Bacillus spp. Inhibit Edwardsiella tarda Quorum-Sensing and Fish Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
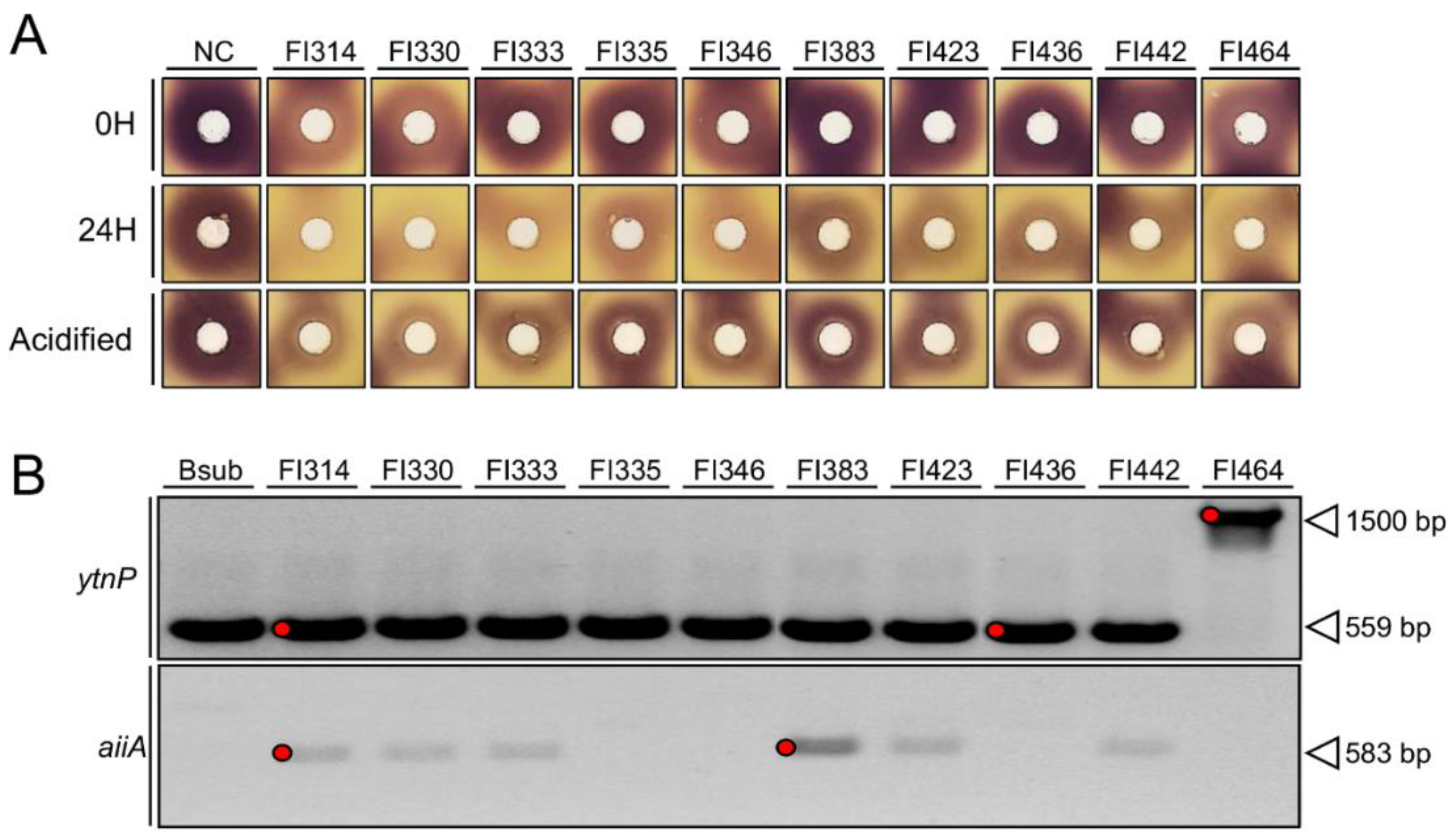
2.1. Fish-Isolates Produce Extracellular Compounds with QQ Capacity
2.2. Isolates QQ Activity Is Mediated through AHLs Enzymatic Inactivation
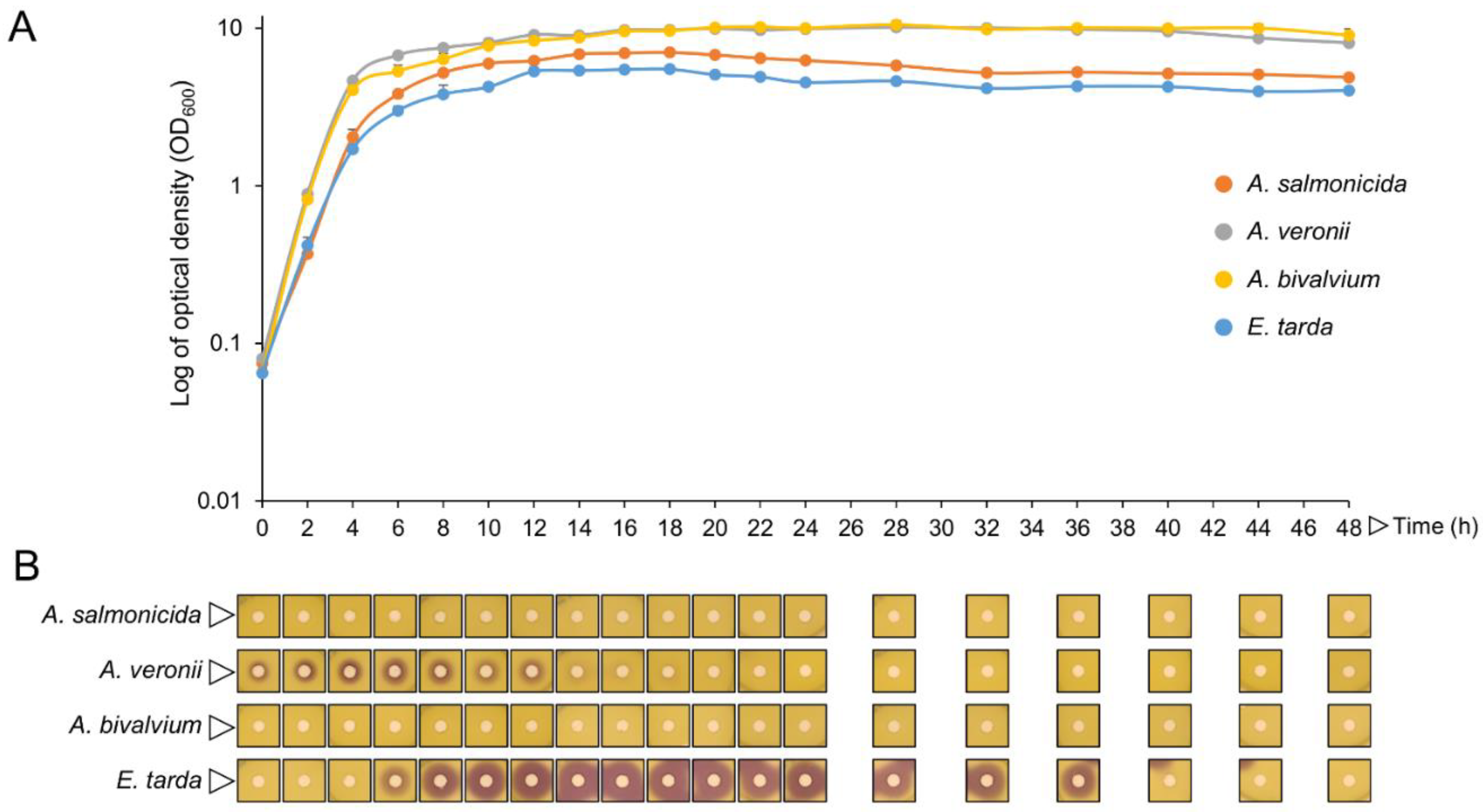
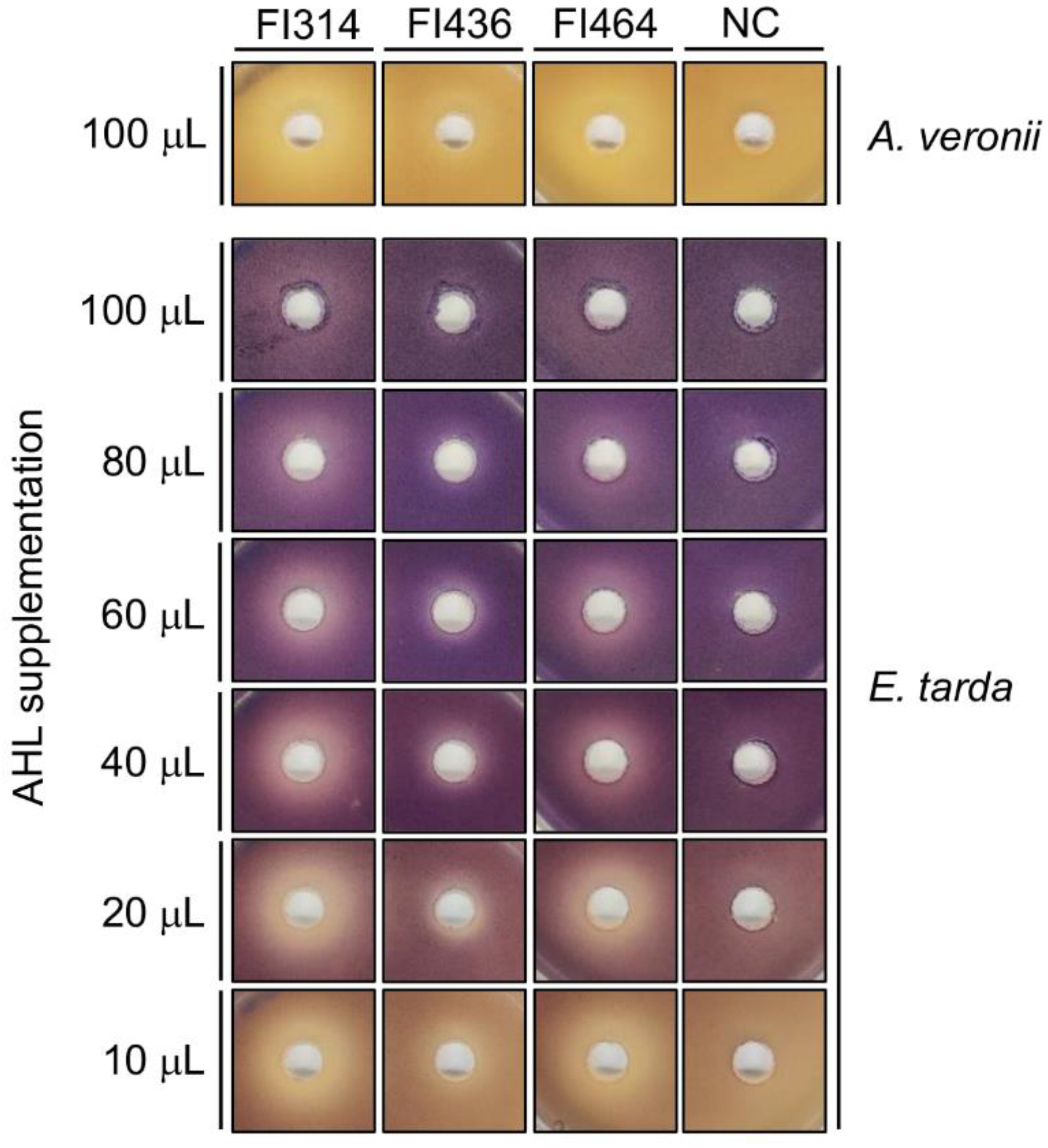
2.3. Isolates QQ Compounds Can Interfere with Fish Pathogens AHLs
2.4. Isolates QQ Compounds Protect Zebrafish Larvae upon E. tarda Challenge
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
4.2. Evaluation of Isolates QQ Activity
4.3. AHLs Enzymatic Inactivation by Isolates’ Extracellular Compounds
4.4. Design of QQ Primers
4.5. PCR Amplification of 16S rRNA Genes and Genes Coding for Putative QQ Enzymes
4.6. AHL Production Profile of Fish Pathogens
4.7. Extraction of Fish Pathogens’ AHLs
4.8. Fish Isolates QQ Activity on Fish Pathogens’ AHLs
4.9. Ethics Statement
4.10. Zebrafish Larvae General Care
4.11. Isolates Extracts Preparation and Testing for Toxicity in Zebrafish Larvae
4.12. E. tarda Infection Model
4.13. Fish Isolates’ Protection Assay against E. tarda Infection in Zebrafish Larvae
4.14. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bayliss, S.C.; Verner-Jeffreys, D.W.; Bartie, K.L.; Aanensen, D.M.; Sheppard, S.K.; Adams, A.; Feil, E.J. The promise of whole genome pathogen sequencing for the molecular epidemiology of emerging aquaculture pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaprakashvel, M.; Subramani, R. Implications of quorum sensing and quorum quenching in aquaculture health management. In Implication of Quorum Sensing and Biofilm Formation in Medicine, Agriculture and Food Industry; Bramhachari, P.V., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 299–312. [Google Scholar]
- Defoirdt, T. Antivirulence therapy for animal production: Filling an arsenal with novel weapons for sustainable disease control. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defoirdt, T. Quorum-sensing systems as targets for antivirulence therapy. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.B.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2001, 55, 165–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abisado, R.G.; Benomar, S.; Klaus, J.R.; Dandekar, A.A.; Chandler, J.R. Bacterial quorum sensing and microbial community interactions. mBio 2018, 9, e02331-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuqua, C.; Winans, S.C.; Greenberg, E.P. Census and consensus in bacterial ecosystems: The LuxR-LuxI family of quorum-sensing transcriptional regulators. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1996, 50, 727–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, M.; Quan, C.S.; Fan, S.D. Mechanisms of quorum sensing and strategies for quorum sensing disruption in aquaculture pathogens. J. Fish Dis. 2015, 38, 771–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton, D.L. Quorum sensing in vibrios: Complexity for diversification. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 296, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croxatto, A.; Chalker, V.J.; Lauritz, J.; Jass, J.; Hardman, A.; Williams, P.; Camara, M.; Milton, D.L. VanT, a homologue of Vibrio harveyi LuxR, regulates serine, metalloprotease, pigment, and biofilm production in Vibrio anguillarum. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 1617–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defoirdt, T. Virulence mechanisms of bacterial aquaculture pathogens and antivirulence therapy for aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2014, 6, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, S.; Karlyshev, A.V.; Fish, L.; Durant, E.L.; Winson, M.K.; Chhabra, S.R.; Williams, P.; Macintyre, S.; Stewart, G.S. Quorum sensing in Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas salmonicida: Identification of the LuxRI homologs AhyRI and AsaRI and their cognate N-acylhomoserine lactone signal molecules. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 5271–5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, M.; Avendano-Herrera, R.; Magarinos, B.; Camara, M.; Otero, A. Acylhomoserine lactone production and degradation by the fish pathogen Tenacibaculum maritimum, a member of the Cytophaga-Flavobacterium-Bacteroides (CFB) group. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 304, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetzner, S. Quorum quenching enzymes. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 201, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandclement, C.; Tannieres, M.; Morera, S.; Dessaux, Y.; Faure, D. Quorum quenching: Role in nature and applied developments. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 40, 86–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.-H.; Xu, J.-L.; Li, X.-Z.; Zhang, L.-H. AiiA, an enzyme that inactivates the acylhomoserine lactone quorum-sensing signal and attenuates the virulence of Erwinia carotovora. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-B.; Wang, L.-H.; Zhang, L.-H. Genetic control of quorum-sensing signal turnover in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 4638–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Oh, T.K.; Oh, J.W.; Koo, B.T.; Yum, D.Y.; Lee, J.K. AhlD, an N-acylhomoserine lactonase in Arthrobacter sp., and predicted homologues in other bacteria. Microbiology 2003, 149, 1541–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.-Z.; Morohoshi, T.; Ikenoya, M.; Someya, N.; Ikeda, T. AiiM, a novel class of N-acylhomoserine lactonase from the leaf-associated bacterium Microbacterium testaceum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2524–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Yepes, A.; Garcia-Betancur, J.C.; Westedt, I.; Mielich, B.; López, D. Streptomycin-induced expression in Bacillus subtilis of YtnP, a lactonase-homologous protein that inhibits development and streptomycin production in Streptomyces griseus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caulier, S.; Nannan, C.; Gillis, A.; Licciardi, F.; Bragard, C.; Mahillon, J. Overview of the antimicrobial compounds produced by members of the Bacillus subtilis Group. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuebutornye, F.K.A.; Lu, Y.; Abarike, E.D.