Structure of the Exopolysaccharide Secreted by a Marine Strain Vibrio alginolyticus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Composition of the Vibrio alginolyticus Exopolysaccharide
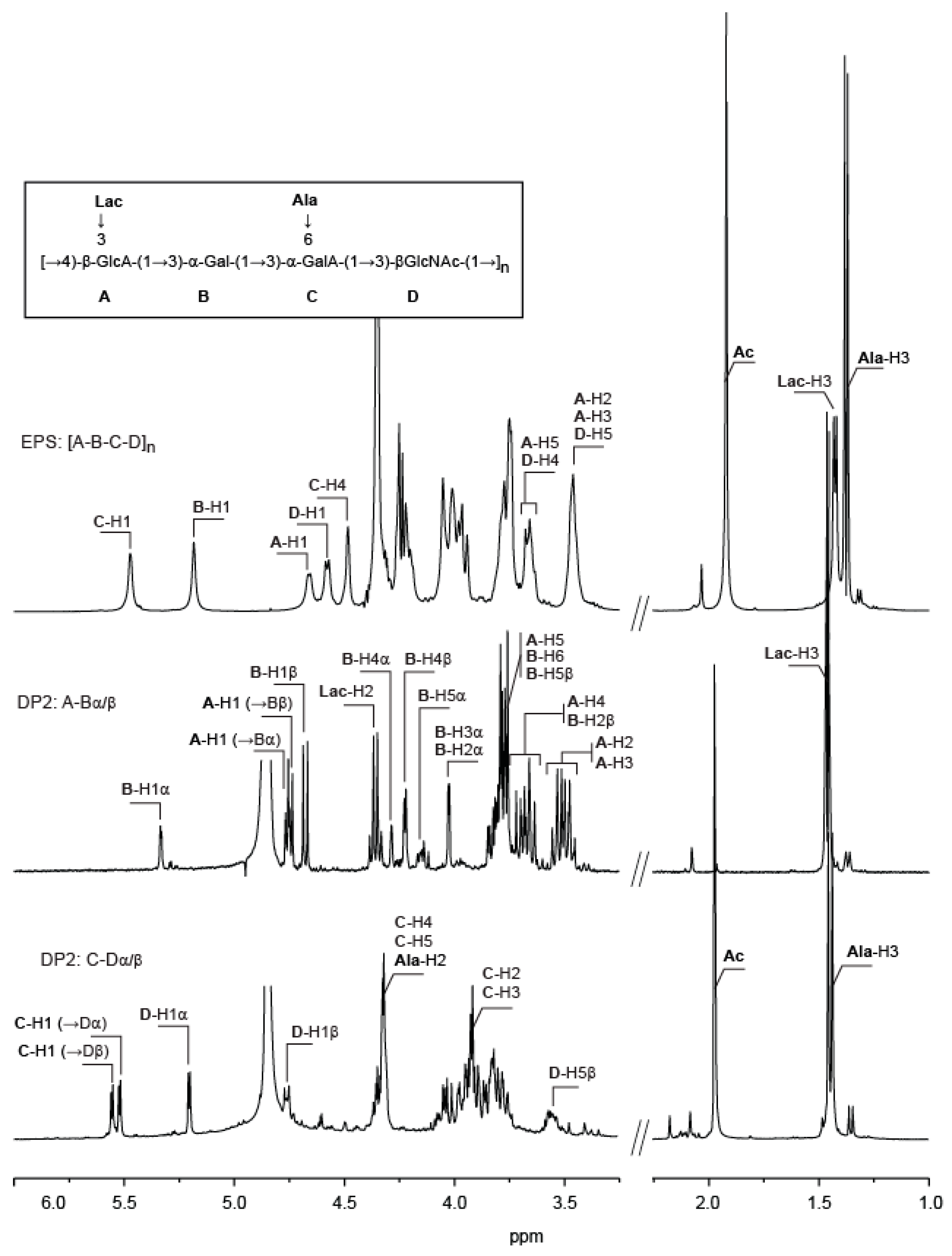
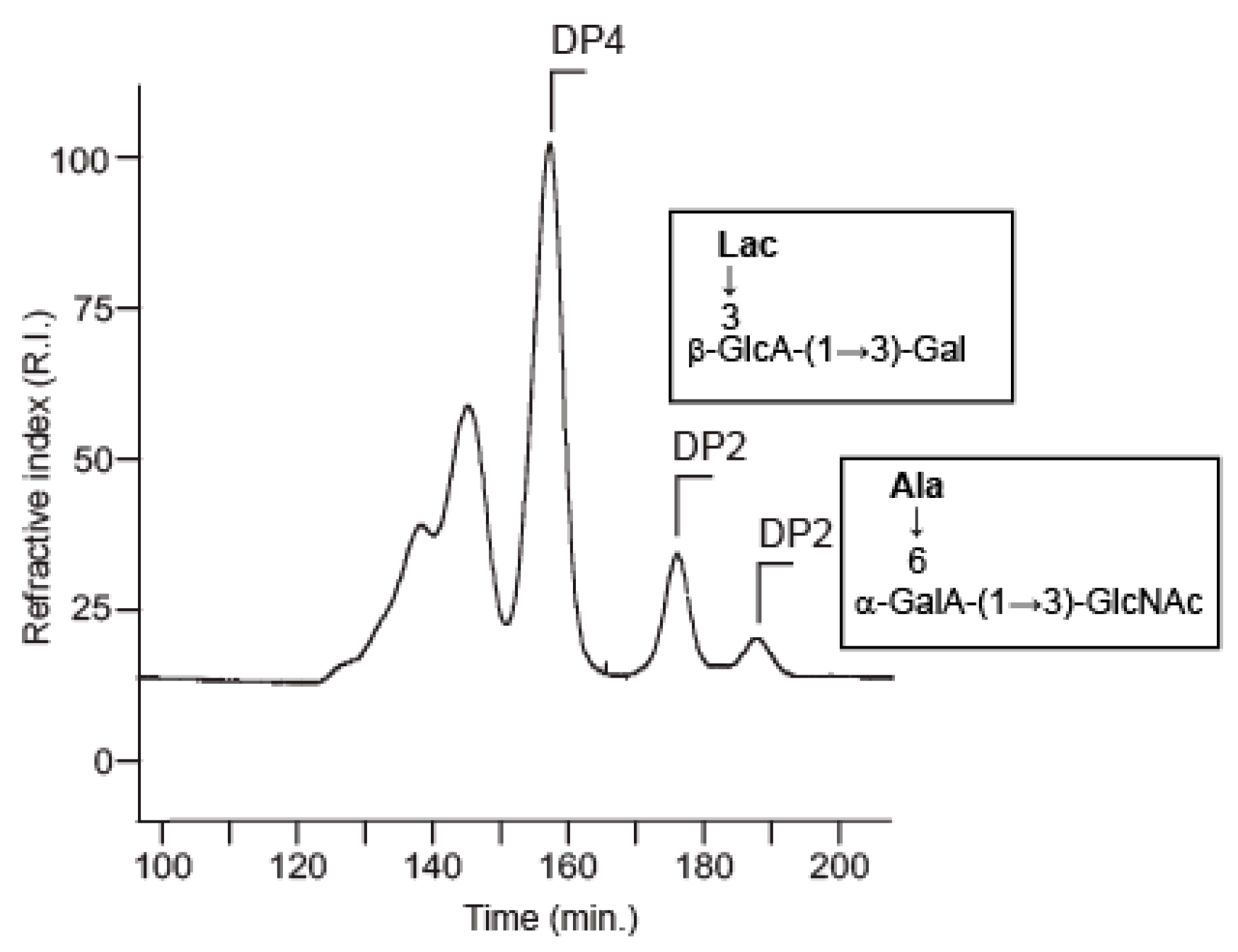
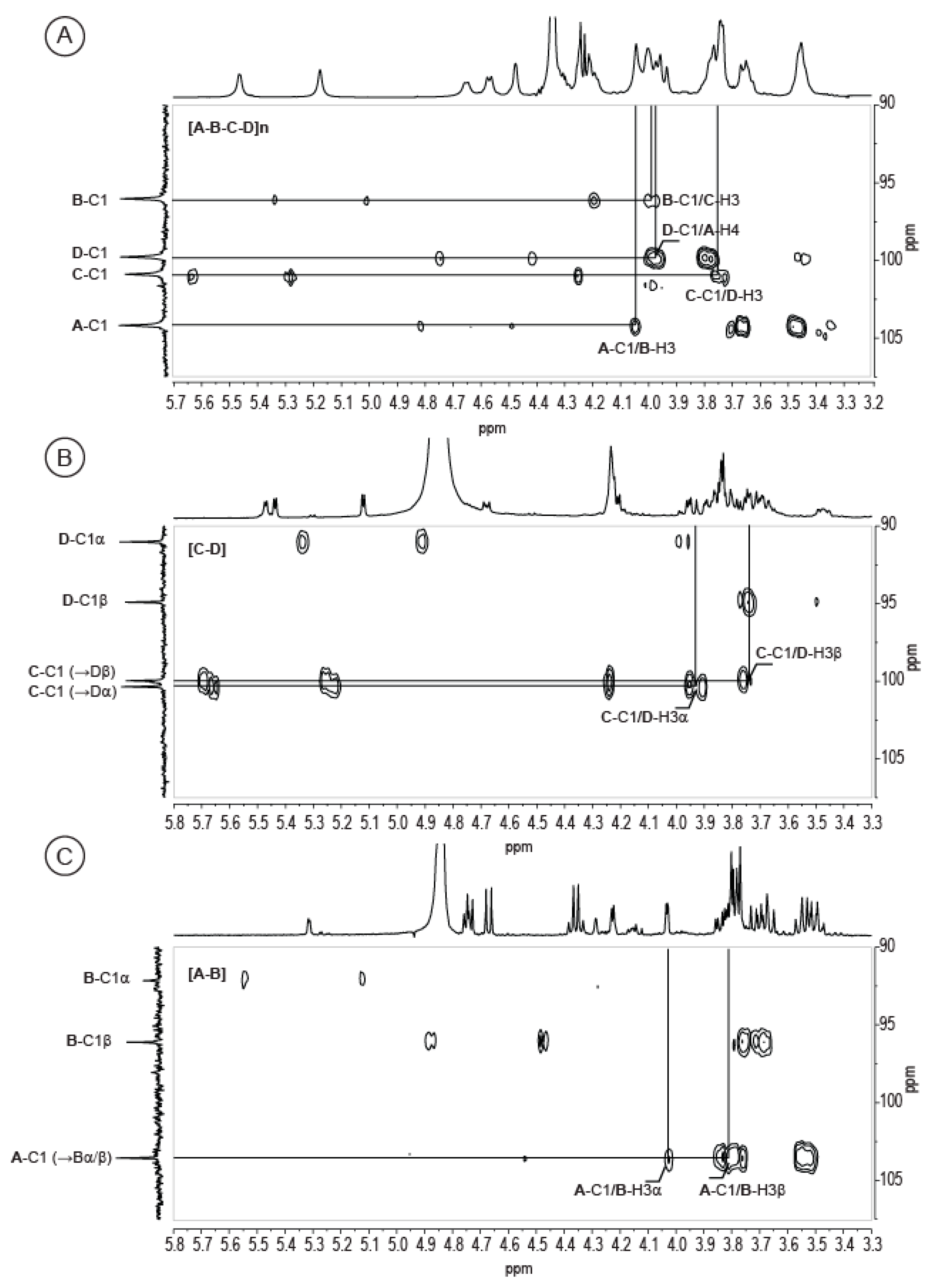
2.2. Structural Analysis of the Two Hydrolysis Products of the V. alginolyticus Exopolysaccharide
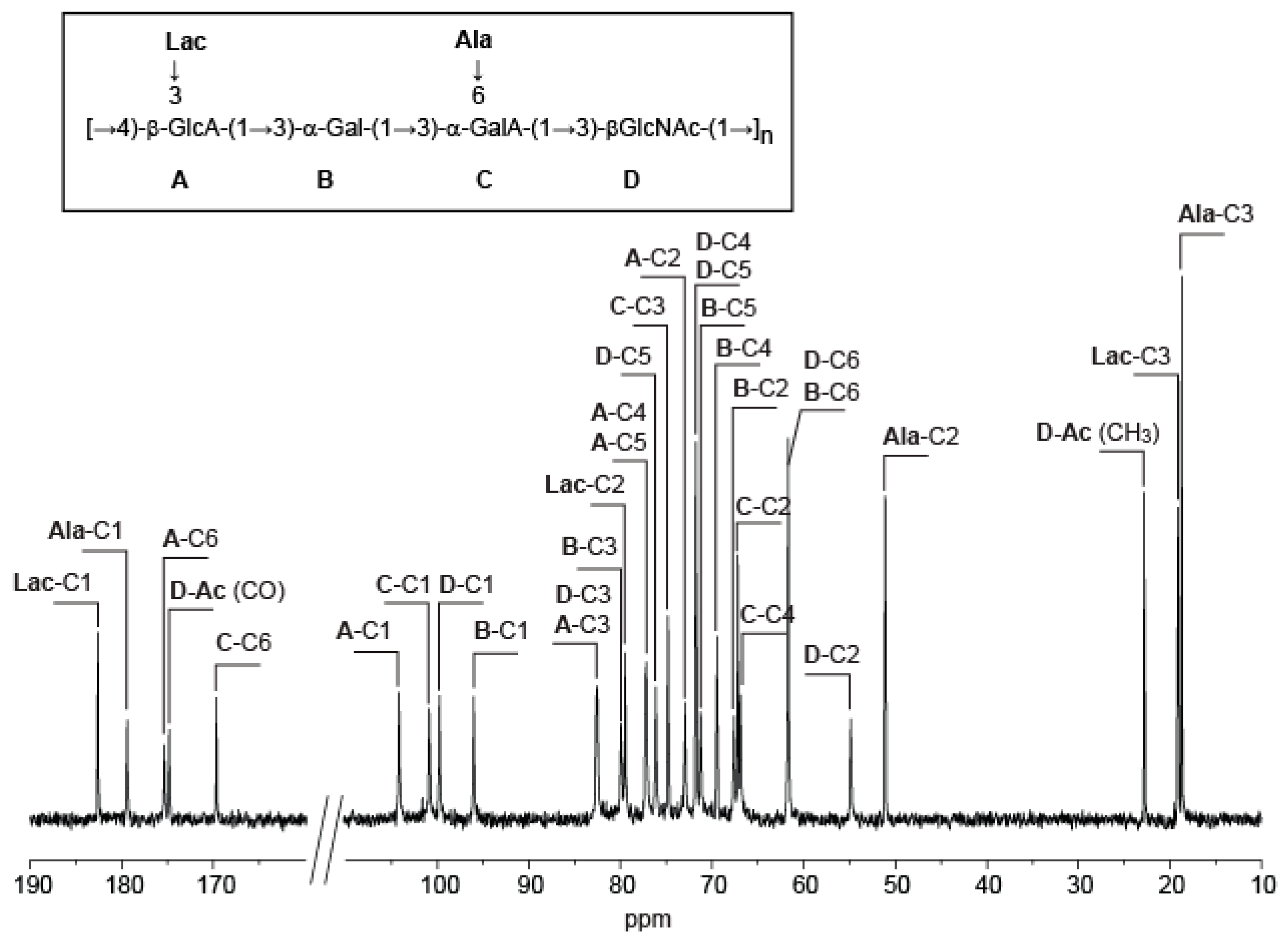
2.3. Complete Structure of the V. alginolyticus Exopolysaccharide
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Production, Isolation and Purification of the Vibrio alginolyticus Exopolysaccharide
3.2. Monosaccharide Analysis
3.3. Methylation Analysis
3.4. Amino Acid Composition
3.5. Determination of Absolute Configuration
3.6. Molecular Weight Determination
3.7. Acid Hydrolysis and Oligosaccharides Purification
3.8. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laine, R.A. A calculation of all oligosaccharide isomers both branched and linear yields 1.05 × 1012 structure for a reducing hexasaccharide: The isomer barrier to development of single-method saccharide sequencing or synthesis systems. Glycobiology 1994, 4, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, I.W. Microbial polysaccharides from Gram-negative bacteria. Int. Dairy J. 2001, 11, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, A.; Maugeri, T.L.; Pavone, B.; Iannello, D.; Gugliandolo, C.; Bisignanoc, G. Antiviral and immunoregulatory effect of a novel exopolysaccharide from a marine thermotolerant Bacillus licheniformis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanchetta, P.; Lagarde, N.; Guezennec, J. Systemic effects on bone healing of a new hyaluronic acid-like bacterial exopolysaccharide. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2003, 73, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtois, A.; Berthou, C.; Guézennec, J.; Boisset, C.; Bordron, A. Exopolysaccharides Isolated from Hydrothermal Vent Bacteria Can Modulate the Complement System. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, F.; Alves, V.D.; Reis, M.A.M. Advances in bacterial exopolysaccharides: From production to biotechnological applications. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedouin, A.; Vallee, R. Cosmetic or Pharmaceutical Composition Comprises Exopolysaccharides. Patent FR_2975906_A1, 7 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Helm, R.F.; Huang, Z.; Edwards, D.; Leeson, H.; Peery, W.; Potts, M. Structural characterization of the released polysaccharide of desiccation-tolerant Nostoc commune DRH-1. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toukach, F.V.; Knirel, Y.A. New database of bacterial carbohydrate structures. Glycoconj. J. 2005, 22, 216–217. [Google Scholar]
- Sadovskaya, I.; Brisson, J.-R.; Khieu, N.H.; Mutharia, L.M.; Altman, E. Structural characterization of the lipopolysaccharide O-antigen and capsular polysaccharide of Vibrio ordalii serotype O:2. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 253, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocharova, N.A.; Perepelov, A.V.; Zatonsky, G.V.; Shashkov, A.S.; Knirel, Y.A.; Jansson, P.