Synthesis and Anti-Influenza A Virus Activity of 6′-amino-6′-deoxy-glucoglycerolipids Analogs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
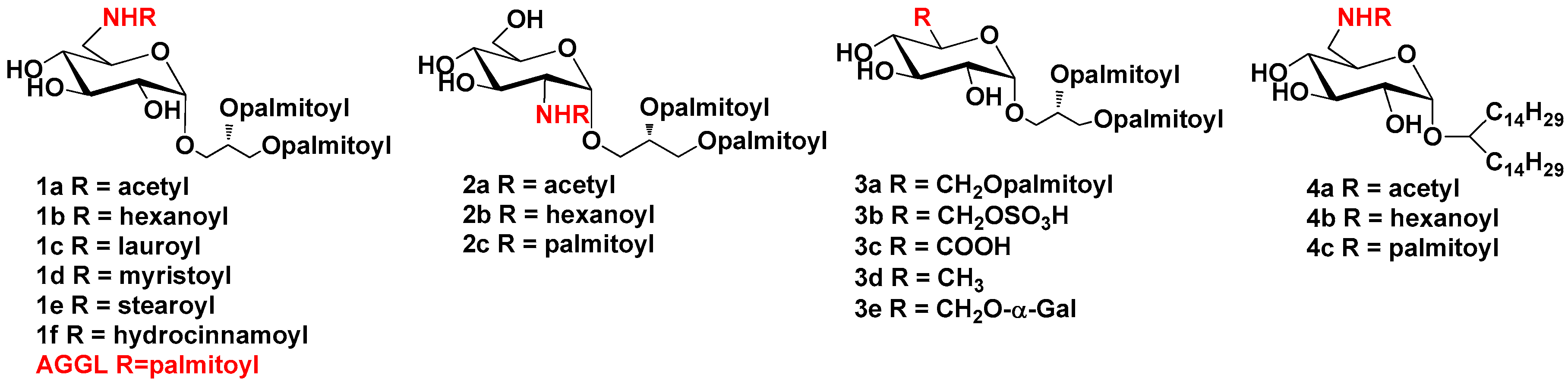
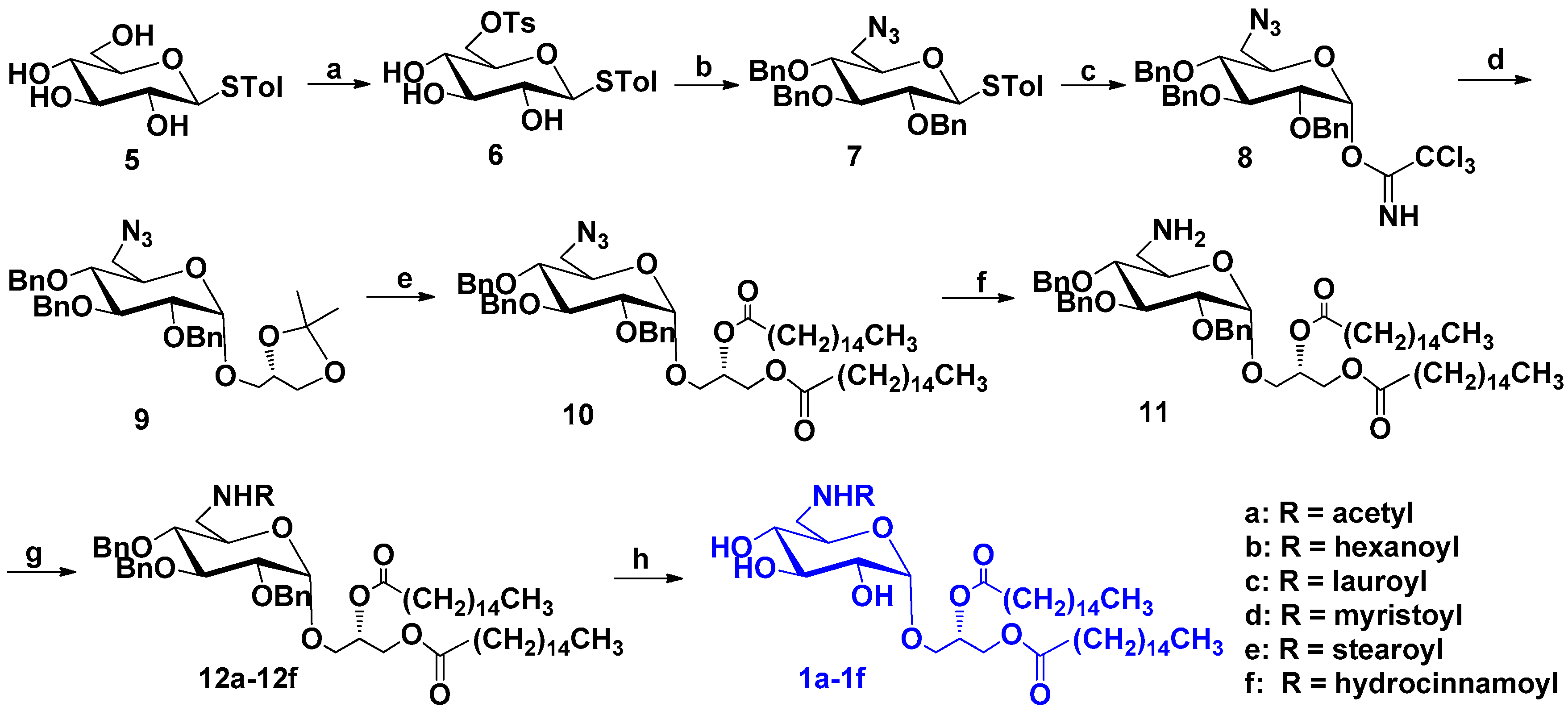
2.1.1. Synthesis of Compounds 1a–1f
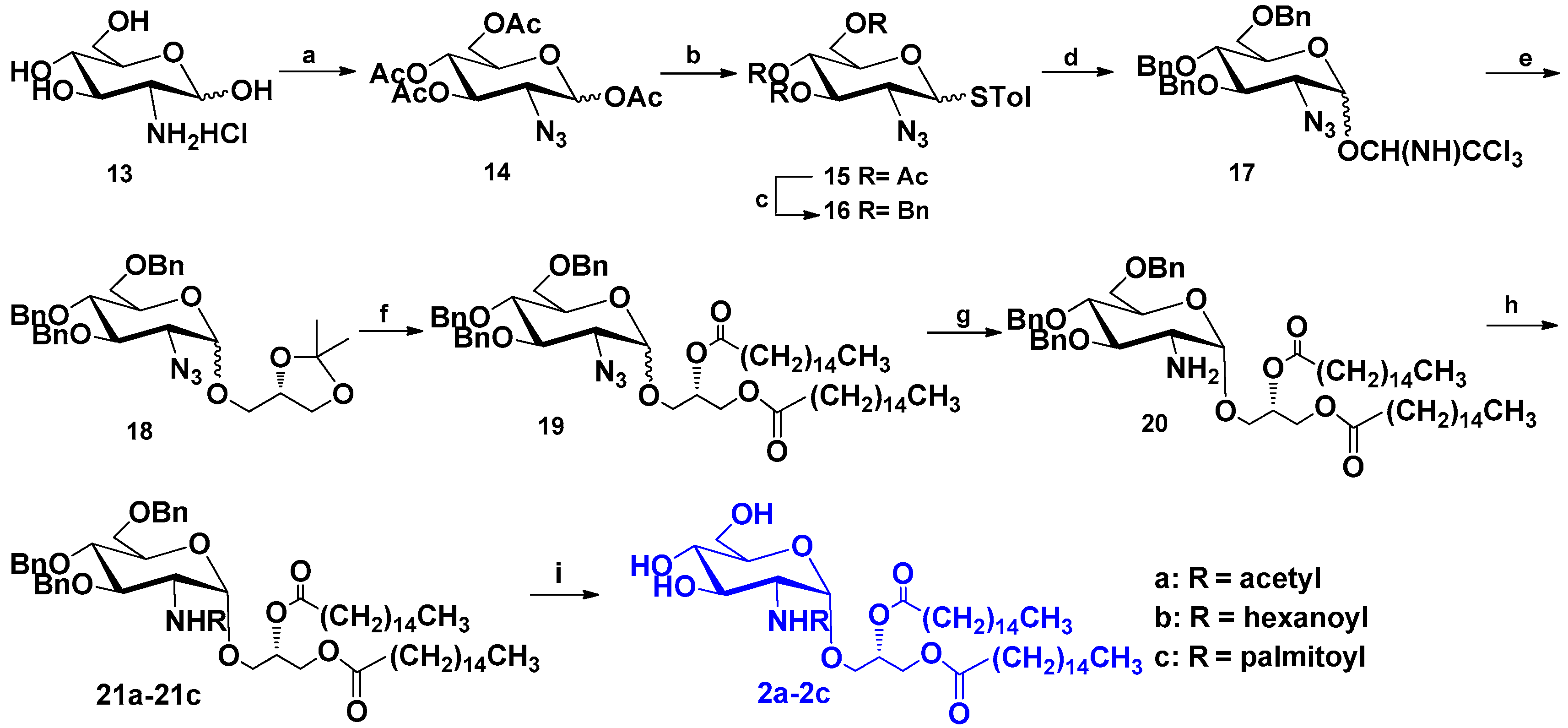
2.1.2. Synthesis of Compounds 2a–2c
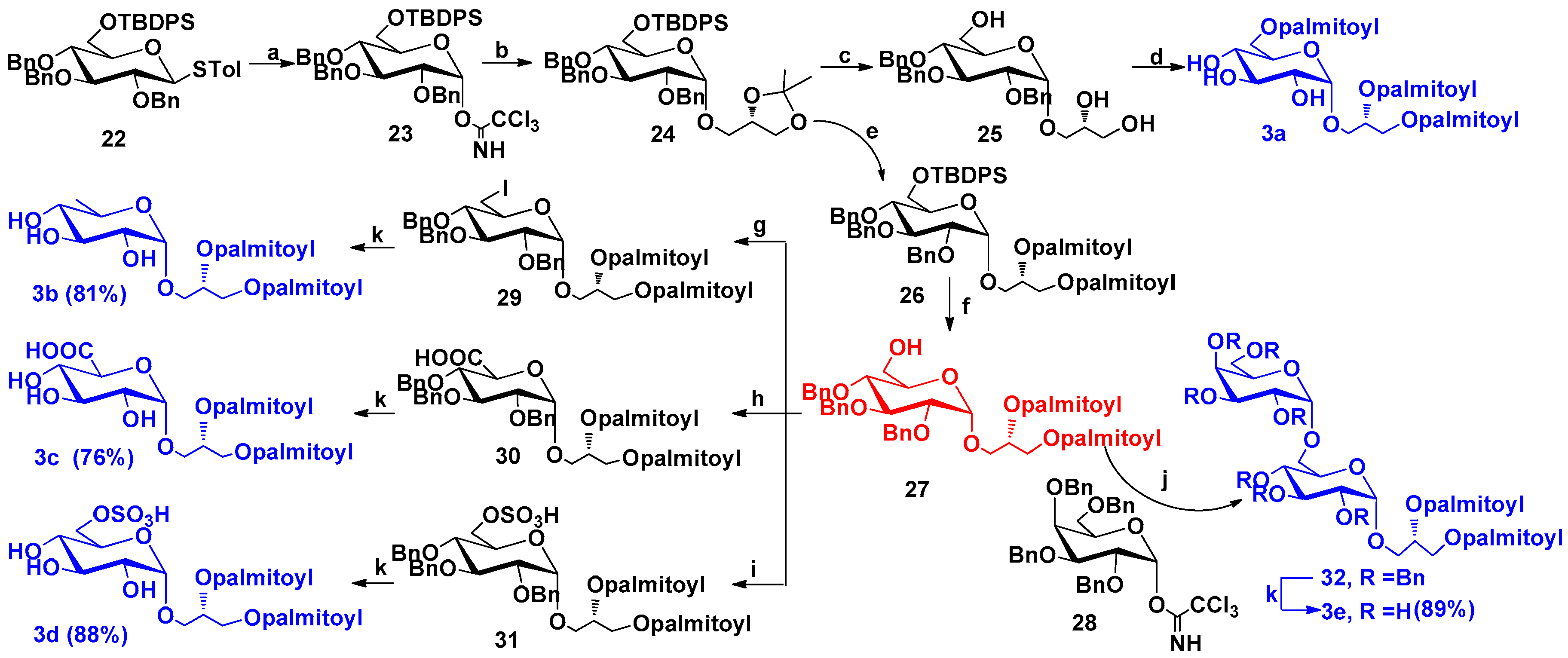
2.1.3. Synthesis of Compounds 3a–3e
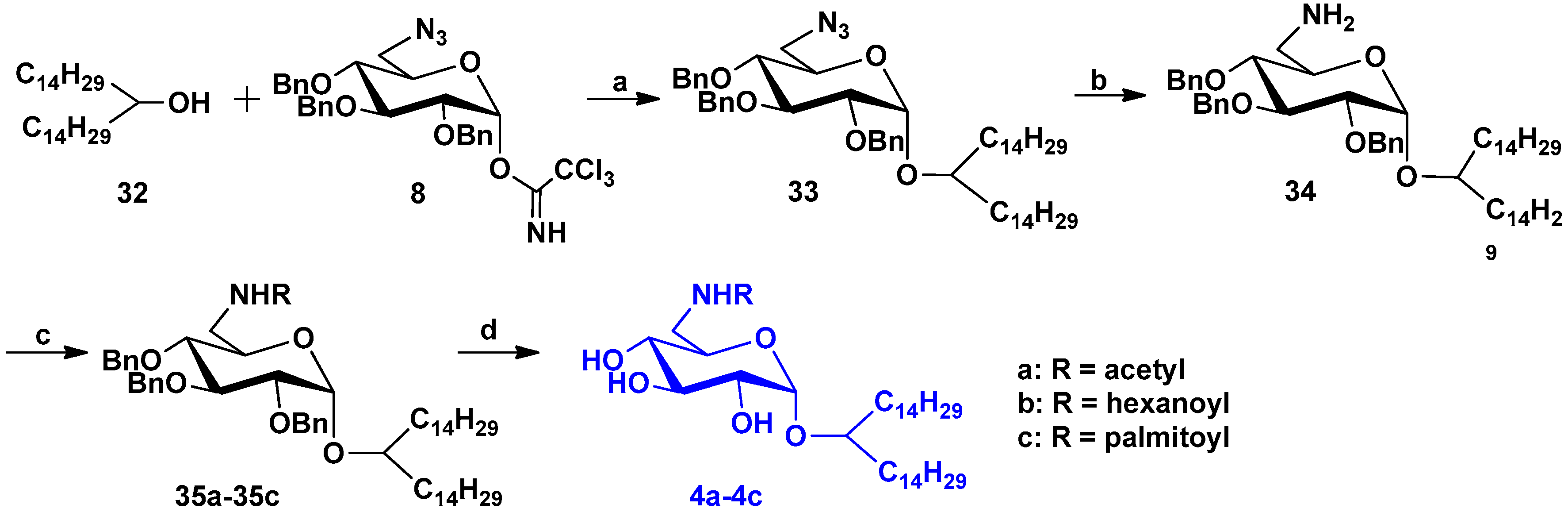
2.1.4. Synthesis of Compounds 4a–4c
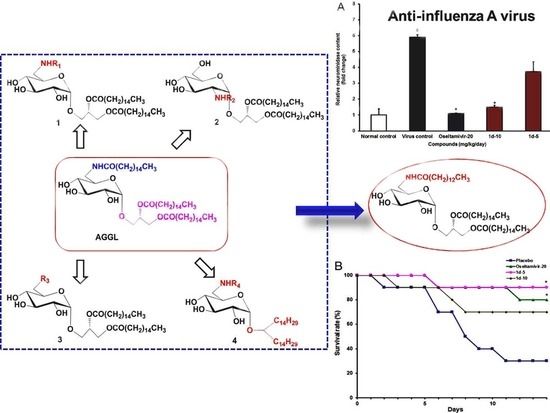
2.2. Biological Evaluation
2.2.1. Inhibition of Influenza A Virus Multiplication in Vitro
2.2.2. IAV Infection in Vivo
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemical Procedures
3.1.1. General Information
3.1.2. Chemistry: General Methods
General Procedure for Compounds 1a–1f
1,2-Dipalmitoyl-3-O-(N-acetyl-6′-amino-6′-deoxy-α-d-glucopyranosyl)-sn-glycerol (1a)
1,2-Dipalmitoyl-3-O-(N-hexanoyl-6′-amino-6′-deoxy-α-d-glucopyranosyl)-sn-glycerol (1b)
1,2-Dipalmitoyl-3-O-(N-lauroyl-6′-amino-6′-deoxy-α-d-glucopyranosyl)-sn-glycerol (1c)
1,2-Dipalmitoyl-3-O-(N-myristoyl-6′-amino-6′-deoxy-α-d-glucopyranosyl)-sn-glycerol (1d)
1,2-Dipalmitoyl-3-O-(N-stearoyl-6′-amino-6′-deoxy-α-d-glucopyranosyl)-sn-glycerol (1e)
1,2-Dipalmitoyl-3-O-(N-hydrocinnamoyl-6′-amino-6′-deoxy-α-d-glucopyranosyl)-sn-glycerol (1f)
General Procedure for 2a–2c
1,2-Dipalmitoyl-3-O-(N-acetyl-2′-amino-2′-deoxy-α-d-glucopyranosyl)-sn-glycerol (2a)
1,2-Dipalmitoyl-3-O-(N-hexanoyl-2′-amino-2′-deoxy-α-d-glucopyranosyl)-sn-glycerol (2b)
1,2-Dipalmitoyl-3-O-(N-palmitoyl-2′-amino-2′-deoxy-α-d-glucopyranosyl)-sn-glycerol (2c)
1,2-O-Dipalmitoyl-3-O-(6′-O-palmitoyl-α-d-glucopyranosyl)-sn-glycerol (3a)
General Procedure for Compounds 3b–3e
1,2-Dipalmitoyl-3-O-(6-deoxy-α-d-glucopyranosyl)-sn-glycerol (3b)
1,2-Dipalmitoyl-3-O-α-d-glucosyluronate-sn-glycerol (3c)
