Genome-Inspired Chemical Exploration of Marine Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus MF071
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
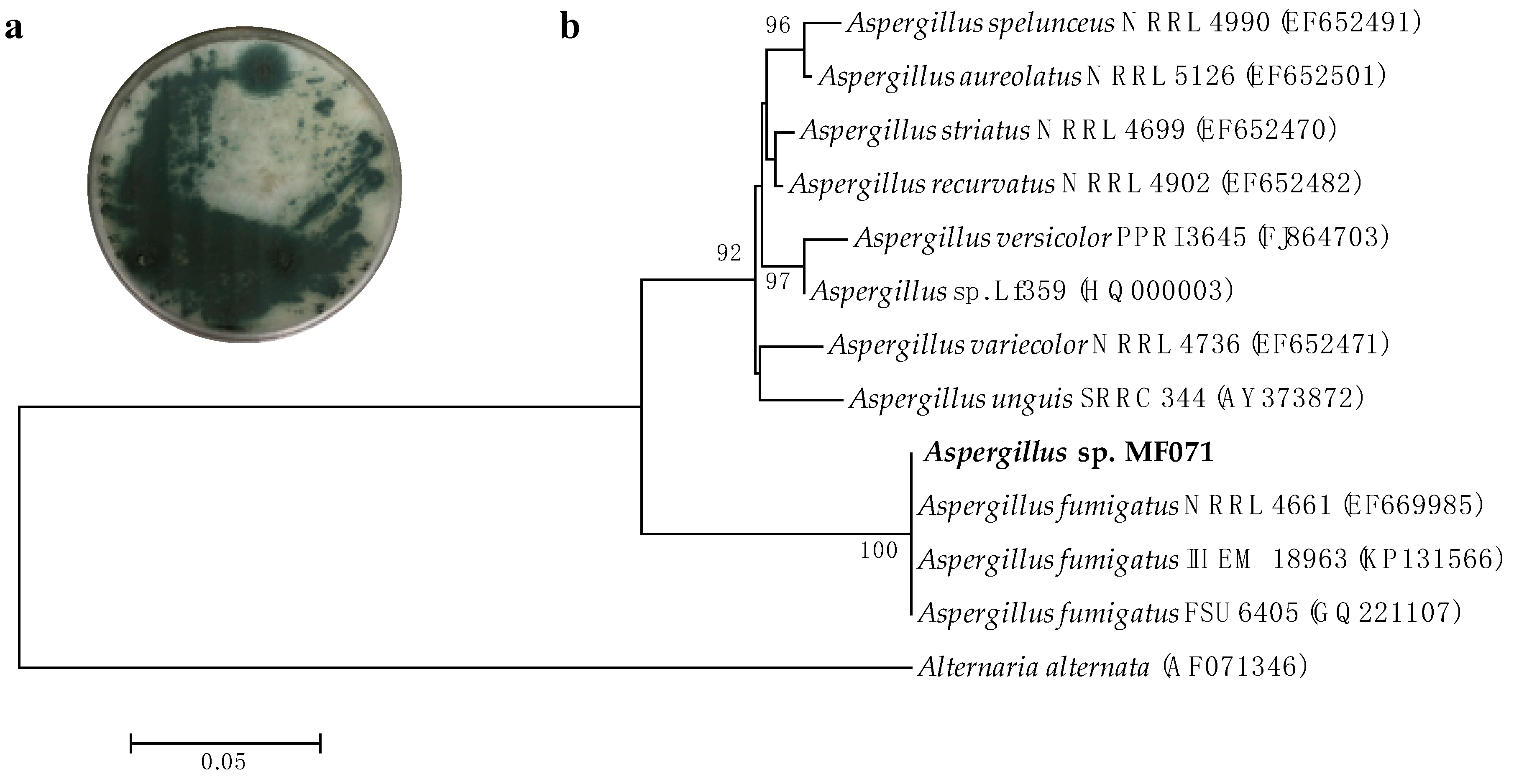
2.1. Characterization and Identification of Strain MF071
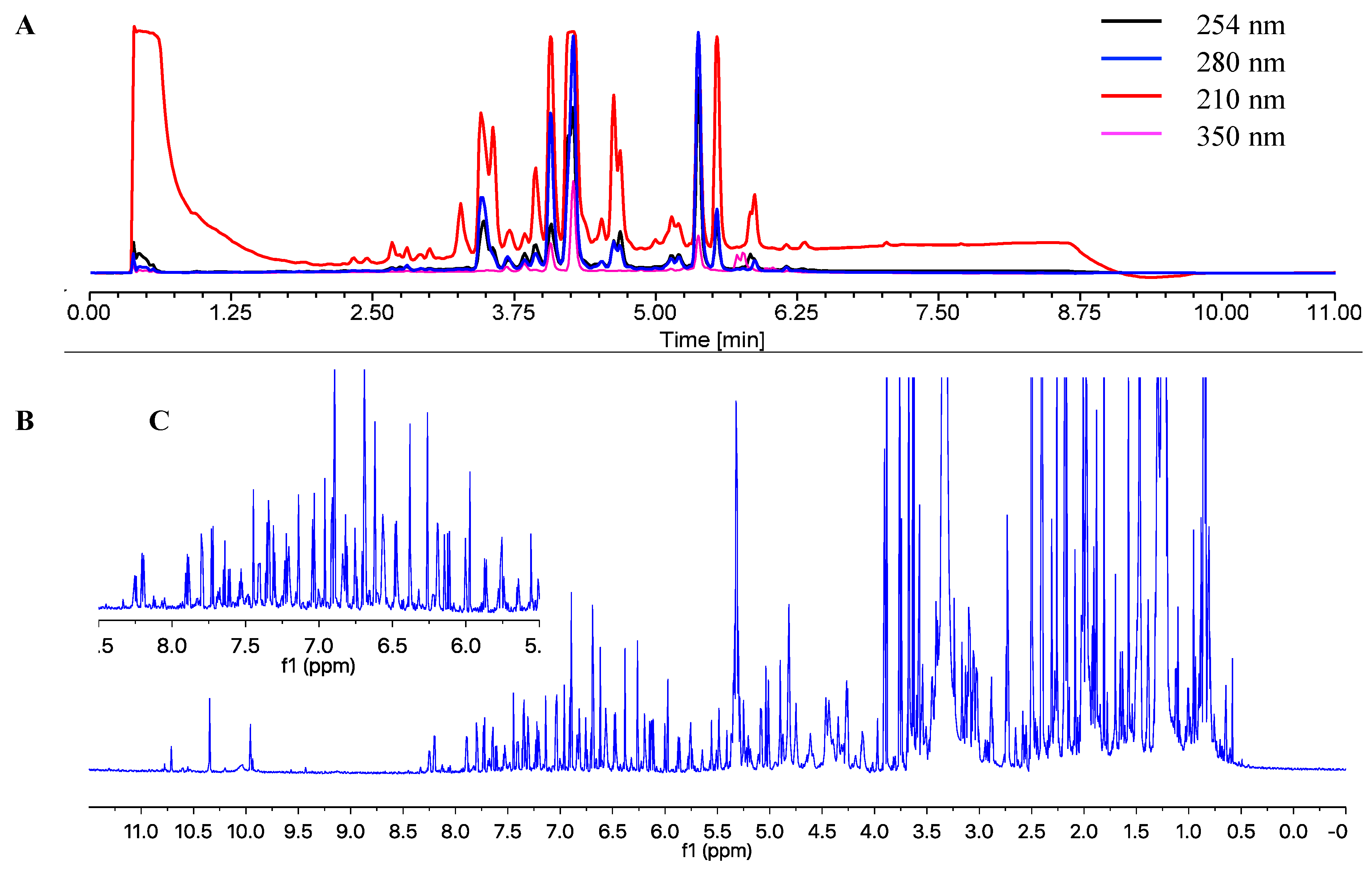
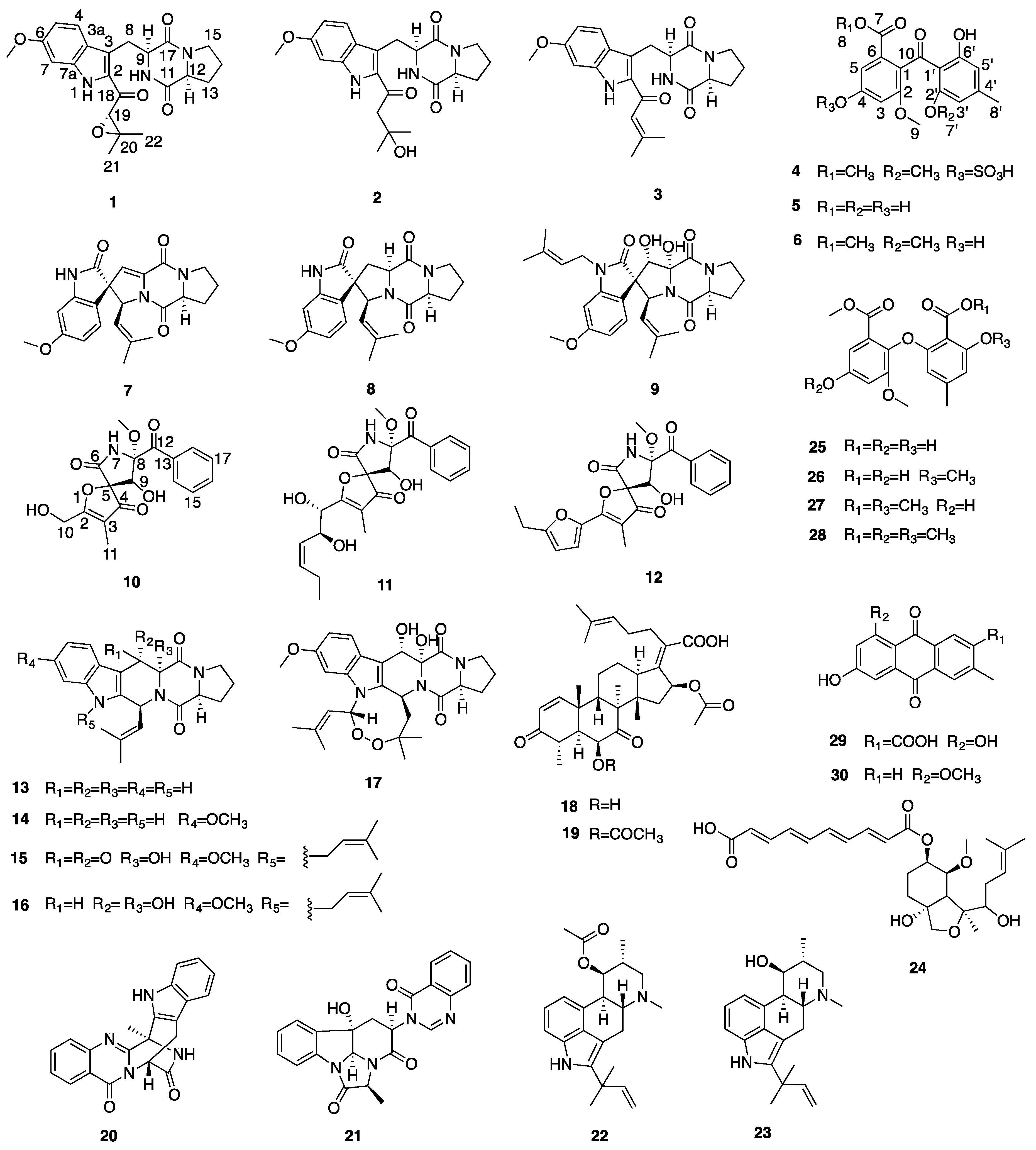
2.2. Structure Elucidation of the Isolated Compounds
2.3. Biological Activities
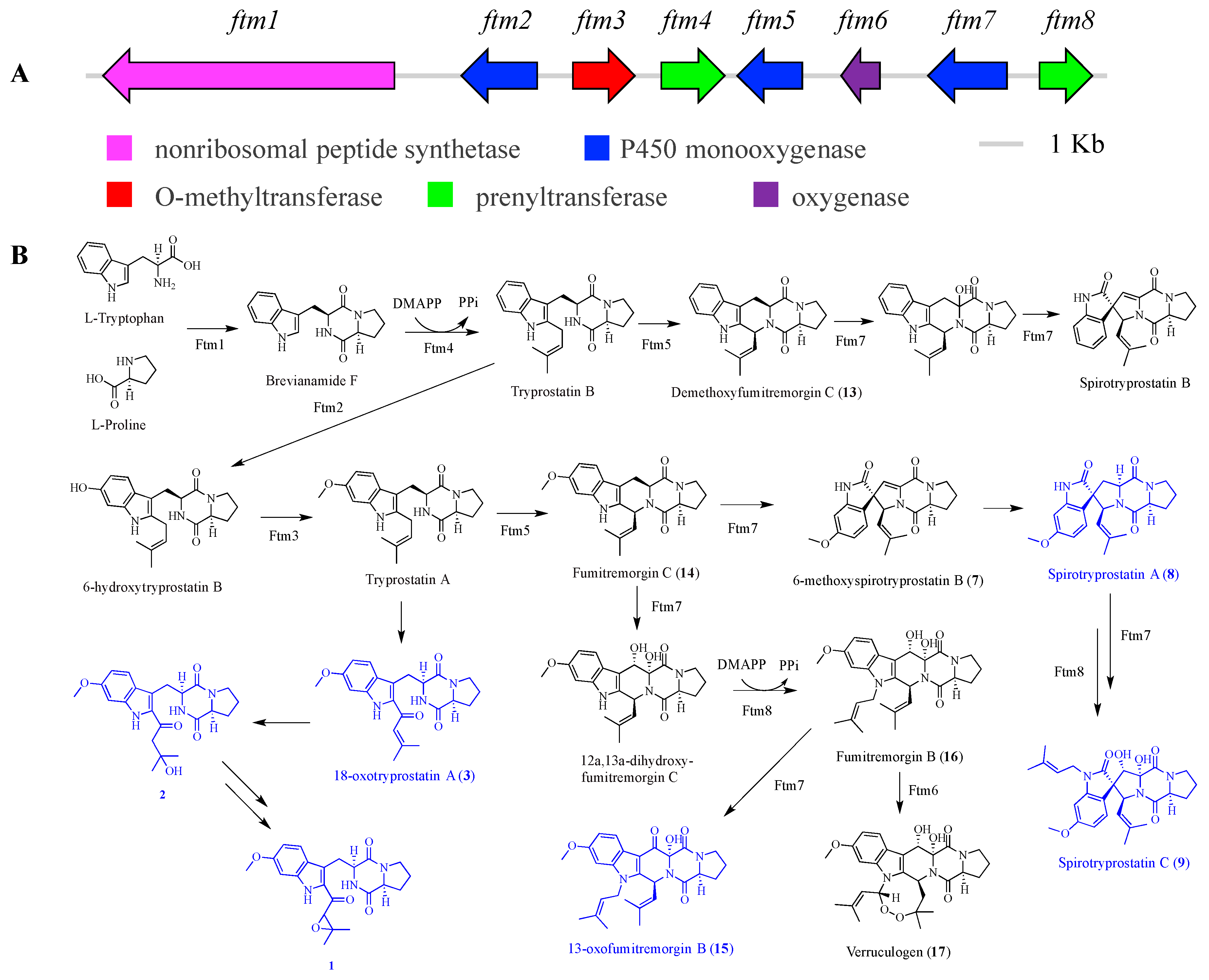
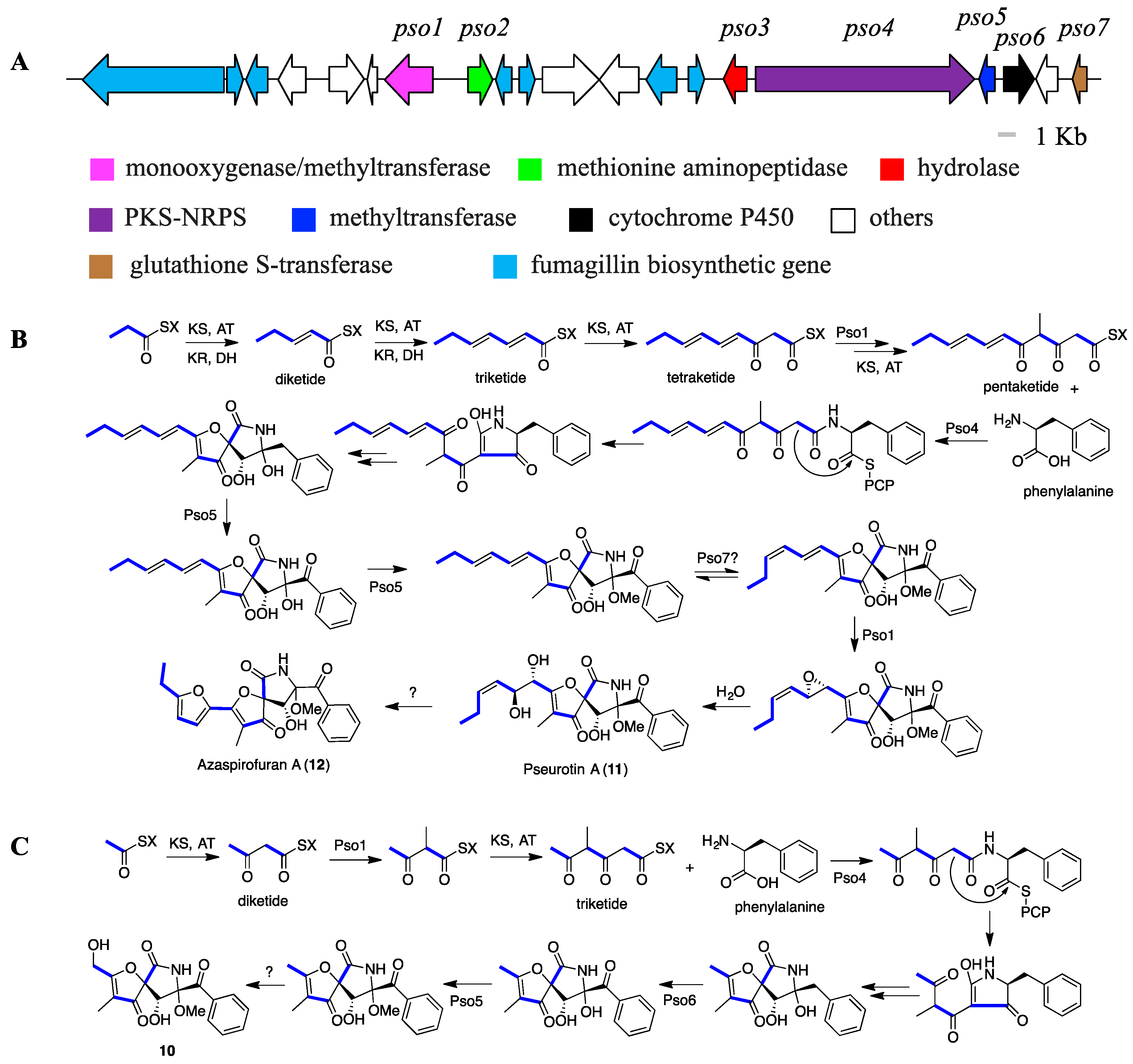
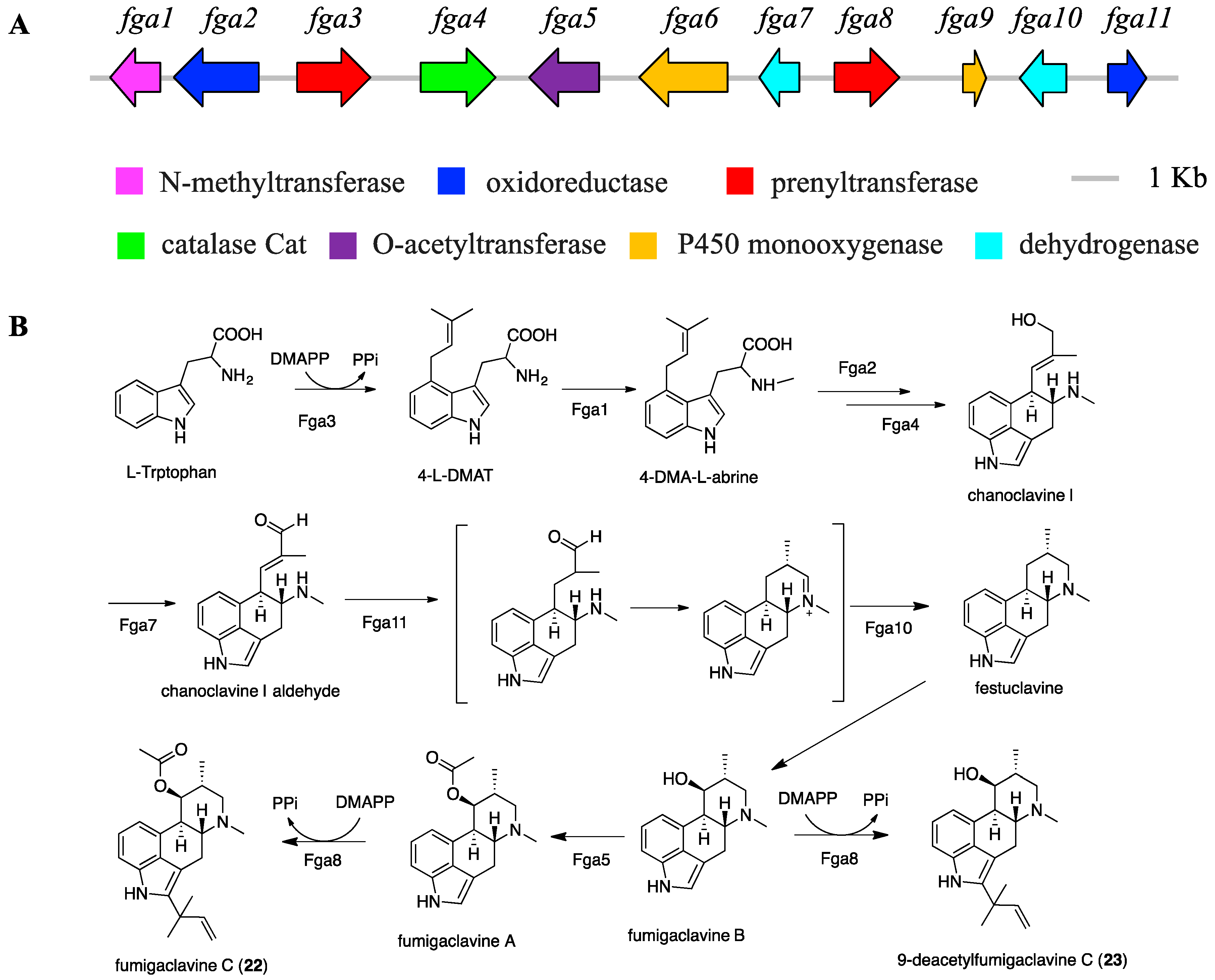
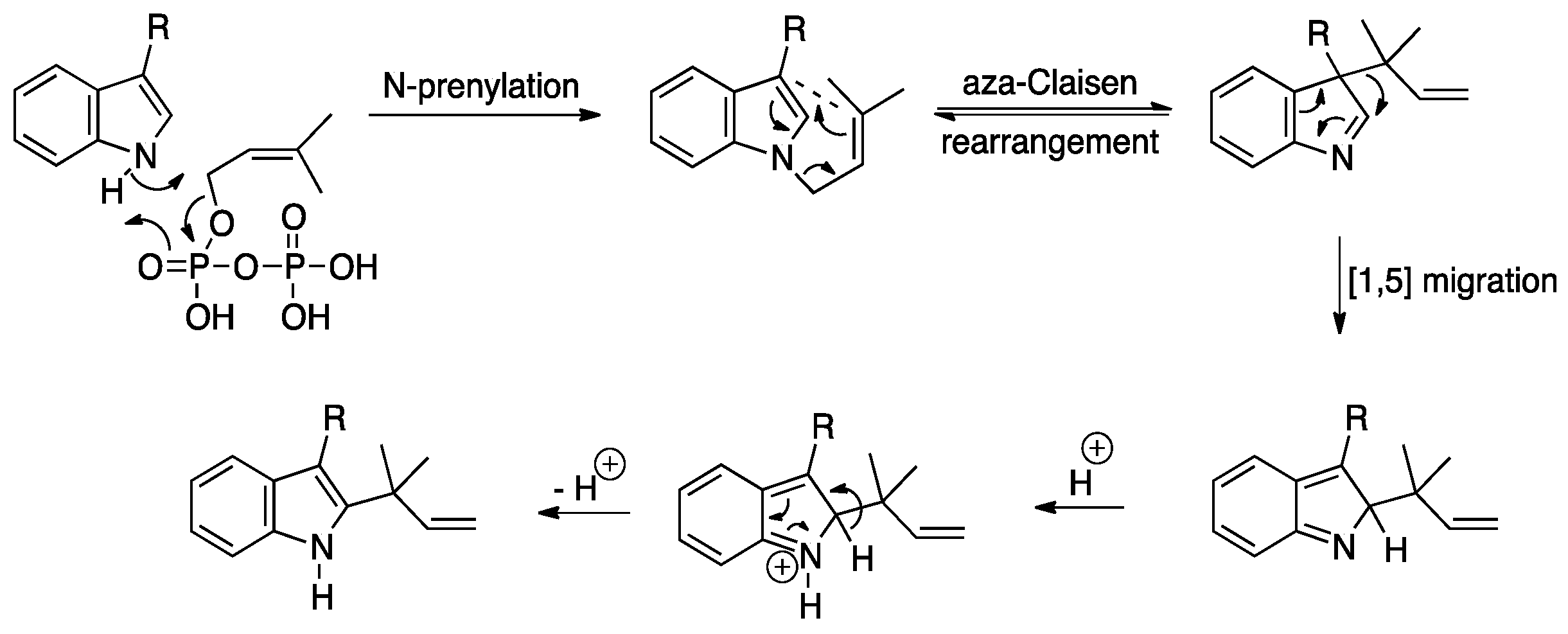
2.4. Proposed BGCs and Biosynthetic Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Procedures
4.2. Microbial Strain Culture and Identification
4.3. Genome Sequencing and Secondary Metabolite BGCs Analysis
4.4. Fermentation, Extraction, and Isolation
4.5. DFT Theory and Calculation
4.6. Bioassays
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bugni, T.S.; Ireland, C.M. Marine-derived fungi: A chemically and biologically diverse group of microorganisms. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2004, 21, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; El-Hossary, E.M.; Oelschlaeger, T.A.; Donia, M.S.; Quinn, R.J.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Potential of marine natural products against drug-resistant bacterial infections. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, e237–e245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashforth, E.J.; Fu, C.; Liu, X.; Dai, H.; Song, F.; Guo, H.; Zhang, L. Bioprospecting for antituberculosis leads from microbial metabolites. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 1709–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yan, K.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, R.; Bian, J.; Zheng, C.; Sun, H.; Chen, Z.; Sun, N.; An, R.; et al. High-throughput synergy screening identifies microbial metabolites as combination agents for the treatment of fungal infections. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4606–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Demain, A.L. Natural Products: Drug Discovery and Therapeutical Medicine; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; p. 382. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, T.E.; Imchen, M.; Kumavath, R. Marine Enzymes: Production and Applications for Human Health; Elsevier: North Andover, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 149–163. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, L.-E.; Kellermann, M.Y.; Schupp, P.J. Secondary Metabolites of Marine Microbes: From Natural Products Chemistry to Chemical Ecology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 159–180. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 122–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Song, F.; Xiao, X.; Huang, P.; Li, L.; Monte, A.; Abdel--Mageed, W.M.; Wang, J.; Guo, H.; He, W.; et al. Abyssomicins from the South China Sea deep--sea sediment Verrucosispora sp.: Natural thioether Michael addition adducts as antitubercular prodrugs. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 1231–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Grkovic, T.; Liu, X.; Han, J.; Zhang, L.; Quinn, R.J. A systems approach using OSMAC, Log P and NMR fingerprinting: An approach to novelty. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2017, 2, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medema, M.H.; Fischbach, M.A. Computational approaches to natural product discovery. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, J.; Song, Z.; Liu, M.; Hu, J.; Hou, C.; Zhu, G.; Jiang, L.; Xia, X.; Quinn, R.J.; et al. Genome-and MS-based mining of antibacterial chlorinated chromones and xanthones from the phytopathogenic fungus Bipolaris sorokiniana strain 11134. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 5167–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, J.; Song, Z.; Zhu, G.; Liu, M.; Dai, H.; Hsiang, T.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Quinn, R.J.; et al. Genome-based mining of new antimicrobial meroterpenoids from the phytopathogenic fungus Bipolaris sorokiniana strain 11134. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, K.-S.; Gao, J.; Doroghazi, J.R.; Wang, K.-K.A.; Thibodeaux, C.J.; Li, S.; Metzger, E.; Fudala, J.; Su, J.; Zhang, J.K.; et al. Discovery of phosphonic acid natural products by mining the genomes of 10,000 actinomycetes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12175–12180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doroghazi, J.R.; Albright, J.C.; Goering, A.W.; Ju, K.-S.; Haines, R.R.; Tchalukov, K.A.; Labeda, D.P.; Kelleher, N.L.; Metcalf, W.W. A roadmap for natural product discovery based on large-scale genomics and metabolomics. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, G.; Xu, Z.; Guo, Z.; Ma, M.; Yang, D.; Zhou, H.; Gansemans, Y.; Zhu, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, L.-X.; et al. Discovery of the leinamycin family of natural products by mining actinobacterial genomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E11131–E11140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Song, F.; Zhang, L. Strategies on the construction of high-quality microbial natural product library--a review. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 2008, 48, 1132–1137. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Hu, Y.; Xiang, S.; Miao, J.; Lou, C.; Zhang, L. Exploiting a precise design of universal synthetic modular regulatory elements to unlock the microbial natural products in Streptomyces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12181–12186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Tan, G.-Y.; Xia, X.; Zhang, L. Learn from microbial intelligence for avermectins overproduction. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 48, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Veerdonk, F.L.; Gresnigt, M.S.; Romani, L.; Netea, M.G.; Latgé, J.-P. Aspergillus fumigatus morphology and dynamic host interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.-B.; Kakeya, H.; Okada, G.; Onose, R.; Ubukata, M.; Takahashi, I.; Isono, K.; Osada, H. Tryprostatins A and B, novel mammalian cell cycle inhibitors produced by Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Antibiot. 