-E.; Weintraub, A. Structural studies of the O-specific polysaccharide of Vibrio cholerae O8 using solvolysis with triflic acid. Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 330, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashii, N.; Isshiki, Y.; Iguchi, T.; Hisatsune, K.; Kondo, S. Structure and serological characterization of 5,7-diamino-3,5,7,9-tetradeoxy-non-2-ulosonic acid isolated from lipopolysaccharides of Vibrio parahaemolyticus O2 and O-untypable strain KX-V212. Carbohydr. Res. 2003, 338, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Vinogradov, E.; Li, J.; Lund, V.; Altman, E. Structural characterization of the lipopolysaccharide O-antigen from atypical isolate of Vibrio anguillarum strain 1282. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 1371–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drouillard, S.; Jeacomine, I.; Buon, L.; Boisset, C.; Courtois, A.; Thollas, B.; Morvan, P.-Y.; Vallée, R.; Helbert, W. Structure of an amino acid-derived decorated exopolysaccharide secreted by a Vibrio alginolyticus strain. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6723–6739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, Y.; Kondo, S.; Isshiki, Y.; Shimada, T.; Hisatsune, K. An N-[(R)-(-)-2-hydroxypropionyl]-a-L-perosamine homopolymer constitutes the O polysaccharide chain of the lipopolysaccharide from Vibrio cholerae O144 which has antigenic factor(s) in common with V. cholerae O76. Microbiol. Immunol. 