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Sakyi, M.E. In vitro assessment of the probiotic characteristics of three Bacillus species from the gut of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Banerjee, G.; Mukherjee, P.; Ray, A.K.; Chandra, G.; Ghosh, K. Antibacterial substances produced by pathogen inhibitory gut bacteria in Labeo rohita: Physico-chemical characterization, purification and identification through MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 130, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, C.R.; Almeida, E.M.; Guerreiro, I.; Santos, R.; Merrifield, D.L.; Tavares, F.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Enes, P. Selection of carbohydrate-active probiotics from the gut of carnivorous fish fed plant-based diets. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meidong, R.; Doolgindachbaporn, S.; Jamjan, W.; Sakai, K.; Tashiro, Y.; Okugawa, Y.; Tongpim, S. A novel probiotic Bacillus siamensis B44v isolated from Thai pickled vegetables (Phak-dong) for potential use as a feed supplement in aquaculture. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 63, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meidong, R.; Khotchanalekha, K.; Doolgindachbaporn, S.; Nagasawa, T.; Nakao, M.; Sakai, K.; Tongpim, S. Evaluation of probiotic Bacillus aerius B81e isolated from healthy hybrid catfish on growth, disease resistance and innate immunity of Pla-mong Pangasius bocourti. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 73, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.A.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Jerusik, R.; Saavedra, M.J.; Enes, P.; Serra, C.R. Isolation and characterization of fish-gut Bacillus spp. as source of natural antimicrobial compounds to fight aquaculture bacterial diseases. Mar. Biotechnol. 2021, 23, 276–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; He, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, M.; Mao, W.; Zhang, H.; Yao, B. Orally administered thermostable N-acyl homoserine lactonase from Bacillus sp. strain AI96 attenuates Aeromonas hydrophila infection in zebrafish. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 1899–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Peng, M.; Tong, W.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Z. The quorum quenching bacterium Bacillus licheniformis T-1 protects zebrafish against Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, W.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, W.; Zhuang, X. Quorum quenching bacteria Bacillus sp. QSI-1 protect zebrafish (Danio rerio) from Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Xia, Y.; Zhu, C.; Chu, W. Isolation of marine Bacillus sp. with antagonistic and organic-substances-degrading activities and its potential application as a fish probiotic. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pande, G.S.; Natrah, F.M.; Flandez, A.V.; Kumar, U.; Niu, Y.; Bossier, P.; Defoirdt, T. Isolation of AHL-degrading bacteria from micro-algal cultures and their impact on algal growth and on virulence of Vibrio campbellii to prawn larvae. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 10805–10813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinoj, G.; Vaseeharan, B.; Thomas, S.; Spiers, A.J.; Shanthi, S. Quorum-quenching activity of the AHL-lactonase from Bacillus licheniformis DAHB1 inhibits Vibrio biofilm formation in vitro and reduces shrimp intestinal colonisation and mortality. Mar. Biotechnol. 2014, 16, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torabi Delshad, S.; Soltanian, S.; Sharifiyazdi, H.; Bossier, P. Effect of quorum quenching bacteria on growth, virulence factors and biofilm formation of Yersinia ruckeri in vitro and an in vivo evaluation of their probiotic effect in rainbow trout. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morohoshi, T.; Kato, M.; Fukamachi, K.; Kato, N.; Ikeda, T. N-acylhomoserine lactone regulates violacein production in Chromobacterium violaceum type strain ATCC 12472. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 279, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClean, K.H.; Winson, M.K.; Fish, L.; Taylor, A.; Chhabra, S.R.; Camara, M.; Daykin, M.; Lamb, J.H.; Swift, S.; Bycroft, B.W.; et al. Quorum sensing and Chromobacterium violaceum: Exploitation of violacein production and inhibition for the detection of N-acylhomoserine lactones. Microbiology 1997, 143, 3703–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, V.C.; Raju, S.C.; Purohit, H.J. Genomic analysis reveals versatile organisms for quorum quenching enzymes: Acyl-homoserine lactone-acylase and -lactonase. Open Microbiol. J. 2011, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Rosales, P.; Chabrillon, M.; Morinigo, M.A.; Balebona, M.C. Survival against exogenous hydrogen peroxide of Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida under different culture conditions. J. Fish Dis. 2003, 26, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, G.; Das, B.C.; Jose, S.; VJ, R.K. Bacillus as an aquaculture friendly microbe. Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 323–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanei-Motlagh, R.; Mohammadian, T.; Gharibi, D.; Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; Mahmoudi, E.; Khosravi, M.; Zarea, M.; El-Matbouli, M. Quorum quenching properties and probiotic potentials of intestinal associated bacteria in Asian sea bass Lates calcarifer. Mar. Drugs 2019, 18, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.H.; Gusti, A.R.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, J.L.; Zhang, L.H. Identification of quorum-quenching N-acyl homoserine lactonases from Bacillus species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 1754–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Contreras, R.; Maeda, T.; Wood, T.K. Resistance to quorum-quenching compounds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 6840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinh, N.T.N.; Dung, N.V.; Trung, C.T.; Thuy, V.T. In vitro characterization of a recombinant AHL-lactonase from Bacillus cereus isolated from a striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) pond. Indian J. Microbiol. 