Butenolide Derivatives with α-Glucosidase Inhibitions from the Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Aspergillus terreus YPGA10
Abstract
:1. Introduction
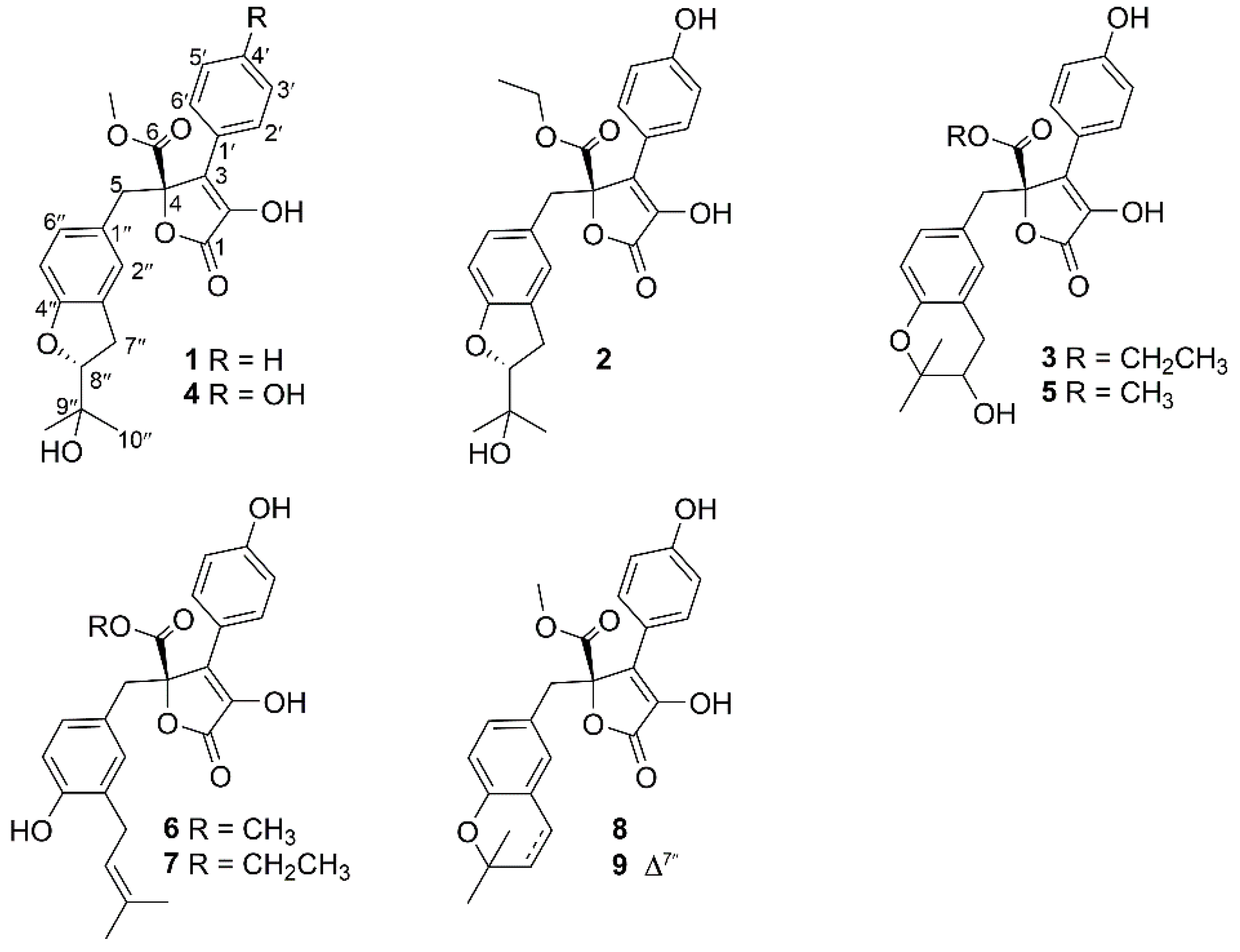
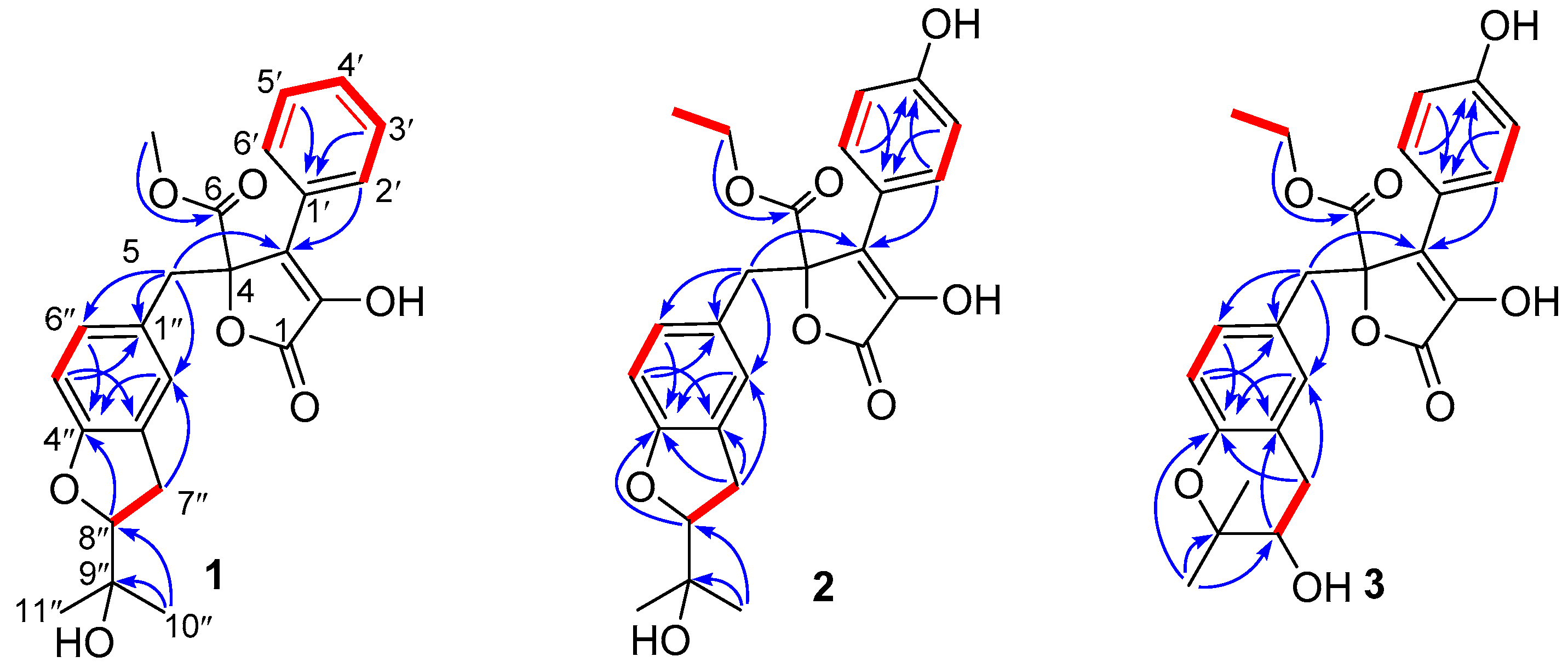
2. Results
