Glycol Chitosan-Based Fluorescent Theranostic Nanoagents for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
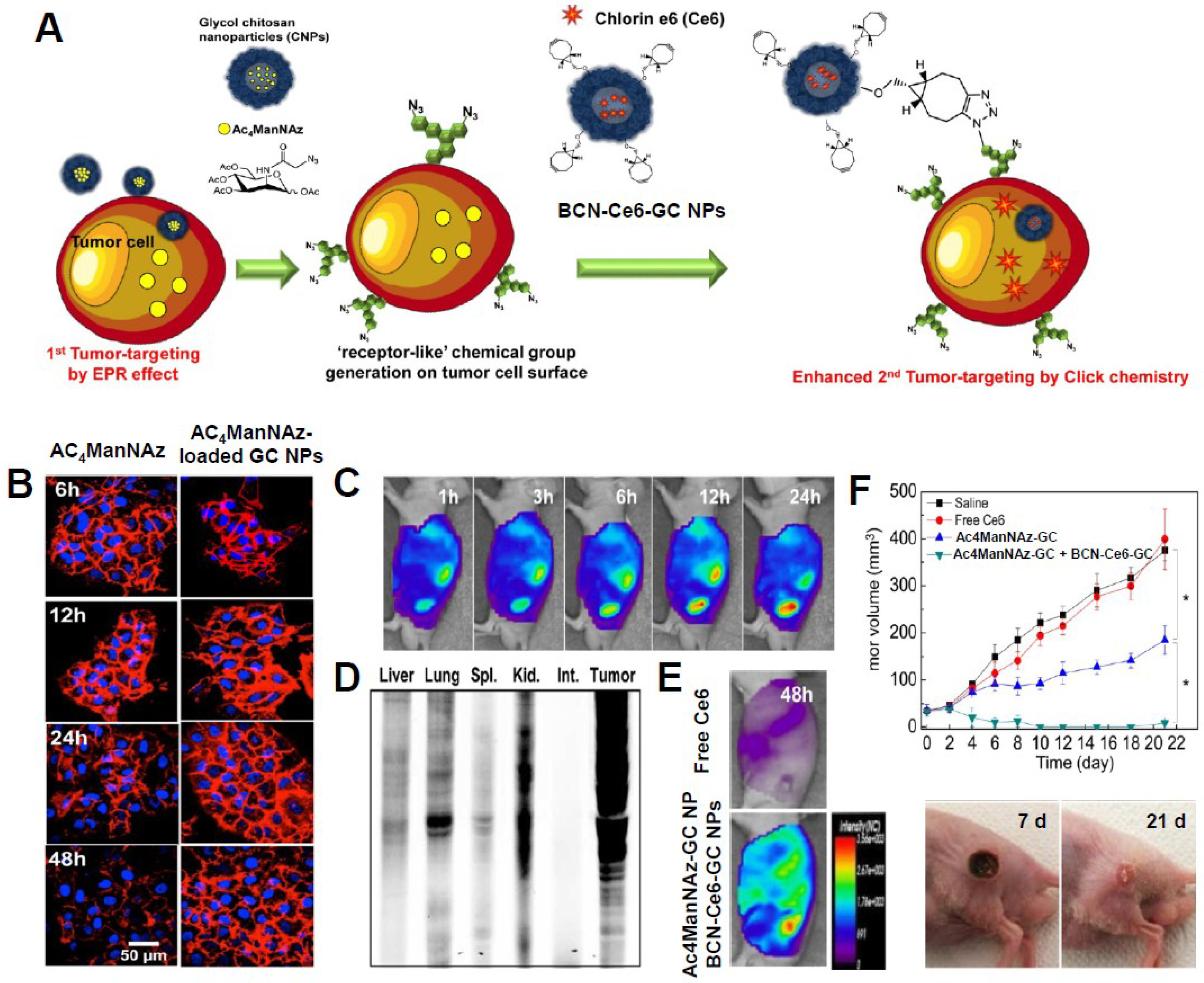
:1. Introduction
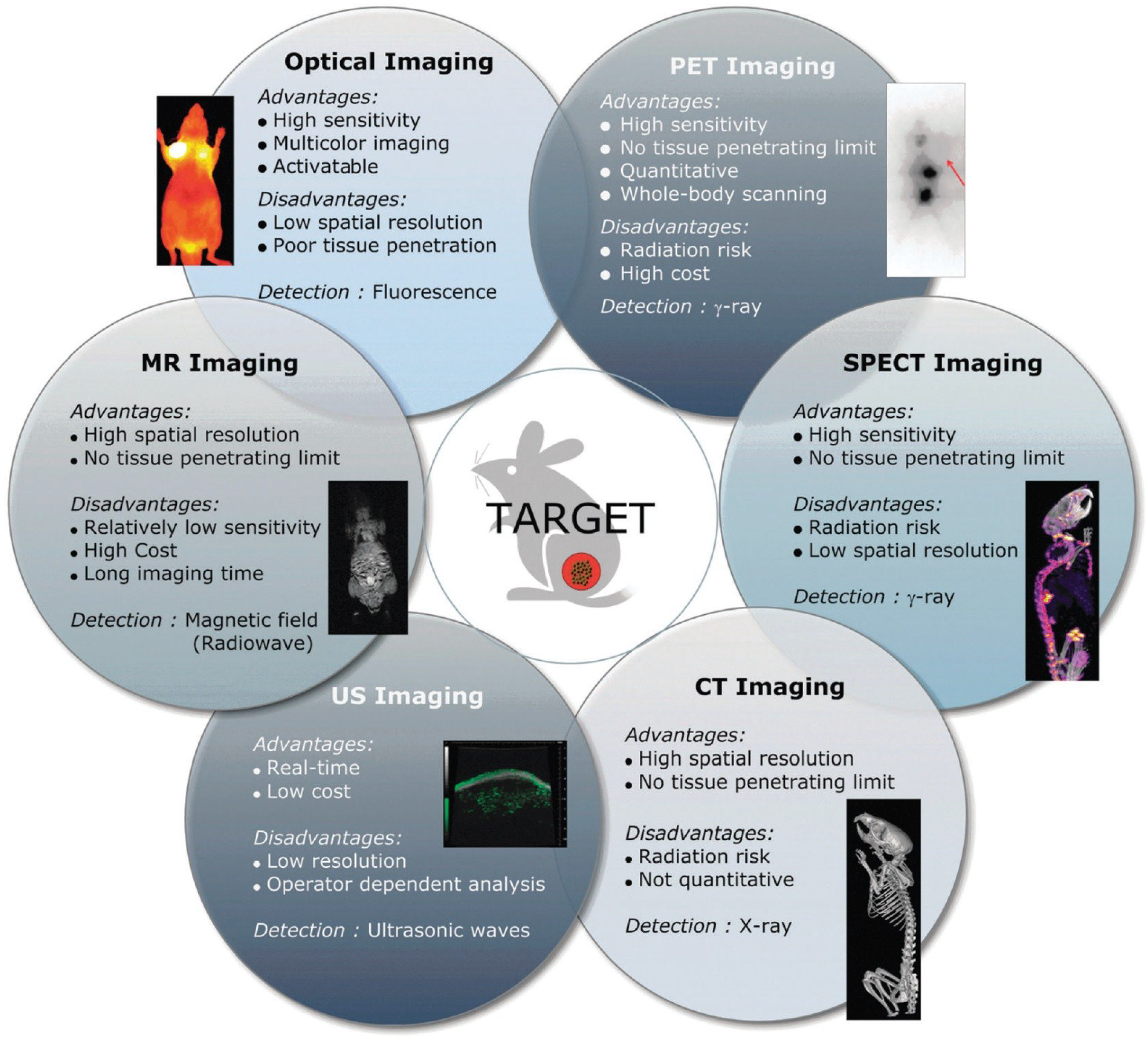
2. Basic Components for Manufacturing Theranostic Nanoagents
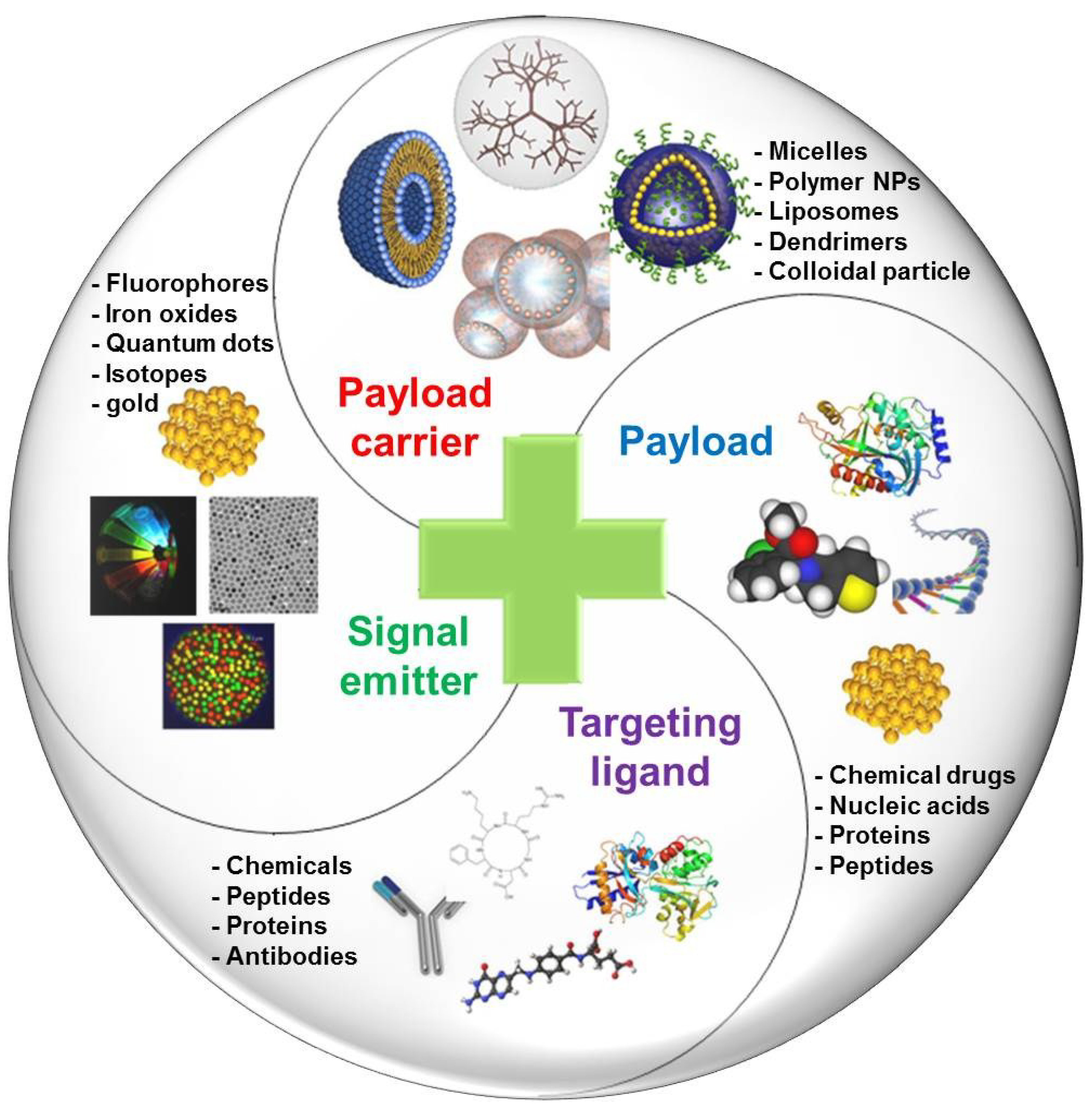
| Components | Examples |
|---|---|
| Signal Emitters | Fluorophores: Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), Alexa Fluor 488, yellow fuorescent protein (YFP), Rhodamine, tetramethylrhodamine (TRITC), cyanine 3(Cy3), red fluorescent protein (RFP), Texas Red, Cy5, Alexa Fluor 647, Cy5.5, Cy7, protoporphyrin IX (PpIX), and chlorine e6 (Ce6), etc. |
| Isotopes: 76Br, 124I, 94mTc, 68Ga, 66Ga, 6°Cu, 64Cu, 89Zr, etc. | |
| Magnetic resonance imaging agents: iron oxide, iron platinum, manganese, gadolinium, etc. | |
| Other metals: Quantom dots, silver and gold nanoparticles, etc. | |
| Payload | Chemical drugs: Doxorubicin, cisplatin, paclitaxel, docetaxel, camptothecin, mitoxantrone, gemcitabin, curcumin, photosensitizers, imatinib, trastuzumab, sinutinib, cetuximab, etc. |
| Protein and peptide drugs: RGD, buserelin, gonadorelin, leuprolide, triptorelin, abarelix, cetrorelix, Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), melanoma differentiation associated-7 (MDA-7), E1A, E4ORF4, VP3 (apoptin), cytokines (interleukin-2, interferon alpha-n3, interferon beta-1, inteferon alpha-2b), monoclonal antibodies (zevalin, mylotarg, bexxar, herceptin, avastin), etc. | |
| Neucleic acids: Plasmids, antisense oligonucleotides, ribozymes, DNAzymes, aptamers, small interfering RNA (siRNA), small hairpin RNA (shRNA), and microRNA, etc. | |
| Payload Carriers | Macromolecular prodrugs, stealth nanoparticles, micelles, nanogels, nanocapsules, polymersomes, liposomes, dendrimers, porous silica nanoparticles, etc. |
| Targeting Ligands | Angiogenic endothelial cell target: RGD, vascular endothelial growth factor, TGN peptide, etc. |
| Cancer cell target: Epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody, epidermal growth factor, human epidermal receptor 2, transferrin, A10 aptamer, As1411 aptamer, cRGD, galactose, hyaluronic acid, folic acid, glycyrrhizin, etc. |
3. Glycol Chitosan-Based Theranostic Nanoagents
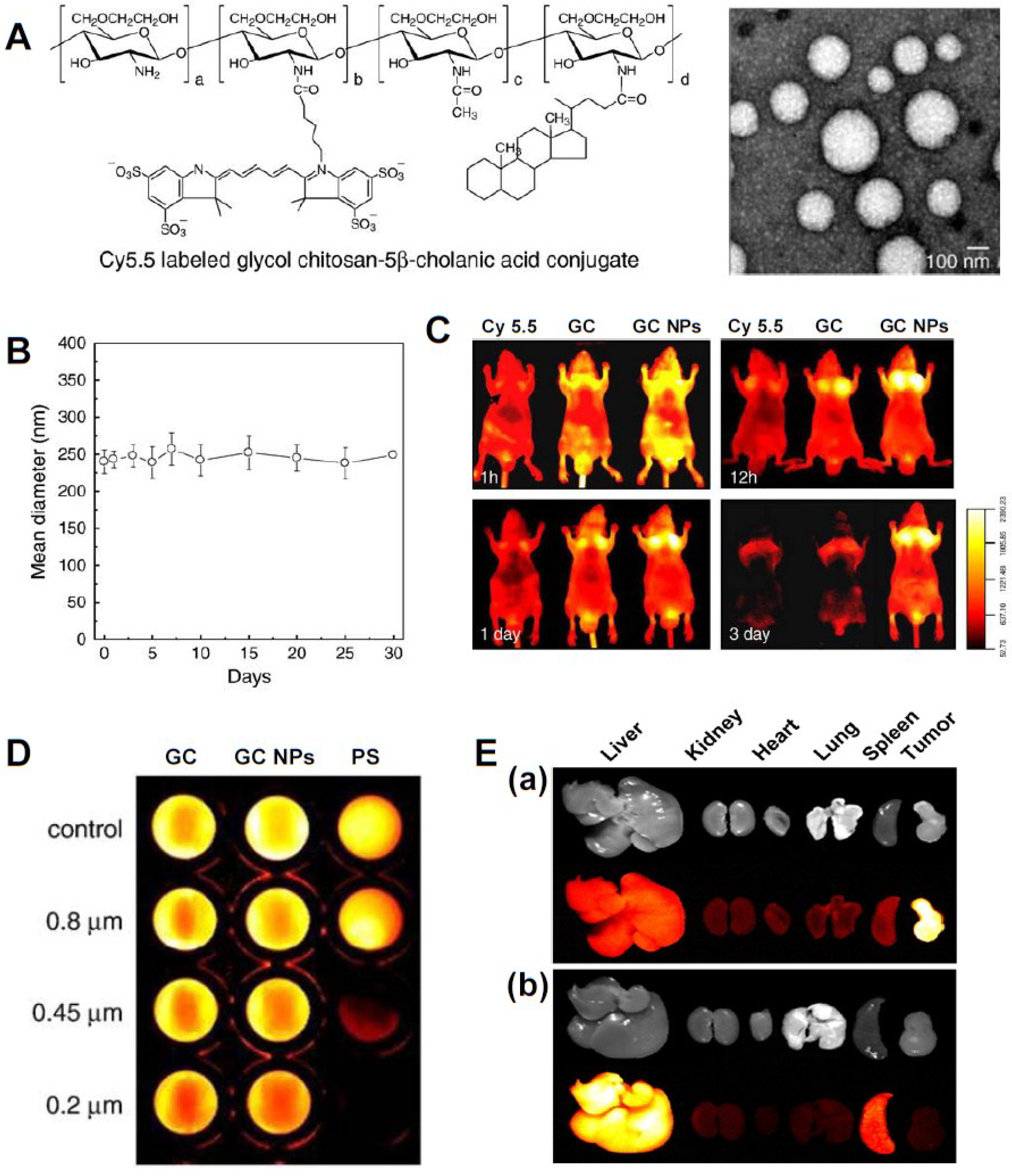
3.1. Small Molecular Drug-Based Theranostic Nanoagents
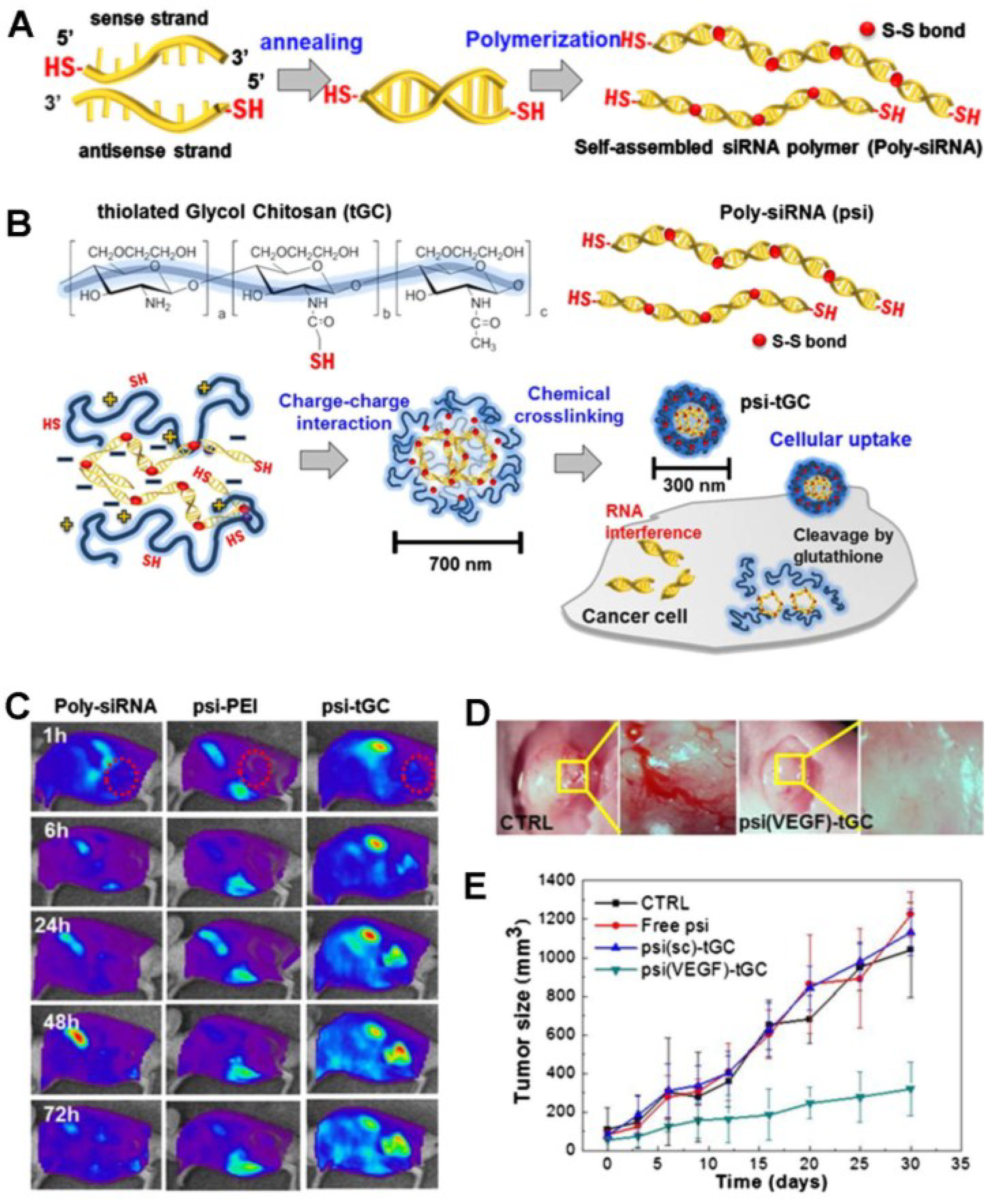
3.2. siRNA-Based Theranostic Glycol Chitosan Nanoagents
3.3. Photosensitizer-Based Theranostic Nanoagents
3.4. Fullerene-Based Theranostic Nanoagents
