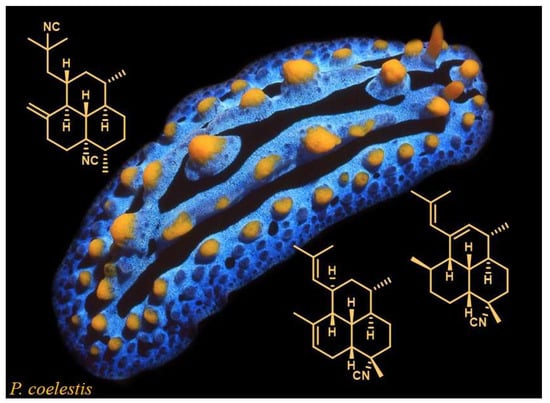
Amphilectene Diterpene Isonitriles and Formamido Derivatives from the Hainan Nudibranch Phyllidia Coelestis
Abstract
1. Introduction
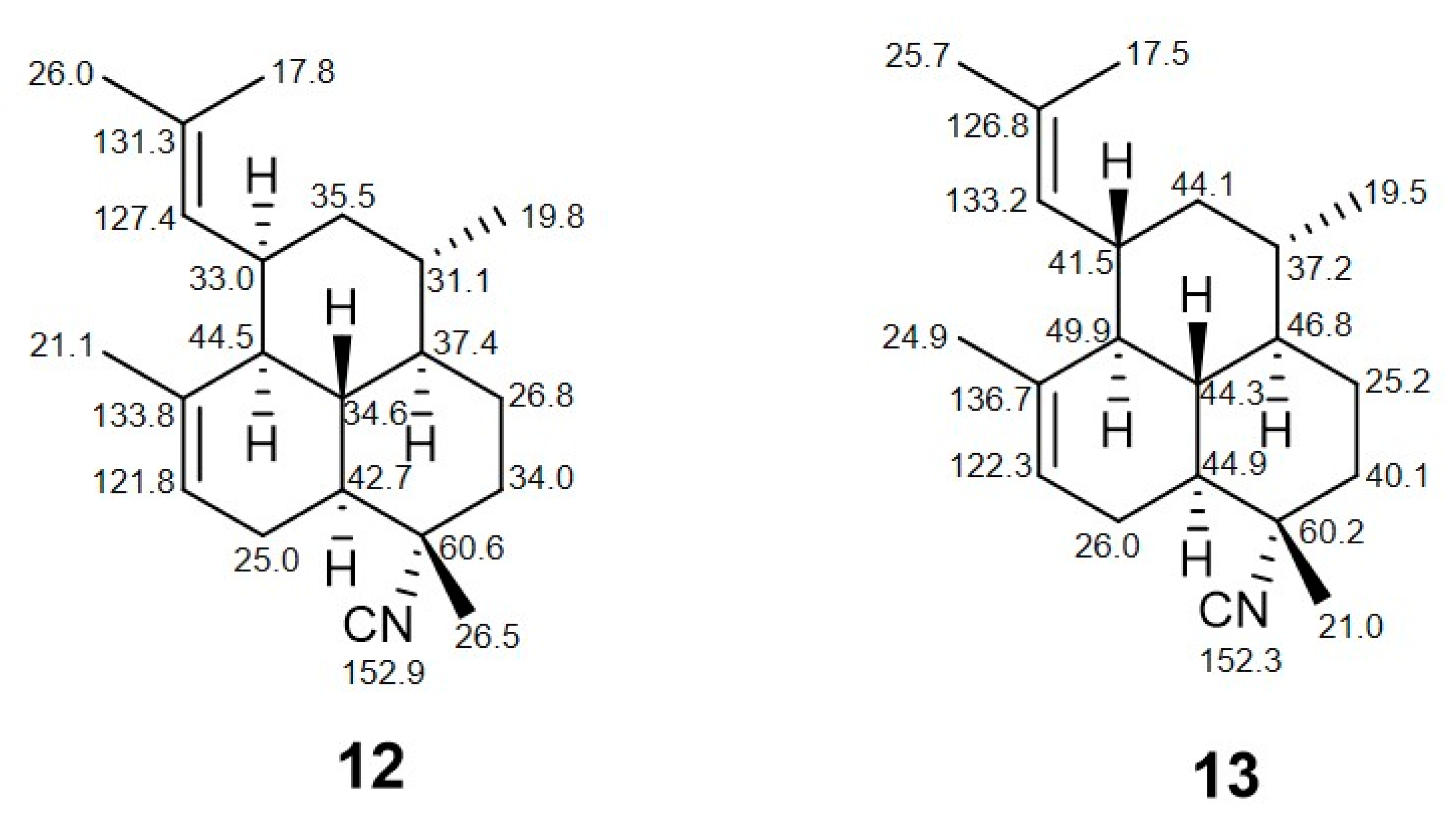
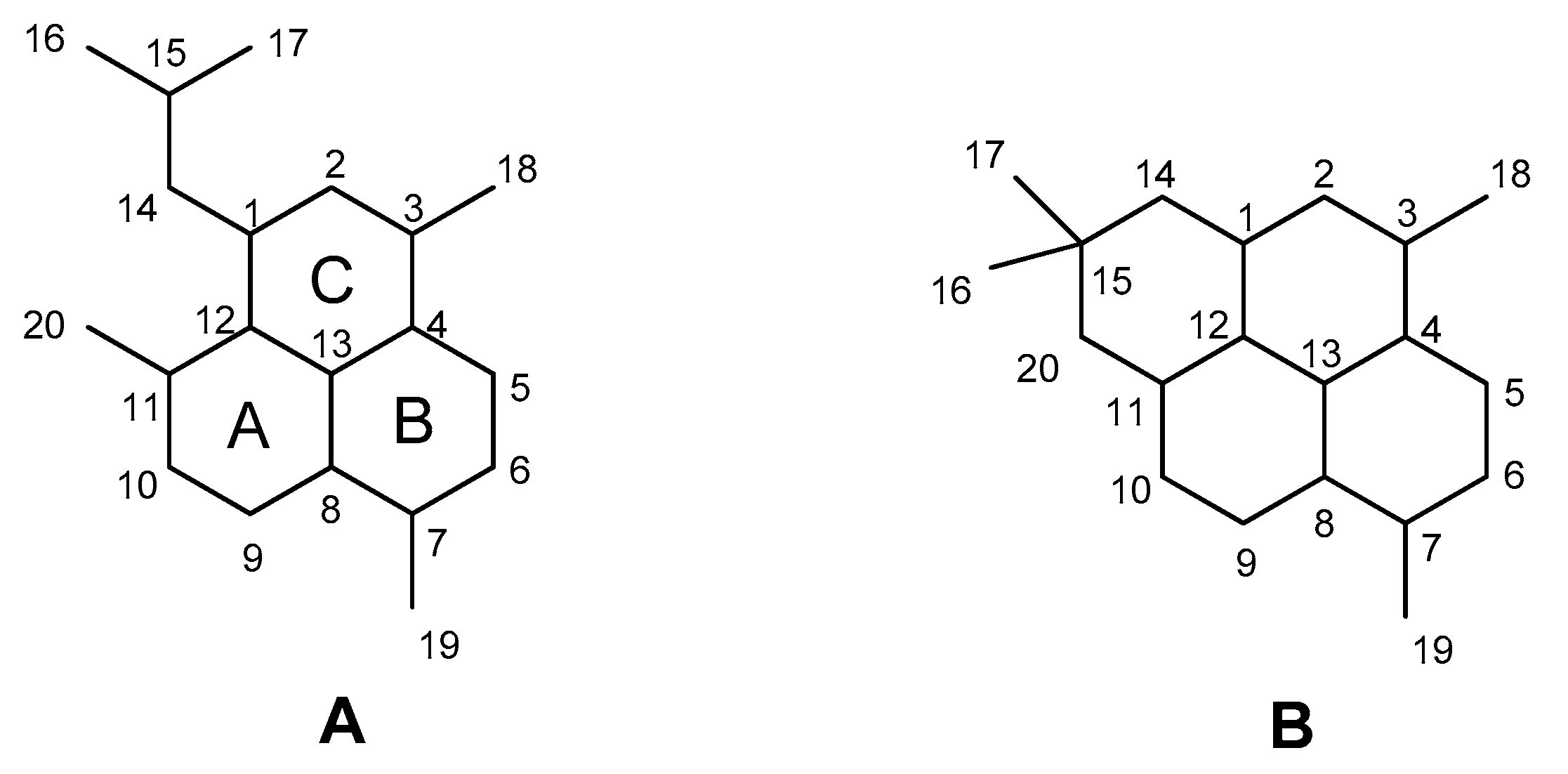
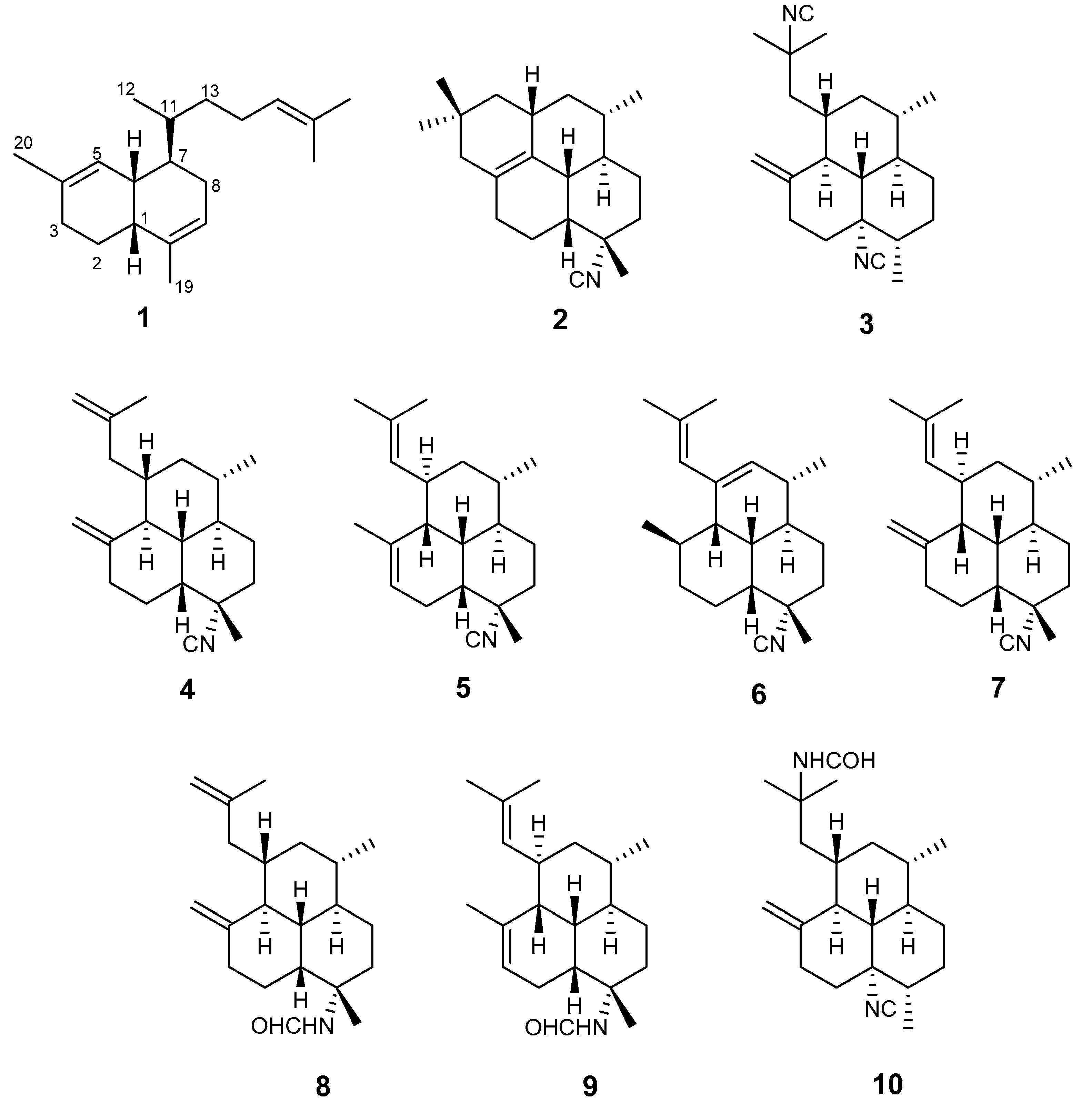
2. Results
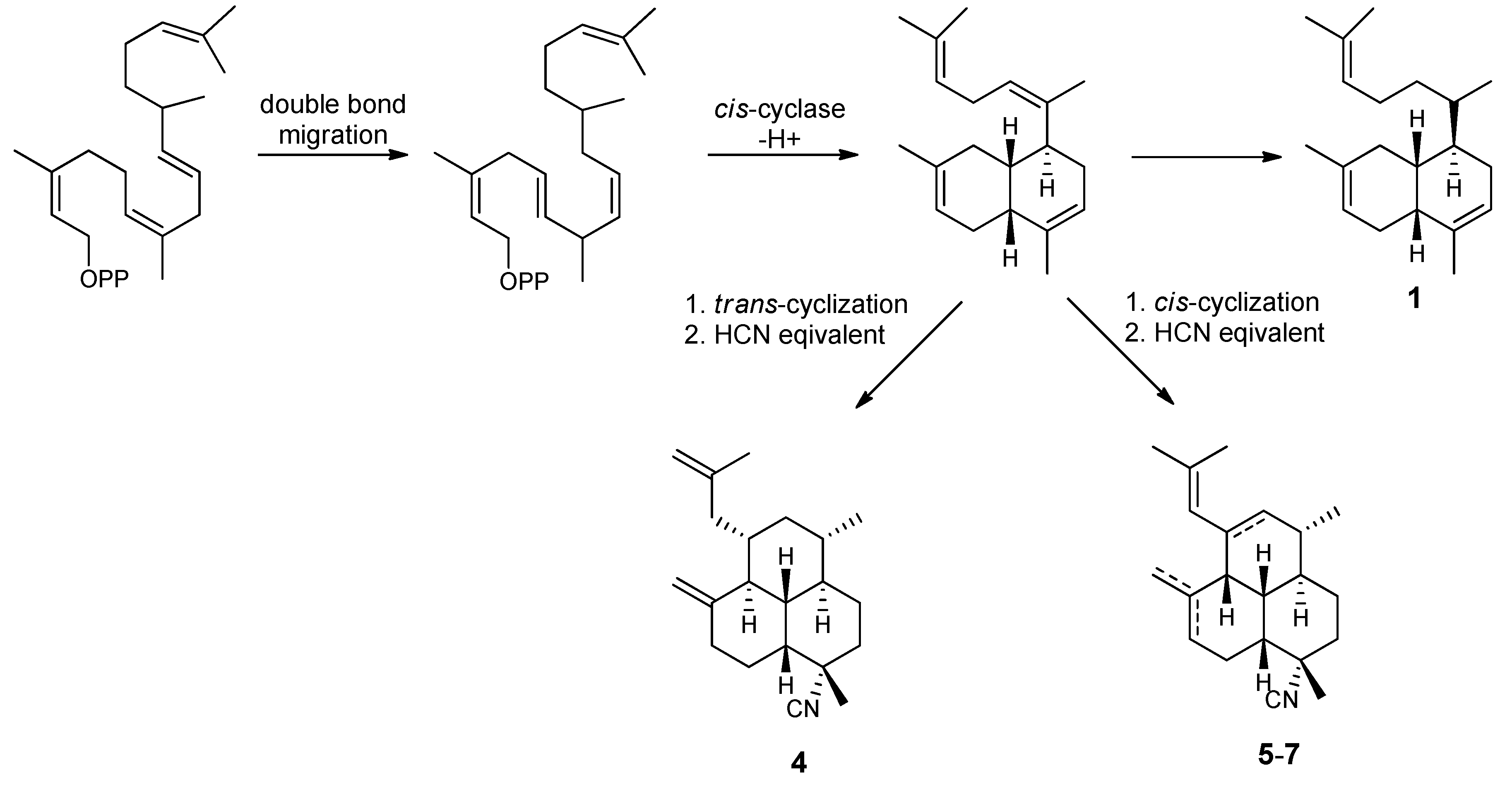
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Procedures
4.2. Biological Material
4.3. Extraction and Isolation Procedures
4.4. Acid Hydrolysis of Compounds 4 and 5
4.5. Feeding Deterrence Assay
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouchet, P.; Rocroi, J.-P.; Hausdorf, B.; Kaim, A.; Kano, Y.; Nützel, A.; Parkhaev, P.; Schrödl, M.; Strong, E.E. Revised classification, nomenclator and typification of gastropod and monoplacophoran families. Malacologia 2017, 61, 1–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino, G.; Ghiselin, M.T. Chemical defense and the evolution of opisthobranch gastropods. Proc. Calif. Acad. Sci. 2009, 60, 175–422. [Google Scholar]
- Bornancin, L.; Bonnard, I.; Mills, S.C.; Banaigs, B. Chemical mediation as a structuring element in marine gastropod predator-prey interactions. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 644–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimino, G.; Fontana, A.; Gavagnin, M. Marine opisthobranch molluscs: Chemistry and ecology in sacoglossans and dorids. Curr. Org. Chem. 1999, 3, 327–372. [Google Scholar]
- Cimino, G.; Ciavatta, M.L.; Fontana, A.; Gavagnin, M. Metabolites of marine opisthobranchs: chemistry and biological activity. In Bioactive Compounds from Natural Sources; Tringali, C., Ed.; Taylor & Francis Ltd.: London, UK, 2001; pp. 578–637. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, L.J.; Prinsep, M.R. The chemistry and chemical ecology of nudibranchs. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 1359–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burreson, B.J.; Scheuer, P.J.; Finer, J.; Clardy, J. Isocyanopupukeanane, a marine invertebrate allomone with a new sesquiterpene skeleton. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 4763–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garson, M.J.; Simpson, J.S. Marine isocyanides and related natural products—structure, biosynthesis and ecology. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2004, 19, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsermann, J.; Kauhl, U.; Opatz, T. Marine isonitriles and their related compounds. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.D.; Wang, H.; Gurrath, M.; König, G.M.; Kocak, G.; Neumann, G.; Loria, P.; Foley, M.L.; Tilley, J. Inhibition of heme detoxification processes underlies the antimalarial activity of terpene isonitrile compounds from marine sponges. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.M.; Adendorff, M.R.; Wright, A.D.; Davies-Coleman, M.T. Antiplasmodial activity: The first proof of inhibition of heme crystallization by marine isonitriles. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 93, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusetani, N.; Hirota, H.; Okino, T.; Tomono, Y.; Yoshimura, E. Antifouling activity of isocyanoterpenoids and related compounds from a marine sponge and nudibranchs. J. Nat. Toxins 1996, 5, 249–259. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, A.D.; McCluskey, A.; Robertson, M.J.; MacGregor, K.A.; Gordon, C.P.; Guenther, J. Anti-malarial, anti-algal, anti-tubercular, anti-bacterial, anti-photosynthetic, and anti-fouling activity of diterpene and diterpene isonitriles from the tropical marine sponge Cymbastela Hooperi. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnermann, M.J.; Shenvi, R.A. Syntheses and biological studies of marine terpenoids derived from inorganic cyanide. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 543–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, M.; Gavagnin, M.; Haber, M.; Guo, Y.-W.; Fontana, A.; Manzo, E.; Genta-Jouve, G.; Tsoukatou, M.; Rudman, W.B.; Cimino, G.; et al. Packaging and delivery of chemical weapons: A defensive Trojan horse stratagem in chromodorid nudibranchs. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, M.; Ciavatta, M.L.; Wang, J.-R.; Cirillo, I.; Mathieu, V.; Kiss, R.; Mollo, E.; Guo, Y.-W.; Gavagnin, M. Extending the record of bis-γ-pyrone polypropionates from marine pulmonate mollusks. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 2065–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.-F.; Li, Y.; Feng, M.-T.; Gavagnin, M.; Mollo, E.; Mao, S.-C.; Guo, Y.-W. New isoquinolinequinone alkaloids from the South China Sea nudibranch Jorunna funebris and its possible sponge-prey Xestospongia sp. Fitoterapia 2014, 96, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, M.; Ciavatta, M.L.; Mathieu, V.; Ingels, A.; Kiss, R.; Pascale, P.; Mollo, E.; Ungur, N.; Guo, Y.-W.; Gavagnin, M. Marine terpenoid diacylguanidines: structure, synthesis and biological evaluation of naturally occurring actinofide and synthetic analogs. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.-F.; Li, X.-L.; Yao, L.-G.; Li, J.; Gavagnin, M.; Guo, Y.-W. Marine bis-γ-pyrone polypropionates of onchidione family and their effects on the XBP1 gene expression. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 1093–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Chen, W.-T.; Li, S.-W.; Ye, J.-Y.; Huan, X.-J.; Gavagnin, M.; Yao, L.-G.; Wang, H.; Miao, Z.-H.; Li, X.