Physicochemical and Biological Characterization of Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus Purified by Dye Affinity Chromatography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
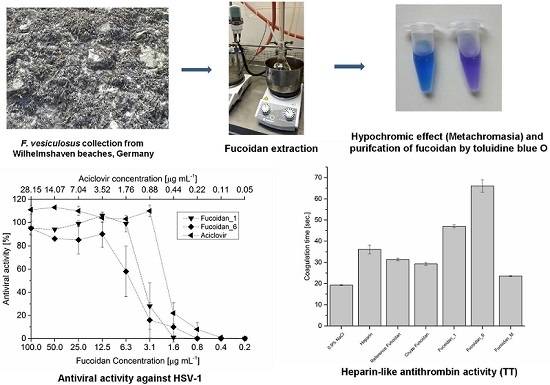
2.1. Extraction and Preparation of Crude Extract
2.2. Purification of Fucoidan from Crude Extract
2.3. Evaluation of the Beads Leakage and Dialysis Process
2.4. Physicochemical Investigations
2.4.1. Appearance and Solubility
2.4.2. Elemental Analysis (CHNS Analysis)
2.4.3. Melting Point
2.4.4. Specific Optical Rotation [α]22589
2.4.5. Molecular Weight Averages (Mw, Mp, Mn)
2.5. Monomeric Composition
2.6. Spectroscopical Investigation
2.7. Biological Investigations
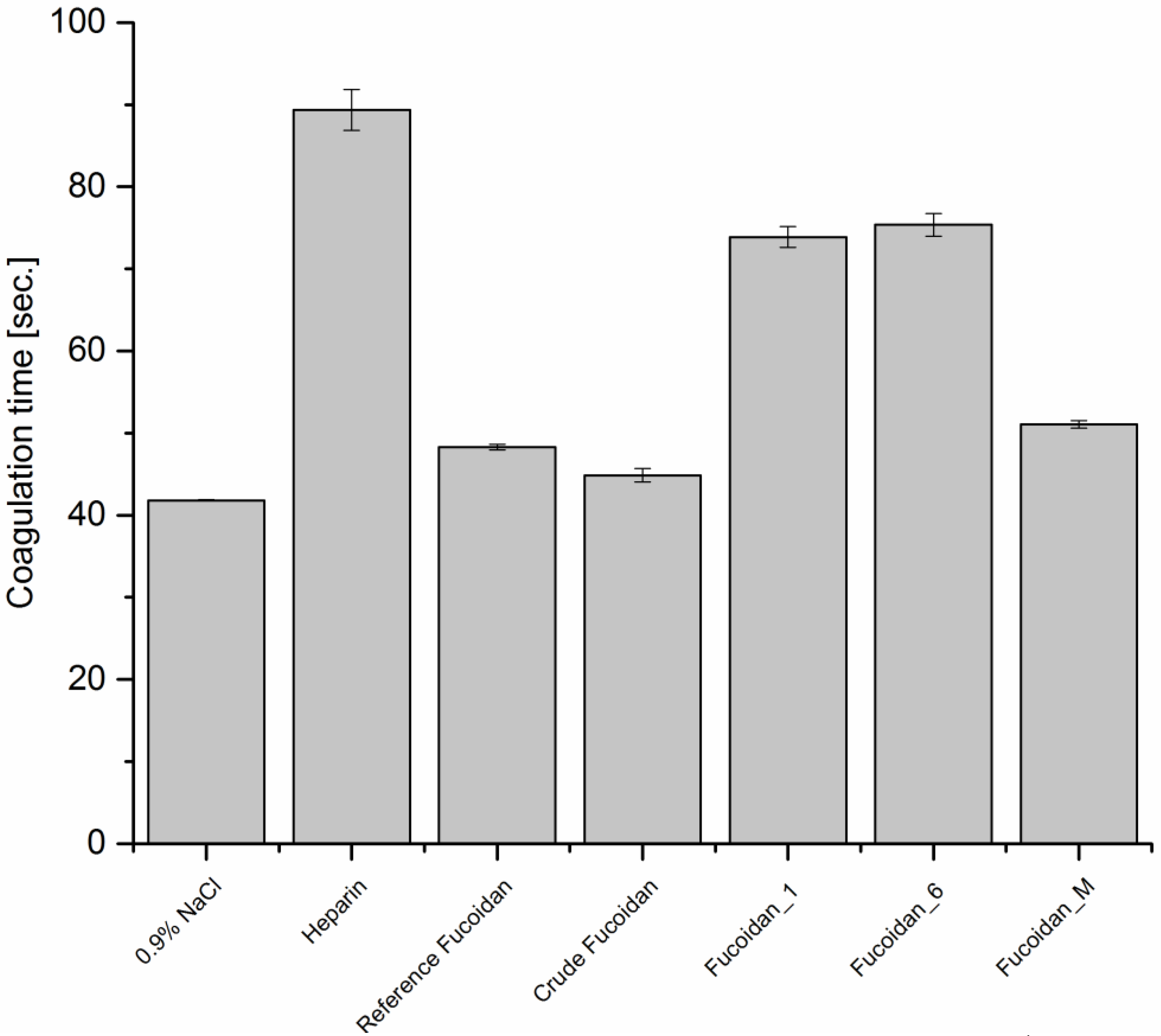
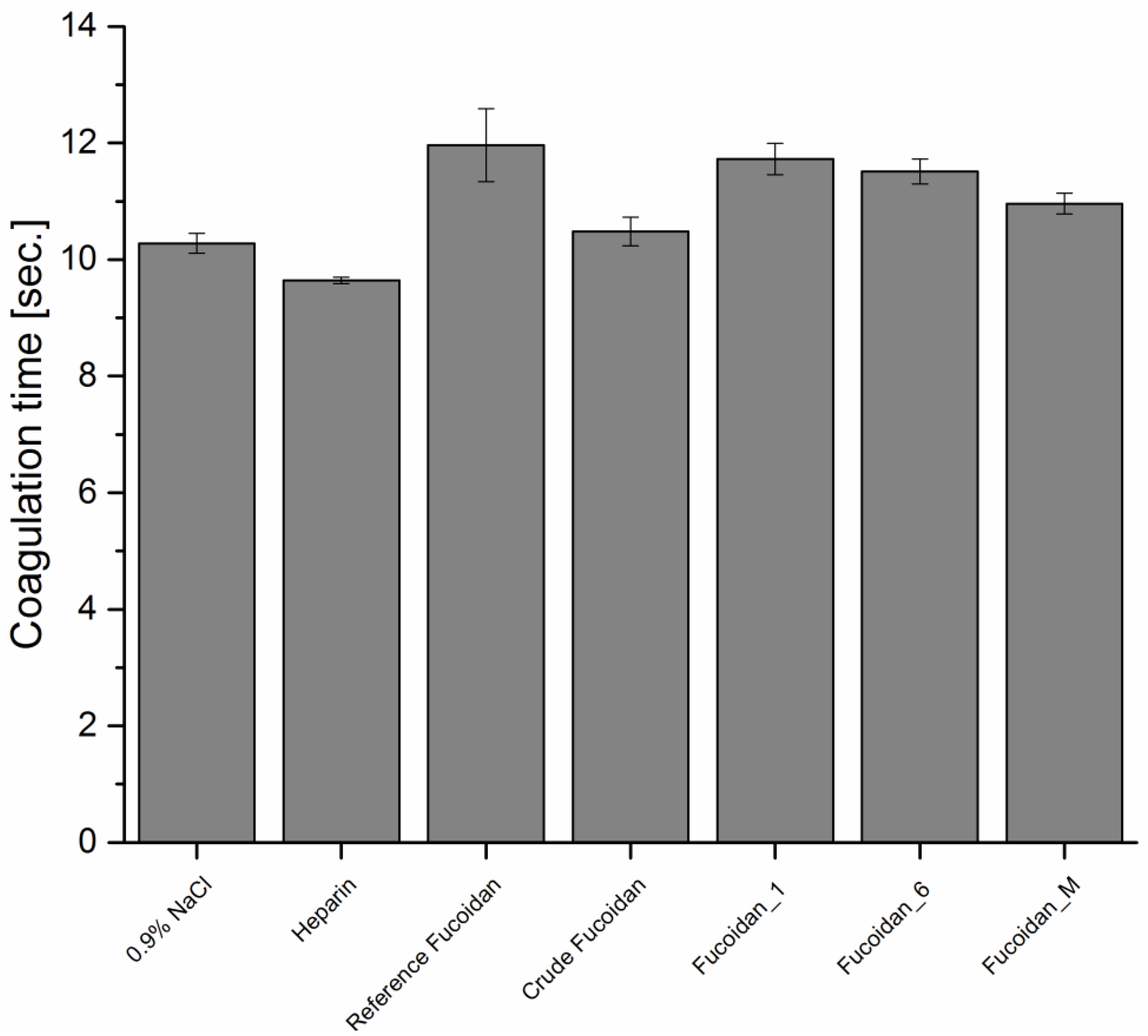
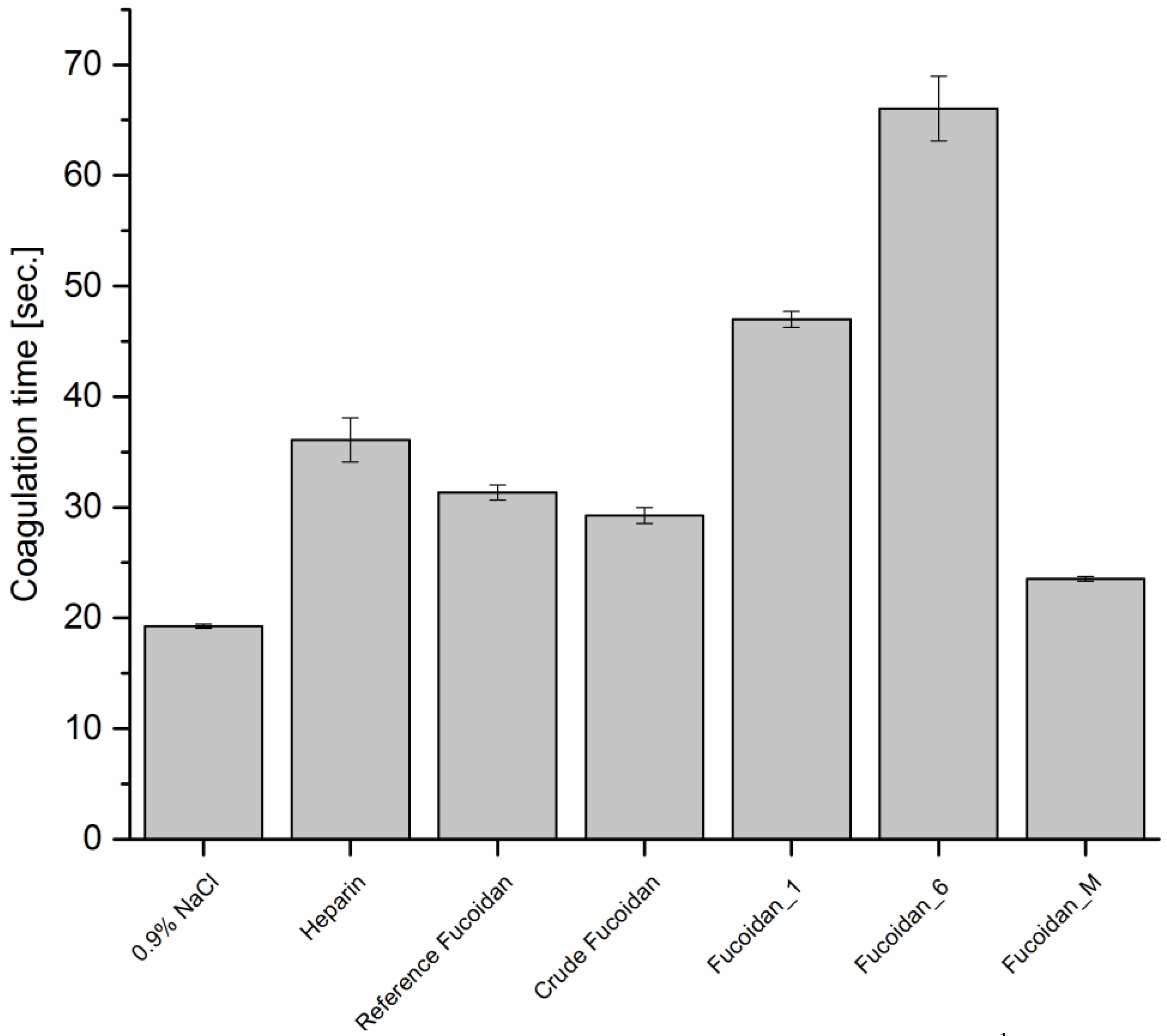
2.7.1. Anticoagulant Activity
Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (APTT)
Prothrombin Time (PT)
Thrombin Time (TT)
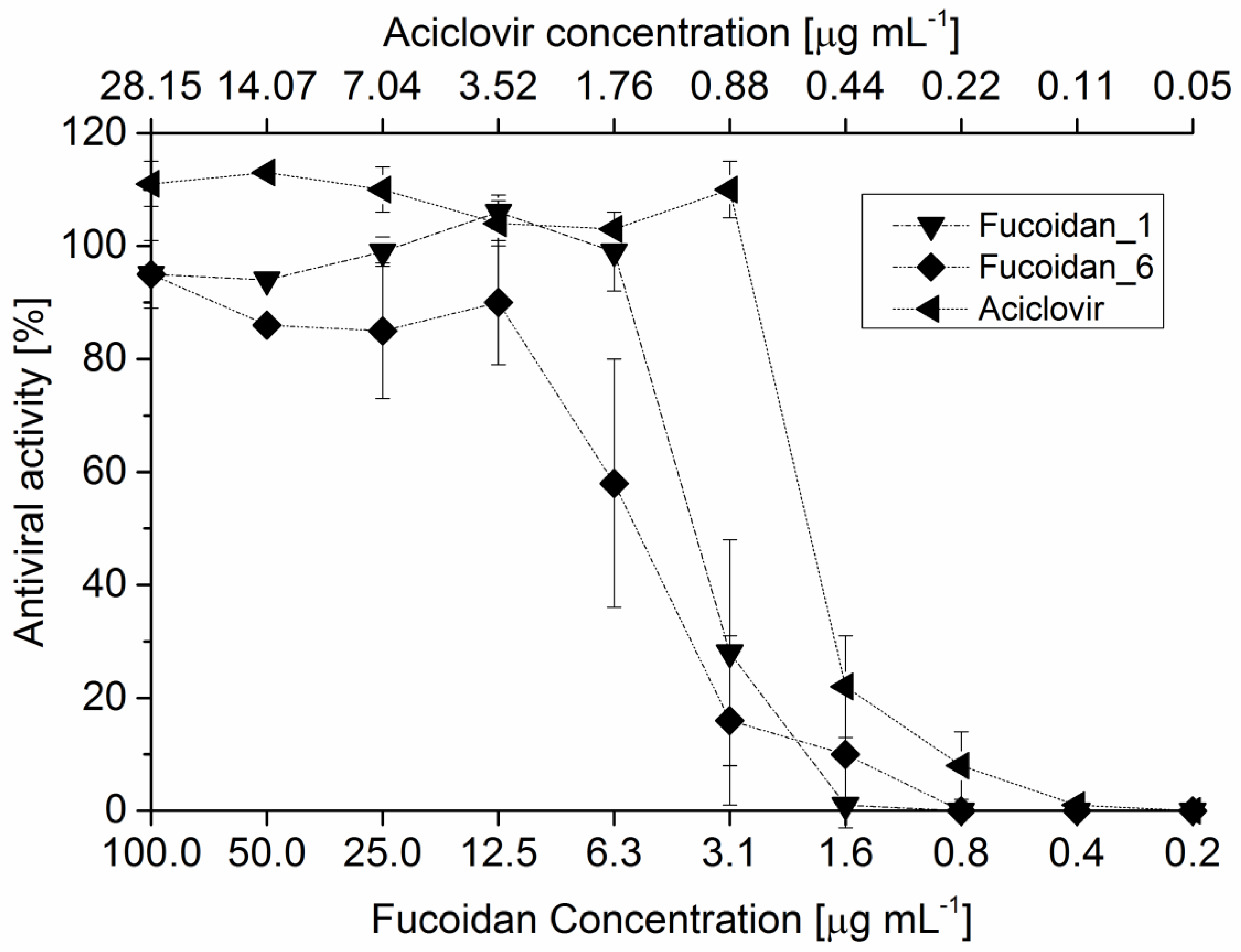
2.7.2. Antiviral Activity
3. Experimental Sections
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Instrumentations
3.3. Extraction and Preparation of the Crude Extract
3.3.1. Algal Preparation and Pretreatment
3.3.2. Extraction
3.3.3. Immobilization of Toluidine Blue, Purification, and Recovery of Fucoidan Fractions
3.3.4 Evaluation of Beads Leakage
3.4 Physicochemical Investigations
3.4.1 Molecular Weight Averages
3.4.2. Melting Point
3.4.3. Specific Optical Rotation
3.5. Monomeric Composition
3.6. Biological Investigations
3.6.1. Anticoagulant Activity
Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (APTT)
Prothrombin Time (PT)
Thrombin Time (TT)
3.7. Antiviral Assay