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sumer, B.; Gao, J. Theranostic nanomedicine for cancer. Nanomedicine 2008, 3, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, J.R. The future of theranostic nanoagents. Nanomedicine 2009, 4, 693–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, J.R. Multifunctional agents for concurrent imaging and therapy in cardiovascular disease. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Zhang, M. Nanoparticle-based theragnostics: Integrating diagnostic and therapeutic potentials in nanomedicine. J. Control. Release 2010, 146, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Theranostic applications of nanoparticles in cancer. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthu, M.S.; Leong, D.T.; Mei, L.; Feng, S.S. Nanotheranostics—Application and further development of nanomedicine strategies for advanced theranostics. Theranostics 2014, 4, 660–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Wu, J.; Sawa, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Hori, K. Tumor vascular permeability and the EPR effect in macromolecular therapeutics: A review. J. Control. Release 2000, 65, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, T.M.; Cullis, P.R. Drug delivery systems: Entering the mainstream. Science 2004, 303, 1818–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerich, D.F.; Thanos, C.G. The pinpoint promise of nanoparticle-based drug delivery and molecular diagnosis. Biomol. Eng. 2006, 23, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, Y.E.; Reddy, G.R.; Bhojani, M.; Schneider, R.; Philbert, M.A.; Rehemtulla, A.; Ross, B.D.; Kopelman, R. Brain cancer diagnosis and therapy with nanoplatforms. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1556–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissleder, R. Molecular imaging in cancer. Science 2006, 312, 1168–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissleder, R.; Pittet, M.J. Imaging in the era of molecular oncology. Nature 2008, 452, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.E.; Koo, H.; Sun, I.C.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C. Multifunctional nanoparticles for multimodal imaging and theragnosis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2656–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Conti, P.S.; Moats, R.A. In vivo near-infrared fluorescence imaging of integrin alphavbeta3 in brain tumor xenografts. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 8009–8014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissleder, R. A clearer vision for in vivo imaging. