Overview on Biological Activities and Molecular Characteristics of Sulfated Polysaccharides from Marine Green Algae in Recent Years
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Green Seaweed Materials
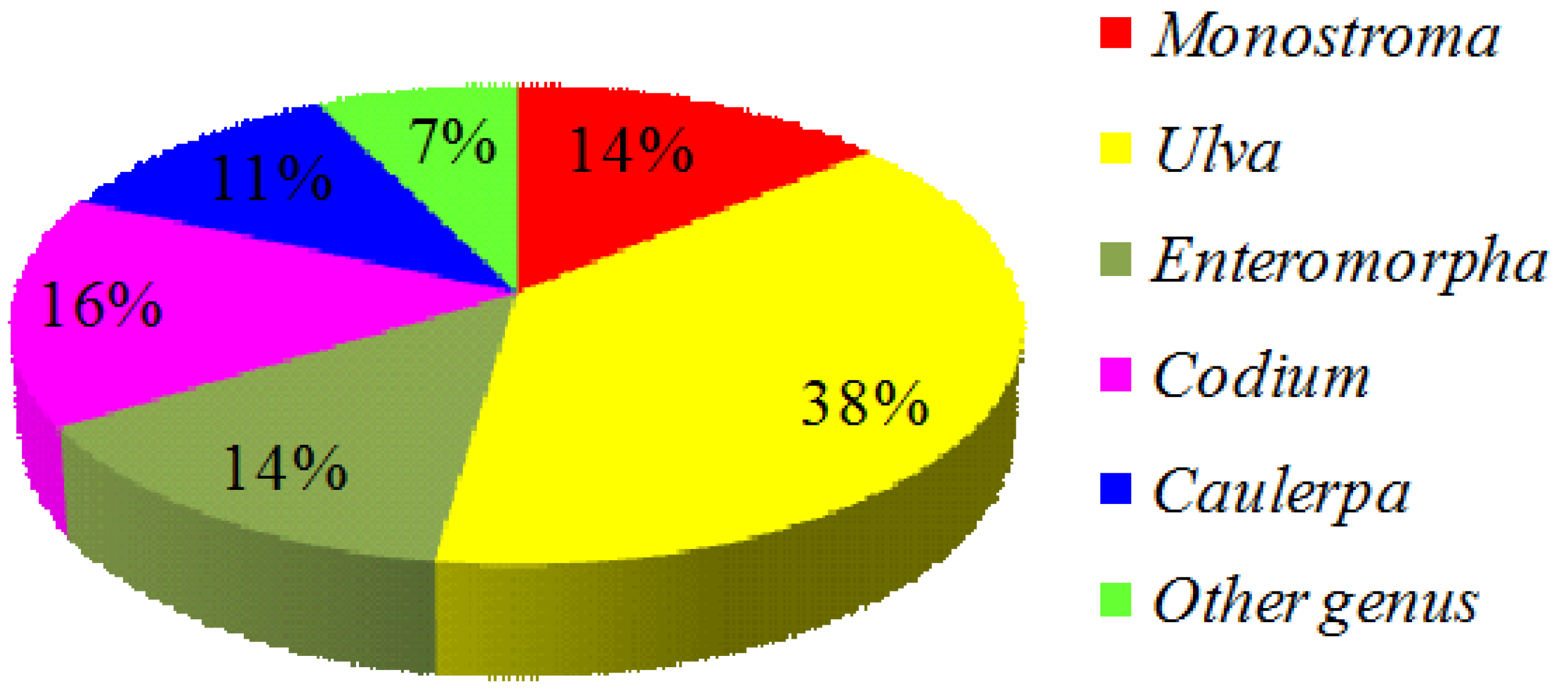
| Families | Genus | Species |
|---|---|---|
| Monostromataceae | Monostroma | M. latissimum |
| M. nitidum | ||
| M. angicava | ||
| Ulvaceae | Enteromorpha | E. clathrata |
| E. compressa | ||
| E. intestinalis | ||
| E. linza | ||
| E. prolifera | ||
| Ulva | U. arasakii | |
| U. armoricana | ||
| U. clathrata | ||
| U. conglobata | ||
| U. fasciata | ||
| U. lactuca | ||
| U. pertusa | ||
| U. reticulata | ||
| U. rigida | ||
| U. rotundata | ||
| Capsosiphonaceae | Capsosiphon | C. fulvescens |
| Cladophoraceae | Chaetomorpha | C. antennina |
| Bryopsidaceae | Bryopsis | B. plumose |
| Halimedaceae | Halimeda | H. monile |
| Caulerpaceae | Caulerpa | C. brachypus |
| C. cupressoides | ||
| C. lentillifera | ||
| C. prolifera | ||
| C. racemosa | ||
| C. sertularioides | ||
| Codiaceae | Codium | C. adhaerens |
| C. cylindricum | ||
| C. dwarkense | ||
| C. fragile | ||
| C. istmocladum | ||
| C. latum | ||
| C. pugniformis | ||
| C. tomentosum | ||
| C. vermilara | ||
| C. yezoense |

3. Biological Activities of Sulfated Polysaccharides of Green Seaweeds
3.1. Antioxidant Activity
3.2. Anticoagulant Activity
| Species | Extraction-Fractionation Procedure | Chemical Characteristics | Anticoagulant Characteristics | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Codium fragile | Extraction with water, purification by GPC (Sepharose 2B) and IEC (Sepharose CL-6B). | A high Mw of proteoglycan with 18.4% sulfate and two SP fractions with 10.2% and 7.5% sulfated contents. | Heparin cofactor II and antithrombin III activity. | [66] |
| Codium dwarkense | Extraction with water at room temperature and purified by IEC and GPC. | Sulfated arabinan and arabinogalactan. | Effective in APTT and TT. | [68] |
| Codium pugniformis | Extraction with water at room temperature and 100 ºC, Purification by IEC (2×) and GPC. | Crude SP with 72.7% of Glc, 17.3% of Ara and 10.0% of Gal in sugar composition, and with 32.6% of sulfate and 5.2% of protein. | Direct inhibition of thrombin activity. | [69] |
| Codium divaricatum | Extraction with water at room temperature and 100 ºC, Purification by IEC (2×) and GPC. | Sulfated heterarabinan with 60% of sulfated degree. | Activation of HCII. Different HCII-binding site to that of heparin and dermatan sulfate. | [64] |
| Codium adhaerence | Sulfated heterarabinan with 80% of sulfated degree. | |||
| Codium latum | Sulfated arabinan with 80% of sulfated degree. | |||
| Codium fragile | Sulfated heterarabinan with 50% of sulfated degree. | |||
| Codium cylindricum | Extraction with water at room temperature and purification by IEC and GPC. | Crude SP with 89% of Gal and 11% of Glc in sugar composition, and with 7.8%of proteins | Inhibition of fibrin polymerization, did not inhibit coagulation enzymes such as factor Xa or thrombin. | [70] |
| Codium dwarkense | Extraction with Cold water and precipitation with KCl, purification by IEC and GPC. | Sulfated arabinans. | Effective in PT, APTT and TT. | [76] |
| C.tomentosum | Sulfated arabinans and arabinogalactans. | |||
| Codium fragile | Extraction with water at room temperature and 90 °C. Purification by IEC. | Sulfated arabinans, galactans and/or arabinogalactans. | APTT, TT, dual effect anticoagulant, but pro-aggregant. | [77] |
| Codium vermilara | Similar structural units to those of C. fragile, but higher amounts of Ara and sulfate. | APTT, TT, more active than that from C. fragile but pro-aggregant | ||
| Monostroma nitidum | Extraction with hot water and purification by chromatography | A high rhamnose-containing sulfated polysaccharide. | Six-fold higher anti-thrombin activity relative to heparin | [62] |
| Monostroma nitidum | Extraction with hot water and purification by anion exchange column chromatography | Two SP fractions had similar high contents of rhamnose, whereas their sulfate contents, sulfation positions, molecular sizes and linkage patterns of rhamnose residues were different. | Potent thrombin inhibitors mediated by heparin cofactor II, also mildly inhibitors of coagulation factor Xa by potentiating antithrombin III. | [72] |
| Monostroma latissimum | Extraction with hot water, purification by IEC and SEC, and degradation by H2O2. | Sulfated rhamnan and its five degraded fragments with different molecular weights. | APTT and TT prolonging activities, but no PT activity. | [73] |
| Monostroma latissimum | Extraction with hot water and purification by IEC and SEC. | High rhamnose-containing SP. | APTT and TT activities, mediated by heparin cofactor II. | [71] |
| Monostroma latissimum | Extraction with hot water and purification by IEC and SEC. | High rhamnose-containing SP with an average molecular weight of about 513 kDa. | High anticoagulant activities in APTT and TT. | [74] |
| Monostroma latissimum | Preparation with mild acid hydrolysis of crude SPs and purification by IEC and GPC. | Sulfated rhamnan with 33.6 kDa of average molecular weight. | APTT and TT activities, mediated by heparin cofactor II. | [75] |
| Ulva conglobata | Extraction with hot water, purification by IEC and SEC. | Crude ulvan containing 23.04%–35.20% sulfate ester groups, 10.82%–14.91% uronic acid and 3.82%–4.51% protein. | APTT activity due to the direct inhibition of thrombin and the potentiation of heparin cofactor II. | [28] |
| Enteromorpha clathrata | hot water and further purified by IEC and SEC. | A high arabinose-containing SP with sulfate ester of 31.0%, and with 511 kDa of average molecular weight. | Effective in APTT and TT. | [29] |
| Enteromorpha linza | Extraction with hot water, purification by IEC and SEC, reaction with chlorosulfuric acid in formamide. | Low molecular weight of SPs with various DS. | Effective in APTT, TT. | [59] |
