Krill Oil-In-Water Emulsion Protects against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Proinflammatory Activation of Macrophages In Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of KO Emulsion or LPS on the Viability of Differentiated Human THP-1 Macrophages
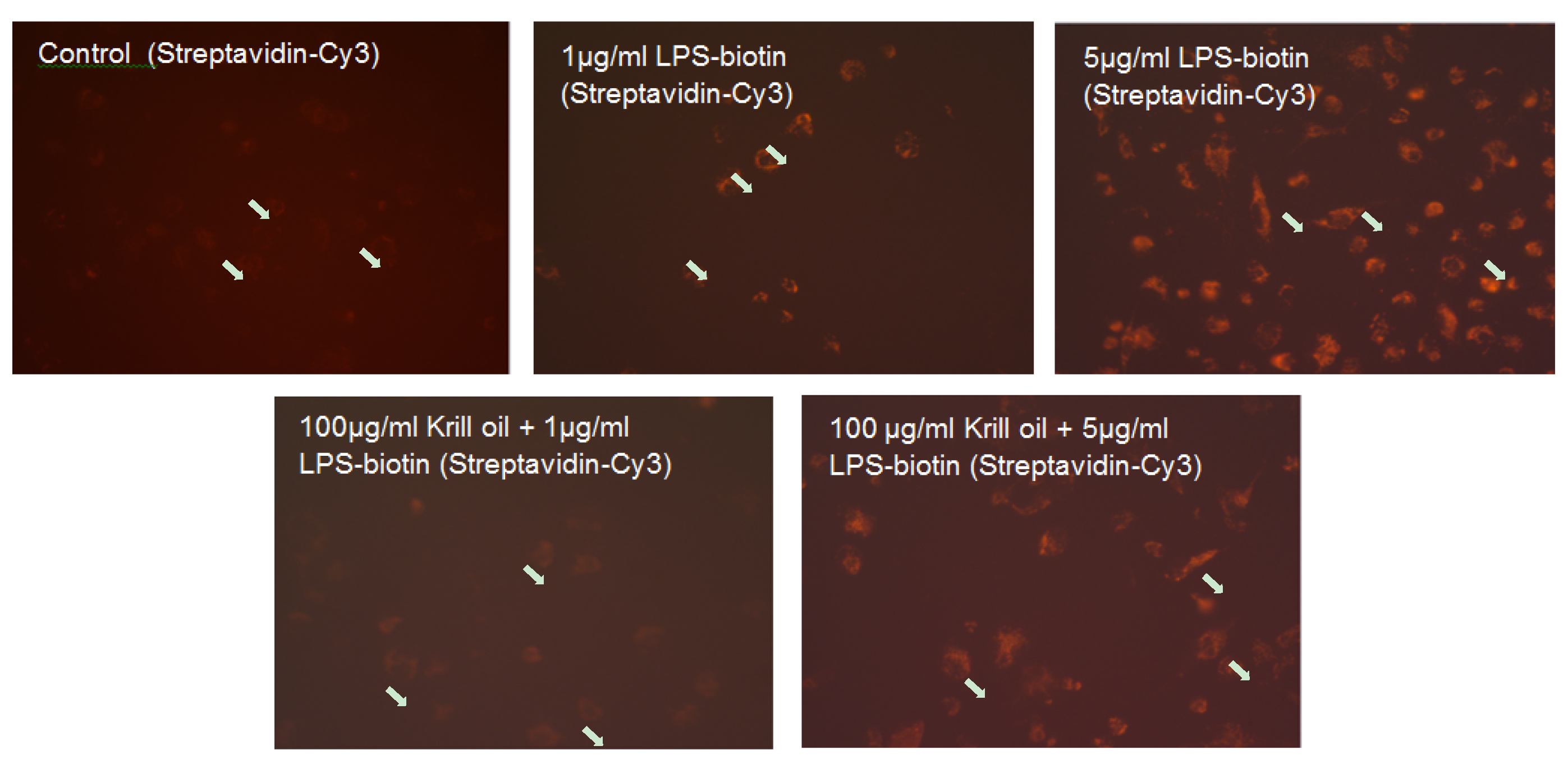
2.2. Effect of KO Emulsion on the LPS Binding
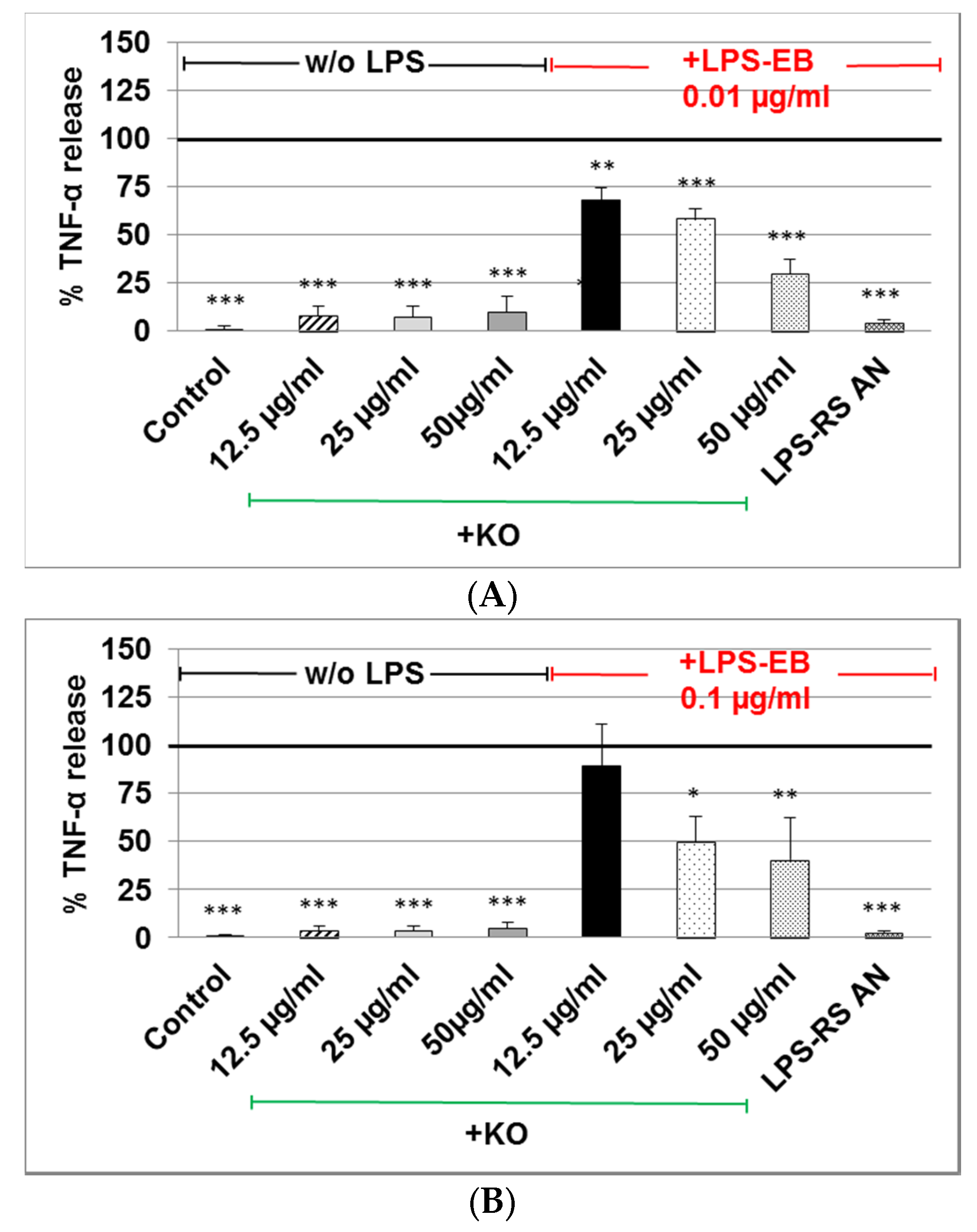
2.3. Effect of KO Emulsion on TNF-α Release of Differentiated Human THP-1 Macrophages Stimulated with LPS-EB
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Krill Oil-In-Water Emulsion
4.2. Cells and Culture Conditions
4.3. Determination of LPS and KO Emulsion Cytotoxicity
4.4. Determination of the LPS Binding on Differentiated THP-1 Macrophages, Effect of the Treatment with KO Emulsion, Detected by Fluorescence Microscopy
4.5. Determination of the LPS Binding on Differentiated THP-1 Macrophages Detected by Spectrophotometry
4.6. Inhibitory Effects of the KO Emulsion on the LPS Binding Capacity
4.7. Effects of the KO Emulsion on TNF-α Release
4.8. Statistical Analyses
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bochsler, P.N.; Maddux, J.M.; Neilsen, N.R.; Slauson, D.O. Differential binding of bacterial lipopolysaccharide to bovine peripheral-blood leukocytes. Inflammation 1993, 17, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.L.; Czuprynski, C.J. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide induces release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha from bovine peripheral blood monocytes and alveolar macrophages in vitro. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1990, 48, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sprague, A.H.; Khalil, R.A. Inflammatory cytokines in vascular dysfunction and vasculardisease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaillon, J.M.; Fitting, C.; Haeffner-Cavaillon, N.; Kirsch, S.J.; Warren, H.S. Cytokine response by monocytes and macrophages to free and lipoprotein-bound lipopolysaccharide. Infect. Immun. 1990, 58, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Emancipator, K.; Csako, G.; Elin, R.J. In vitro inactivation of bacterial endotoxin by human lipoproteins and apolipoproteins. Infect. Immunol. 1992, 60, 596–601. [Google Scholar]
