2. Results and Discussion
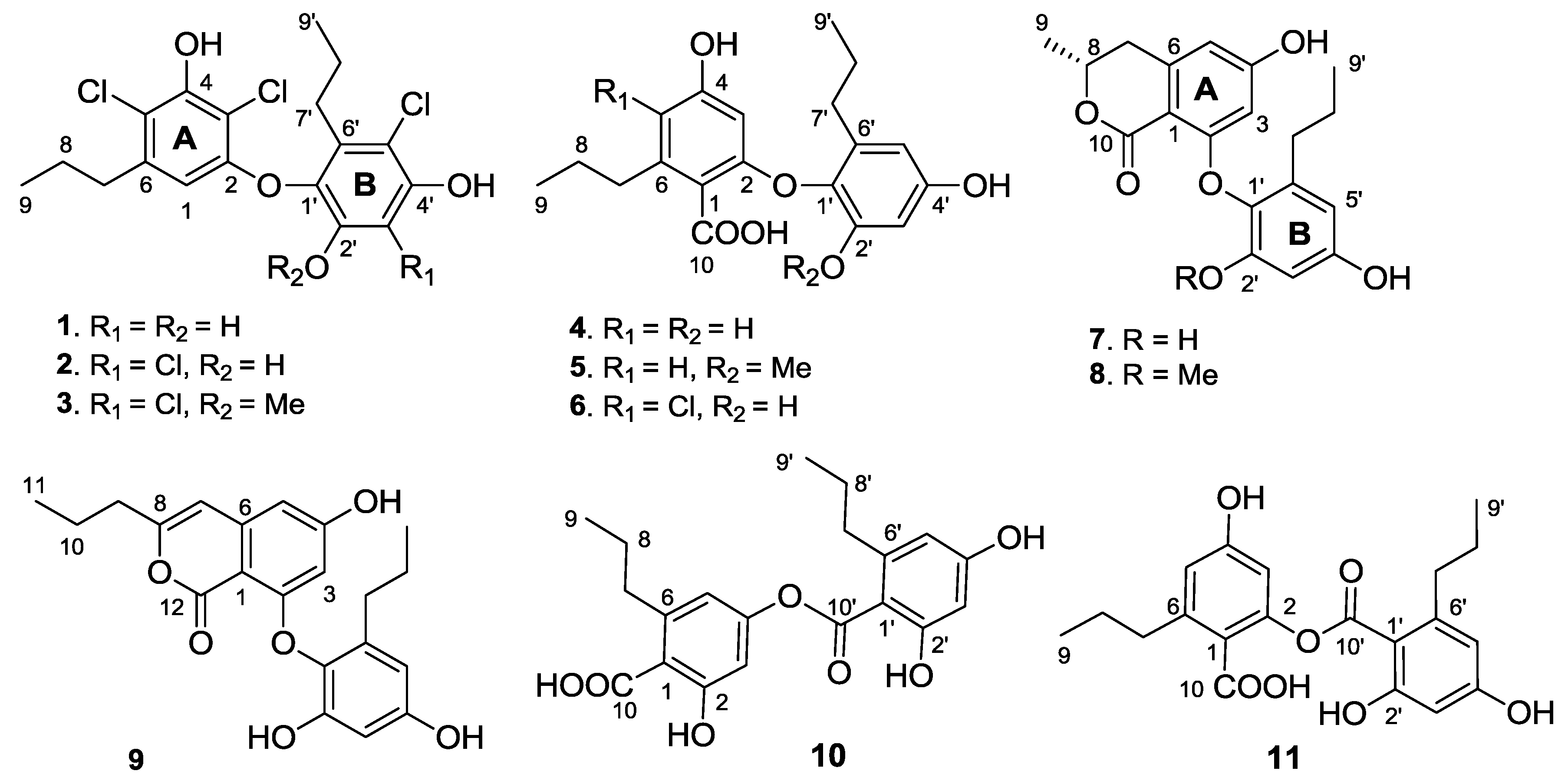
Spiromastol A (
1) was isolated as a colorless oil (
Figure 1). Its molecular formula was deduced as C
18H
19Cl
3O
4 on the basis of the HRESIMS (
m/z 403.0272 [M − H]
−) and NMR data, requiring eight degrees of unsaturation and containing three chlorine atoms. The IR absorption bands at 3408, 1651 and 1601 cm
−1 suggested the presence of hydroxy and aromatic functionalities. The
1H NMR spectrum displayed three exchangeable protons (δ
H 10.00, 9.99 and 9.73), two aromatic singlets at δ
H 5.97 (1H, s, H-1) and 6.57 (1H, s, H-3′), and the alkyl protons for four methylene and two methyl groups. The
13C NMR spectrum exhibited a total of 18 carbon resonances, including 12 aromatic carbons for two phenyl moieties (rings A and B) and six alkyl carbons for two
n-propyl groups, which were assigned by the COSY and HMBC correlations (
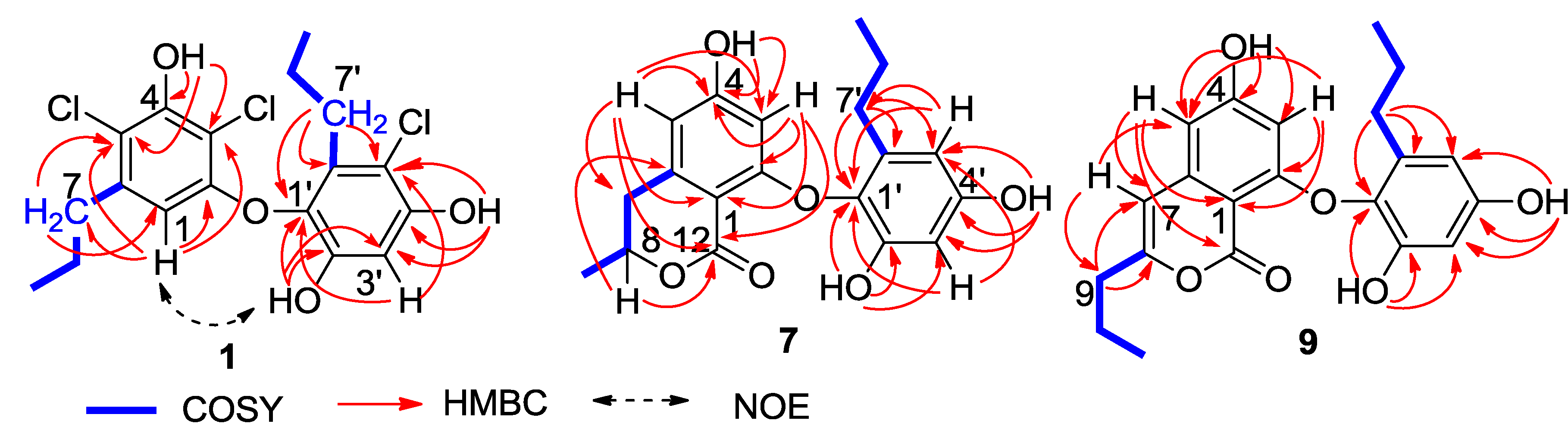
Figure 2). In regard to the substitution of the aromatic ring A, the HMBC interaction of H-1 with a
n-propyl methylene (δ
C 35.6, C-7) allowed to assign the location of the
n-propyl group vicinal to C-1 (δ
C 106.7). Additional HMBC interactions from H-1 to C-2 (δ
C 153.1), C-3 (δ
C 108.4), and C-5 (δ
C 114.8), and a weak correlation with C-4 (δ
C 150.3), H
2-7 (δ
H 2.48, m) to C-1, C-5 and C-6 (δ
C 139.0), and a phenol proton at δ
H 10.00 (brs, OH-4) to C-3, C-4 and C-5 established a 3,5-disubstituted and 2,4-dioxygenated 6-propylphenyl segment, in which C-4 was hydroxylated. Similarly, the substitution of the aromatic ring B was established on the basis of the HMBC relationships. The observation of the HMBC interactions from the aromatic proton H-3′ to C-1′ (δ
C 132.7), C-2′ (δ
C 149.3), C-4′ (δ
C 151.5) and C-5′ (δ
C 110.4), the phenol proton at δ
H 9.73 (s, OH-2′) to C-1′, C-2′ and C-3′ (δ
C 102.7), and the other phenol proton at δ
H 9.99 (s, OH-4′) to C-3′, C-4′ and C-5′, in addition to the HMBC interactions of the second
n-propyl protons, assigned a 5′-substituted and 1′-oxygenated 2′,4′-dihydroxy-6′-propylphenyl ring. Since two aromatic rings covered eight degrees of the molecular unsaturation, the connection of rings A and B was suggested through a C-C bond or an ether bond. The observation of NOE interaction between H-1 and OH-2′ (
Figure 2) assumed an ether linkage across C-2 and C-1′. Thus, the quaternary carbons C-3, C-5 and C-5′ were substituted by chlorine atoms.
Figure 2.
Key 2D NMR correlations of 1, 7 and 9.
Figure 2.
Key 2D NMR correlations of 1, 7 and 9.
The molecular formula of spiromastol B (2) was determined as C18H18Cl4O4 by the HRESIMS (m/z 436.9873 [M − H]−) and NMR data, indicating the presence of one more chlorine atom and the absence of a proton in comparison with those of 1. The NMR data of 2 were very similar to those of 1, with the exception of a quaternary carbon (δC 109.6, C-3′) of 2 to replace an aromatic methine of 1. Comparison of the NMR data in association with the HMBC interactions, such as from H2-7 (δH 2.49, m) to C-1 (δC 106.8), C-5 (δC 115.4) and C-6 (δC 139.3), from the phenol proton OH-4 (δH 10.10, s) to C-3 (δC 108.9), C-4 (δC 150.5) and C-5, and from H-1 (δH 5.97, s) to C-2 (δC 152.9), C-3, C-4 and C-5, indicated both compounds sharing the partial structure of the aromatic ring A. Thus, the additional chlorine atom was placed in the aromatic ring B. The HMBC relationships of both phenol protons at δH 9.91 (s, OH-2′) and 9.86 (s, OH-4′) with the quaternary carbon C-3′, clarified the structure of 2 to be a 3′-chlorinated analogue of 1.
Spiromastol C (3) has a molecular formula of C19H20Cl4O4 as determined by the HRESIMS data (m/z 451.0042 [M − H]−), containing a CH2 unit more than that of 2. The similar NMR data with the exception of the presence of methoxy resonances whose protons (δH 3.83, s) correlated to C-2′ (δC 150.5) in the HMBC spectrum, clarified compound 3 to be a 2′-methoxy analogue of 2. The downfield shifted C-1′ (Δ 3.8 ppm), C-2′ (Δ 4.1 ppm) and C-3′ (Δ 6.1 ppm) in comparison with the corresponding carbons of 2 further supported the methoxy substitution.
The molecular formula of spiromastol D (4) was determined as C19H22O6 based on the HRESIMS (m/z 345.1341 [M − H]−) and NMR data. The 13C NMR spectrum provided a total of 19 carbon resonances, including 12 aromatic carbons for two phenyl rings, a carboxylic carbon, and six alkyl carbons which were assigned to two n-propyl groups based on the COSY and HMBC data. The COSY spectrum displayed two aromatic spin systems of meta-couplings between δH 5.77 (1H, d, J = 2.3 Hz, H-3)/6.21(1H, d, J = 2.3 Hz, H-5) for ring A, and δH 6.27 (1H, d, J = 2.8 Hz, H-3′)/6.11 (1H, d, J = 2.8 Hz, H-5′) for ring B. In the aromatic ring A, the HMBC interactions from a phenol proton at δH 9.45 (s, OH-4) to C-3 (δC 98.7), C-4 (δC 158.8) and C-5 (δC 109.1) indicated C-4 to be hydroxylated. Additional HMBC interactions from H-5 to the methylene carbon at δC 35.5 and from H-3 and H-5 to C-1 (δC 115.7) and the carboxylic carbon at δC 169.5 through 4JH-C coupling, revealed the position of a n-propyl group at C-6 (δC 141.9) and the carboxylic group at C-1. The oxygenated C-2 (δC 157.1) was assigned by the 2JH-C coupling between H-3 and C-2 in the HMBC spectrum. The substitution of the second n-propyl group at C-6′ (δC 137.0) in the aromatic ring B was evident from the HMBC interaction between H-5′ and the methylene carbon at δC 32.0 (C-7′), while the NOE interactions between a phenol proton at δH 9.21 (s, OH-2′) and H-3′, and from the other phenol proton at δH 9.11 (s, OH-4′) to H-3′ and H-5′ assigned a 2′, 4′-dihydroxy-6′-propylphenyl ring. Since C-4 was positioned by a hydroxy group, the connection of the aromatic ring B at C-1′ (δC 132.6) with the aromatic ring A through an ether bond with C-2 or ester bond with C-10 was suggested. The observation of the carboxylic proton at δH 12.58 (brs) clarified C-10 to be an acidic group. Thus, the linkage of ring B with ring A though an ether bond across C-2 and C-1′ was assumed.
