Identification and Structure–Activity Relationship of Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function Protective Collagen Peptides from Alaska Pollock Skin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
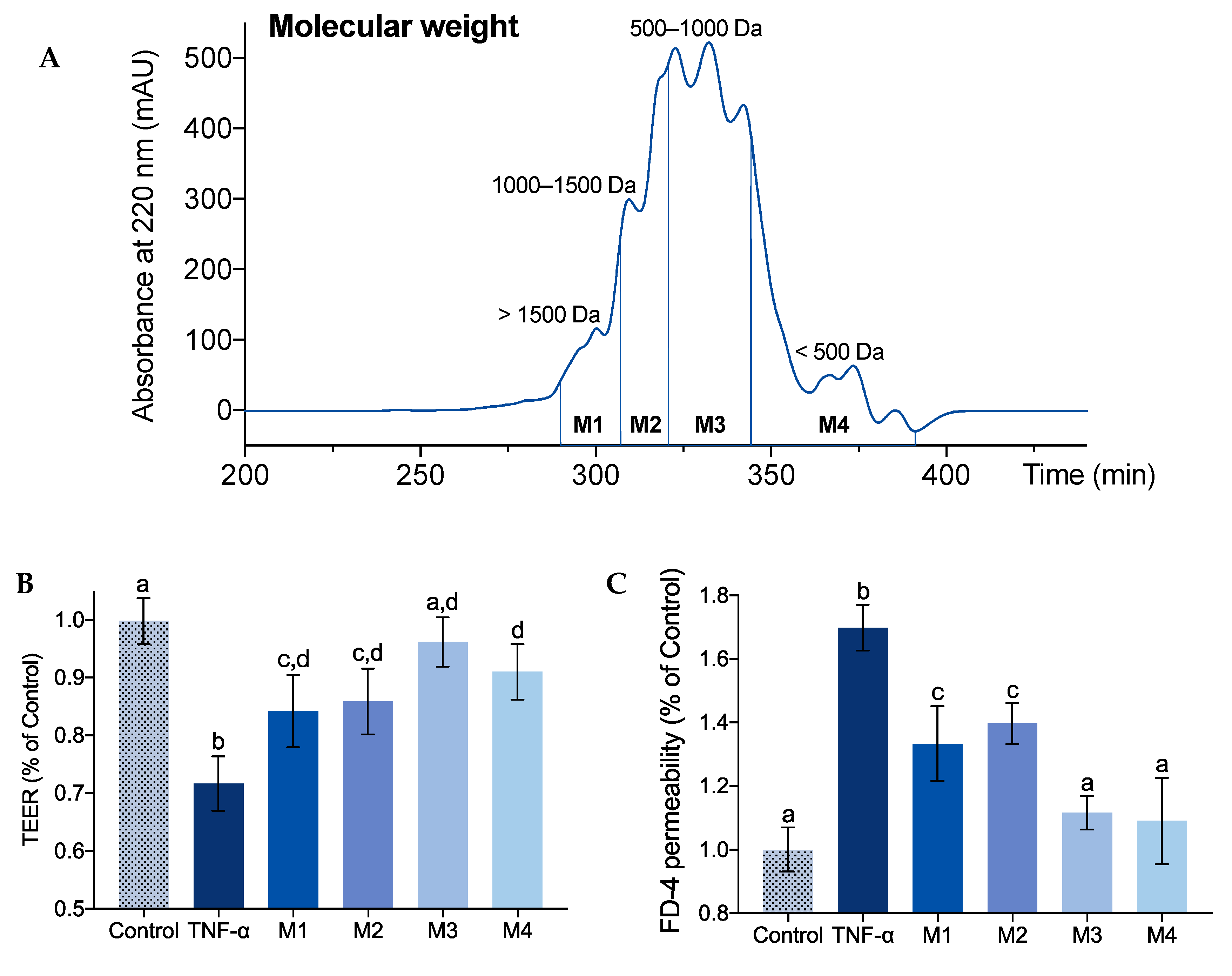
2.1. Effect of Molecular Weight on IEBF Protection of Collagen Peptides
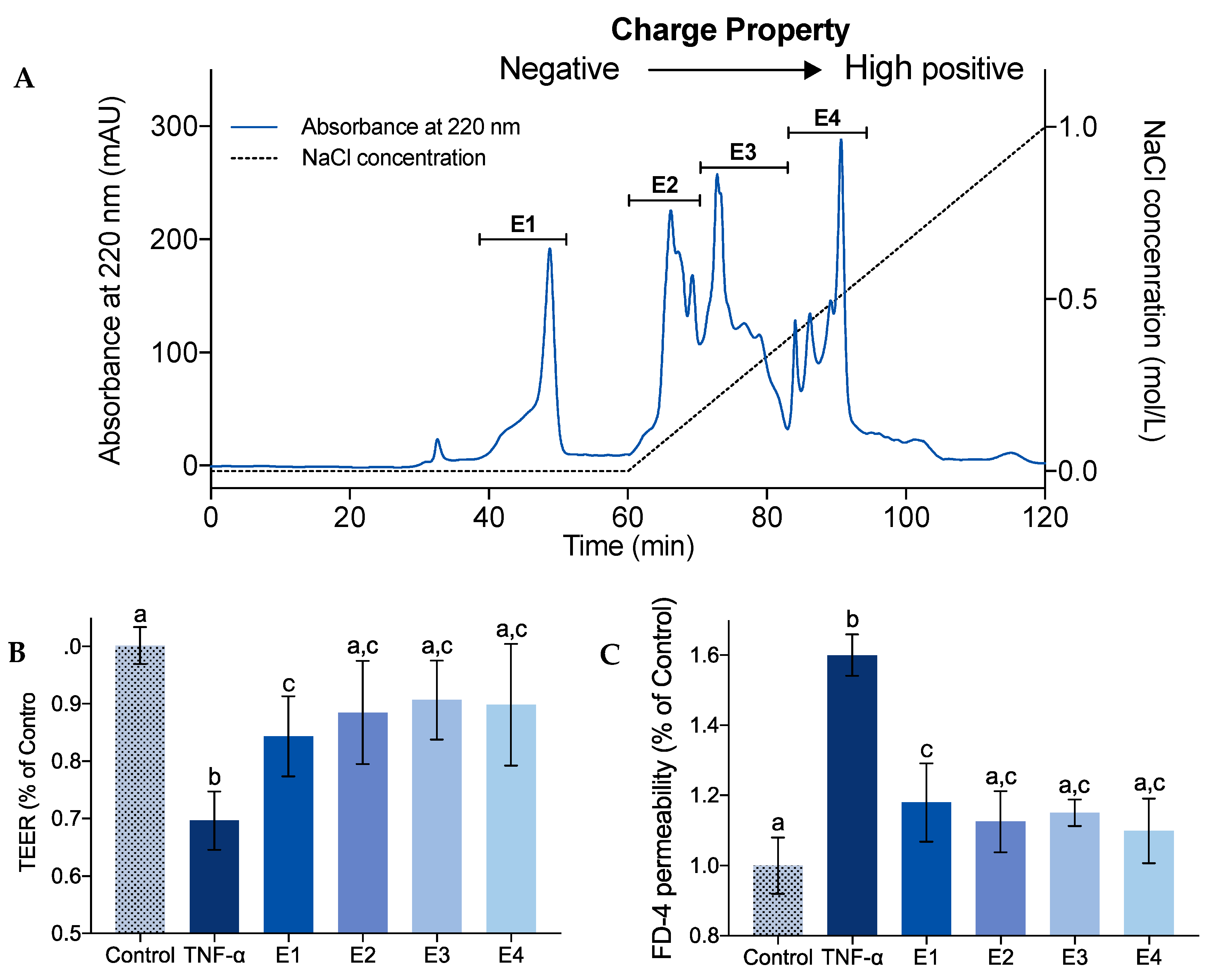
2.2. Effect of Charge Property on IEBF Protection of Collagen Peptides
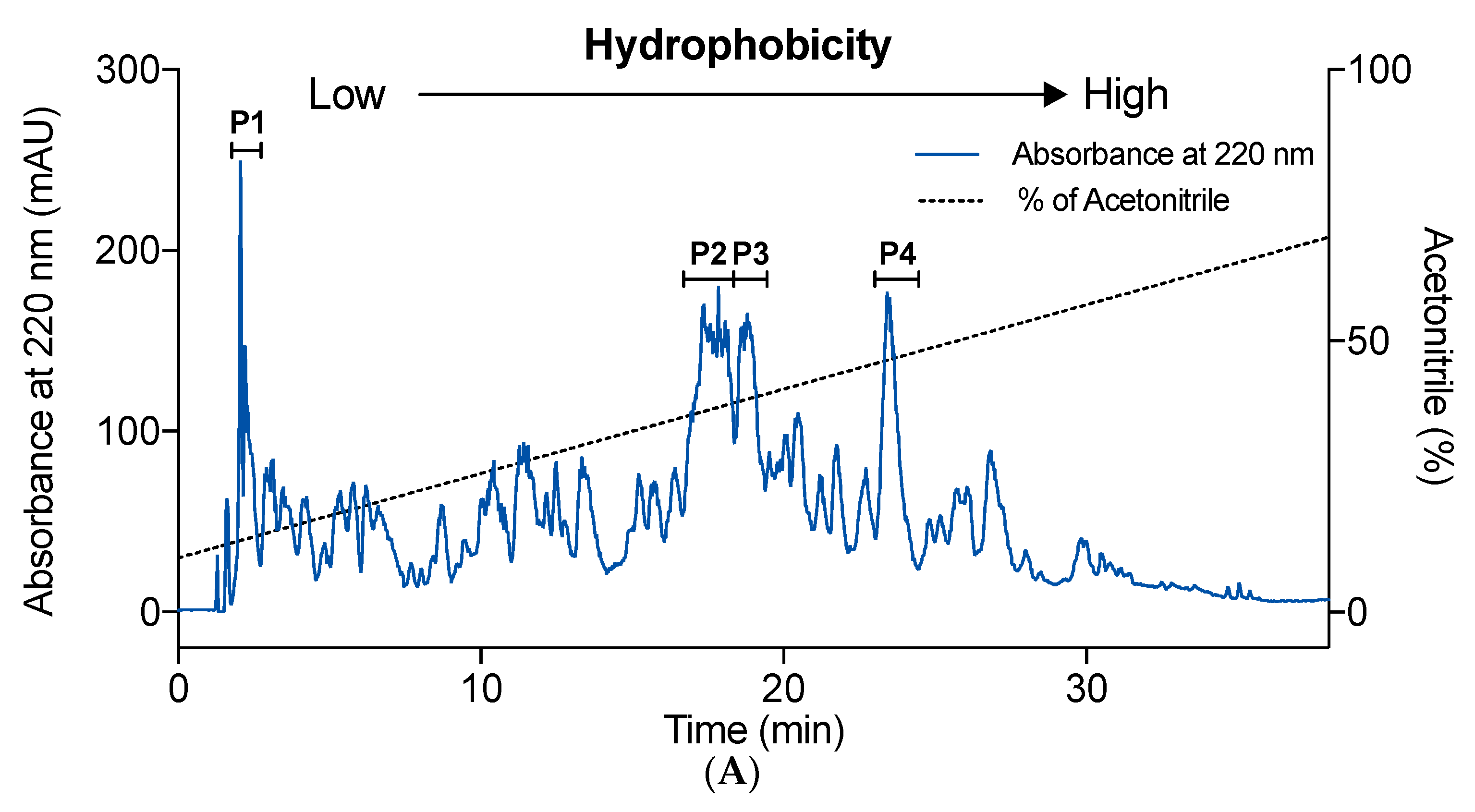
2.3. Effect of Hydrophobicity on IEBF Protection of Collagen Peptides
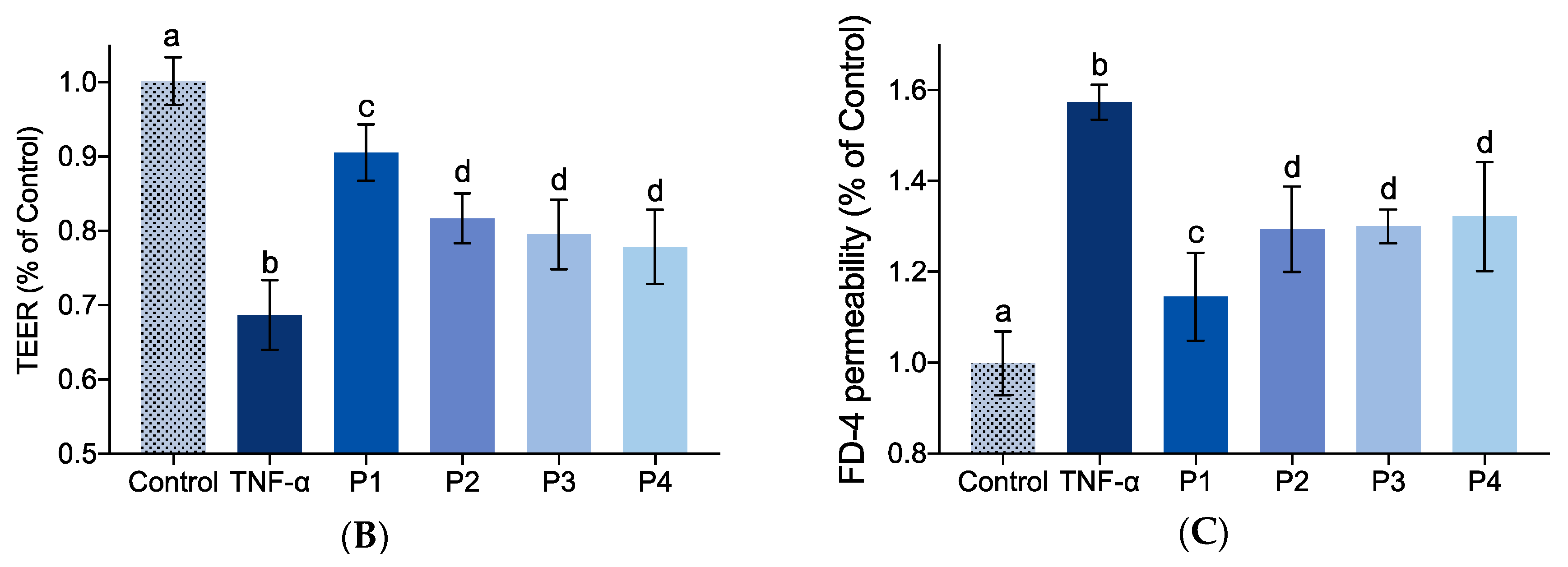
2.4. Identification of High-Active IEBF Protective Collagen Peptide Sequences
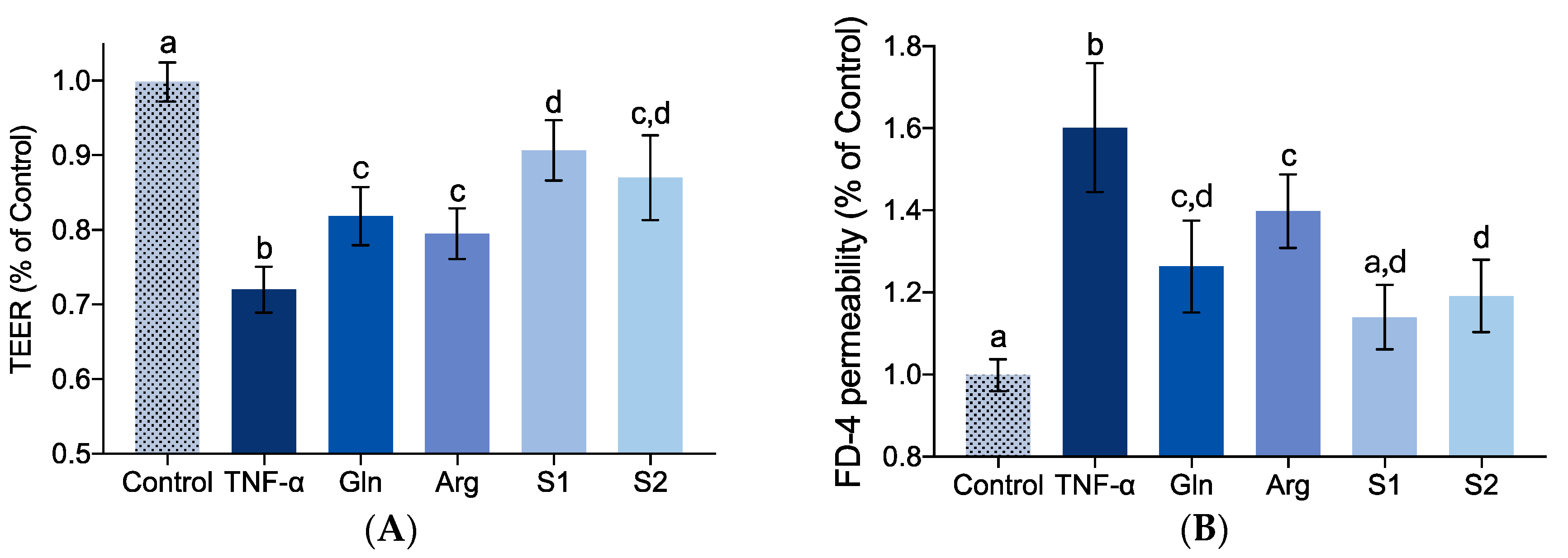
2.5. Effect of Identified Collagen Peptide Sequences on IEBF of TNF-α-Induced Caco-2 Cell Monolayers
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of APS-Derived Collagen Peptides