1996, 40, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, S.; Sano, Y.; Isshiki, Y.; Hisatsune, K. The O polysaccharide chain of the lipopolysaccharide from Vibrio cholerae O76 is a homopolymer of N-[(S)-(+)-2-hydroxypropionyl]-a-l-perosamine. Microbiology 1996, 142, 2879–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knirel, Y.A.; Kochetkov, N.K. The structure of lipopolysaccharides of gram-negative bacteria. III. The structure of O-antigens: A review. Biochemistry 1994, 59, 1325–1383. [Google Scholar]
- Poirot, E.; Zhang, X.; Whittaker, N.F.; Kovác, P. Syntheses of the L-manno and some other analogs of the terminal determinants of the O-PS of Vibrio cholerae O:1. Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 330, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamerling, J.P.; Gerwig, G.J.; Vliegenthart, J.F.; Clamp, J.R. Characterization by gas-liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and proton-magnetic-resonance spectroscopy of pertrimethylsilyl methyl glycosides obtained in the methanolysis of glycoproteins and glycopeptides. Biochem. J. 1975, 151, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montreuil, J.; Bouquelet, S.; Debray, H.; Fournet, B.; Spik, G.; Strecker, G. Glycoproteines. In Carbohydrates Analysis: A Practical Approach; Chaplin, M.F., Kennedy, J.K., Eds.; IRL Press: Oxford, UK, 1986; pp. 143–204. [Google Scholar]