Spiromastol E (
5) has a molecular formula of C
20H
24O
6 as determined by the HRESIMS (
m/z 359.1498 [M − H]
−) and NMR data, bearing a CH
2 unit more than that of
4. Apart from
5 containing an additional methoxy group (δ
H 3.66, δ
C 56.0), the NMR data of both
5 and
4 were closely similar (
Table 1 and
Table 2). The methoxy group of
5 was positioned at C-2′ (δ
C 153.2) on the basis of the HMBC relationship between the methoxy protons and C-2′. Thus, compound
5 was determined as a 2′-methoxylated analogue of
4.
Table 1.
The 1H NMR data of spiromastols A–K (1–11) (δH ppm, J in Hz).
Table 1.
The 1H NMR data of spiromastols A–K (1–11) (δH ppm, J in Hz).
| No | 1 a | 2 a | 3 b | 4 b | 5 b | 6 c | 7 b | 8 a | 9 b | 10 b | 11 a |
|---|
| 1 | 5.97 s | 5.97 s | 6.00 s | | | | | | | | |
| 3 | | | | 5.77 (d, 2.3) | 5.67 (d, 1.8) | 6.05 s | 5.90 brs | 5.81 (d, 1.8) | 5.96 (d, 2.2) | 6.59 (d, 1.9) | 6.55 (d, 1.7) |
| 5 | | | | 6.21 (d, 2.3) | 6.20 (d, 1.8) | | 6.26 brs | 6.26 (d, 1.8) | 6.35 (d, 2.2) | 6.51 (d, 1.9) | 6.47 (d, 1.7) |
| 7 | 2.48 m | 2.49 m | 2.51 m | 2.51 (t, 6.5) | 2.49 m | 2.62 (t, 7.7) | 2.77 (dd, 10.6, 16.2) 2.87 (dd, 2.7, 16.2) | 2.77 (dd, 10.4, 16.0) 2.87 (dd, 2.5, 16.0) | 6.32 s | 2.61 m | 2.65 (t, 7.5) |
| 8 | 1.40 m | 1.39 m | 1.41 m | 1.56 m | 1.56 m | 1.55 m | 4.50 m | 4.51 m | | 1.55 m | 1.55 m |
| 9 | 0.81 (t, 7.2) | 0.81 (t, 7.2) | 0.81 (t, 7.3) | 0.90 (t, 7.3) | 0.90 (t, 7.2) | 0.93 (t, 7.4) | 1.37 (d, 6.3) | 1.37 (d, 6.3) | 2.42 (t, 7.3) | 0.89 (t, 7.3) | 0.89 (t, 7.5) |
| 10 | | | | | | | | | 1.63 m | | |
| 11 | | | | | | | | | 0.95 (t, 7.5) | | |
| 3′ | 6.57 s | | | 6.27 (d, 2.8) | 6.39 (d, 2.4) | 6.26 (d, 2.7) | 6.28 (d, 2.6) | 6.42 (d, 2.3) | 6.31 (d, 2.6) | 6.25 (d, 1.7) | 6.24 (d, 1.8) |
| 5′ | | | | 6.11 (d, 2.8) | 6.25 (d, 2.4) | 6.09 (d, 2.7) | 6.14 (d, 2.6) | 6.28 (d, 2.3) | 6.15 (d, 2.6) | 6.20 (d, 1.7) | 6.19 (d, 1.8) |
| 7′ | 2.46 m | 2.43 m | 2.48 m | 2.28 (t, 7.4) | 2.30 (t, 7.6) | 2.26 (t, 7.6) | 2.27 (t, 7.6) | 2.28 m | 2.26 (t, 7.6) | 2.59 m | 2.59 (t, 7.7) |
| 8′ | 1.39 m | 1.38 m | 1.40 m | 1.40 m | 1.40 m | 1.38 m | 1.45 m | 1.43 m | 1.46 m | 1.55 m | 1.56 m |
| 9′ | 0.82 (t, 7.2) | 0.82 (t, 7.5) | 0.83 (t, 7.3) | 0.79 (t, 7.3) | 0.78 (t, 7.4) | 0.77 (t, 7.2) | 0.78 (t, 7.4) | 0.77 (t, 7.5) | 0.77 (t, 7.4) | 0.90 (t, 7.3) | 0.90 (t, 7.3) |
| 1-COOH | | | | 12.58 brs | 12.37 brs | 12.78 brs | | | | 12.23 brs | 12.20 brs |
| 2-OH | | | | | | | | | | 9.87 s | |
| 4-OH | 10.00 brs | 10.10 s | | 9.45 s | 9.39 brs | 10.10 s | 10.20 s | 10.22 s | 10.46 s | | 9.87 s |
| 2′-OH | 9.73 s | 9.91 s | | 9.21 s | | 9.33 brs | 9.27 s | | 9.37 s | 10.14 s | 10.14 s |
| 2′-OCH3 | | | 3.83 s | | 3.66 s | | | 3.65 s | | | |
| 4′-OH | 9.99 s | 9.86 s | | 9.11 brs | 9.34 brs | 9.12 s | 9.12 s | 9.37 s | 9.18 s | 9.87 s | 9.88 s |
Table 2.
13C NMR data of spiromastols A–K (1–11) (δC ppm).
Table 2.
13C NMR data of spiromastols A–K (1–11) (δC ppm).