-W.; et al. Cytotoxic nitrogenous terpenoids from two South China Sea nudibranchs Phyllidiella pustulosa, Phyllidia coelestis, and their sponge-prey Acanthella cavernosa. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wratten, S.J.; Faulkner, D.J.; Hirotsu, K.; Clardy, J. Diterpenoid isocyanides from the marine sponge Hymeniacidon amphilecta. Tetrahedron Lett. 1978, 19, 4345–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, H.; Tomono, Y.; Fusetani, N. Terpenoids with antifouling activity against barnacle larvae from the marine sponge Acanthella cavernosa. Tetrahedron 1996, 57, 2359–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavatta, M.L.; Fontana, A.; Puliti, R.; Scognamiglio, G.; Cimino, G. Structures and absolute stereochemistry of isocyanide and isothiocyanate amphilectenes from the Caribbean sponge Cribochalina sp. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 12629–12636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavatta, M.L.; Gavagnin, M.; Manzo, E.; Puliti, R.; Mattia, C.A.; Mazzarella, L.; Cimino, G.; Simpson, J.S.; Garson, M.J. Structural and stereochemical revision of isocyanide and isothiocyanate amphilectenes from the Caribbean marine sponge Cribochalina sp. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 8049–8053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinski, T.F.; Faulkner, D.J.; Van Duyne, G.D.; Clardy, J. Three new diterpene isonitriles from a Palauan sponge of the genus Halichondria. J. Org. Chem. 1987, 52, 3334–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoral-Theys, D.; Fattorusso, E.; Mangoni, A.; Perinu, C.; Kiss, R.; Costantino, V. Evaluation of the antiproliferative activity of diterpene isonitriles from the sponge Pseudoaxinella flava in apoptosis-sensitive and apoptosis-resistant cancer cell lines. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2299–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, G.M.; Wright, A.D.; Angerhofer, C.K. Novel potent antimalarial diterpene isocyanates, isothiocyanates, and isonitriles from the tropical marine sponge Cymbastela hooperi. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 3259–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, A.; König, G.M.; Wright, A.D. Four diterpene isonitriles from the sponge Cymbastela hooperi. Acta Cryst. Sect. C 1996, 52, 2601–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitome, H.; Shirato, N.; Miyaoka, H.; Yamada, Y.; van Soest, R.W.M. Terpene isocyanides, isocyanates, and isothiocyanates from the Okinawan marine sponge Stylissa sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 833–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, R.; Casapullo, A.; Ciasullo, L.; Gomez-Paloma, L.; Payá, M. Cycloamphilectenes, a new type of potent marine diterpenes: Inhibition of nitric oxide production in murine macrophages. Life Sci. 2003, 72, 2543–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollo, E.; Gavagnin, M.; Carbone, M.; Castelluccio, F.; Pozone, F.; Roussis, V.; Templado, J.; Ghiselin, M.T.; Cimino, G. Factors promoting marine invasions: A chemoecological approach. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4582–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garson, M.J.; Simpson, J.S.; Flowers, A.E.; Dumdei, E.J. Cyanides and thiocyanate-derived functionality in marine organisms—structures, biosynthesis and ecology. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Rahman, A., Ed.; Elsevier Science, B.V.: Amsterdam, NL, The Netherlands, 2000; Volume 21, pp. 329–372. [Google Scholar]
