Separation and Characterization of Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptides from Saurida elongata Proteins Hydrolysate by IMAC-Ni2+
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
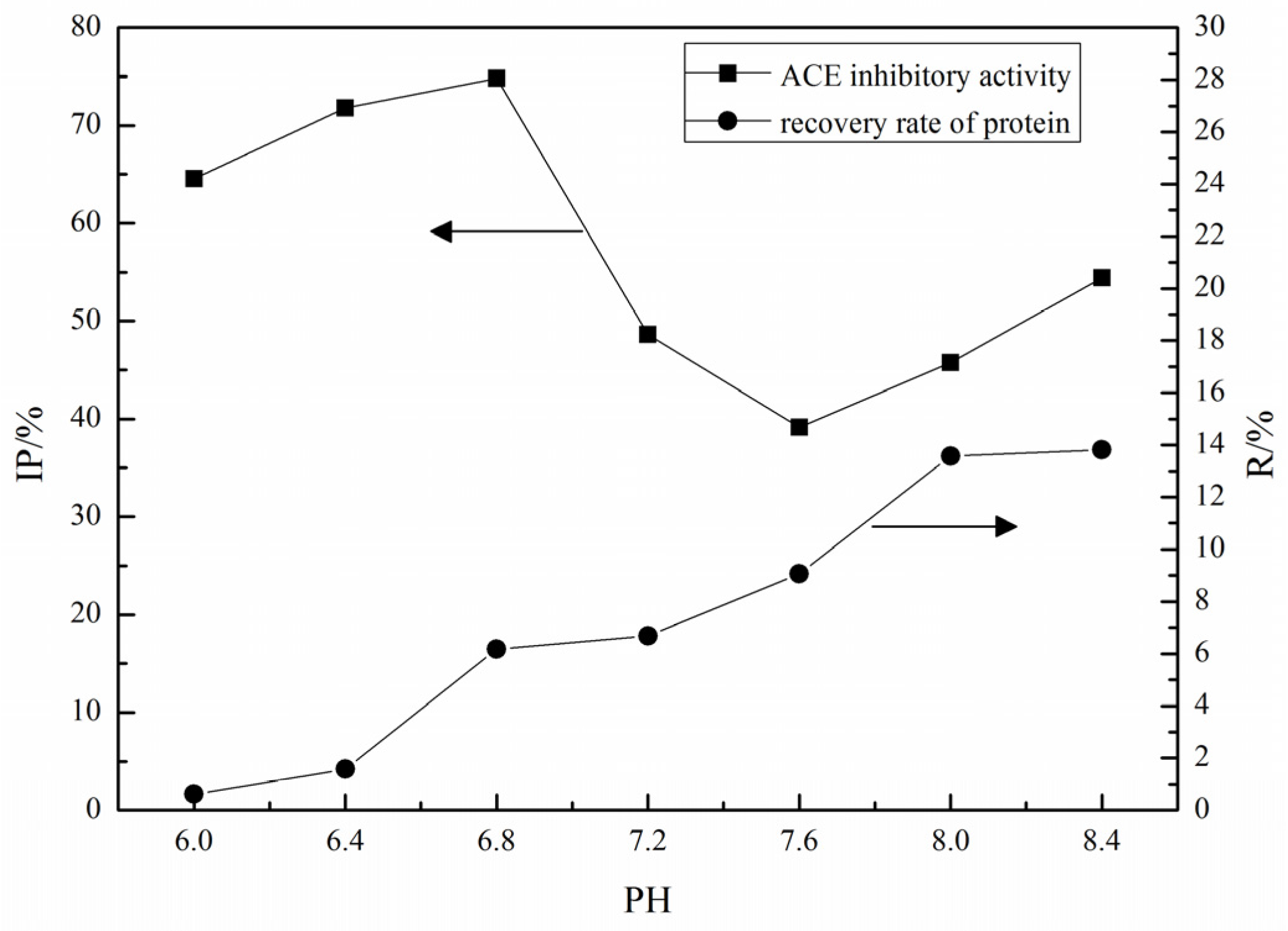
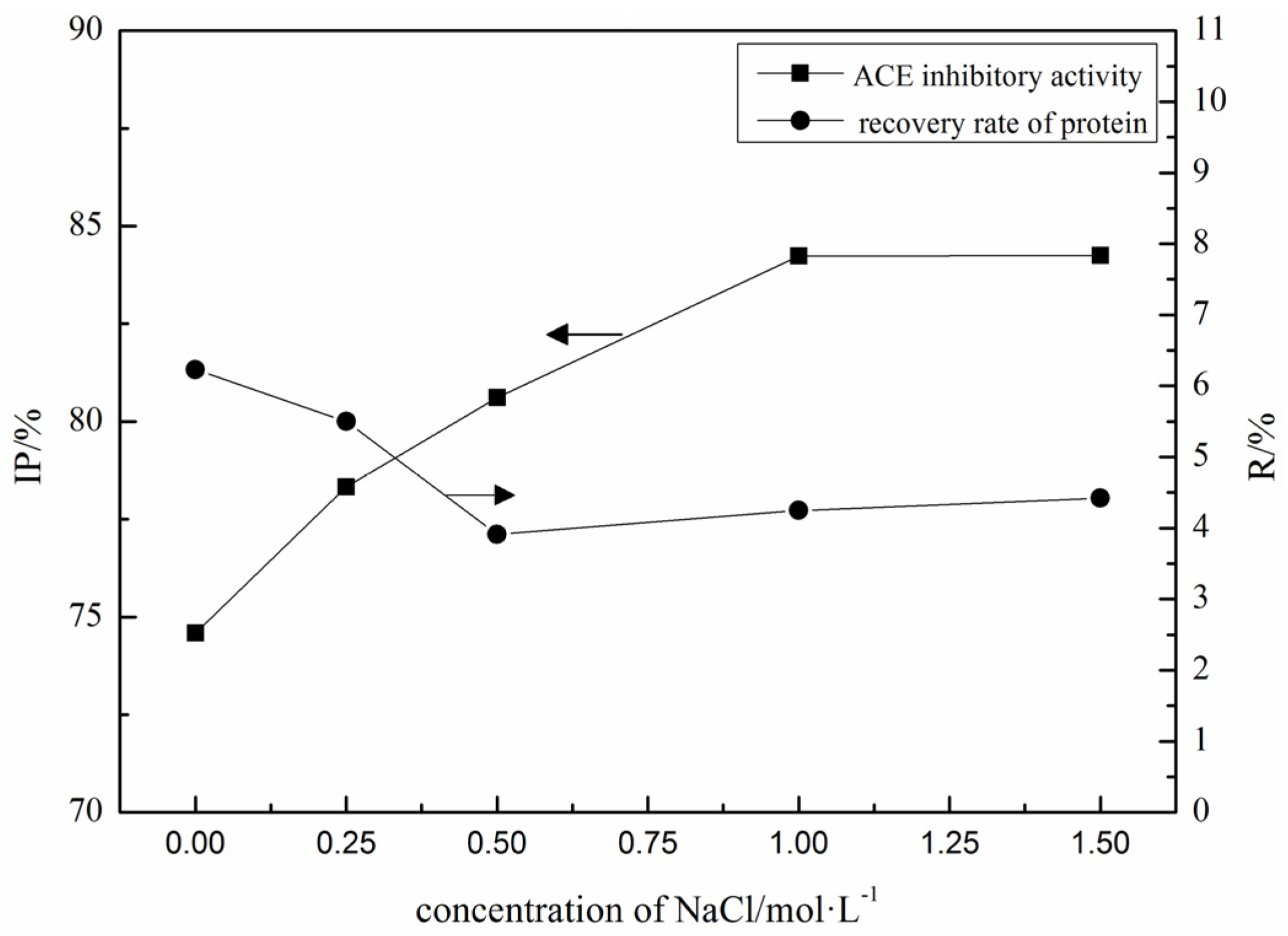
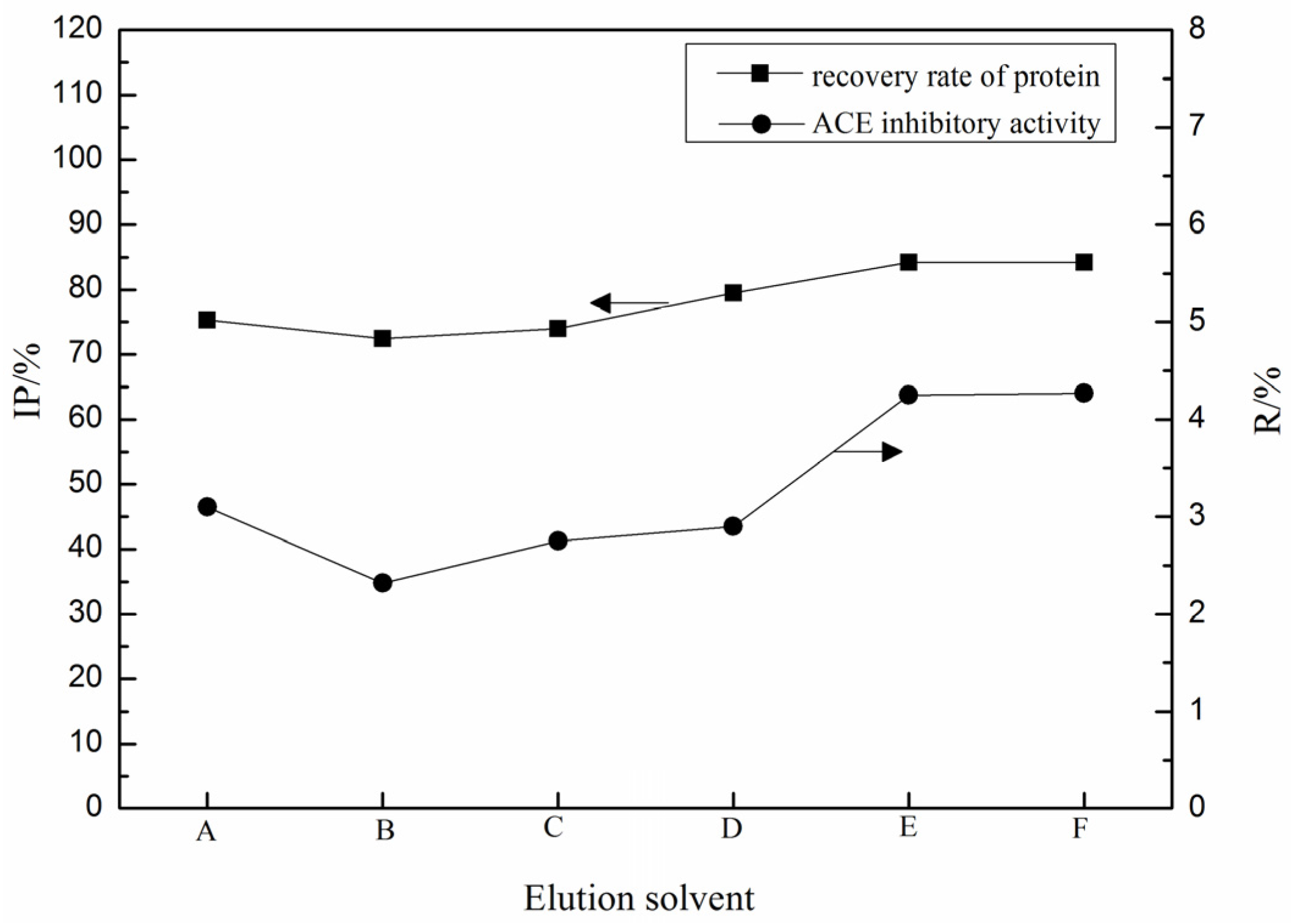
2.1. Purification of ACE Inhibitory