| No | 1 a | 2 a | 3 b | 4 b | 5 b | 6 c | 7 b | 8 a | 9 b | 10 b | 11 a |
|---|
| 1 | 106.7 CH | 106.8 CH | 106.8 CH | 115.7 C | 115.9 C | 116.4 C | 105.0 C | 104.7 C | 100.8 C | 113.6 CH | 118.8 C |
| 2 | 153.1 C | 152.9 C | 152.5 C | 157.1 C | 156.9 C | 153.9 C | 162.4 C | 162.4 C | 158.3 C | 157.4 C | 158.3 C |
| 3 | 108.4 C | 108.9 C | 109.0 C | 98.7 CH | 98.3 CH | 99.3 CH | 100.6 CH | 100.2 CH | 100.7 CH | 107.5 CH | 107.5 CH |
| 4 | 150.3 C | 150.5 C | 150.6 C | 158.8 C | 158.7 C | 154.2 C | 162.8 C | 162.8 C | 164.2 C | 152.2 C | 152.2 C |
| 5 | 114.8 C | 115.4 C | 115.6 C | 109.1 CH | 108.9 CH | 112.0 C | 107.6 CH | 107.7 CH | 103.9 CH | 119.1 C | 113.5 CH |
| 6 | 139.0 C | 139.3 C | 139.5 C | 141.9 C | 141.7 C | 137.9 C | 144.1 C | 144.2 C | 141.9 C | 143.1 C | 143.5 C |
| 7 | 35.6 CH2 | 35.5 CH2 | 35.5 CH2 | 35.5 CH2 | 35.5 CH2 | 33.2 CH2 | 35.8 CH2 | 35.8 CH2 | 103.1 CH | 35.9 CH2 | 36.1 CH2 |
| 8 | 22.8 CH2 | 22.8 CH2 | 22.8 CH2 | 24.3 CH2 | 24.2 CH2 | 22.6 CH2 | 73.5 CH | 73.5 CH | 158.1 C | 24.4 CH2 | 24.4 CH2 |
| 9 | 13.8 CH3 | 13.8 CH3 | 13.8 CH3 | 14.2 CH3 | 14.4 CH3 | 14.2 CH3 | 20.9 CH3 | 20.9 CH3 | 34.8 CH2 | 14.3 CH3 | 14.3 CH3 |
| 10 | | | | 169.5 C | 169.2 C | 168.4 C | 168.5 C | 168.5 C | 20.1 CH2 | 170.2 C | 170.4 C |
| 11 | | | | | | | | | 13.8 CH3 | | |
| 12 | | | | | | | | | 162.8 C | | |
| 1′ | 132.7 C | 134.2 C | 138.0 C | 132.6 C | 133.2 C | 131.8 C | 132.6 C | 133.1 C | 132.2 C | 110.0 C | 110.0 C |
| 2′ | 149.3 C | 146.4 C | 150.5 C | 150.8 C | 153.2 C | 150.3 C | 150.4 C | 152.7 C | 150.3 C | 159.0 C | 159.1 C |
| 3′ | 102.7 CH | 109.6 C | 115.7 C | 102.0 CH | 99.0 CH | 101.6 CH | 102.1 CH | 99.1 CH | 102.2 CH | 101.0 CH | 101.0 CH |
| 4′ | 151.5 C | 148.0 C | 147.0 C | 155.2 C | 155.5 C | 154.9 C | 155.3 C | 155.7 C | 155.4 C | 160.9 C | 160.9 C |
| 5′ | 110.4 C | 112.8 C | 118.8 C | 107.4 CH | 108.3 CH | 106.9 CH | 107.4 CH | 108.3 CH | 107.5 CH | 108.9 CH | 108.9 CH |
| 6′ | 134.6 C | 132.7 C | 133.5 C | 137.0 C | 137.0 C | 136.4 C | 136.5 C | 136.8 C | 136.3 C | 144.2 C | 144.2 C |
| 7′ | 30.1 CH2 | 30.1 CH2 | 30.1 CH2 | 32.0 CH2 | 31.8 CH2 | 31.5 CH2 | 32.2 CH2 | 32.0 CH2 | 32.2 CH2 | 36.3 CH2 | 36.4 CH2 |
| 8′ | 22.3 CH2 | 22.1` CH2 | 22.1 CH2 | 23.5 CH2 | 23.4 CH2 | 23.0 CH2 | 23.1 CH2 | 23.0 CH2 | 23.0 CH2 | 24.6 CH2 | 24.6 CH2 |
| 9′ | 14.4 CH3 | 14.3 CH3 | 14.3 CH3 | 14.4 CH3 | 14.1 CH3 | 13.7 CH3 | 14.3 CH3 | 14.3 CH3 | 14.3 CH3 | 14.4 CH3 | 14.4 CH3 |
| 10′ | | | | | | | | | | 167.3 C | 167.4 C |
| 2′-OCH3 | | | 60.8 CH3 | | 56.0 CH3 | | | 56.0 CH3 | | | |
The molecular formula of spiromastol F (6) was determined as C19H21ClO6 by the HRESIMS (m/z 379.0951 [M − H]−) and NMR data, with one chlorine atom more than that of 4. Comparison of the NMR data revealed that both compounds had the same partial structure of the aromatic ring B, whereas a quaternary carbon at δC 112.0 (C-5) in the aromatic ring A of 6 was recognized to replace the aromatic methine C-5 of 4. This finding reflected C-5 of 6 to be substituted by a chlorine atom. This assignment was supported by the HMBC correlations from H2-7 and OH-4′ (δH 10.10, s) to C-5, in association with the similar NMR data and HMBC relationships of the remaining resonances.
Spiromastol G (
7) has a molecular formula of C
19H
20O
6, as determined by the HRESIMS (
m/z 343.1176 [M − H]
−) and NMR data, requiring ten degrees of unsaturation. The NMR data of
7 regarding the aromatic ring B were compatible to those of
4, indicating that both compounds share the same partial structure of ring B. The distinction was attributed to the substitution of the propyl group at C-6 of the aromatic ring A, in which the methyl protons (δ
H 1.37, d,
J = 6.3 Hz, H
3-9) showed a COSY correlation with an oxymethine proton (δ
H 4.50, m, H-8) and the HMBC interactions with C-8 (δ
C 73.5) and C-7 (δ
C 35.8). These facts indicated C-8 to be substituted by an oxygen atom. Additional HMBC interaction between H-8 and the carbonyl carbon at δ
C 168.5 (C-10) allowed the formation of a δ-lactone. Thus, ring A was assigned as a 8-methyldihydroisocoumarine unit. The HMBC interactions of phenol protons at δ
H 10.20 (1H, s, OH-4), 9.27 (1H, s, OH-2′) and 9.12 (1H, s, OH-4′) with the aromatic carbons allowed the assignment of C-4 (δ
C 162.8), C-2′ (δ
C 150.4) and C-4′ (δ
C 155.3) to be hydroxylated. Additional HMBC relationships from the aromatic protons to the aromatic carbons (
Figure 2) assigned C-2 (δ
C 162.4) and C-1′ (δ
C 132.6) to be substituted by oxygen atoms. The absence of phenol protons for OH-2 and OH-1′ conducted the connection of rings A and B through an ether bond across C-2/C-1′. Based on the helicity rule of the chiral benzoic ester chromophore [
15,
16], the negative circular dichroism (CD) effect (
Figure 3) at 273 nm (Δε-1.23) for the n-π* transition reflected 8
R configuration.