1995, 48, 1382–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, W.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, W. Cytotoxic alkaloids and antibiotic nordammarane triterpenoids from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sydowi. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Liu, H.; Fang, Y.; Gu, Q. A new diphenyl ether from marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. BF-2. J. Antibiot. 2006, 59, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Ninomiya, T.; Akabane, H.; Kushida, N.; Tsujiuchi, G.; Ohyama, M.; Gomi, S.; Shito, K.; Murata, T. Pseurotin A and its analogues as inhibitors of immunoglobuline E production. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 1457–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, P.; Tamm, C. Isolation and structure of pseurotin A, a microbial metabolite of Pseudeurotium ovalis Stolk with an unusual heterospirocyclic system. Helv. Chim. Acta. 1981, 64, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natori, S.; Nishikawa, H. Structures of osoic acids and related compounds, metabolites of Oospora sulphurea-ochracea v. BEYMA. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1962, 10, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cui, C.-B.; Kakeya, H.; Osada, H. Novel mammalian cell cycle inhibitors, spirotryprostatins A and B, produced by Aspergillus fumigatus, which inhibit mammalian cell cycle at G2/M phase. Tetrahedron 1996, 529, 12651–12666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, M.; Lin, A.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, W. Seven new prenylated indole diketopiperazine alkaloids from holothurian-derived fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 7986–7991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Liu, R.; Chen, L.; Zhu, T.; Zhu, W.M.; Gu, Q.Q. Two new hetero-spirocyclic γ-lactam derivatives from marine sediment-derived fungus Aspergillus sydowi D2–6. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2010, 33, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.-B.; Kakeya, H.; Osada, H. Novel mammalian cell cycle inhibitors, tryprostatins A, B and other diketopiperazines produced by Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Antibiot. 1996, 49, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, H.; Fujimaki, T.; Okuyama, E.; Yamazaki, M. Immunosuppressive constituents from an Ascomycete, Sordaria gondaensis. JSM Mycotoxins 2000, 50, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fujimoto, H.; Negishi, E.; Yamaguchi, K.; Nishi, N.; Yamazaki, M. Isolation of new tremorgenic metabolites from an Ascomycete, Corynascus setosus. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1996, 44, 1843–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnaweera, P.B.; Williams, D.E.; de Silva, E.D.; Wijesundera, R.L.; Dalisay, D.S.; Andersen, R.J. Helvolic acid, an antibacterial nortriterpenoid from a fungal endophyte, Xylaria sp. of orchid Anoectochilus setaceus endemic to Sri Lanka. Mycology 2014, 5, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Li, L.; Zou, J.; Han, T.; Qin, L. Identification of a quinazoline alkaloid produced by Penicillium vinaceum, an endophytic fungus from Crocus sativus. Pharm. Biol. 2012, 50, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, R.H.; Xu, S.; Liu, J.Y.; Ge, H.M.; Ding, H.; Xu, C.; Zhu, H.L.; Tan, R.X. Chaetominine, a cytotoxic alkaloid produced by endophytic Chaetomium sp. IFB-E015. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 5709–5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, H.M.; Yu, Z.G.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.H.; Tan, R.X. Bioactive alkaloids from endophytic Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 753–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, W.; Blunt, J.W.; Cole, A.L.; Munro, M.H. Fumagiringillin, a new fumagillin derivative from a strain of the fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1434–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttachon, S.; Zin, W.W.M.; Dethoup, T.; Gales, L.; Pereira, J.A.; Silva, A.M.; Kijjoa, A. Secondary metabolites from the culture of the marine sponge-associated fungi Talaromyces tratensis and Sporidesmium circinophorum. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, H.; Akiyama, H.; Nishikori, K.; Mochizuki, J.-I. Asterric acid, a new endothelin binding inhibitor. J. Antibiot. 1992, 45, 1684–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waser, M.; Lackner, B.; Zuschrader, J.; Müller, N.; Falk, H. An efficient regioselective synthesis of endocrocin and structural related natural anthraquinones starting from emodin. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 2377–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, H.; Fujimaki, T.; Okuyama, E.; Yamazaki, M. Immunomodulatory constituents from an ascomycete, Microascus tardifaciens. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 47, 1426–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunematsu, Y.; Ishikawa, N.; Wakana, D.; Goda, Y.; Noguchi, H.; Moriya, H.; Hotta, K.; Watanabe, K. Distinct mechanisms for spiro-carbon formation reveal biosynthetic pathway crosstalk. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.-M. Genome mining and biosynthesis of fumitremorgin-type alkaloids in ascomycetes. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wiemann, P.; Guo, C.-J.; Palmer, J.M.; Sekonyela, R.; Wang, C.C.; Keller, N.P. Prototype of an intertwined secondary-metabolite supercluster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17065–17070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiya, S.; Grundmann, A.; Li, X.; Li, S.M.; Turner, G. Identification of a hybrid PKS/NRPS required for pseurotin A biosynthesis in the human pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. Chembiochem 2007, 8, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunematsu, Y.; Fukutomi, M.; Saruwatari, T.; Noguchi, H.; Hotta, K.; Tang, Y.; Watanabe, K. Elucidation of pseurotin biosynthetic pathway points to trans--acting C--methyltransferase: Generation of chemical diversity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 8475–8479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unsöld, I.A.; Li, S.M. Reverse prenyltransferase in the biosynthesis of fumigaclavine C in Aspergillus fumigatus: Gene expression, purification, and characterization of fumigaclavine C synthase FGAPT1. Chembiochem 2006, 7, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Steffan, N.; Yin, W.B.; Li, S.M. Ergot alkaloid biosynthesis in Aspergillus fumigatus: FgaAT catalyses the acetylation of fumigaclavine B. Chembiochem 2009, 10, 2325–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigbers, O.; Li, S.