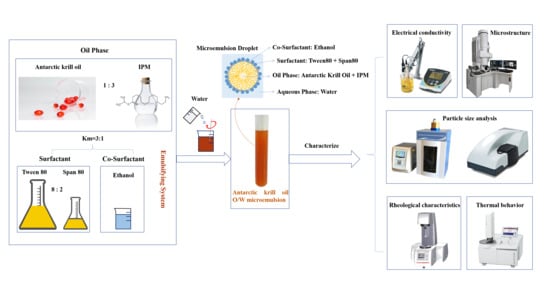
Preparation and Characterization of Microemulsions Based on Antarctic Krill Oil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
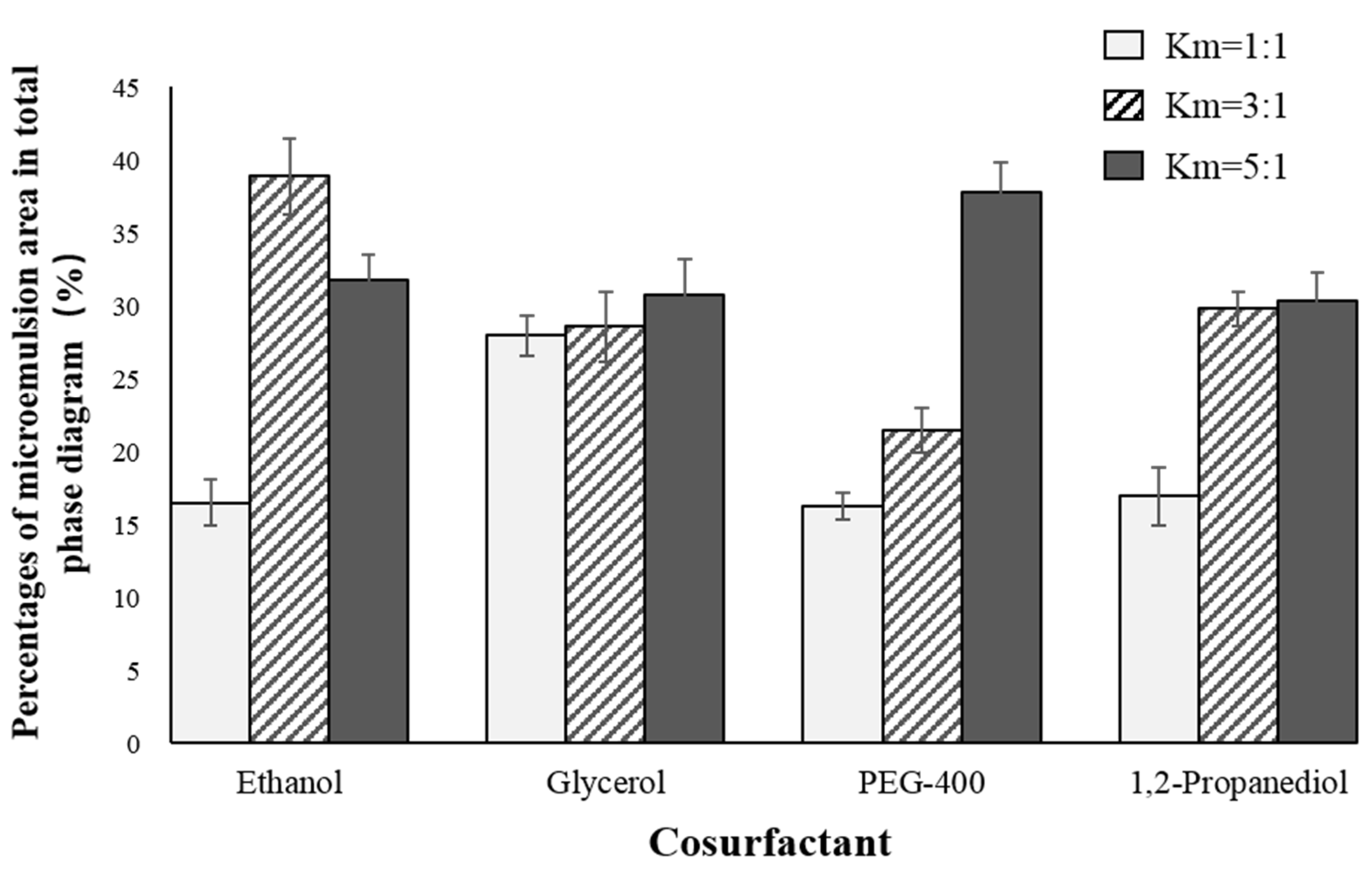
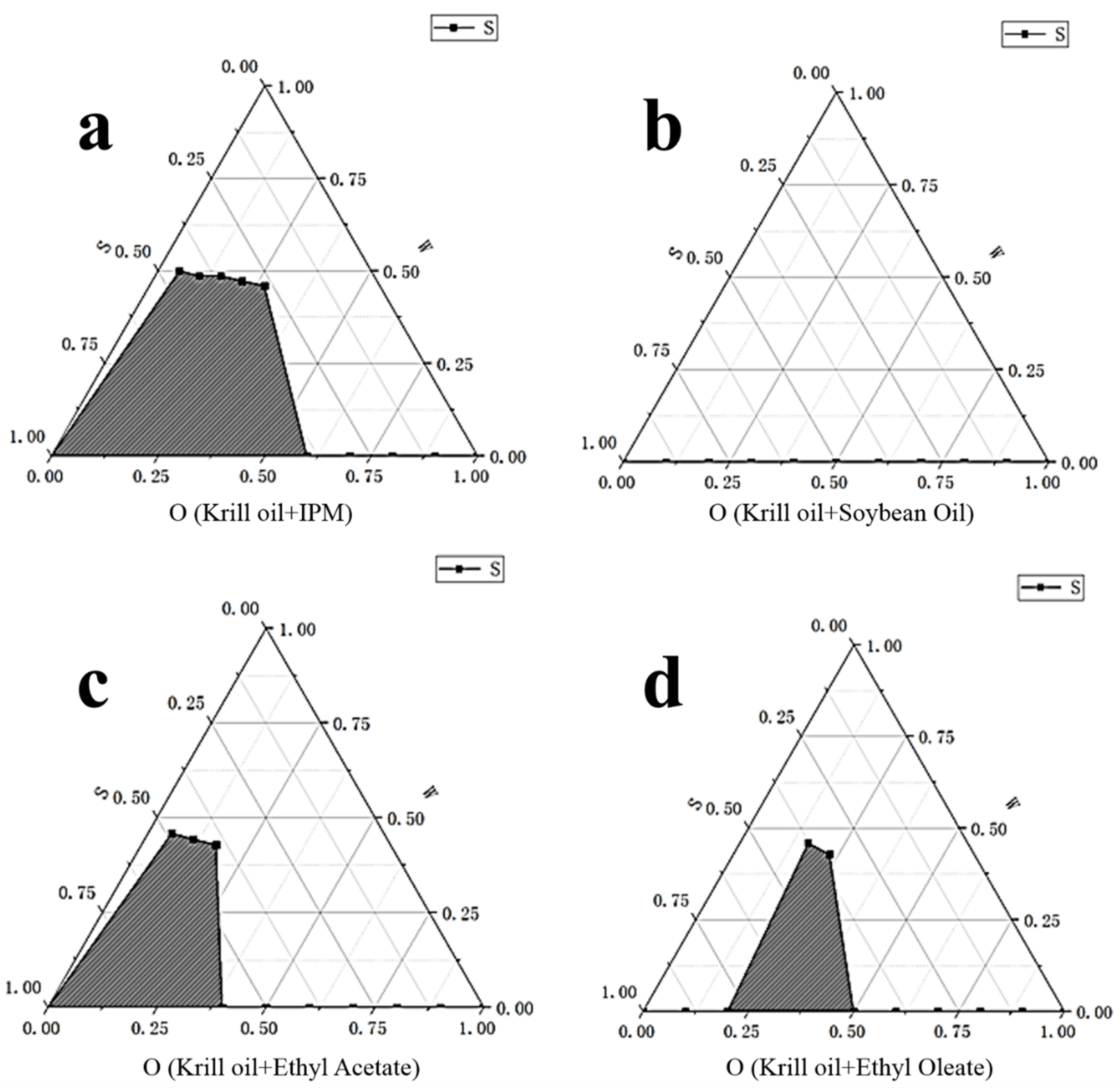
2.1. Determination of Antarctic Krill Oil O/W Microemulsion