Figure 3.
Circular dichroism (CD) curves of 7 and 8.
Figure 3.
Circular dichroism (CD) curves of 7 and 8.
Spiromastol H (
8) has a molecular formula of C
20H
22O
6 as provided by the HRESIMS (
m/z 357.1338 [M − H]
−) and NMR data, containing a CH
2 unit more than that of
7. The NMR data of both
8 and
7 were very similar, except for
8 presenting an additional methoxy group (δ
H 3.65, δ
C 56.0). These findings indicated
8 to be a methoxylated analogue of
7. The HMBC relationship between the methoxy protons and C-2′ (δ
C 152.7) determined
8 as a 2′-methoxylated analogue of
7. The similar CD effects [Δε-1.84 (272)] (
Figure 3) revealed the same configuration at C-8 of both compounds.
The molecular formula of spiromastol I (9) was established as C21H22O6 based on the HRESIMS (m/z 369.1339 [M − H]−) and NMR data, requiring 11 degrees of unsaturation. Comparison of the NMR data resulted in the partial structure regarding the aromatic ring B to be the same as that of 7. Analysis of 1D and 2D NMR (COSY, HMQC and HMBC) data disclosed an isocoumarin core, based on the presence of meta-spin system at H-3 (δH 5.96, d, J = 2.2 Hz) and H-5 (δH 6.35, d, J = 2.2 Hz), in association with the HMBC interactions from H-5 to C-1 (δC 100.8), C-3 (δC 100.7), C-4 (δC 164.2), C-7 (δC 103.1) and C-12 (δC 162.8), H-3 to C-1, C-2 (δC 158.3), C-4, C-5 (δC 103.9) and C-12, H-7 (δH 6.32, s) to C-1, C-5, C-6 (δC 141.9), and C-9 (δC34.8), as well as a phenol proton at δH 10.46 (s, OH-4) to C-3, C-4 and C-5. These findings ascertained C-4 to be hydroxylated, while C-2 was substituted by an oxygen atom. The COSY correlations afforded an additional n-propyl group, whose methylene protons at δH 2.42 (2H, t, J = 7.3 Hz, H2-9) showed the HMBC correlations with C-8 and C-7, indicating the n-propyl group to be positioned at C-8. Since the phenol protons OH-4, OH-2′ (δH 9.36, s) and OH-4′ (δH 9.18, s) were defined, the only possibility for the connection of isocoumarin moiety with the aromatic ring B through a C-2/C-1′ ether bond was determined.
Spiromastol J (
10) had a molecular formula of C
20H
22O
7 as determined by the HRESIMS (
m/z 373.1287 [M − H]
−) and NMR data. Analysis of the
1H and
13C NMR data revealed the presence of two aromatic rings, two
n-propyl groups and two carboxylic carbons, while the HMQC spectrum assigned the protons and their associated carbons. In the COSY spectrum, two spin systems for
meta-coupling aromatic protons between δ
H 6.59 (d,
J = 1.9 Hz, H-3)/6.51 (d,
J = 1.9 Hz, H-5) and δ
H 6.25 (d,
J = 1.7 Hz, H-3′)/6.20 (d,
J = 1.7 Hz, H-5′) were observed. The substitution of the
n-propyl groups at C-6 (δ
C 143.1) and C-6′ (δ
C 144.2), respectively, was evident from the HMBC interactions between H-5/C-7 (δ
C 35.9) and H-5′/C-7′ (δ
C 36.3). A phenol proton at δ
H 10.14 (s) showed the HMBC correlations with C-1′ (δ
C 110.0), C-2′ (δ
C 159.0) and C-3′ (δ
C 101.0) assigned C-2′ to be hydroxylated. Although the absence of the HMBC interaction for remaining phenol protons due to their broad signals, the HMBC correlations of the aromatic protons enabled to assign C-2 (δ
C 157.4) and C-4 (δ
C 152.2) of the aromatic ring A, and C-4′ (δ
C 160.9) of the aromatic ring B to be oxygenated. The
4JH-C correlations observed from H-3 and H-5 to the carboxylic carbon at δ
C 170.2 (C-10) and from H-3′ and H-5′ to δ
C 167.3 (C-10′) conducted the carboxylic groups to be located at C-1 and C-1′, respectively. In order to establish the connection of both aromatic rings A and B, compound
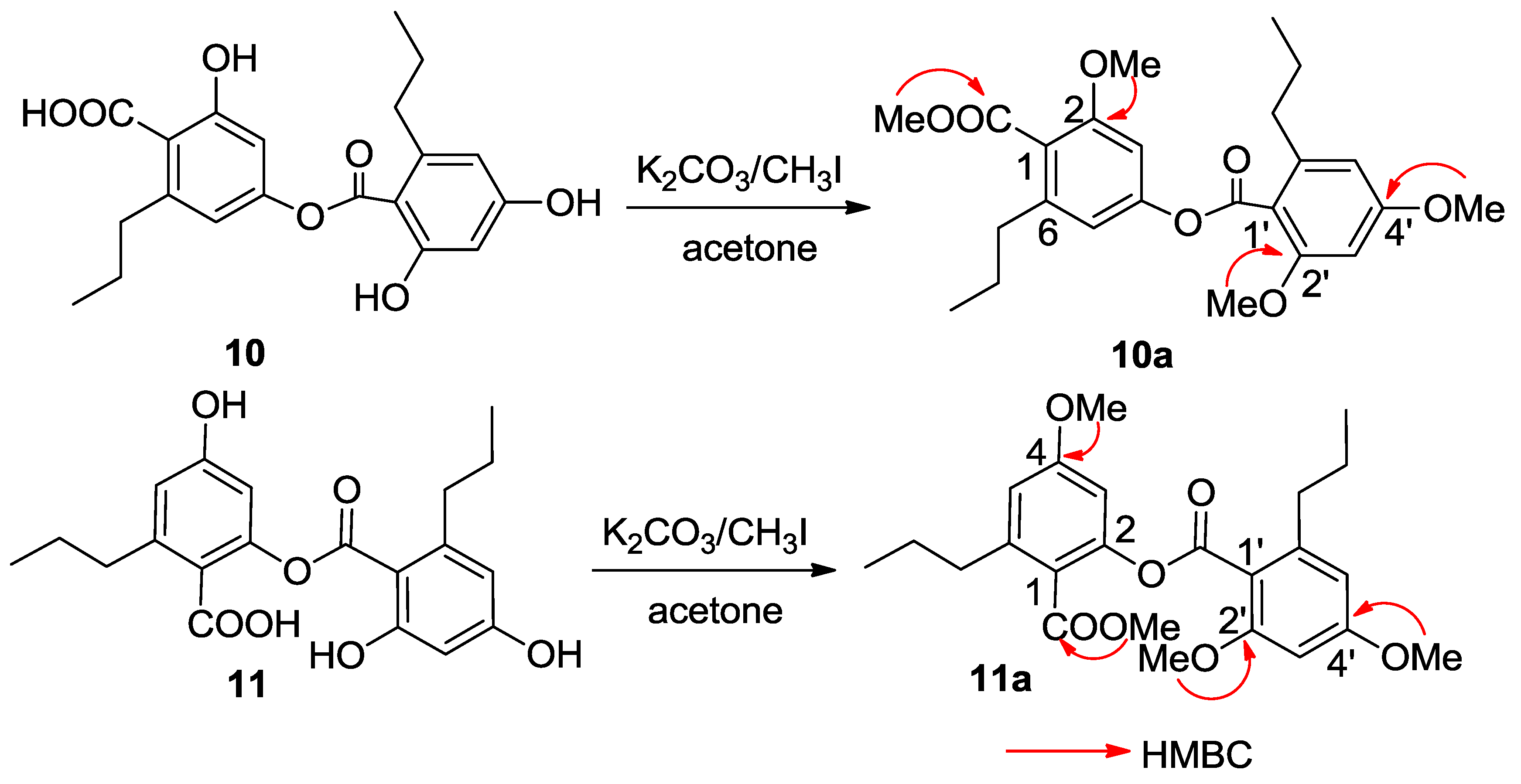
10 was methylated [
17] to form an analogue
10a (
Figure 4), which displayed four methoxy resonances in the
1H NMR spectrum. The HMBC interactions of
10a between δ
H 3.92 (3H, s, OMe)/δ
C 168.5 (s, C-10), δ
H 3.85 (3H, s, OMe)/δ
C 157.3 (s, C-2), δ
H 3.86 (3H, s, OMe)/δ
C 158.6 (s, C-2′), and δ
H 3.89 (3H, s, OMe)/δ
C 161.9 (s, C-4′), clarified an ester bond formed across C-4 and C-10′.
Spiromastol K (
11) has the same molecular formula as that of
10 as determined by the HRESIMS (
m/z 373.1281 [M − H]
−) data. The NMR data of both
11 and
10 were virtually similar. The presence of the phenol protons OH-2′ (δ
H 10.14, s) and OH-4′ (δ
H 9.88, s) in addition to their HMBC correlations with the aromatic carbons resulted in the partial structure regarding the aromatic ring B of