1,2-Dipalmitoyl-3-O-(6′-O-sulfonato-α-d-glucopyranoside)-sn-glycerol (3d)
1,2-Dipalmitoyl-3-O-[α-d-galactopyranosyl-(1′′→6′)-α-d-glucopyranosyl]-sn-glycerol (3e)
General procedures for 4a–4c
Bis(tetradecyl)methyl-N-acetyl-6-amino-6-deoxy-α-d-glucopyranoside (4a)
Bis(tetradecyl)methyl-N-hexanoyl-6-amino-6-deoxy-α-d-glucopyranoside (4b)
Bis(tetradecyl)methyl-N-palmitoyl-6-amino-6-deoxy-α-d-glucopyranoside (4c)
3.2. Biological Methods
3.2.1. Cell Culture and Virus Infection
3.2.2. Infectivity Antiviral Assays
3.2.3. In Vivo Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yewdell, J.; Garcia-Sastre, A. Influenza virus still surprises. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2002, 5, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garten, R.J.; Davis, C.T.; Russell, C.A.; Shu, B.; Lindstrom, S.; Balish, A.; Sessions, W.M.; Xu, X.; Skepner, E.; Deyde, V. Antigenic and genetic characteristics of swine-origin 2009 A (H1N1) influenza viruses circulating in humans. Science 2009, 325, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, G.; Noda, T.; Kawaoka, Y. Emergence and pandemic potential of swine-origin H1N1 influenza virus. Nature 2009, 459, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista, E.; Chotpitayasunondh, T.; Gao, Z.; Harper, S.A.; Shaw, M.; Uyeki, T.M.; Zaki, S.R.; Hayden, F.G.; Hayden, F.; Hui, D. Clinical aspects of pandemic 2009 influenza A (H1N1) virus infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1708–1719. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kim, E.H.; Lee, C.; Kim, M.H.; Rho, J.R. Two New Monogalactosyl Diacylglycerols from Brown Alga Sargassum thunbergii. Lipids 2007, 42, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illijas, M.I.; Indy, J.R.; Yasui, H.; Itabashi, Y. Lipid Class and Fatty Acid Composition of a Little-known and Rarely Collected Alga Exophyllum wentii Weber-van Bosse from Bali Island, Indonesia. J. Oleo Sci. 2009, 58, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, B.W.; Cho, Y.J.; Kim, N.K.; Choi, H.D. New glyceroglycolipids from the brown alga Sargassum Thunbergii. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 1992, 13, 584. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Fadhli, A.; Wahidulla, S.; D’Souza, L. Glycolipids from the red alga Chondria armata (Kütz.) Okamura. Glycobiology 2006, 16, 902–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Choi, J.S.; Hong, J.; Yoo, J.; Kim, M. Identification of acylated glycoglycerolipids from a cyanobacterium, Synechocystis sp., by tandem mass spectrometry. Lipids 1999, 34, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Choi, J.S.; Yoo, J.S.; Park, Y.M.; Kim, M.S. Structural Identification of Glycerolipid Molecular Species Isolated from CyanobacteriumSynechocystissp. PCC 6803 Using Fast Atom Bombardment Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 1999, 267, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcolongo, G.; de Appolonia, F.; Venzo, A.; Berrie, C.P.; Carofiglio, T.; Ceschi Berrini, C. Diacylglycerolipids isolated from a thermophile cyanobacterium from the Euganean hot springs. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 20, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, T.; Nagatsu, A.; Murakami, N.; Sakakibara, J.; Tokuda, H.; Nishino, H.; Iwashima, A. Anti-tumour-promoting glyceroglycolipids from the green alga, Chlorella vulgaris. Phytochemistry 1995, 40, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, C.; Kumagai, T.; Hada, T.; Kanekazu, U.; Nakazawa, S.; Kamisuki, S.; Maeda, N.; Xu, X.; Yoshida, H.; Sugawara, F. Effects of glycolipids from spinach on mammalian DNA polymerases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 65, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirasuwan, N.; Chaiklahan, R.; Kittakoop, P.; Chanasattru, W.; Ruengjitchatchawalya, M.; Tanticharoen, M.; Bunnag, B. Anti HSV-1 activity of sulphoquinovosyl diacylglycerol isolated from Spirulina platensis. Sci. Asia 2009, 35, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loya, S.; Reshef, V.; Mizrachi, E.; Silberstein, C.; Rachamim, Y.; Carmeli, S.; Hizi, A. The Inhibition of the Reverse Transcriptase of HIV-1 by the Natural Sulfoglycolipids from Cyanobacteria: Contribution of Different Moieties to Their High Potency. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reshef, V.; Mizrachi, E.; Maretzki, T.; Silberstein, C.; Loya, S.; Hizi, A.; Carmeli, S. New Acylated Sulfoglycolipids and Digalactolipids and Related Known Glycolipids from Cyanobacteria with a Potential to Inhibit the Reverse Transcriptase of HIV-1. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, T.S.; Ngo, D.H.; Ta, Q.V.; Kim, S.K. Marine organisms as a therapeutic source against herpes simplex virus infection. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 44, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergé, J.P.; Debiton, E.; Dumay, J.; Durand, P.; Barthomeuf, C. In Vitro Anti-inflammatory and Anti-proliferative Activity of Sulfolipids from the Red Alga Porphyridium cruentum. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2002, 50, 6227–6232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetro, M.; Costa, B.; Donvito, G.; Arrighetti, N.; Cipolla, L.; Perego, P.; Compostella, F.; Ronchetti, F.; Colombo, D. Anionic glycolipids related to glucuronosyldiacylglycerol inhibit protein kinase Akt. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Guan, H. Synthesis and antiviral evaluation of 6′-acylamido-6′-deoxy-α-d-mannoglycerolipids. Carbohydr. Res. 2013, 381, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Guan, H.; Yu, G. Synthesis of glycoglycerolipid of 1,2-dipalmitoyl-3-(N-palmitoyl-6′-amino-6′-deoxy-α-d-glucosyl)-sn-glycerol and its analogues, inhibitors of human Myt1-kinase. Carbohydr. Res. 2012, 355, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, G.; Guan, H. Synthesis of 6′-acylamido-6′-deoxy-α-d-galactoglycerolipids. Carbohydr. Res. 2013, 376, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.N.; Tang, S.; Johnson, R.K.; Mattern, M.P.; Lazo, J.S.; Sharlow, E.R.; Harich, K.; Kingston, D.G.I. New glycolipid inhibitors of Myt1 kinase. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- France, R.R.; Compton, R.G.; Davis, B.G.; Fairbanks, A.J.; Rees, N.V.; Wadhawan, J.D. Selective electrochemical glycosylation by reactivity tuning. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2004, 2, 2195–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goddard-Borger, E.D.; Stick, R.V. An efficient, inexpensive, and shelf-stable diazotransfer reagent: Imidazole-1-sulfonyl azide hydrochloride. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 3797–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Wang, P.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y. Reactivity-based One-pot Synthesis of Immunosuppressive Glycolipids from the Caribbean Sponge Plakortis simplex. Chin. J. Chem. 2009, 27, 2217–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulueta, M.; Lin, S.; Lin, Y.; Huang, C.; Wang, C.; Ku, C.; Shi, Z.; Chyan, C.; Irene, D.; Lim, L.; et al. α-Glycosylation by d-Glucosamine-Derived Donors: Synthesis of Heparosan and Heparin Analogues That Interact with Mycobacterial Heparin-Binding Hemagglutinin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 8988–8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigudkar, S.; Demchenko, A. Stereocontrolled 1,2-cis glycosylation as the driving force of progress in synthetic carbohydrate chemistry. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 2687–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauwels, N.; Aspeslagh, S.; Vanhoenacker, G.; Sandra, K.; Yu, E.D.; Zajonc, D.M.; Elewaut, D.; Linclau, B.; van Calenbergh, S. Divergent synthetic approach to 6′′-modified α-GalCer analogues. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 8413–8421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mico, A.; Margarita, R.; Parlanti, L.; Vescovi, A.; Piancatelli, G. A Versatile and Highly Selective Hypervalent Iodine (III)/2,2,6,6-Tetramethyl-1-piperidinyloxyl-Mediated Oxidation of Alcohols to Carbonyl Compounds. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 6974–6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grachev, A.A.; Gerbst, A.G.; Ustuzhanina, N.E.; Khatuntseva, E.A.; Shashkov, A.S.; Usov, A.I.; Nifantiev, N.E. Synthesis, NMR, and Conformational Studies of Fucoidan Fragments. VII. 1 Influence of Length and 2, 3-Branching on the Conformational Behavior of Linear (13)-Linked Oligofucoside Chains. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2005, 24, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Song, S.; Lee, T.; Jung, S.; Kim, D. Practical synthesis of KRN7000 from phytosphingosine. Synthesis 2004, 6, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roosjen, A.; Šmisterová, J.; Driessen, C.; Anders, J.T.; Wagenaar, A.; Hoekstra, D.; Hulst, R.; Engberts, J.B. Synthesis and characteristics of biodegradable pyridinium amphiphiles used for in vitro DNA delivery. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 2002, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, H.C.; Tseng, C.P.; Yang, J.M.; Ju, Y.W.; Tseng, S.N.; Chen, Y.F.; Chao, Y.S.; Hsieh, H.P.; Shih, S.R.; Hsu, J.T.A. Aurintricarboxylic acid inhibits influenza virus neuraminidase. Antivir. Res. 2009, 81, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichelberger, M.C.; Hassantoufighi, A.; Wu, M.; Li, M. Neuraminidase activity provides a practical read-out for a high throughput influenza antiviral screening assay. Virol. J. 2008, 5, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, P.; Yu, G.L.; Li, C.X.; Hao, C.; Qi, X.; Zhang, L.J.; Guan, H.S. Preparation and anti-influenza A virus activity of κ-carrageenan oligosaccharide and its sulphated derivatives. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, D.P.; Reichl, U. Neuraminidase activity assays for monitoring MDCK cell culture derived influenza virus. J. Virol. Methods 2004, 122, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnard, D.L. Animal models for the study of influenza pathogenesis and therapy. Antivir. Res. 2009, 82, A110–A122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.H.; Ohgami, K.; Shiratori, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Koyama, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Ilieva, I.; Tanaka, T.; Onoe, K.; Ohno, S. Effects of blue honeysuckle (Lonicera caerulea L.) extract on lipopolysaccharideinduced inflammation in vitro and in vivo. Exp. Eye Res. 2006, 82, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, T.; Miyazawa, T. Digestion of plant monogalactosyldiacylglycerol and digalactosyldiacylglycerol in rat alimentary canal. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2000, 11, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, N.; Kokai, Y.; Hada, T.; Yoshida, H.; Mizushina, Y. Oral administration of monogalactosyl diacylglycerol from spinach inhibits colon tumor growth in mice. Exp. Ther. Med. 2013, 5, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Sample | Virus Inhibition (%) | Sample | Virus Inhibition (%) | Sample | Virus Inhibition (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | 27.1 | 2a | 6.1 | 3a | 12.0 |
