Lemnalol Modulates the Electrophysiological Characteristics and Calcium Homeostasis of Atrial Myocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
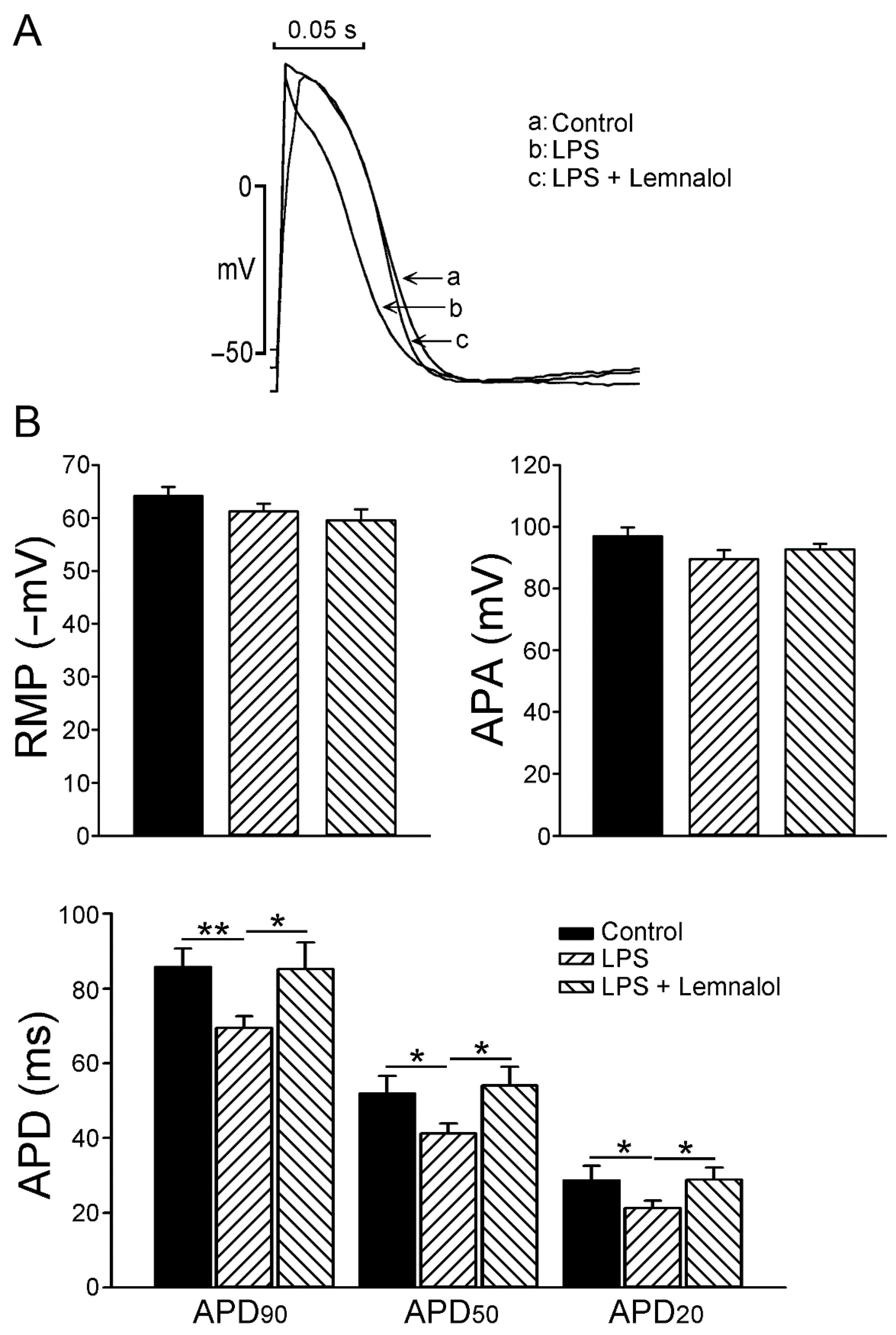
2.1. Effects of Lemnalol on the Action Potential of LA Myocytes
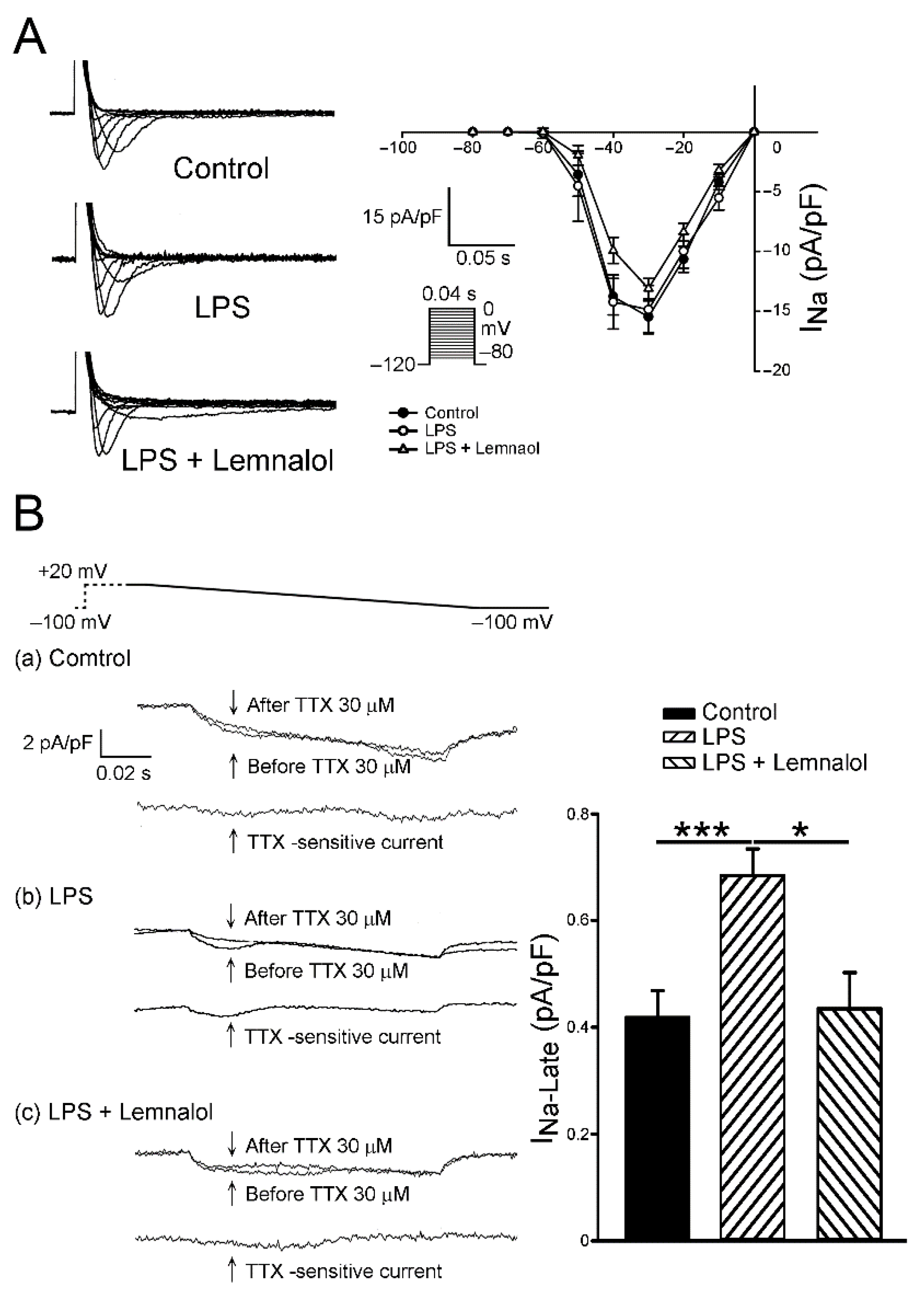
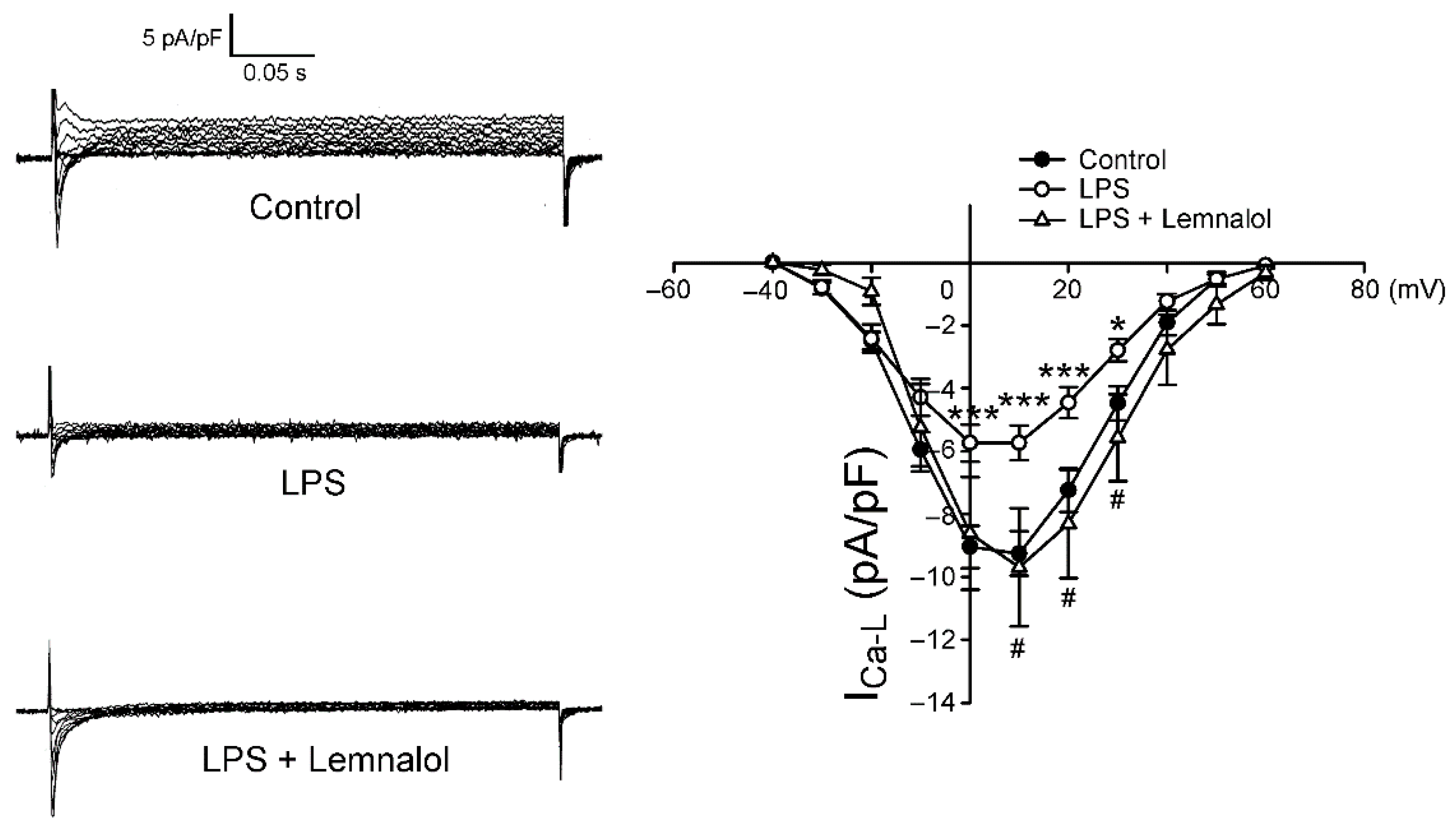
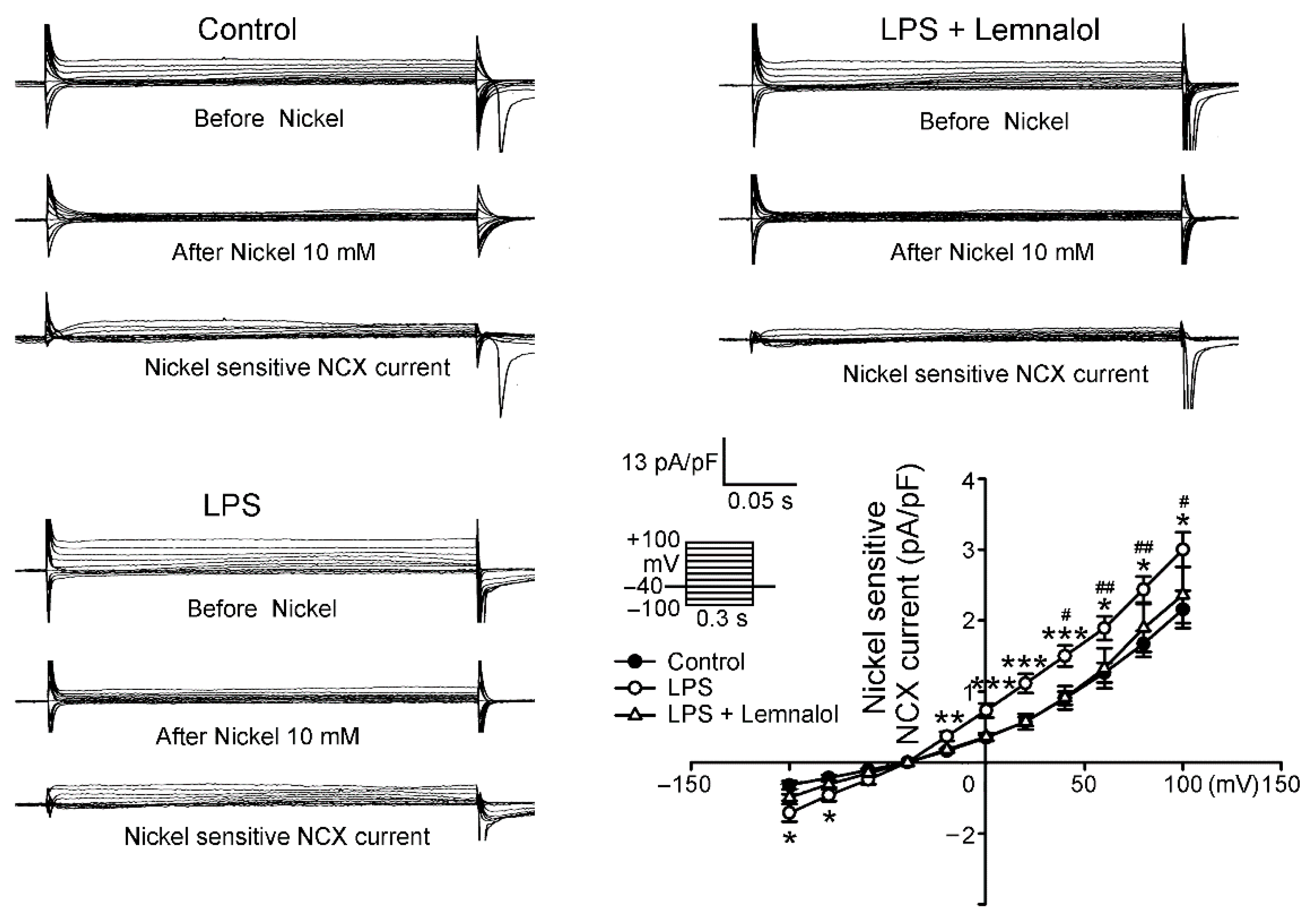
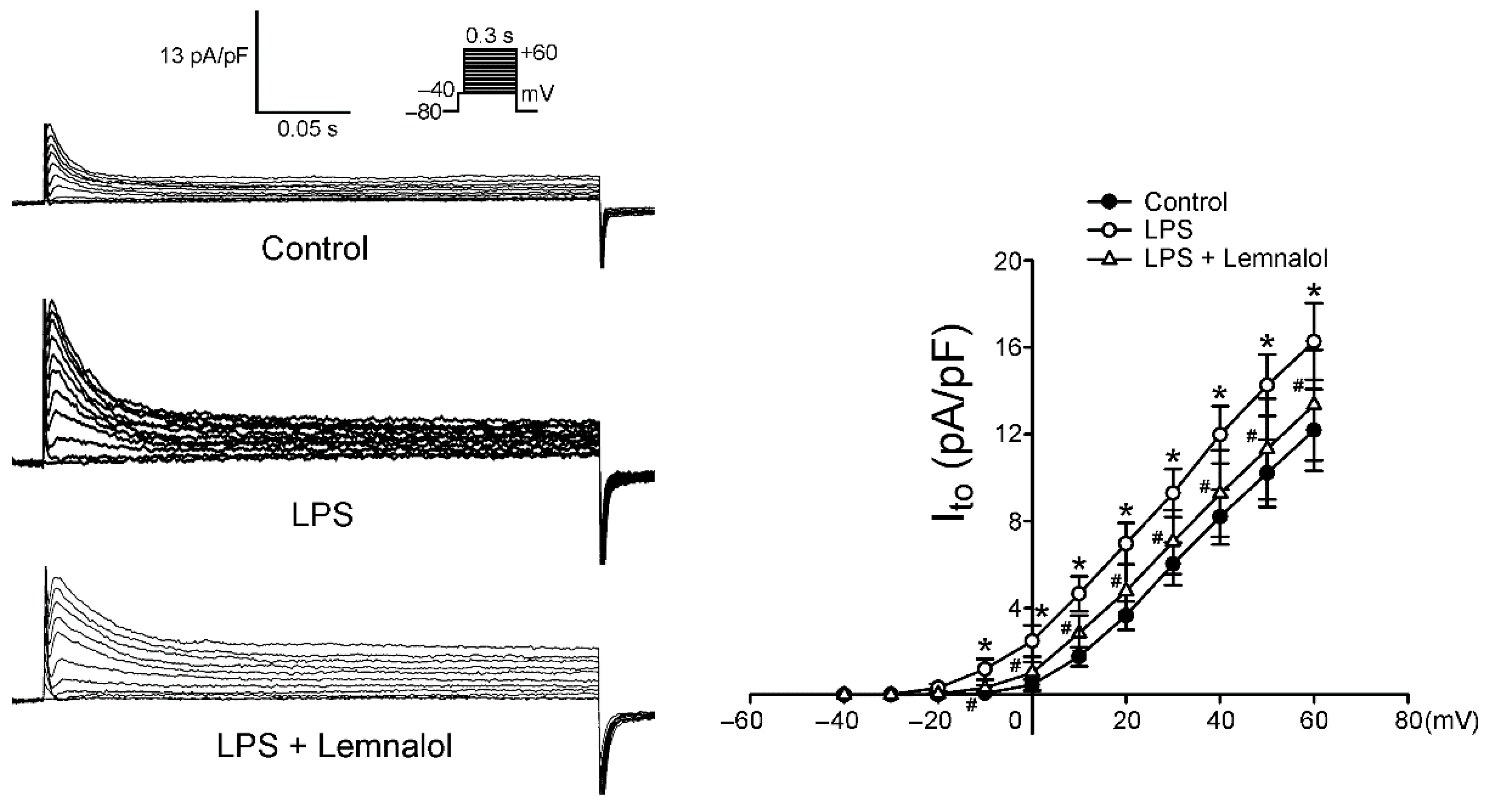
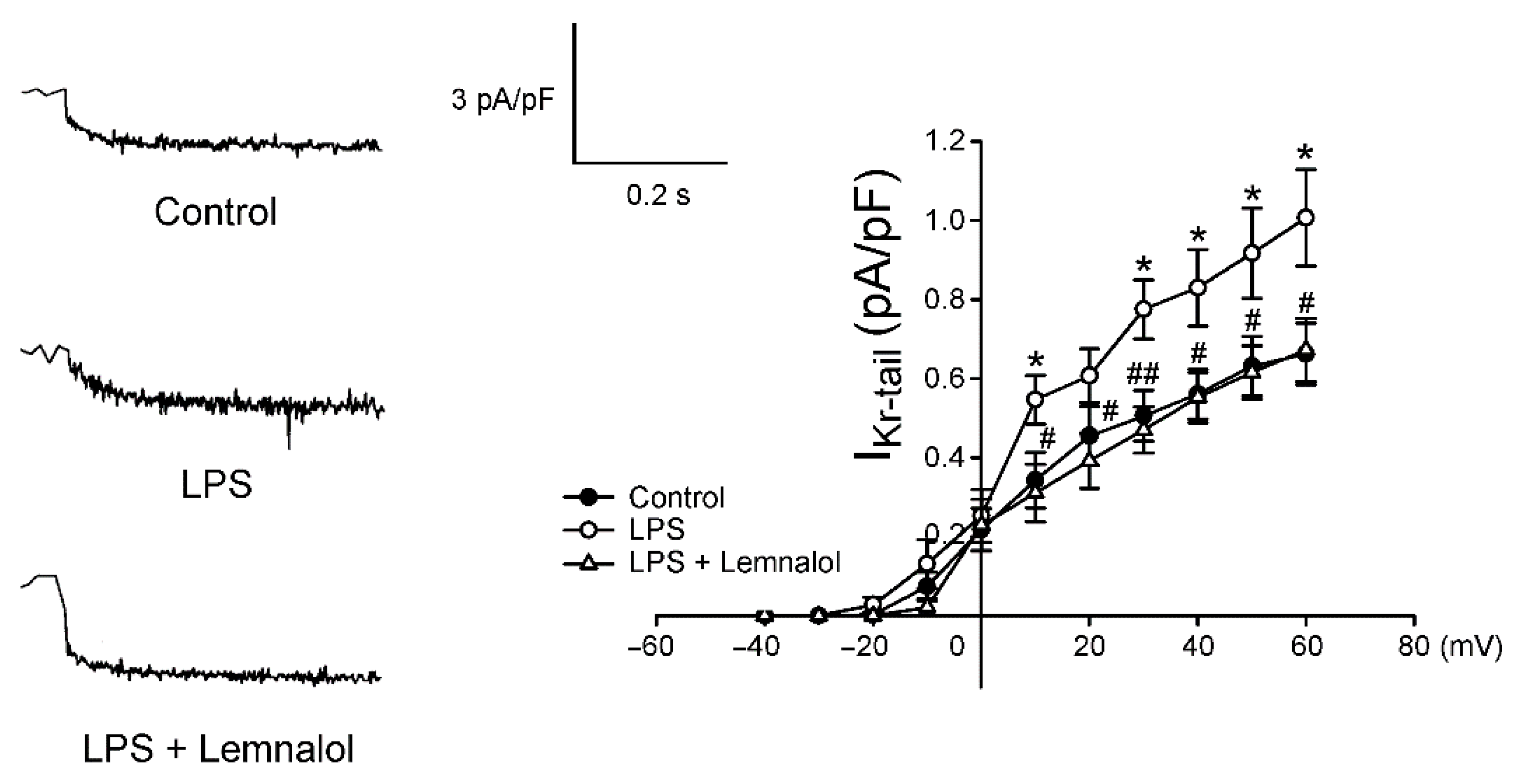
2.2. Effects of Lemnalol on the Membrane Currents of LA Myocytes
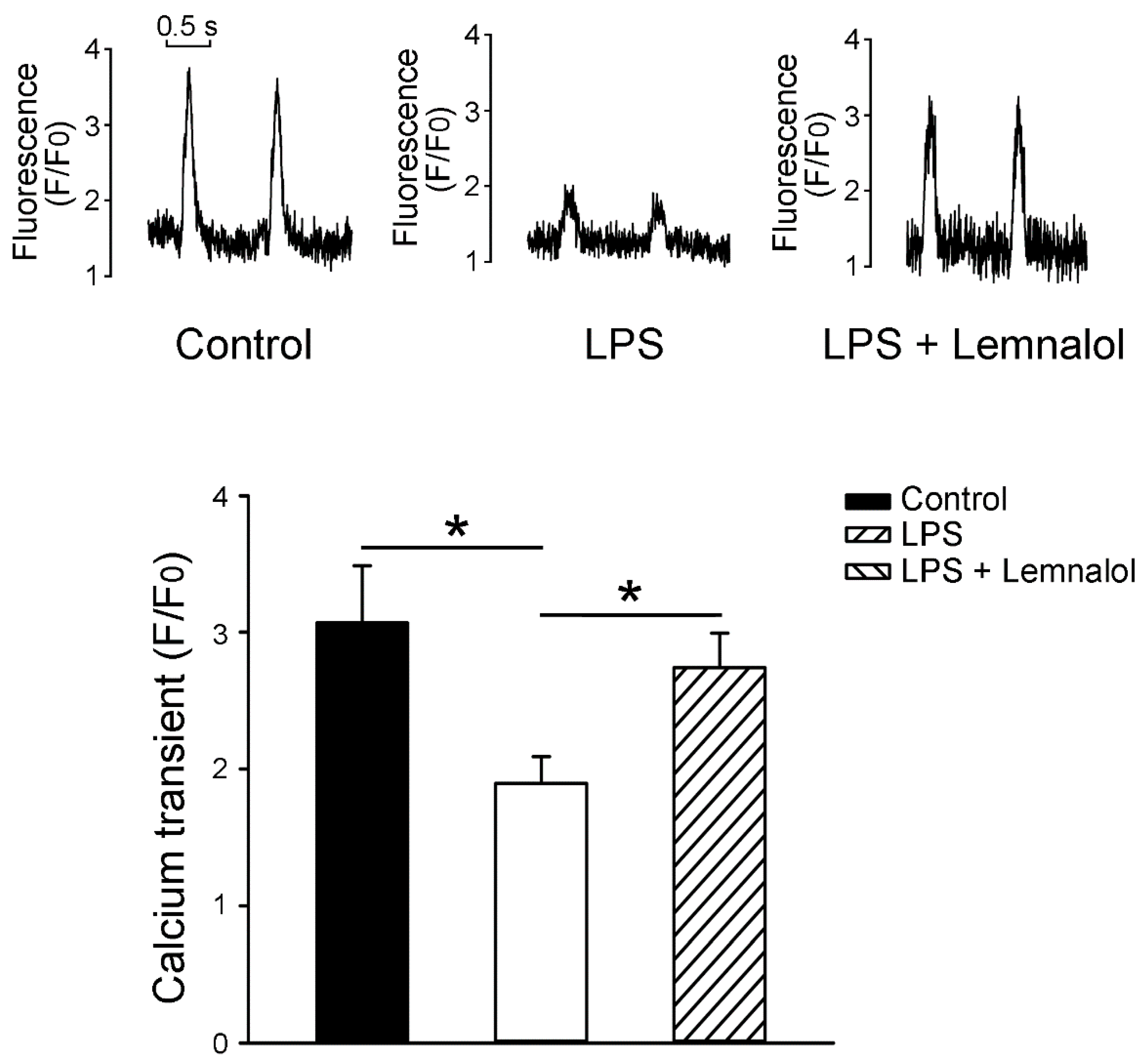
2.3. Effects of Lemnalol on Calcium Handling of LA myocytes
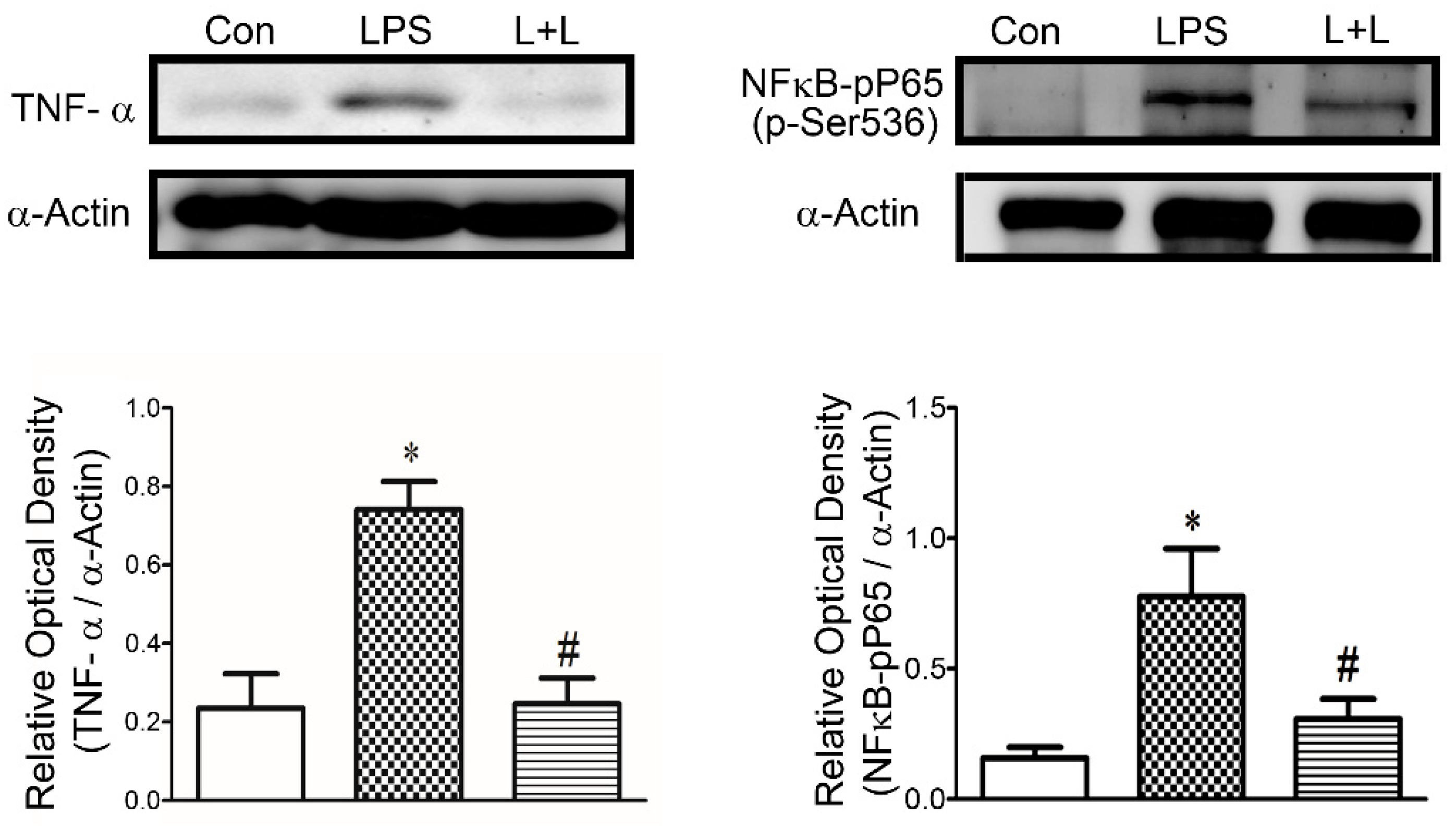
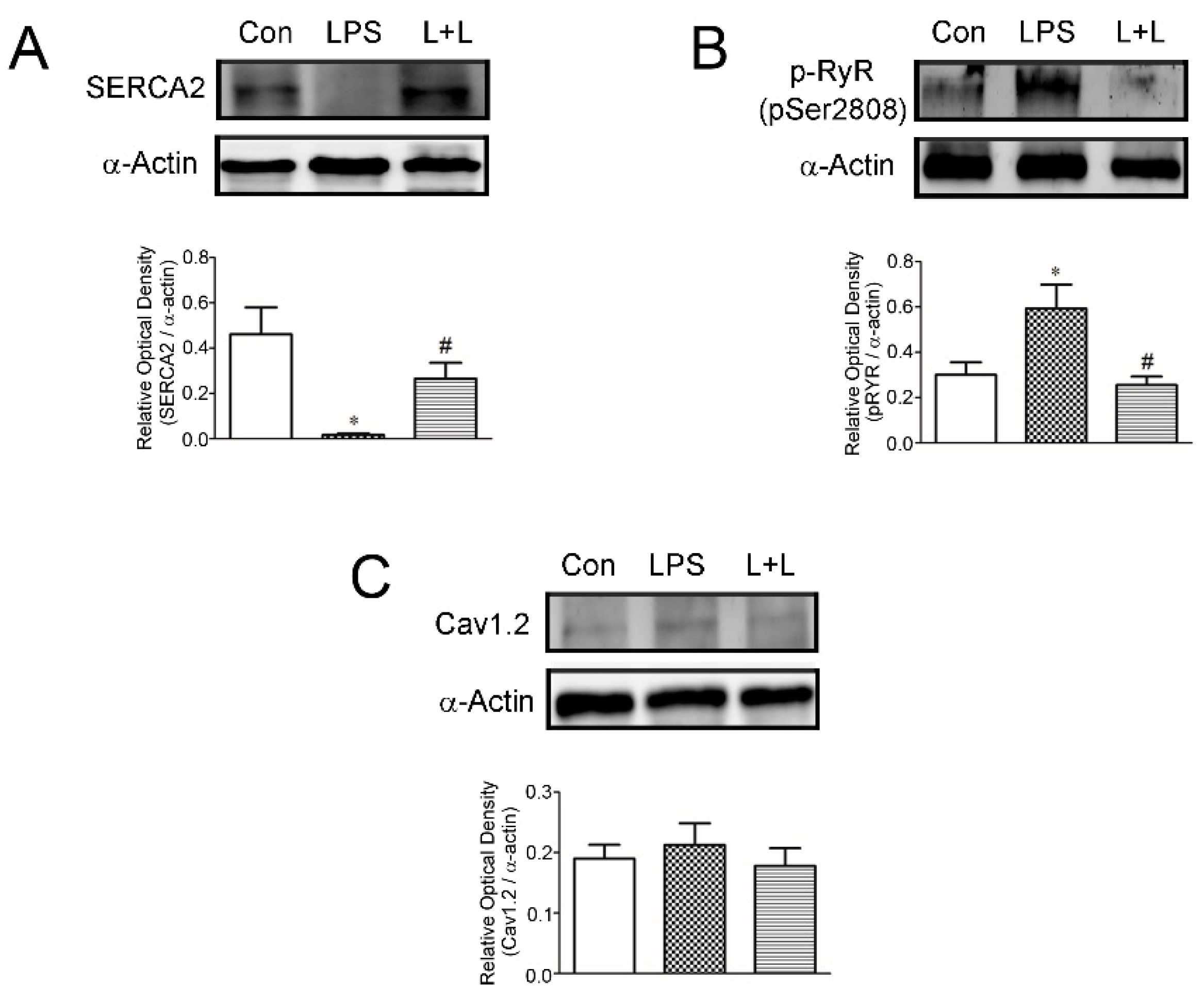
2.4. Effects of Lemnalol on Protein Expression in LA Myocytes
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Materials
4.2. Isolation of Single LA Myocytes
4.3. Electrophysiological Study
4.4. Measurement of the Changes in the Intracellular Calcium and SR Calcium Contents
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bassani, J.W.; Bassani, R.A.; Bers, D.M. Calibration of indo-1 and resting intracelluar [Ca]i in intact rabbit cardiac myocytes. Biophys. J. 1995, 68, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwin, S.V.A.; Theo, J.C.V.B.; Johan, K. Receptors, mediators, and mechanisms involved in bacterial sepsis and septic shock. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 379–414. [Google Scholar]
- Bone, R.C. The pathogenesis of sepsis. Ann. Int. Med. 1991, 115, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bone, R.C. Why new definitions of sepsis are needed. Am. J. Med. 1993, 95, 348–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiemstra, P.S.; Eisenhauer, P.B.; Harwig, S.S.L.; Barselaar, M.T.V.D.; Furth, R.V.; Lehrer, R.I. Antimicrobiol proteins of murine macrophages. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 3038–3046. [Google Scholar]