3.3. Separation of Collagen Peptide Fractions Based on Molecular Weight
3.4. Separation of Collagen Peptide Fractions Based on Charge Property
3.5. Separation of Collagen Peptide Fractions Based on Hydrophobicity
3.6. Identification of High-Active IEBF Protective Collagen Peptide Sequences
3.7. Protection of Collagen Peptides on IEBF
3.7.1. Caco-2 Cell Model
3.7.2. The Impact of Collagen Peptides on Barrier Function of Caco-2 Cell Monolayer
3.7.3. FD-4 Permeability
3.8. Statistics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peterson, L.W.; Artis, D. Intestinal epithelial cells: Regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelakkot, C.; Ghim, J.; Ryu, S.H. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odenwald, M.A.; Turner, J.R. The intestinal epithelial barrier: A therapeutic target? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artis, D. Epithelial-cell recognition of commensal bacteria and maintenance of immune homeostasis in the gut. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, J.R. Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szefel, J.; Kruszewski, W.J.; Buczek, T. Enteral feeding and its impact on the gut immune system and intestinal mucosal barrier. Gastroenterol. Rev. 2015, 10, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Augustin, O.; Rivero-Gutierrez, B.; Mascaraque, C.; Sanchez de Medina, F. Food derived bioactive peptides and intestinal barrier function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 22857–22873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, C.A.; Kovacs-Nolan, J.; Mine, Y. Bioactive dietary peptides and amino acids in inflammatory bowel disease. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 2127–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Albenberg, L.; Compher, C.; Baldassano, R.; Piccoli, D.; Lewis, J.D.; Wu, G.D. Diet in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 1087–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulluwishewa, D.; Anderson, R.C.; McNabb, W.C.; Moughan, P.J.; Wells, J.M.; Roy, N.C. Regulation of tight junction permeability by intestinal bacteria and dietary components. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, S. Short peptide modules for enhancing intestinal barrier function. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasumatsu, H.; Tanabe, S. The casein peptide Asn-Pro-Trp-Asp-Gln enforces the intestinal tight junction partly by increasing occludin expression in Caco-2 cells. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenore, G.C.; Pagano, E.; Lama, S.; Vanacore, D.; Di Maro, S.; Maisto, M.; Capasso, R.; Merlino, F.; Borrelli, F.; Stiuso, P.; et al. Intestinal Anti-Inflammatory Effect of a Peptide Derived from Gastrointestinal Digestion of Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) Mozzarella Cheese. Nutrients 2019, 11, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemán, A.N.; Martínez-Alvarez, O. Marine Collagen as a Source of Bioactive Molecules A Review. Nat. Prod. J. 2013, 3, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.H.; Moreira-Silva, J.; Marques, A.L.; Domingues, A.; Bayon, Y.; Reis, R.L. Marine origin collagens and its potential applications. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5881–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czech, I. Collagen Peptides Source Properties and Benefits. 2016. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/3757/27db2b7b5799cd911929970e0861cfd49de4.pdf (accessed on 13 July 2017).