Peptides by Immobilized Ni+ Ions on IDA-Conjugated Agarose Microspheres (AS-IDA-Ni2+)
2.2. Amino Acid (AA) Composition
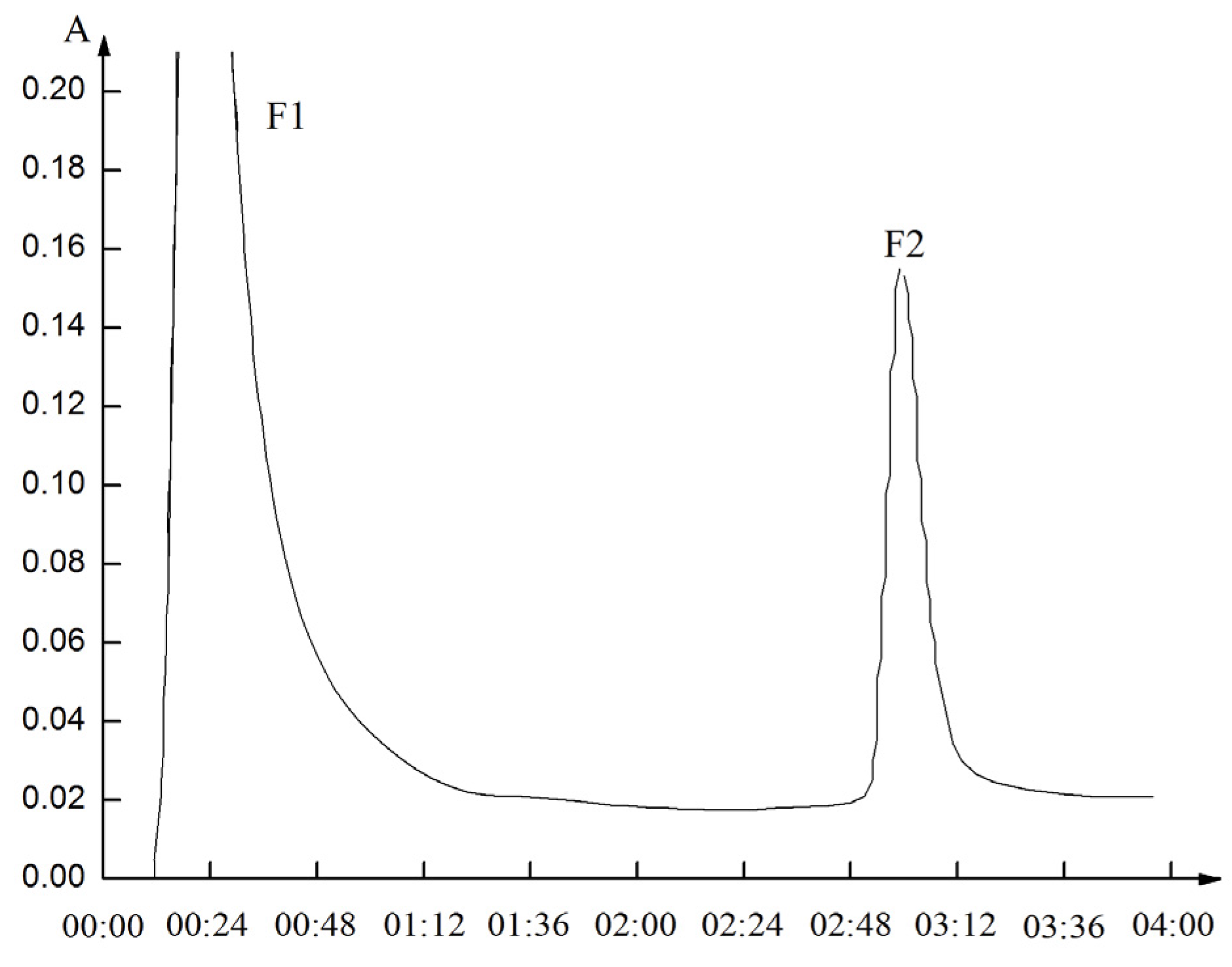
