Abstract
Three new steroids, petasitosterones A and B (1 and 2) and a spirosteroid petasitosterone C (3), along with eight known steroids (4–11), were isolated from a Formosan marine soft coral Umbellulifera petasites. The structures of these compounds were elucidated by extensive spectroscopic analysis and comparison of spectroscopic data with those reported. Compound 3 is a marine steroid with a rarely found A/B spiro[4,5]decane ring system. Compounds 1–3 and 5 displayed inhibitory activity against the proliferation of a limited panel of cancer cell lines, whereas 2 and 5 exhibited significant anti-inflammatory activity to inhibit nitric oxide (NO) production. The inhibitory activities for superoxide anion generation and elastase release of compounds 1–11 were also examined to evaluate the anti-inflammatory potential, and 2–4 were shown to exhibit significant activities.
1. Introduction
Marine organisms, including octocorals (Coelenterata: Anthozoa), have been shown to be a rich source of a variety of polyoxygenated steroids [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. Some of these metabolites possess important bioactivities, such as cytotoxic [1,3,5,6,9,11,12,13,14], anti-inflammatory [3,6,8,11,13,14], antiviral [3,4], and antibacterial activities [3,7,10]. In order to discover medicinally useful natural compounds, we investigated the chemical constituents of a soft coral Umbellulifera petasites, which was chemically examined for the first time. The study led to the isolation of two new steroids, petasiterones A and B (1 and 2), and a novel spirosteroid, petasitosterone C (3), along with eight known steroids, 5α-pregna-20-en-3-one (4) [15], 5α-pregna-1,20-dien-3-one (5) [15], 5α,8α-epidioxycholesta-6,22-dien-3β-ol (6) [16], 25α,8α-epidioxy-24(S)-methylcholesta-6,22-dien-3β-ol (7) [16], 5α,8α-epidioxy-24(R)-methylcholesta-6,22-dien-3β-ol (8) [16], 5α,8α-epidioxycholest-6-en-3β-ol (9) [16], 5α,8α-epidioxy-24α-ethylcholesta-6,22-dien-3β-ol (10) [16], and 5α,8α-epidioxy-24α-ethylcholesta-6-en-3β-ol (11) [16] (Figure 1). The structures of the new metabolites were determined on the basis of extensive spectroscopic analysis (Supplementary Materials, Figures S1–S9), including HRESIMS and 1D and 2D NMR (COSY, HMQC, HMBC, and NOESY) spectroscopy. With the aim of discovering the bioactivities of the isolated natural products, the anti-inflammatory activity including nitric oxide (NO) inhibition activity of compounds 1–11 was evaluated by assay of LPS-stimulated NO production in activated RAW264.7 cells. The ability of suppressing superoxide anion generation and elastase release in N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine/cytochalasin B (fMLP/CB)-induced human neutrophils were also studied. Furthermore, the cytotoxicities of compounds 1–11 against the cancer cell lines human erythroleukemia (K-562), lymphoid T carcinoma (MOLT-4), and human colorectal adenocarcinoma (DLD-1) were assayed. We report herein the isolation, structure elucidation, and biological activities of these marine natural products.
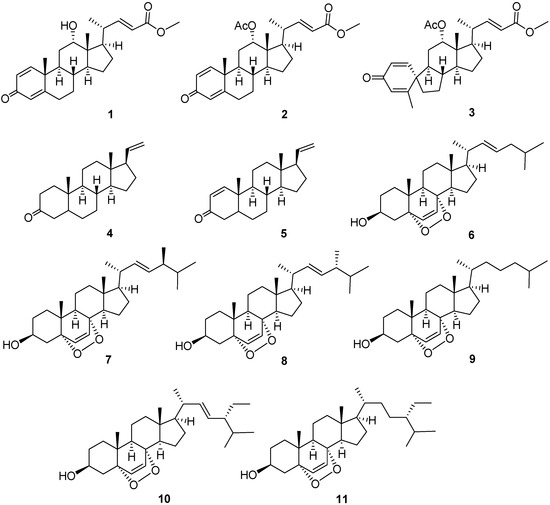
Figure 1.