- Manzo, E.; Ciavatta, M.L.; Gavagnin, M.; Mollo, E.; Guo, Y.-W.; Cimino, G. Isocyanide terpene metabolites of Phyllidiella pustulosa, a nudibranch from the South China Sea. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1701–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Avilés, E.; Rodríguez, A.D. Marine sponge Hymeniacidon sp. amphilectane metabolites potently inhibit rat brain microglia thromboxane B2 generation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avilés, E.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Vicente, J. Two rare-class tricyclic diterpenes with antitubercular activity from the Caribbean sponge Svenzea flava. Application of vibrational circular dichroism spectroscopy for determining absolute configuration. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 11294–11301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
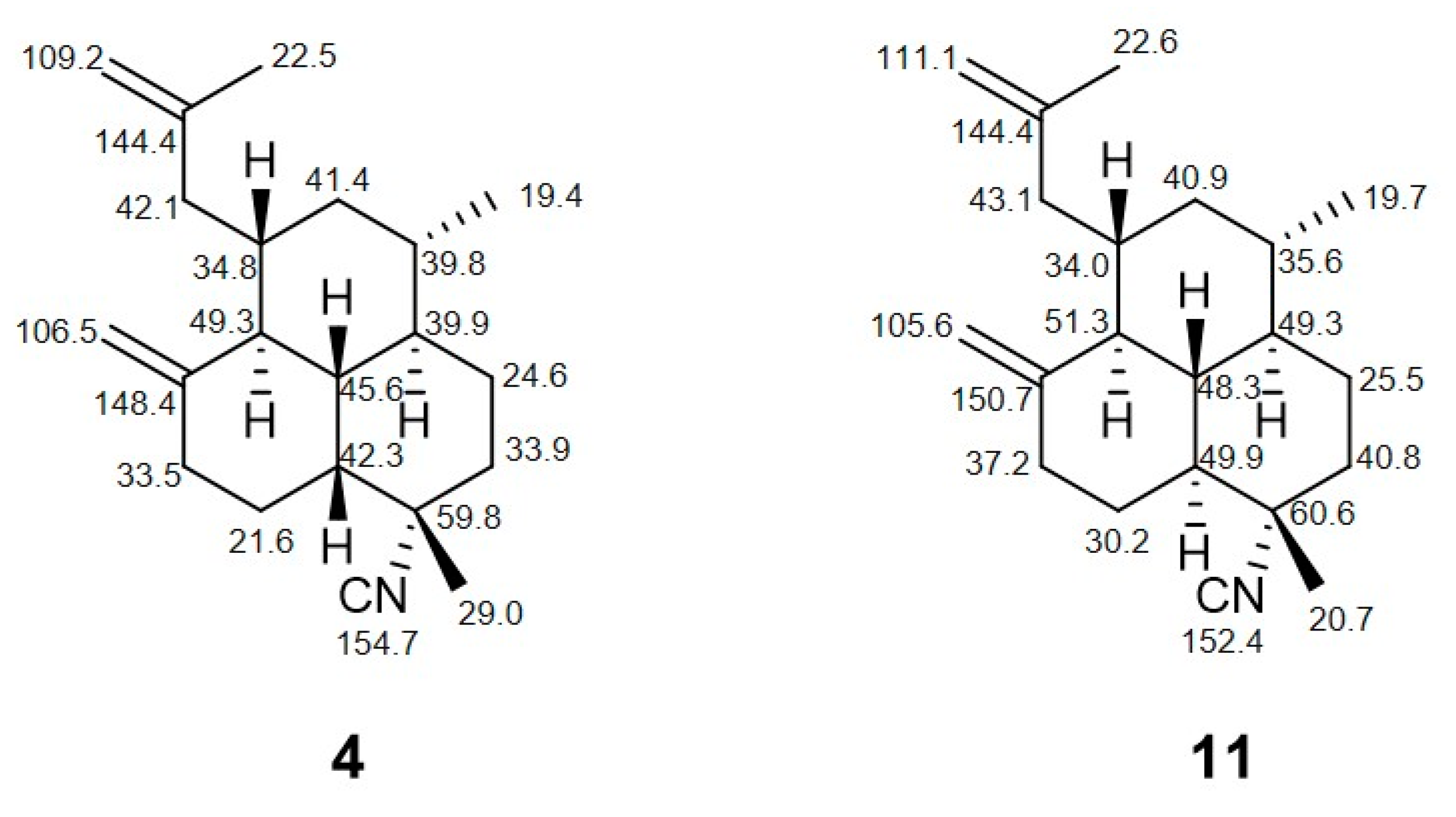

| H | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH (J in Hz) | δH (J in Hz) | δH (J in Hz) | δH (J in Hz) | δH (J in Hz) | |
| 1 | 2.93, m | - | 2.98, app. br s | 1.77, m | 2.91, app. t (9) |
| 2 | 1.07 eq, ddd, (13,4,1) 1.29 ax, m | 5.32, br s | 1.29, m 1.57, m | 0.68, m 1.92, m | 1.07 eq, ddd, (13, 4, 2) 1.29, m |
| 3 | 1.28, m | 1.85, m | 1.31, m | 1.19, m | 1.28, m |
| 4 | 0.95, m | 1.28, m | 1.04, m | 0.98, m | 0.95, m |
| 5 | 0.93, m 1.89, m | 0.93, m 1.30, m | 1.06, m 1.88, m | 1.10, m 1.87, m | 1.11, m 1.90, m |
| 6 | 1.80, m 2.05, m | 1.76, m 1.95, m | 1.74, m 1.90, m | 1.55, m | 1.50, m (1.60, m) |
| 8 | 1.82, m | 1.63, m | 1.68, m | 2.02, m (1.99, m) | 1.75, m (2.44, m) |
| 9 | 2.14, m 2.27, m | 1.56, m | 1.60, m 1.97, m | 1.52, m | 1.95, m |
| 10 | 5.44, m | 1.73, m | 2.05, m 2.43, m | 2.19, m 2.36, m | 5.40, br d (7) |
| 11 | - | 1.94, m | - | - | |
| 12 | 2.01, m | 1.99, m | 1.99, m | 1.53, m | 2.03, m |
| 13 | 1.70, m | 1.70, m | 1.87, m | 1.24, m | 1.80, m (1.92, m) |
