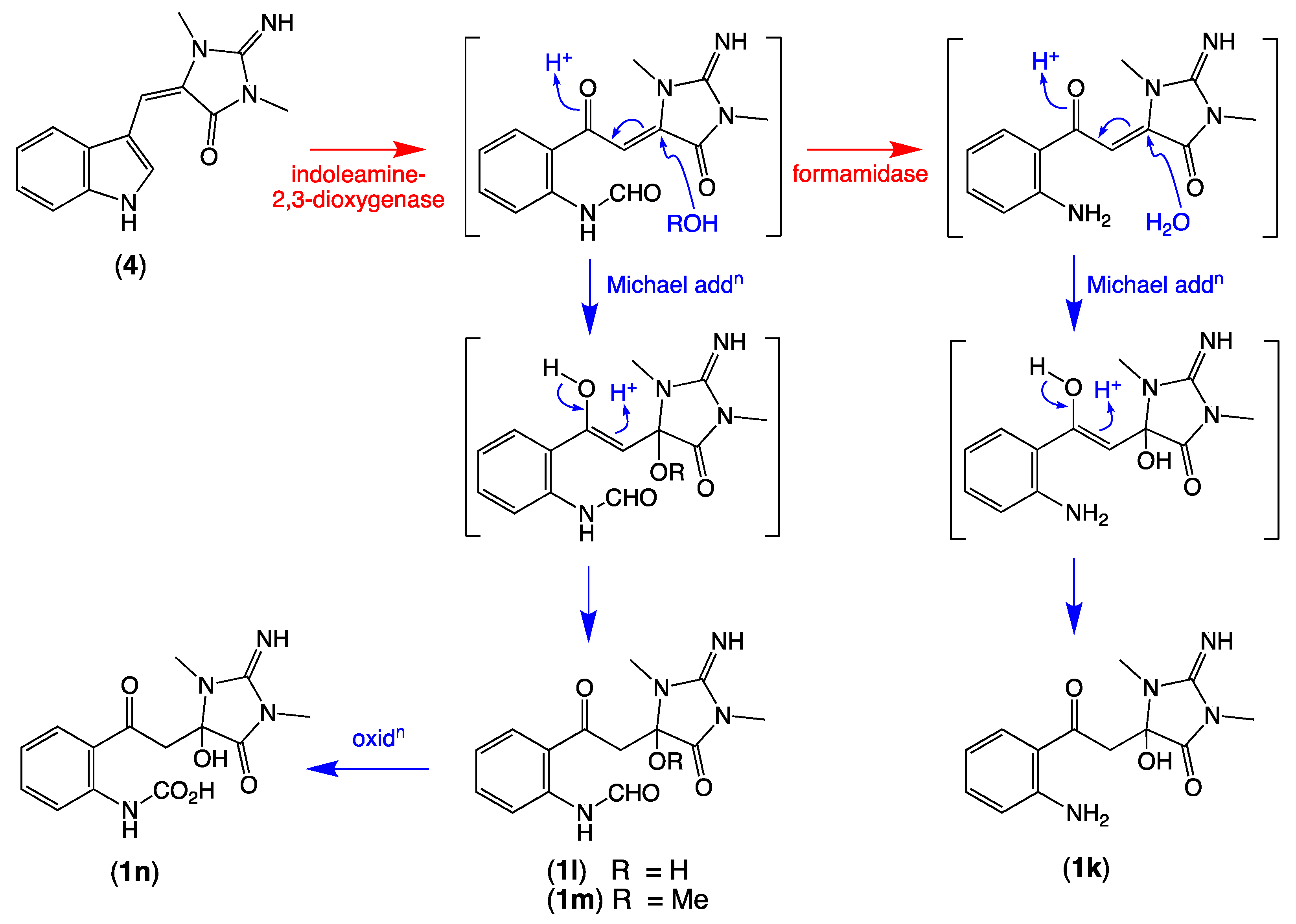
We also detected nodes that were tentatively attributed to a methanol (1c, M + H m/z 397, C15H17BrN4O4) adduct of 1a, and water (1d, M + H m/z 355, C13H15BrN4O3), methanol (1e, M + H m/z 369, C14H17BrN4O3), ethanol (1f, M + H m/z 383, C15H19BrN4O3), and n-butanol (1g, M + H m/z 411, C17H23BrN4O3) adducts of 1 (Table 2, Figure 3). While these adducts 1c–1g are believed to be solvolysis artifacts induced by long-term storage of Thorectandra choanoides (CMB-01889) in aqueous ethanol, followed by n-butanol partitioning and the use of methanol to dissolve dried extract, the absence of a rational solvolysis pathway from 1a to 1c, and 1 to 1d–1g, warranted consideration. We hypothesized that in addition to 6-bromo-1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin (2), Thorectandra choanoides (CMB-01889) produces 6-bromoaplysinopsin (3), which was comparably transformed by an indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-like enzyme to reactive Michael adducts (N-formyl-Δ1′−8-thorectandrin A and Δ1′−8-thorectandrin A), with both undergoing Michael addition solvolysis during storage, fractionation and handling, to 1c–1g (Scheme 5). A recent review highlights the prevalence of solvolysis adduct artifacts among marine natural products, including among imidazoles/imidazolones [15].