- Chen, Q.; Hou, H.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X.; Li, B. Effects of early enteral nutrition supplemented with collagen peptides on post-burn inflammatory responses in a mouse model. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1933–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, O.; Martins, I.M.; Hou, H.; Zhao, X.; Blumberg, J.B.; Li, B. Collagen peptides ameliorate intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction in immunostimulatory Caco-2 cell monolayers via enhancing tight junctions. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sadi, R.; Boivin, M.; Ma, T. Mechanism of cytokine modulation of epithelial tight junction barrier. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2009, 14, 2765–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelblum, K.L.; Turner, J.R. The tight junction in inflammatory disease: Communication breakdown. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyei, D.; Pan, S.; Acquah, C.; Danquah, M.K. Bioactivity Profiling of Peptides from Food Proteins. In Soft Chemistry and Food Fermentation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 49–77. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhu, J.; Chen, G.; Zuo, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 preserves intestinal epithelial barrier function from TNF-alpha induced injury via suppression of NF-kB p65 mediated MLCK-P-MLC signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 460, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sadi, R.; Guo, S.H.; Ye, D.M.; Rawat, M.; Ma, T.Y. TNF-alpha Modulation of Intestinal Tight Junction Permeability Is Mediated by NIK/IKK-alpha Axis Activation of the Canonical NF-kappa B Pathway. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 1151–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sadi, R.; Guo, S.; Ye, D.; Ma, T.Y. TNF-alpha modulation of intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier is regulated by ERK1/2 activation of Elk-1. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 1871–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, B.; Kolli, A.R.; Esch, M.B.; Abaci, H.E.; Shuler, M.L.; Hickman, J.J. TEER Measurement Techniques for In Vitro Barrier Model Systems. J. Lab. Autom. 2015, 20, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sila, A.; Bougatef, A. Antioxidant peptides from marine by-products: Isolation, identification and application in food systems. A review. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 21, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiari, Z.; Rico, D.; Martin-Diana, A.B.; Barry-Ryan, C. Structure elucidation of ACE-inhibitory and antithrombotic peptides isolated from mackerel skin gelatine hydrolysates. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 1663–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Y.M.; Chi, C.F.; Luo, H.Y.; Deng, S.G.; Ma, J.Y. Isolation and characterization of collagen and antioxidant collagen peptides from scales of croceine croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4641–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendis, E.; Rajapakse, N.; Kim, S.K. Antioxidant properties of a radical-scavenging peptide purified from enzymatically prepared fish skin gelatin hydrolysate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Hou, H.; Fan, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, Q.; Si, L.; Li, B. Protective effect of gelatin peptides from pacific cod skin against photoaging by inhibiting the expression of MMPs via MAPK signaling pathway. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 165, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, J.; Knight, C.G.; Farndale, R.W.; Barnes, M.J. Structure of the Integrin α2β1-binding Collagen Peptide. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 335, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, C.; Khan, F.F.; Khan, M.I.; Iqbal, J. Marine bioactive peptides: Types, structures, and physiological functions. Food Rev. Int. 2016, 33, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xie, N.; Li, B. Charge properties of peptides derived from casein affect their bioavailability and cytoprotection against H2O2-induced oxidative stress. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 2468–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wang, C.; Huo, Y.; Li, B. The absorbates of positively charged peptides from casein show high inhibition ability of LDL oxidation in vitro: Identification of intact absorbed peptides. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 20, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, B. Charge and hydrophobicity of casein peptides influence transepithelial transport and bioavailability. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acquah, C.; Stefano, E.D.; Udenigwe, C.C. Role of hydrophobicity in food peptide functionality and bioactivity. J. Food Bioact. 2018, 4, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Wang, B.; Jiang, L.; Liu, C.; Li, B. Hydrophobicity exerts different effects on bioavailability and stability of antioxidant peptide fractions from casein during simulated gastrointestinal digestion and Caco-2 cell absorption. Food Res. Int. 2015, 76 Pt 3, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.M.; Edwards, M.A.; Li, J.; Yip, C.M.; Deber, C.M. Roles of Hydrophobicity and Charge Distribution of Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides in Peptide-Membrane Interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 7738–7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajfathalian, M.; Ghelichi, S.; García-Moreno, P.J.; Moltke Sørensen, A.-D.; Jacobsen, C. Peptides: Production, bioactivity, functionality, and applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 58, 3097–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, L.G. Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins. In Organic Chemistry; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 1153–1199. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Wu, G.; Zhou, Z.; Dai, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ji, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Han, F.; et al. Glutamine and intestinal barrier function. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 2143–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurmis, R.; Parker, A.; Greenwood, J. The use of immunonutrition in burn injury care: Where are we? J. Burn Care Res. 2010, 31, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandell, S.P.; Gibran, N.S. Early Enteral Nutrition for Burn Injury. Adv. Wound Care 2014, 3, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, Z.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, G. Glycine metabolism in animals and humans: Implications for nutrition and health. Amino Acids 2013, 45, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Wu, C.; Li, P.; Li, N.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, Q.; Ren, W.; Peng, Y. Functions and Signaling Pathways of Amino Acids in Intestinal Inflammation. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9171905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faure, M.; Mettraux, C.; Moennoz, D.; Godin, J.P.; Vuichoud, J.; Rochat, F.; Breuille, D.; Obled, C.; Corthesy-Theulaz, I. Specific amino acids increase mucin synthesis and microbiota in dextran sulfate sodium-treated rats. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 1558–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; He, L.; Wan, D.; Liu, G.; Wu, X.; Yin, Y. Serine prevents LPS-induced intestinal inflammation and barrier damage via p53-dependent glutathione synthesis and AMPK activation. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 39, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Zhang, S.H.; Zeng, X.F.; Liu, H.; Qiao, S.Y. Branched-chain Amino Acids are Beneficial to Maintain Growth Performance and Intestinal Immune-related Function in Weaned Piglets Fed Protein Restricted Diet. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 28, 1742–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.D.; Deng, Y.P.; Zhou, X.Q.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Kuang, S.Y.; Tang, L.; Tang, W.N.; Wu, P.; Zhang, Y.A.; et al. Towards the modulation of oxidative damage, apoptosis and tight junction protein in response to dietary leucine deficiency: A likely cause of ROS-induced gill structural integrity impairment. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 70, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Goudoever, J.B.; Stoll, B.; Henry, J.F.; Burrin, D.G.; Reeds, P.J. Adaptive regulation of intestinal lysine metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11620–11625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidon, G.L.; Lee, H.J. Absorption of peptide and peptidomimetic drugs. Annu. Rev. Pharm. Toxicol. 1994, 34, 321–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
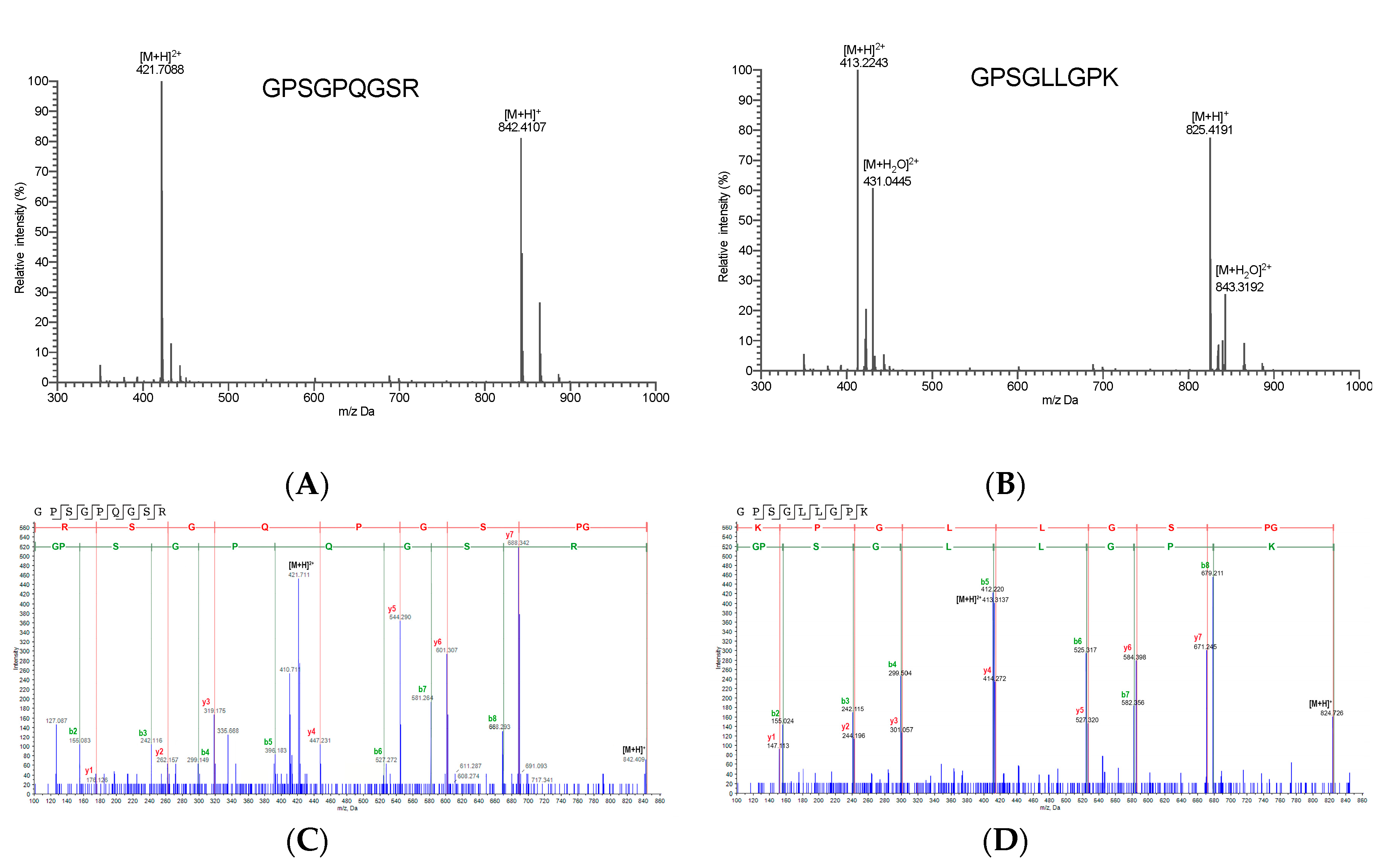
| Peptide Sequences | Molecular Weight (Da) | Homogenous (or Close Homogenous) to: | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organism | Protein | ||
| GPSGPQGSR | 841.4098511 | Gasterosteus aculeatus | Collagen alpha-2(I) chain |
| GPSGLLGPK | 824.3828735 | Ictalurus punctatus | Collagen alpha-1(XXI) chain |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, W.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, B.; Yu, G. Identification and Structure–Activity Relationship of Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function Protective Collagen Peptides from Alaska Pollock Skin. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080450
Song W, Chen Q, Wang Y, Han Y, Zhang H, Li B, Yu G. Identification and Structure–Activity Relationship of Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function Protective Collagen Peptides from Alaska Pollock Skin. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(8):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080450
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Wenkui, Qianru Chen, Ying Wang, Yan Han, Hongwei Zhang, Bo Li, and Guangli Yu. 2019. "Identification and Structure–Activity Relationship of Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function Protective Collagen Peptides from Alaska Pollock Skin" Marine Drugs 17, no. 8: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080450
APA StyleSong, W., Chen, Q., Wang, Y., Han, Y., Zhang, H., Li, B., & Yu, G. (2019). Identification and Structure–Activity Relationship of Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function Protective Collagen Peptides from Alaska Pollock Skin. Marine Drugs, 17(8), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080450