- Eggesbo, J.B.; Hjermann, I.; Hostmark, A.T.; Kierulf, P. LPS induced release of IL-1 beta, IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-alpha in EDTA or heparin anticoagulated whole blood from persons with high or low levels of serum HDL. Cytokine 1996, 8, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumberger, C.; Ulevitch, R.J.; Dayer, J.M. Modulation of endotoxic activity oflipopolysaccharide by high-density lipoprotein. Pathobiology 1991, 59, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.; Hinds, C.J.; Thiemermann, C. High-density lipoproteins in sepsis and septic shock: Metabolism, actions, and therapeutic applications. Shock 2004, 21, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shor, R.; Wainstein, J.; Oz, D.; Boaz, M.; Matas, Z.; Fux, A.; Halabe, A. Low serum LDL cholesterol levels and the risk of fever, sepsis, and malignancy. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2007, 37, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, inflammation, and inflammatory diseases. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83 (Suppl. 6), 1505S–1519S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arterburn, L.M.; Hall, E.B.; Ojen, H. Distribution, interconversion and dose response of n-3 fatty acids in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83 (Suppl. 6), 1467S–1476S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nash, S.M.B.; Schlabach, M.; Nichols, P.D. A nutritional-toxicological assessment of antarctic krill oil versus fish oil dietary supplements. Nutrients 2014, 6, 3382–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wichmann, M.W.; Thul, P.; Czarnetski, H.D.; Morlion, B.J.; Kemen, M.; Jauch, K.W. Evaluation of clinical safety and beneficial effects of a fish oil containing lipid emulsion (Lipoplus, MLF541): Data from a prospective, randomized, multicenter trial. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, A.R.; Rössler, S.; Litz, R.J.; Stehr, S.N.; Heller, S.C.; Koch, R.; Koch, T. Omega-3 fatty acids improve diagnosis-related clinical outcome. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, V.M.; Miles, E.A.; Calhau, C.; Lafuente, E.; Calder, P.C. Effects of a fish oil containing lipid emulsion on plasma phospholipid fatty acids, inflammatory markers, and clinical outcomes in septic patients: A randomized, controlled clinical trial. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, K.; Fegbeutel, C.; Hattar, K.; Sibelius, U.; Krämer, H.J.; Heuer, K.U.; Temmesfeld-Wollbrück, B.; Gokorsch, S.; Grimminger, F.; Seeger, W. Omega-3 vs. omega-6 lipid emulsions exert differential influence on neutrophils in septic shock patients: Impact on plasma fatty acids and lipid mediator generation. Intensive Care Med. 2003, 29, 1472–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsumi, R.; Horikawa, Y.T.; Kume, K.; Tanaka, K.; Kasai, A.; Kadota, T.; Tsutsumi, Y.M. Peptide-Based Formulas With ω-3 Fatty Acids Are Protective in LPS-Mediated Sepsis. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2015, 39, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Marine omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: Effects, mechanisms and clinical relevance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1851, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsvik, M.S.; Bjørndal, B.; Bruheim, I.; Bohov, P.; Berge, R.K. A Phospholipid-Protein Complex from Krill with Antioxidative and Immunomodulating Properties Reduced Plasma Triacylglycerol and Hepatic Lipogenesis in Rats. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4375–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemifard, S.; Turchini, G.M.; Sinclair, A.J. Omega-3 long chain fatty acid “bioavailability”: A review of evidence and methodological considerations. Prog. Lipid Res. 2014, 56C, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cansell, M.; Nacka, F.; Combe, N. Marine lipid-based liposomes increase in vivo FA bioavailability. Lipids 2003, 38, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bistrian, B.R. Clinical aspects of essential fatty acid metabolism: Jonathan Rhoads Lecture. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2003, 27, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlmuth, C.; Dünser, M.W.; Wurzinger, B.; Deutinger, M.; Ulmer, H.; Torgersen, C.; Schmittinger, C.A.; Grander, W.; Hasibeder, W.R. Early fish oil supplementation and organ failure in patients with septic shock from abdominal infections: A propensitymatchedcohort study. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2010, 34, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, G.L. Lipopolysaccharides in liver injury: Molecular mechanisms of Kupffer cell activation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2002, 283, G256–G265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yegenaga, I.; Hoste, E.; Van Biesen, W.; Vanholder, R.; Benoit, D.; Kantarci, G.; Dhondt, A.; Colardyn, F.; Lameire, N. Clinical characteristics of patients developing ARF due to sepsis/systemic inflammatory response syndrome: Results of a prospective study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2004, 43, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angus, D.C.; Linde-Zwirble, W.T.; Lidicker, J.; Clermont, G.; Carcillo, J.; Pinsky, M.R. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: Analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 29, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annane, D.; Belissant, E.; Cavaillon, J.M. Septic shock. Lancet 2005, 365, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Balasubramanian, K.A. Role of intestine in postsurgical complications: Involvement of free radicals. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 36, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coquerel, D.; Kušíková, E.; Mulder, P.; Coëffier, M.; Renet, S.; Dechelotte, P.; Richard, V.; Thuillez, C.; Tamion, F. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids delay the progression of endotoxic shock-induced myocardial dysfunction. Inflammation 2013, 36, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, C.M.; Calder, P.C.; Ed Rainger, G. Pharmacology and therapeutics of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in chronic inflammatory disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 14, 272–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaterra, G.A.; Wakenhut, F.; Röthlein, D.; Wolf, M.; Bistrian, B.R.; Driscoll, D.; Kinscherf, R. Cytoprotection by omega-3 fatty acids as a therapeutic drug vehicle when combined with nephrotoxic drugs in an intravenous emulsion: Effects on intraglomerular mesangial cells. Toxicol. Rep. 2014, 1, 843–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Joshi-Barve, S.; Barve, S.; Chen, L.H. Eicosapentaenoic acid prevents LPS induced TNF-α expression by preventing NF-κB activation. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2004, 23, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Use of fish oil in parenteral nutrition: Rationale and reality. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2006, 65, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trebble, T.; Arden, N.K.; Stroud, M.A.; Wootton, S.A.; Burdge, G.C.; Miles, E.A.; Ballinger, A.B.; Thompson, R.L.; Calder, P.C. Inhibition of tumour necrosis factor-α and interleukin-6 production by mononuclear cells following dietary fish-oil supplementation in healthy men and response to antioxidant co-supplementation. Br. J. Nutr. 2003, 90, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, F.A.; Miles, E.A.; Calder, P.C. Comparison of the effects of linseed oil and different doses of fish oil on mononuclear cell function in healthy human subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2003, 89, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascioli, E.A.; Leader, L.; Flores, E.; Trimbo, S.; Bistrian, B.; Blackburn, G. Enhanced survival to endotoxin in guinea pigs fed iv fish oil emulsion. Lipids 1988, 23, 623–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulabukhov, V.V. Use of an endotoxin adsorber in the treatment of severe abdominal sepsis. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2008, 52, 1024–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstock, C.; Ullrich, H.; Hohe, R.; Berg, A.; Baumstark, M.W.; Frey, I.; Northoff, H.; Flegel, W.A. Low density lipoproteins inhibit endotoxin activation of monocytes. Arterioscler. Thromb. 