- Beutler, B.; Milsark, I.W.; Cerami, A.C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science 1985, 229, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hack, C.E.; Aarden, L.A.; Thijs, L.G. Role of cytokines in sepsis. Adv. Immunol. 1997, 66, 101–195. [Google Scholar]
- Lucaks, N.W.; Hogaboam, C.; Campbell, E.; Kunkel, S.I. Chemokines: Function, regulation and alteration of inflammatory responses. Chem. Immunol. 1999, 72, 102–120. [Google Scholar]
- Grewe, M.; Gausling, R.; Gyufko, K.; Hoffman, R.; Decker, K. Regulation of the mRNA expression for tumor necrosis factor-α in rat liver macrophages. J. Hepatol. 1994, 20, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, G.M. Markers of inflammation before and after curative ablation of atrial flutter. Heart Rhythm 2008, 5, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, G.M. Intracardiac and extracardiac markers of inflammation during atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm 2010, 7, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, S.; Viacheslav, N.B.; Stephanie, R.; Peter, N.; Neil, D.P. Transcriptional profiling of the LPS-induced NF-κB response in macrophages. BMC Immunol. 2007, 8, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Jessy, C.C.; Donna, W.Y.; Douglas, T.G.; William, J.C.; Fabian, G. Toll-like Receptor-4 Mediates Lipopolysaccharide-induced Signal Transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 