New Enzyme-Inhibitory Triterpenoid from Marine Macro Brown Alga Padina boergesenii Allender & Kraft
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
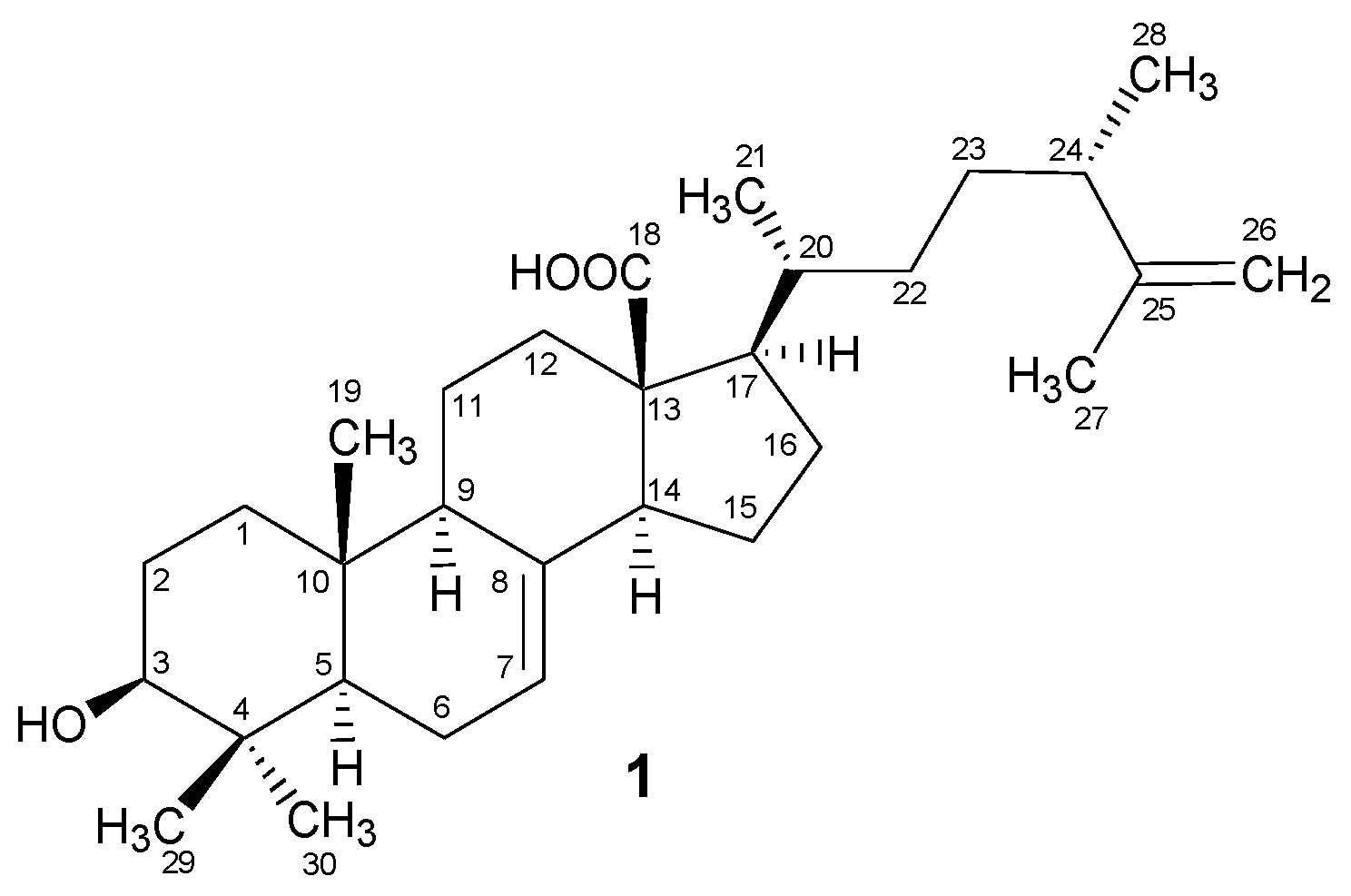
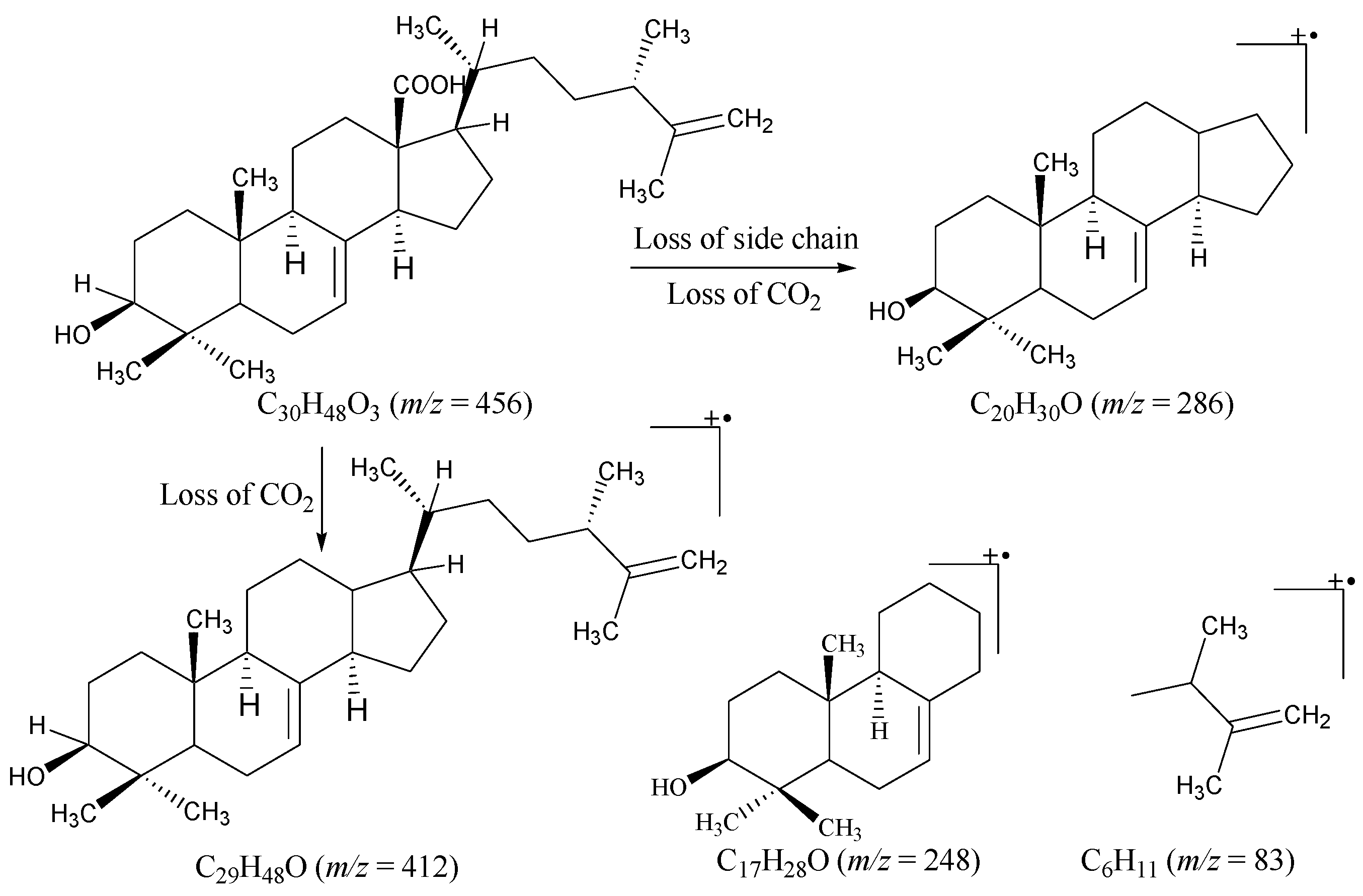
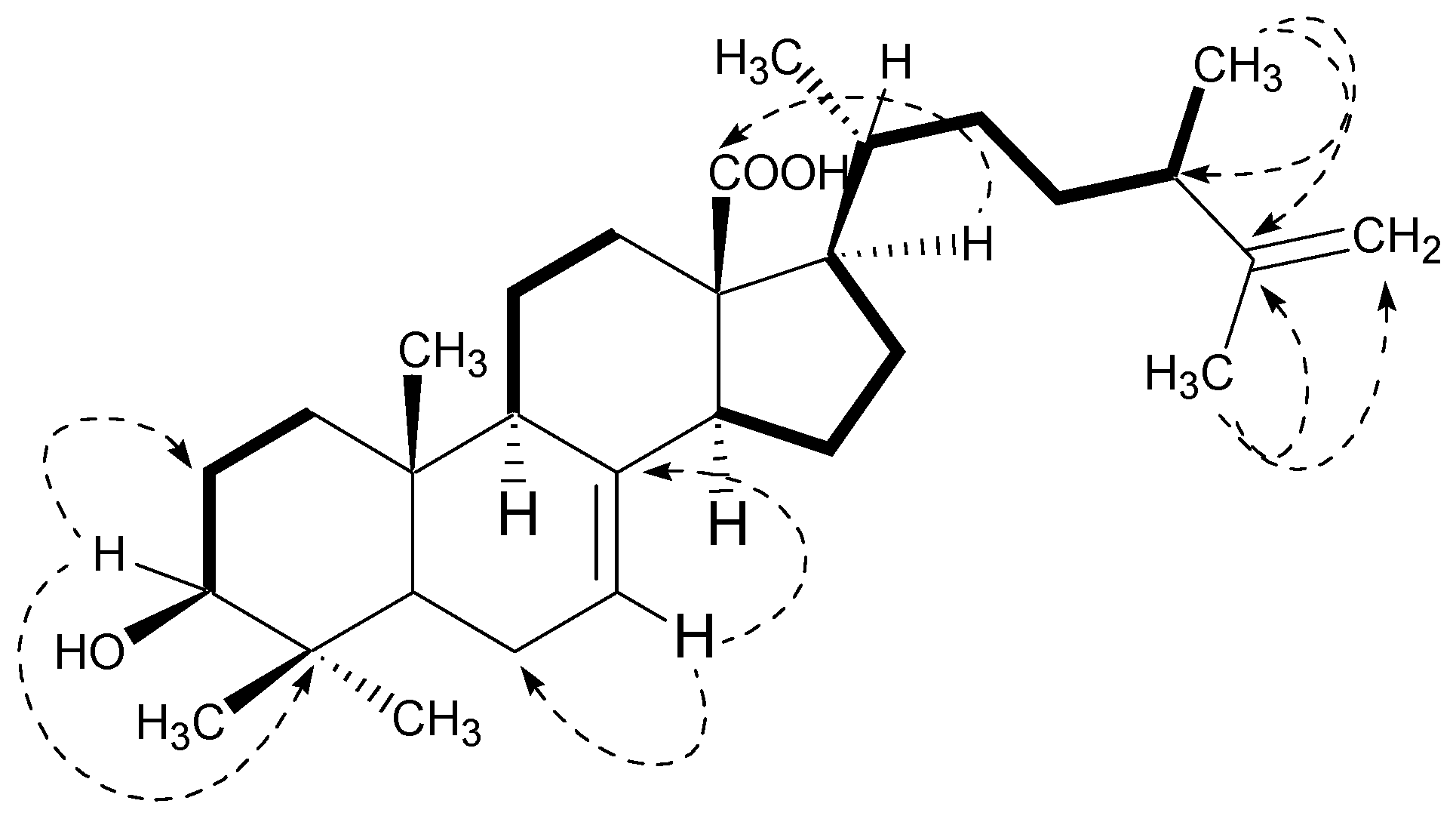
2.1. Structural Characterization
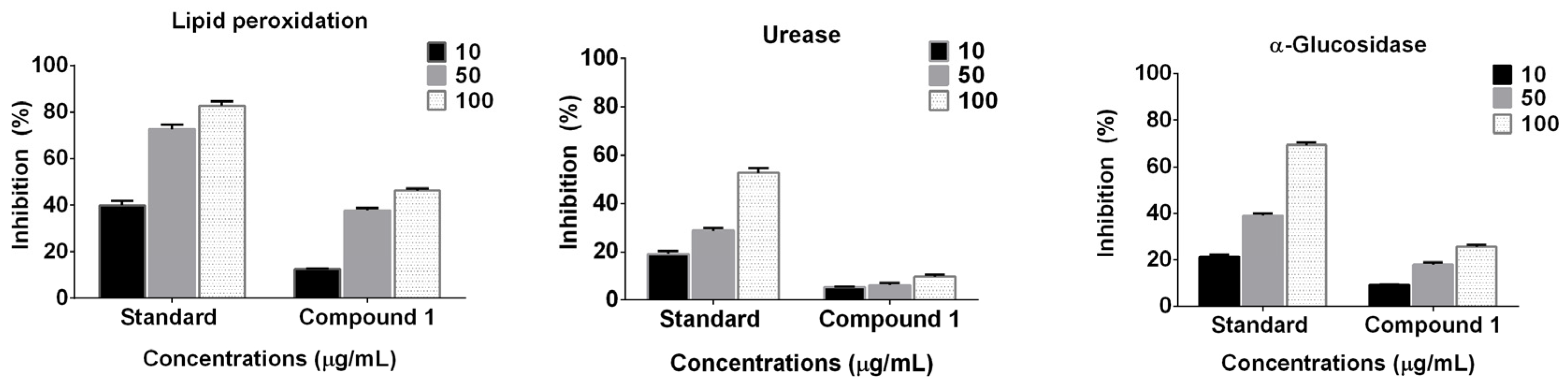
2.2. Enzyme Inhibition and Anti-Lipid Peroxidation Studies
3. Material and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
Padinolic Acid (1)
3.4. Enzyme Inhibition and Anti-Lipid Peroxidation Assay
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elsayed, K.N.; Radwan, M.M.; Hassan, S.H.; Abdelhameed, M.S.; Ibraheem, I.B.; Ross, S.A. Phytochemical and biological studies on some Egyptian seaweeds. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2012, 7, 1209–1210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Karagozlu, M.Z. Marine algae: Natural product source for gastrointestinal cancer treatment. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2011, 64, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Ta, Q.V. Potential beneficial effects of marine algal sterols on human health. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2011, 64, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ayyad, S.E.; Slama, M.O.; Mokhtar, A.H.; Anter, A.F. Cytotoxic bicyclic diterpene from brown alga Sargassum crispum. Boll. Chim. Farm. 2001, 140, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.F.; Yang-Hua, Y.; Yao, X.S.; Xu, Q.Z.; Zhang, S.Y.; Lin, H.W. Bioactive steroids from the brown alga Sargassum carpophyllum. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2002, 4, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunden, G. Biologically active compounds from marine organisms. Phytother. Res. 2001, 15, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthikeyan, R.; Somasundaram, S.T.; Manivasagam, T.; Balasubramanian, T.; Anantharaman, P. Hepatoprotective activity of brown alga Padina boergesenii against CCl4 induced oxidative damage in Wistar rats. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2010, 3, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsler, C.D.; Fairhead, V.A. Defensive and sensory chemical ecology of brown algae. Adv. Bot. Res. 2006, 43, 1–91. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuyama, Y.; Kodama, M.; Miura, I.; Kinzyo, Z.; Mori, H.; Nakayama, Y.; Takahashi, M. Anti-plasmin inhibitor. VI. Structure of phlorofuco-furoeckol A, a novel phlorotannin with both dibenzo-1,4-dioxin and dibenzofuran elements from Ecklonia kurome. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suqiura, Y.; Matsuda, K.; Yamada, Y.; Nishikawa, M.; Shioya, K.; Katsuzaki, H.; Imai, K.; Amano, H. Isolation of a new anti-allergic phlorotannin, phlorofucofuroeckol B, from an edible brown alga, Eisenia arborea. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 2807–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ham, Y.M.; Baik, J.S.; Hyun, J.W.; Lee, N.H. Isolation of a new phlorotannin, fucodiphlorethol G, from a brown alga, Ecklonia cava. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2007, 28, 1595–1597. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Narwal, S.; Kumar, V.; Prakash, O. α-Glucosidase inhibitors from plants: A natural approach to treat diabetes. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2011, 5, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Health Estimates: Deaths by Cause, Age, Sex and Country, 2000–2012; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- Kim, K.Y.; Nam, K.A.; Kurihara, H.; Kim, S.M. Potent α-glucosidase inhibitors purified from the red alga Grateloupia elliptica. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 2820–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, S. Alpha glucosidase inhibitors. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2014, 64, 474–476. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wehmeier, U.F.; Piepersberg, W. Biotechnology and molecular biology of the alpha-glucosidase inhibitor acarbose. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 63, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, H. Pharmacology of α-glucosidase inhibition. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 24, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, L.; Khan, A.L.; Al-Kharusi, L.; Hussain, J.; Al-Harrasi, A. New α-glucosidase inhibitory triterpenic acid from marine macro green alga Codium dwarkense. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4344–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Fan, X.; Han, L.; Lou, Q.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Y. Screening for alpha-glucosidase inhibitors from the macroalgal extracts. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2002, 21, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Okuzumi, J.; Takahashi, T.; Yamane, T.; Kitao, Y.; Inagake, M.; Ohya, K.; Nishino, H.; Tanaka, Y. Inhibitory effects of fucoxanthin, a natural carotenoid, on N-ethyl-N′-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine induced mouse duodenal carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 1993, 68, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Araki, S.; Kim, D.J.; Park, C.B.; Takasuka, N.; Baba-Toriyama, H.; Ota, T.; Nir, Z.; Khachik, F.; Shimidzu, N.; et al. Chemopreventive effects of carotenoids and curcumins on mouse colon carcinogenesis after 1,2-dimethylhydrazine initiation. Carcinogenesis 1998, 19, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasuki, S.; Ganesan, M.; Rao, P.V.S. Effect of light intensity, photoperiod, ESP medium and nitrogen sources on growth of marine brown alga Padina boergesenii (Dictyotales, Phaeophyta). Indian J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 2001, 30, 228–231. [Google Scholar]
- Karthikeyan, R.; Manivasagam, T.; Anantharaman, P.; Balasubramanian, T.; Somasundaram, S.T. Chemopreventive effect of Padina boergesenii on ferric nitrilotriacetate (Fe-NTA)-induced oxidative damage in Wistar rats. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permeh, P.; Gohari, A.; Saeidnia, S.; Jamili, S.; Permeh, S.; Mostafavi, P.G. Alpha amylase inhibitory and antioxidant activity of Padina boergesenii (Allander and Kraft) from Persian Gulf. Planta Med. 2013, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.L.; Xiong, J.; Wu, S.B.; Zhu, J.J.; Hong, J.L.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, G.; Hu, J.F. Tetracyclic triterpenoids and terpenylated coumarins from the bark of Ailanthus altissima (“Tree of Heaven”). Phytochemistry 2013, 86, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hpu, Y.; Cao, S.; Brodie, P.J.; Miller, J.S.; Birkinshaw, C.; Andrianjafy, M.N.; Andriantsiferana, R.; Rasamison, V.E.; TenDyke, K.; Shen, Y.; et al. Euphane triterpenoids of Cassipourea lanceolata from the Madagascar rainforest. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 669–674. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.Z. A review of ergostane and cucurbitane triterpenoids of mushroom origin. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.J.; Leu, Y.L.; Chen, C.H.; Chao, C.H.; Shen, D.Y.; Chan, H.H.; Lee, E.J.; Wu, T.S.; Wang, Y.H.; Shen, Y.C. Camphoratins A–J, potent cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory triterpenoids from the fruiting body of Taiwanofungus camphorates. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1756–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brill, G.M.; Kati, W.M.; Montgomery, D.; Karwowski, J.P.; Humphrey, P.E.; Jackson, M.; Clement, J.J.; Kadam, S.; Chen, R.H.; McAlpine, J.B. Novel triterpene sulfates from Fusarium compactum using a rhinovirus 3C protease inhibitor screen. J. Antibiot. 1996, 49, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harnedy, P.A.; FitzGerald, R.J. Bioactive proteins, peptides, and amino acids from macroalgae. J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srikong, W.; Mittraparp-arthorn, P.; Rattanaporn, O.; Bovornreungroj, N.; Bovornreungroj, P. Antimicrobial activity of seaweed extracts from Pattani, southeast cost of Thailand. Food Appl. Biosci. J. 2015, 3, 39–49. [Google Scholar]
- Oki, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Osajima, Y. Inhibitory effect of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors varies according to its origin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golbabaei, S.; Bazl, R.; Golestanian, S.; Nabati, R.; Omrany, R.B.; Yousefi, B.; Hajiaghaee, R.; Rezazadeh, S.; Amanlou, M. Urease inhibitory activities of β-boswellic acid derivatives. Daru 2013, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulati, V.; Harding, I.H.; Palombo, E.A. Enzyme inhibitory and antioxidant activities of traditional medicinal plants: Potential application in the management of hyperglycemia. BMC Complemnt. Altern. Med. 2012, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| C. No. | 13C (δ) | 1H (δ) | DEPT | C. No. | 13C (δ) | 1H (δ) | DEPT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 40.1 | 0.99, m; 1.71, m | CH2 | 16 | 31.7 | 1.35, m | CH2 |
| 2 | 28.0 | 1.57, m | CH2 | 17 | 50.4 | 1.63, m | CH |
| 3 | 79.6 | 3.16, m | CH | 18 | 180.1 | - | C |