1992, 12, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, B.R.; Parker, T.S.; Levine, D.M.; Feuerbach, F.; Saal, S.D.; Sloan, B.J.; Chu, C.; Stenzel, K.H.; Parrillo, J.E.; Rubin, A.L. Neutralization of endotoxin by a phospholipid emulsion in healthy volunteers. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 191, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellenger, R.P.; Tomayko, J.F.; Angus, D.C.; Opal, S.; Cupo, M.A.; McDermott, S.; Ducher, A.; Calandra, T.; Cohen, J. Lipid Infusion and Patient Outcomes in Sepsis (LIPOS) Investigators. Efficacy and safety of a phospholipid emulsion (GR270773) in gram-negative severe sepsis: Results of a phase II multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, dose finding trial. Crit. Care 2009, 37, 2929–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Panel on Biological Hazards. Scientific opinión on fish oil for human consumption. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1874. [Google Scholar]


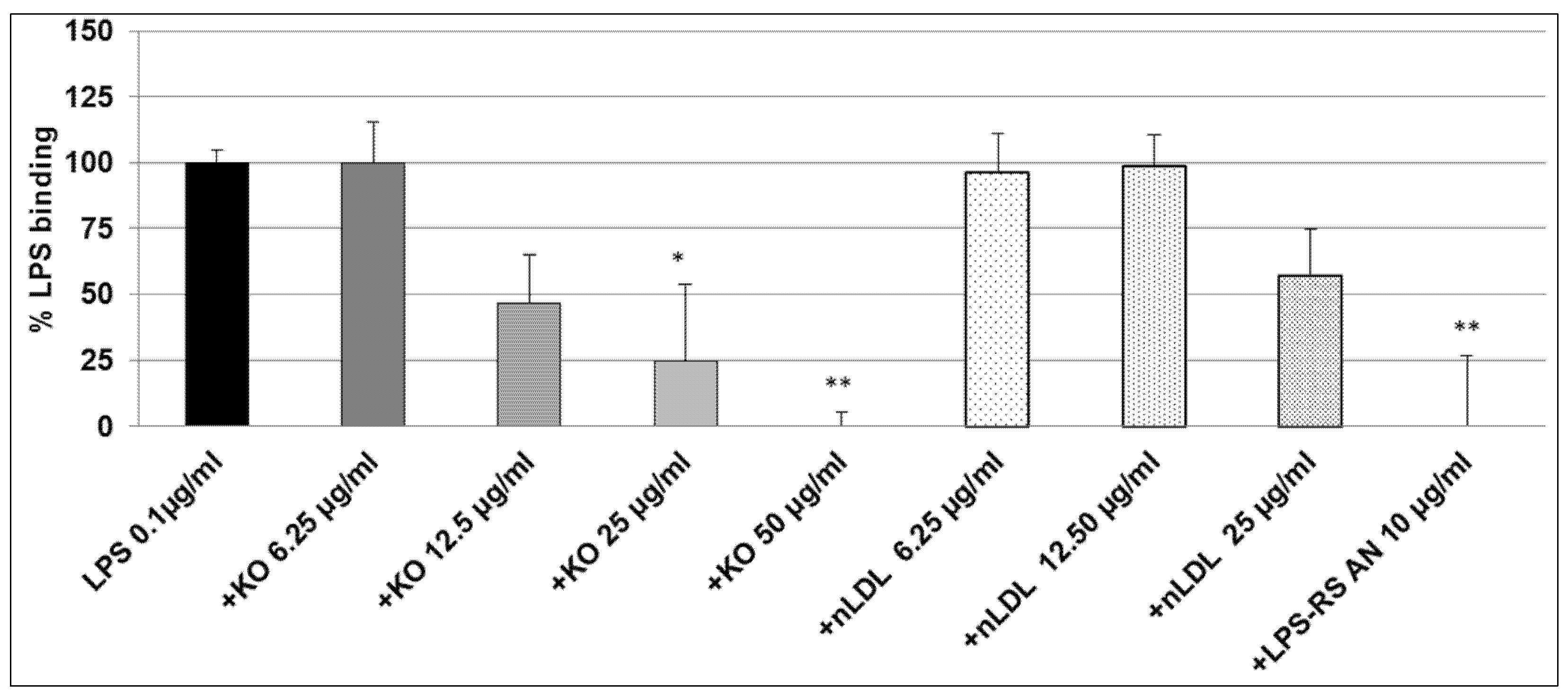

| Ingredient | Amount/1000 mL |
|---|---|
| Glycerol | 25.0 g |
| Krill Oil * | 50.0 g |
| Sterile Water for Injection | 1000 mL |
| pH | 6.89 ± 0.06 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonaterra, G.A.; Driscoll, D.; Schwarzbach, H.; Kinscherf, R. Krill Oil-In-Water Emulsion Protects against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Proinflammatory Activation of Macrophages In Vitro. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15030074
Bonaterra GA, Driscoll D, Schwarzbach H, Kinscherf R. Krill Oil-In-Water Emulsion Protects against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Proinflammatory Activation of Macrophages In Vitro. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(3):74. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15030074
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonaterra, Gabriel A., David Driscoll, Hans Schwarzbach, and Ralf Kinscherf. 2017. "Krill Oil-In-Water Emulsion Protects against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Proinflammatory Activation of Macrophages In Vitro" Marine Drugs 15, no. 3: 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15030074
APA StyleBonaterra, G. A., Driscoll, D., Schwarzbach, H., & Kinscherf, R. (2017). Krill Oil-In-Water Emulsion Protects against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Proinflammatory Activation of Macrophages In Vitro. Marine Drugs, 15(3), 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15030074