10689–10692. [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi, H.; Manda, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Yamada, Y.; Iguchi, K. Anti-tumor activity of Lemnalol isolated from the soft coral Lemnalia tenuis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1983, 31, 1086–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duh, C.Y.; El-Gamal, A.A.; Song, P.Y.; Wang, S.K.; Dai, C.F. Steroidsand sesquiterpenoids from the soft corals Dendronephthya gigantea and Lemn Cervicorni. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1650–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jean, Y.H.; Chen, W.F.; Duh, C.Y.; Huang, S.Y.; Hsu, C.H.; Lin, C.S.; Sung, C.S.; Chen, I.M.; Wen, Z.H. Inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 participate in anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of the natural marine compound lemnalol from Formosan soft coral Lemnalia cervicorni. Eur. J. Pharm. 2008, 578, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.C.; Huang, S.Y.; Jean, Y.H.; Chen, W.F.; Sung, C.S.; Kao, E.S.; Wang, H.M.; Chakraborty, C.; Duh, C.Y.; Wen, Z.H. Intrathecal lemnalol, a natural marine compound obtained from Formosan soft coral, attenuates nociceptive responses and the activity of spinal glial cells in neuropathic rats. Behav. Pharm. 2011, 22, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.P.; Huang, S.Y.; Lin, Y.Y.; Wang, H.M.; Jean, Y.H.; Wu, S.F.; Duh, C.Y.; Wen, Z.H. Soft coral-derived lemnalol alleviates monosodium urate-induces gouty arthritis in rats by inhibiting leukocyte infiltration and iNOS, COX-2 and c-Fos protein expression. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.P.; Lin, Y.Y.; Duh, C.Y.; Huang, S.Y.; Wang, H.M.; Wu, S.F.; Lin, S.C.; Jean, Y.H.; Wen, Z.H. Lemnalol attenuates mast cell activation and osteoclast activity in a gouty arthritis model. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 67, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Villamil, J.P.; D′Annunzio, V.; Finocchietto, P. Cardiac-specific overexpression of thioredoxin 1 attenuates mitochondrial and myocardial dysfunction in septic mice. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 81, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, C.; Andrades, M.; Frota, M.L.C. Junior Oxidative parameters and mortality in sepsis induced by cecal ligation and perforation. Intensive Care Med. 2003, 29, 1782–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, D.S. Oxidative stress in critically ill children with sepsis. Open Inflamm. J. 2011, 4, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosker, C.; Salvarani, N.; Schmutz, S.; Grand, T.; Rohr, S. Abolishing myofibroblast arrhythmogeneicity by pharmacological ablation of alpha-smooth muscle actin containing stress fibers. Circ. Res. 2011, 109, 1120–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochanek, K.D.; Kirmeyer, S.E.; Martin, J.A.; Strobino, D.M.; Guyer, B. Annual summary of vital statistics: 2009. Pediatrics 2012, 129, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinberg, W.M.; Blackshear, J.L.; Laupacis, A.; Kronmal, R.; Hart, R.G. Prevalence, age distribution, and gender of patients with atrial fibrillation. Analysis and implications. Arch. Intern. Med. 1995, 155, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, P.A.; Abbott, R.D.; Kannel, W.B. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: The Framingham Study. Stroke 1991, 22, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furberg, C.D.; Psaty, B.M.; Manolio, T.A.; Gardin, J.M.; Smith, V.E.; Rautaharju, P.M. Prevalence of atrial fibrillation in elderly subjects (the Cardiovascular Health Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 1994, 74, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psaty, B.M.; Manolio, T.A.; Kuller, L.H.; Kronmal, R.A.; Cushman, M.; Fried, L.P.; White, R.; Furberg, C.D.; Rautaharju, P.M. Incidence of and risk factors for atrial fibrillation in older adults. Circulation 1997, 96, 2455–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, P.A.; Abbott, R.D.; Kannel, W.B. Atrial fibrillation: A major contributor to stroke in the elderly. The Framingham study. Arch. Intern. Med. 1987, 147, 1561–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahn, A.D.; Manfreda, J.; Tate, R.B.; Mathewson, F.A.L.; Cuddy, T.E. The natural history of atrial fibrillation: Incidence, risk factors, and prognosis in the manitoba follow-up study. Am. J. Med. 1995, 98, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubart, M.; Zipes, D.P. Mechanisms of sudden cardiac death. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 2305–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Court, O.; Kumar, A.; Parrillo, J.E.; Kumar, A. Clinical review: Myocardial depression in sepsis and septic shock. Crit. Care 2002, 6, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, Y.; Hatakeyama, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Kinoshita, H.; Matsuda, N.; Hattori, Y.; Yamazaki, M. Role of ion channels in sepsis-induced atrial tachyarrhythmias in guinea pigs. Br. J. Pharm. 