Structures of compounds 1–11.
2. Results and Discussion
The frozen bodies of Umbellulifera petasites were sliced and extracted with ethyl acetate (EtOAc). The EtOAc extracts were evaporated and the residue was repeatedly chromatographed over silica gel and RP-HPLC to afford three new steroids, along with eight known steroids (4–11). Petasitosterone A (1), obtained as an amorphous solid, was found to possess a molecular formula C25H34O4 as established by HRESIMS (m/z 421.2350, [M + Na]+), appropriated for nine degrees of unsaturation. The IR spectrum revealed the presence of hydroxy (3445 cm−1), and carbonyl (1715 and 1663 cm−1) groups. The 1H NMR spectral data (Table 1) of 1 showed the presence of five olefinic methine protons (δH 6.98, dd, J = 15.6, 10.0 Hz; 6.97, d, J = 10.4 Hz; 6.21, dd, J = 10.4, 2.0 Hz; 6.06, s; 5.83, d, J = 15.6 Hz), and one oxymethine proton (δH 3.74, br s). The 13C NMR data (Table 1) and DEPT spectra indicated the presence of 25 carbons, including four methyl groups (containing a methoxy carbon), five methylenes, 11 methines, and five quaternary carbons (including two carbonyl groups). The carbon resonances at δC 186.4 (C), 155.4 (CH), 127.7 (CH), 123.9 (CH), and 169.0 (C) as well as the proton resonances at δH 6.97 (1H, d, J = 10.4 Hz), 6.21 (1H, dd, J = 10.4, 2.0 Hz), and 6.06 (1H, s) were characteristic signals of steroids with a 1,4-dien-3-one moiety in ring A [9]. Careful analysis of the COSY and HMBC spectra (Figure 2) allowed us to determine the molecular skeleton of 1. H-12 (δH 3.74, br s) showed HMBC correlations to C-9 and C-14, and H3-18 (δH 0.72, s) exhibited HMBC correlations to C-12, C-13, C-14, and C-17; revealing the position of a hydroxyl at C-12. As C-24 resonated at δC 167.4, and protons of the methoxyl (δH 3.74) gave HMBC correlation to this carbonyl carbon, thus the position of the methoxy group at C-24 carbonyl carbon was confirmed. On the basis of the molecular framework, the gross structure of 1 was established (Figure 2).

Table 1.
1H and 13C NMR spectroscopic data of 1–3.
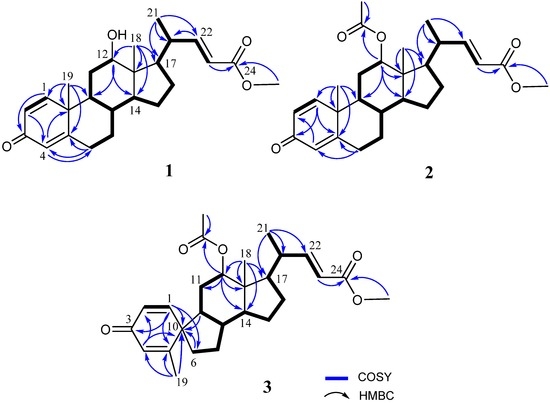
Figure 2.
Selected COSY and HMBC correlations of 1–3.
The relative configuration of 1 was established by the NOE correlations observed in a NOESY experiment. H-8 was found to show NOE correlations with both H3-18 and H3-19, and H3-18 exhibited correlations with one of the methylene protons at C-11 (δH 1.87, m), H-12, and H-20; therefore, due to the β-orientation of H3-18, all of H-8, H-12, H3-19, and H-20 should also be positioned on the β-face. Furthermore, NOE responses between H-11α (δH 1.75, m) and H-9, H-9 and H-14, and H-14 and H-17, were observed on the α-orientation of H-9, H-14 and H-17 (Figure 3).