11 to be the same as that of
10. A phenol proton at δ
H 9.87 (s) in ring A showing the HMBC interactions with C-3 (δ
C 107.5), C-4 (δ
C 152.2) and C-5 (δ
C 113.5) revealed C-4 to be hydroxylated. Thus, the connection of aromatic rings B with A through an ester bond across C-10′ (δ
C 167.4) and C-2 (δ
C 158.3) was assumed. The HMBC interactions of the methylated analogue
11a (
Figure 4) further supported the structural assignment.
Figure 4.
Methylation of 10 and 11.
Figure 4.
Methylation of 10 and 11.
Spiromastols (
1–
11) were tested against a panel of bacterial strains, including
Xanthomanes vesicatoria ATCC 11633,
Pseudomonas lachrymans ATCC11921,
Agrobacterium tumefaciens ATCC11158,
Ralstonia solanacearum ATCC11696,
Bacillus thuringensis ATCC 10792,
Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 and
Bacillus subtilis CMCC 63501. As shown in
Table 3, compounds
1–
3 exhibited potent antibacterial activities against all strains of bacteria with minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) values ranging from 0.25 to 4 µg/mL, while compounds
9–11 showed moderate inhibition with MIC values in the range of 8–64 µg/mL. However, no inhibition was observed for compounds
4–8. Analysis of the structure-activity relationships of spiromastols revealed that antibacterial activities depended on the substitution in rings A and B. The dichlorinated ring A (
1–
3) increased the inhibitory effects against bacteria, while the 2′-methoxylated analogue
3 showed more potent effect than that with a 2′-hydroxy group (
2). The analogues with a carboxylic acid at C-1 (
4–
6) dramatically decreased the antibacterial activity. Comparison of the data of
7–
9 (
Table 3) revealed that isocoumarin
9 showed stronger inhibition than those with dihydroisocoumarin scaffold (
7–
8). The analogues with an ester bond connecting rings A and B (
10–
11) showed stronger effects than these with an ether bond (
4–
6). These data may help to design or modify new analogues with potential antibacterial effects.
Table 3.
Antibacterial activities of compounds 1–11.
Table 3.
Antibacterial activities of compounds 1–11.
| | MIC (µg/mL) |
|---|
| Compound | Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | Bacillussubtilis CMCC 63501 | Bacillus thuringensis ATCC 10792 | Ralstonia solanacearum ATCC 11696 | Xanthomanes vesicatoria ATCC 11633 | Agrobacterium tumefaciens ATCC11158 | Pseudomonas lachrymans ATCC11921 |
|---|
| 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 4 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 5 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 6 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 7 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 8 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 | >128 |
| 9 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 16 | 8 | 16 |
| 10 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 64 | 32 | 32 |
| 11 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 32 | 64 | 32 | 32 |
| CP a | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
Optical rotations were measured on a Rudolph IV Autopol automatic polarimeter at 25 °C. UV spectra were measured on a Cary 300 spectrometer. IR spectra were measured on a Thermo Nicolet Nexus 470 FT-IR spectrometer. CD spectra were measured on a JASCO J-810 spectropolarimeter. 1H, 13C, and 2D NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Advance 400, 500, and 600 NMR spectrometers, respectively. Chemical shifts are expressed in δ (ppm) referenced to the solvent peaks at δH 2.50 and δC 39.5 for DMSO-d6, and δH 7.26 and δC 77.2 for CDCl3, respectively, and coupling constants are in Hz. HRESIMS spectra were obtained from Xevo G2 Q-TOF mass spectrometer. Materials for column chromatography (CC) involved silica gel (100–200 and 200–300 mesh, Qingdao Marine Chemistry Co. Ltd., Qingdao, China), ODS gel (50 μm, YMC, Japan) and Sephadex LH-20 (18–110 μm, Amersham Pharmacia Biotech AB, Uppsala, Sweden). Precoated silica gel plates (Merck, Kieselgel 60 F254, 0.25 mm) were used for TLC analysis. HPLC chromatography was performed on a Waters e2695 separation Module coupled with a Waters 2998 photodiode array detector and a semi-preparative reversed-phased column (YMC-packed C18, 5 μm, 250 mm × 10 mm) was used for purification.