| Caulerpa cupressoides var. flabellata | Extraction by proteolytic digestion, fractionation by acetone and molecular sieving in Sephadex G-100. | Four fractions of sulfated hetergalactan with various sulfate/sugar ratio. | APTT and PT activities, APTT activity was similar to that of Clexane. | [50] |
| Caulerpa cupressoides var. lycopodium | Extraction by proteolytic digestion, fractionation by IEC. | Crude SP and its three fractions. | Effective in APTT. | [60] |
| Caulerpa cupressoides var. lycopodium | Extraction by proteolytic digestion, fractionation by IEC and GPC. | Three SP fractions with galactose as their main sugar unit and presence of sulfate ester, galactose-6-sulfate, uronic acid. | Being both thrombin and factor Xa target proteases inhabitation. | [78] |
3.3. Immunomodulatory and Antitumor Activities
3.5. Anti-Inflammatory and Antinociceptive Activities
| Rawmaterial of Green Seaweeds | Tested SPs | Time (Day) | Dosage (mg/kg/day) | Analgesic Action | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibition in Acetic Acid-Induced Writhing Test (%) | Inhibition of Licking Times in Formalin Test (%) for the First Phase (Left Column) and Secondphase (Right Column) | Effectiveness in Hot-Plate Test | |||||
| Caulerpa curpressoides | Cc-SP2 | 14 | 3 | 57.0 | no | 68.95 | no |
| 9 | 89.9 | 42.47 | 82.34 | yes | |||
| 27 | 90.6 | 52.1 | 84.61 | no | |||
| Caulerpa cupressoides var. lycopodium | SP1 | 3 | 3 | 44.21 | no | 56.41 | no |
| 9 | 47.72 | no | 72.08 | no | |||
| 27 | 90.87 | 51.61 | 83.48 | no | |||
3.6. Antihyperlipidemic and Antihepatotoxic Activities
4. Structural Diversity of Green Algal SPs
4.1. Ulvans from Ulva and Enteromorpha
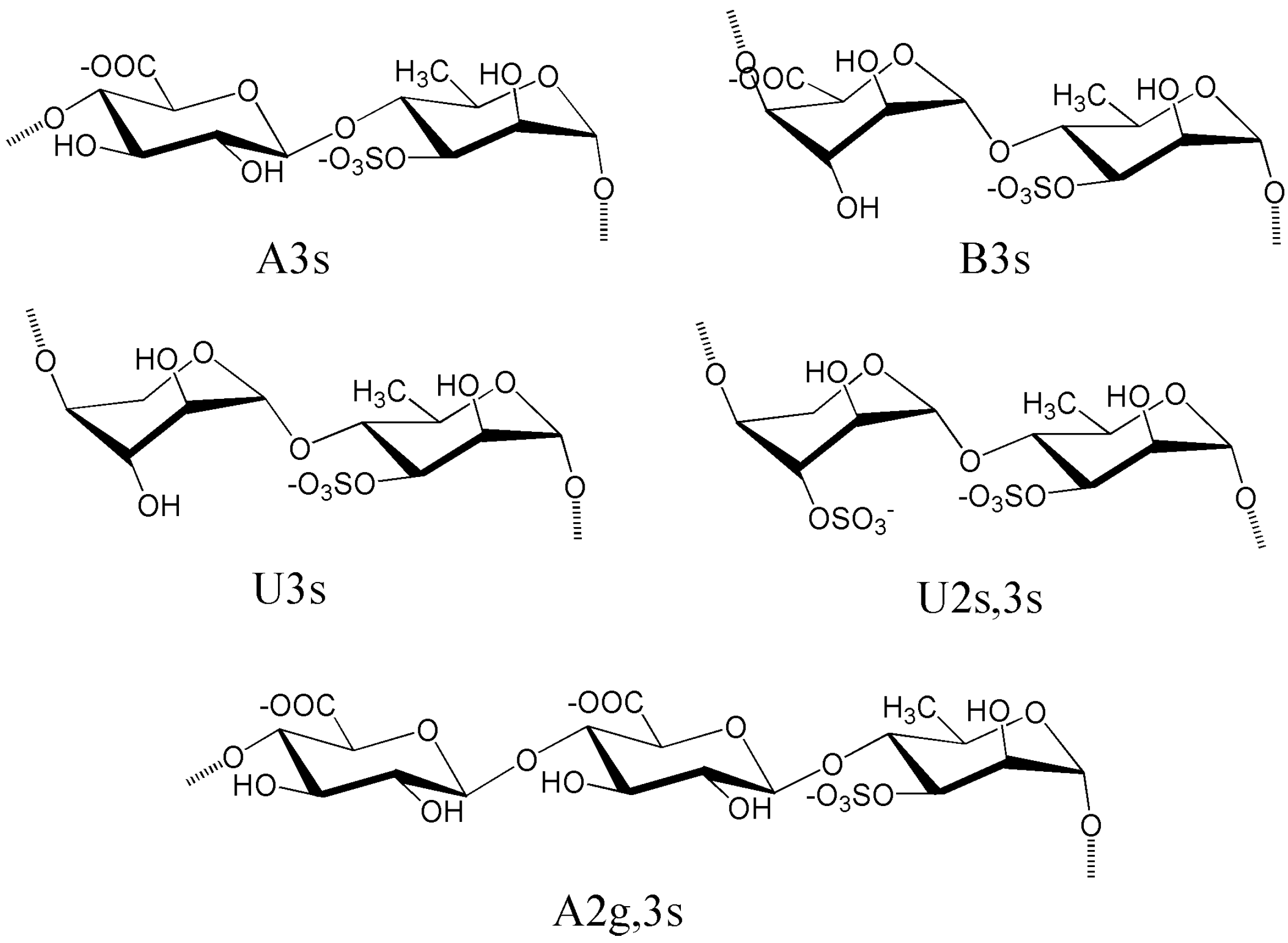
4.2. Sulfated Rhamnans from Monostroma
4.3. Sulfated Arabinogalactans from Codium
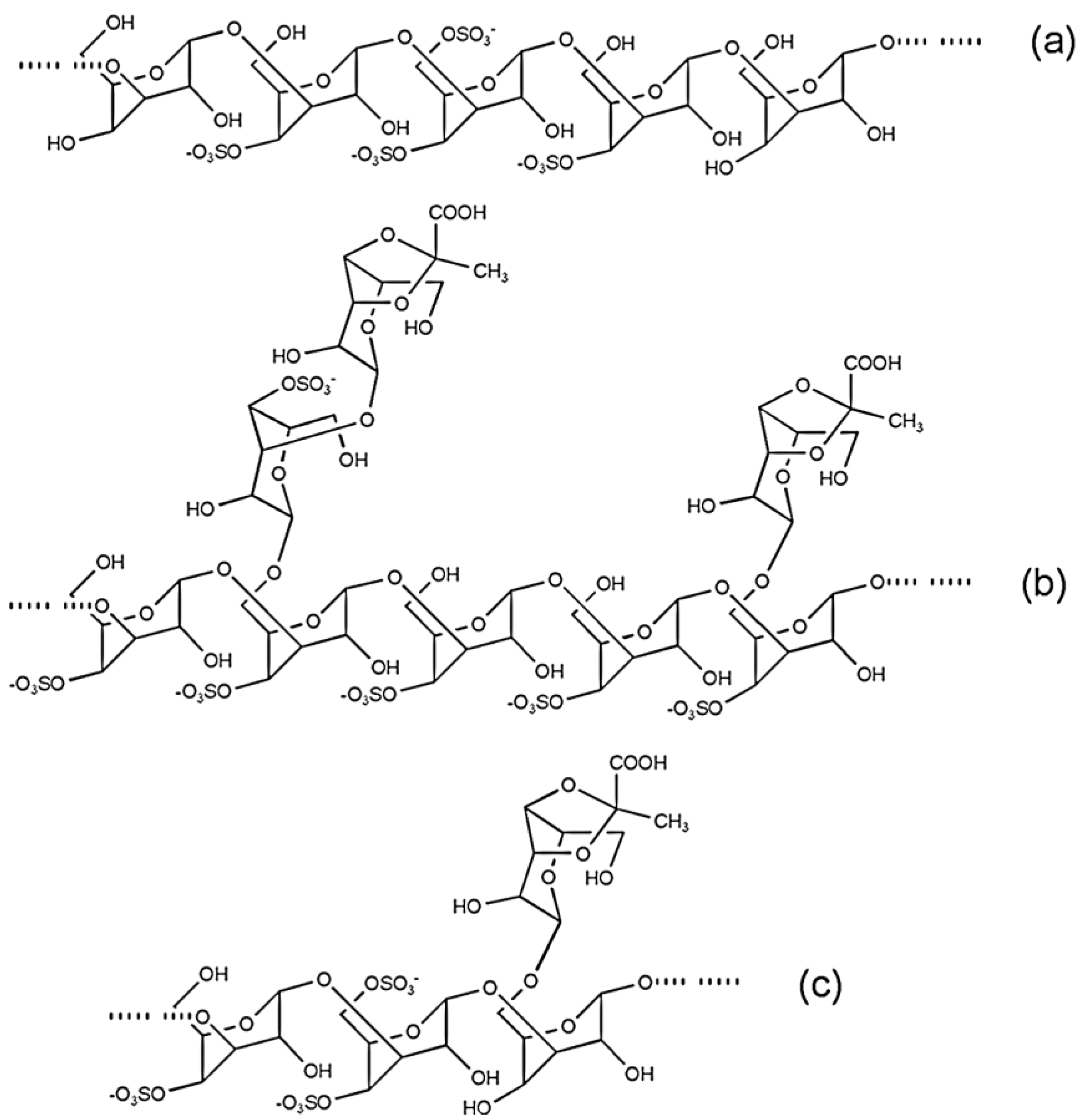
4.4. Sulfated Galacotans from Caulerpa
| SP | Yield (%) | Total Sugar Content (%) | Sulfate Content (%) | Sulfated Degree (%) | Molecular Weight (kDa) | Molarratio of Monosaccharide Composition | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gal | Glu | Man | Xyl | Rha | Fuc | ||||||
| CCB-F0.3 | 13.43 | 54.91 | 34.63 | 0.63 ± 0.02 | 155 ± 10 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | - | - |
| CCB-F0.5 | 46.91 | 52.38 | 38.05 | 0.73 ± 0.04 | 130 ± 10 | 1.0 | - | 0.1 | tr | - | - |
| CCB-F1.0 | 39.23 | 76.47 | 17.95 | 0.23 ± 0.01 | 155 ± 10 | 1.0 | tr | 0.1 | 0.6 | tr | - |
| CCB-F2.0 | 0.43 | 59.60 | 31.64 | 0.53 ± 0.02 | 170 ± 10 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 1.8 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
4.5. Sulfated Mannans from Green Seaweeds

5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ibñez, E.; Cifuentes, A. Benefits of using algae as natural sources of functional ingredients. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra-Rivas, G.; Mariana Gomez-Gutierrez, C.; Alarcon-Arteaga, G.; Esthela Soria-Mercado, I.; Ernestina Ayala-Sanchez, N. Screening for anticoagulant activity in marine algae from the Northwest Mexican Pacific coast. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellogg, J.; Lila, M.A. Chemical and in vitro assessment of Alaskan coastal vegetation antioxidant capacity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 11025–11032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Li, Y.X. Medicinal benefits of sulfated polysaccharides from sea vegetables. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2011, 64, 391–402. [Google Scholar]
- Taboada, C.; Millan, R.; Miguez, I. Evaluation of the marine alga Ulva rigida as a Food Supplement: Effect of intake on intestinal, hepatic, and renal enzyme activities in rats. J. Med. Food 2011, 14, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, A.; Caridade, S.G.; Mano, J.F.; Sousa, R.A.; Reis, R.L. Extraction and physico-chemical characterization of a versatile biodegradable polysaccharide obtained from green algae. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo, L.; Stadnik, M.J. Cultivar-specific and ulvan-induced resistance of apple plants to glomerella leaf spot are associated with enhanced activity of peroxidases. Acta Sci. Agric. 2013, 35, 287–293. [Google Scholar]
- Ciancia, M.; Alberghina, J.; Ximena Arata, P.; Benavides, H.; Leliaert, F.; Verbruggen, H.; Manuel Estevez, J. Characterization of cell wall polysaccharides of the coencocytic green seaweed Byropsis plumose (Bropsidaceae, Chlorophyta) from the Argentine cost. J. Phycol. 2012, 48, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulert, R.; Talamini, V.; Cassolato, J.E.F.; Duarte, M.E.R.; Noseda, M.D.; Smania, A., Jr.; Stadnik, M.J. Effects of sulfated polysaccharide and alcoholic extracts from green seaweed Ulva fasciata on anthracnose severity and growth of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J. Plant Dis. Protect. 2009, 116, 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Paulert, R.; Ebbinghaus, D.; Urlass, C.; Moerschbacher, B.M. Priming of the oxidative burst in rice and wheat cell cultures by ulvan, a polysaccharide from green macroalgae, and enhanced resistance against powdery mildew in wheat and barley plants. Plant Pathol. 2010, 59, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, G.; Prasad, K.; Meena, R.; Siddhanta, A.K. Facile preparation of Chaetomorpha antennina based porous polysaccharide-PMMA hybrid material by radical polymerization under microwave irradiation. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 4062–4068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samara, E.M.; Okab, A.B.; Abdoun, K.A.; El-Waziry, A.M.; Al-Haidary, A.A. Subsequent influences of feeding intact green seaweed Ulva lactuca to growing lambs on the seminal and testicular characteristics in rams. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 5654–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godard, M.; Decorde, K.; Ventura, E.; Soteras, G.; Baccou, J.C.; Cristol, J.P.; Rouanet, J.M. Polysaccharides from the green alga Ulva rigida improve the antioxidant status and prevent fatty streak lesions in the high cholesterol fed hamster, an animal model of nutritionally-induced atherosclerosis. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, C.L.; Rodrigues, S.D.; Bristot, D.; Gaeta, H.H.; Toyama, D.D.O.; Lobo Farias, W.R.; Toyama, M.H. Evaluation of Macroalgae Sulfated Polysaccharides on the Leishmania (L.) amazonensis Promastigote. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 934–943. [Google Scholar]