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skriptsova, A.V. Fucoidans of brown algae: Biosynthesis, localization, and physiological role in thallus. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2015, 41, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtkamp, A.D.; Kelly, S.; Ulber, R.; Lang, S. Fucoidans and fucoidanases-focus on techniques for molecular structure elucidation and modification of marine polysaccharides. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 82, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estelle, D.B.; Kervarec, N.; Michel, G.; Tonon, T.; Kloareg, B.; Herve, C. Chemical and enzymatic fractionation of cell walls from fucales: Insights into the structure of the extracellular matrix of brown algae. Ann. Bot. 2014, 114, 1203–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitton, J.H. Therapies from Fucoidan; Multifunctional Marine Polymers. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1731–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastyuk, S.D.; Shevchenko, N.M.; Nazarenko, E.L.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Zvyagintseva, T.N. Structural analysis of a fucoidan from the brown alga Fucus evanescens by MALDI-TOF and tandem ESI mass spectrometry. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylin, H. The biochemistry of seaweed. Hoppe Seylers Z. Physiol. Chem. 1913, 83, 171–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, F.; Wei, X.; Zhao, R. Fucoidan: Structure and Bioactivity. Molecules 2008, 13, 1671–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, T.; Lang, S.; Ulber, R.; Muffler, K. Novel procedures for the extraction of fucoidan from brown algae. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ale, M.T.; Meyer, A.S. Fucoidans from brown seaweeds: An update on structures, extraction techniques and use of enzymes as tools for structural elucidation. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 8131–8141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ale, M.T.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Meyer, A.S. Important determinants for fucoidan bioactivity: A critical review of structure-function Relations and extraction methods for fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides from brown seaweeds. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2106–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, T.; Zayed, A.; Kovacheva, M.; Stadtmüller, R.; Lang, S.; Muffler, K.; Ulber, R. Dye affinity chromatography for fast and simple purification of fucoidan from marine brown algae. Eng. Life Sci. 2016, 16, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.H.; Jang, D.S.; Kim, S.B. Utilization of Marine Products, 2nd ed.; Hyoungsul Press: Seoul, South Korea, 1997; pp. 283–336. [Google Scholar]
- Obluchinskaya, E.D.; Voskoboinikov, G.M.; Galynkin, V.A. Contents of alginic acid and fucoidan in fucus algae of the Barents Sea. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2002, 38, 186–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, S.; Deniaud, E.; Jam, M.; Descamps, V.; Chevolot, Y.; Kervarec, N.; Yvin, J.C.; Barbeyron, T.; Michel, G.; Kloareg, B. Cloning and biochemical characterization of the fucanase FcnA: Definition of a novel glycoside hydrolase family specific for sulfated fucans. Glycobiology 2006, 16, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Descamps, V.; Colin, S.; Lahaye, M.; Jam, M.; Richard, C.; Potin, P.; Barbeyron, T.; Yvin, J.C.; Kloareg, B. Isolation and culture of a marine bacterium degrading the sulfated fucans from marine brown algae. Mar. Biotechnol. 