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedure
3.2. Fungal Strain and Identification
3.3. Fermentation
3.4. Extraction and Isolation
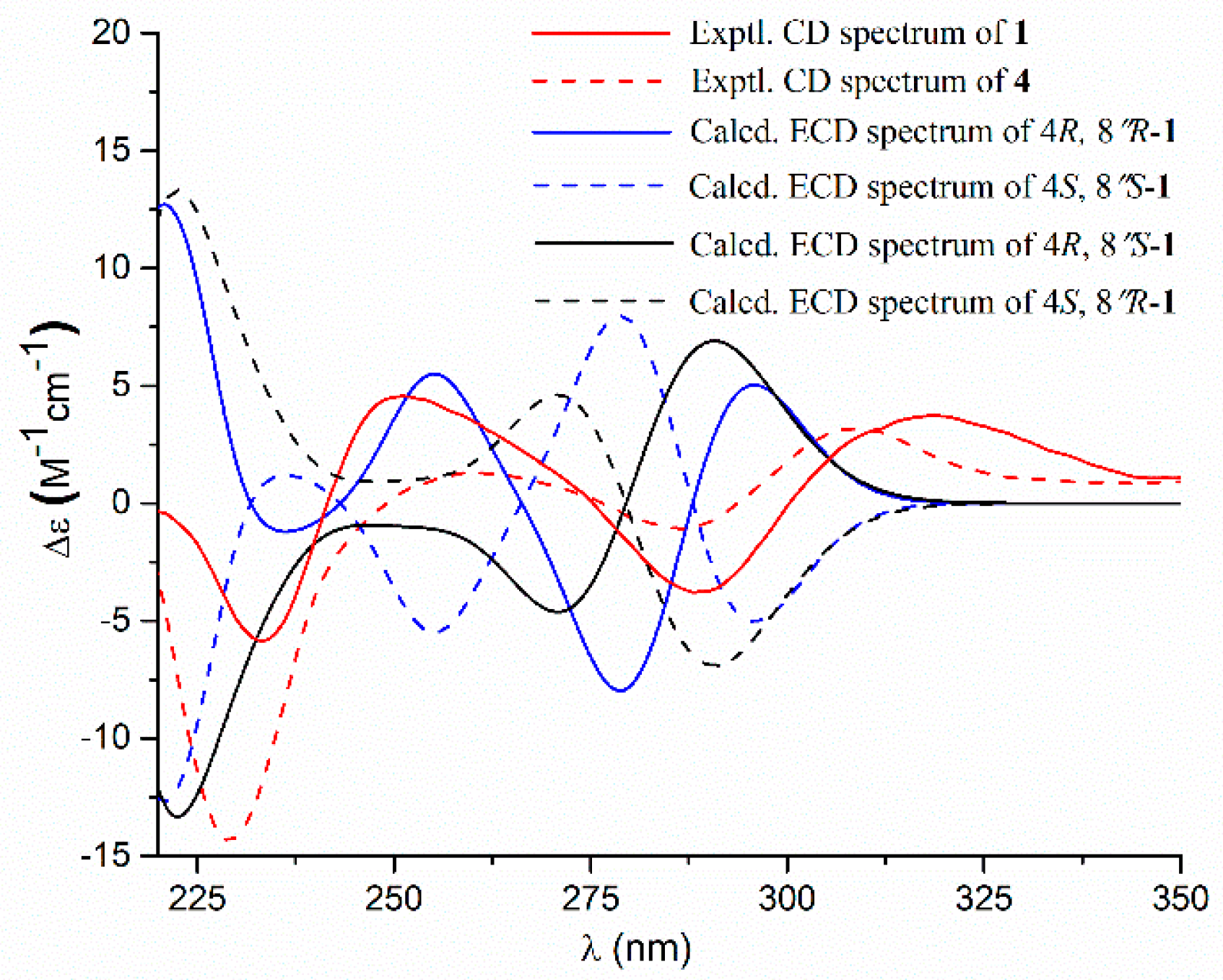
- Aspernolide N (1): Colorless oil; [α] +59 (c 0.03, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 201 (4.39), 287 (3.73) nm; ECD (c 2.8 × 10−4 M, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 286 (−1.09), 229 (−14.39), 202 (+43.55); 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; HRESIMS m/z 447.1403 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C24H24O7Na+, 447.1414).