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 316–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.K.; Mishra, A.K.; Arotiba, O.A.; Mamba, B.B. Chitosan-based nanomaterials: A state-of-the-art review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 59, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, Y.J.; Jang, J.S.; Cho, Y.W.; Chung, H.; Park, R.W.; Kwon, I.C.; Kim, I.S.; Park, J.Y.; Seo, S.B.; Park, C.R.; et al. Biodistribution and anti-tumor efficacy of doxorubicin loaded glycol-chitosan nanoaggregates by EPR effect. J. Control. Release 2003, 91, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyung Park, J.; Kwon, S.; Lee, M.; Chung, H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, R.W.; Kim, I.S.; Bong Seo, S.; Kwon, I.C.; et al. Self-assembled nanoparticles based on glycol chitosan bearing hydrophobic moieties as carriers for doxorubicin: In vivo biodistribution and anti-tumor activity. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, S.; Park, J.H.; Kim, K.; Choi, K.; Chung, H.; Jeong, S.Y.; Park, R.W.; Kim, I.S.; et al. Hydrophobically modified glycol chitosan nanoparticles as carriers for paclitaxel. J. Control. Release 2006, 111, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Kwon, S.; Nam, J.O.; Park, R.W.; Chung, H.; Seo, S.B.; Kim, I.S.; Kwon, I.C.; Jeong, S.Y. Self-assembled nanoparticles based on glycol chitosan bearing 5beta-cholanic acid for RGD peptide delivery. J. Control. Release 2004, 95, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, K.; Kang, E.; Lee, S.; Nam, H.Y.; Kim, K.; Park, J.H.; Chi, D.Y.; Park, R.W.; et al. Self-assembled glycol chitosan nanoparticles for the sustained and prolonged delivery of antiangiogenic small peptide drugs in cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1920–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.S.; Lee, J.E.; Chung, H.; Kwon, I.C.; Jeong, S.Y. Self-assembled nanoparticles containing hydrophobically modified glycol chitosan for gene delivery. J. Control. Release 2005, 103, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, M.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, S.; Lee, S.; Chung, H.; Lee, S.; Choi, Y.; Oh, Y.K.; Park, J.H.; Jeong, S.Y.; et al. Tumor-homing glycol chitosan/polyethylenimine nanoparticles for the systemic delivery of siRNA in tumor-bearing mice. J. Control. Release 2010, 144, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Kim, J.H.; Nam, Y.S.; Lee, S.; Nam, H.Y.; Kim, K.; Park, J.H.; Kim, I.S.; Choi, K.; Kim, S.Y.; et al. Effect of polymer molecular weight on the tumor targeting characteristics of self-assembled glycol chitosan nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2007, 122, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Ryu, J.H.; Park, K.; Lee, A.; Lee, S.Y.; Youn, I.C.; Ahn, C.H.; Yoon, S.M.; Myung, S.J.; Moon, D.H.; et al. Polymeric nanoparticle-based activatable near-infrared nanosensor for protease determination in vivo. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 4412–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, T.; Park, S.