2.2. Characteristics of Prepared Antarctic Krill Oil O/W Microemulsion
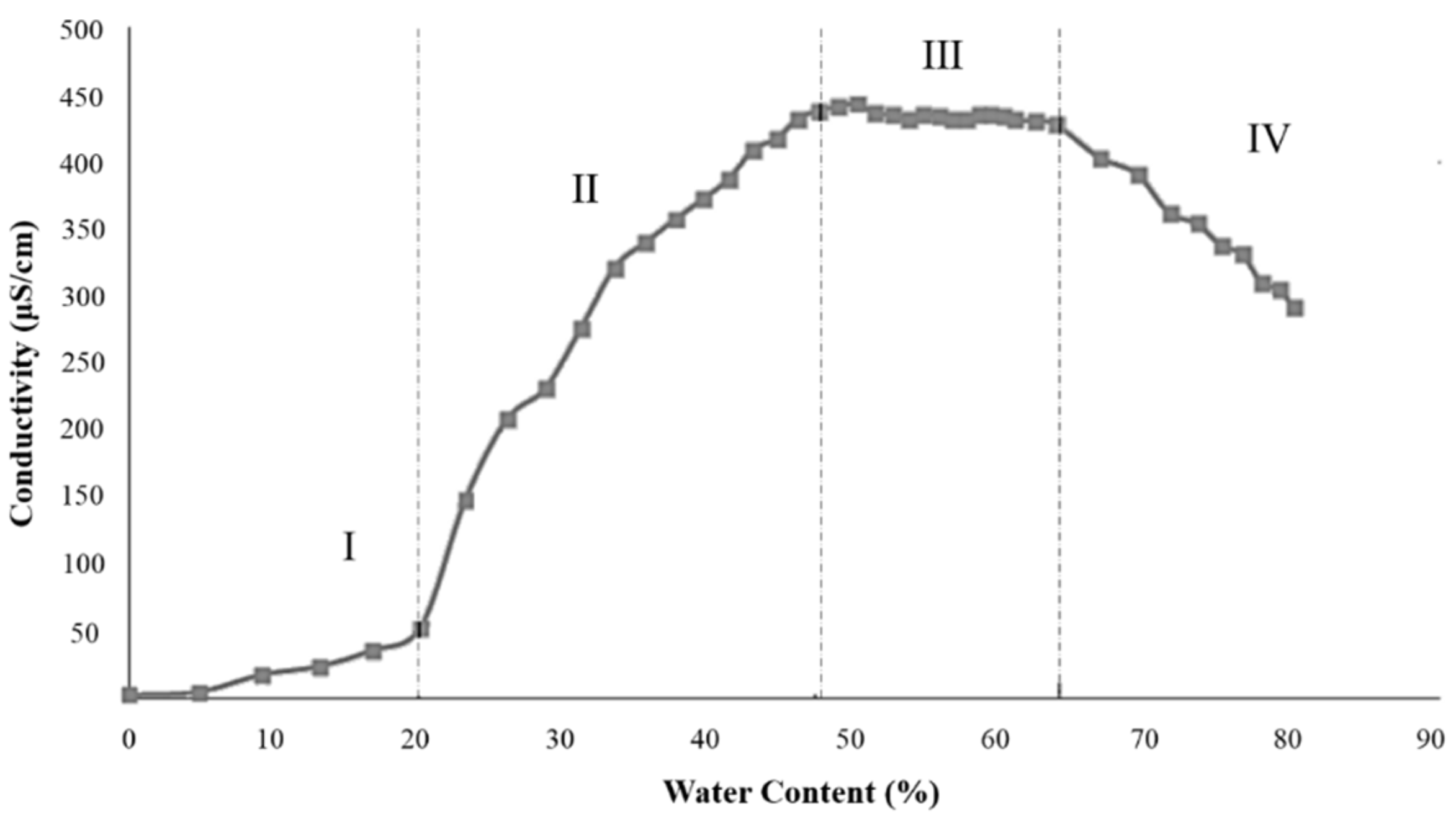
2.2.1. Electrical Conductivity
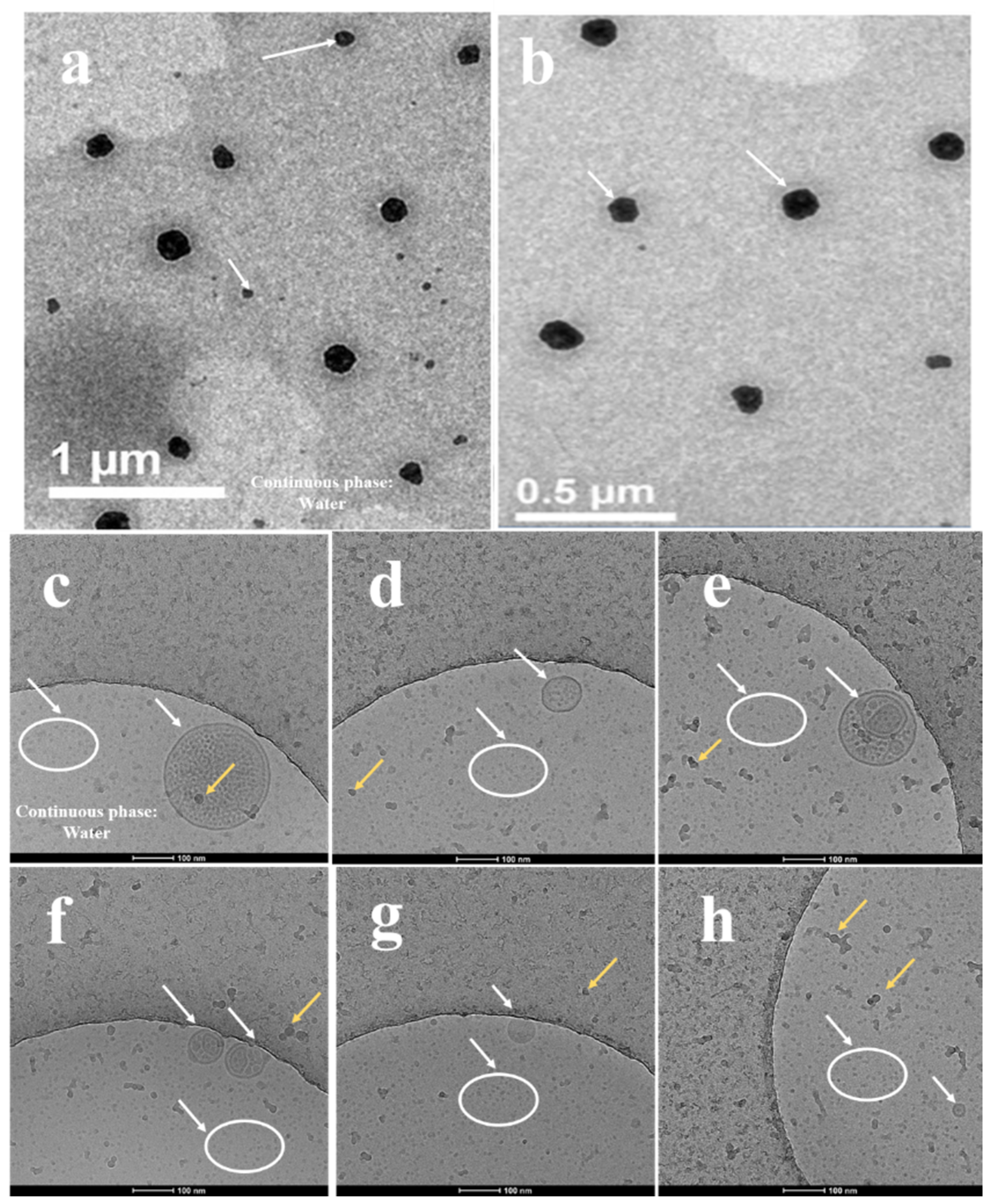
2.2.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and Cryogenic TEM (Cryo-TEM)
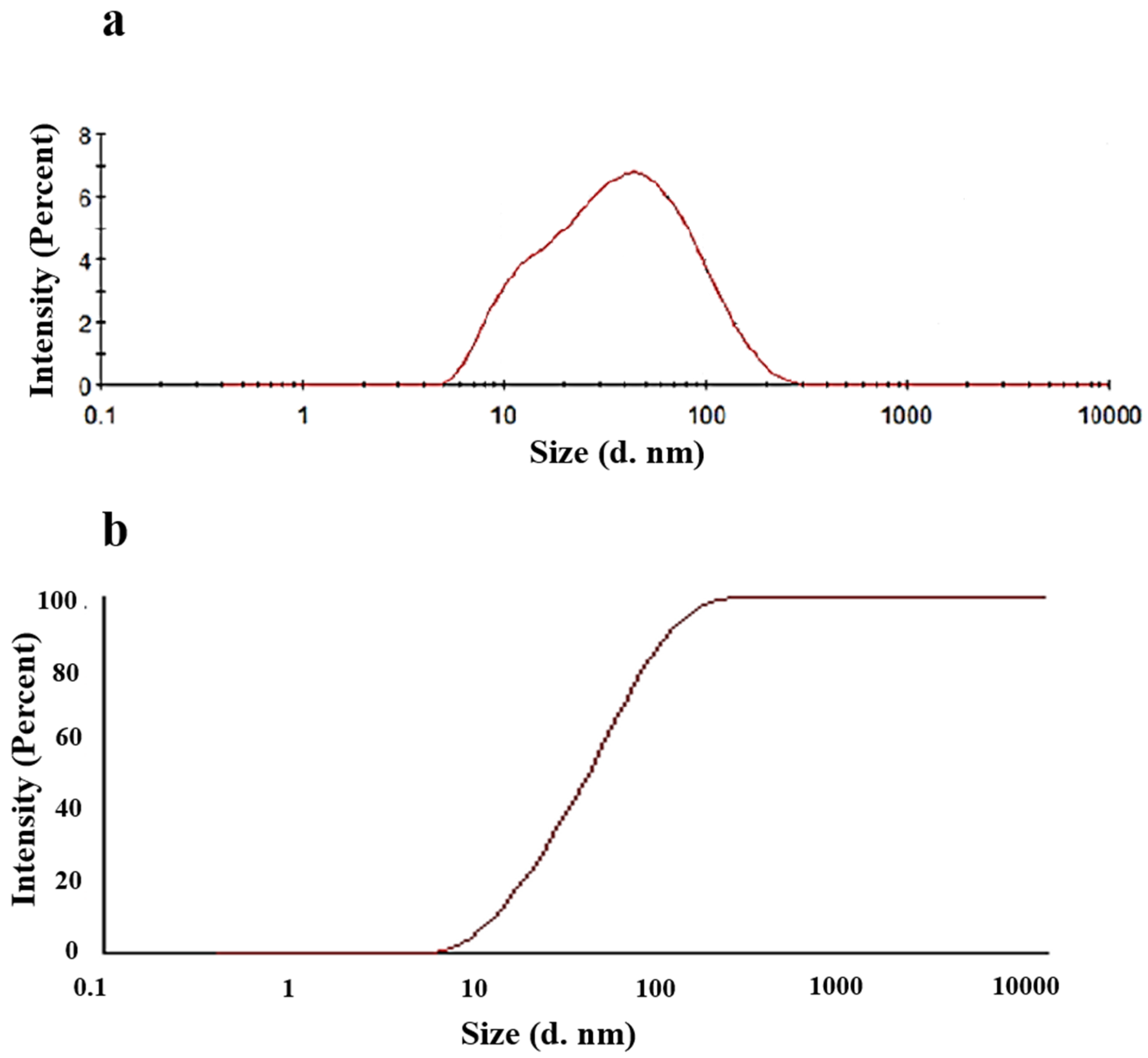
2.2.3. Droplet Size Analysis