- Devaki, T.; Sathivel, A.; BalajiRaghavendran, H.R. Stabilization of mitochondrial and microsomal function by polysaccharide of Ulva lactuca on d-Galactosamine induced hepatitis in rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2009, 177, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Go, H.; Hwang, H.J.; Taek-Jeong, N. Polysaccharides from Capsosiphon fulvescens stimulate the growth of IEC-6 cells by activating the MAPK signaling pathway. Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 13, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, W.J.; Li, Y.; Wu, L.G.; Wang, H.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zang, X.X.; Zhang, H.J. Chemical characterization and radio protective effect of polysaccharide from Monostroma angicava (Chlorophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 2005, 17, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Cheng, C.; Zhao, H.; Jing, J.; Gong, N.; Lu, W. In vivo anti-radiation activities of the Ulva pertusa polysaccharides and polysaccharide-iron (III) complex. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 60, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, A.R.; Robaina, M.C.S.; Mendes, G.S.; Silva, T.S.L.; Gestinari, L.M.S.; Pamplona, O.S.; Yoneshigue-Valentin, Y.; Kaiser, C.R.; Villela Romanos, M.T. Antiviral activity of extracts from Brazilian seaweeds against herpes simplex virus. Rev. Bra. Farm. Braz. J. Pharm. 2012, 22, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Jiang, P.; Zhang, L.; Wu, M. Antitumor and immunomodulating activity of polysaccharides from Enteromorpha intestinalis. Biotechnol. Biopro. Eng. 2010, 15, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Cho, M.L.; Karnjanapratum, S.; Shin, I.S.; You, S.G. In vitro and in vivo immunomodulatory activity of sulfated polysaccharides from Enteromorpha prolifera. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiro, J.M.; Castro, R.; Arranz, J.A.; Lamas, J. Immunomodulating activities of acidic sulphated polysaccharides obtained from the seaweed Ulva rigida C. Agardh. Agardh. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2007, 7, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabarsa, M.; Han, J.H.; Kim, C.Y.; You, S.G. Molecular characteristics and immunomodulatory activities of water-soluble sulfated polysaccharides from Ulva pertusa. J. Med. Food 2012, 15, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabarsa, M.; Lee, S.J.; You, S. Structural analysis of immunostimulating sulfated polysaccharides from Ulva pertusa. Carbohydr. Res. 2012, 361, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.; Huang, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, S. Antihyperlipidemic activity of high sulfate content derivative of polysaccharide extracted from Ulva pertusa (Chlorophyta). Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 1637–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Duan, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q. Synthesis and antihyperlipidemic activity of acetylated derivative of ulvan from Ulva pertusa. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 270–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, G.K.; Manivannan, K.; Thirumaran, G.; Rajathi, F.A.A.; Anantharaman, P. In vitro antioxidant activities of selected seaweeds from Southeast coast of India. Asian Pacific J. Trop. Med. 2011, 4, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Zang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. Sulfated polysaccharides from marine green algae Ulva conglobata and their anticoagulant activity. J. Appl. Phycol. 2006, 18, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Mao, W.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, C.; Li, N.; Wang, C.; Yan, M.; Lin, C.; et al. Chemical characteristic of an anticoagulant-active sulfated polysaccharide from Enteromorpha clathrata. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1804–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, K.; Liu, D.; Huang, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Q. Subchronic toxicity study of ulvan from Ulva pertusa (Chlorophyta) in Wistar rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Pub. Br. Industri. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2013, 62, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domozych, D.S.; Kiemle, S.N.; Domozych, C.R.; Sorensen, I.; Willats, W.G.; Gretz, M.R. Differential occurrence of land plant extracellular polysaccharides in the charophycean green algae and implications for plant evolution. J. Phycol. 2007, 43, 27–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, P.V.; Ciancia, M.; Miravalles, A.B.; Estevez, J.M. Cell wall polymer mapping in the coenocyticmacroalga Codium vermilara. J. Phycol. 2010, 46, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, J.M.; Fernández, P.V.; Kasulin, L.; Dupree, P.; Ciancia, M. Chemical and in situ characterization of macromolecular components of the cell walls from the green seaweed Codium fragile. Glycobioogy 2009, 19, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, Q. Extraction of the polysaccharides from five algae and their potential antioxidant activity in vitro. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athukorala, Y.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, S.K.; Jeon, Y.J. Anticoagulant activity of marine green and brown algae collected from Jeju Island in Korea. Bioresource Technol. 2007, 98, 1711–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomster, J.; Maggs, C.A.; Stanhope, M.J.J. Molecular and morphological analysis of Enteromorpha intestinalis and E. compressa (Chlorophyta) in the British Isles. J. Phycol. 