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, K.; Choi, K.; Song, I.C.; Han, M.H.; Leary, J.J.; Yuk, S.A.; Kwon, I.C.; et al. Tumor targeting chitosan nanoparticles for dual-modality optical/MR cancer imaging. Bioconjugate Chem. 2010, 21, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiseh, O.; Gunn, J.W.; Zhang, M. Design and fabrication of magnetic nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery and imaging. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 284–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandrowski, K.U.; Gresser, J.D.; Wise, D.L.; Trantol, D.J. Bioresorbable bone graft substitutes of different osteoconductivities: A histologic evaluation of osteointegration of poly(propylene glycol-co-fumaric acid)-based cement implants in rats. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamrungsap, S.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, T.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Fu, T.; Tan, W. Nanotechnology in therapeutics: A focus on nanoparticles as a drug delivery system. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 1253–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M. Calcium phosphate/chitosan composite scaffolds for controlled in vitro antibiotic drug release. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 62, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, J.H.; Koo, H.; Lee, S.; Min, K.H.; Park, K.; Yoo, H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, J.H.; Kwon, I.C.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, K. Real-time and non-invasive optical imaging of tumor-targeting glycol chitosan nanoparticles in various tumor models. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 5252–5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barshtein, G.; Ben-Ami, R.; Yedgar, S. Role of red blood cell flow behavior in hemodynamics and hemostasis. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2007, 5, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kim, J.H.; Park, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, K.; Nam, H.; Lee, S.; Park, J.H.; Park, R.W.; Kim, I.S.; et al. Tumor-homing multifunctional nanoparticles for cancer theragnosis: Simultaneous diagnosis, drug delivery, and therapeutic monitoring. J. Control. Release 2010, 146, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanakumar, G.; Min, K.H.; Min, D.S.; Kim, A.Y.; Lee, C.M.; Cho, Y.W.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, K.; Jeong, S.Y.; Park, K.; et al. Hydrotropic oligomer-conjugated glycol chitosan as a carrier of paclitaxel: Synthesis, characterization, and in vivo biodistribution. J. Control. Release 2009, 140, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, K.; Lee, S.; Nam, H.Y.; Min, K.H.; Jo, H.G.; Park, J.H.; Choi, K.; Jeong, S.Y.; et al. Antitumor efficacy of cisplatin-loaded glycol chitosan nanoparticles in tumor-bearing mice. J. Control. Release 2008, 127, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, K.H.; Park, K.; Kim, Y.S.; Bae, S.M.; Lee, S.; Jo, H.G.; Park, R.W.; Kim, I.S.