3.2. Fungal Material and Fermentation
The fungal Spiromastix sp. MCCC 3A00308 was isolated from a deep ocean sediment, which was collected with TV-multicore in June 2011 from the South Atlantic Ocean at site S015-TVMC06 (GPS 13.75° W, 15.17° S) at a depth of 2869 m during the Comra 22nd oceanic cruise Leg 5. The fungus was identified as Spiromastix genus by ITS gene sequence analysis (GeneBank accession number KJ010057). The strain MCCC 3A00308 was deposited in the Marine Culture Collection Center (MCCC), Third Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration, Xiamen, China. The fungus Spiromastix sp. MCCC 3A00308 was cultured on PDA slants at 25 °C for 10 days. The fermentation was carried out in Erlenmeyer flasks (50 × 500 mL), each containing 100 g of rice, to which distilled H2O (140 mL) was added. The contents were soaked overnight before autoclaving at 15 psi for 30 min. After cooling to about 30 °C, each flask was inoculated with 5 mL of the spore inoculum and incubated at 25 °C for 50 days.
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
The fermentation broth of Spiromastix sp. MCCC 3A00308 fungus was extracted three times with ethyl acetate (3 × 10 L). The organic extracts were evaporated under vacuum to afford crude extracts (58.4 g). The crude extract was subjected to silica gel vacuum liquid chromatography (VLC) eluted with petroleum ether–Me2CO (50:1–1:1) to afford 10 fractions (FA–FJ). FG (6.1 g) was purified through an ODS column eluted with MeOH-H2O (1:1–1:0) to give eleven sub-fractions (SFG1–SFG11). SFG9 (165 mg) was separated sequentially on ODS column eluted with MeOH–H2O (1:1–1:0), and semi-preparative HPLC with a mobile phase of MeCN-H2O (4:1) to yield compound 3 (3.8 mg). FH (8.2 g) was separated by ODS chromatography eluted with MeOH–H2O (1:1–1:0) to obtain ten sub-fractions (SFH1–SFH10). SFH5 (423 mg) was purified by silica gel column eluted with petroleum ether-acetone (10:1) and then by semi-preparative HPLC with a mobile phase of MeCN–H2O (11:9) to obtain 6 (1.2 mg), while compounds 9 (6.5 mg), 11 (4.1 mg), and 10 (18.7 mg) were separated from SFH4 (120 mg) by the same protocol as for SFH5. SFH6 (72 mg) was subjected to a Sephadex LH-20 column eluting with MeOH to afford compound 1 (4.6 mg). SFH7 (1.1 g) was purified by an ODS column eluted with MeOH–H2O (2:3–1:0), and then by semi-preparative HPLC with a mobile phase of MeCN-H2O (33:17) to obtain 2 (2.0 mg). FI (2.7 g) was separated by ODS chromatography eluted with MeOH-H2O (1:1–1:0) to obtain twenty-eight sub-fractions (SFI1–SFI28). SFI20 (168 mg) was separated by a Sephadex LH-20 column eluted with MeOH to collect three fractions (SFI20-1 to SFI20-3). The semi-preparative HPLC separation of SFI20-1 (28 mg) with a mobile phase of MeCN-H2O (11:9) to yield compounds 5 (3.5 mg) and 8 (1.6 mg), while compounds 7 (5.0 mg) and 4 (22.3 mg) were obtained from SFI20-2 (46 mg) by the same protocol as for SFI20-1.
Spiromastol A (
1): Colorless oil; UV (MeOH) λ
max (logε) 215 (4.48), 288 (3.71); IR (KBr) ν
max 3408, 2962, 2871, 1651, 1601, 1459, 1242, 1154 cm
−1;
1H and
13C NMR data, see
Table 1 and
Table 2; HRESIMS
m/z 403.0272 [M − H]
− (calcd for C
18H
18O
4Cl
3, 403.0271).
Spiromastol B (
2): Colorless oil; UV (MeOH) λ
max (logε) 213 (4.42), 288 (3.54); IR (KBr) ν
max 3450, 2961, 2930, 2870, 1716, 1580, 1442, 1335, 1227, 1180 cm
−1;
1H and
13C NMR data, see
Table 1 and
Table 2; HRESIMS
m/z 436.9873 [M − H]
− (calcd for C
18H
17O
4Cl
4, 436.9881).
Spiromastol C (
3): Colorless oil; UV (MeOH) λ
max (logε) 215 (4.59), 288 (3.46); IR (KBr) ν
max 3360, 2960, 2933, 2870, 1655, 1581, 1461, 1419, 1313, 1246, 1198 cm
−1;
1H and
13C NMR data, see
Table 1 and
Table 2; HRESIMS
m/z 451.0042 [M − H]
− (calcd for C
19H
19O
4Cl
4, 451.0037).
Spiromastol D (
4): Colorless oil; UV (MeOH) λ
max (logε) 213 (4.37), 282 (3.67); IR (KBr) ν
max 3276, 2961, 2930, 2870, 1705, 1605, 1459, 1317, 1239, 1193 cm
−1;
1H and
13C NMR data, see
Table 1 and
Table 2; HRESIMS
m/z 345.1341 [M − H]
− (calcd for C
19H
21O
6, 345.1338).
Spiromastol E (
5): Colorless oil; UV (MeOH) λ
max (logε) 208 (4.19), 279 (3.46); IR (KBr) ν
max 3281, 2959, 2930, 2870, 1705, 1604, 1458, 1321, 1251, 1195 cm
−1;
1H and
13C NMR data, see
Table 1 and
Table 2; HRESIMS
m/z 359.1498 [M − H]
− (calcd for C
20H
23O
6, 359.1495).
Spiromastol F (
6): Colorless oil; UV (MeOH) λ
max (logε) 215 (4.26), 282 (3.52); IR (KBr) ν
max 3306, 2961, 2931, 2871, 1701, 1607, 1458, 1364, 1231, 1196 cm
−1;
1H and
13C NMR data, see
Table 1 and
Table 2; HRESIMS
m/z 379.0951 [M − H]
− (calcd for C
19H
20O
6Cl, 379.0948).