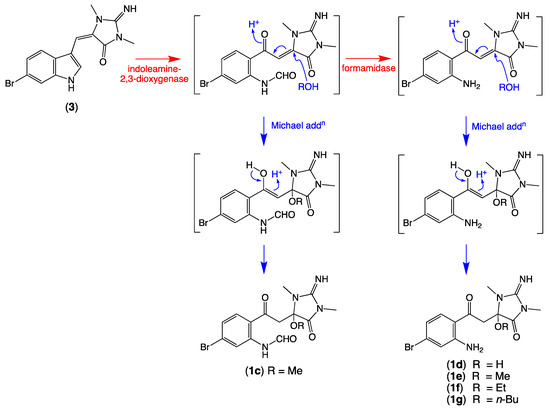
Scheme 5.
Possible biosynthetic link between 6-bromoaplysinopsin (3) and the solvolysis artifacts 1c–1g.
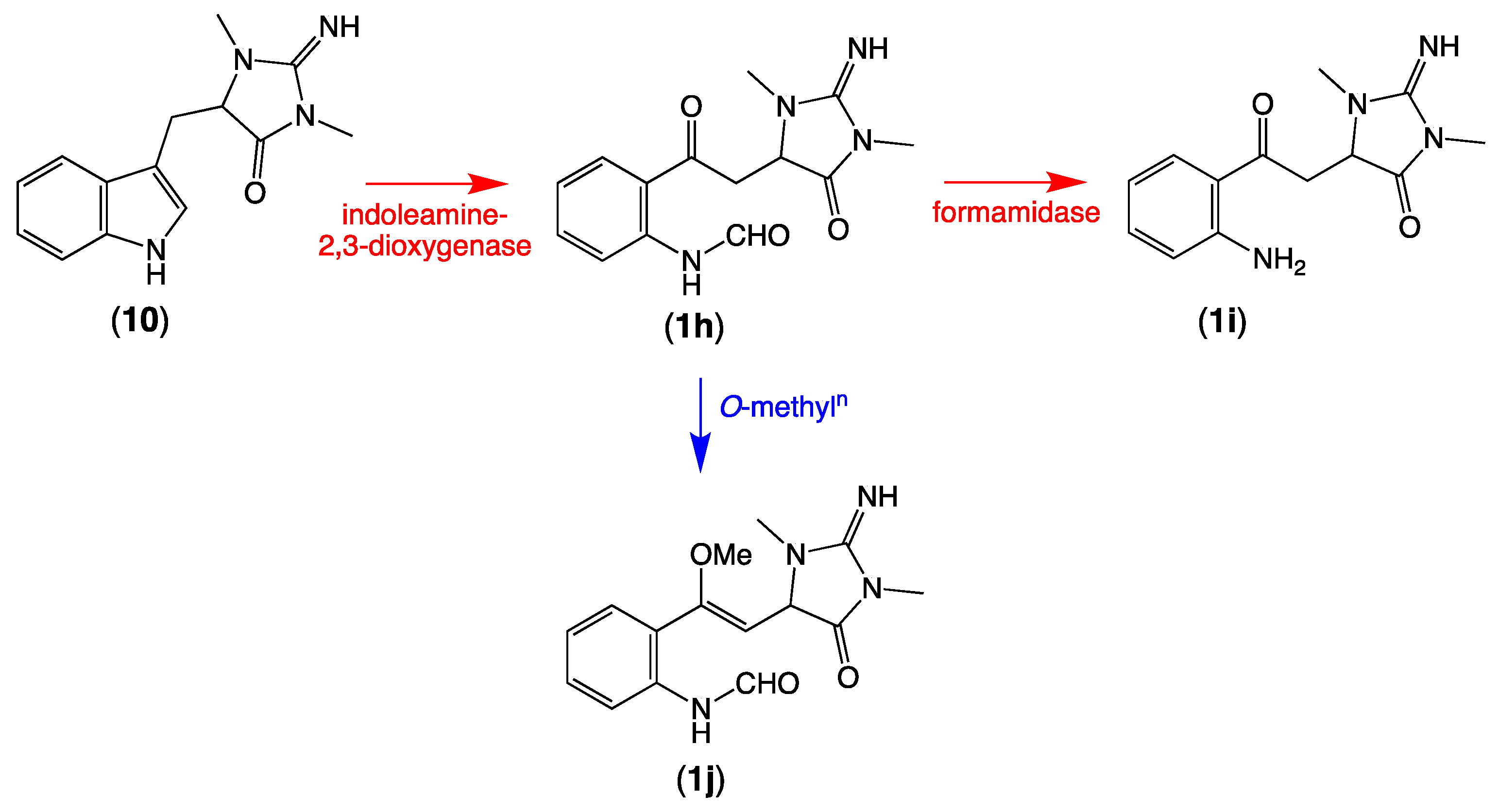
Of note, the thorectandrin GNPS cluster also featured nodes tentatively attributed to debromo analogues (1h, M + H m/z 289, C14H16N4O3; 1i, M + H m/z 261, C13H16N4O2) 1j, M + H m/z 303, C15H18N4O3), consistent with indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-like enzyme transformation of 1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin (10) (Scheme 6, Table 2, Figure 3). It also