-M. Ergot alkaloid biosynthesis in Aspergillus fumigatus overproduction and biochemical characterization of a 4-dimethylallyltryptophan N-methyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 26859–26868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Hu, D.; Gao, H.; Kushiro, T.; Awakawa, T.; Chen, G.; Wang, C.; Abe, I.; Yao, X. Biosynthesis of helvolic acid and identification of an unusual C-4-demethylation process distinct from sterol biosynthesis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Zhu, L.; Luo, Q.; Li, X.; Xi, J.; Kong, G.; Song, Y. Fumigaclavine I, a new alkaloid isolated from endophyte Aspergillus terreus. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2015, 13, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Rashid, M.M.; Zaidi, N.; Kumar, R.; Singh, H. Secondary Metabolites of Metarhizium spp. and Verticillium spp. and Their Agricultural Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 27–58. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, A.; Gao, J. Metabolites from Aspergillus fumigatus, an endophytic fungus associated with Melia azedarach, and their antifungal, antifeedant, and toxic activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3424–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanmanoch, W.; Mongkolthanaruk, W.; Kanokmedhakul, S.; Aimi, T.; Boonlue, S. Helvolic acid, a secondary metabolite produced by Neosartorya spinosa KKU-1NK1 and its biological activities. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2016, 43, 483–493. [Google Scholar]
- Ganaha, M.; Yoshii, K.; Ōtsuki, Y.; Iguchi, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Iseki, K.; Ban, S.; Ishiyama, A.; Hokari, R.; Iwatsuki, M. In vitro antitrypanosomal activity of the secondary metabolites from the mutant strain IU-3 of the insect pathogenic fungus Ophiocordyceps coccidiicola NBRC 100683. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 64, 988–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawadsitang, S.; Mongkolthanaruk, W.; Suwannasai, N.; Sodngam, S. Antimalarial and cytotoxic constituents of Xylaria cf. cubensis PK108. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 2033–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, E.A.A.; Carvalho, J.M.; dos Santos, D.C.P.; Feitosa, A.D.O.; Marinho, P.S.B.; Guilhon, G.M.S.P.; de Souza, A.D.L.; da Silva, F.M.A.; Marinho, A.M.D.R. Antibacterial activity of alkaloids produced by endophytic fungus Aspergillus sp. EJC08 isolated from medical plant Bauhinia guianensis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Han, J.; Wang, Y.; Lin, R.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Wei, S.; Polyak, S.W.; Song, F. Two new spiro-heterocyclic γ-lactams from a marine-derived Aspergillus fumigatus strain CUGBMF170049. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenke, J.; Anke, H.; Sterner, O. Pseurotin A and 8-O-demethylpseurotin A from Aspergillus fumigatus and their inhibitory activities on chitin synthase. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1993, 57, 961–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guruceaga, X.; Perez-Cuesta, U.; Abad-Diaz de Cerio, A.; Gonzalez, O.; Alonso, R.M.; Hernando, F.L.; Ramirez-Garcia, A.; Rementeria, A. Fumagillin, a mycotoxin of Aspergillus fumigatus: Biosynthesis, biological activities, detection, and applications. Toxins 2020, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.J.; Gerwick, W.H. Lyngbyatoxin biosynthesis: Sequence of biosynthetic gene cluster and identification of a novel aromatic prenyltransferase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 11432–11433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wet, J.R.D.; Cavalcoli, J.; Li, S.; Greshock, T.J.; Miller, K.A.; Finefield, J.M.; Sunderhaus, J.D.; McAfoos, T.J.; Tsukamoto, S.; et al. Genome-based characterization of two prenylation steps in the assembly of the stephacidin and notoamide anticancer agents in a marine-derived Aspergillus sp. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12733–12740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Grundmann, A.; Cheng, J.; Li, S. Acetylaszonalenin biosynthesis in Neosartorya fischeri identification of the biosynthetic gene cluster by genomic mining and functional proof of the genes by biochemical investigation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Yu, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.-Q.; Li, S.-M. Identification of a brevianamide F reverse prenyltransferase BrePT from Aspergillus versicolor with a broad substrate specificity towards tryptophan-containing cyclic dipeptides. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 1649–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunsch, C.; Mundt, K.; Li, S.-M. Targeted production of secondary metabolites by coexpression of non-ribosomal peptide synthetase and prenyltransferase genes in Aspergillus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 4213–4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möller, E.; Bahnweg, G.; Sandermann, H.; Geiger, H. A simple and efficient protocol for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from filamentous fungi, fruit bodies, and infected plant tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, J.; Fehr, A.; Gray, J.; Luong, K.; Lyle, J.; Otto, G.; Peluso, P.; Rank, D.; Baybayan, P.; Bettman, B.; et al. Real-time DNA sequencing from single polymerase molecules. Science 2009, 323, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.-S.; Alexander, D.H.; Marks, P.; Klammer, A.A.; Drake, J.; Heiner, C.; Clum, A.; Copeland, A.; Huddleston, J.; Eichler, E.E.; et al. Nonhybrid, finished microbial genome assemblies from long-read SMRT sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanke, M.; Diekhans, M.; Baertsch, R.; Haussler, D. Using native and syntenically mapped cDNA alignments to improve de novo gene finding. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Steinke, K.; Villebro, R.; Ziemert, N.; Lee, S.Y.; Medema, M.H.; Weber, T. antiSMASH 5.0: Updates to the secondary metabolite genome mining pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W81–W87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.; Zaretskaya, I.; Raytselis, Y.; Merezhuk, Y.; McGinnis, S.; Madden, T.L. NCBI BLAST: A better web interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W5–W9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Fan, Y.; Tao, G.; Fu, P.; Zhai, J.; Ye, B.; Zhu, W. Sekgranaticin, a SEK34b-granaticin hybrid polyketide from Streptomyces sp. 166#. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 9087–9092. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.G.; Goodman, J.M. Assigning stereochemistry to single diastereoisomers by GIAO NMR calculation: The DP4 probability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12946–12959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.F.; Dai, H.Q.; Wei, Y.L.; Zhu, H.J.; Yan, Y.M.; Wang, Y.H.; Long, C.L.; Zhong, H.M.; Zhang, L.X.; Cheng, Y.X. Antituberculosis agents and an inhibitor of the para--aminobenzoic acid biosynthetic pathway from hydnocarpus anthelminthica seeds. Chem. Biodivers. 2010, 7, 2046–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taneja, N.K.; Tyagi, J.S. Resazurin reduction assays for screening of anti-tubercular compounds against dormant and actively growing Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium bovis BCG and Mycobacterium smegmatis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 60, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Ren, B.; Yu, K.; Chen, C.; Guo, H.; Yang, N.; Gao, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Tong, Y.; et al. Quinazolin-4-one coupled with pyrrolidin-2-iminium alkaloids from marine-derived fungus Penicillium aurantiogriseum. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Position | 1 | 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC, Type | δH, Mult (J in Hz) | δC, Type | δH, Mult (J in Hz) | |
| 1 | 11.57 s | |||
| 2 | 131.7, C | 133.8, C | ||
| 3 | 119.8, C | 119.2, C | ||
| 3a | 122.4, C | 122.3, C | ||
| 4 | 123.0, CH | 7.68 d (8.9) | 122.7, CH | 7.64 d (8.9) |
| 5 | 112.5, CH | 6.77 dd (8.9, 2.3) | 112.2, CH | 6.74 dd (8.9, 2.3) |
| 6 | 159.8, C | 159.3, C | ||
| 7 | 94.1, CH | 6.89 d (2.3) | 94.1, CH | 6.88 d (2.3) |
| 7a | 138.7, C | 138.0, C | ||
| 8 | 26.0, CH2 | 3.62 m, 3.32 m | 25.5, CH2 | 3.61 dd (14.2, 4.9), 3.27 m |
| 9 | 56.1, CH | 4.42 t (6.5) | 56.6, CH | 4.36 t (6.1) |
| 10 | 7.45 s | 7.42 s | ||
| 11 | 167.2, C | 167.0, C | ||
| 12 | 58.9, CH | 4.16 t (8.0) | 58.8, CH | 4.14 t (8.0) |
| 13 | 28.1, CH2 | 2.07 m, 1.72 m | 28.0, CH2 | 2.06 m, 1.73 m |
| 14 | 22.6, CH2 | 1.75 m | 22.7, CH2 | 1.75 m |
| 15 | 45.5, CH2 | 3.39 m, 3.28 m | 45.3, CH2 | 3.38 m, 3.32 m |
| 17 | 165.9, C | 166.0, C | ||
| 18 | 187.2, C | 194.1, C | ||
| 19 | 63.9, CH | 4.36 s | 52.9, CH2 | 3.05 d (13.9), 3.02 d (13.9) |
| 20 | 61.8, C | 70.1, C | ||
| 21 | 24.7, CH3 | 1.48 s | 30.3, CH3 | 1.25 s |
| 22 | 18.6, CH3 | 1.17 s | 30.3, CH3 | 1.25 s |
| 6-OCH3 | 55.6, CH3 | 3.81 s | 55.6, CH3 | 3.80 s |