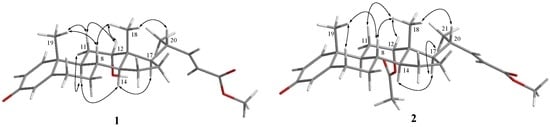
Figure 3.
Selected NOE correlations for 1 and 2.
Metabolite 2 was isolated as an amorphous solid and was found to possess a molecular formula C27H36O5, as established by the HRESIMS m/z 463.2458 [M + H]+ and NMR data (Table 1). The IR absorption bands at νmax 1731 and 1665 cm−1 also revealed the presence of carbonyl groups. Comparison of the NMR spectral data of 2 with those of the known metabolite 1 (Table 1) suggested that 2 is the 12-O-acetyl derivative of 1. This was further supported by the downfield shifts observed for H-12 (δH 4.75, br s) and C-12 (δC 74.2) relative to those of 1. The planar structure of 2, including the positions of acetoxy group, carboxylate, and the olefinic double bond of this metabolite, could be further deduced from the detailed analyses of the COSY, HMQC, and HMBC spectral correlations (Figure 2). Finally, the relative stereochemistry of 2 was established by the analysis of the NOE correlations in NOESY spectrum of 2, as illustrated in Figure 3.
The molecular formula of petasitosterone C (3) was found to be C27H36O5 as deduced from HRESIMS and 13C NMR data, appropriate for 10 degrees of unsaturation. The IR spectrum of 3 again showed the presence of carbonyl (νmax 1737 and 1661 cm−1) groups. The 13C NMR and DEPT spectra showed signals of five methyls (including a methoxy carbon), five methylenes, 11 methines, and six quaternary carbons (including two ester carbonyls and one keto-carbonyl). The 1H NMR spectrum of 3 exhibited two doublet methyl signals at δH 1.90 (J = 1.2 Hz) and 0.99 (J = 6.4 Hz), three singlet methyl signals at δH 3.71, 2.04, and 0.72, an oxygenated methine group at δH 4.69, and five olefinic protons at δH 6.82, 6.61, 6.18, 6.14, and 5.76, respectively. The carbon skeleton of 3 was determined by 2D NMR experiments, in particular the analysis of COSY, HMQC, and HMBC corrections (Figure 2). The COSY correlations from H-1 to H-2 and the HMBC correlations from H-1 to C-3, C-5, C-6, and C-10; H-4 to C-2 and C-10; and H3-19 to C-4, C-5, and C-10, suggested a cross-conjugated dienone moiety in 3. This was further supported by signals of protons at δH 6.82 (1H, d, J = 10.0 Hz), 6.18 (1H, dd, J = 10.0, 1.6 Hz), 6.14 (1H, s), and 1.90 (3H, d, J = 1.2 Hz). The aforementioned information, along with the HMBC correlations from H-1 to C-3 and C-6, and H-6 to C-9 and C-10, suggested a spiro[4,5]decane ring with a 1,4-diene-3-one partial structure in the A ring of compound 3 [17]. From all of the 1H and 13C NMR data and other COSY and HMBC correlations, it was found that the rest part of the structure (rings C and D, and side chain) is the same as that of 1. The configuration of 3 was determined by the correlations observed in a NOESY experiment (Figure 4). The NOE correlations between H-1 and one proton of H2-6 (δH 1.77), and H3-19 and H3-18, established the β-orientation of C-5, and the α-orientation of C-1. In addition, H3-18 was found to show NOE responses with H-12 and H-20, revealing the α-orientation of H3-21 the acetoxy group. Steroid 3 is the third natural product possessing a spiro[4,5]decane unit transformed from A and B rings [7,17] and was found to be a compound with a new carbon skeleton after considering the entire molecular framework.
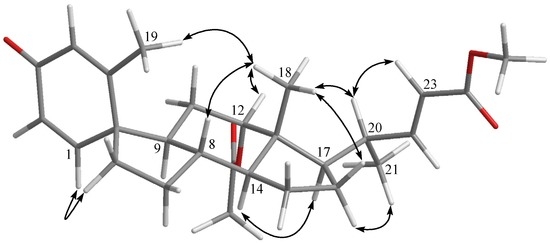
Figure 4.