revealed nodes tentatively attributed to solvolysis adduct (1k, M + H m/z 277, C13H16N4O3; 1l, M + H m/z 305; 1m, M + H m/z 319, C15H18N4O5; 1n, M + H m/z 321), derived from intermediates generated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-like transformation of aplysinopsin (4) (Scheme 7, Table 2, Figure 3).
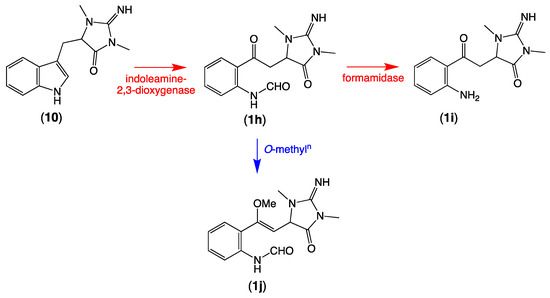
Scheme 6.
Possible biosynthetic link between 1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin (10) and 1h–1j.
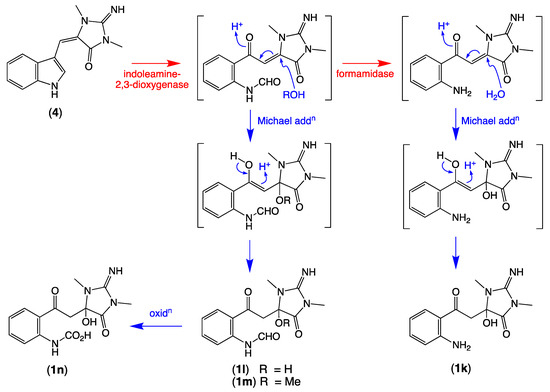
Scheme 7.
Possible biosynthetic link between aplysinopsin (4) and 1k–1n.