- Hakomori, S.I. A rapid permethylation of glycolipid, and polysaccharide catalyzed by methylsulfinyl carbanion in dimethyl sulfoxide. J. Biochem. 1964, 55, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.L.; Conrad, H.E. Stoichiometric depolymerization of polyuronides and glycosaminoglycans to monosaccharides following reduction of their carbodiimide activated carboxyl groups. Biochemistry 1972, 11, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvernheim, A.L. Methylation analysis of polysaccharides with butyllithium in dimethyl sulfoxide. Acta Chem. Scand. B 1987, 41, 150–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gerwig, G.J.; Kamerling, J.P.; Vliegenthart, F.G. Determination of the D and L configuration of neutral polysaccharides by high resolution capillary G.L.C. Carbohydr. Res. 1978, 62, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerwig, G.J.; Kamerling, J.P.; Vliegenthart, F.G. Determination of the absolute configuration of monosaccharides in complex carbohydrate by capillary G.L.C. Carbohydr. Res. 1979, 77, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Type of Sugar | Partially Methylated Alditol Acetate | Deduced Linkage |
|---|---|---|
| Galactose | 1,5-Di-O-acetyl-1-deuterio-2,3,4,6-tetra-O-methyl-d-galactitol | Galp-(1→ |
| Galactose | 1,3,5-Tri-O-acetyl-1-deuterio-2,4,6-tri-O-methyl-d-galactitol | →3)-Galp-(1→ |
| N-acetyl glucosamine | 1,3,5-Tri-O-acetyl-2-(acetylmethylamino)-2-deoxy-1-deuterio-4,6-di-O-methyl-d-Glucitol | →3)-GlcNAc-(1→ |
| VA-EPS [ABCD]n | DP2 ABα/β | DP2 CDα/β | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A: 3Lac-GlcA | |||
| H1 | 4.66 | 4.75/4.74 a | |
| H2 | 3.46 | 3.52 | |
| H3 | 3.46 | 3.48 | |
| H4 | 3.98 | 3.66 | |
| H5 | 3.67 | 3.77 | |
| Lac-H2 | 4.32 | 4.36 | |