Selected NOE correlations for 3.
The biosynthesis of 3 might come from the initial protonation of 2 at the carbonyl oxygen of the α,β-unsaturated ketone, followed by the 1,2-shift of the methyl substituent from C-10 to carbonium carbon C-5 and the subsequent 1,2-shift of C-6 residue to C-5, as suggested previously [17].
To find the future biomedical potential for the above steroids, the cytotoxicity of compounds 1–11 against the proliferation of a limited panel of cancer cell lines, including human erythroleukemia (K-562), lymphoid T carcinoma (MOLT-4), and human colorectal adenocarcinoma (DLD-1), was evaluated. The results showed compound 5 exhibited cytotoxicity toward K-562, MOLT-4, and DLD-1 cancer cell lines with IC50 values of 13.5 ± 3.1, 5.9 ± 1.9, and 9.7 ± 3.2 μg/mL, respectively, while 2 was found to show cytoxicity toward MOLT-4 and DLD-1 with IC50 values of 12.1 ± 4.5 and 5.8 ± 1.7 μg/mL. Also, 1 and 3 showed cytotoxicity toward the DLD-1 cell line, as show in Table 2.

Table 2.
Cytotoxicity (IC50 μg/mL) of compounds 1–3 and 5.
Compounds 1–11 were also evaluated for anti-inflammatory activity by suppressing superoxide anion generation and elastase release by human neutrophils in response to fMLP/CB stimulation. The results revealed that compounds 2 and 3 showed moderate activities toward superoxide anion generation with IC50 values of 4.43 ± 0.23 and 2.76 ± 0.92 μM, respectively. Compound 4 did not exhibit inhibition activity toward superoxide anion generation (IC50 > 10 μM), but significantly inhibited the fMLP/CB-induced elastase release with IC50 value of 6.80 ± 0.18 μM (Table 3).

Table 3.
Effect of 1–11 on superoxide anion generation and elastase release in fMLP/CB induced human neutrophils.
In addition, the nitric oxide (NO) inhibitory activities of compounds 1–11 were further evaluated by assay of LPS-stimulated NO production in activated RAW264.7 cells, as shown in Figure 5. The results indicated that compound 5 could effectively reduce the level of NO to 6.6% at a concentration of 5 μg/mL, with 79.3% retention of cell viability. Moreover, compounds 2 and 5 at the concentration of 10 μg/mL exhibited good inhibitory activity compared to the positive control aminoguanidine (AG), with the levels of NO reduced significantly to 16.9% and 0.3%, respectively, while giving 96.8% and 53.9% retention of cell viability. Thus, compounds 2 and 5 are promising metabolites that might become lead compounds in future anti-inflammatory drug development.
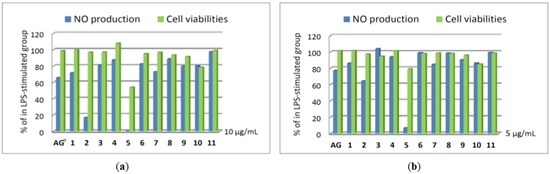
Figure 5.
Nitric oxide (NO) production and cell viabilities of compounds 1–11 in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells (a) at 10 μg/mL (b) at 5 μg/mL. a AG: aminoguanidine used as a positive control.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
Optical rotations were measured on a JASCO P-1020 digital polarimeter (JASCO Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). IR spectra were recorded on a JASCO J-815 spectrophotometer (JASCO Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). Ultraviolet spectra were recorded on a JASCO V-650 spectrophotometer (JASCO Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). The 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra were recorded on Varian 400MR NMR (400 MHz for 1H and 100 MHz for 13C) instruments (Varian Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA). The chemical shifts were referenced to the solvent residue of CDCl3 (δH 7.265 ppm and δC 77.0 ppm). The ESIMS and HRESIMS were acquired via a Bruker APEX II mass spectrometer with an ESI ionization source (Bruker, Bremen, Germany). Silica gel 60 (40–63 μm, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany), and C18 gel (LiChroprep RP-18, 40–63 μm, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) were used for column chromatography. TLC analysis was performed on precoated silica gel plates (Kieselgel 60 F254, 0.25 mm, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was performed using a Shimadzu LC-10ATVP series pump equipped with a UV detector and a semipreparative RP-18 column (5 μm, 250 mm × 10 mm, Hibar Purospher RP-18e, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany).