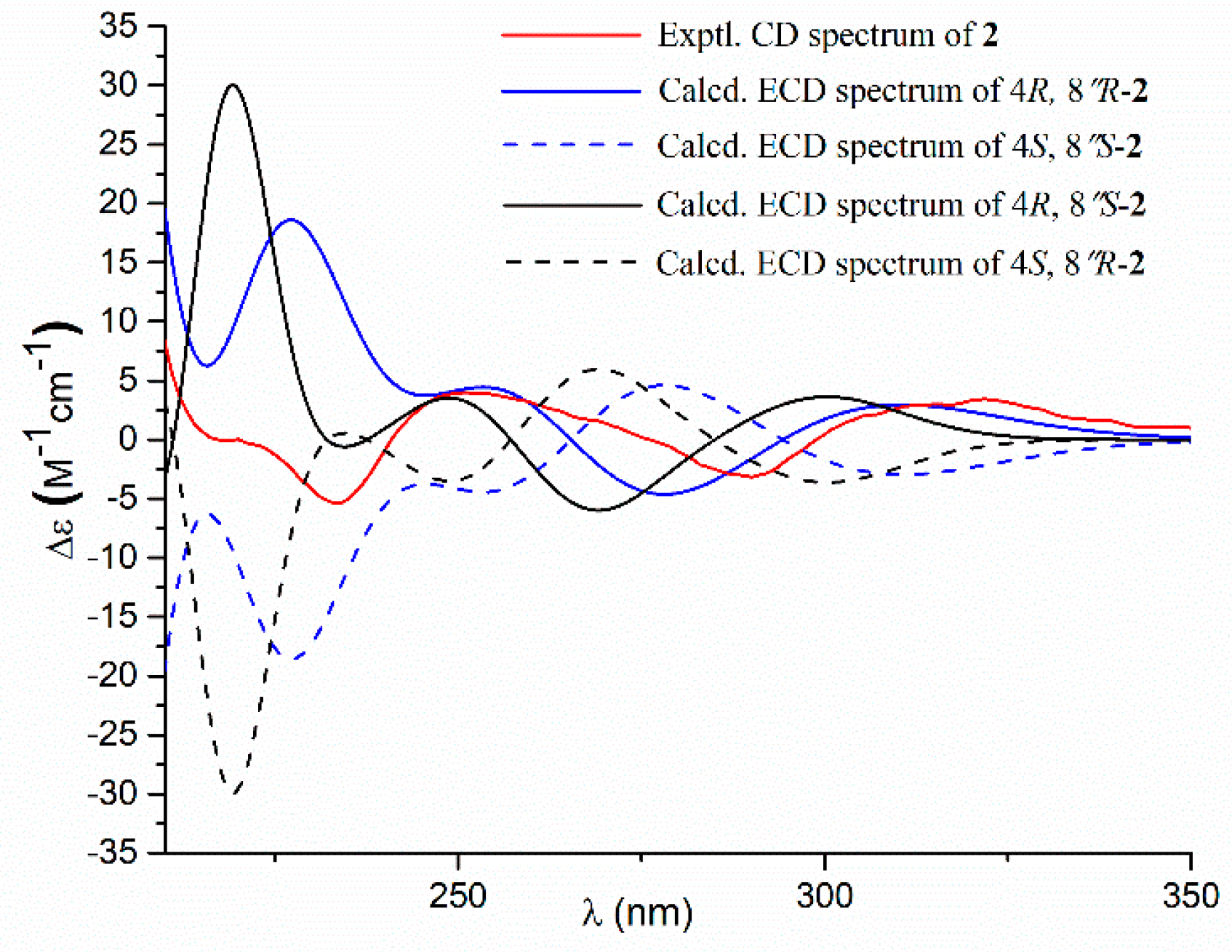
- Aspernolide O (2): Colorless oil; [α] +63 (c 0.16, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 226 (4.15), 306 (4.33) nm; ECD (c 2.2 × 10−4 M, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 290 (−3.16), 251 (+3.99), 235 (−5.35), 202 (+47.49); 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; HRESIMS m/z 477.1525 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C25H26O8Na+, 477.1520).
