Design and Synthesis of Analogues of Marine Natural Product Galaxamide, an N-methylated Cyclic Pentapeptide, as Potential Anti-Tumor Agent in Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
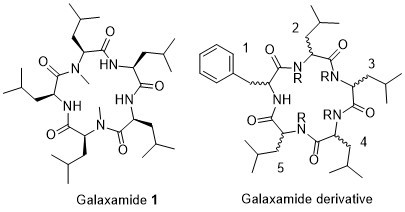
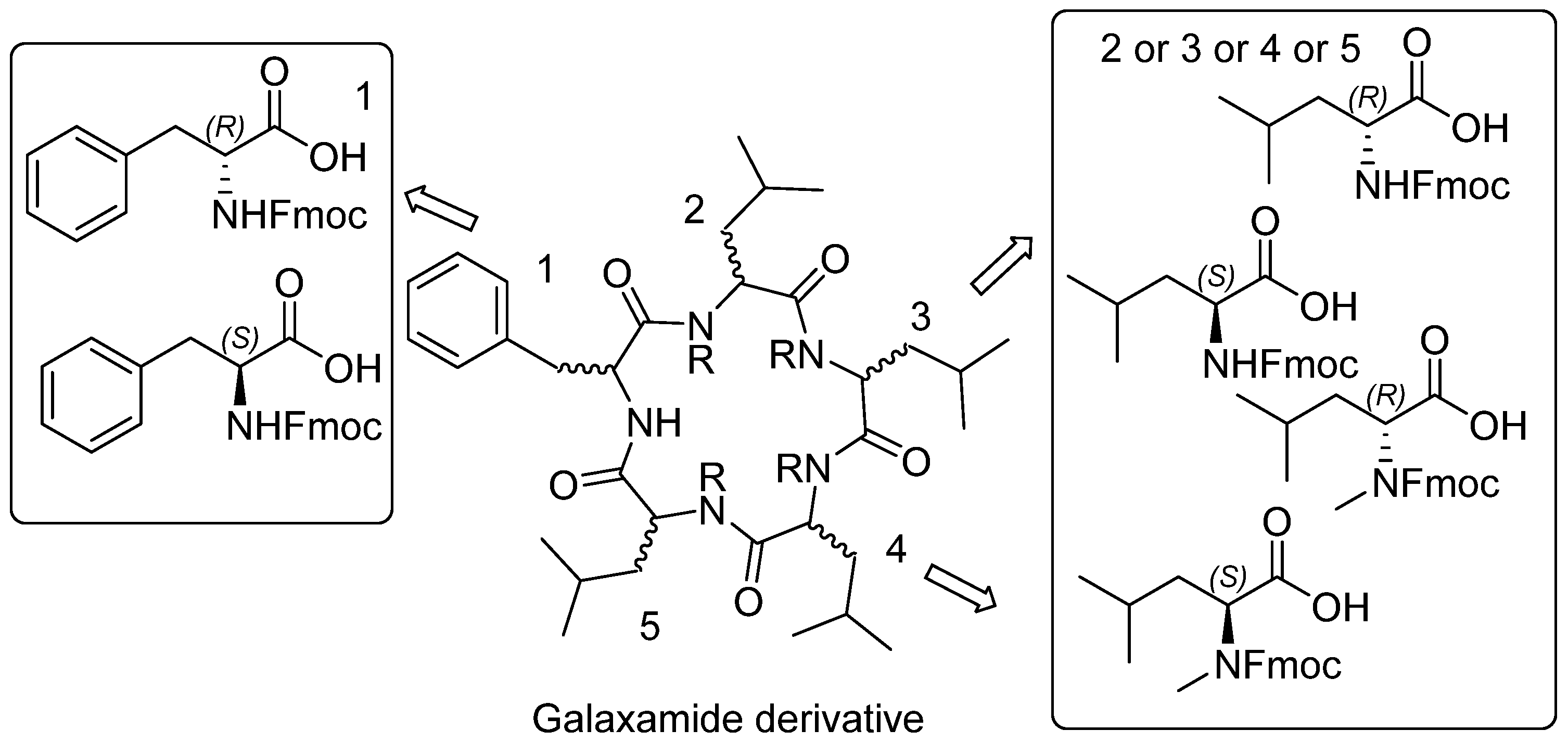
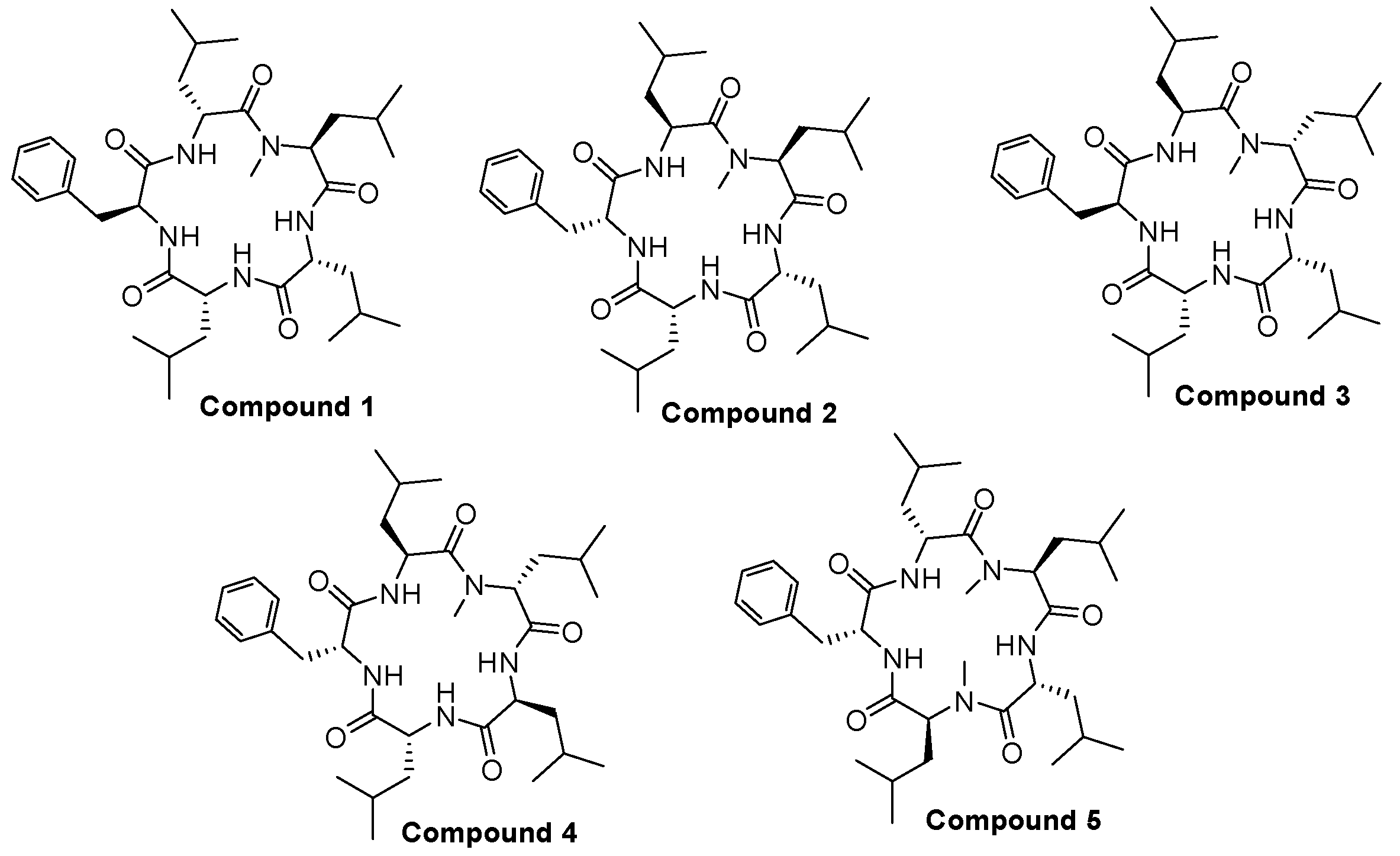
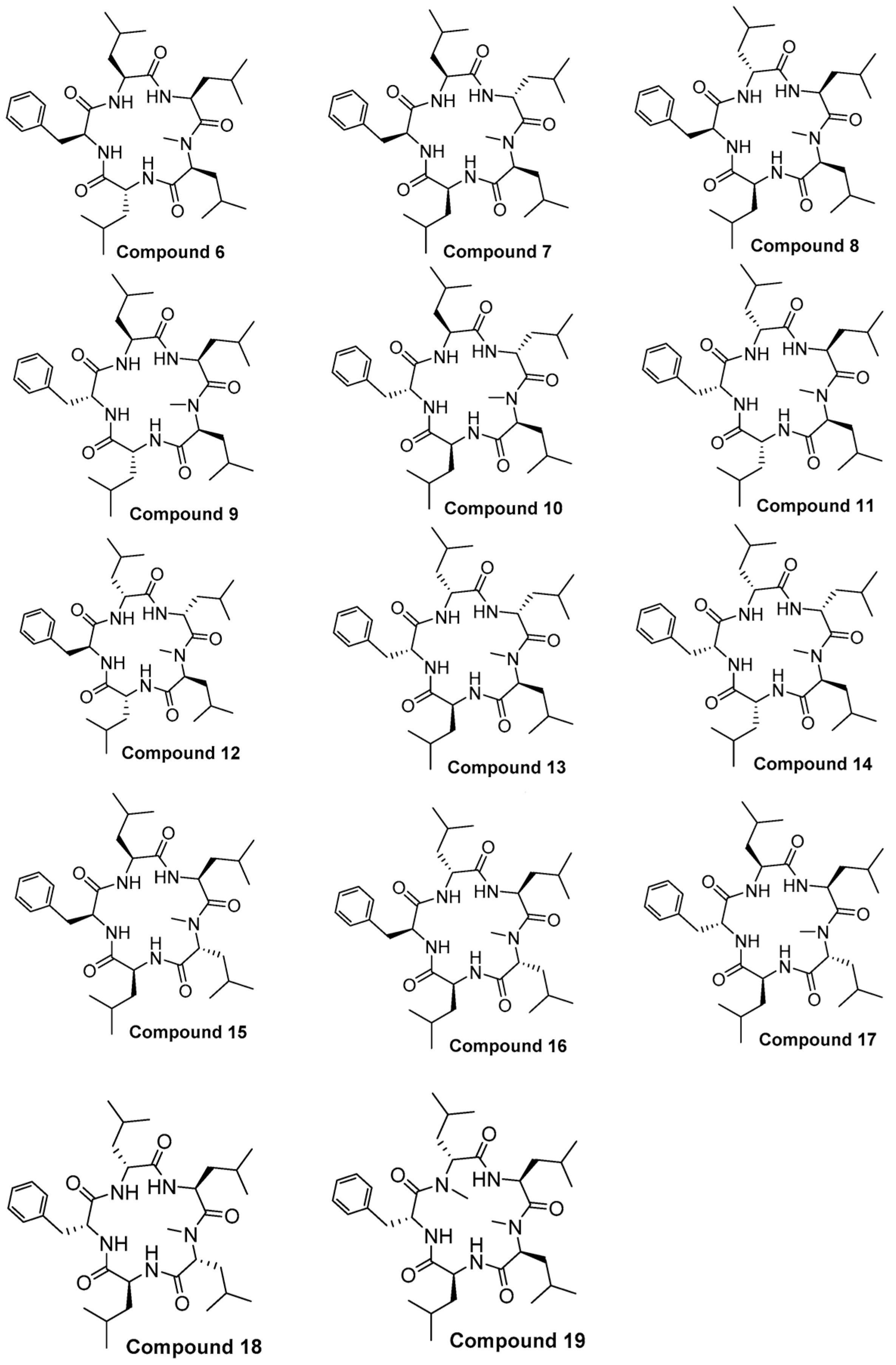
2.1. Chemistry
Structure of Macrocyclic Analogues
2.2. Biological Activity
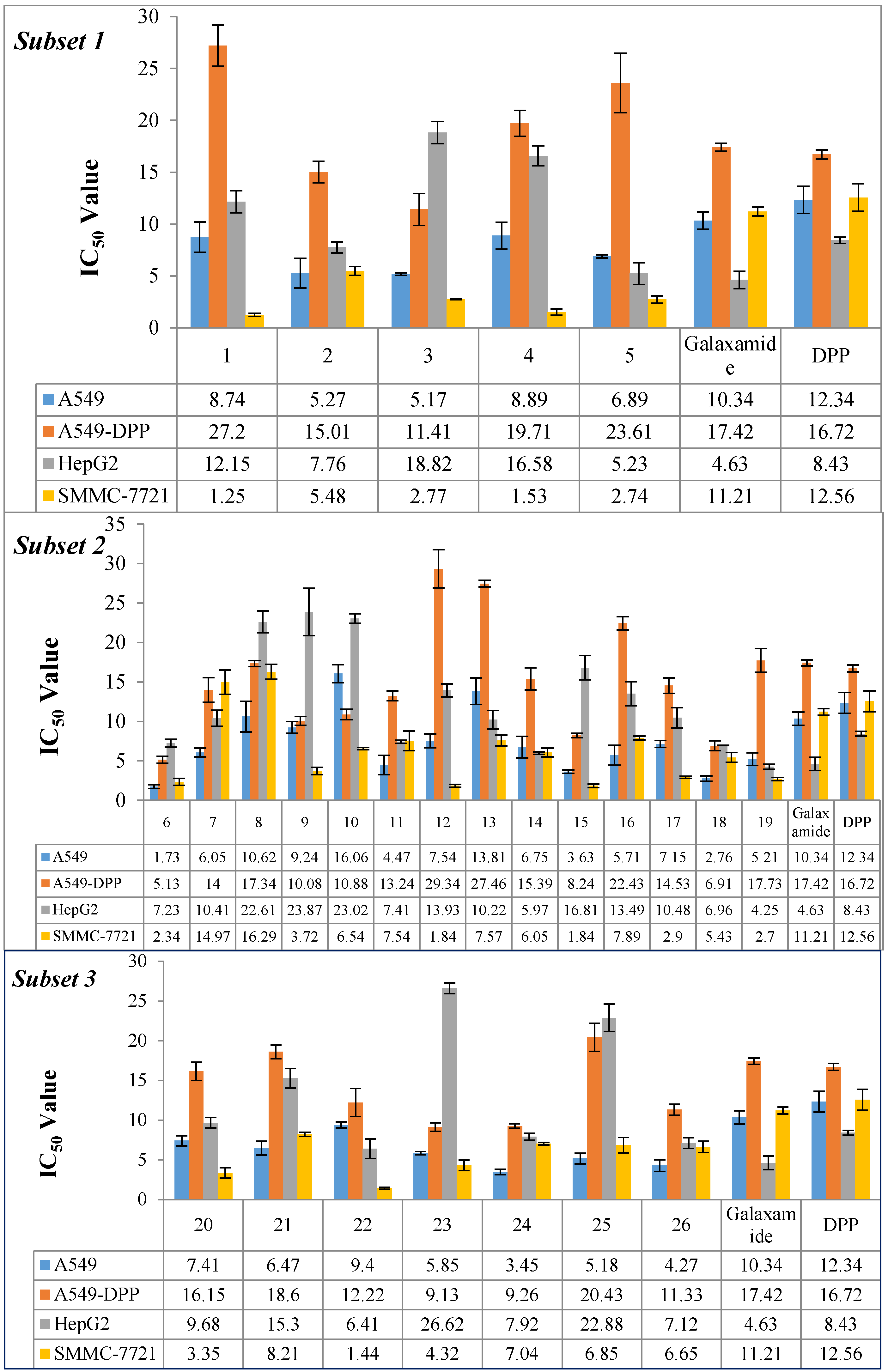
2.2.1. Inhibitory Activity of Galaxamide and Its Analogues
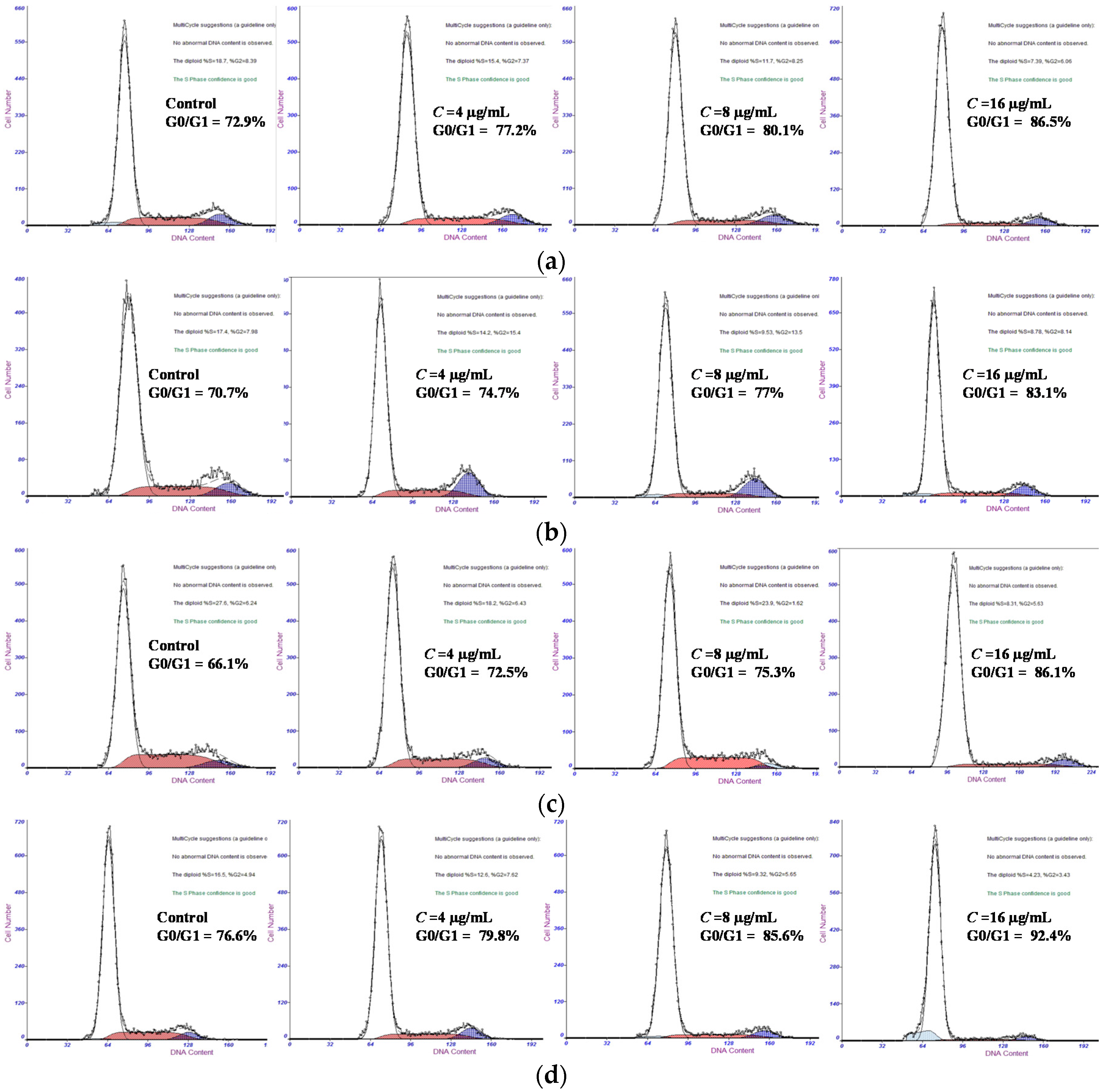
2.2.2. Galaxamide and Its Analogues Caused G0/G1 Arrest
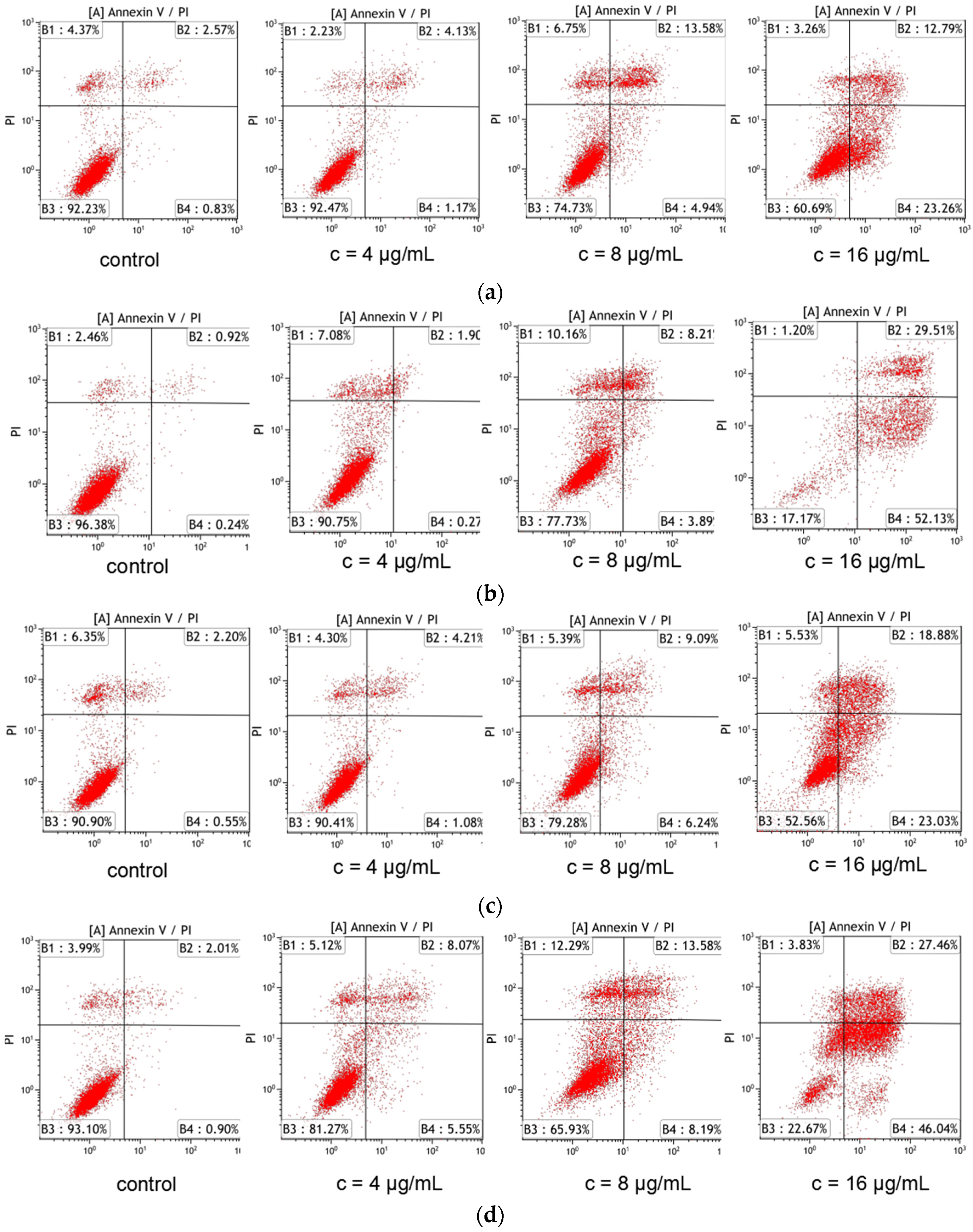
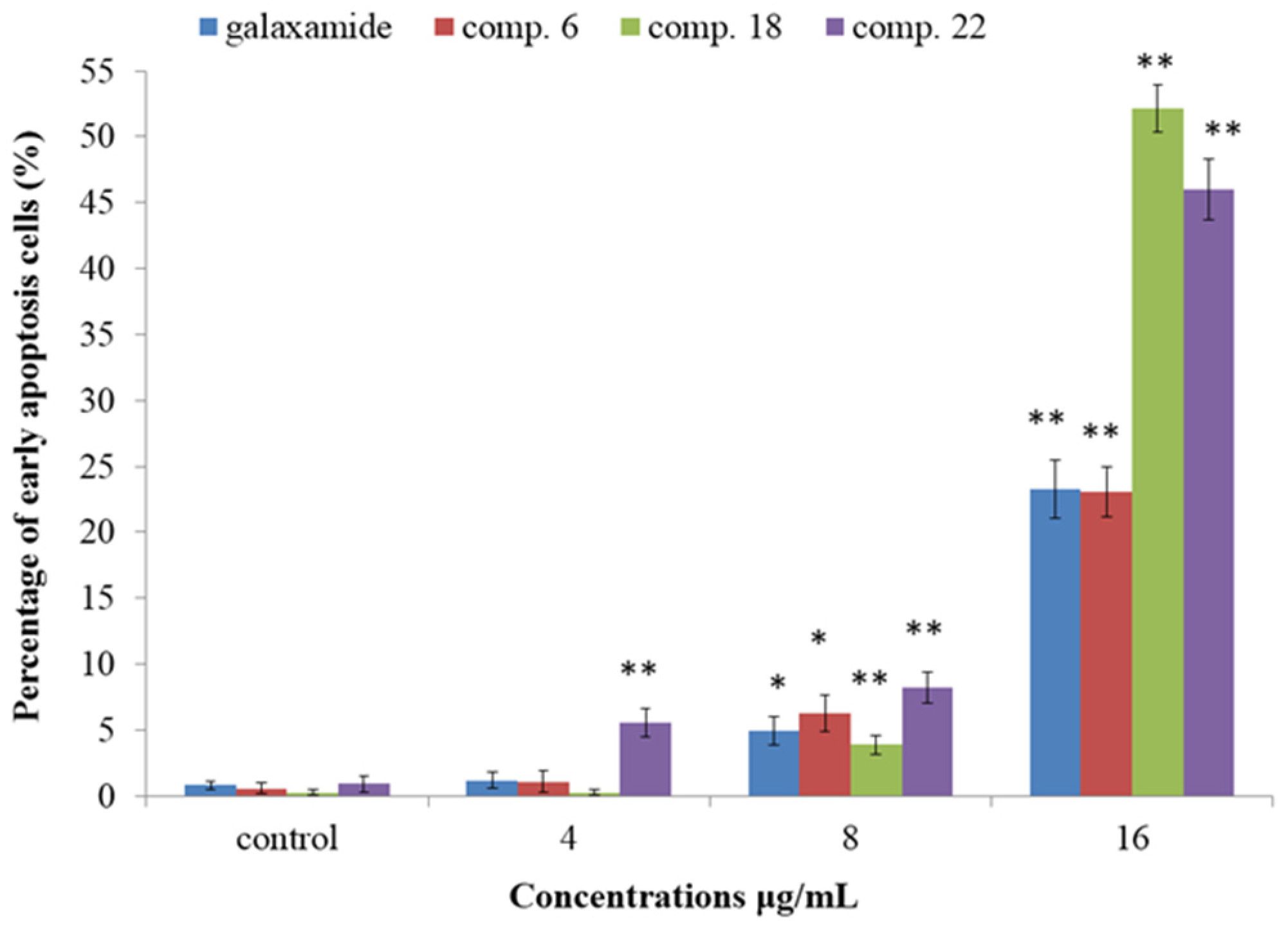
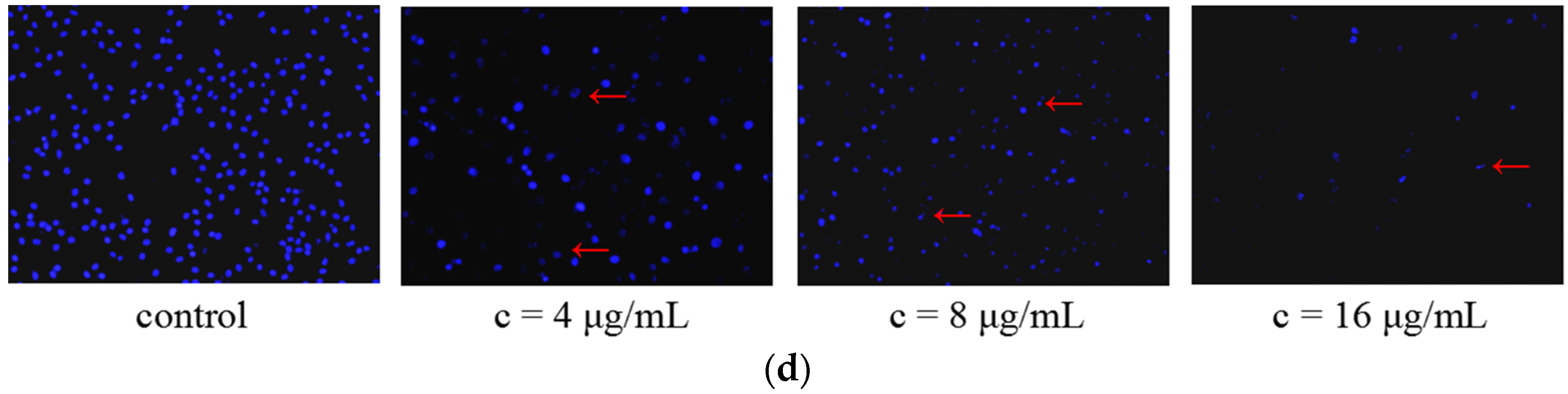
2.2.3. Galaxamide and Its Analogues Induced Apoptosis of SMMC-7721 Cells
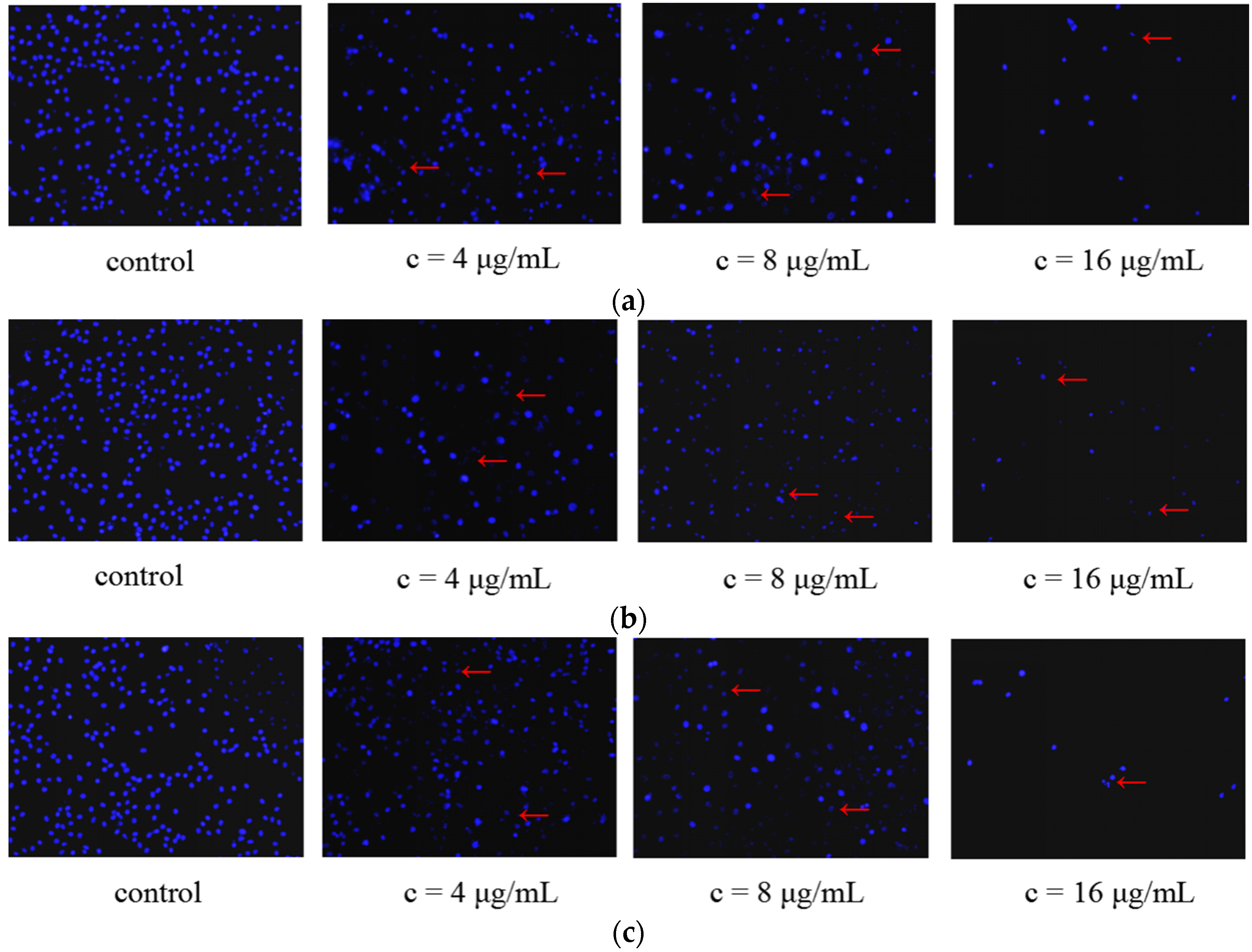
2.2.4. Morphological Changes of SMMC-7721 Cells Induced by the Treatment of Galaxamide and Its Analogues
3. Discussion
3.1. Structure-Activity Relationship
3.2. Mechanism of Apoptosis Pathway
4. Experimental Section
4.1. General
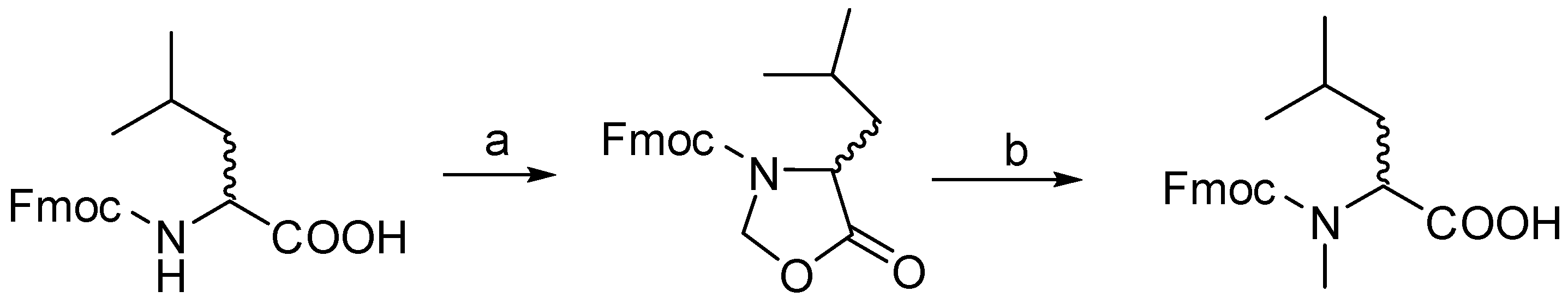
4.2. Procedure for d/l Fmoc-N-Me Leucine
4.2.1. Step-1 Synthesis of Oxazolidinones from Fmoc Leu
4.2.2. Step-2 Synthesis of N-methylated Fmoc Leu from Oxazolidinones
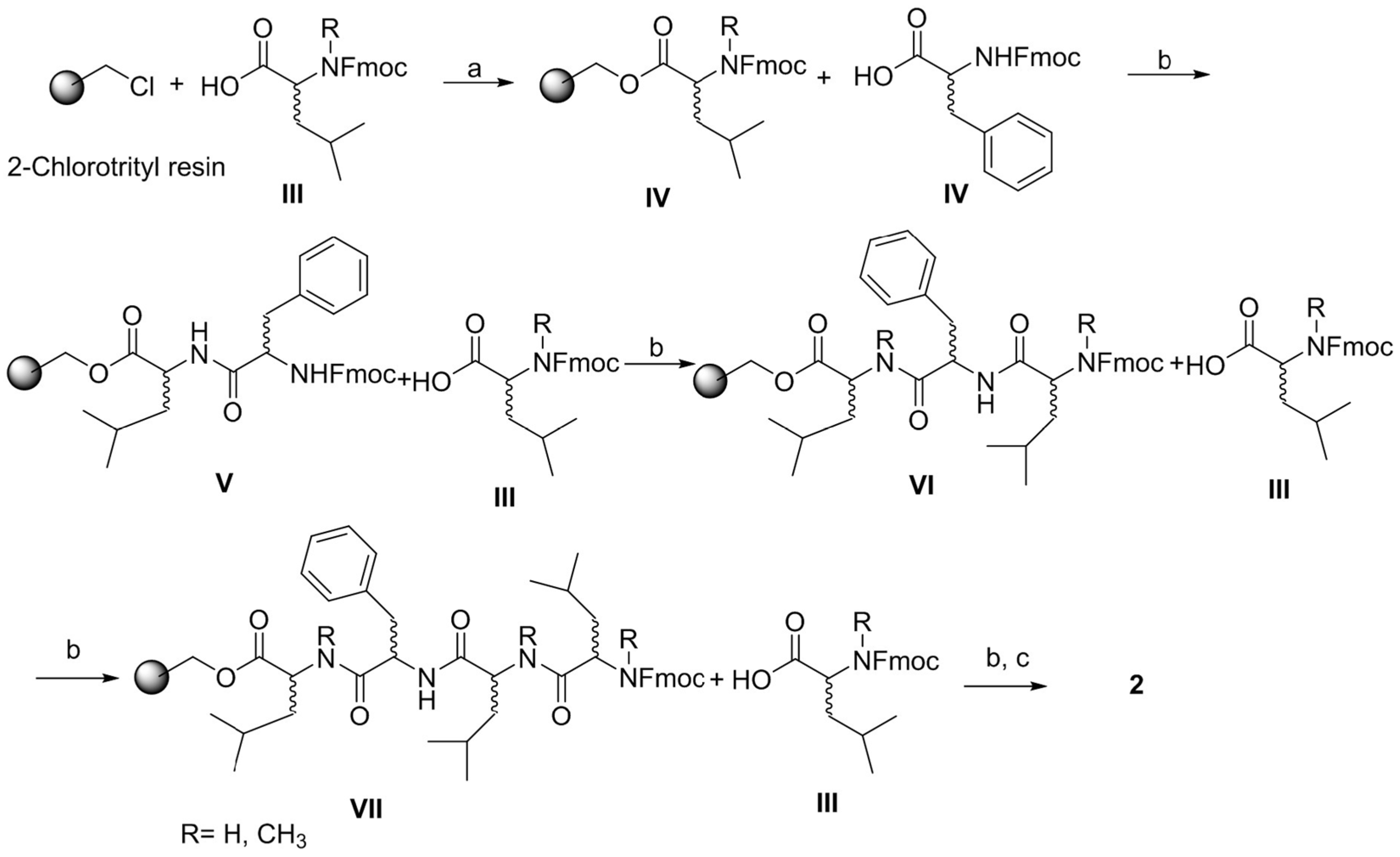
4.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Pentapeptides-COOH
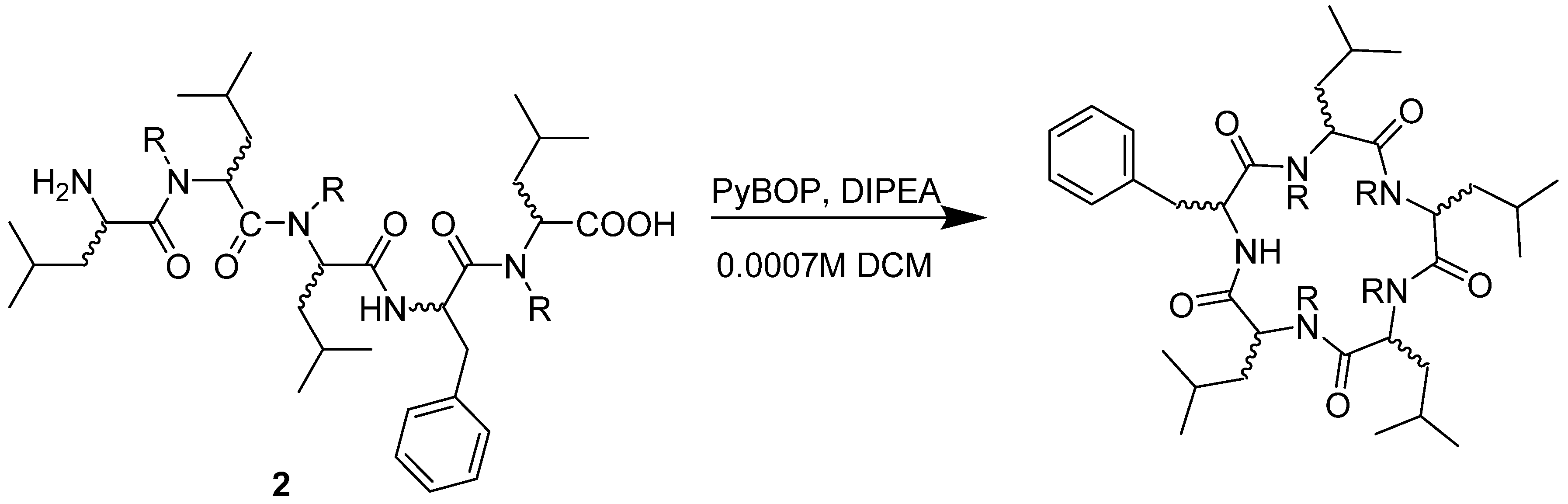
4.4. General Procedure for Macrocyclisation Reaction
4.5. Spectral Data
4.6. In Vitro Anti-Tumor Activity
4.6.1. Maintenance of Cell Culture
4.6.2. MTT Assay
4.6.3. Cell Apoptotic Analysis
4.6.4. Cell Morphological Observation