3.2. Animal Material
The soft coral Umbellulifera petasites was collected by hand using scuba on reefs at depths of 10–15 m, along the coast of Kaohsiung, located at Southern Taiwan in October 2008. The material was frozen at −20 °C until extraction in the laboratory. Species identification of this coral was performed by C.-F. Dai (National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan).
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
The frozen bodies of U. petasites (1.2 kg, wet wt) were sliced and exhaustively extracted with EtOAc (3 × 2 L). The EtOAc extract (12.6 g) was chromatographed over silica gel by column chromatography and eluting with EtOAc in n-hexane (0%–100%, stepwise) then with MeOH in EtOAc (5%–50%, stepwise) to yield 24 fractions. Fraction 11, eluting with n-hexane–EtOAc (15:1), was further purified over silica gel using n-hexane–EtOAc (13:1) to yield compounds 4 (20.0 mg) and 5 (53.0 mg). Fraction 15, eluting with n-hexane–EtOAc (10:1), was further purified by reversed-phase HPLC using MeOH–H2O (15:1) to afford 6 (0.9 mg), 7 (2.5 mg), 8 (1.1 mg), 9 (0.8 mg), 10 (1.5 mg), and 11 (0.9 mg). Fraction 16, eluting with n-hexane–EtOAc (9:1), was further purified by reversed-phase HPLC using acetonitrile–H2O (5:1) to afford 1 (1.5 mg), 2 (13.0 mg), and 3 (1.2 mg).
Petasitosterone A (1): amorphous solid; +186 (c 0.375, CHCl3); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 241 (4.4) and 220 (4.4); IR (neat) νmax 3445, 2948, 2871, 1715, 1653, 1437, 1341 and 1246 cm−1; 13C and 1H NMR data, Table 1; ESIMS m/z 421 [M + Na]+; HRESIMS m/z 421.23500 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C25H34O4Na, 421.23493).
Petasitosterone B (2): amorphous solid; +139 (c 3.25, CHCl3); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 242 (3.9) and 217 (3.9); IR (neat) νmax 2967, 2873, 1731, 1665, 1625, 1435, 1270 and 1241 cm–1; 13C and 1H NMR data, Table 1; ESIMS m/z 463 [M + Na]+; HRESIMS m/z 463.24579 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C27H36O5Na, 463.24550).
Petasitosterone C (3): amorphous solid; −8 (c 0.300, CHCl3); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 243 (4.1) and 206 (4.3); IR (neat) νmax 2952, 2871, 1737, 1661 and 1241 cm–1; 13C and 1H NMR data, Table 1; ESIMS m/z 463 [M + Na]+; HRESIMS m/z 463.24524 [M + Na]+ (calcd. for C27H36O5Na, 463.24550).
5α-Pregna-20-en-3-one (4): amorphous solid; +15 (c 0.20, CHCl3); lit. +12.5 (c 0.20, CHCl3); MS, 1H and 13C NMR data were found to be in full agreement with those reported previously [15].
5α-Pregna-1,20-dien-3-one (5): amorphous solid; +35 (c 0.50, CHCl3); lit. +35.4 (c 0.50, CHCl3); MS, 1H and 13C NMR data were found to be in full agreement with those reported previously [15].
5α,8α-Epidioxycholesta-6,22-dien-3β-ol (6): amorphous solid; +95 (c 0.50, CHCl3); MS, 1H and 13C NMR data were found to be in full agreement with those reported previously [16].