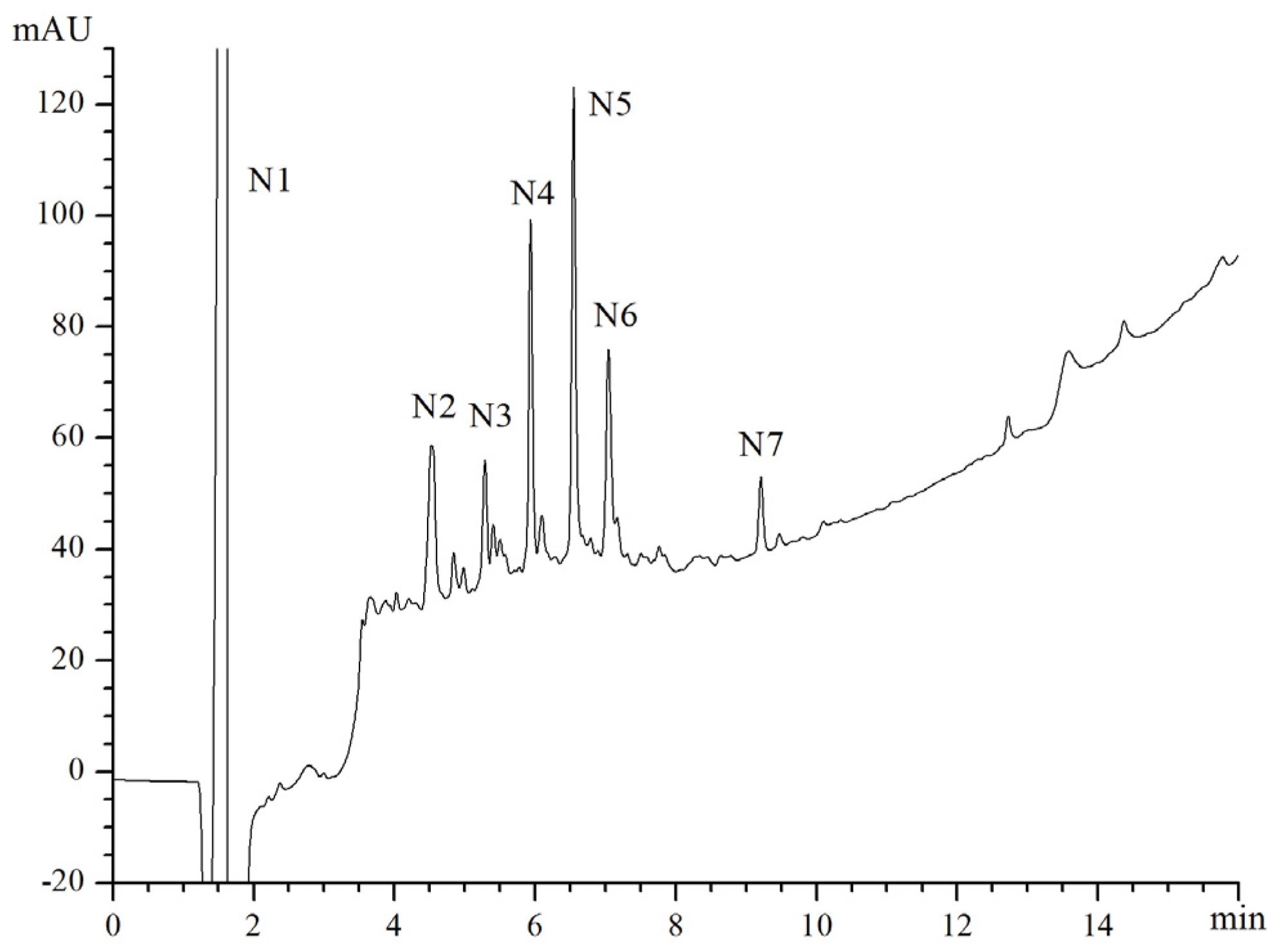
2.3. Separation of Metal Chelating Peptides (F2) by Reverse Phase (RP)-HPLC
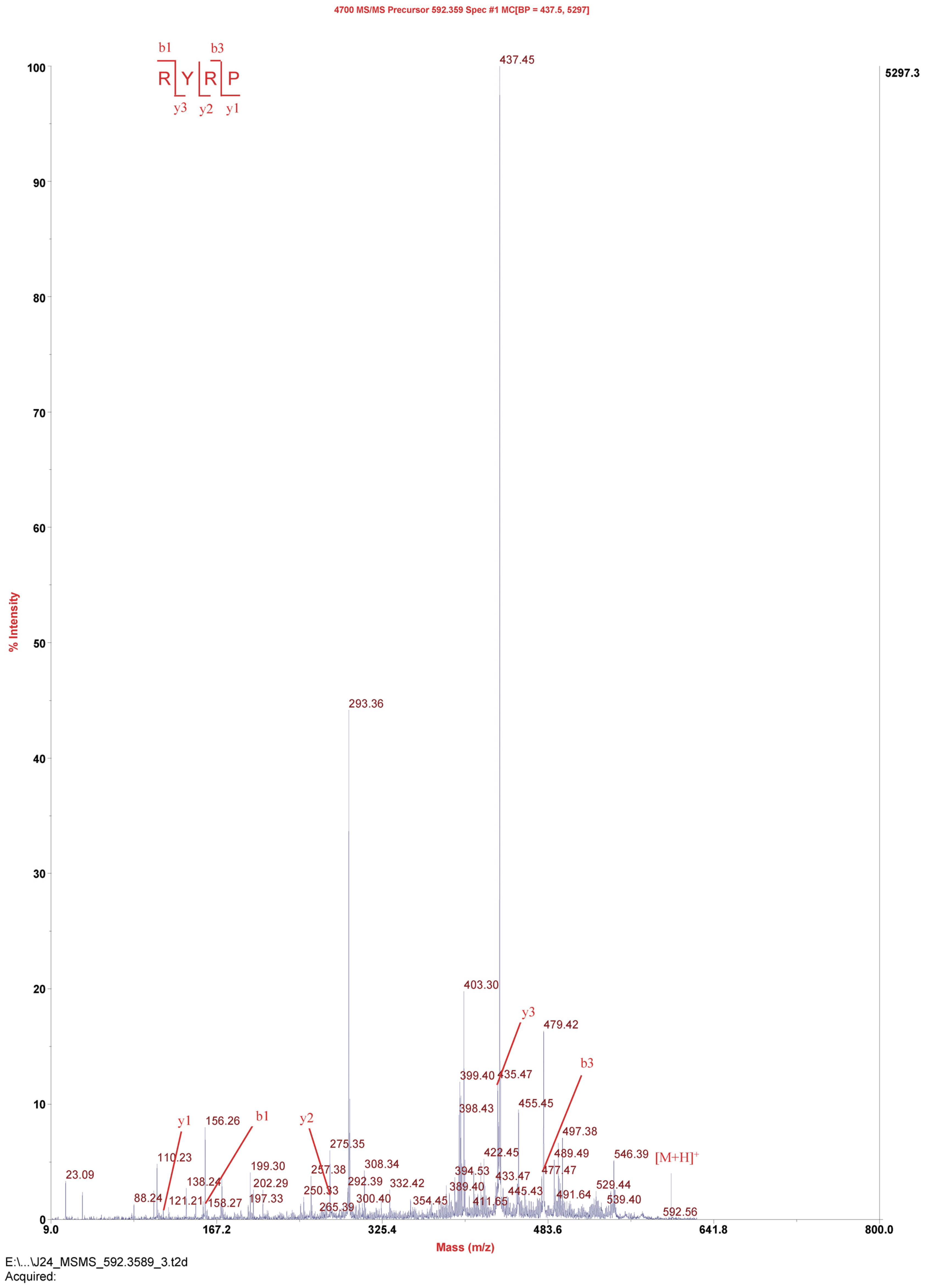
2.4. Amino Acid Sequence Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Agarose-Based IMAC Adsorbents
3.3. Preparation of Hydrolysates from Lizard Fish Muscle Protein
3.4. IMAC Chromatographic Procedures
- R—Recovery rate of protein, %;
- m—Protein content of the sample eluted from IMAC (IMAC fractions), mg;
- M—Protein content of the sample before treatment of IMAC chromatographic procedures, mg.