4.6.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aneiros, A.; Garateix, A. Bioactive peptides from marine sources: Pharmacological properties and isolation procedures. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 803, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, A. Strategies for discovering drugs from previously unexplored natural products. Drug Discov. Today 2000, 5, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Gui, Y.; Chen, L.; Yuan, G.; Lu, H.-Z.; Xu, X. Use of natural products as chemical library for drug discovery and network pharmacology. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, C.A.; Pearce, G.; Scheer, J.; Moura, D.S. Polypeptide hormones. Plant Cell 2002, 14, S251–S264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, C.; Marchiò, M.; Timofeeva, E.; Biagini, G. Neuroactive peptides as putative mediators of antiepileptic ketogenic diets. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, M.S. Role of peptide growth factors in the prostate: A review. Urology 1993, 42, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutertre, S.; Lewis, R.J. Use of venom peptides to probe ion channel structure and function. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 13315–13320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yount, N.Y.; Yeaman, M.R. Emerging themes and therapeutic prospects for anti-infective peptides. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 52, 337–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fosgerau, K.; Hoffmann, T. Peptide therapeutics: Current status and future directions. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, F.R.; Kay, A.B.; Larche, M. The potential of peptide immunotherapy in allergy and asthma. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2002, 2, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luban, S.; Li, Z.G. Citrullinated peptide and its relevance to rheumatoid arthritis: An update. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 13, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, K.X.; Jiao, W.H.; Yang, F.; Li, J.; Wang, S.P.; Li, Y.S.; Han, B.N.; Lin, H.W. Reniochalistatins A–E, cyclic peptides from the marine sponge Reniochalina stalagmitis. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2678–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, T.-S.; Kim, S.-K. Down-regulation of histamine-induced endothelial cell activation as potential anti-atherosclerotic activity of peptides from Spirulina maxima. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 50, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De León, D.D.; Crutchlow, M.F.; Ham, J.-Y.N.; Stoffers, D.A. Role of glucagon-like peptide-1 in the pathogenesis and treatment of diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 38, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Salhy, M.; Mazzawi, T.; Gundersen, D.; Hatlebakk, J.G.; Hausken, T. The role of peptide YY in gastrointestinal diseases and disorders (review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zampella, A.; Sepe, V.; Luciano, P.; Bellotta, F.; Monti, M.C.; D’Auria, M.V.; Jepsen, T.; Petek, S.; Adeline, M.T.; Laprevote, O.; et al. Homophymine A, an anti-HIV cyclodepsipeptide from the sponge Homophymiasp. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 5319–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onishi, J.; Meinz, M.; Thompson, J.; Curotto, J.; Dreikorn, S.; Rosenbach, M.; Douglas, C.; Abruzzo, G.; Flattery, A.; Kong, L.; et al. Discovery of novel antifungal (1,3)-β-d-glucan synthase inhibitors. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, C.B.; Cho, Y.S.; Je, J.Y. Purification and anti-inflammatory action of tripeptide from salmon pectoral fin byproduct protein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miljanich, G.P. Ziconotide: Neuronal calcium channel blocker for treating severe chronic pain. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 3029–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlig, T.; Kyprianou, T.; Martinelli, F.G.; Oppici, C.A.; Heiligers, D.; Hills, D.; Calvo, X.R.; Verhaert, P. The emergence of peptides in the pharmaceutical business: From exploration to exploitation. EuPA Open Proteom. 2014, 4, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchwald, H.; Dorman, R.B.; Rasmus, N.F.; Michalek, V.N.; Landvik, N.M.; Ikramuddin, S. Effects on GLP-1, PYY, and leptin by direct stimulation of terminal ileum and cecum in humans: Implications for ileal transposition. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2014, 10, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loffet, A. Peptides as drugs: Is there a market? J. Pept. Sci. 2002, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlieghe, P.; Lisowski, V.; Martinez, J.; Khrestchatisky, M. Synthetic therapeutic peptides: Science and market. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L. Peptide-Based Drug Development. Mod. Chem. Appl. 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lax, R. The future of peptide development in the pharmaceutical industry. PharManuf. Int. Pept. Rev. 2010, 2, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Gu, W.; Lo, D.; Ding, X.Z.; Ujiki, M.; Adrian, T.E.; Soff, G.A.; Silverman, R.B. N-methylsansalvamide a peptide analogues. Potent new antitumor agents. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 3630–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, P.S.; McGuire, K.L.; McAlpine, S.R. Identification of Sansalvamide a analog potent against pancreatic cancer cell lines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 5072–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ujiki, M.B.; Milam, B.; Ding, X.Z.; Roginsky, A.B.; Salabat, M.R.; Talamonti, M.S.; Bell, R.H.; Gu, W.; Silverman, R.B.; Adrian, T.E. A novel peptide sansalvamide analogue inhibits pancreatic cancer cell growth through G0/G1 cell-cycle arrest. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 340, 1224–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belofsky, G.N.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Sansalvamide: A new cytotoxic cyclic depsipeptide produced by a marine fungus of the genus Fusarium. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 2913–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styers, T.J.; Kekec, A.; Rodriguez, R.; Brown, J.D.; Cajica, J.; Pan, P.-S.; Parry, E.; Carroll, C.L.; Medina, I.; Corral, R.; et al. Synthesis of Sansalvamide A derivatives and their cytotoxicity in the colon cancer cell line HT-29. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 5625–5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otrubova, K.; Styers, T.J.; Pan, P.-S.; Rodriguez, R.; McGuire, K.L.; McAlpine, S.R. Synthesis and novel structure-activity relationships of potent Sansalvamide A derivatives. Chem. Commun. 2006, 9, 1033–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, C.L.; Johnston, J.V.C.; Kekec, A.; Brown, J.D.; Parry, E.; Cajica, J.; Medina, I.; Cook, K.M.; Corral, R.; Pan, P.-S.; et al. Synthesis and cytotoxicity of novel Sansalvamide A derivatives. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 3481–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otrubova, K.; Lushington, G.; Vander Velde, D.; McGuire, K.; McAlpine, S.R. Comprehensive study of Sansalvamide A derivatives and their structure–activity relationships against drug-resistant colon cancer cell lines. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 530–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, R.A.; Pan, P.-S.; Pan, C.-M.; Ravula, S.; Lapera, S.; Singh, E.K.; Styers, T.J.; Brown, J.D.; Cajica, J.; Parry, E.; et al. Synthesis of second-generation Sansalvamide A derivatives: Novel templates as potential antitumor agents. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 1980–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.-J.; Liao, X.-J.; Xu, S.-H.; Diao, J.-Z.; Du, B.; Zhou, X.-L.; Pan, S.-S. Isolation, structure determination, and synthesis of galaxamide, a rare cytotoxic cyclic pentapeptide from a marine algae Galaxaura filamentosa. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 4569–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Liao, X.; Qui, S.; Liu, Z.; Du, B.; Xu, S. Paper synthesis, cytotoxicity and apoptosis induction in human tumor cells by galaxamide and its analogues. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4512–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Govender, T.; Norstrom, T.; Arvidsson, P.I. An improved synthesis of Fmoc-N-methyl-α-amino acids. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 6918–6920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, S.T.; Leo Benoiton, N. N-Methylamino acids in peptide synthesis. V. The synthesis of N-tert-butyloxycarbonyl, N-methylamino acids by N-methylation. Can. J. Chem. 1977, 55, 