Inhibition of Skin Inflammation by Scytonemin, an Ultraviolet Sunscreen Pigment
Abstract
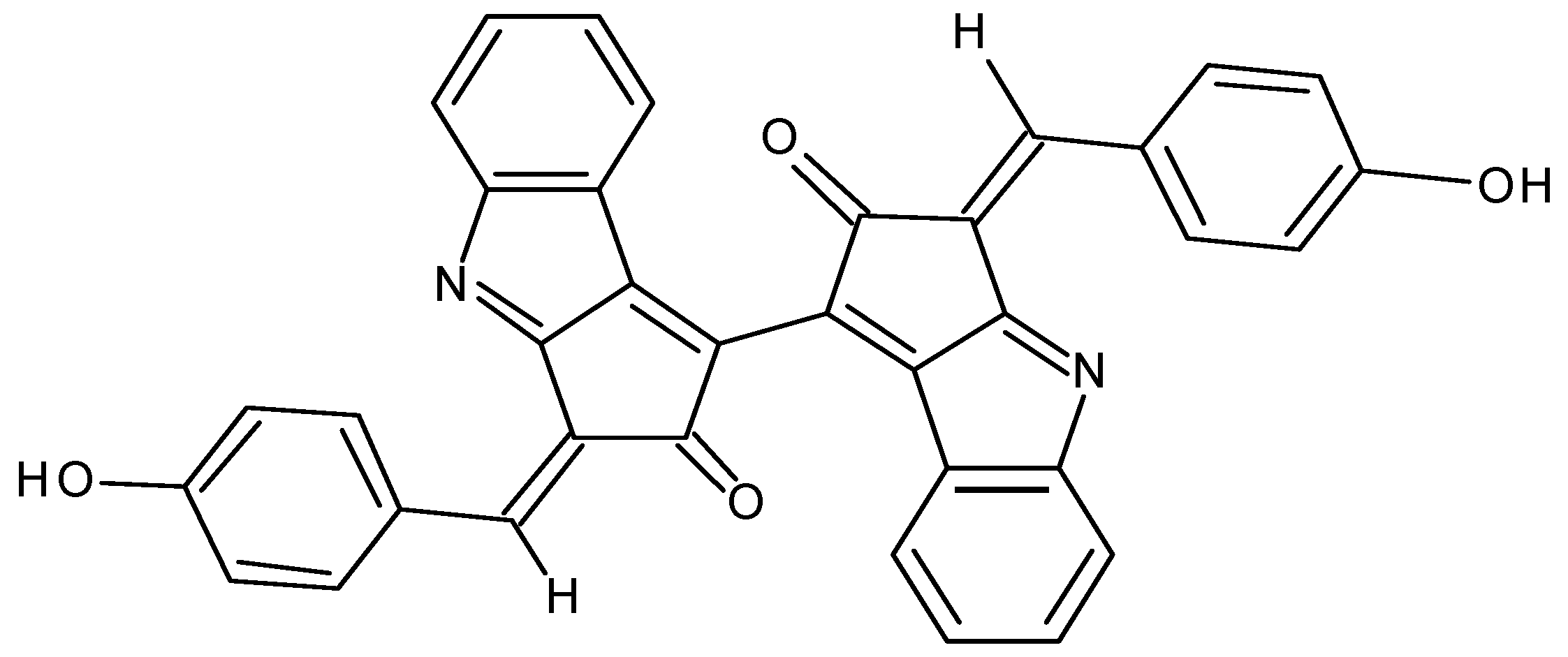
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Scytonemin on 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-Induced Ear Swelling in BALB/c Mice
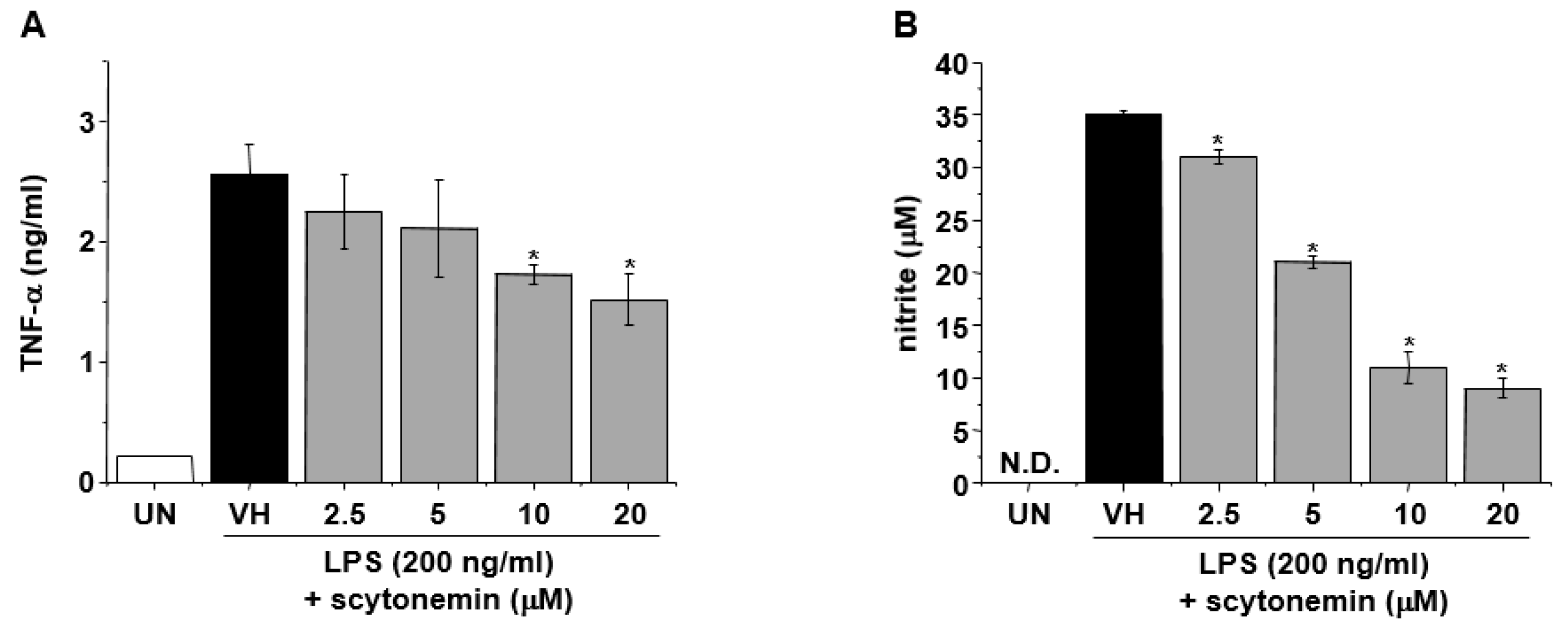
2.2. Effect of Scytonemin on Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced Production of Inflammatory Mediators in RAW 264.7 Cells
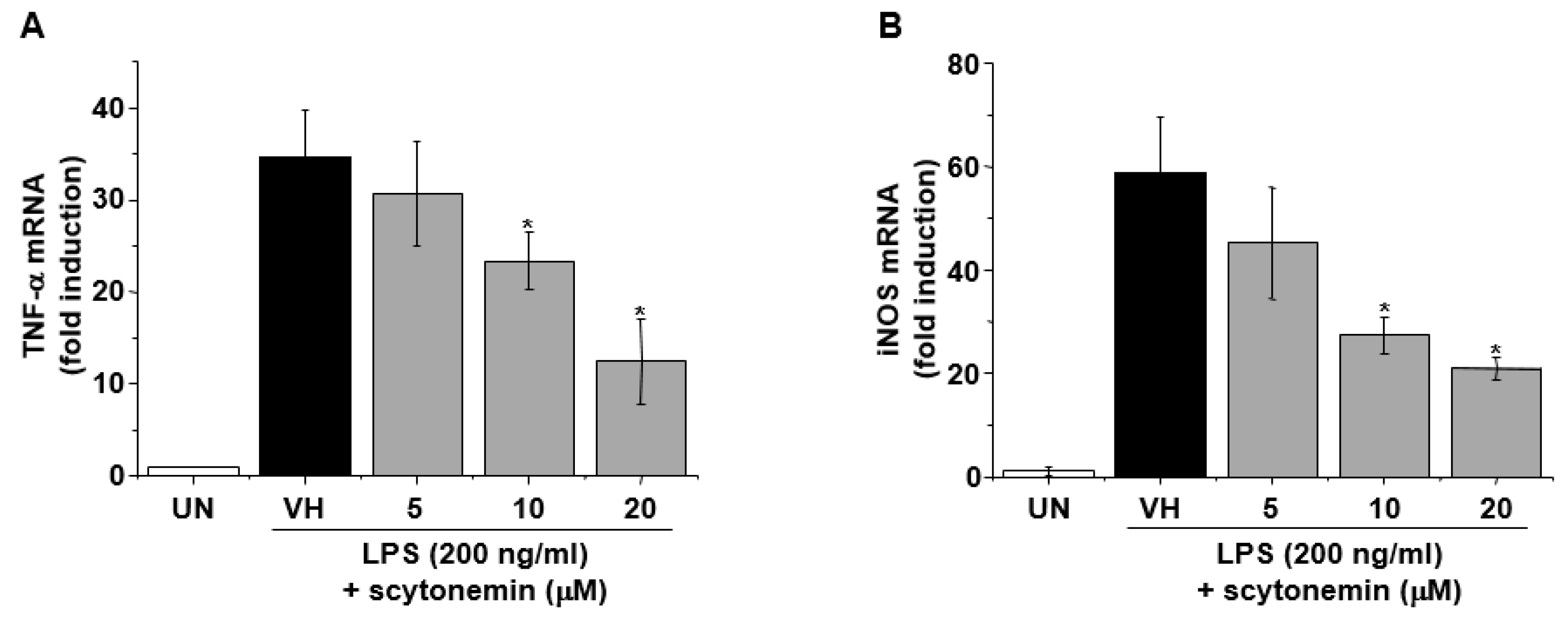
2.3. Effect of Scytonemin on LPS-induced mRNA Expression of Inflammatory Mediators in RAW 264.7 Cells
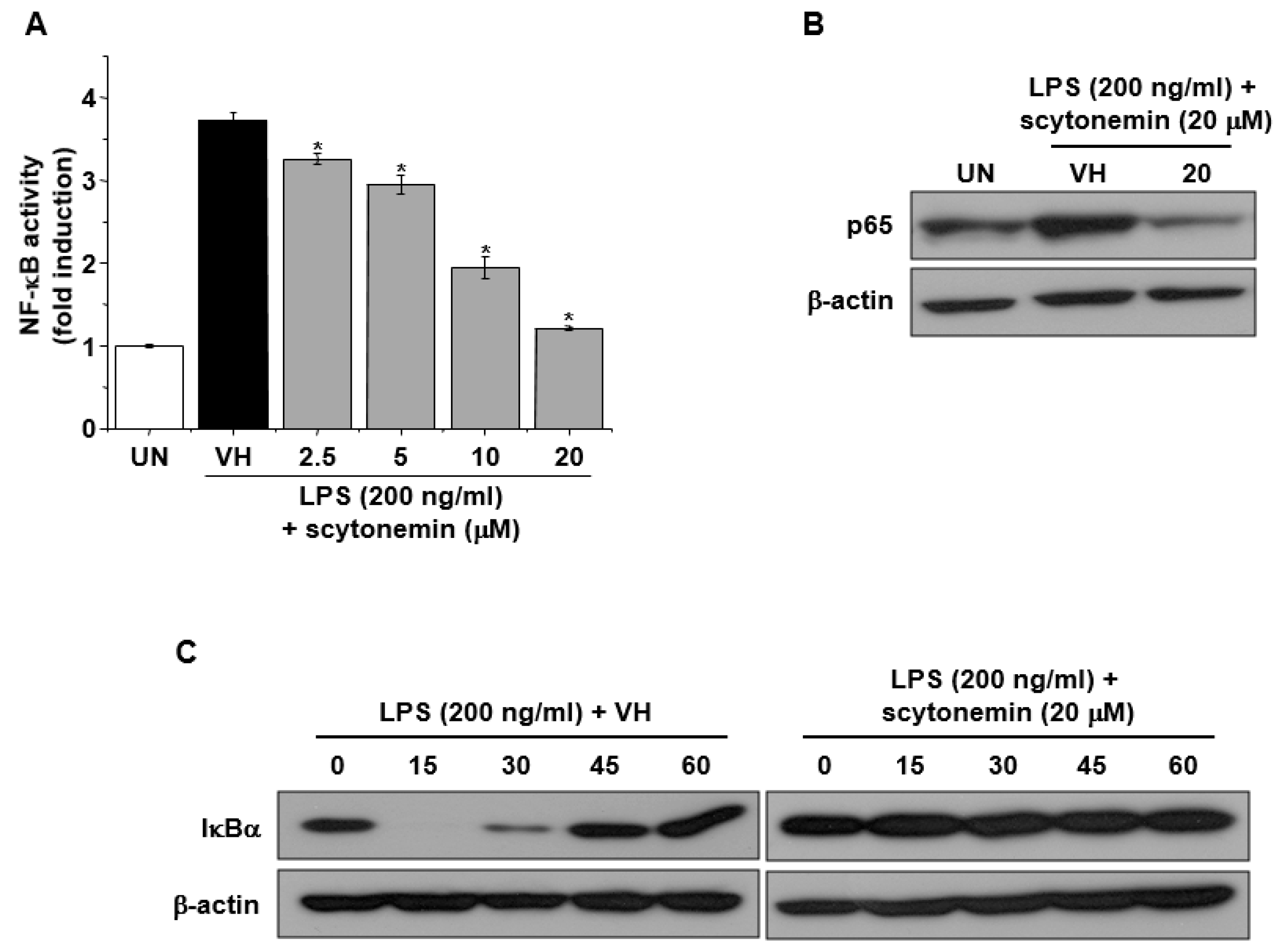
2.4. Effect of Scytonemin on LPS-induced NF-κB Signaling in RAW 264.7 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals, Animals and Cell Culture
4.2. TPA-induced Skin Inflammation
4.3. Total RNA Isolation and Quantification of mRNA Expression
4.4. Nitrite Quantification
4.5. Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.6. Transient Transfection and Luciferase Reporter Gene Assay
4.7. Western Immunoblot Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rastogi, R.P.; Sonani, R.R.; Madamwar, D. Cyanobacterial Sunscreen Scytonemin: Role in Photoprotection and Biomedical Research. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 176, 1551–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proteau, P.J.; Gerwick, W.H.; Garcia-Pichel, F.; Castenholz, R. The structure of scytonemin, an ultraviolet sunscreen pigment from the sheaths of cyanobacteria. Experientia 1993, 49, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamatsu, S.; Hodges, T.W.; Rajbhandari, I.; Gerwick, W.H.; Hamann, M.T.; Nagle, D.G. Marine natural products as novel antioxidant prototypes. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, C.S.; Capper, E.A.; Roshak, A.K.; Marquez, B.; Eichman, C.; Jackson, J.R.; Mattern, M.; Gerwick, W.H.; Jacobs, R.S.; Marshall, L.A. The identification and characterization of the marine natural product scytonemin as a novel antiproliferative pharmacophore. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther 2002, 303, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uluckan, O.; Guinea-Viniegra, J.; Jimenez, M.; Wagner, E.F. Signalling in inflammatory skin disease by AP-1 (Fos/Jun). Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, S44–S49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Proinflammatory cytokines. Chest 2000, 118, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palladino, M.A.; Bahjat, F.R.; Theodorakis, E.A.; Moldawer, L.L. Anti-TNF-alpha therapies: The next generation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, S. Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, N.; Kobayashi, K. Macrophages in inflammation. Curr. Drug Targets Inflamm. Allergy 2005, 4, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, M.; Maini, R.N. Anti-TNF alpha therapy of rheumatoid arthritis: What have we learned? Annu Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 163–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Hamid, H.; Ali, A.; Alam, M.S.; Athar, M. Antiinflammatory evaluation of alcoholic extract of galls of Quercus infectoria. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 90, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.H.; Yoon, Y.D.; Han, S.B.; Oh, S.J.; Yun, J.; Lee, C.W.; Lee, K.; Park, S.K.; Kim, H.M.; Kang, J.S. Artemisinin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced interferon-beta production in RAW 264.7 cells: Implications on signal transducer and activator of transcription-1 signaling and nitric oxide production. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 14, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.W.; Kashiwabara, Y.; Nathan, C. Role of transcription factor NF-kappa B/Rel in induction of nitric oxide synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 4705–4708. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, M.J.; Ryu, H.S.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, H.K.; Kang, J.S.; Yun, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, M.K.; Hong, J.T.; Kim, Y.; et al. Platycodon grandiflorum polysaccharide induces dendritic cell maturation via TLR4 signaling. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 72, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasparakis, M.; Haase, I.; Nestle, F.O. Mechanisms regulating skin immunity and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musthaq, S.; Mazuy, A.; Jakus, J. The microbiome in dermatology. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 36, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neagu, M.; Constantin, C.; Caruntu, C.; Dumitru, C.; Surcel, M.; Zurac, S. Inflammation: A key process in skin tumorigenesis. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 4068–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canedo-Dorantes, L.; Canedo-Ayala, M. Skin Acute Wound Healing: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Inflam. 