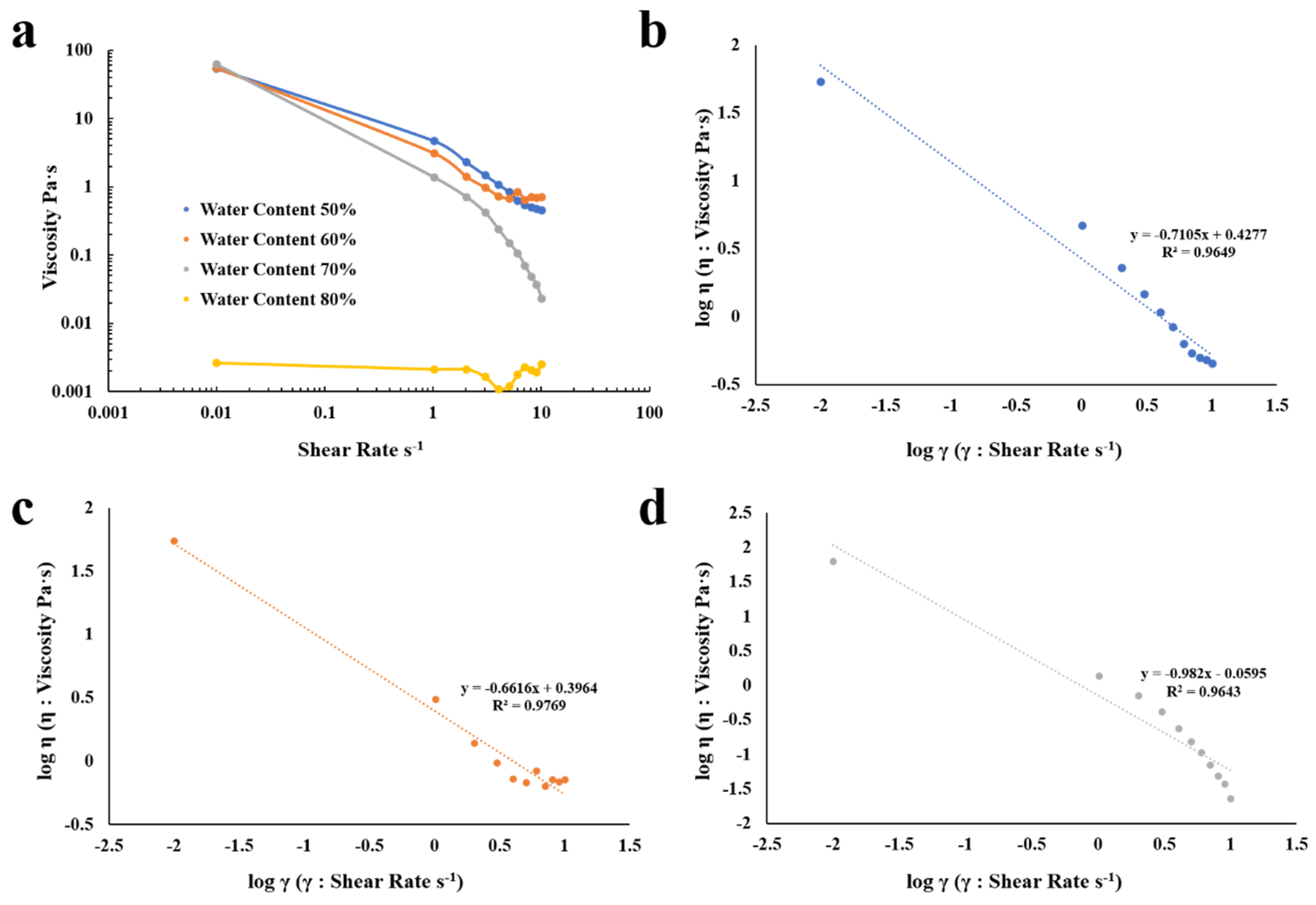
2.2.4. Rheological Characteristics
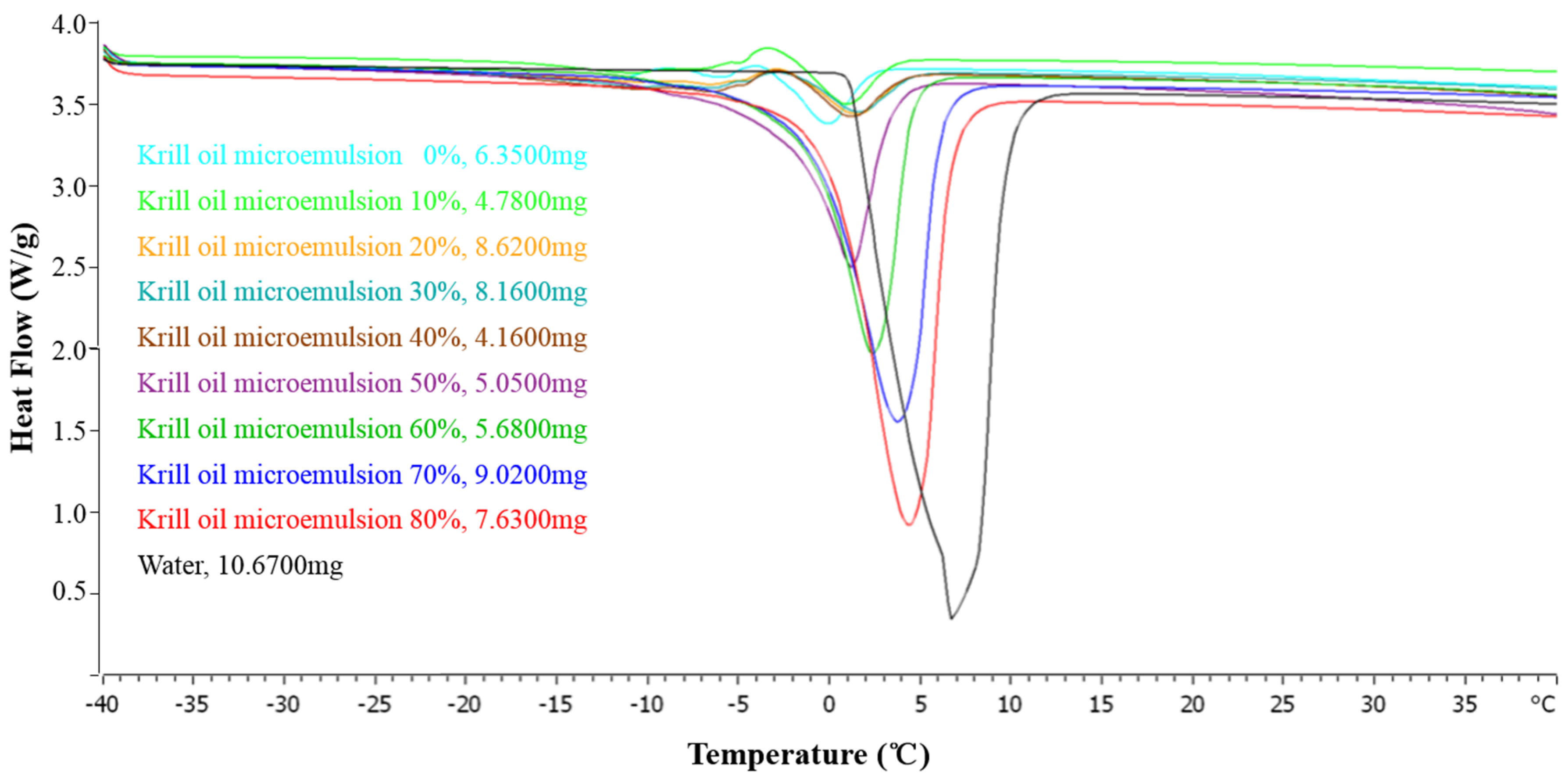
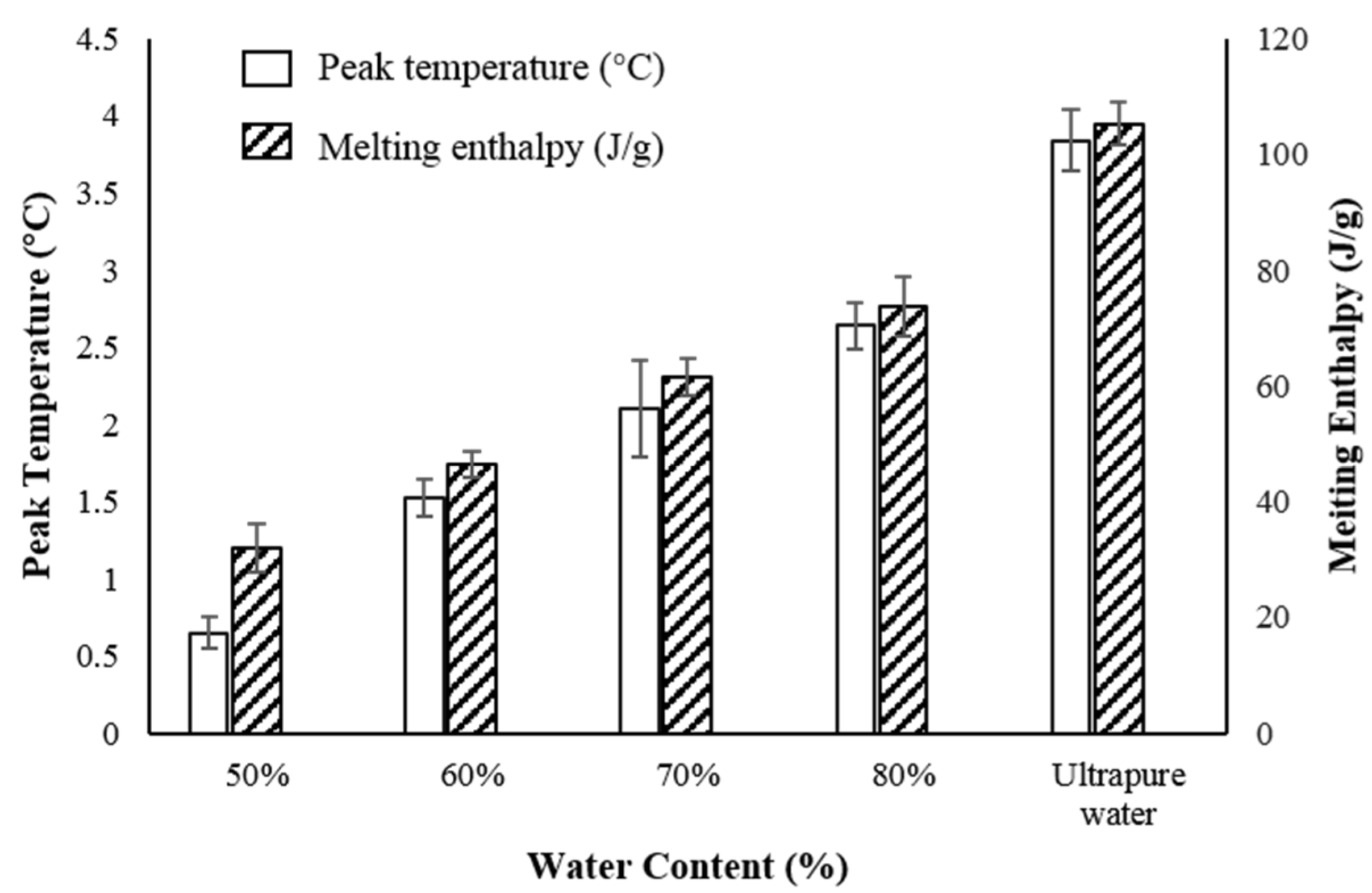
2.2.5. Thermal Behavior
2.3. Stability of Prepared Antarctic Krill Oil O/W Microemulsion
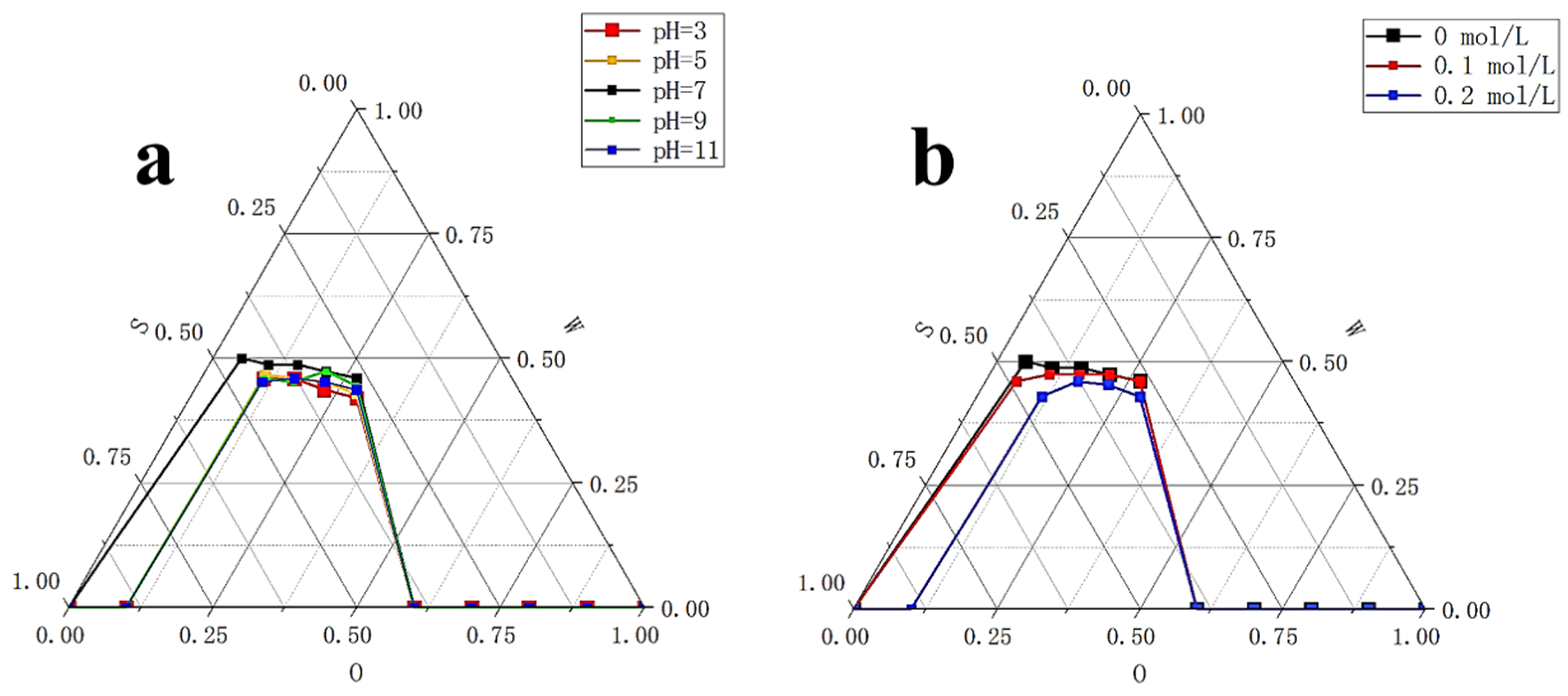
2.3.1. Effect of pH on the Stability of Krill Oil Microemulsion