3. Conclusions
Our application of the GNPS molecular networking to a library of Southern Australian marine sponges reinforced the value of this approach, in both dereplicating and prioritizing extracts for detailed investigation, and in guiding the discovery of new scaffolds. It also revealed itself to be a valuable tool for interrogating the halo of co-clustering minor analogues (including solvolysis artifacts), chemistry that typically defines traditional methods of isolation and structure elucidation.
Our study of an Australian deep water (45 m) marine sponge, Thorectandra choanoides (CMB-01889), lead to the discovery of a new class of alkaloid, thorectandrin A (1). In proposing a biosynthetic origin of 1, we speculated that Thorectandra choanoides (CMB-01889) possesses enzymes functionally related to indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, leading to transformation of the known (albeit rare and minor) sponge natural product 6-bromo-1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin (2) to its ring-opened N-formyl derivative 1a, which was then rapidly hydrolyzed to thorectandrin A (1). Supportive of this hypothesis, we tentatively identified 1a in the thorectandrin GNPS cluster, along with the O-methyl product 1b, debromo analogues 1h–1j, solvolysis adducts 1c–1g and 1k–1m, and a natural/artifact oxidation product 1n. Studies into minor solvolysis artifacts led us to speculate that Thorectandra choanoides (CMB-01889) was capable of producing four known alkaloids, 6-bromo-1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin (2) [7], 6-bromoaplysinopsin (3) [7], aplysinopsin (4) [16], and 1′,8-dihydroaplysinopsin (10) [7], all of which were susceptible to a sponge indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-like enzyme. Where the 1′,8-dihydro alkaloids 2 and 10 were fully transformed by this enzyme to stable ring-opened analogues 1 and 1a–1b, and 1h–1j, respectively, the related conjugated scaffolds 3 and 4 were fully transformed to highly reactive Michael acceptors that underwent complete transformation to 1c–1g, and 1k–1n, respectively.
As members of the aplysinopsin family of marine natural product are long known for their biological properties (i.e., anticancer, antibiotic, antidepressant, antimalarial, and antimicrobial properties) [11], the realisation that they are possible substrates for indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenases is significant. With human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase upregulated in key human tissues (i.e., small intestine and lung), and a number of cancers (i.e., acute myeloid leukemia, ovarian, and colorectal carcinoma), knowledge that aplysinopsins are substrates, and yield potent Michael acceptors, could inform future development of this pharmacophore. For example, one might take advantage of the tissue selective abundance of human indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenases for in situ production of highly reactive Michael acceptors (i.e., as warheads within cancer cells). Alternatively, one might seek to diminish the susceptibility of aplysinopsin chemotherapeutics to indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenases, to improve in vivo pharmacokinetics. Either way, an understanding of the biotransformation of aplysinopsins to thorectandrins and spiroreticulatine, and the Michael acceptor status of key intermediates, would inform researchers seeking to exploit the therapeutic potential of these closely related and uniquely marine pharmacophores.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Procedures
Chiroptical measurements ([α]D) were obtained on a JASCO P-1010 polarimeter (JASCO International Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) in a 100 × 2 mm cell at 23 °C. Electronic Circular Dichroism (ECD) measurement were obtained on a JASCO J-810 spectropolarimeter (JASCO International Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) in a 0.1 cm path-length cell. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra were acquired on a Bruker Avance 600 MHz spectrometer (Bruker Pty. Ltd., Alexandria, Australia) with a 5 mm PASEL 1H/D-13C Z-Gradient probe at 25 °C in methanol-d4 by referencing to residual 1H or 13C signals (δH 3.30 and δC 49.15). High-resolution ESIMS spectra were obtained on a Bruker micrOTOF mass spectrometer (Bruker Daltonik Pty. Ltd., Preston, Australia) by direct injection in MeOH at 3 μL/min, using sodium formate clusters as an internal calibrant. Semi-preparative HPLC was performed using Agilent 1100 series HPLC instrument (Agilent Technologies Inc., Mulgrave, Australia) with corresponding detector, fraction collector and software inclusively. Analytical-grade solvents were used for extractions and partitions. Chromatography solvents were of HPLC grade and filtered/degassed through 0.45 μm polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) membrane prior to use. Deuterated solvents were purchased from Cambridge Isotopes (Cambridge Isotope Laboratories, Tewksbury, MA, USA). The human colorectal (SW620) and lung (NCI-H460) carcinoma cell lines were kindly provided by Susan E. Bates and Robert W. Robey of the National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, MD, USA.