| 4 | 41.9 | - | C | 19 | 15.1 | 1.03, s | CH3 |
| 5 | 56.9 | 0.73, m | CH | 20 | 39.6 | 1.67, m | CH |
| 6 | 19.4 | 1.56, m | CH2 | 21 | 16.7 | 0.88, d, J = 5.5 Hz | CH3 |
| 7 | 126.9 | 5.25, m | CH | 22 | 35.6 | 1.42, m | CH2 |
| 8 | 139.7 | - | C | 23 | 33.3 | 1.52, m | CH2 |
| 9 | 54.4 | 2.21, m | CH | 24 | 40.4 | 2.33, m | CH |
| 10 | 38.3 | - | C | 25 | 152.0 | - | C |
| 11 | 22.1 | 1.46, m | CH2 | 26 | 110.2 | 4.62/4.73, each d, J = 1.6 Hz | CH2 |
| 12 | 30.8 | 1.94, m | CH2 | 27 | 19.5 | 1.73, s | CH3 |
| 13 | 57.5 | - | C | 28 | 16.6 | 0.99, overlap | CH3 |
| 14 | 48.5 | 3.06, m | CH | 29 | 16.1 | 0.77, s | CH3 |
| 15 | 26.9 | 1.08, m | CH2 | 30 | 28.6 | 0.97, overlap | CH3 |
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, L.; Khan, A.L.; Al-Broumi, M.; Al-Harrasi, R.; Al-Kharusi, L.; Hussain, J.; Al-Harrasi, A. New Enzyme-Inhibitory Triterpenoid from Marine Macro Brown Alga Padina boergesenii Allender & Kraft. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15010019
Ali L, Khan AL, Al-Broumi M, Al-Harrasi R, Al-Kharusi L, Hussain J, Al-Harrasi A. New Enzyme-Inhibitory Triterpenoid from Marine Macro Brown Alga Padina boergesenii Allender & Kraft. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Liaqat, Abdul Latif Khan, Muhammad Al-Broumi, Rashid Al-Harrasi, Lubna Al-Kharusi, Javid Hussain, and Ahmed Al-Harrasi. 2017. "New Enzyme-Inhibitory Triterpenoid from Marine Macro Brown Alga Padina boergesenii Allender & Kraft" Marine Drugs 15, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15010019
APA StyleAli, L., Khan, A. L., Al-Broumi, M., Al-Harrasi, R., Al-Kharusi, L., Hussain, J., & Al-Harrasi, A. (2017). New Enzyme-Inhibitory Triterpenoid from Marine Macro Brown Alga Padina boergesenii Allender & Kraft. Marine Drugs, 15(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15010019