2.3.2. Effect of Salinity on the Stability of Krill Oil Microemulsion
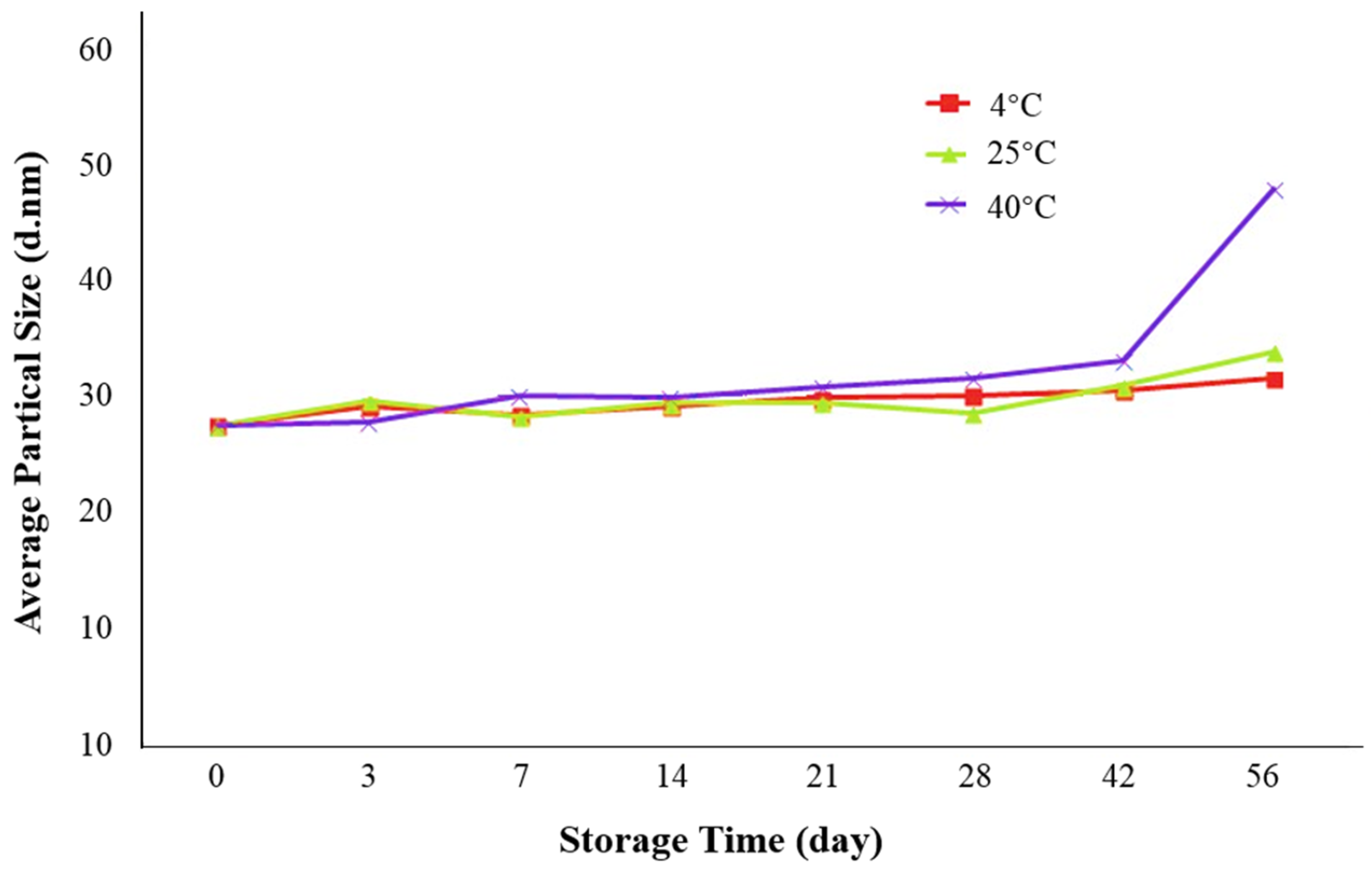
2.3.3. Effects of Storage Time and Temperature on the Stability of Krill Oil Microemulsion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
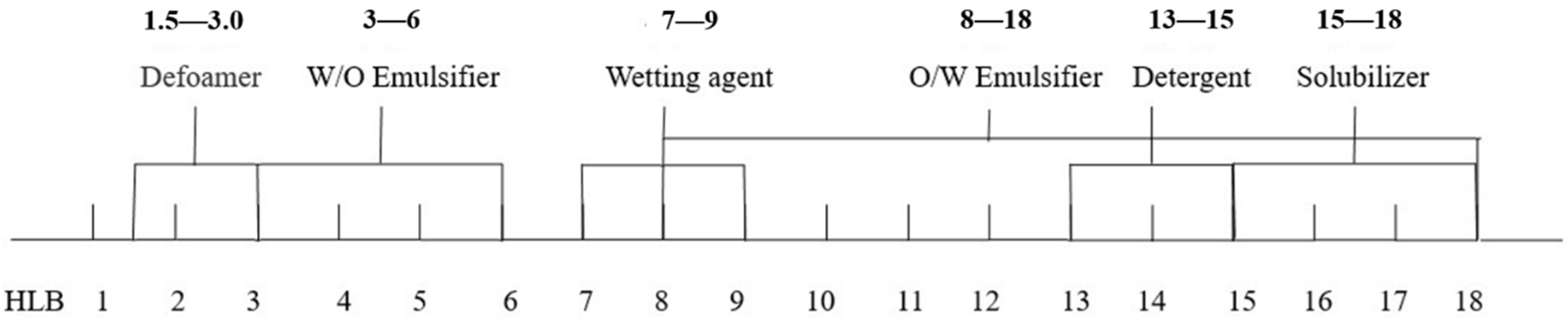
3.2.1. Formula Selection of the Microemulsions
3.2.2. Electrical Conductivity
3.2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and Cryo-TEM
3.2.4. Droplet Size Analysis
3.2.5. Rheological Characteristics
3.2.6. Thermal Behavior
3.2.7. Stability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krill Oil. Monograph. Altern. Med. Rev. 2010, 15, 84–86.