Spiromastol G (
7): Colorless oil;
−4 (
c = 0.2, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λ
max (logε) 206 (4.27), 227 (4.25), 266 (3.98), 292 (3.64); IR (KBr) ν
max 3349, 2960, 2928, 2869, 1676, 1608, 1464, 1340, 1257, 1186, 1158 cm
−1; CD (MeOH) λ (Δε) 301 (−1.06), 291 (−1.02), 273 (−1.23), 259 (0.30), 238 (−3.47), 215 (7.38).
1H and
13C NMR data, see
Table 1 and
Table 2; HRESIMS
m/z 343.1176 [M − H]
− (calcd for C
19H
19O
6, 343.1182).
Spiromastol H (
8): Colorless oil;
−6 (
c 0.2, MeOH); UV (MeOH) λ
max (logε) 205 (4.16), 226 (4.02), 265 (3.81), 292 (3.51); IR (KBr) ν
max 3358, 2961, 2930, 2870, 1688, 1607, 1463, 1337, 1249, 1193 cm
−1; CD (MeOH) λ (Δε) 301 (−1.06), 291 (−0.75), 272 (−1.84), 257 (−0.11), 243 (−0.47), 213 (4.12).
1H and
13C NMR data, see
Table 1 and
Table 2; HRESIMS
m/z 357.1338 [M − H]
− (calcd for C
20H
21O
6, 357.1338).
Spiromastol I (
9): Colorless oil; UV (MeOH) λ
max (logε) 207 (4.26), 245 (4.60), 278 (3.88), 321 (3.64); IR (KBr) ν
max 3246, 2960, 2871, 1689, 1597, 1461, 1359 cm
−1;
1H and
13C NMR data, see
Table 1 and
Table 2; HRESIMS
m/z 369.1339 [M − H]
− (calcd for C
21H
21O
6, 369.1338).
Spiromastol J (
10): Colorless oil; UV (MeOH) λ
max (logε) 216 (4.41), 270 (4.13), 301 (3.92); IR (KBr) ν
max 3396, 2960, 2872, 1656, 1614, 1451, 1311, 1248, 1192 cm
−1;
1H and
13C NMR data, see
Table 1 and
Table 2; HRESIMS
m/z 373.1287 [M − H]
− (calcd for C
20H
21O
7, 373.1287).
Spiromastol K (
11): Colorless oil; UV (MeOH) λ
max (logε) 216 (4.32), 270 (4.04), 300 (3.85); IR (KBr) ν
max 3163, 2959, 2870, 1654, 1591, 1453, 1310, 1248, 1195 cm
−1;
1H and
13C NMR data, see
Table 1 and
Table 2; HRESIMS
m/z 373.1281 [M − H]
− (calcd for C
20H
21O
7, 373.1287).
3.4. Methylation
Compound 10 (5.0 mg) was dissolved in anhydrous acetone (900 µL), and then K2CO3 (3.8 mg) and CH3I (650 μL) were added to the solution, which was stirred for 16 h at 0 °C. After filtration, the solution was concentrated in vacuo, and the residue was purified on a silica gel column eluting with petroleum ether-Me2CO (20: 1) to obtain the methyl ether 10a (2.9 mg, 58% yield). Compound 11 is submitted to the same protocol as for 10 to derive a methylated product 11a.
Compound 10a: 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δH 6.72 (1H, d, J = 1.8, H-3), 6.68 (1H, d, J = 1.8, H-5), 6.41 (1H, d, J = 2.1, H-5′), 6.39 (1H, d, J = 2.1, H-3′), 3.92 (3H, s, OMe-10), 3.89 (3H, s, OMe-2′), 3.86 (3H, s, OMe-4′), 3.85 (3H, s, OMe-2), 2.70 (2H, t, J = 7.8, H2-7′), 2.58 (2H, t, J = 7.9, H2-7), 1.72 (2H, m, H2-8′), 1.65 (2H, m, H2-8), 1.00 (3H, t, J = 7.3, H3-9′), 0.97 (3H, t, J = 7.4, H3-9); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δC 168.5 (C-10), 166.4 (C-10′), 161.9 (C-4′), 158.6 (C-2′), 157.3 (C-4), 152.5 (C-2), 143.5 (C-6′), 142.4 (C-6), 121.1 (C-5), 115.2 (C-1′), 114.4 (C-1), 106.1 (C-5′), 102.7 (C-3), 96.3 (C-3′), 56.1 (OMe-2′), 56.0 (OMe-2), 55.4 (OMe-4′), 52.2 (OMe-10), 36.1 (C-7′), 35.6 (C-7), 24.6 (C-8′), 24.0 (C-8), 14.1 (C-9′), 14.0 (C-9). ESIMS m/z 431.32 [M + H]+, 453.26 [M + Na]+.
Compound 11a: 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δH 6.70 (1H, d, J = 2.0, H-3), 6.66 (1H, d, J = 2.0, H-5), 6.40 (1H, d, J = 2.0, H-5′), 6.38 (1H, d, J = 2.0, H-3′), 3.92 (3H, s, OMe-10), 3.87 (3H, s, OMe-2′), 3.86 (3H, s, OMe-4′), 3.82 (3H, s, OMe-4), 2.71 (2H, t, J = 7.8, H2-7′), 2.56 (2H, t, J = 7.9, H2-7), 1.71 (2H, m, H2-8′), 1.67 (2H, m, H2-8), 1.01 (3H, t, J = 7.0, H3-9′), 0.96 (3H, t, J = 7.0, H3-9); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δC 168.3 (C-10), 166.5 (C-10′), 161.8 (C-4′), 158.5 (C-2′), 157.8 (C-4), 152.3 (C-2), 143.4 (C-6′), 142.5 (C-6), 119.0 (C-5), 115.3 (C-1′), 114.2 (C-1), 106.0 (C-5′), 102.2 (C-3), 96.4 (C-3′), 56.2 (OMe-2′), 56.1 (OMe-4), 55.3 (OMe-4′), 52.1 (OMe-10), 36.0 (C-7′), 35.5 (C-7), 24.7 (C-8′), 24.4 (C-8), 14.0 (C-9′), 14.1 (C-9). ESIMS m/z 431.30 [M + H]+.
3.5. Antibacterial Assay
Spiromastols A–K (
1–
11) were tested against a panel of seven bacterial strains, including
Xanthomanes vesicatoria ATCC 11633,
Pseudomonas lachrymans ATCC11921,
Agrobacterium tumefaciens ATCC11158,
Ralstonia solanacearum ATCC11696,
Bacillus thuringensis ATCC 10792,
Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 and
Bacillus subtilis CMCC 63501, according to previously described methods [
14].