Immunomodulatory Effects of the Mycosporine-Like Amino Acids Shinorine and Porphyra-334
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
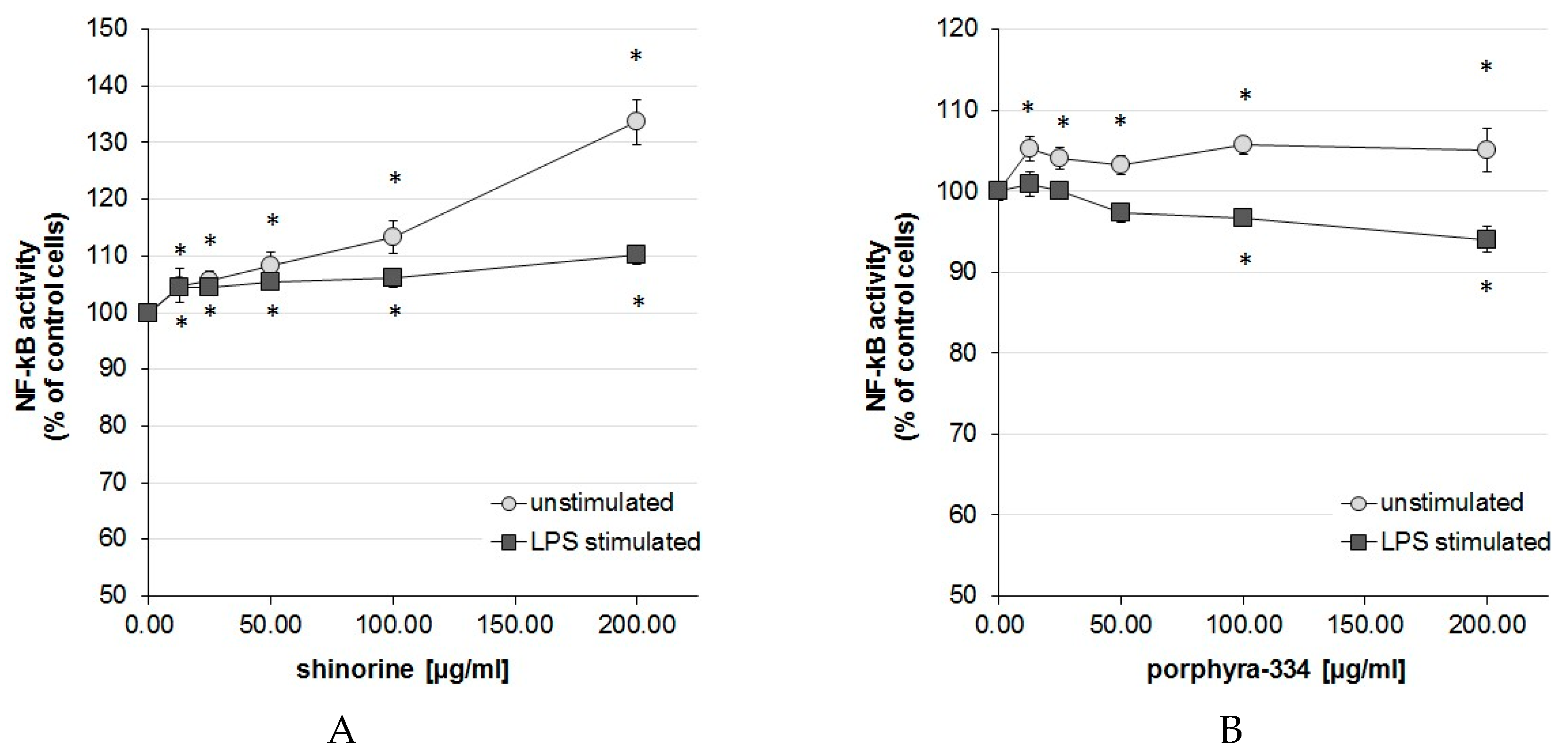
2.1. Activation Degree of the Central Inflammation Marker NF-κB
2.2. Expression of NFKB1 and IL1B
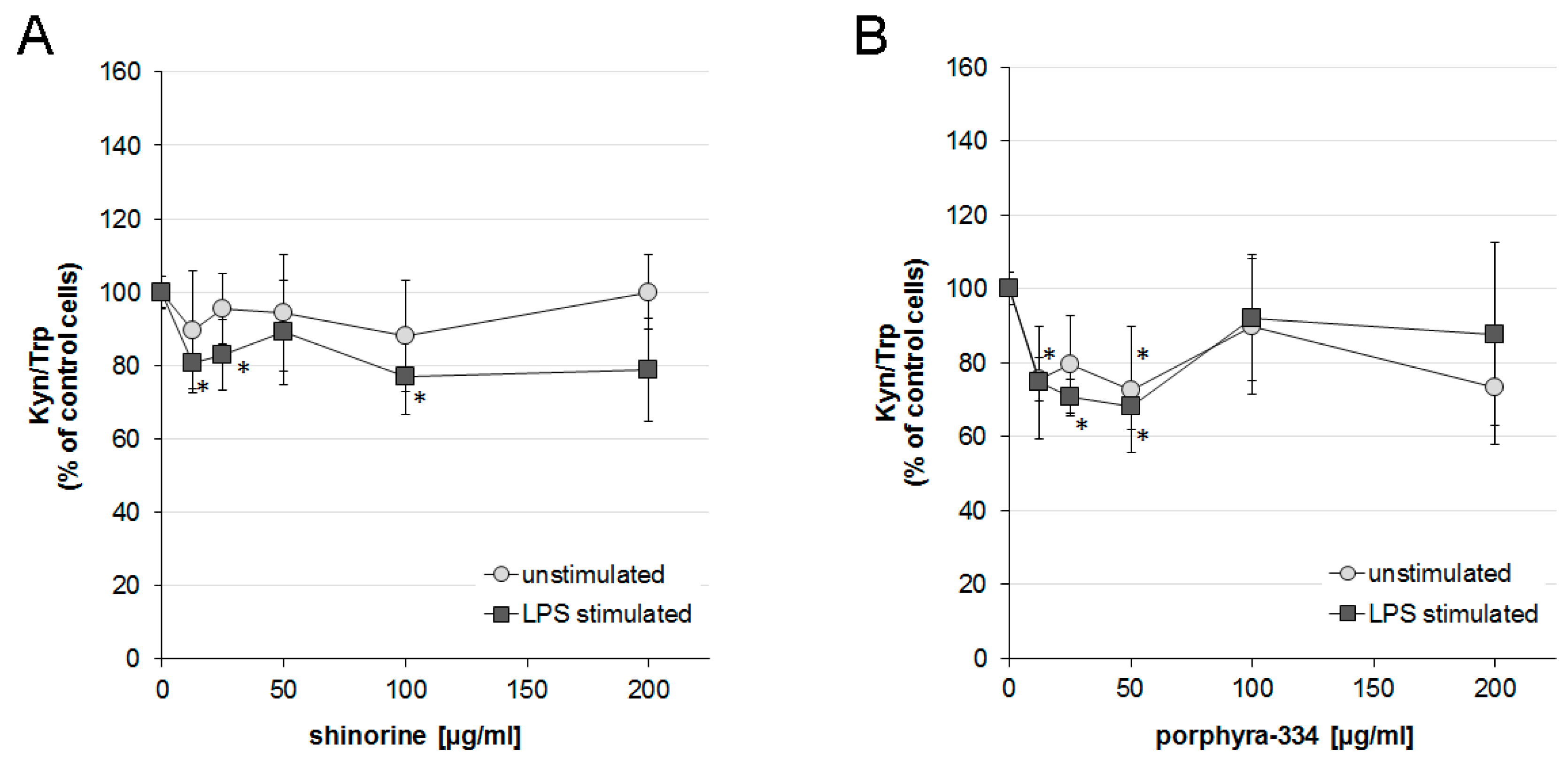
2.3. Effects of Shinorine and Porphyra-334 on Tryptophan Metabolism
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Preparation
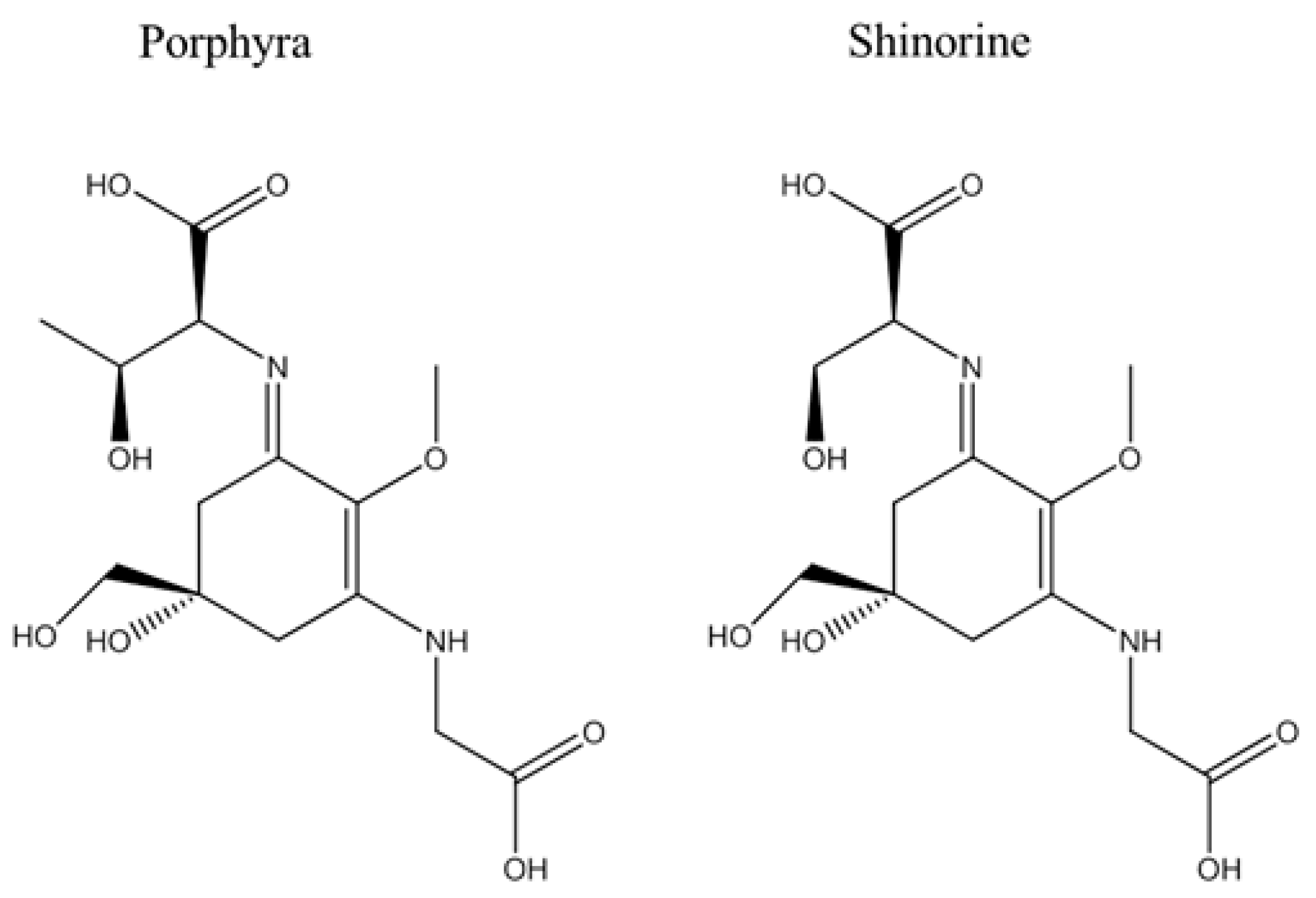
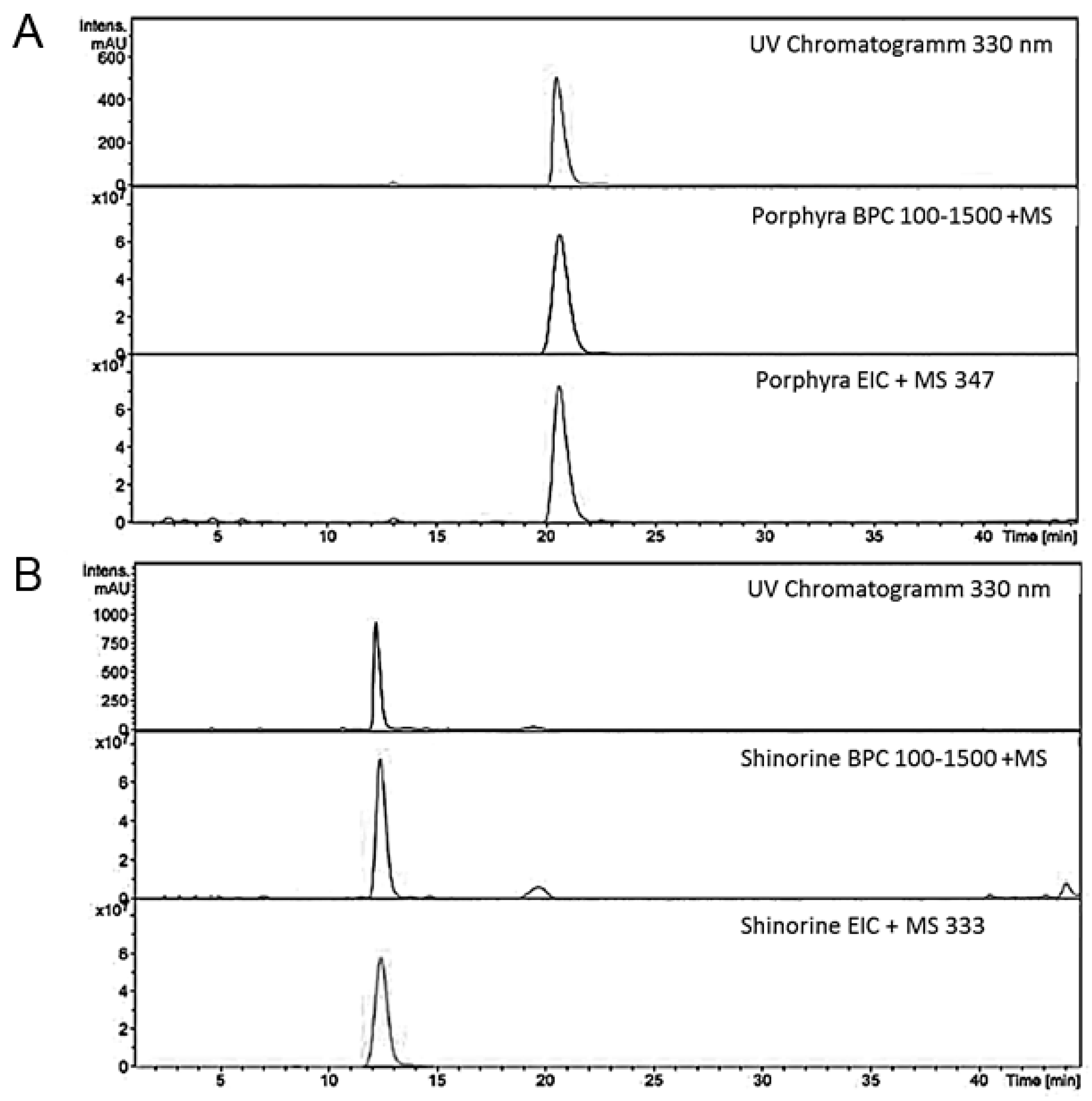
4.2. Structural Analysis of MAA
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Measurement of NF-κB Activation and IDO-1 Activity
4.5. Expression of NFKB1 and IL1B
4.6. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AP1 | activator protein |
| IDO-1 | indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase |
| IFN-α | interferon gamma |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MAA | mycosporine-like amino acid |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa B |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SEAP | secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase |
References
- Carreto, J.I.; Carignan, M.O. Mycosporine-like amino acids: Relevant secondary metabolites. Chemical and ecological aspects. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 387–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsten, U.; West, J.A. Living in the intertidal zone—Seasonal effects on heterosides and sun-screen compounds in the red alga Bangia atropurpurea (Bangiales). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2000, 254, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabani, P.; Singh, O.V. Radiation-resistant extremophiles and their potential in biotechnology and therapeutics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, S.; Zille, A.; Micheletti, E.; Moradas-Ferreira, P.; de, P.R.; Tamagnini, P. Complexity of cyanobacterial exopolysaccharides: Composition, structures, inducing factors and putative genes involved in their biosynthesis and assembly. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 33, 917–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misonou, T.; Saitoh, J.; Oshiba, S.; Tokitomo, Y.; Maegawa, M.; Inoue, Y.; Hori, H.; Sakurai, T. UV-absorbing substance in the red alga Porphyra yezoensis (Bangiales, Rhodophyta) block thymine photodimer production. Mar. Biotechnol. 2003, 5, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, A.; Gostner, J.; Fuchs, J.E.; Chaita, E.; Aligiannis, N.; Skaltsounis, L.; Ganzera, M. Inhibition of Collagenase by Mycosporine-like Amino Acids from Marine Sources. Planta Med. 2015, 81, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.J.; Li, X.M.; Wang, B.G. Highly brominated mono- and bis-phenols from the marine red alga Symphyocladia latiuscula with radical-scavenging activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1210–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colacevich, A.; Caruso, T.; Borghini, F.; Bargagli, R. Photosynthetic pigments in soils from northern Victoria Land (continental Antarctica) as proxies for soil algal community structure and function. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 2105–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S.C.; Alonso-Varona, A.; Palomares, T.; Zubillaga, V.; Labidi, J.; Bulone, V. Exploiting mycosporines as natural molecular sunscreens for the fabrication of UV-absorbing green materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 16558–16564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, P.D.; Huang, B.W.; Tsuji, Y. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis and redox regulation in cellular signaling. Cell Signal. 2012, 24, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, T. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Crosstalk in NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Hayden, M.S. Celebrating 25 years of NF-kappaB research. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asehnoune, K.; Strassheim, D.; Mitra, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Abraham, E. Involvement of reactive oxygen species in Toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of NF-kappaB. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 2522–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, E.R.; Werner-Felmayer, G.; Fuchs, D.; Hausen, A.; Reibnegger, G.; Wachter, H. Parallel induction of tetrahydrobiopterin biosynthesis and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity in human cells and cell lines by interferon-γ. Biochem. J. 1989, 262, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, D.; Forsman, A.; Hagberg, L.; Larsson, M.; Norkrans, G.; Reibnegger, G.; Werner, E.R.; Wachter, H. Immune activation and decreased tryptophan in patients with HIV-1 infection. J. Interferon Res. 1990, 10, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellor, A.L.; Munn, D.; Chandler, P.; Keskin, D.; Johnson, T.; Marshall, B.; Jhaver, K.; Baban, B. Tryptophan catabolism and T cell responses. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2003, 527, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gostner, J.M.; Becker, K.; Fuchs, D.; Sucher, R. Redox regulation of the immune response. Redox Rep. 2013, 18, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroecksnadel, K.; Fischer, B.; Schennach, H.; Weiss, G.; Fuchs, D. Antioxidants suppress Th1-type immune response in vitro. Drug Metab. Lett. 2007, 1, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ten, R.M.; Paya, C.V.; Israel, N.; Le, B.O.; Mattei, M.G.; Virelizier, J.L.; Kourilsky, P.; Israel, A. The characterization of the promoter of the gene encoding the p50 subunit of NF-kappaB indicates that it participates in its own regulation. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hiscott, J.; Marois, J.; Garoufalis, J.; D’Addario, M.; Roulston, A.; Kwan, I.; Pepin, N.; Lacoste, J.; Nguyen, H.; Bensi, G. Characterization of a functional NF-kappaB site in the human interleukin 1 beta promoter: Evidence for a positive autoregulatory loop. Mol. Cell Biol. 1993, 13, 6231–6240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.; Park, S.J.; Kim, I.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Nam, T.J. Protective effect of porphyra-334 on UVA-induced photoaging in human skin fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Coba, F.; Aguilera, J.; Figueroa, F.L.; de Gálvez, M.V.; Herrera, E. Antioxidant activity of mycosporine-like amino acids isolated from three red macroalgae and one marine lichen. J. Appl. Phycol. 2009, 21, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Coba, F.; Aguilera, J.; de Gálvez, M.V.; Alvarez, M.; Gallego, E.; Figueroa, F.L.; Herrera, E. Prevention of the ultraviolet effects on clinical and histopathological changes, as well as the heat shock protein-70 expression in mouse skin by topical application of algal UV-absorbing compounds. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2009, 55, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, D.; Schürch, C.; Zülli, F.; Nissen, H.P.; Prieur, H. Mycosporine-like amino acids: Natural UV-screening compounds from red algae to protect the skin against photoaging. SOFW J. 2003, 129, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, G.; Babele, P.K.; Shahi, S.K.; Sinha, R.P.; Tyagi, M.B.; Kumar, A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using cell extracts of Anabaena doliolum and screening of its antibacterial and antitumor activity. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 1354–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llewellyn, C.A.; Airs, R.L. Distribution and abundance of MAAs in 33 species of microalgae across 13 classes. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1273–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richa; Sinha, R.P. Biochemical characterization of sunscreening mycosporine-like amino acids from two Nostoc species inhabiting diverse habitats. Protoplasma 2015, 252, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancino, A.; Lawrence, T. Nuclear factor-kappaB and tumor-associated macrophages. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartarotti, B.; Sommaruga, R. The effect of different methanol concentrations and temperatures on the extraction of mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) in algae and zooplankton. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2002, 154, 691–703. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, A.; Becker, K.; Karsten, U.; Remias, D.; Ganzera, M. Analysis of Mycosporine-Like Amino Acids in Selected Algae and Cyanobacteria by Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography and a Novel MAA from the Red Alga Catenella repens. Mar. Drugs 2002, 154, 6291–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carignan, M.O.; Cardozo, K.H.; Oliveira-Silva, D.; Colepicolo, P.; Carreto, J.I. Palythine-threonine, a major novel mycosporine-like amino acid (MAA) isolated from the hermatypic coral Pocillopora capitata. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2009, 94, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroecksnadel, S.; Jenny, M.; Kurz, K.; Klein, A.; Ledochowski, M.; Uberall, F.; Fuchs, D. LPS-induced NF-kappaB expression in THP-1Blue cells correlates with neopterin production and activity of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 399, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widner, B.; Werner, E.R.; Schennach, H.; Wachter, H.; Fuchs, D. Simultaneous measurement of serum tryptophan and kynurenine by HPLC. Clin. Chem. 1997, 43, 2424–2426. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maess, M.B.; Sendelbach, S.; Lorkowski, S. Selection of reliable reference genes during THP-1 monocyte differentiation into macrophages. BMC Mol. Biol. 2010, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Horgan, G.W.; Dempfle, L. Relative expression software tool (REST©) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| (A) LPS-Treated Compared to Control | ||