2012, 166, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wagoner, D.R.; Pond, A.L.; Lamorgese, M.; Rossie, S.S.; McCarthy, P.M.; Nerbonne, J.M. Atrial L-type Ca2+ currents and human atrial fibrillation. Circ. Res. 1999, 85, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Melnyk, P.; Feng, J.; Wang, Z.; Petrecca, K.; Shrier, A.; Nattel, S. Effects of experimental heart failure on atrial cellular and ionic electrophysiology. Circulation 2000, 101, 2631–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Grand, B.L.; Hatem, S.; Deroubaix, E.; Couetil, J.P.; Coraboeuf, E. Depressed transient outward and calcium currents in dilated human atria. Cardiovasc. Res. 1994, 28, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makielski, J.C.; Farley, A.L. Na+ current in human ventricle: Implications for sodium loading and homeostasis. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2006, 17, S15–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongcharoen, W.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Chang, C.M.; Yeh, H.I.; Lin, C.I.; Chen, S.A. Effects of a Na+/Ca2+ exchanger inhibitor on pulmonary vein electrical activity and ouabain-induced arrhythmogenicity. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 70, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, L.S. A novel mechanism for the treatment of angina, arrhythmias, and diastolic dysfunction: Inhibition of late INa using ranolazine. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2009, 54, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, M. Mechanisms of Ca2+ overload in reperfused ischemic myocardium. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1990, 52, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigekawa, M.; Iwamoto, T. Cardiac Na+-Ca2+ exchange: Molecular and pharmacological aspects. Circ. Res. 2001, 88, 864–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, D.; Noble, P.J. Late sodium current in the pathophysiology of cardiovascular disease: Consequences of sodium-calcium overload. Heart 2006, 92, iv1–iv5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bers, D.M.; Bassani, J.W.; Bassani, R.A. Na+-Ca2+ exchange and Ca2+ fluxes during contraction and relaxation in mammalian ventricular muscle. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1996, 779, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.W. Digitalis: Mechanisms of action and clinical use. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 318, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, G.R.; Feng, J.; Wang, Z.; Fermini, B.; Nattel, S. Comparative mechanisms of 4-aminopyridine-resistant Ito in human and rabbit atrial myocytes. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 269, H463–H472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobloch, K.; Brendel, J.; Rosenstein, B.; Bleich, M.; Busch, A.E.; Wirth, K.J. Atrial selective antiarrhythmic actions of novel IKur vs. IKr, IKs, and IKAch class Ic drugs and beta blockers in pigs. Med. Sci. Monit. 2004, 10, BR221–BR228. [Google Scholar]
- Cimolai, M.C.; Alvarez, S.; Bode, C.; Bugger, H. Mitochondrial Mechanisms in Septic Cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 17763–17778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severn, A.; Rapsos, N.T.; Hunter, C.A.; Liew, F.Y. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor production by adrenaline and beta-adrenergic agonists. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 3441–3445. [Google Scholar]