| 1b | 46.1 | 2b | 50.1 | 3b | 6.4 |
| 1c | 29.3 | 2c | 19.0 | 3c | 12.5 |
| 1d | 46.1 | 4a | 4.0 | 3d | 3.7 |
| 1e | 9.4 | 4b | 2.9 | 3e | 51.5 |
| 1f | 10.4 | 4c | 0 | AGGL | 25.5 |
| - | - | - | - | Ribavirin | 50.0 |
| Groups | Dose (mg/kg/d) | Lung Index a (X ± SD) | Inhibitory Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Virus control | - | 1.24 ± 0.31 # | 0 |
| Normal control | - | 0.79 ± 0.10 | - |
| Oseltamivir | 20 | 0.87 ± 0.41 * | 29.7 |
| 1d | 5 | 1.05 ± 0.31 | 15.3 |
| 1d | 10 | 1.15 ± 0.49 | 7.3 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, L.; Zhang, J.; Ma, H.; Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Yu, G.; Guan, H.; Wang, W.; Li, C. Synthesis and Anti-Influenza A Virus Activity of 6′-amino-6′-deoxy-glucoglycerolipids Analogs. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14060116
Ren L, Zhang J, Ma H, Sun L, Zhang X, Yu G, Guan H, Wang W, Li C. Synthesis and Anti-Influenza A Virus Activity of 6′-amino-6′-deoxy-glucoglycerolipids Analogs. Marine Drugs. 2016; 14(6):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14060116
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Li, Jun Zhang, Haizhen Ma, Linlin Sun, Xiaoshuang Zhang, Guangli Yu, Huashi Guan, Wei Wang, and Chunxia Li. 2016. "Synthesis and Anti-Influenza A Virus Activity of 6′-amino-6′-deoxy-glucoglycerolipids Analogs" Marine Drugs 14, no. 6: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14060116
APA StyleRen, L., Zhang, J., Ma, H., Sun, L., Zhang, X., Yu, G., Guan, H., Wang, W., & Li, C. (2016). Synthesis and Anti-Influenza A Virus Activity of 6′-amino-6′-deoxy-glucoglycerolipids Analogs. Marine Drugs, 14(6), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14060116