- Ramprasath, V.R.; Eyal, I.; Zchut, S.; Jones, P.J. Enhanced increase of omega-3 index in healthy individuals with response to 4-week n-3 fatty acid supplementation from krill oil versus fish oil. Lipids Health Dis. 2013, 12, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolakowska, A.; Kolakowski, E.; Szczygielski, M. Winter season krill (Euphausia superba D.) as a source of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Food/Nahrung 1994, 38, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghmur, A.; Lotfi, S.; Ariabod, S.A.; Bor, G.; Gontsarik, M.; Salentinig, S. Internal Lamellar and Inverse Hexagonal Liquid Crystalline Phases During the Digestion of Krill and Astaxanthin Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuchardt, J.P.; Schneider, I.; Meyer, H.; Neubronner, J.; Von Schacky, C.; Hahn, A. Incorporation of EPA and DHA into plasma phospholipids in response to different omega-3 fatty acid formulations—A comparative bioavailability study of fish oil vs. krill oil. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andraka, J.M.; Sharma, N.; Marchalant, Y. Can krill oil be of use for counteracting neuroinflammatory processes induced by high fat diet and aging? Neurosci. Res. 2019, 157, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, S.B.; Chavan, B. Comparative study of hormone analysis in PCOS induced rat and treated with fish oil, shell fish oil and metformin. Paripex Indian J. Res. 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferhatoğlu, M.F.; Kıvılcım, T.; Vural, G.; Kartal, A.; Filiz, A.I.; Kebudi, A. Comparison of the effects of two different marine-derived omega-3 fatty acid sources, krill oil, and fish oil, on the healing of primary colonic anastomoses after colectomy applied Wistar albino rat model. Turk. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2019, 25, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Gong, M.; Wei, W.; Jin, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Jin, Q. Antarctic Krill (Euphausia superba) Oil: A Comprehensive Review of Chemical Composition, Extraction Technologies, Health Benefits, and Current Applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 514–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Jin, J.; Sun, J.; Liang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Jin, Q. Comparison of solvents for extraction of krill oil from krill meal: Lipid yield, phospholipids content, fatty acids composition and minor components. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Q.; Tian, Y.; Dai, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xue, C.; Wang, J. Antarctic krill oil promotes longitudinal bone growth in adolescent male mice. Food Biosci. 2019, 28, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, K.; Tian, D.; Jiang, G. Antarctic Krill Oil Improves Learning and Memory of Rats. Food Sci. 2011, 32, 273–276. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, S.Z.; Moustafa, E.M.; Hassan, A.A.; Thabet, N.M. Protective role of Krill oil against estrogen deficiency induced neurodegeneration in ovariectomized rats. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2017, 55, 279–285. [Google Scholar]
- Konagai, C.; Yanagimoto, K.; Hayamizu, K.; Han, L.; Tsuji, T.; Koga, Y. Effects of krill oil containing n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in phospholipid form on human brain function: A randomized controlled trial in healthy elderly volunteers. Clin. Interv. Aging 2013, 8, 1247–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, J.; Mulcahy, R.; Power, R.; Moran, R.; Howard, A.N. Nutritional Intervention to Prevent Alzheimer’s Disease: Potential Benefits of Xanthophyll Carotenoids and Omega-3 Fatty Acids Combined. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 64, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Ru, Q.; Tian, X.; Zhou, M.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Li, C. Krill oil protects PC12 cells against methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity by inhibiting apoptotic response and oxidative stress. Nutr. Res. 2018, 58, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awada, M.; Meynier, A.; Soulage, C.O.; Hadji, L.; Geloen, A.; Viau, M.; Ribourg, L.; Benoit, B.; Debard, C.; Guichardant, M.; et al. n-3 PUFA added to high-fat diets affect differently adiposity and inflammation when carried by phospholipids or triacylglycerols in mice. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigerust, N.F.; Bjørndal, B.; Bohov, P.; Brattelid, T.; Svardal, A.; Berge, R.K. Krill oil versus fish oil in modulation of inflammation and lipid metabolism in mice transgenic for TNF-α. Eur. J. Nutr. 2012, 52, 1315–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Rosticci, M.; Morbini, M.; Cagnati, M.; Grandi, E.; Parini, A.; Borghi, C. Lipid-lowering and anti-inflammatory effects of omega 3 ethyl esters and krill oil: A randomized, cross-over, clinical trial. Arch. Med. Sci. 2016, 12, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobraico, J.M.; DiLello, L.C.; Butler, A.D.; Cordisco, M.E.; Petrini, J.R.; Ahmadi, R. Effects of krill oil on endothelial function and other cardiovascular risk factors in participants with type 2 diabetes, a randomized controlled trial. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2015, 3, e000107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, Z.; Bjørndal, B.; Grigorova, N.; Roussenov, A.; Vachkova, E.; Berge, K.; Burri, L.; Berge, R.; Stanilova, S.A.; Milanova, A.; et al. Effect of fish and krill oil supplementation on glucose tolerance in rabbits with experimentally induced obesity. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 54, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berge, K.; Musa-Veloso, K.; Harwood, M.; Hoem, N.; Burri, L. Krill oil supplementation lowers serum triglycerides without increasing low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in adults with borderline high or high triglyceride levels. Nutr. Res. 2014, 34, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanzo, M.; Cesi, V.; Prete, E.; Negroni, A.; Palone, F.; Cucchiara, S.; Oliva, S.; Leter, B.; Stronati, L. Krill oil reduces intestinal inflammation by improving epithelial integrity and impairing adherent-invasive Escherichia coli pathogenicity. Dig. Liver Dis. 2016, 48, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Choi, J.-H.; Oh, H.-J.; Park, S.-H.; Lee, J.-B.; Yoon, K.C. Effects of Eye Drops Containing a Mixture of Omega-3 Essential Fatty Acids and Hyaluronic Acid on the Ocular Surface in Desiccating Stress-induced Murine Dry Eye. Curr. Eye Res. 2014, 39, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaterra, G.A.; Driscoll, D.F.; Schwarzbach, H.; Kinscherf, R. Krill Oil-In-Water Emulsion Protects against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Proinflammatory Activation of Macrophages In Vitro. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Fukushima, M.; Sakuraba, K.; Sawaki, K.; Sekigawa, K. Krill Oil Improves Mild Knee Joint Pain: A Randomized Control Trial. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laslett, L.L.; Antony, B.S.E.; Wluka, A.E.; Hill, C.L.; March, L.M.; Keen, H.I.; Otáhal, P.; Cicuttini, F.; Jones, G. KARAOKE: Krill oil versus placebo in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: Protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials 2020, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iu, F.; Smith, A.D.; Solano-Aguilar, G.; Wang, T.T.Y.; Pham, Q.; Beshah, E.; Tang, Q.; Urban, J.F.; Xue, C.; Li, R.W. Mechanistic insights into the attenuation of intestinal inflammation and modulation of the gut microbiome by krill oil using in vitro and in vivo models. Microbiome 2020, 8, 83. [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava, R.; Chandra, M.; Bansal, U.; Singh, D.; Ranjan, S.; Sharma, S. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Omega 3 Fatty Acids in Rosacea Patients with Dry Eye Symptoms. Curr. Eye Res. 2016, 41, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, S.; Jin, Y.; Ecoiffier, T.; Barabino, S.; Schaumberg, D.A.; Dana, M.R. Topical Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids for Treatment of Dry Eye. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2008, 126, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cort, A.; Ozturk, N.; Akpinar, D.; Unal, M.; Yucel, G.; Ciftcioglu, A.; Yargicoglu, P.; Aslan, M. Suppressive effect of astaxanthin on retinal injury induced by elevated intraocular pressure. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 58, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yixin, T.; Zhang, H.-Z. Effect of Antarctic Krill Oil on Astaxanthin in Rat Serum. Int. J. Sci. 2019, 8, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhuang, P.; Luan, L.; Sun, Q.; Cao, F. Preparation and characterization of novel nanocarriers containing krill oil for food application. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołakowska, A. Changes in lipids during the storage of krill (Euphausia superba Dana) at 3 degrees C. Z. Lebensm. Unters. Forsch. 1988, 186, 519. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.F.S.; Bruheim, I.; Jacobsen, C. Oxidative stability and non-enzymatic browning reactions in Antarctic krill oil (Euphausia superba). Lipid Technol. 2014, 26, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulven, S.M.; Kirkhus, B.; Lamglait, A.; Basu, S.; Elind, E.; Haider, T.; Berge, K.; Vik, H.; Pedersen, J.I. Metabolic Effects of Krill Oil are Essentially Similar to Those of Fish Oil but at Lower Dose of EPA and DHA, in Healthy Volunteers. Lipids 2010, 46, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Beamer, S.K.; Yang, H.; Jaczynski, J. Micro-emulsification/encapsulation of krill oil by complex coacervation with krill protein isolated using isoelectric solubilization/precipitation. Food Chem. 2018, 244, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermasha, S.; Aziz, S.; Gill, J.; Neufeld, R. Microencapsulation of esterified krill oil, using complex coacervation. J. Microencapsul. 2017, 35, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ré, I.M. Microencapsulation by spray drying. Dry. Technol. 1998, 16, 1195–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulik, S.; Paul, B. Structure, dynamics and transport properties of microemulsions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 78, 99–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsson, I.; Lindman, B. The definition of microemulsion. Colloids Surf. 1981, 3, 391–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.K.; Shah, D.O. Introduction to Macro- and Microemulsions. Mech. Enzymol. Bridg. Struct. Funct. 1985, 272, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Schulman, J.H.; Stoeckenius, W.; Prince, L.M. Mechanism of Formation and Structure of Micro Emulsions by Electron Microscopy. J. Phys. Chem. 1959, 63, 1677–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-C.; Lin, H.-Y.; Chen, H.-C.; Yu, M.-W.; Lee, M.-H. Stability and characterisation of phospholipid-based curcumin-encapsulated microemulsions. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenjarla, S.N. Microemulsions: An overview and pharmaceutical applications. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 1999, 16, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.J.; Rees, G.D. Microemulsion-based media as novel drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, W.C. Classification of Surface-Active Agents by “HLB”. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 1949, 1, 311–337. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, W.C. Calculation of HLB Values of Non-Ionic Surfactants. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 1954, 5, 249–305. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.-L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.-N.; Liu, F. Study on food-grade vitamin E microemulsions based on nonionic emulsifiers. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 339, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente-Massaguer, E.; Saccardo, P.; Ferrer-Miralles, N.; Lecina, M.; Gòdia, F. Coupling Microscopy and Flow Cytometry for a Comprehensive Characterization of Nanoparticle Production in Insect Cells. Cytom. Part A 2020, 97, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.E.; Tam, K.C.; Bernardes, J.S.; Loh, W. Double stabilization mechanism of O/W Pickering emulsions using cationic nanofibrillated cellulose. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 574, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Ko, J.A.; Kim, J.T.; Cha, D.S.; Cho, J.H.; Park, H.J.; Shin, G.H. Preparation of a Capsaicin-Loaded Nanoemulsion for Improving Skin Penetration. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roger, K.; Cabane, B.; Olsson, U. Emulsification through Surfactant Hydration: The PIC Process Revisited. Langmuir 2011, 27, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostwald called it the de Waele-Ostwald equation. Kolloid Z. 1929, 47, 176–187.