| Lac-H3 | 1.42 | 1.46 | |
| B: Gal | |||
| H1 | 5.18 | 5.33/4.68 | |
| H2 | 4.05 | 4.02/3.69 | |
| H3 | 4.05 | 4.02/3.82 | |
| H4 | 4.22 | 4.28/4.22 | |
| H5 | 4.20 | 4.15/3.76 | |
| H6 | 3.74 | 3.77 | |
| C: 6Ala-GalA | |||
| H1 | 5.47 | 5.51/5.55 b | |
| H2 | 4.01 | 3.91/3.90 b | |
| H3 | 4.01 | 3.93 | |
| H4 | 4.48 | 4.32 | |
| H5 | 4.26 | 4.32 | |
| Ala-H2 | 4.24 | 4.31 | |
| Ala-H3 | 1.38 | 1.44 | |
| D: GlcNAc | |||
| H1 | 4.58 | 5.20/4.75 | |
| H2 | 3.79 | 4.04/3.82 | |
| H3 | 3.78 | 4.01/3.82 | |
| H4 | 3.65 | 3.78/3.77 | |
| H5 | 3.46 | 3.96/3.55 | |
| H6 | 3.95 | 3.87/3.91 | |
| H6’ | 3.75 | 3.80/3.80 | |
| NHAc:CH3 | 1.92 | 1.97 | |
| VA-EPS [ABCD]n | DP2 ABα/β | DP2 CDα/β | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A: 3Lac-GlcA | |||
| C1 | 104.20 | 104.19 | |
| C2 | 72.96 | 72.94 | |
| C3 | 82.53 | 84.63 | |
| C4 | 77.32 | 72.86 | |
| C5 | 77.16 | 76.98 | |
| C6 | 175.33 | 176.43 | |
| Lac-C1 | 182.60 | 182.77 | |
| Lac-C2 | 79.48 | 79.40 | |
| Lac-C3 | 19.09 | 19.40 | |
| B: Gal | |||
| C1 | 96.04 | 92.75/96.72 | |
| C2 | 67.61 | 67.90/71.45 | |
| C3 | 79.93 | 80.26/83.39 | |
| C4 | 69.45 | 69.51/68.95 | |
| C5 | 71.25 | 70.84/75.48 | |
| C6 | 61.68 | 61.63/61.82 | |
| C: 6AlaGalA | |||
| C1 | 100.90 | 101.08/100.70 a | |
| C2 | 67.20 | 68.58/68.74 a | |
| C3 | 74.80 | 69.55 | |
| C4 | 66.91 | 70.44/70.36 a | |
| C5 | 71.76 | 71.98/71.92 a | |
| C6 | 169.55 | 170.20/170.32 a | |
| Ala-C1 | 179.40 | 180.01 | |
| Ala-C2 | 51.11 | 51.25 | |
| Ala-C3 | 18.77 | 18.63 | |
| D: GlcNAc | |||
| C1 | 99.79 | 91.76/95.64 | |