| 14 | 5.46, m | 5.44, s | 5.48, br d (8) | 2.65, m 1.44, m | 5.48, br d (9) |
| 16 | 1.72, br s | 1.76, br s | 1.72, br s | 4.63, br s 4.73, br s | 1.72,br s |
| 17 | 1.65, br s | 1.81, br s | 1.61, br s | 1.71, br s | 1.64, br s |
| 18 | 0.82, d (6) | 1.05, d (6) | 0.82, d (7) | 0.89, d (6)e [0.88, d (6)]e | 0.82, d (7) |
| 19 | 1.57, s | 1.54, s | 1.58, s | 1.34, s (1.45, s) | 1.50, s (1.59, s) |
| 20 | 1.72, br s | 0.82, d (7) | 4.79, br s 4.95, br s | 4.62, br s 4.87, br s | 1.69, s |
| NHCHO | - | - | - | 8.25 d (12) [8.09, d, (2)] | 8.24, d (12) [8.03, d (2)] |
| NHCHO | - | - | - | 5.08 (5.66) | 5.46, br s [5.02, s] |
| C | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC | Type b | δC | Type b | δC | Type b | δC | Type b | δC | Type b | |
| 1 | 32.8 | CH | 125.7 | C | 33.1 | CH | 34.0 | CH | 33.5 | CH |
| 2 | 35.5 | CH2 | 131.1 | CH | 35.6 | CH2 | 41.5 | CH2 | 35.7 | CH2 |
| 3 | 31.3 | CH | 38.2 | CH | 33.9 | CH | 38.2 | CH | 31.3 | CH |
| 4 | 37.5 | CH | 36.2 | CH | 36.5 | CH | 42.9 | CH | 37.6 | CH |
| 5 | 26.6 | CH2 | 27.6 | CH2 | 26.6 | CH2 | 23.0 | CH2 | 26.7 | CH2 |
| 6 | 33.8 | CH2 | 34.1 | CH2 | 33.9 | CH2 | 32.4 | CH2 | 33.1 (34.8) | CH2 |
| 7 | 61.8 | C | 64.0 | C | 60.9 | C | 54.0 (56.1) | C | 54.0 (56.9) | C |
| 8 | 43.8 | CH | 46.3 | CH | 46.2 | CH | 42.7 (40.4) | CH | 44.6 (40.8) | CH |
| 9 | 24.8 | CH2 | 18.1 | CH2 | 24.6 | CH2 | 19.0 | CH2 | 24.4 | CH2 |
| 10 | 121.9 | CH | 32.1 | CH2 | 36.3 | CH2 | 33.3 | CH2 | 122.1 | CH |
| 11 | 134.2 | C | 29.0 | CH | nd | - | 147.3 | C | 134.4 | C |
| 12 | 44.5 | CH | 44.2 | CH | 46.6 | CH | 49.8 | CH | 44.6 | CH |
| 13 | 34.5 | CH | 37.4 | CH | 37.5 | CH | 44.7 | CH | 35.3 (37.9) | CH |
| 14 | 127.3 | CH | 126.0 | CH | 127.9 | CH | 41.3 | CH2 | 127.8 | CH |
| 15 | 132.3 | C | 134.0 | C | 130.5 | C | 144.0 | C | 130.9 | C |