2006, 8, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reviers, B. Fucans and alginates without phenolic compounds. J. Appl. Phycol. 1989, 1, 75–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, T.; Schulz, M.; Stadtmüller, R.; Zayed, A.; Muffler, K.; Lang, S.; Ulber, R. A cationic dye for the specific determination of sulfated polysaccharides. Anal Lett. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumashi, A.; Ushakova, N.A.; Preobrazhenskaya, M.E.; D’Incecco, A.; Piccoli, A.; Totani, L.; Tinari, N.; Morozevich, G.E.; Berman, A.E.; Bilan, M.I.; et al. A comparative study of the anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant, antiangiogenic, and antiadhesive activities of nine different fucoidans from brown seaweeds. Glycobiology 2007, 17, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, J.B. A relation between the molecular weights and melting points of organic compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1930, 52, 1049–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, A.C.; Vassy, R.; di Benedetto, M.; Lavigne, D.; Visage, C.L.; Perret, G.Y.; Letourneur, D. Low molecular weight fucoidan increases VEGF165-induced endothelial cell migration by enhancing VEGF165 binding to VEGFR-2 and NRP1. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 37844–37852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourão, P.A.S. Use of sulfated fucans as anticoagulant and antithrombotic agents: Future perspectives. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 967–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, T.; Yokoyama, G.; Dobahi, K. Isolation, purification and characterization of fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides from the brown seaweed Ecklonia