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, K.; et al. Hydrophobically modified glycol chitosan nanoparticles-encapsulated camptothecin enhance the drug stability and tumor targeting in cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2008, 127, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.Y.; Kim, I.S.; Kwon, I.C.; Kim, Y.H. Tumor targetability and antitumor effect of docetaxel-loaded hydrophobically modified glycol chitosan nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2008, 128, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasool, A.A.; Hussain, A.A.; Dittert, L.W. Solubility enhancement of some water-insoluble drugs in the presence of nicotinamide and related compounds. J. Pharm. Sci. 1991, 80, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.S.; Park, K.; Park, S.; Kim, G.C.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.; Kil, H.; Oh, S.J.; Chi, D.; Kim, K.; et al. Tumor targeting efficiency of bare nanoparticles does not mean the efficacy of loaded anticancer drugs: Importance of radionuclide imaging for optimization of highly selective tumor targeting polymeric nanoparticles with or without drug. J. Control. Release 2010, 147, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelkar, S.S.; Reineke, T.M. Theranostics: Combining imaging and therapy. Bioconjugate Chem. 2011, 22, 1879–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niidome, T.; Huang, L. Gene therapy progress and prospects: Nonviral vectors. Gene Ther. 2002, 9, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Huh, M.S.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.J.; Chung, H.; Park, J.H.; Oh, Y.K.; Choi, K.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C. Stability and cellular uptake of polymerized siRNA (poly-siRNA)/polyethylenimine (PEI) complexes for efficient gene silencing. J. Control. Release 2010, 141, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Huh, M.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Min, S.; Lee, S.; Koo, H.; Chu, J.U.; Lee, K.E.; Jeon, H.; Choi, Y.; et al. Tumor-homing poly-siRNA/glycol chitosan self-cross-linked nanoparticles for systemic siRNA delivery in cancer treatment. Angew. Chem. 2012, 51, 7203–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Chiang, L.Y.; Hamblin, M.R. Photodynamic therapy with fullerenes in vivo: Reality or a dream? Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 1813–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostinis, P.; Berg, K.; Cengel, K.A.; Foster, T.H.; Girotti, A.W.; Gollnick, S.O.; Hahn, S.M.; Hamblin, M.R.; Juzeniene, A.; Kessel, D.; et al. Photodynamic therapy of cancer: An update. Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 250–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolmans, D.E.; Fukumura, D.; Jain, R.K. Photodynamic therapy for cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, B.W.; Dougherty, T.J. How does photodynamic therapy work? Photochem. Photobiol. 1992, 55, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josefsen, L.B.; Boyle, R.W. Unique diagnostic and therapeutic roles of porphyrins and phthalocyanines in photodynamic therapy, imaging and theranostics. Theranostics 2012, 2, 916–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, C.M.; Pendse, D.; Emberton, M. Photodynamic therapy for prostate cancer—A review of current status and future promise. Nat. Clin. Pract. Urol. 2009, 6, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awan, M.A.; Tarin, S.A. Review of photodynamic therapy. Surgeon 2006, 4, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, Z.L.; Yang, X.X.; Huang, P.; Zhou, X.P.; Du, X.X. Magnetic chitosan nanoparticles as a drug delivery system for targeting photodynamic therapy. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 135102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillemard, V.; Saragovi, H.U. Taxane-antibody conjugates afford potent cytotoxicity, enhanced solubility, and tumor target selectivity. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bechet, D.; Couleaud, P.; Frochot, C.; Viriot, M.L.; Guillemin, F.; Barberi-Heyob, M. Nanoparticles as vehicles for delivery of photodynamic therapy agents. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Park, K.; Oh, Y.K.; Kwon, S.H.; Her, S.; Kim, I.S.; Choi, K.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.G.; et al. Tumor specificity and therapeutic efficacy of photosensitizer-encapsulated glycol chitosan-based nanoparticles in tumor-bearing mice. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2929–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Koo, H.; Jeong, H.; Huh, M.S.; Choi, Y.; Jeong, S.Y.; Byun, Y.; Choi, K.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C. Comparative study of photosensitizer loaded and conjugated glycol chitosan nanoparticles for cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2011, 152, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, Y.H.; Yin, H. Stability issues of polymeric micelles. J. Control. Release 2008, 131, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Koo, H.; Lee, D.E.; Min, S.; Lee, S.; Chen, X.; Choi, Y.; Leary, J.F.; Park, K.; Jeong, S.Y.; et al. Tumor-homing photosensitizer-conjugated glycol chitosan nanoparticles for synchronous photodynamic imaging and therapy based on cellular on/off system. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 4021–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskin, J.M.; Prescher, J.A.; Laughlin, S.T.; Agard, N.J.; Chang, P.V.; Miller, I.A.; Lo, A.; Codelli, J.A.; Bertozzi, C.R. Copper-free click chemistry for dynamic in vivo imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16793–16797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.V.; Prescher, J.A.; Sletten, E.M.; Baskin, J.M.; Miller, I.A.; Agard, N.J.; Lo, A.; Bertozzi, C.R. Copper-free click chemistry in living animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1821–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prescher, J.A.; Bertozzi, C.R. Chemistry in living systems. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005, 1, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostovtsev, V.V.; Green, L.G.; Fokin, V.V.; Sharpless, K.B. A stepwise huisgen cycloaddition process: Copper(I)-catalyzed regioselective “ligation” of azides and terminal alkynes. Angew. Chem. 2002, 41, 2596–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornoe, C.W.; Christensen, C.; Meldal, M. Peptidotriazoles on solid phase: [1,2,3]-triazoles by regiospecific copper(i)-catalyzed 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions of terminal alkynes to azides. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 3057–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agard, N.J.; Prescher, J.A.; Bertozzi, C.R. A strain-promoted [3 + 2] azide-alkyne cycloaddition for covalent modification of biomolecules in living systems. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15046–15047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, J.T.; Champion, J.A.; Mahdavi, A.; Tanrikulu, I.C.; Beatty, K.E.; Connor, R.E.; Yoo, T.H.; Dieterich, D.C.; Schuman, E.M.; Tirrell, D.A. Cell-selective metabolic labeling of proteins. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Al Zaki, A.; Hui, J.Z.; Muzykantov, V.R.; Tsourkas, A. Multifunctional nanoparticles: Cost versus benefit of adding targeting and imaging capabilities. Science 2012, 338, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gartner, Z.J.; Bertozzi, C.R. Programmed assembly of 3-dimensional microtissues with defined cellular connectivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4606–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertozzi, C.R.; Kiessling, L.L. Chemical glycobiology. Science 2001, 291, 2357–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Koo, H.; Na, J.H.; Han, S.J.; Min, H.S.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, S.H.; Yun, S.H.