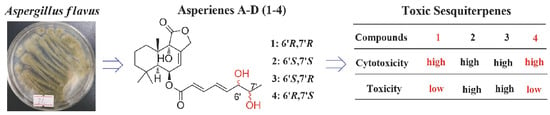
Asperienes A–D, Bioactive Sesquiterpenes from the Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus flavus
Abstract
1. Introduction
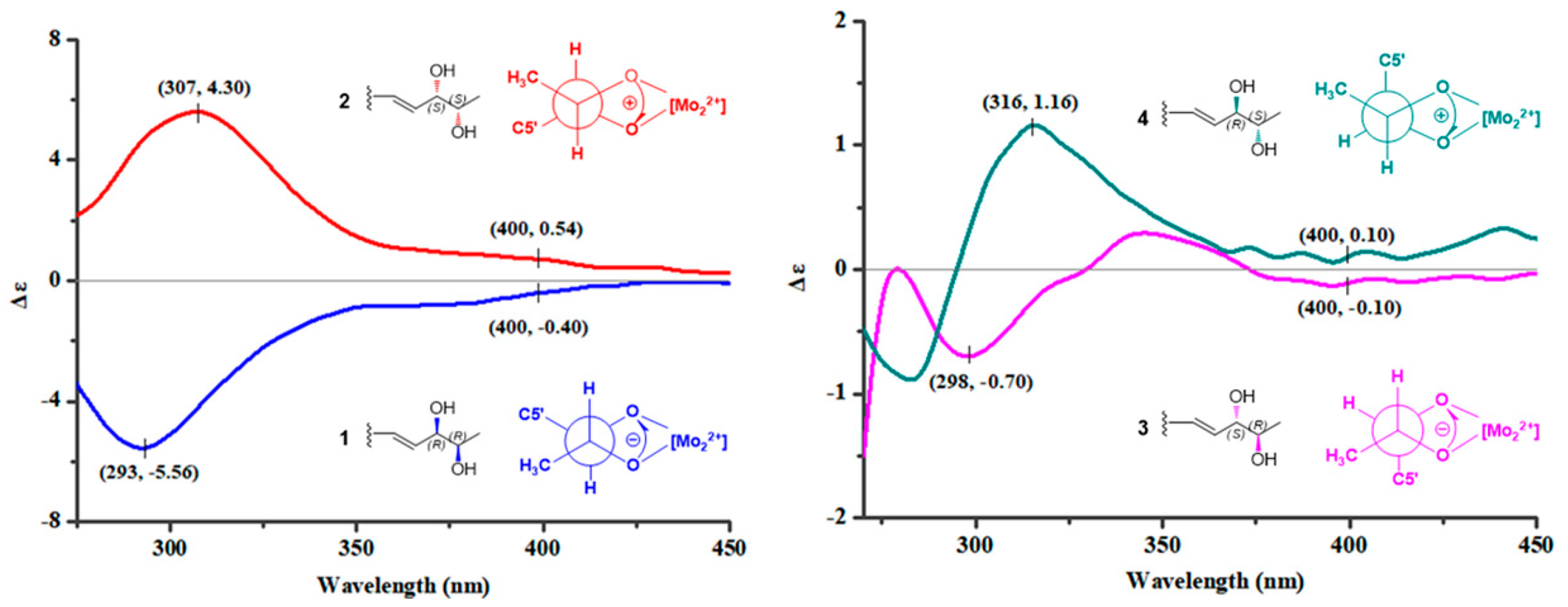
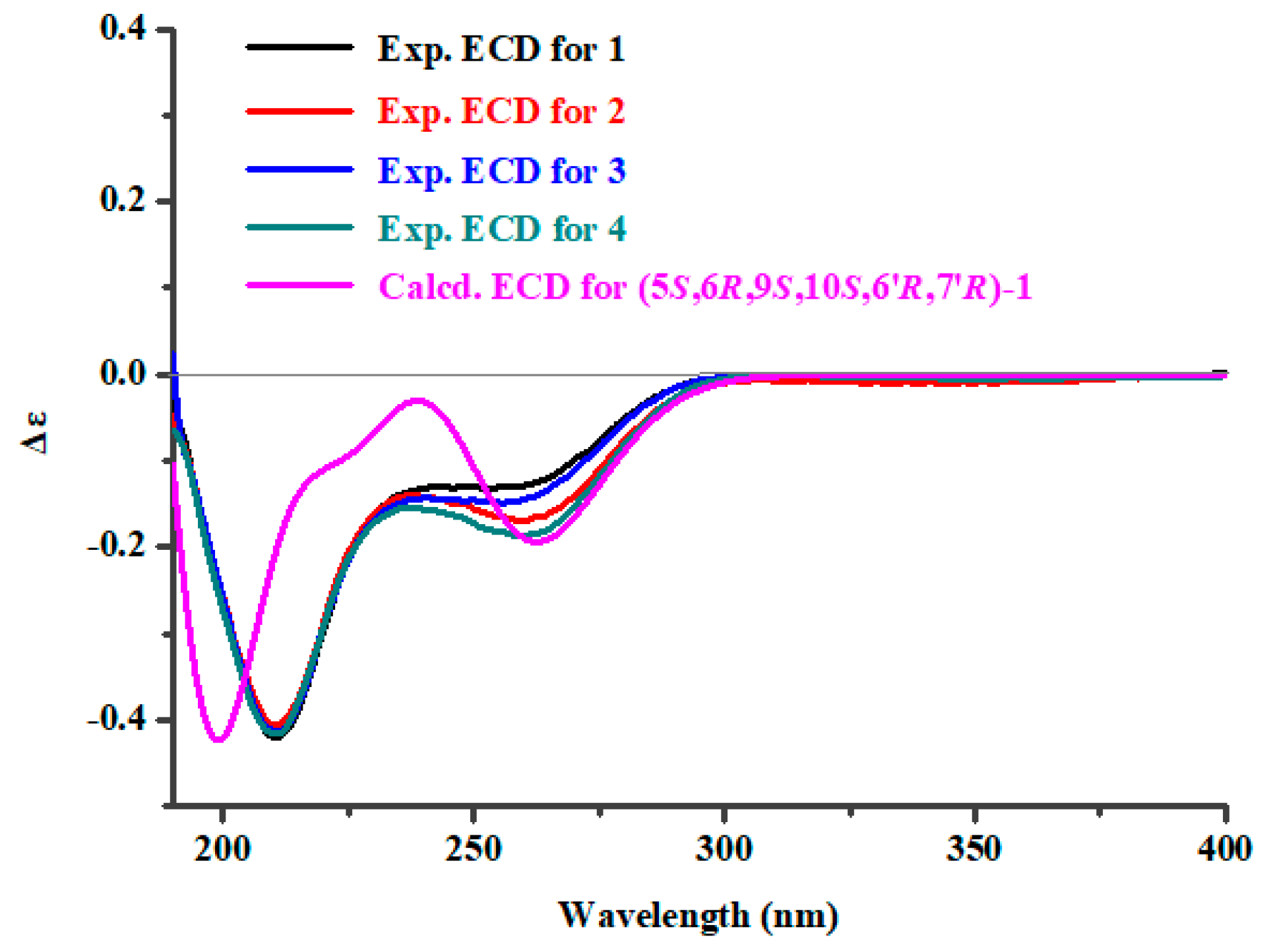
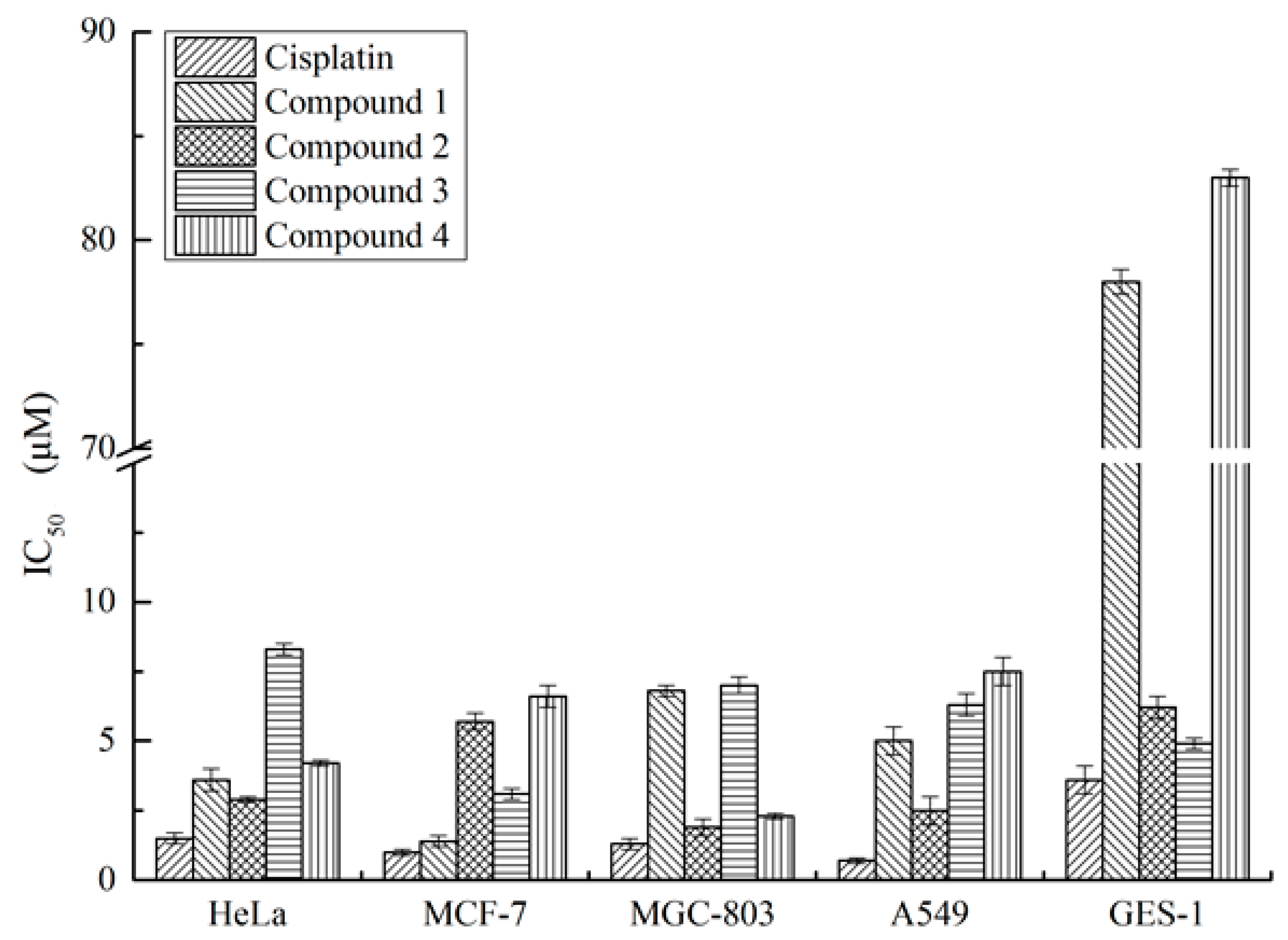
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. General Experimental Procedures
4.2. Isolation of the Fungal Material
4.3. General Computational Procedure
4.4. Snatzke’s Method
4.5. Biological Assays
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 122–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.M.; Wang, C.Y.; Gerwick, W.H.; Shao, C.L. Marine natural products as potential anti-tubercular agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 165, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.M.; Li, Y.Y.; Shi, Y.W.; Fang, Y.W.; Chao, R.; Gu, Y.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Shao, C.L. Integrating molecular networking and 1H NMR to target the isolation of chrysogeamides from a library of marine-derived Penicillium fungi. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Dai, H.; Konuklugil, B.; Orfali, R.S.; Lin, W.; Kalscheuer, R.; Liu, Z.; Proksch, P. Phenolic bisabolanes from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. Phytochem. Lett. 2016, 18, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, M.; Tang, J.; Li, X. Eremophilane sesquiterpenes from a deep marine-derived fungus, Aspergillus sp. SCSIOW2, cultivated in the presence of epigenetic modifying agents. Molecules 2016, 21, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.Y.; Anbuchezhian, R.; Sun, W.; Shao, C.L.; Zhang, F.L.; Yin, Y.; Yu, Z.S.; Li, Z.Y.; Wang, C.Y. Cytotoxic nitrobenzoyloxy-substituted sesquiterpenes from sponge-derived endozoic fungus Aspergillus insulicola MD10-2. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2016, 17, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.M.; Ju, G.L.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, X.F.; Du, F.Y. Cyclodepsipeptides and sesquiterpenes from marine-derived fungus Trichothecium roseum and their biological functions. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Xie, C.L.; Zhong, T.; Xu, W.; Luo, Z.H.; Shao, Z.; Yang, X.W. Sesquiterpenes from a deep-sea-derived fungus Graphostroma sp. MCCC 3A00421. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 7267–7273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.P.; Fang, S.T.; Miao, F.P.; Yin, X.L.; Ji, N.Y. Diterpenes and sesquiterpenes from the marine algicolous fungus Trichoderma harzianum X-5. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 2553–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.B.; Tao, J.; Miao, X.S.; Bu, W.; Zhang, S.; Dong, Z.J.; Li, Z.H.; Feng, T.; Liu, J.K. Seven new drimane-type sesquiterpenoids from cultures of fungus Laetiporus sulphureus. Fitoterapia 2015, 102, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.; Lee, H.; Seo, Y.H.; Yun, J.; Lee, J.; Kwon, H.C.; Guo, Y.; Kang, J.S.; Kim, J.J.; Lee, D. Cytotoxic drimane sesquiterpenoids isolated from Perenniporia maackiae. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1444–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.; Yang, M.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Shao, C.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Hu, L.D.; Cao, F.; Zhu, H.J. Absolute configurations of 14,15-hydroxylated prenylxanthones from a marine-derived Aspergillus sp. fungus by chiroptical methods. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.; Zhang, X.W.; Zhang, M.; Li, W.; Ma, Z.Y.; Zhu, H.J.; Cao, F. Aspergixanthones I–K, new anti-Vibrio prenylxanthones from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. ZA-01. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.Y.; Yang, J.K.; Yang, J.K.; Hu, L.D.; Zhu, H.J.; Cao, F. New oxygenated steroid from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus flavus. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2018, 13, 949–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.Q.; Lin, X.P.; Wang, J.F.; Zhou, X.F.; Liu, J.; Yang, B.; Yang, X.W.; Liao, S.R.; Wang, L.S.; Liu, Y.H. New meroterpenoids from the endophytic fungus Aspergillus flavipes AIL8 derived from the mangrove plant Acanthus ilicifolius. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Li, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhu, W. Indole diterpenoids and isocoumarin from the fungus, Aspergillus flavus, isolated from the prawn, Penaeus vannamei. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3970–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.N.; Kong, F.D.; Ma, Q.Y.; Huang, S.Z.; Luo, D.Q.; Zhou, L.M.; Dai, H.F.; Yua, Z.F.; Zhao, Y.X. Drimane-type sesquiterpenoids from cultures of the fungus, Xylaria polymorpha. Phytochem. Lett. 2017, 20, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Lin, L.; Hu, J.; Jiao, F.; Duan, D.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, H.; Gao, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, X. Highly oxygenated caryophyllene-type and drimane-type sesquiterpenes from Pestalotiopsis adusta, an endophytic fungus of Sinopodophyllum hexandrum. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 29071–29079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, K.W. Natural new sesquiterpenes: Structural diversity and bioactivity. Curr. Org. Chem. 2016, 20, 994–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Ebel, R.; Wang, Y.; Schulz, B.; Draeger, S.; Muller, W.E.; Wray, V.; Lin, W.; Proksch, P. Drimane sesquiterpenoids from the fungus Aspergillus ustus isolated from the marine sponge Suberites domuncula. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1585–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, B.L.; Pescitelli, G.; Pratelli, C.; Pini, D.; Salvadori, P. Determination of absolute configuration of acyclic 1,2-diols with Mo2(OAc)4. 1. Snatzke’s method revisited. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 4819–4825. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.C.; Xu, L.L.; Yang, R.Y.; Yang, M.Y.; Hu, L.D.; Zhu, H.J.; Cao, F. Anti-Vibrio indole-diterpenoids and C-25 epimeric steroids from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium janthinellum. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.J. Organic Stereochemistry Experimental and Computational Methods; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Ding, S.S.; Zhu, A.; Cao, F.; Zhu, H.J. Bioactive azaphilone derivatives from the fungus Talaromyces aculeatus. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2199–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.; Meng, Z.H.; Mu, X.; Yue, Y.F.; Zhu, H.J. Absolute configuration of bioactive azaphilones from the marine-derived fungus Pleosporales sp. CF09-1. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, B.J.M.; Groot, A.D. The occurrence and biological activity of drimane sesquiterpenoids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1991, 8, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Slebodnick, C.; Rakotondraibe, L.H. Bioactive drimane sesquiterpenoids and aromatic glycosides from Cinnamosma fragrans. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 1754–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratoni, E.; Claudino, V.D.; Yunes, R.A.; Franchi, G.C.; Nowill, A.E.; Cechinel Filho, V.; Monache, F.D.; Malheiros, A. Further drimane sesquiterpenes from Drimys brasiliensis stem barks with cytotoxic potential. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2016, 389, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, B.M. Natural sesquiterpenoids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 1334–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.H.; Miao, F.P.; Qiao, M.F.; Cichewicz, R.H.; Ji, N.Y. Terretonin, ophiobolin, and drimane terpenes with absolute configurations from an algicolous Aspergillus ustus. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaike, S.; Keller, N.P. Aspergillus flavus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2011, 49, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.Y.; Yu, S.; Qiu, M.G.; Wang, X.N.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.H.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.H. Aspergillus flavus SUMO contributes to the fungal virulence and toxin attributes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6772–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshinari, T.; Sakuda, S.; Watanabe, M.; Kamata, Y.; Ohnishi, T.; Sugita-Konishi, Y. New metabolic pathway for converting blasticidin S in Aspergillus flavus and inhibitory activity of aflatoxin production by blasticidin S metabolites. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 7925–7931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.B.; Ban, F.F.; Li, H.; Qian, P.P.; Shen, Q.S.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Mo, H.Z.; Zhou, X.H. Thymol induces conidial apoptosis in Aspergillus flavus via stimulating K+ eruption. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 8530–8536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wild, C.P.; Turner, P.C. The toxicology of aflatoxins as a basis for public health decisions. Mutagenesis 2002, 17, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umemura, M.; Nagano, N.; Koike, H.; Kawano, J.; Ishii, T.; Miyamura, Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Tamano, K.; Yu, J.J.; Shin-Ya, K.; et al. Characterization of the biosynthetic gene cluster for the ribosomally synthesized cyclic peptide ustiloxin B in Aspergillus flavus. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2014, 68, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.P.; Cao, F.; Shao, C.L.; Chen, M.; Liu, H.J.; Zheng, C.J.; Wang, C.Y. Subergorgiaols A-L, 9,10-secosteroids from the South China Sea gorgonian Subergorgia rubra. Steroids 2015, 94, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Meth. 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Position | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.98, dt (13.2, 3.6) | 1.98, dt (13.2, 3.6) | 1.98, dt (13.2, 4.2) | 1.98, dt (13.2, 4.2) |
| 1.84, d (13.2) | 1.84, d (13.2) | 1.84, d (13.2) | 1.82, d (13.2) | |
| 2 | 1.61, dd (13.8, 13.2) | 1.61, dd (13.8, 13.2) | 1.61, m | 1.60, m |
| 1.48, d (13.2) | 1.48, d (13.2) | 1.48, d (13.2) | 1.48, d (12.6) | |
| 3 | 1.35, d (13.2) | 1.35, d (13.2) | 1.35, d (13.2) | 1.35, d (12.6) |
| 1.21, m | 1.22, m | 1.23, d (13.2) | 1.21, d (12.6) | |
| 5 | 2.02, d (3.6) | 2.02, d (3.6) | 2.02, d (3.6) | 2.02, d (3.6) |
| 6 | 5.59, s | 5.59, s | 5.59, s | 5.59, s |
| 7 | 5.80, s | 5.80, s | 5.80, s | 5.80, s |
| 12 | 4.79, d (12.6) | 4.79, d (13.2) | 4.79, d (12.6) | 4.80, d (12.6) |
| 4.89, d (12.6) | 4.89, d (13.2) | 4.89, d (12.6) | 4.89, d (12.6) | |
| 13 | 0.93, s | 0.93, s | 0.93, s | 0.93, s |
| 14 | 1.07, s | 1.07, s | 1.07, s | 1.07, s |
| 15 | 1.07, s | 1.07, s | 1.07, s | 1.07, s |
| 2′ | 5.95, d (15.6) | 5.95, d (13.2) | 5.95, d (15.6) | 5.95, d (12.6) |
| 3′ | 7.24, dd (15.6, 3.6) | 7.24, dd (13.2, 3.6) | 7.23, dd (15.6, 3.6) | 7.22, t (12.6) |
| 4′ | 6.47, td (15.6, 3.6) | 6.47, t (13.2) | 6.44, td (15.6, 4.8) | 6.43, t (12.6) |
| 5′ | 6.33, m | 6.30, dd (13.2, 3.6) | 6.36, dd (15.6, 4.8) | 6.33, m |
| 6′ | 3.98, brs | 3.96, t (6.0) | 3.87, brs | 3.84, brs |
| 7′ | 3.57, t (6.0) | 3.57, t (5.4) | 3.49, brs | 3.48, brs |
| 8′ | 0.96, d (6.0) | 0.96, d (6.0) | 1.04, d (6.0) | 1.03, d (6.0) |
| 9-OH | 6.30, brs | 6.29, brs | 6.31, brs | 6.31, brs |
| Position | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 29.6, CH2 | 29.6, CH2 | 29.6, CH2 | 29.6, CH2 |