- Raemy, A.; Nouzille, C.A.; Frossard, P.; Sagalowicz, L.; Leser, M.-E. Thermal behaviour of emulsifier-water systems studied by micro-DSC. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2005, 80, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spernath, A.; Aserin, A.; Garti, N. Phase transition induced bywater dilution in phospholipid U-type food-grade microemulsions studied by DSC. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2006, 83, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senatra, D.; Gambi, C.M.C.; Carlà, M.; Chittofrati, A. Thermal Behaviour of Perfluoropolyether w/o Percolative Microemulsions. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 1999, 56, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.O. Macro- and microemulsions. Energy Conv. Manag. 1985, 49, 1898. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, M.-Y.; Liu, F.; Wang, Z.-W.; Baoyindugurong, J.-H. Formation and characterization of self-assembling fish oil microemulsions. Colloid J. 2011, 73, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestana, K.; Formariz, T.; Franzini, C.; Sarmento, V.H.V.; Chiavacci, L.A.; Scarpa, M.; Egito, E.; De Oliveira, A.G. Oil-in-water lecithin-based microemulsions as a potential delivery system for amphotericin B. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 66, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinoda, K.; Lindman, B. Organized surfactant systems: Microemulsions. Langmuir 1987, 3, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruckenstein, E.; Krishnan, R. Effect of electrolytes and mixtures of surfactants on the oil-water interfacial tension and their role in formation of microemulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1980, 76, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ye, L.; Chang, C.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Cao, F. Preparation and stability study of krill oil microemulsion. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 17, 80–87. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, J.; Zhu, Q.; Qin, F.; Wang, M.; Chen, J.; Zheng, Z.-P. Preparation of steppogenin and ascorbic acid, vitamin E, butylated hydroxytoluene oil-in-water microemulsions: Characterization, stability, and antibrowning effects for fresh apple juice. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
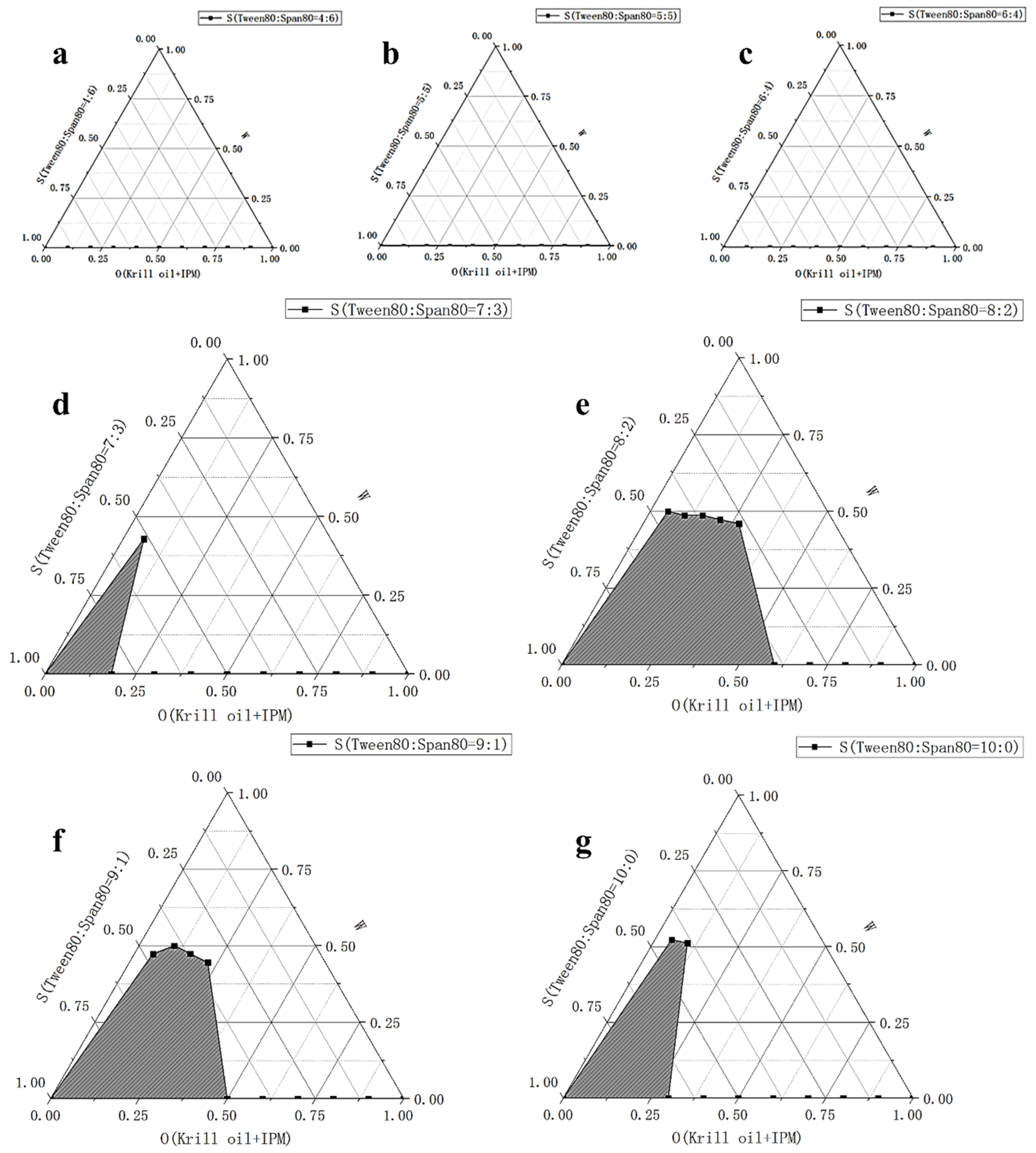
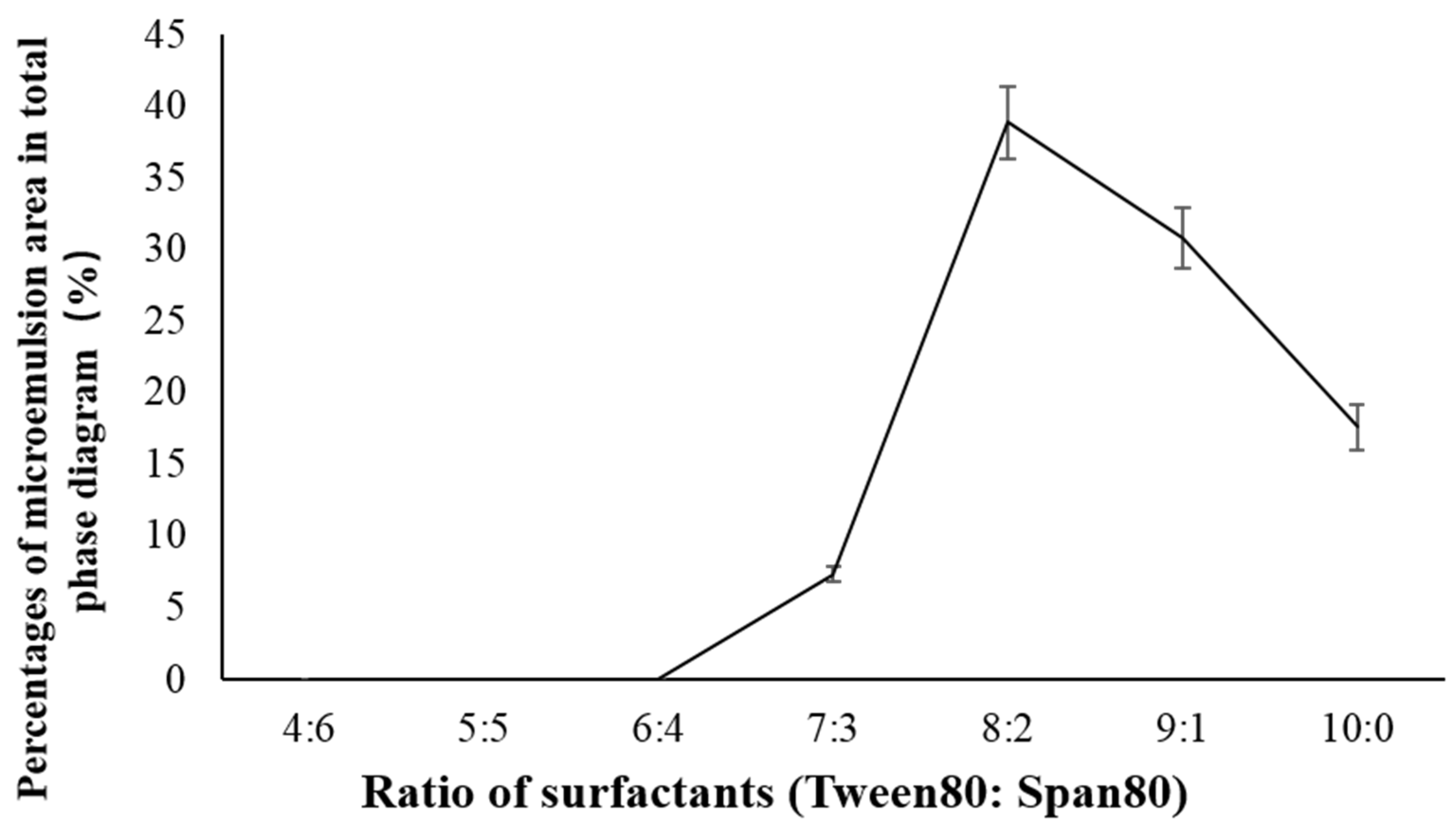
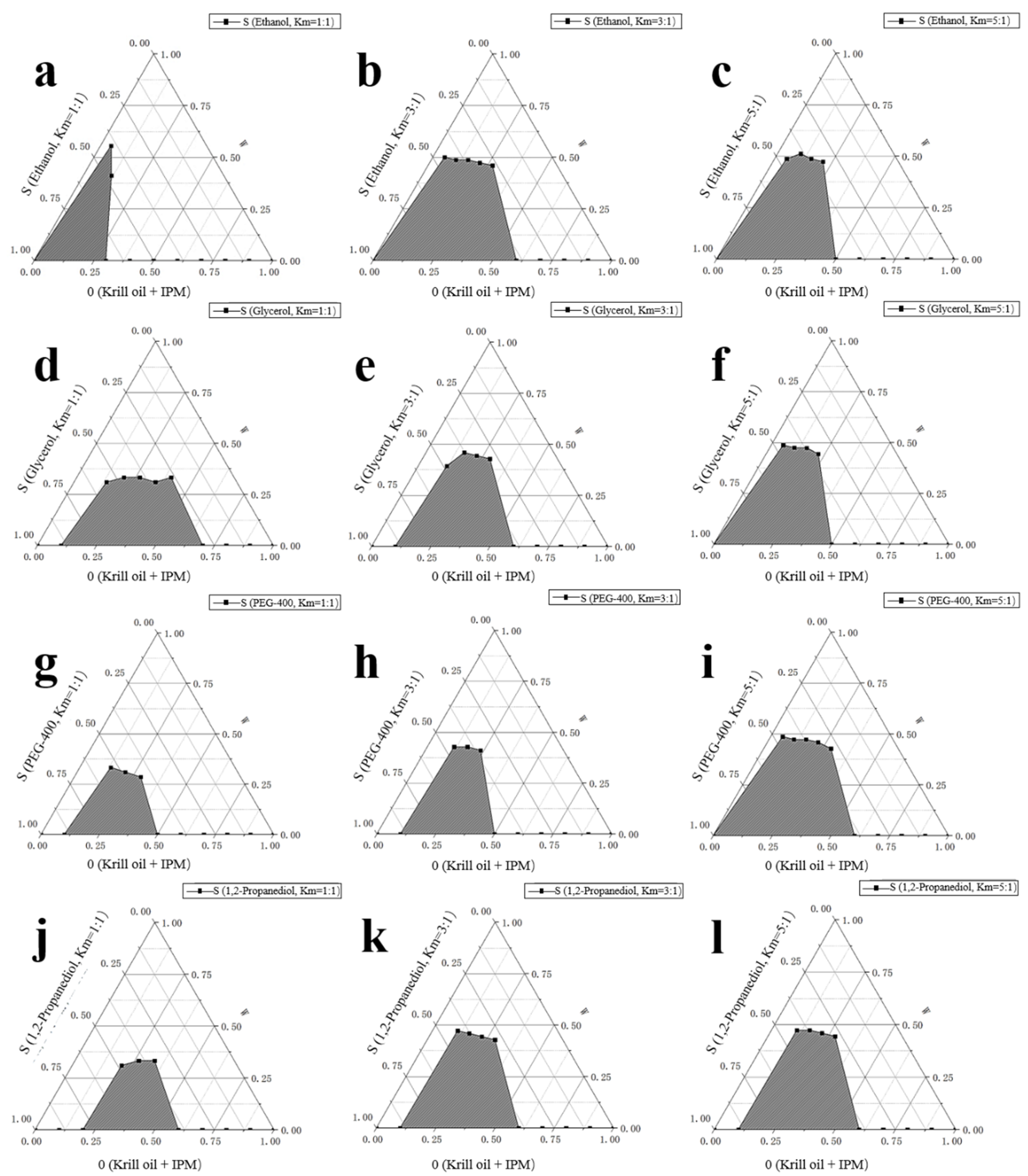