- Khadour, F.H.; Panas, D.; Ferdinandy, P.; Schulze, C.; Csont, T.; Lalu, M.M. Enhanced NO and superoxide generation in dysfunctional hearts from endotoxemic rats. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2002, 283, H1108–H1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Harrison, S.M.; Steele, D.S. ATP-dependent effects of halothane on SR Ca2+ regulation in permeabilized atrial myocytes. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005, 65, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tai, B.-Y.; Wen, Z.-H.; Cheng, P.-Y.; Yang, H.-Y.; Duh, C.-Y.; Chen, P.-N.; Hsu, C.-H. Lemnalol Modulates the Electrophysiological Characteristics and Calcium Homeostasis of Atrial Myocytes. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110619
Tai B-Y, Wen Z-H, Cheng P-Y, Yang H-Y, Duh C-Y, Chen P-N, Hsu C-H. Lemnalol Modulates the Electrophysiological Characteristics and Calcium Homeostasis of Atrial Myocytes. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(11):619. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110619
Chicago/Turabian StyleTai, Buh-Yuan, Zhi-Hong Wen, Pao-Yun Cheng, Hsiang-Yu Yang, Chang-Yih Duh, Ping-Nan Chen, and Chih-Hsueng Hsu. 2019. "Lemnalol Modulates the Electrophysiological Characteristics and Calcium Homeostasis of Atrial Myocytes" Marine Drugs 17, no. 11: 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110619
APA StyleTai, B.-Y., Wen, Z.-H., Cheng, P.-Y., Yang, H.-Y., Duh, C.-Y., Chen, P.-N., & Hsu, C.-H. (2019). Lemnalol Modulates the Electrophysiological Characteristics and Calcium Homeostasis of Atrial Myocytes. Marine Drugs, 17(11), 619. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110619