4.2. Collection and Taxonomy
Sponge specimen CMB-01889 was collected in July 1995 using epibenthic sled (RV Franklin vessel) at a depth of 45 m in the Great Australian Bight. The specimen was immediately frozen and transported at 0 °C to the laboratory, where it was thawed, documented, diced, and stored in EtOH, at −30 °C prior to chemical investigation. The specimen was taxonomically classified as a Thorectandra choanoides (Class Demospongiae, Order Dictyoceratida, Family Thorectidae).
4.3. Extraction and Fractionation
An aliquot (60 mL) of the EtOH crude extract was decanted, concentrated in vacuo, and partitioned between n-BuOH (20 mL) and H2O (20 mL) (Figure S3). MS analysis of the partitions indicated localization of the target GNPS cluster in the n-BuOH partition. The n-BuOH soluble material was dissolved in MeOH and subjected to HPLC fractionation (Agilent Zorbax SB-CN 9.4 × 250 mm, 5 μm, 3 mL/min gradient elution over 25 min from 10% MeCN/H2O to 60% MeCN/H2O, with constant 0.01% TFA modifier), to yield thorectandrin A (1) (tR = 15.2 min, 1.2 mg, 0.6%) (Figure S4).
4.4. Global Natural Product Social (GNPS) Molecular Networking
Aliquots (10 μL) of the n-BuOH soluble stock plates prepared from 980 Southern Australian marine sponges were dispensed into 96-well plates, dried under N2 gas, resuspended in DMSO (10 μL). A total of 0.1 μL of DMSO aliquot was injected into an Agilent 6545 QTOF LC/MS (Agilent Technologies Inc., Mulgrave, Australia) equipped with an Agilent 1290 infinity II UHPLC system, utilizing an Agilent SB-C8 1.8 μm, 2.1 × 50 mm column, with a 0.5 mL/min, 4.5 min gradient elution from 90% H2O/MeCN to 100% MeCN, followed by isocratic elution with 100% MeCN for 1 min, with a constant isocratic 0.1% formic acid modifier. The UPLC-QTOF-(+)MS/MS (Agilent Technologies Inc., Mulgrave, Australia) data were acquired for all samples at a fixed collision energy of 40 eV, converted from Agilent MassHunter data files (.d) to mzXML file format, and transferred to the GNPS server (gnps.ucsd.edu) [17]. The full MS/MS data of the 980 sponge extracts could be accessed (accessed on 20 December 2020) from ftp://massive.ucsd.edu/MSV000086621/. Molecular networking was performed using the GNPS data analysis workflow using the spectral clustering algorithm, and a cosine score of 0.7 and a minimum of 6 matched peaks. The resulting spectral networks were visualized using Cytoscape version 3.5.1 (open source software, https://cytoscape.org (accessed on 20 December 2020)) [18], where nodes represented parent m/z and edge thickness corresponded to cosine scores, which showed a network featuring ~43,000 nodes, and many hundreds of clusters (Figure S1). Careful review of this GNPS data highlighted a promising cluster (Figure S2) with possible new compounds, associated uniquely with only one sponge specimen, CMB-01889.
4.5. Metabolite Characterization
Thorectandrin A (1): light yellow oil; 0 (c 0.08, MeOH); NMR (methanol-d4), Table 1 and Figures S5–S10. HRESIMS m/z 339.0460/341.0454 [M + H]+ (calculated for C13H1679BrN4O2, 339.0451; C13H1681BrN4O2, 341.0431).
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1660-3397/19/2/97/s1. Full GNPS molecular network, isolation scheme and HPLC chromatogram, 1D and 2D NMR spectra, and HRMS spectrum and bioassay protocols.