2013, 53, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chowdhary, P.K.; Keshavan, N.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Peterson, J.A.; Gonzalez, J.E.; Haines, D.C. Bacillus megaterium CYP102A1 oxidation of acyl homoserine lactones and acyl homoserines. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 14429–14437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nithya, C.; Aravindraja, C.; Pandian, S.K. Bacillus pumilus of Palk Bay origin inhibits quorum-sensing-mediated virulence factors in Gram-negative bacteria. Res. Microbiol. 2010, 161, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, Z.; Li, X. Quorum quenching enzymes and their application in degrading signal molecules to block quorum sensing-dependent infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 17477–17500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, E.A.; Philipp, B.; Buckley, C.; Atkinson, S.; Chhabra, S.R.; Sockett, R.E.; Goldner, M.; Dessaux, Y.; Cámara, M.; Smith, H.; et al. N-acylhomoserine lactones undergo lactonolysis in a pH-, temperature-, and acyl chain length-dependent manner during growth of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 5635–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Huang, T.; Yao, F.; Huang, Z.; Powell, C.A.; Qiu, S.; Guan, X. Expression and characterization of aiiA gene from Bacillus subtilis BS-1. Microbiol. Res. 2008, 163, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daiyasu, H.; Osaka, K.; Ishino, Y.; Toh, H. Expansion of the zinc metallo-hydrolase family of the β-lactamase fold. FEBS Lett. 2001, 503, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.-T.; Xu, L.; Fan, S.-S.; Xu, L.-N.; Li, D.-C.; Liu, Z.-Y. Isolation and characterization of an AHL lactonase gene from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruhn, J.B.; Dalsgaard, I.; Nielsen, K.F.; Buchholtz, C.; Larsen, J.L.; Gram, L. Quorum sensing signal molecules (acylated homoserine lactones) in gram-negative fish pathogenic bacteria. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2005, 65, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, M.; Wu, R.; Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, P. Effects of quorum quenching by AHL lactonase on AHLs, protease, motility and proteome patterns in Aeromonas veronii LP-11. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 252, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morohoshi, T.; Inaba, T.; Kato, N.; Kanai, K.; Ikeda, T. Identification of quorum-sensing signal molecules and the LuxRI homologs in fish pathogen Edwardsiella tarda. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2004, 98, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Li, X.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, X.H.; Bossier, P. Detection of different quorum-sensing signal molecules in a virulent Edwardsiella tarda strain LTB-4. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton, D.L.; Chalker, V.J.; Kirke, D.; Hardman, A.; Camara, M.; Williams, P. The LuxM homologue VanM from Vibrio anguillarum directs the synthesis of N-(3-hydroxyhexanoyl)homoserine lactone and N-hexanoylhomoserine lactone. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 3537–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milton, D.L.; Hardman, A.; Camara, M.; Chhabra, S.R.; Bycroft, B.W.; Stewart, G.S.; Williams, P. Quorum sensing in Vibrio anguillarum: Characterization of the vanI/vanR locus and identification of the autoinducer N-(3-oxodecanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 3004–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defoirdt, T.; Boon, N.; Sorgeloos, P.; Verstraete, W.; Bossier, P. Quorum sensing and quorum quenching in Vibrio harveyi: Lessons learned from in vivo work. ISME J. 2008, 2, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valiente, E.; Bruhn, J.B.; Nielsen, K.F.; Larsen, J.L.; Roig, F.J.; Gram, L.; Amaro, C. Vibrio vulnificus produces quorum sensing signals of the AHL-class. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 69, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangid, K.; Kong, R.; Patole, M.S.; Shouche, Y.S. luxRI homologs are universally present in the genus Aeromonas. BMC Microbiol. 2007, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Reis Ponce-Rossi, A.; Pinto, U.M.; de Oliveira Barros Ribon, A.; Bazzolli, D.M.S.; Vanetti, M.C.D. Quorum sensing regulated phenotypes in Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 7966 deficient in AHL production. Ann. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pascual, D.; Lunazzi, A.; Magdelenat, G.; Rouy, Z.; Roulet, A.; Lopez-Roques, C.; Larocque, R.; Barbeyron, T.; Gobet, A.; Michel, G.; et al. The complete genome sequence of the fish pathogen Tenacibaculum maritimum provides insights into virulence mechanisms. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangid, K.; Parameswaran, P.S.; Shouche, Y.S. A variant quorum sensing system in Aeromonas veronii MTCC 3249. Sensors 2012, 12, 3814–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, M.; Liu, L.; Wu, R.; Hu, J.; Wang, S.; Li, P. Detection of new quorum sensing N-Acyl homoserine lactones from Aeromonas veronii. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.; Lu, F.; Zhu, W.; Kang, C. Isolation and characterization of new potential probiotic bacteria based on quorum-sensing system. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 110, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yu, Z.; Chu, W. Effect of quorum-quenching bacterium Bacillus sp. QSI-1 on protein profiles and extracellular enzymatic activities of Aeromonas hydrophila YJ-1. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, M.; Muras, A.; Mayer, C.; Buján, N.; Magariños, B.; Otero, A. In vitro quenching of fish pathogen Edwardsiella tarda AHL production using marine bacterium Tenacibaculum sp. strain 20J cell extracts. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2014, 108, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, N.; Toranzo, A.E.; Barja, J.L.; Núñez, S.; Magariños, B. Characterization of Edwardsiella tarda strains isolated from turbot, Psetta maxima (L.). J. Fish Dis. 2006, 29, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, N.; Toranzo, A.E.; Devesa, S.; González, A.; Nuñez, S.; Magariños, B. First description of Edwardsiella tarda in Senegalese sole, Solea senegalensis (Kaup). J. Fish Dis. 2012, 35, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miniero Davies, Y.; Xavier de Oliveira, M.G.; Paulo Vieira Cunha, M.; Soares Franco, L.; Pulecio Santos, S.L.; Zanolli Moreno, L.; Túlio de Moura Gomes, V.; Zanolli Sato, M.I.; Schiavo Nardi, M.; Micke Moreno, A.; et al. Edwardsiella tarda outbreak affecting fishes and aquatic birds in Brazil. Vet. Q. 2018, 38, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abo El-Yazeed, H.; Ibrahem, M.D. Studies on Edwardsiella tarda infection in catfish and Tilapia nilotica. J. Vet. Med. Res. 2009, 19, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iregui, C.A.; Guarín, M.; Tibatá, V.M.; Ferguson, H.W. Novel brain lesions caused by Edwardsiella tarda in a red tilapia (Oreochromis spp.). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2012, 24, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, Y.; Asahata-Tago, S.; Ainoda, Y.; Fujita, T.; Kikuchi, K. Edwardsiella tarda bacteremia. A rare but fatal water- and foodborne infection: Review of the literature and clinical cases from a single centre. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 26, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaven, E.M.; Lopez, F.A.; Hart, S.M.; Sanders, C.V. Myonecrosis Caused by Edwardsiella tarda: A Case Report and Case Series of Extraintestinal E. tarda Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 1430–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Zhou, Z.; Cao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Yao, B. High yield expression of an AHL-lactonase from Bacillus sp. B546 in Pichia pastoris and its application to reduce Aeromonas hydrophila mortality in aquaculture. Microb. Cell. Fact. 2010, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, S.H.M.; Wang, X.H.; Lim, T.M.; Leung, K.Y. Green fluorescent protein-tagged Edwardsiella tarda reveals portal of entry in fish. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 194, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeigler, D.R.; Prágai, Z.; Rodriguez, S.; Chevreux, B.; Muffler, A.; Albert, T.; Bai, R.; Wyss, M.; Perkins, J.B. The Origins of 168, W23, and Other Bacillus subtilis Legacy Strains. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 6983–6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, P.D.; Ping, G.; Daly, S.L.; Cha, C.; Cronan, J.E.; Rinehart, K.L.; Farrand, S.K. Detecting and characterizing N-acyl-homoserine lactone signal molecules by thin-layer chromatography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 6036–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Test No. 236: Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test; OECD: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]


| Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Amplicon (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16S rRNA | |||
| 27F | AGAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG | 1465 | [38] |
| 1492R | GGYTTACCTTGTTAYGACTT | [38] | |