kurome and their blood-anticoagulant activities. Carbohydr Res. 1989, 186, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobashi, K.; Nishino, T.; Fujihara, M. Isolation and preliminary characterization of fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides with blood-anticoagulant activity from seaweed Hizikia fusiforme. Carbohydr. Res. 1989, 194, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Rui, X.Z.; Xin, J.W. Anticoagulant activity of fucoidan from Hizikia fusiforme. Agro Food Ind. Hi-Tech 2008, 19, 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, Z.; Ying, W.; Junjie, Q.; Jing, Z.; Hong, Y.; Yvxin, L. Isolation, purification and the anticoagulant activities of fucoidan. J. Mol. Sci. 2002, 18, 109–112. [Google Scholar]
- Mandal, P.; Mateu, C.G.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Pujol, C.A.; Damonte, E.B.; Ray, B. Structural features and antiviral activity of sulphated fucans from the brown seaweed Cystoseira indica. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2007, 18, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rühmann, B.; Schmid, J.; Sieber, V. Fast carbohydrate analysis via liquid chromatography coupled with ultra violet and electrospray ionization ion trap detection in 96-well format. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1350, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, L.O.; Barrowcliffe, T.W.; Holmer, E.; Johnson, E.A.; Sims, G.E.C. Anticoagulant properties of heparin fractionated by affinity chromatography on matrix-bound antithrombin-3 and by gel-filtration. Thromb. Res. 1976, 9, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quick, A.J. The clinical application of the hippuric acid and the prothrombin test. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1940, 10, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denson, K.W.E.; Bonnar, J. The measurement of heparin: Method based on the potentiation of anti-factor Xa. Thromb. Diath. Haemorrh. 1973, 30, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kleymann, G.; Werling, H.O. A generally applicable, highthroughput screening-compatible assay to identify, evaluate, and optimize antimicrobial agents for drug therapy. J. Biomol. Screen. 2004, 9, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample | N (%) ± 0.02 * | C (%) ± 0.06 | H (%) ± 0.1 | S (%) ± 0.00 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dextran | n.d. ** | 40.00 | 6.53 | n.d. |
| Dextran after incubation | n.d. | 41.23 | 6.45 | n.d. |
| Sample | N (%) ± 0.03 | C (%) ± 0.04 | H (%) ± 0.01 | S (%) ± 0.06 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Fucoidan 1 | n.d. * | 24.78 | 4.42 | 8.89 |
| Fucoidan 2 | 0.3 | 24.14 | 4.43 | 11.18 |
| Fucoidan 3 | 0.34 | 26.12 | 4.63 | 9.83 |
| Fucoidan_M 4 | 0.26 | 23.31 | 4.28 | 12.11 |
| Sample | Start (°C) | Color Change (°C) | Decomposition (°C) | Specific Optical Rotation [α]22589 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Fucoidan 1 | - * | - | - | −121 |
| Fucoidan_1 2 | 130 | 132–133 | 135 | −128 |
| Fucoidan_6 3 | 140 | 153–156 | 161 | −117 |
| Fucoidan_M 4 | 130 | 133–134 | 136 | −130 |
| Molarity of NaCl (M) | Adsorbed Fucoidan (%) ± SD | Eluted Fucoidan (%) ± SD | Molecular Weight Averages (×104) Da | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mw | Mn | Mp | |||
| 1 | 87.13 ± 0.008 | 42.4 ± 0.28 | 5.7 | 4.1 | 3.7 |
| 2 | 57.75 ± 0.49 | 6.6 | 4.8 | 4.9 | |
| 3 | 70.3 ± 0.98 | 9.2 | 4.9 | 4.4 | |