| - | NFKB1 | IL1B |
| expression | 3.297 | 92.893 |
| std. error | 2.364–5.062 | 9.594–351.935 |
| p-value | 0.000 * | 0.000 * |
| - | - | - |
| (B) MAA-Treated Compared to Control | ||
| shinorine | ||
| - | NFKB1 | IL1B |
| expression | 1.034 | 1.193 |
| std. error | 0.895–1.222 | 0.132–7.152 |
| p-value | 0.568 | 0.777 |
| porphyra-334 # | ||
| - | NFKB1 | IL1B |
| expression | 1.153 | 1.193 |
| std. error | 1.033–1.289 | 0.916–1.572 |
| p-value | 0.036 * | 0.325 |
| - | - | - |
| (C) MAA + LPS-Treated Compared to LPS | ||
| shinorine (+ LPS) | ||
| - | NFKB1 | IL1B |
| expression | 0.823 | 1.017 |
| std. error | 0.599–1.109 | 0.458–2.479 |
| p-value | 0.178 | 0.958 |
| porphyra-334 (+ LPS) # | ||
| - | NFKB1 | IL1B |
| expression | 0.851 | 1.373 |
| std. error | 0.650–1.114 | 0.537–3.605 |
| p-value | 0.249 | 0.466 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Becker, K.; Hartmann, A.; Ganzera, M.; Fuchs, D.; Gostner, J.M. Immunomodulatory Effects of the Mycosporine-Like Amino Acids Shinorine and Porphyra-334. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14060119
Becker K, Hartmann A, Ganzera M, Fuchs D, Gostner JM. Immunomodulatory Effects of the Mycosporine-Like Amino Acids Shinorine and Porphyra-334. Marine Drugs. 2016; 14(6):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14060119
Chicago/Turabian StyleBecker, Kathrin, Anja Hartmann, Markus Ganzera, Dietmar Fuchs, and Johanna M. Gostner. 2016. "Immunomodulatory Effects of the Mycosporine-Like Amino Acids Shinorine and Porphyra-334" Marine Drugs 14, no. 6: 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14060119
APA StyleBecker, K., Hartmann, A., Ganzera, M., Fuchs, D., & Gostner, J. M. (2016). Immunomodulatory Effects of the Mycosporine-Like Amino Acids Shinorine and Porphyra-334. Marine Drugs, 14(6), 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14060119