| 16 | 25.8 | CH3 | 26.7 | CH3 | 26.0 | CH3 | 20.9 | CH3 | 26.1 | CH3 |
| 17 | 17.7 | CH3 | 19.5 | CH3 | 17.8 | CH3 | 109.1 | CH2 | 17.8 | CH3 |
| 18 | 19.6 | CH3 | 19.9 | CH3 | 19.7 | CH3 | 18.4 | CH3 | 20.0 | CH3 |
| 19 | 26.4 | CH3 | 26.0 | CH3 | 26.4 | CH3 | 27.1 (23.9) | CH3 | 26.8 (23.6) | CH3 |
| 20 | 21.0 | CH3 | 17.2 | CH3 | 108.1 | CH2 | 104.6 | CH2 | 21.1 | CH3 |
| NC | nd | - | 153.4 | C | 153.1 | C | - | - | - | - |
| NHCHO | - | - | - | 162.7 (159.9) | CH | 162.8 (160.0) | CH | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carbone, M.; Ciavatta, M.L.; Manzo, E.; Li, X.-L.; Mollo, E.; Mudianta, I.W.; Guo, Y.-W.; Gavagnin, M. Amphilectene Diterpene Isonitriles and Formamido Derivatives from the Hainan Nudibranch Phyllidia Coelestis. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110603
Carbone M, Ciavatta ML, Manzo E, Li X-L, Mollo E, Mudianta IW, Guo Y-W, Gavagnin M. Amphilectene Diterpene Isonitriles and Formamido Derivatives from the Hainan Nudibranch Phyllidia Coelestis. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(11):603. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110603
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarbone, Marianna, Maria Letizia Ciavatta, Emiliano Manzo, Xiao-Lu Li, Ernesto Mollo, I Wayan Mudianta, Yue-Wei Guo, and Margherita Gavagnin. 2019. "Amphilectene Diterpene Isonitriles and Formamido Derivatives from the Hainan Nudibranch Phyllidia Coelestis" Marine Drugs 17, no. 11: 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110603
APA StyleCarbone, M., Ciavatta, M. L., Manzo, E., Li, X.-L., Mollo, E., Mudianta, I. W., Guo, Y.-W., & Gavagnin, M. (2019). Amphilectene Diterpene Isonitriles and Formamido Derivatives from the Hainan Nudibranch Phyllidia Coelestis. Marine Drugs, 17(11), 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110603