| Composition | % Galactose | % Xylose | % Fucose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fucoidan_1 1 | 7.4 ± 0.06 | 4.0 ± 0.06 | 88.59 ± 0.03 |
| Fucoidan_6 2 | 8.99 ± 0.25 | 4.2 ± 0.45 | 86.8 ± 0.45 |
| Fucoidan_M 3 | 7.56 ± 0.2 | - * | 92.43 ± 0.2 |
| IC50 (μg·mL−1) | |
|---|---|
| Reference Fucoidan 1 | 3.3 |
| Fucoidan_1 2 | 4.09 |
| Fucoidan_6 3 | 5.69 |
| Fucoidan_M 4 | 2.41 |
| Crude fucoidan | 3.99 |
| Acicolvir | 0.52 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zayed, A.; Muffler, K.; Hahn, T.; Rupp, S.; Finkelmeier, D.; Burger-Kentischer, A.; Ulber, R. Physicochemical and Biological Characterization of Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus Purified by Dye Affinity Chromatography. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14040079
Zayed A, Muffler K, Hahn T, Rupp S, Finkelmeier D, Burger-Kentischer A, Ulber R. Physicochemical and Biological Characterization of Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus Purified by Dye Affinity Chromatography. Marine Drugs. 2016; 14(4):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14040079
Chicago/Turabian StyleZayed, Ahmed, Kai Muffler, Thomas Hahn, Steffen Rupp, Doris Finkelmeier, Anke Burger-Kentischer, and Roland Ulber. 2016. "Physicochemical and Biological Characterization of Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus Purified by Dye Affinity Chromatography" Marine Drugs 14, no. 4: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14040079
APA StyleZayed, A., Muffler, K., Hahn, T., Rupp, S., Finkelmeier, D., Burger-Kentischer, A., & Ulber, R. (2016). Physicochemical and Biological Characterization of Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus Purified by Dye Affinity Chromatography. Marine Drugs, 14(4), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14040079