2019, 2019, 3706315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowes, M.A.; Chamian, F.; Abello, M.V.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Lin, S.L.; Nussbaum, R.; Novitskaya, I.; Carbonaro, H.; Cardinale, I.; Kikuchi, T.; et al. Increase in TNF-alpha and inducible nitric oxide synthase-expressing dendritic cells in psoriasis and reduction with efalizumab (anti-CD11a). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 19057–19062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R.; Chen, X.; Hu, J.; Fu, Y.; Peng, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, P.; Liu, L.; Cao, J.; et al. Ghrelin protects against contact dermatitis and psoriasiform skin inflammation by antagonizing TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, R.; Figueiredo, C.P.; Passos, G.F.; Calixto, J.B. Reduced skin inflammatory response in mice lacking inducible nitric oxide synthase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.W.; Whisnant, R.; Nathan, C. Promoter of the mouse gene encoding calcium-independent nitric oxide synthase confers inducibility by interferon gamma and bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J. Exp. Med. 1993, 177, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.S.; Jeon, Y.J.; Kim, H.M.; Han, S.H.; Yang, K.H. Inhibition of inducible nitric-oxide synthase expression by silymarin in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 302, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.S.; Yoon, Y.D.; Lee, M.Y.; Lee, C.W.; Lee, S.J.; Han, S.B. Testing Cell-Based Immunotherapy for Colorectal Cancer. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1765, 299–305. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.R.; Park, K.H.; Lee, C.W.; Lee, M.Y.; Han, S.B.; Li, L.C.; Kang, J.S. Small activating RNA induced expression of VHL gene in renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 97, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomczynski, P.; Mackey, K. Substitution of chloroform by bromo-chloropropane in the single-step method of RNA isolation. Anal. Biochem. 1995, 225, 163–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, M.R.; Jo, S.A.; Lee, H.; Yoon, Y.D.; Kwon, J.-H.; Yang, J.-W.; Choi, B.J.; Park, K.H.; Lee, M.Y.; Lee, C.W.; et al. Inhibition of Skin Inflammation by Scytonemin, an Ultraviolet Sunscreen Pigment. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18060300
Kang MR, Jo SA, Lee H, Yoon YD, Kwon J-H, Yang J-W, Choi BJ, Park KH, Lee MY, Lee CW, et al. Inhibition of Skin Inflammation by Scytonemin, an Ultraviolet Sunscreen Pigment. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(6):300. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18060300
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Moo Rim, Sun Ah Jo, Hyunju Lee, Yeo Dae Yoon, Joo-Hee Kwon, Jeong-Wook Yang, Byeong Jo Choi, Ki Hwan Park, Myeong Youl Lee, Chang Woo Lee, and et al. 2020. "Inhibition of Skin Inflammation by Scytonemin, an Ultraviolet Sunscreen Pigment" Marine Drugs 18, no. 6: 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18060300
APA StyleKang, M. R., Jo, S. A., Lee, H., Yoon, Y. D., Kwon, J.-H., Yang, J.-W., Choi, B. J., Park, K. H., Lee, M. Y., Lee, C. W., Lee, K.-R., & Kang, J. S. (2020). Inhibition of Skin Inflammation by Scytonemin, an Ultraviolet Sunscreen Pigment. Marine Drugs, 18(6), 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18060300