906–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jiang, X.; Ye, Y.H.; Fan, C.; Romoff, T.; Goodman, M. 3-(Diethoxyphosphoryloxy)-1,2,3-benzotriazin-4(3H)-one (DEPBT): A new coupling reagent with remarkable resistance to racemization. Org. Lett. 1990, 1, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, E.; Colescott, R.L.; Bossinger, C.D.; Cook, P.I. Color test for detection of free terminal amino groups in the solid-phase synthesis of peptides. Anal. Biochem. 1970, 34, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojkovsky, T. Detection of secondary amines on solid phase. Pept. Res. 1995, 8, 236–237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thakkar, A.; Trinh, T.B.; Pei, D. Global Analysis of Peptide Cyclization Efficiency. ACS Comb. Sci. 2013, 15, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hengartner, M.O. The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 2000, 407, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.-M.; Zhao, L.-M.; Chen, X.-Q.; Zeng, G.-Z.; Tan, N.-H. Rubipodanin A, the first natural N-desmonomethyl rubiaceae-type cyclopeptide from Rubia podantha, indicating an important role of the N9-methyl group in the conformation and bioactivity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.-Y.; Chen, W.; Fan, J.-T.; Song, R.; Wang, L.; Gu, Y.-H.; Zeng, G.-Z.; Shen, Y.; Wu, X.-F.; Tan, N.-H.; et al. Plant cyclopeptide RA-V kills human breast cancer cells by inducing mitochondria-mediated apoptosis through blocking PDK1–AKT interaction. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 267, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucci, B.; Kasten, M.; Giordano, A. Cell cycle and apoptosis. Neoplasia 2000, 2, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, G.I.; Harper, J.W. Anticancer drug targets: Cell cycle and checkpoint control. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridman, J.S.; Lowe, S.W. Control of apoptosis by p53. Oncogene 2003, 22, 9030–9040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evan, G.I.; Vousden, K.H. Proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature 2001, 411, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lunagariya, J.; Zhong, S.; Chen, J.; Bai, D.; Bhadja, P.; Long, W.; Liao, X.; Tang, X.; Xu, S. Design and Synthesis of Analogues of Marine Natural Product Galaxamide, an N-methylated Cyclic Pentapeptide, as Potential Anti-Tumor Agent in Vitro. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14090161
Lunagariya J, Zhong S, Chen J, Bai D, Bhadja P, Long W, Liao X, Tang X, Xu S. Design and Synthesis of Analogues of Marine Natural Product Galaxamide, an N-methylated Cyclic Pentapeptide, as Potential Anti-Tumor Agent in Vitro. Marine Drugs. 2016; 14(9):161. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14090161
Chicago/Turabian StyleLunagariya, Jignesh, Shenghui Zhong, Jianwei Chen, Defa Bai, Poonam Bhadja, Weili Long, Xiaojian Liao, Xiaoli Tang, and Shihai Xu. 2016. "Design and Synthesis of Analogues of Marine Natural Product Galaxamide, an N-methylated Cyclic Pentapeptide, as Potential Anti-Tumor Agent in Vitro" Marine Drugs 14, no. 9: 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14090161
APA StyleLunagariya, J., Zhong, S., Chen, J., Bai, D., Bhadja, P., Long, W., Liao, X., Tang, X., & Xu, S. (2016). Design and Synthesis of Analogues of Marine Natural Product Galaxamide, an N-methylated Cyclic Pentapeptide, as Potential Anti-Tumor Agent in Vitro. Marine Drugs, 14(9), 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14090161