3.5. Determination of Amino Acid (AA) Composition
3.6. Purification of ACE-Inhibitory Peptides by HPLC
3.7. Amino Acid Sequence Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vermeirssen, V.; Van Camp, J.; Verstraete, W. Bioavailability of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides. Br. J. Nutr. 2004, 92, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, A.J.; Raizada, M.K. Are we poised to target ACE2 for the next generation of antihypertensives? J. Mol. Med. 2008, 86, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Ledesma, B.; Contreras, M.D.; Recio, I. Antihypertensive peptides: Production, bioavailability and incorporation into foods. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 165, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesekara, I.; Kim, S.K. Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors from marine resources: Prospects in the pharmaceutical industry. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1080–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Fandino, R.; Otte, J.; Van Camp, J. Physiological, chemical and technological aspects of milk-protein-derived peptides with antihypertensive and ACE-inhibitory activity. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 1277–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, J.S. Isolation and characterization of a novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide derived from the edible mushroom Tricholoma giganteum. Peptides 2004, 25, 621–627. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Z.J.; Jung, W.K.; Kim, S.K. Free radical scavenging activity of a novel antioxidative peptide purified from hydrolysate of bullfrog skin, Rana catesbeiana Shaw. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 1690–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.P.; Aluko, R.E.; Muir, A.D. Production of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from defatted canola meal. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5283–5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pihlanto, A.; Virtanen, T.; Korhonen, H. Angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity and antihypertensive effect of fermented milk. Int. Dairy J. 2010, 20, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.L.; Chen, X.L.; Wu, H.; Sun, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhou, B.C. High throughput and rapid screening of marine protein hydrolysates enriched in peptides with angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory activity by capillary electrophoresis. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 3499–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winzerling, J.J.; Berna, P.; Porath, J. How to use immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography. Methods 1992, 4, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaga, G.S. Twenty-five years of immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography: Past, present and future. J. Biochem. Biophs. Methods 2001, 49, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, R.J.; Brodin, J.D.; Salgado, E.N.; Tezcan, F.A. Expanding the utility of proteins as platforms for coordination chemistry. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, M.; Coghlan, C.J.; Hearn, M.T.W. Studies with an immobilized metal affinity chromatography cassette system involving binuclear triazacyclononane-derived ligands: Automation of batch adsorption measurements with tagged recombinant proteins. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1351, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, C.M.; Wang, C.Z.; Wei, Y.M. Novel bis(5-methyltetrazolium)amine ligand-bonded stationary phase with reduced leakage of metal ions in immobilized metal affinity chromatography of proteins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 7595–7605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakus, C.; Uslu, M.; Yazici, D.; Salih, B.A. Evaluation of immobilized metal affinity chromatography kits for the purification of histidine-tagged recombinant CagA protein. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1021, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.M.; Zhu, G.T.; Lu, W.; Yuan, B.F.; Wang, H.; Feng, Y.Q. Nickel(II)-immobilized sulfhydryl cotton fiber for selective binding and rapid separation of histidine-tagged proteins. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1405, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavan, G.L.; Bresolin, I.T.L.; Borsoi-Ribeiro, M.; Vijayalakshmi, M.; Bueno, S.M.A. The effect of NaCl on the adsorption of human IgG onto CM-Asp–PEVA hollow fiber membrane-immobilized nickel and cobalt metal ions. Adsorption 2014, 20, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megias, C.; Pedroche, J.; Yust, M.M.; Girón-Calle, J.; Alaiz, M.; Millán, F.; Vioque, J. Production of copper-chelating peptides after hydrolysis of sunflower proteins with pepsin and pancreatin. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 1973–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thewissen, B.G.; Pauly, A.; Celus, I.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J. Inhibition of angiotensin I-converting enzyme by wheat gliadin hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1653–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, W.M.Y.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y. Angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from in vitro pepsin-pancreatin digestion of soy protein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 3369–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.G.; Sun, J.G.; Tong, Z.F.; Lan, X.D.; Zhao, Z.X.; Liao, D.K. Optimization of hydrolysis conditions for the production of angiotensin-I converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides and isolation of a novel peptide from lizard fish (Saurida elongata) muscle protein hydrolysate. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1066–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.G.; Feng, X.Z.; Lan, X.D.; Xu, Y.J.; Liao, D.K. Purification and identification of Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from lizard fish (Saurida elongata) hydrolysate. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 13, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.L.; Liu, D.; Ma, C.B. Review on the Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitor Peptides from Marine Proteins. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 169, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, X.G.; Cheng, G.X.; Zhao, K.Y. Preparation and characterization of protein imprinted agarose microspheres. Polym. Bull. 2010, 65, 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.R.; Sun, J.H.; Huang, Q.X.; Liao, D.K. Detection and quantification of amino acids of Pinctada martensii by reversed-phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Guangxi Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2009, 346, 744–748. [Google Scholar]
| Amino Acid | Crude Protein (LFPH-I)/mol % | F2/mol % | The Increased Percentage of Amino Acid Levels/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASP | 9.29 | 9.36 | 0.75 |
| Thr | 5.09 | 5.09 | 0.00 |
| Ser | 5.07 | 5.02 | −0.99 |
| Glu | 13.71 | 13.42 | −2.12 |
| Gly | 8.09 | 8.21 | 1.48 |
| Ala | 8.86 | 8.96 | 1.13 |
| Cys | 0.39 | 0.07 | −82.05 |
| Val | 4.89 | 2.87 | −41.31 |
| Met | 1.49 | 2.40 | 61.07 |
| Ile | 4.33 | 4.62 | 6.70 |
| Leu | 8.56 | 8.97 | 4.79 |
| Tyr | 2.36 | 2.76 | 16.95 |
| Phe | 3.08 | 2.40 | −22.08 |
| Lys | 8.07 | 7.80 | −3.35 |
| His | 1.70 | 2.61 | 53.53 |
| Arg | 4.49 | 4.32 | −3.79 |
| Pro | 7.36 | 7.96 | 8.15 |
| Trp | 3.19 | 3.16 | −0.94 |
| Fraction | IP% |
|---|---|
| N1 | 51.28 |
| N2 | 24.09 |
| N3 | 28.96 |
| N4 | 36.11 |
| N5 | 73.05 |
| N6 | 26.42 |
| N7 | 0.00 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, L.; Wu, S.; Zhou, L.; Wang, F.; Lan, X.; Sun, J.; Tong, Z.; Liao, D. Separation and Characterization of Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptides from Saurida elongata Proteins Hydrolysate by IMAC-Ni2+. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15020029
Sun L, Wu S, Zhou L, Wang F, Lan X, Sun J, Tong Z, Liao D. Separation and Characterization of Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptides from Saurida elongata Proteins Hydrolysate by IMAC-Ni2+. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(2):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15020029
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Lixia, Shanguang Wu, Liqin Zhou, Feng Wang, Xiongdiao Lan, Jianhua Sun, Zhangfa Tong, and Dankui Liao. 2017. "Separation and Characterization of Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptides from Saurida elongata Proteins Hydrolysate by IMAC-Ni2+" Marine Drugs 15, no. 2: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15020029
APA StyleSun, L., Wu, S., Zhou, L., Wang, F., Lan, X., Sun, J., Tong, Z., & Liao, D. (2017). Separation and Characterization of Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptides from Saurida elongata Proteins Hydrolysate by IMAC-Ni2+. Marine Drugs, 15(2), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15020029