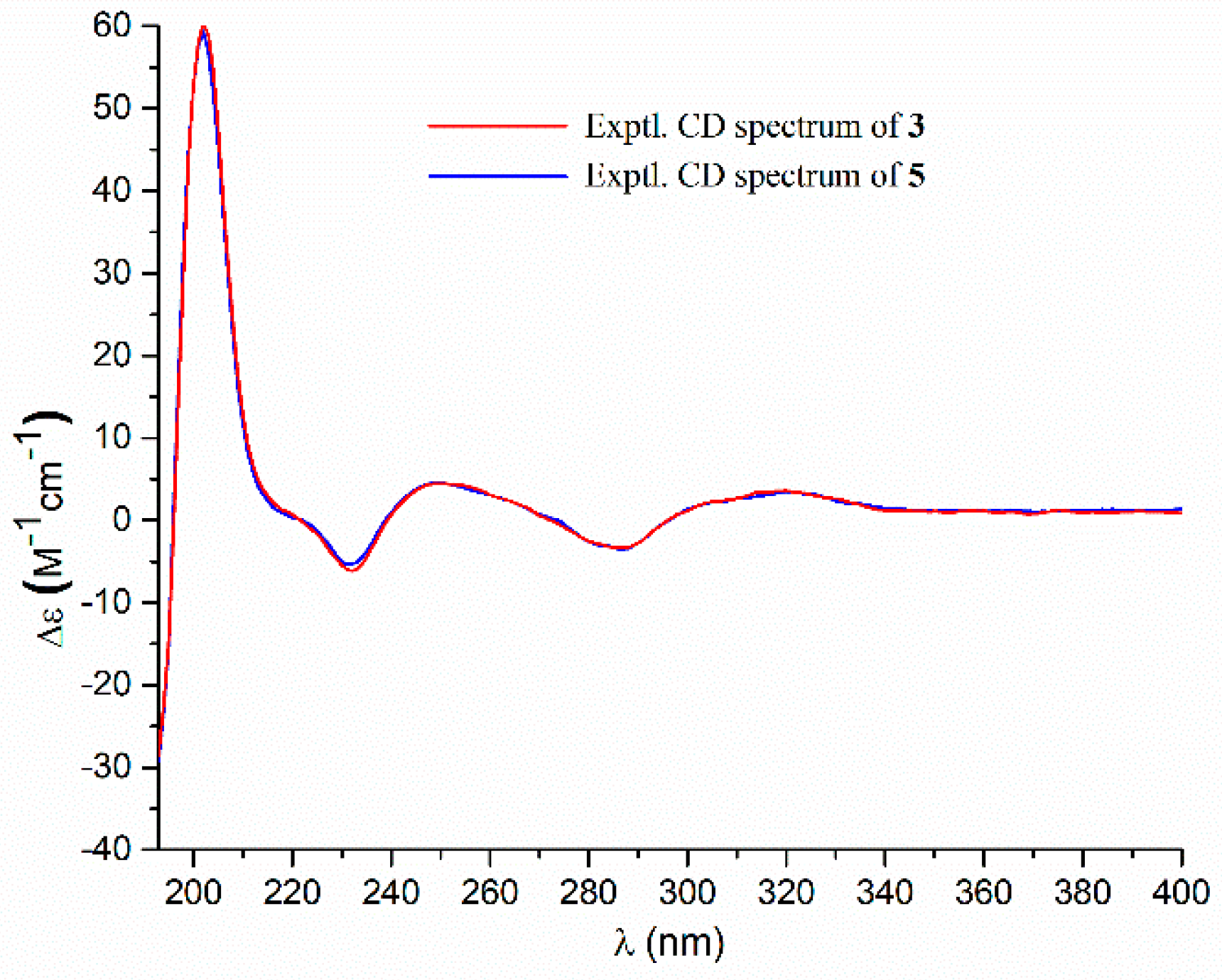
- Aspernolide P (3): Colorless oil; [α] +73 (c 0.14, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 226 (4.33), 306 (4.43) nm; ECD (c 2.1 × 10−4 M, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 286 (−3.32), 249 (+4.45), 232 (−6.16), 202 (+60.34); 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; HRESIMS m/z 477.1518 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C25H26O8Na+, 477.1520).
- Butyrolactone IV (4): ECD (c 2.2 × 10−4 M, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 288 (−3.78), 233 (−5.86), 203 (+48.20).
- Butyrolactone V (5): ECD (c 2.8 × 10−4 M, MeOH) λmax (Δε) 286 (−3.50), 249 (+4.61), 232 (−5.31), 202 (+59.41).