| Tween 80:Span 80 | 4:6 | 5:5 | 6:4 | 7:3 | 8:2 | 9:1 | 10:0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HLB value | 8.58 | 9.65 | 10.72 | 11.79 | 12.86 | 13.93 | 15.00 |
| Example 1. Ratio of Surfactant Phase (Surfactant and Cosurfactant) to Oil Phase (Krill Oil and Solvent): 8:2 | ||||||
| Tween 80/g | Span 80/g | Oil solvent/g | Krill oil/g | Cosurfactant/g | ||
| Mass ratios of Tween 80 to Span 80 | 4:6 | 4.8 | 7.2 | 3.0 | 1.0 | 4.0 |
| 5:5 | 6.0 | 6.0 | ||||
| 6:4 | 7.2 | 4.8 | ||||
| 7:3 | 8.4 | 3.6 | ||||
| 8:2 | 9.6 | 2.4 | ||||
| 9:1 | 10.8 | 1.2 | ||||
| 10:0 | 12.0 | 0.0 | ||||
| Mass ratios of surfactant to cosurfactant | 1:1 | 9.6 | 2.4 | 4.5 | 1.5 | 12.0 |
| 3:1 | 3.0 | 1.0 | 4.0 | |||
| 5:1 | 2.7 | 0.9 | 2.4 | |||
| Example 2. Ratio of Surfactant Phase (Surfactant and Cosurfactant) to Oil Phase (Krill Oil and Solvent): 5:5 | ||||||
| Tween 80/g | Span 80/g | Oil solvent/g | Krill oil/g | Cosurfactant/g | ||
| Mass ratios of Tween 80 to Span 80 | 4:6 | 4.8 | 7.2 | 12.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| 5:5 | 6.0 | 6.0 | ||||
| 6:4 | 7.2 | 4.8 | ||||
| 7:3 | 8.4 | 3.6 | ||||
| 8:2 | 9.6 | 2.4 | ||||
| 9:1 | 10.8 | 1.2 | ||||
| 10:0 | 12.0 | 0.0 | ||||
| Mass ratios of surfactant to cosurfactant | 1:1 | 9.6 | 2.4 | 18.0 | 6.0 | 12.0 |
| 3:1 | 12.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | |||
| 5:1 | 10.8 | 3.6 | 2.4 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Jiang, K.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhu, J. Preparation and Characterization of Microemulsions Based on Antarctic Krill Oil. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18100492
Zhao J, Jiang K, Chen Y, Chen J, Zheng Y, Yu H, Zhu J. Preparation and Characterization of Microemulsions Based on Antarctic Krill Oil. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(10):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18100492
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jiawen, Kening Jiang, Yixuan Chen, Juan Chen, Yangfan Zheng, Huilin Yu, and Jiajin Zhu. 2020. "Preparation and Characterization of Microemulsions Based on Antarctic Krill Oil" Marine Drugs 18, no. 10: 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18100492
APA StyleZhao, J., Jiang, K., Chen, Y., Chen, J., Zheng, Y., Yu, H., & Zhu, J. (2020). Preparation and Characterization of Microemulsions Based on Antarctic Krill Oil. Marine Drugs, 18(10), 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18100492