25α,8α-Epidioxy-24(S)-methylcholesta-6,22-dien-3β-ol (7): amorphous solid; +13 (c 0.20, CHCl3); MS, 1H and 13C NMR data were found to be in full agreement with those reported previously [16].
5α,8α-Epidioxy-24(R)-methylcholesta-6,22-dien-3β-ol (8): amorphous solid; −8 (c 0.16, CHCl3); MS, 1H and 13C NMR data were found to be in full agreement with those reported previously [16].
5α,8α-Epidioxycholest-6-en-3β-ol (9): amorphous solid; −30 (c 0.50, CHCl3); MS, 1H and 13C NMR data were found to be in full agreement with those reported previously [16].
5α,8α-Epidioxy-24α-ethylcholesta-6,22-dien-3β-ol (10): amorphous solid; −6 (c 0.50, CHCl3); MS, 1H and 13C NMR data were found to be in full agreement with those reported previously [16].
5α,8α-Epidioxy-24α-ethylcholesta-6-en-3β-ol (11): amorphous solid; −27 (c 0.50, CHCl3); MS, 1H and 13C NMR data were found to be in full agreement with those reported previously [16].
3.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
The Alamar Blue assays were performed as previous reported [18,19]. After the cell lines (K-562, MOLT-4, and DLD-1) were cultured for 15 h according to the published procedure [20], the tested compounds in DMSO solutions were added and cultured for 72 h. The attached cells were incubated with Alamar Blue (10 μL/well, 4 h) and the absorbance was measured at wavelength of 595 nm using a microplate reader.
3.5. Human Neutrophil Superoxide Anion Generation and Elastase Release
The human neutrophils were isolated using a standard method of dextran sedimentation and Ficoll centrifugation [21,22]. As in previously described procedures, the assay of superoxide anion generation was conducted according to the SOD-inhibitable reduction of ferricytochrome C. The elastase release experiment was performed using MeO–Suc–Ala–Ala–Pro–Val–p-nitroanilide as the enzyme substrate [23]. Idelalisib, a selective inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase, was used as a positive control for inhibition of superoxide anion generation and elastase release with IC50 0.07 ± 0.01 and 0.3 ± 0.1 μM [24].
3.6. Nitric Oxide Inhibitory Activity
The nitrite concentration in the culture medium was measured as an indicator of NO production according to the Griess reaction [25]. Briefly, 80 μL of cell culture supernatant was reacted with 100 μL of Griess reagent (1:1 mixture of 0.1% N-(1-naphthyl)ethylenediamine dihydrochloride in water and 1% sulfanilamide in 5% phosphoric acid) in a 96-well plate and incubated at room temperature for 10 min. The absorbance at 550 nm was recorded using the ELISA reader [26,27]. Fresh medium was used as the blank. The results are expressed as the percentage of inhibition calculated relative to the cells treated with vehicle and LPS.
3.7. Statistical Analysis
Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM, and comparisons were made using Student’s t-test. A probability value of 0.05 or less was considered significant. The software SigmaPlot was used for the statistical analysis.
4. Conclusions
Umbellulifera petasites (Thomson and Dean, 1931) [28], which is here investigated for the first time, afforded three new steroids petasitosterones A–C (1–3), along with eight known steroids 4–11. It is worthwhile to mention that compound 3 represents a novel steroid with an A/B spiro[4,5]decane ring system. Our present study shows that compounds 1–3 and 5 exhibited significant cytotoxicity toward a limited panel of cancer cell lines. Moreover, compounds 2–5 are promising compounds, which have displayed potent anti-inflammatory activity in different assays.