| Position | 4 | 6 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC, Type | δH, Mult (J in Hz) | δC, Type | δH, Mult (J in Hz) | |
| 1 | 129.4, C | 125.8, C | ||
| 2 | 155.8, C | 156.6, C | ||
| 3 | 108.3, CH | 7.06 d (2.1) | 103.2, CH | 6.69 d (2.2) |
| 4 | 154.1, C | 158.1, C | ||
| 5 | 112.4, CH | 7.43 d (2.1) | 107.2, CH | 6.89 d (2.2) |
| 6 | 127.1, C | 128.0, C | ||
| 7 | 165.5, C | 165.8, C | ||
| 8 | 52.3, CH3 | 3.66 s | 52.1, CH3 | 3.62 s |
| 9 | 56.2, CH3 | 3.65 s | 56.0, CH3 | 3.63 s |
| 10 | 199.1, C | 199.4, C | ||
| 1’ | 109.9, C | 110.1, C | ||
| 2’ | 160.9, C | 160.8, C | ||
| 3’ | 103.7, CH | 6.27 s | 103.5, CH | 6.26 s |
| 4’ | 148.2, C | 147.8, C | ||
| 5’ | 110.2, CH | 6.39 s | 110.1, CH | 6.38 s |
| 6’ | 163.4, C | 163.3, C | ||
| 7’ | 55.9, CH3 | 3.31 s | 55.9, CH3 | 3.33 s |
| 8’ | 22.0, CH3 | 2.26 s | 21.9, CH3 | 2.26 s |
| 6′-OH | 12.90 s | 12.95 s | ||
| 4-OH | 10.05 s | |||
| Position | δC, Type | δH, Mult (J in Hz) | Position | δC, Type | δH, Mult (J in Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11 | 5.2, CH3 | 1.65 s | ||
| 2 | 186.0, C | 12 | 196.4, C | ||
| 3 | 110.1, C | 13 | 133.4, C | ||
| 4 | 196.6, C | 14 | 130.3, CH | 8.25 dd (8.4, 1.2) | |
| 5 | 91.4, C | 15 | 128.4, CH | 7.52 dd (8.4, 7.4) | |
| 6 | 166.4, C | 16 | 133.8, CH | 7.67 tt (7.4, 1.2) | |
| 7 | 9.92 s | 17 | 128.4, CH | 7.52 dd (8.4, 7.4) | |
| 8 | 92.5, C | 18 | 130.3, CH | 8.25 dd (8.4, 1.2) | |
| 9 | 74.9, CH | 4.39 s | 8-OCH3 | 51.6, CH3 | 3.24 s |
| 10 | 57.1, CH2 | 4.42 d (3.0) |
| Compounds | Pathogenic Bacteria (MIC, μg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. smegmatis | S. aureus | E. coli | P. aeruginosa | |
| 15 | >100 | 100 | >100 | >100 |
| 16 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 18 | >100 | 6.25 | 6.25 | >100 |
| 19 | 100 | 3.13 | 3.13 | >100 |
| 20 | 100 | 100 | >100 | >100 |
| 23 | 100 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
| 30 | >100 | 100 | 100 | >100 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, J.; Liu, M.; Jenkins, I.D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Quinn, R.J.; Feng, Y. Genome-Inspired Chemical Exploration of Marine Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus MF071. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18070352
Han J, Liu M, Jenkins ID, Liu X, Zhang L, Quinn RJ, Feng Y. Genome-Inspired Chemical Exploration of Marine Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus MF071. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(7):352. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18070352
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Jianying, Miaomiao Liu, Ian D. Jenkins, Xueting Liu, Lixin Zhang, Ronald J. Quinn, and Yunjiang Feng. 2020. "Genome-Inspired Chemical Exploration of Marine Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus MF071" Marine Drugs 18, no. 7: 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18070352
APA StyleHan, J., Liu, M., Jenkins, I. D., Liu, X., Zhang, L., Quinn, R. J., & Feng, Y. (2020). Genome-Inspired Chemical Exploration of Marine Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus MF071. Marine Drugs, 18(7), 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18070352