Author Contributions
R.J.C. conceptualized the research and assembled the marine sponge collection; S.K. performed dereplication and GNPS analyses, carried out the isolation and spectroscopic characterization of thorectandrin A; L.N. performed bioassays; A.H.E. acquired ECD spectrum; A.A.S. and S.K. constructed the Supplementary Materials document; R.J.C. reviewed all data and drafted the manuscript, with support from S.K. and A.A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported in part by The University of Queensland and the Institute for Molecular Bioscience.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The full MS/MS data of the 980 sponge extracts could be accessed from ftp://massive.ucsd.edu/MSV000086621/.
Acknowledgments
We thank L Goudie for sponge identification and Z Khalil for bioassays support. S.K., A.H.E. and L.N. acknowledge The University of Queensland for international postgraduate scholarships.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cambie, R.C.; Craw, P.A. Chemistry of Sponges, III. Manoalide Monoacetate and Thorectolide Monoacetate, Two New Sesterterpenoids from Thorectandra excavatus. J. Nat. Prod. 1988, 51, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, S.; Capon, R.J. A New Furanoditerpene from a Southern Australian Marine Sponge, Thorectandra choanoides. Aust. J. Chem. 1995, 48, 1903–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charan, R.D.; McKee, T.C.; Boyd, M.R. Thorectandrols A and B, New Cytotoxic Sesterterpenes from the Marine Sponge Thorectandra Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charan, R.D.; McKee, T.C.; Boyd, M.R. Thorectandrols C, D, and E, New Sesterterpenes from the Marine Sponge Thorectandra sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charan, R.D.; McKee, T.C.; Gustafson, K.R.; Pannell, L.K.; Boyd, M.R. Thorectandramine, a novel β-carboline alkaloid from the marine sponge Thorectandra sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 5201–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charan, R.D.; McKee, T.C.; Boyd, M.R. Cytotoxic Alkaloids from the Marine Sponge Thorectandra sp. Nat. Prod. Res. 2004, 18, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segraves, N.L.; Crews, P. Investigation of Brominated Tryptophan Alkaloids from Two Thorectidae Sponges: Thorectandra and Smenospongia. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1484–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khushi, S.; Nahar, L.; Salim, A.A.; Capon, R.J. Trachycladindoles H–M: Molecular Networking Guided Exploration of a Library of Southern Australian Marine Sponges. Aust. J. Chem. 2020, 73, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushi, S.; Nahar, L.; Salim, A.; Capon, R. Cacolides: Sesterterpene Butenolides from a Southern Australian Marine Sponge, Cacospongia sp. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushi, S.; Salim, A.A.; Elbanna, A.H.; Nahar, L.; Bernhardt, P.V.; Capon, R.J. Dysidealactams and Dysidealactones: Sesquiterpene Glycinyl- Lactams, Imides, and Lactones from a Dysidea sp. Marine Sponge Collected in Southern Australia. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialonska, D.; Zjawiony, J. Aplysinopsins—Marine Indole Alkaloids: Chemistry, Bioactivity and Ecological Significance. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 166–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botting, N.P. Chemistry and neurochemistry of the kynurenine pathway of tryptophan metabolism. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1995, 24, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tang, X.; Luo, X.; Voogd, N.J.; Li, P.; Li, G. (+)- and (−)-Spiroreticulatine, A Pair of Unusual Spiro Bisheterocyclic Quinoline-imidazole Alkaloids from the South China Sea Sponge Fascaplysinopsis reticulata. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 3458–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Tang, X.; Luo, X.; Voogd, N.J.; Li, P.; Li, G. Aplysinopsin-type and Bromotyrosine-derived Alkaloids from the South China Sea Sponge Fascaplysinopsis reticulata. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J. Extracting value: Mechanistic insights into the formation of natural product artifacts—Case studies in marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 55–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazlauskas, R.; Murphy, P.T.; Quinn, R.J.; Wells, R.J. Aplysinopsin, a new tryptophan derivative from a sponge. Tetrahedron Lett. 1977, 1, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with GNPS. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).