1998, 34, 319–340. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, L.S.; Fidelis, G.P.; Cordeiro, S.L.; Oliveira, R.M.; Sabry, D.A.; Camara, R.B.G.; Nobre, L.T.D.B.; Costa, M.S.S.P.; Almeida-Lima, J.; Farias, E.H.C.; et al. Biological activities of sulfated polysaccharides from tropical seaweeds. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2010, 64, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, G.; Yu, G.; Wang, W.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Ewart, S.H. Properties of polysaccharides in several seaweeds from Atlantic Canada and their potential anti-influenza viral activities. J. Ocean Univ. China 2012, 11, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciancia, M.; Quintana, I.; Cerezo, A.S. Overview of anticoagulant activity of sulfated polysaccharides from seaweeds in relation to their structures, focusing on those of green seaweeds. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 2503–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, G.; Yu, G.; Zhang, J.; Ewart, H.S. Chemical structures and bioactivities of sulfated polysaccharides from marine algae. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 196–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahaye, M.; Robic, A. Structure and functional properties of ulvan, a polysaccharide from green seaweeds. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misurcova, L.; Skrovankova, S.; Samek, D.; Ambrozova, J.; Machu, L. Health benefits of algal polysaccharides in human nutrition. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2012, 66, 75–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.H.; Mao, W.J.; Fang, F.; Li, H.Y. Polysaccharides from marine green seaweed Ulva species and their characteristics. Agro Food Ind. Hi-Tech. 2007, 18, 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wijesekara, I.; Pangestuti, R.; Kim, S.K. Biological activities and potential health benefits of sulfated polysaccharides derived from marine algae. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.; Sousa, R.A.; Reis, R.L. In vitro cytotoxicity assessment of ulvan, a polysaccharide extracted from green algae. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurgel Rodrigues, J.A.; Oliveira Vanderlei, E.D.S.; Fernandes de Araujo, I.W.; Gomes Quindere, A.L.; Coura, C.O.; Barros Benevides, N.M. In vivo toxicological evaluation of crude sulfated polysaccharide from the green seaweed Caulerpa cupressoides var. lycopodium in Swiss mice. Acta Sci. Technol. 2013, 35, 603–610. [Google Scholar]
- Batista-Gonzalez, A.E.; De Oliveira E Silva, A.M.; Vidal-Novoa, A.; Pinto, J.R.; Portari Mancini, D.A.; Mancini-Filho, J. Analysis of in vitro and in vivo antioxidant properties of hydrophilic fractions from the seaweed Halimeda monile L. J. Food Biochem. 2012, 36, 189–197. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, S.; Abd El-Twab, S.; Hetta, M.; Mahmoud, B. Improvement of lipid profile and antioxidant of hypercholesterolemic albino rats by polysaccharides extracted from the green alga Ulva lactuca Linnaeus. Saudi J. Biologic. Sci. 2011, 18, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J. In vitro antioxidant activity of polysaccharides extracted from Bryopsis plumosa. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos Pereira Costa, M.S.; Costa, L.S.; Cordeiro, S.L.; Almeida-Lima, J.; Dantas-Santos, N.; Magalhaes, K.D.; Sabry, D.A.; Lopes Albuquerque, I.R.; Pereira, M.R.; et al. Evaluating the possible anticoagulant and antioxidant effects of sulfated polysaccharides from the tropical green alga Caulerpa cupressoides var. flabellata. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 24, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezghani, S.; Bourguiba, I.; Hfaiedh, I.; Amri, M. Antioxidant potential of Ulva rigida extracts: protection of heLa cells against H2O2 cytotoxicity. Biol. Bull. 2013, 225, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.M.; Zhang, Q.B.; Zhao, T.T.; Chen, R.; Zhang, H.; Niu, X.Z.; Li, Z. Antioxidant activity of different sulfate content derivatives of polysaccharide extracted from Ulva pertusa (Chlorophyta) in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2005, 37, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.M.; Zhao, T.T.; Zhang, Q.B.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Xing, R. Antioxidant activity of different molecular weight sulfated polysaccharides from Ulva pertusa Kjellm (Chlorophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 2005, 17, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z. In intro antioxidant activity of acetylated derivatives of polysaccharide extracted from Ulva pertusa (Cholorophta). J. Med. Plants Res. 2010, 4, 2445–2451. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yu, S.; Yin, L.; Zhao, M.; Han, Z. Synthesized oversulfated and acetylated derivatives of polysaccharide extracted from Enteromorpha linza and their potential antioxidant activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 1012–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.M.; Zhang, Q.B.; Zhao, T.T.; Hu, R.G.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z. In vitro antioxidant activity of acetylated and benzoylated derivatives of polysaccharide extracted from Ulva pertusa (Chlorophyta). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 2441–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Liu, S.; Xing, R.; Li, K.; Li, R.; Qin, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, Z.; Li, P. Degradation of sulfated polysaccharides from Enteromorpha prolifera and their antioxidant activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1991–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, P.; Chen, M.; Pei, Y.; Sun, P. In intro antioxidant activities of different sulfated polysaccharides from chlorophytan seaweeds Ulva fasciata. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 59, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, M.; Qi, H. Sulfation, anticoagulant and antioxidant activities of polysaccharide from green algae Enteromorpha linza. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 58, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurgel Rodrigues, J.A.; Lino de Queiroz, I.N.; Gomes Quindere, A.L.; Vairo, B.C.; de Souza Mourao, P.A.; Barros Benevides, N.M. An antithrombin-dependent sulfated polysaccharide isolated from the green alga Caulerpa cupressoides has in vivo anti- and prothrombotic effects. Cienc. Rural 2011, 41, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurgel Rodrigues, J.A.; Oliveira Vanderlei, E.D.S.; Bessa, E.F.; Magalhaes, F.D.A.; Monteiro de Paula, R.C.; Lima, V.; Barros Benevides, N.M. Anticoagulant activity of a sulfated polysaccharide isolated from the green seaweed Caulerpa cupressoides. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2011, 54, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, M.; Uehara, T.; Harada, N.; Sekiguchi, M.; Hiraoka, A. Heparinoid-active sulfated polysaccharide from Monostroma-nitidum and their distribution in the Chlorophyta. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 3611–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, M.; Ramavat, B.K.; Mody, K.H.; Oza, R.M.; Tewari, A. Distribution of heparinoid-active sulphated polysaccharides in some Indian marine green algae. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 2001, 30, 222–227. [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Lee, J.B.; Srisomporn, P.; Maeda, M.; Ozawa, T.; Sakuragawa, N. Inhibition of thrombin by sulfated polysaccharides isolated from green algae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 2000, 1543, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, M.; Mody, K.H.; Ramavat, B.K.; Murthy, A.S.K.; Siddhanta, A.K. Screening of Codiacean algae (Chlorophyta) of the Indian coasts for blood anticoagulant activity. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 2002, 31, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Jurd, K.M.; Rogers, D.J.; Blunden, G.; McLellan, D.S. Anticoagulant properties of sulfated polysaccharide and a proteoglycan from Codium fragile ssp atlanticum. J. Appl. Phycol. 1995, 7, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddhanta, A.K.; Shanmugam, M. Metabolites of tropical marine algae of the family Codiaceae (Chlorophyta): Chemistry and bioactivity. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 1999, 76, 323–334. [Google Scholar]
- Siddhanta, A.K.; Shanmugam, M.; Mody, K.H.; Goswami, A.M.; Ramavat, B.K. Sulphated polysaccharides of Codium dwarkense Boergs from the west coast of India: Chemical composition and blood anticoagulant activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1999, 26, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, K.; Matsuura, Y.; Hori, K.; Miyazawa, K. An anticoagulant proteoglycan from the marine green alga, Codium pugniformis. J. Appl. Phycol. 2000, 12, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, K.; Matsuura, Y.; Bacic, A.; Liao, M.L.; Hori, K.; Miyazawa, K. Anticoagulant properties of a sulfated galactan preparation from a marine green alga, Codium cylindricum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2001, 28, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, W.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qi, X.; Sun, H.; Chen, Y.; Guo, S. Chemical characteristic and anticoagulant activity of the sulfated polysaccharide isolated from Monostroma latissimum (Chlorophyta). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2009, 44, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, W.J.; Fang, F.; Li, H.Y.; Qi, X.H.; Sun, H.H.; Chen, Y.; Guo, S.D. Heparinoid-active two sulfated polysaccharides isolated from marine green algae Monostroma nitidum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Mao, W.J.; Fang, F.; Li, H.Y.; Sun, H.H.; Chen, Y.; Qi, X.H. Chemical characteristics and anticoagulant activities of a sulfated polysaccharide and its fragments from Monostroma latissimum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Mao, W.; Zhang, X.; Qi, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhao, C.; Hou, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. Structural characterization of an anticoagulant-active sulfated polysaccharide isolated from green alga Monostroma latissimum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 85, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Mao, W.; Hou, Y.; Gao, Y.; Qi, X.; Zhao, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, C. Preparation, structure and anticoagulant activity of a low molecular weight fraction produced by mild acid hydrolysis of sulfated rhamnan from Monostroma latissimum. Bioresource Technol. 2012, 114, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, M.; Mody, K.H.; Siddhanta, A.K. Blood anticoagulant sulphated polysaccharides of the marine green algae Codium dwarkense (Boergs.) and C. tomentosum (Huds.) Stackh. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 39, 365–370. [Google Scholar]