3.5. Computation Section
3.6. α-Glucosidase Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parvatkar, R.R.; D’Souza, C.; Tripathi, A.; Naik, C.G. Aspernolides A and B, butenolides from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Bao, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Tu, Z.C.; Shi, Y.M.; Qi, S.H. Asperterrestide A, a cytotoxic cyclic tetrapeptide from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus SCSGAF0162. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, I.P.; Brissow, E.; Kellner Filho, L.C.; Senabio, J.; de Siqueira, K.A.; Vandresen Filho, S.; Damasceno, J.L.; Mendes, S.A.; Tavares, D.C.; Magalhães, L.G.; et al. Bioactive compounds of Aspergillus terreus F7, an endophytic fungus from Hyptis suaveolens (L.) Poit. World J. Microb. Biot. 2017, 33, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuclear, P.; Sommit, D.; Boonyuen, N.; Pudhom, K. Butenolide and furandione from an endophytic Aspergillus terreus. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 1221–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Y.B.; Lei, X.-L.; Qian, Z.J. Butyrolactone-I from coral-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus attenuates neuro-inflammatory response via suppression of NF-κB pathway in BV-2 cells. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, K.V.; Sadhukhan, A.K.; Veerender, M.; Ravikumar, V.; Mohan, E.V.S.; Dhanvantri, S.D.; Sitaramkumar, M.; Moses Babu, J.; Vyas, K.; Om Reddy, G. Butyrolactones from Aspergillus terreus. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 48, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haritakun, R.; Rachtawee, P.; Chanthaket, R.; Boonyuen, N.; Isaka, M. Butyrolactones from the fungus Aspergillus terreus BCC 4651. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 1545–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.-H.; Ou-Yang, H.; Yan, X.; Tang, B.W.; Fang, M.J.; Wu, Z.; Chen, J.W.; Qiu, Y.-K. Open-ring butenolides from a marine-derived anti-neuroinflammatory fungus Aspergillus terreus Y10. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Gong, C.; Wang, S.; Yang, F.; Hua, H.; Lin, H. New butenolide derivatives from the marine sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Qi, C.; Sun, W.; Shen, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Lai, Y.; Xue, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y. α-Glucosidase inhibitors from the coral-associated fungus Aspergillus terreus. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munasaroh, S.R.; Tamat, S.; Dewi, R. Isolation and identification of α-glucosidase inhibitor from Aspergillus terreus F38. Indones. J. Pharm. 2018, 29, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skropeta, D.; Wei, L. Recent advances in deep-sea natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 999–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Bai, S.; Liu, L.; Luo, Z.; Yuan, W.; Li, Q. Two new meroterpenoids and two new monoterpenoids from the deep sea-derived fungus Penicillium sp. YPGA11. Fitoterapia 2019, 133, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Xu, W.; Li, S.; Chen, M.; Cheng, Y.; Yuan, W.; Cheng, Z.; Li, Q. Penicindopene A, a new indole diterpene from the deep-sea fungus Penicillium sp. YPCMAC1. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, Oct 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Xu, W.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Yuan, W.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Q. Peniginsengins B–E, new farnesylcyclohexenones from the deep sea-derived fungus Penicillium sp. YPGA11. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liu, D.; Proksch, P.; Zhao, Z.; Lin, W. Eremophilane-type sesquiterpenoids from an Acremonium sp. fungus isolated from deep-sea sediments. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Xu, W.; Zeng, X.; Cheng, Z.; Li, Q. Aspterrics A and B, new sesquiterpenes from deep sea-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus YPGA10. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Lu, C.; Shen, Y. Secondary metabolites of Aspergillus sp. F1, a commensal fungal strain of Trewia nudiflora. Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 23, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sybyl Software, version X 2.0; Tripos Associates Inc.: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2013.