| C2 | 54.86 | 53.07/55.74 | |
| C3 | 82.65 | 79.92/81.46 | |
| C4 | 71.76 | 71.26/71.24 | |
| C5 | 76.13 | 71.85/76.18 | |
| C6/C6’ | 61.68 | 60.97/61.10 | |
| NHAc:CO | 174.81 | 174.86/175.16 | |
| NHAc:CH3 | 22.81 | 22.44/22.70 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drouillard, S.; Jeacomine, I.; Buon, L.; Boisset, C.; Courtois, A.; Thollas, B.; Morvan, P.-Y.; Vallée, R.; Helbert, W. Structure of the Exopolysaccharide Secreted by a Marine Strain Vibrio alginolyticus. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16050164
Drouillard S, Jeacomine I, Buon L, Boisset C, Courtois A, Thollas B, Morvan P-Y, Vallée R, Helbert W. Structure of the Exopolysaccharide Secreted by a Marine Strain Vibrio alginolyticus. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(5):164. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16050164
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrouillard, Sophie, Isabelle Jeacomine, Laurine Buon, Claire Boisset, Anthony Courtois, Bertrand Thollas, Pierre-Yves Morvan, Romuald Vallée, and William Helbert. 2018. "Structure of the Exopolysaccharide Secreted by a Marine Strain Vibrio alginolyticus" Marine Drugs 16, no. 5: 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16050164
APA StyleDrouillard, S., Jeacomine, I., Buon, L., Boisset, C., Courtois, A., Thollas, B., Morvan, P.-Y., Vallée, R., & Helbert, W. (2018). Structure of the Exopolysaccharide Secreted by a Marine Strain Vibrio alginolyticus. Marine Drugs, 16(5), 164. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16050164