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kwon, I.C.; et al. Chemical tumor-targeting of nanoparticles based on metabolic glycoengineering and click chemistry. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 2048–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Baik, H.J.; Oh, Y.T.; Oh, K.T.; Youn, Y.S.; Lee, E.S. A smart polysaccharide/drug conjugate for photodynamic therapy. Angew. Chem. 2011, 50, 1644–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A.W.; Wilson, S.R.; Schuster, D.I. Biological applications of fullerenes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1996, 4, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwag, D.S.; Oh, N.M.; Oh, Y.T.; Oh, K.T.; Youn, Y.S.; Lee, E.S. Photodynamic therapy using glycol chitosan grafted fullerenes. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 431, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwag, D.S.; Park, K.; Oh, K.T.; Lee, E.S. Hyaluronated fullerenes with photoluminescent and antitumoral activity. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, D.J.; Kwag, D.S.; Lee, U.Y.; Youn, Y.S.; Lee, E.S. Acid pH-activated glycol chitosan/fullerene nanogels for efficient tumor therapy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.R.; Oh, K.T.; Baik, H.J.; Youn, Y.S.; Lee, E.S. A charge-switched nano-sized polymeric carrier for protein delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 392, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kean, T.; Thanou, M. Biodegradation, biodistribution and toxicity of chitosan. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, S.; Dionísio, M.; López, C.R.; Grenha, A. Biocompatibility of chitosan carriers with application in drug delivery. J. Funct. Biomater. 2012, 3, 615–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rhee, J.-K.; Park, O.K.; Lee, A.; Yang, D.H.; Park, K. Glycol Chitosan-Based Fluorescent Theranostic Nanoagents for Cancer Therapy. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 6038-6057. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12126038
Rhee J-K, Park OK, Lee A, Yang DH, Park K. Glycol Chitosan-Based Fluorescent Theranostic Nanoagents for Cancer Therapy. Marine Drugs. 2014; 12(12):6038-6057. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12126038
Chicago/Turabian StyleRhee, Jin-Kyu, Ok Kyu Park, Aeju Lee, Dae Hyeok Yang, and Kyeongsoon Park. 2014. "Glycol Chitosan-Based Fluorescent Theranostic Nanoagents for Cancer Therapy" Marine Drugs 12, no. 12: 6038-6057. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12126038
APA StyleRhee, J.-K., Park, O. K., Lee, A., Yang, D. H., & Park, K. (2014). Glycol Chitosan-Based Fluorescent Theranostic Nanoagents for Cancer Therapy. Marine Drugs, 12(12), 6038-6057. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12126038