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 09, Rev. C 01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Boue, S.M.; Daigle, K.W.; Chen, M.-H.; Cao, H.; Heiman, M.L. Antidiabetic potential of purple and red rice (Oryza sativa L.) bran extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 5345–5353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, R.; Li, L.; Yuan, T.; Seeram, N.P. α-Glucosidase inhibitory hydrolyzable tannins from Eugenia jambolana seeds. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1505–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH | δC | δH | δC | δH | δC | |
| 1 | 170.3 | 170.5 | 170.7 | |||
| 2 | not detected | 140.0 | 140.2 | |||
| 3 | 128.1 | 129.1 | 129.0 | |||
| 4 | 86.9 | 86.9 | 86.9 | |||
| 5 | 3.49, s | 39.6 | 3.46, s | 39.7 | 3.44, s | 39.5 |
| 6 | 171.5 | 171.0 | 171.0 | |||
| 1′ | 132.1 | 123.2 | 123.3 | |||
| 2′, 6′ | 7.70, dd (8.4, 1.2) | 128.5 | 7.60, d (8.9) | 130.4 | 7.59, d (8.7) | 130.3 |
| 3′, 5′ | 7.46, dd (8.4, 7.4) | 129.8 | 6.87, d (8.9) | 116.6 | 6.87, d (8.7) | 116.5 |
| 4′ | 7.37, dd (7.4, 1.2) | 129.6 | 159.3 | 159.2 | ||
| 1″ | 126.2 | 126.3 | 126.2 | |||
| 2″ | 6.59, d (1.6) | 127.9 | 6.61, d (1.5) | 127.9 | 6.48, d (1.8) | 132.9 |
| 3″ | 128.1 | 128.0 | 120.5 | |||
| 4″ | 160.5 | 160.4 | 153.4 | |||
| 5″ | 6.45, d (8.2) | 109.1 | 6.46, d (8.2) | 109.1 | 6.48, d (8.2) | 117.2 |
| 6″ | 6.52, dd (8.2, 1.6) | 131.0 | 6.54, dd (8.2, 1.5) | 131.0 | 6.56, dd (8.5, 1.8) | 130.4 |
| 7″ | 2.99, m | 31.3 | 2.99, m | 31.3 | 2.77, dd (16.6, 5.4); 2.53, dd (16.6, 7.5) | 32.0 |
| 8″ | 4.50, dd (9.3, 8.6) | 90.4 | 4.49, dd (9.3, 8.6) | 90.4 | 3.67, dd (7.5, 5.4) | 70.4 |
| 9″ | 72.5 | 72.5 | 77.9 | |||
| 10″ | 1.19, s | 25.2 | 1.19, s | 25.2 | 1.27, s | 25.8 |
| 11″ | 1.16, s | 25.3 | 1.16, s | 25.3 | 1.17, s | 20.9 |
| OCH2/3 | 3.79, s | 53.9 | 4.25, q (7.1) | 63.7 | 4.25, q (7.0) | 63.7 |
| CH3 | 1.21, t (7.1) | 14.2 | 1.21, t (7.0) | 14.2 | ||
| No. | %Inhibition (100 μM) | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 18.62 | - c |
| 2 | 23.18 | - c |
| 3 | 26.43 | - c |
| 4 | 37.29 | - c |
| 5 | 21.57 | - c |
| 6 | 100/89.41 b | 3.87 ± 0.33 |
| 7 | 100/98.69 b | 1.37 ± 0.05 |
| 8 | 89.17 | 6.98 ± 0.22 |
| 9 | 90.43 | 8.06 ± 0.21 |
| Acarbose a | 190.2 ± 2.4 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Yuan, W.; Luo, Z.; Xu, W.; Li, Q. Butenolide Derivatives with α-Glucosidase Inhibitions from the Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Aspergillus terreus YPGA10. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17060332
Cheng Z, Li Y, Liu W, Liu L, Liu J, Yuan W, Luo Z, Xu W, Li Q. Butenolide Derivatives with α-Glucosidase Inhibitions from the Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Aspergillus terreus YPGA10. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(6):332. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17060332
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Zhongbin, Yuanli Li, Wan Liu, Lijun Liu, Jie Liu, Wangjun Yuan, Zhuhua Luo, Wei Xu, and Qin Li. 2019. "Butenolide Derivatives with α-Glucosidase Inhibitions from the Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Aspergillus terreus YPGA10" Marine Drugs 17, no. 6: 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17060332
APA StyleCheng, Z., Li, Y., Liu, W., Liu, L., Liu, J., Yuan, W., Luo, Z., Xu, W., & Li, Q. (2019). Butenolide Derivatives with α-Glucosidase Inhibitions from the Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Aspergillus terreus YPGA10. Marine Drugs, 17(6), 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17060332