| N-acyl homoserine lactonase/aiiA a | |||
| aiiA–309F | TCACTTACATTTTGATCATGCAGGAGGAAA | 267 | [37] |
| aiiA–576R | TCCGGTTCAGTTTTATTAACGATTGATGCA | [37] | |
| aiiA–1F | ATGACAGTAAAGAAGCTTTATT | 584 | This study |
| aiiA–584R | CATCTTCAAAATTCTCTTTCG | This study | |
| Probable quorum-quenching lactonase/ytnP b | |||
| ytnP–149F | ATCGGATAATCATCGTAAGC | 559 | This study |
| ytnP–708R | ATTGAACTAAGAACAGACCC | This study | |
| Gene | FI nº | Closest known Protein a | QC (%) b | Identity (%) c |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ytnP | 314 | ytnP-like metallo-hydrolase | 99 | 100 |
| 436 | MBL fold metallo-hydrolase | 100 | 100 | |
| 464 | DAK2 domain-containing protein | 88 | 99.2 | |
| aiiA | 314 | MBL fold metallo-hydrolase – Rhodanese Homology Domain | 96 | 100 |
| 383 | MBL fold metallo-hydrolase – Rhodanese Homology Domain | 95 | 100 |
| Bacterial Species | Strain | Origin/Source a |
|---|---|---|
| Fish pathogens | ||
| Aeromonas salmonicida | LMG 3780 | BCCM/LMG |
| Aeromonas veronii | Fish isolate | NUTRIMU collection |
| Aeromonas bivalvium | Fish isolate | NUTRIMU collection |
| Aeromonas hydrophila subsp. hydrophila | LMG 2844 | BCCM/LMG |
| Vibrio anguillarum | DSM 21597 | DSMZ |
| Vibrio harveyi | Fish isolate | NUTRIMU collection |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus | LMG 2850 | BCCM/LMG |
| Vibrio vulnificus | LMG 13545 | BCCM/LMG |
| Photobacterium damselae subsp. damselae | LMG 7892 | BCCM/LMG |
| Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida | Lgh41/01 | [39] |
| Tenacibaculum maritimum | LMG 11612 | BCCM/LMG |
| Edwarsiella tarda | LMG 2793 | BCCM/LMG |
| Shigella sonnei | LMG 10473 | BCCM/LMG |
| Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis | 168 (BGSC1A1) | A.O. Henriques |
| Chromobacterium violaceum WT | CECT 494 | CECT |
| Chromobacterium violaceum CV026 | CECT 5999 | CECT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, R.A.; Monteiro, M.; Rangel, F.; Jerusik, R.; Saavedra, M.J.; Carvalho, A.P.; Oliva-Teles, A.; Serra, C.R. Bacillus spp. Inhibit Edwardsiella tarda Quorum-Sensing and Fish Infection. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19110602
Santos RA, Monteiro M, Rangel F, Jerusik R, Saavedra MJ, Carvalho AP, Oliva-Teles A, Serra CR. Bacillus spp. Inhibit Edwardsiella tarda Quorum-Sensing and Fish Infection. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(11):602. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19110602
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, Rafaela A., Marta Monteiro, Fábio Rangel, Russell Jerusik, Maria J. Saavedra, António Paulo Carvalho, Aires Oliva-Teles, and Cláudia R. Serra. 2021. "Bacillus spp. Inhibit Edwardsiella tarda Quorum-Sensing and Fish Infection" Marine Drugs 19, no. 11: 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19110602
APA StyleSantos, R. A., Monteiro, M., Rangel, F., Jerusik, R., Saavedra, M. J., Carvalho, A. P., Oliva-Teles, A., & Serra, C. R. (2021). Bacillus spp. Inhibit Edwardsiella tarda Quorum-Sensing and Fish Infection. Marine Drugs, 19(11), 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19110602