Supplementary Materials
HRESIMS, 1H, and 13C spectra of new compounds 1–3 are available online at www.mdpi.com/1660-3397/14/10/180/s1. Figure S1: HRESIMS spectrum of 1, Figure S2: 1H NMR spectrum of 1 in CDCl3 at 400 MHz, Figure S3: 13C NMR spectrum of 1 in CDCl3 at 100 MHz, Figure S4: HRESIMS spectrum of 2, Figure S5: 1H NMR spectrum of 2 in CDCl3 at 400 MHz, Figure S6: 13C NMR spectrum of 2 in CDCl3 at 100 MHz, Figure S7: HRESIMS spectrum of 3, Figure S8: 1H NMR spectrum of 3 in CDCl3 at 400 MHz, Figure S9: 13C NMR spectrum of 3 in CDCl3 at 100 MHz.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST 102-2628-B-110-002-MY2 and 104-2320-B-110-001-MY2), and NSYSU-KMU Joint Research Project (NSYSUKMU 105-I008) of Taiwan awarded to J.-H.S. Partial Finacial support from Taiwan Protein Project (MOST 105-0210-01-12-01) to J.-H.S. is also acknowledged.
Author Contributions
Jyh-Horng Sheu designed and guided the whole experiment. Chiung-Yao Huang contributed to structure elucidation, manuscript preparation and cytotoxicity assay. Che-Wei Chang isolated the compounds and performed data acquisition and structure elucidation. Yen-Ju Tseng, Ping-Jyun Sung and Jui-Hsin Su performed the structure elucidation. Chang-Feng Dai contributed to the collection of soft coral and species identification. Jessica Lee and Tsong-Long Hwang performed the inhibition of superoxide anion generation, and the inhibition of neutrophil elastase release assays. Hui-Chun Wang performed the nitric oxide inhibitory assay.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Tanaka, J.; Trianto, A.; Musman, M.; Issa, H.H.; Ohtani, I.I.; Ichiba, T.; Higa, T.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Scheuer, P.J. New polyoxygenated steroids exhibiting reversal of multidrug resistance from the gorgonian Isis hippuris. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 6259–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Deng, Z.; Pei, Y.; Fu, H.; Li, J.; van Ofwegen, L.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Polyhydroxylated steroids from the soft coral Sinularia dissecta. Steroids 2005, 70, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarma, N.S.; Krishna, M.S.; Pasha, S.G.; Rao, T.S.; Venkateswarlu, Y.; Parameswaran, P.S. Marine metabolites: The sterols of soft coral. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 2803–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.H.; Wang, S.K.; Duh, C.Y. Polyhydroxylated steroids from the bamboo coral Isis hippuris. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1829–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.W.; Chang, S.M.; Huang, C.Y.; Su, J.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Sheu, J.H. Hirsutosterols A–G, polyoxygenated steroids from a Formosan soft coral Cladiella hirsuta. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 3272–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, C.H.; Chou, K.J.; Wen, Z.H.; Wang, G.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Dai, C.F.; Sheu, J.H. Paraminabeolides A–F, cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory marine withanolides from the soft coral Paraminabea acronocephala. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Marrero, A.R.; Porras, G.; Aragon, Z.; de la Rosa, J.M.; Dorta, E.; Cueto, M.; D’Croz, L.; Mate, J.; Darias, J. Carijodienone from the octocoral Carijoa multiflora. A spiropregnane-based steroid. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, C.H.; Chou, K.J.; Huang, C.Y.; Wen, Z.H.; Hsu, C.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Dai, C.F.; Sheu, J.H. Steroids from the soft coral Sinularia crassa. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Y.; Liaw, C.C.; Chen, B.W.; Chen, P.C.; Su, J.H.; Sung, P.J.; Dai, C.F.; Chiang, M.Y.; Sheu, J.H. Withanolide-based steroids from the cultured soft coral Sinularia brassica. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1902–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.F.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Liu, H.L.; Li, J.; Lan, L.F.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Y.W. Bioactive polyhydroxylated steroids from the Hainan soft coral Sinularia depressa Tixier-Durivault. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 1334–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.Y.; Hsu, C.H.; Chao, C.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Dai, C.F.; Sheu, J.H. Cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory metabolites from the soft coral Scleronephthya gracillimum. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1853–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.X.; Tang, X.L.; van Ofwegen, L.; Xue, L.; Song, W.J.; Li, P.L.; Li, G.Q. Cyclopentenone derivatives and polyhydroxylated steroids from the soft coral Sinularia acuta. Chem. Biodivers. 2015, 12, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.R.; Huang, C.Y.; Chen, B.W.; Tsai, Y.Y.; Shih, S.P.; Hwang, T.L.; Dai, C.F.; Wan, S.Y.; Sheu, J.H. New Bioactive Steroids from the Soft Coral Klyxum flaccidum. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 12546–12554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, W.R.; Huang, C.Y.; Tsai, Y.Y.; Lin, Y.S.; Hwang, T.L.; Su, J.H.; Sung, P.J.; Dai, C.F.; Sheu, J.H. New cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory steroids from the soft coral Klyxum flaccidum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 3253–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, Y.; Jung, J.H.; Rho, J.R.; Shin, J. Isolation of novel bioactive steroids from the soft coral Alcyonium gracillimum. Tetrahedron 1995, 51, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunatilaka, A.A.L.; Gopichand, Y.; Schmitz, F.J.; Djerassi, C. Minor and trace sterols in marine invertebrates. Isolation and structure elucidation of nine new 5α,8α-epidioxy sterols from four marine organisms. J. Org. Chem. 1981, 46, 3860–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.H.; Line, F.Y.; Huang, H.C.; Dai, C.F.; Wu, Y.C.; Hu, W.P.; Hsu, C.H.; Sheu, J.H. Novel Steroids from the Soft Coral Nephthea chabrolii. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.; Wilson, I.; Orton, T.; Pognan, F. Investigation of the Alamar Blue (resazurin) fluorescent dye for the assessment of mammalian cell cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 5421–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, G.R.; Caton, M.C.; Nova, M.P.; Parandoosh, Z. Assessment of the Alamar Blue assay for cellular growth and viability in vitro. J. Immunol. Methods 1997, 204, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.H.; Huang, T.Z.; Wu, C.Y.; Chen, B.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Hwang, T.L.; Dai, C.F.; Sheu, J.H. Steroidal and α-tocopherylhydroquinone glycosides from two soft corals Cladiella hirsuta and Sinularia nanolobata. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 74256–74262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, T.L.; Wang, C.C.; Kuo, Y.H.; Huang, H.C.; Wu, Y.C.; Kuo, L.M.; Wu, Y.H. The hederagenin saponin SMG-1 is a natural FMLP receptor inhibitor that suppresses human neutrophil activation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1190–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, T.L.; Leu, Y.L.; Kao, S.H.; Tang, M.C.; Chang, H.L. Viscolin, a new chalcone from Viscum coloratum, inhibits human neutrophil superoxide anion and elastase release via a cAMP-dependent pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 41, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.C.; Chung, P.J.; Ho, C.M.; Kuo, C.Y.; Hung, M.F.; Huang, Y.T.; Chang, W.Y.; Chang, Y.W.; Chan, K.H.; Hwang, T.L. Propofol inhibits superoxide production, elastase release, and chemotaxis in formyl peptide-activated human neutrophils by blocking formyl peptide receptor 1. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 6511–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Y.; Tseng, Y.J.; Chokkalingam, U.; Hwang, T.L.; Hsu, C.H.; Dai, C.F.; Sung, P.J.; Sheu, J.H. Bioactive isoprenoid-derived natural products from a Dongsha atoll soft coral Sinularia erecta. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Cheon, B.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.P. Effects of naturally occurring flavonoids on nitric oxide production in the macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 and their structure–activity relationships. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999, 58, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H.H.W.; Kelm, M. Determination of nitrite and nitrate by the Griess reaction. In Methods in Nitric Oxide Research; Feelisch, M., Stamler, J., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1996; pp. 491–497. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, Y.H.; Kuo, P.M.; Chien, S.C.; Shyur, L.F.; Wang, S.Y. Effects of Chamaecyparis formosensis Matasumura extractives on lipopolysaccharide-induced release of nitric oxide. Phytomedicine 2007, 14, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, E. Inventory of zoological type specimens in the museum of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory. Publ. Seto Mar. Biol. Lab. 1991, 35, 171–233. [Google Scholar]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).