- Ciancia, M.; Quintana, I.; Vizcarguenaga, M.I.; Kasulin, L.; de Dios, A.; Estevez, J.M.; Cerezo, A.S. Polysaccharides from the green seaweeds Codium fragile and C. vermilara with controversial effects on hemostasis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2007, 41, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurgel Rodrigues, J.A.; Moura Neto, E.; Castro Teixeira, L.A.; Monteiro de Paula, R.C.; de Souza Mourao, P.A.; Barros Benevides, N.M. Structural features and inactivation of coagulation proteases of a sulfated polysaccharidic fraction from Caulerpa cupressoides var. lycopodium (Caulerpaceae, Chlorophyta). Acta Sci. Technol. 2013, 35, 611–619. [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos, A.F.D.; Dekker, R.F.H.; Barbosa, A.M.; Carbonero, E.R.; Silveira, J.L.M.; Glauser, B.; Pereira, M.S.; Corradi da Silva, M.D.L. Sulfonation and anticoagulant activity of fungal exocellular beta-(1→6)-d-glucan (lasiodiplodan). Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1908–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Mao, W.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, C.; Li, N.; Wang, C. Chemical characteristics and anticoagulant activities of two sulfated polysaccharides from Enteromorpha linza (Chlorophyta). J. Ocean Univ. China 2013, 12, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, N.; Maeda, M. Chemical structure of antithrombin-active rhamnansulfate from Monostroma nitidum. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1998, 62, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnjanapratum, S.; You, S. Molecular characteristics of sulfated polysaccharides from Monostroma nitidum and their in vitro anticancer and immunomodulatory activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 48, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, L.; Li, X.; Li, T.; Jiang, P.; Zhang, L.; Wu, M.; Zhang, L. Characterization and anti-tumor activity of alkali-extracted polysaccharide from Enteromorpha intestinalis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaeffer, B.; Benard, C.; Lahaye, M.; Blottiere, H.M.; Cherbut, C. Biological properties of ulvan, a new source of green seaweed sulfated polysaccharides, on cultured normal and cancerous colonic epithelial tells. Planta Med. 1999, 65, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, P.; Chen, X.; Sun, P. In vitro antioxidant and antitumor activities of different sulfated polysaccharides isolated from three algae. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.B.; Ohta, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Hayashi, T. Immunostimulating effects of a sulfated galactan from Codium fragile. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 1452–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, R.; Ida, T.; Inara, H.; Sakamoto, T. Immunostimulatory activity of polysaccharides isolated from Caulerpa lentillifera on macrophage cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2012, 76, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Shao, H.; Zhang, C.; Hong, P.; Xiong, H. Separation of the polysaccharides in Caulerpa racemosa and their chemical composition and antitumor activity. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 1435–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, Y.S.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, S.M.; Park, J.K.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, S.O.; Synytsya, A.; Park, Y.I. Purification, characterization and immunostimulating activity of water-soluble polysaccharide isolated from Capsosiphon fulvescens. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2010, 10, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, T.; Kido, N.; Sugiyama, T.; Yokochi, T. Antiviral activity of acidic polysaccharides from Coccomyxa gloeobotrydiformi, a green alga, against an in vitro human influenza A virus infection. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2013, 35, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.B.; Hayashi, K.; Hayashi, T.; Sankawa, U.; Maeda, M. Antiviral activities against HSV-1, HCMV, and HIV-1 of rhamnan sulfate from Monostroma latissimum. Planta Med. 1999, 65, 439–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.B.; Hayashi, K.; Maeda, M.; Hayashi, T. Antiherpetic activities of sulfated polysaccharides from green algae. Planta Med. 2004, 70, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, P.; Adhikari, U.; Ghosal, P.K.; Pujol, C.A.; Carlucci, M.J.; Damonte, E.B.; Ray, B. In vitro anti-herpetic activity of sulfated polysaccharide fractions from Caulerpa racemosa. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 3151–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassolato, J.E.F.; Noseda, M.D.; Pujolb, C.A.; Pellizzaric, F.M.; Damonte, E.B.; Duarte, M.E.R. Chemical structure and antiviral activity of the sulfated heterorhamnan isolated from the green seaweed Gayralia oxysperma. Carbohydr. Res. 2008, 343, 3085–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.B.; Koizumi, S.; Hayashi, K.; Hayashi, T. Structure of rhamnan sulfate from the green alga Monostroma nitidum and its anti-herpetic effect. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.H.; Chan, Y.L.; Li, T.L.; Wu, C.J. Inhibition of Japanese encephalitis virus infection by the sulfated polysaccharide extracts from Ulva lactuca. Mar. Biotechnol. 2012, 14, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujol, C.A.; Ray, S.; Ray, B.; Damonte, E.B. Antiviral activity against dengue virus of diverse classes of algal sulfated polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazlowski, B.; Chiu, Y.H.; Kazlowska, K.; Pan, C.L.; Wu, C.J. Prevention of Japanese encephalitis virus infections by low-degree-polymerisation sulfated saccharides from Gracilaria sp. and Monostroma nitidum. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margret, R.J.; Kumaresan, S.; Ravikumar, S. A preliminary study on the anti-inflammatory activity of methanol extract of Ulva lactuca in rat. J. Environ. Biol. 2009, 30, 899–902. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pires, C.L.; Rodrigues, S.D.; Bristot, D.; Gaeta, H.H.; Toyama, D.d.O.; Lobo Farias, W.R.; Toyama, M.H. Sulfated polysaccharide extracted of the green algae Caulerpa racemosa increase the enzymatic activity and paw edema induced by sPLA2 from Crotalus durissus terrificus venom. Rev. Bra. Farm. Braz. J. Pharm. 2013, 23, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurgel Rodrigues, J.A.; Oliveira Vanderlei, E.D.S.; Silva, L.M.; de Araujo, I.W.; de Queiroz, I.N.; de Paula, G.A.; Abreu, T.M.; Ribeiro, N.A.; Bezerra, M.M.; Chaves, H.V.; et al. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of a sulfated polysaccharide isolated from the green seaweed Caulerpa cupressoides. Pharmacol. Rep. 2012, 64, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurgel Rodrigues, J.A.; Oliveira Vanderlei, E.D.S.; Gomes Quindere, A.L.; Monteiro, V.S.; Mendes de Vasconcelos, S.M.; Barros Benevides, N.M. Antinociceptive activity and acute toxicological study of a novel sulfated polysaccharide from Caulerpa cupressoides var. lycopodium (Chlorophyta) in Swiss mice. Acta Sci. Technol. 2013, 35, 417–425. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, Z.; Qian, L.; Zhou, Y. Hypolipidemic activity of the polysaccharides from Enteromorpha prolifera. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.Z.; Zhang, Q.B.; Li, N.; Xu, Z.H.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, Z.E. Polysaccharides from Ulva pertusa (Chlorophyta) and preliminary studies on their antihyperlipidemia activity. J. Appl. Phycol. 2003, 15, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.Z.; Li, N.; Liu, X.G.; Zhou, G.F.; Zhang, Q.B.; Li, P.C. Antihyperlipidemic effects of different molecular weight sulfated polysaccharides from Ulva pertusa (Chlorophyta). Pharmacol. Res. 2003, 48, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathivel, A.; Raghavendran, H.R.B.; Srinivasan, P.; Devaki, T. Anti-peroxidative and anti-hyperlipidemic nature of Ulva lactuca crude polysaccharide on d-Galactosamine induced hepatitis in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 3262–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, H.B.R.; Sathivel, A.; Devaki, T. Antihepatotoxic nature of Ulva reticulata (Chlorophyceae) on acetaminophen-induced hepatoxicity in experimental rats. J. Med. Food 2004, 7, 495–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pengzhan, Y.; Ning, L.; Xiguang, L.; Gefei, Z.; Quanbin, Z.; Pengcheng, L. Antihyperlipidemic effects of different molecular weight sulfated polysaccharides from Ulva pertusa (Chlorophyta). Pharmacol. Res. Offic. J. Ital. Pharmacol. Soc. 2003, 48, 543–549. [Google Scholar]
- Charles, A.L.; Chang, C.K.; Wu, M.L.; Huang, T.C. Studies on the expression of liver detoxifying enzymes in rats fed seaweed (Monostroma nitidum). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 2390–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobin-Dubigeon, C.; Lahaye, M.; Guillon, F.; Barry, J.L.; Gallant, D.J.J. Factors limiting the biodegradation of Ulva sp. cell-wall polysaccharides. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1997, 75, 341–351. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, A.; Sousa, R.A.; Reis, R.L. A practical perspective on ulvan extracted from green algae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robic, A.; Sassi, J.F.; Lahaye, M. Impact of stabilization treatments of the green seaweed Ulva rotundata (Chlorophyta) on the extraction yield, the physico-chemical and rheological properties of ulvan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 74, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Alves, A.; Pinto, P.R.; Sousa, R.A.; Borges da Silva, E.A.; Reis, R.L.; Rodrigues, A.E. Characterization of ulvan extracts to assess the effect of different steps in the extraction procedure. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, K.; Mandal, P.; Lerouge, P.; Driouich, A.; Ghosal, P.; Ray, B. Sulphated polysaccharides from Indian samples of Enteromorpha compressa (Ulvales, Chlorophyta): Isolation and structural features. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Yang, C.; Kim, S.M.; You, S. Molecular characterization and biological activities of watersoluble sulfated polysaccharides from Enteromorpha prolifera. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 19, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brading, J.W.E.; Georg-Plant, M.M.T.; Hardy, D.M. The polysaccharide from the alga Ulva lactuca: Purification, hydrolysis, and methylation of the polysaccharide. J. Chem. Soc. 1954, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinnel, J.P.; Percival, E. Acid polysaccharide from green seaweed Ulva lactuca. J. Chem. Soc. 1962, 2082–2083. [Google Scholar]
- De Reviers, B.; Leproux, A. Characterization of polysaccharides from Enteromorpha intestinalis (L.) link, Chlorophyta. Carbohydr. Polym. 1993, 22, 253–259. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, M.F.; Li, C.F.; Li, C.Y. Characterization and thermal behavior of six sulphated polysaccharides from seaweeds Ulva arasakii. Food Hydrocolloid. 1994, 8, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quemener, B.; Lahaye, M.; Bobin Dubigeon, C. Sugar determination in ulvans by a chemical-enzymatic method coupled to high performance anion exchange chromatography. J. Appl. Phycol. 1997, 9, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahaye, M.; Brunel, M.; Bonnin, E. Fine chemical structure analysis of oligosaccharides produced by an ulvan-lyase degradation of the water-soluble cell-wall polysaccharides from Ulva sp. (Ulvales, Chlorophyta). Carbohydr. Res. 1997, 304, 325–333. [Google Scholar]
- Coat, G.; Dion, P.; Noailles, M.C.; De Reviers, B.; Fontaine, J.M.; Berger-Perrot, Y.; Goer, L.D. Ulva armoricana (Ulvales, Chlorophyta) from the coasts of Brittany (France). II. Nuclear rDNA ITS sequence analysis. Eur. J. Phycol. 1998, 33, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, B.; Lahaye, M. Cell-wall polysaccharides from the marine green alga Ulva rigida (Ulvales, Chlorophyta): Extraction and chemical composition. Carbohydr. Res. 1995, 274, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, B. Polysaccharides from Enteromorpha compressa: Isolation, purification and structural features. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 66, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delattre, C.; Michaud, P.; Keller, C.; Elboutachfaiti, R.; Beven, L.; Courtois, B.; Courtois, J. Purification and characterization of a novel glucuronan lyase from Trichoderma sp. GL2. Appl. Microbiol. Biotech. 2006, 70, 437–443. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Garibay, E.; Zertuche-Gonzalez, J.A.; Pacheco-Ruiz, I. Isolation and chemical characterization of algal polysaccharides from the green seaweed Ulva clathrata (Roth) C. Agardh. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradossi, G.; Cavalieri, F.; Pissoferrato, L.; Liquori, A.M.A. Physico-chemical study on the polysaccharide ulvan from hot water extraction of the macroalga Ulva. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1999, 25, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddhanta, A.K; Goswami, A.M.; Ramavat, B.K.; Mody, K.H.; Mairh, O.P. Water soluble polysaccharides of marine algal species of Ulva (Ulvales, Chlorophyta) of Indian waters. Indian J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 2001, 30, 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- Paradossi, G.; Cavalieri, F.; Chiessi, E.A. Conformational study on the algal polysaccharide ulvan. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 6404–6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robic, A.; Gaillard, C.; Sassi, J.F.; Lerat, Y.; Lahaye, M. Ultrastructure of ulvan: A polysaccharide from green seaweeds. Biopolymers 2009, 91, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robic, A.; Rondeau-Mouro, C.; Sassi, J.F.; Lerat, Y.; Lahaye, M. Structure and interactions of ulvan in the cell wall of the marine green algae Ulva rotundata (Ulvales, Chlorophyceae). Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 206–216. [Google Scholar]
- Robic, A.; Bertrand, D.; Sassi, J.F.; Lerat, Y.; Lahaye, M. Determination of the chemical composition of ulvan, a cell wall polysaccharide from Ulva spp. (Ulvales, Chlorophyta) by FT-IR and chemometrics. J. Appl. Phycol. 2009, 21, 451–456. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.B.; Yamagaki, T.; Maeda, M.; Nakanishi, H. Rhamnan sulfate from cell walls of Monostroma latissimum. Phytochemistry 1998, 48, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, T.; Takeshita, M.; Maeda, M. Studies on anticoagulant-active arabinan sulfates from the green alga, Codium latum. Carbohydr. Res. 1992, 235, 309–331. [Google Scholar]
- Bilan, M.I.; Vinogradova, E.V.; Shashkov, A.S.; Usov, A.I. Structure of a highly pyruvylated galactan sulfate from the pacific green alga Codium yezoense (Bryopsidales, Chlorophyta). Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, M.; Mody, K.H.; Oza, R.M.; Ramavat, B.K. Blood anticoagulant activity of a green marine alga Codium dwarkense (Codiaceae, Chlorophyta) in relation to its growth stages. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 2001, 30, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Farias, E.H.C.; Pomin, V.H.; Valente, A.P.; Nader, H.B.; Rocha, H.A.O.; Mourao, P.A.S. A preponderantly 4-sulfated, 3-linked galactan from the green alga Codium isthmocladum. Glycobiology 2008, 18, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, Y.; Lee, J.B.; Hayashi, K.; Hayashi, T. Isolation of sulfated galactan from Codium fragile and its antiviral effect. Biol. Pharmaceutic. Bull. 2009, 32, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, D.A.; Jurd, K.M.; Blunden, G.; Paoletti, S.; Zanetti, F. Anticoagulant activity of a proteoglycan in extracts from Codium fragile ssp. Atlanticum. J. Appl. Phycol. 1990, 2, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, J.; Percival, E. The polysaccharides of the green seaweed Codium fragile: Part II. The water-soluble sulphated polysaccharides. J. Chem. Soc. 1964, 3338–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, K.; Adhikari, U.; Lerouge, P.; Ray, B. Polysaccharides from Caulerpa racemosa: Purification and structural features. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 68, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, N.M.; Burtseva, Y.V.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Makar’eva, T.N.; Sergeeva, O.S.; Zakharenko, A.M.; Isakov, V.V.; Nguyen Thi, L.; Nguyen Xuan, H.; et al. Polysaccharides and sterols from green algae Caulerpa lentillifera and C. sertularioides. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2009, 45, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaihou, S.; Hayashi, T.; Otsuru, O.; Maeda, M. Studies on the cell-wall mannan of the siphonous green algae Codium latum. Carbohydr. Res. 1993, 240, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, P.V.; Estevez, J.M.; Cerezo, A.S.; Ciancia, M. Sulfated β-d-mannan from green seaweed Codium vermilara. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 916–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabarsa, M.; Karnjanapratum, S.; Cho, M.; Kim, J.K.; You, S. Molecular characteristics and biological activities of anionic macromolecules from Codium fragile. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 59, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnjanapratum, S.; Tabarsa, M.; Cho, M.; You, S. Characterization and immunomodulatory activities of sulfated polysaccharides from Capsosiphon fulvescens. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Liu, R. Overview on Biological Activities and Molecular Characteristics of Sulfated Polysaccharides from Marine Green Algae in Recent Years. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4984-5020. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12094984
Wang L, Wang X, Wu H, Liu R. Overview on Biological Activities and Molecular Characteristics of Sulfated Polysaccharides from Marine Green Algae in Recent Years. Marine Drugs. 2014; 12(9):4984-5020. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12094984
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lingchong, Xiangyu Wang, Hao Wu, and Rui Liu. 2014. "Overview on Biological Activities and Molecular Characteristics of Sulfated Polysaccharides from Marine Green Algae in Recent Years" Marine Drugs 12, no. 9: 4984-5020. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12094984
APA StyleWang, L., Wang, X., Wu, H., & Liu, R. (2014). Overview on Biological Activities and Molecular Characteristics of Sulfated Polysaccharides from Marine Green Algae in Recent Years. Marine Drugs, 12(9), 4984-5020. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12094984