| 2 | 17.4, CH2 | 17.5, CH2 | 17.4, CH2 | 17.4, CH2 |
| 3 | 44.4, CH2 | 44.4, CH2 | 44.4, CH2 | 44.4, CH2 |
| 4 | 33.3, C | 33.3, C | 33.3, C | 33.3, C |
| 5 | 44.2, CH | 44.2, CH | 44.2, CH | 44.2, CH |
| 6 | 65.8, CH | 65.8, CH | 65.8, CH | 65.8, CH |
| 7 | 121.4, CH | 121.4, CH | 121.4, CH | 121.4, CH |
| 8 | 136.6, C | 136.6, C | 136.6, C | 136.6, C |
| 9 | 73.1, C | 73.1, C | 73.1, C | 73.1, C |
| 10 | 37.3, C | 37.3, C | 37.3, C | 37.3, C |
| 11 | 174.4, C | 174.4, C | 174.4, C | 174.4, C |
| 12 | 68.2, CH2 | 68.2, CH2 | 68.2, CH2 | 68.2, CH2 |
| 13 | 32.1, CH3 | 32.1, CH3 | 32.1, CH3 | 32.1, CH3 |
| 14 | 24.3, CH3 | 24.3, CH3 | 24.3, CH3 | 24.3, CH3 |
| 15 | 18.3, CH3 | 18.2, CH3 | 18.3, CH3 | 18.3, CH3 |
| 1′ | 165.4, C | 165.4, C | 165.4, C | 165.4, C |
| 2′ | 119.8, CH | 119.9, CH | 119.9, CH | 120.0, CH |
| 3′ | 145.3, CH | 145.2, CH | 145.4, CH | 145.4, CH |
| 4′ | 127.3, CH | 127.3, CH | 126.9, CH | 127.1, CH |
| 5′ | 145.3, CH | 145.3, CH | 146.1, CH | 146.0, CH |
| 6′ | 74.4, CH | 74.6, CH | 74.9, CH | 75.1, CH |
| 7′ | 69.3, CH | 69.3, CH | 69.6, CH | 69.6, CH |
| 8′ | 18.2, CH3 | 18.2, CH3 | 19.2, CH3 | 19.3, CH3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.-F.; Yue, Y.-F.; Feng, L.-X.; Zhu, H.-J.; Cao, F. Asperienes A–D, Bioactive Sesquiterpenes from the Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus flavus. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17100550
Liu Y-F, Yue Y-F, Feng L-X, Zhu H-J, Cao F. Asperienes A–D, Bioactive Sesquiterpenes from the Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus flavus. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(10):550. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17100550
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yun-Feng, Yu-Fei Yue, Li-Xi Feng, Hua-Jie Zhu, and Fei Cao. 2019. "Asperienes A–D, Bioactive Sesquiterpenes from the Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus flavus" Marine Drugs 17, no. 10: 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17100550
APA StyleLiu, Y.-F., Yue, Y.-F., Feng, L.-X., Zhu, H.-J., & Cao, F. (2019). Asperienes A–D, Bioactive Sesquiterpenes from the Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus flavus. Marine Drugs, 17(10), 550. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17100550