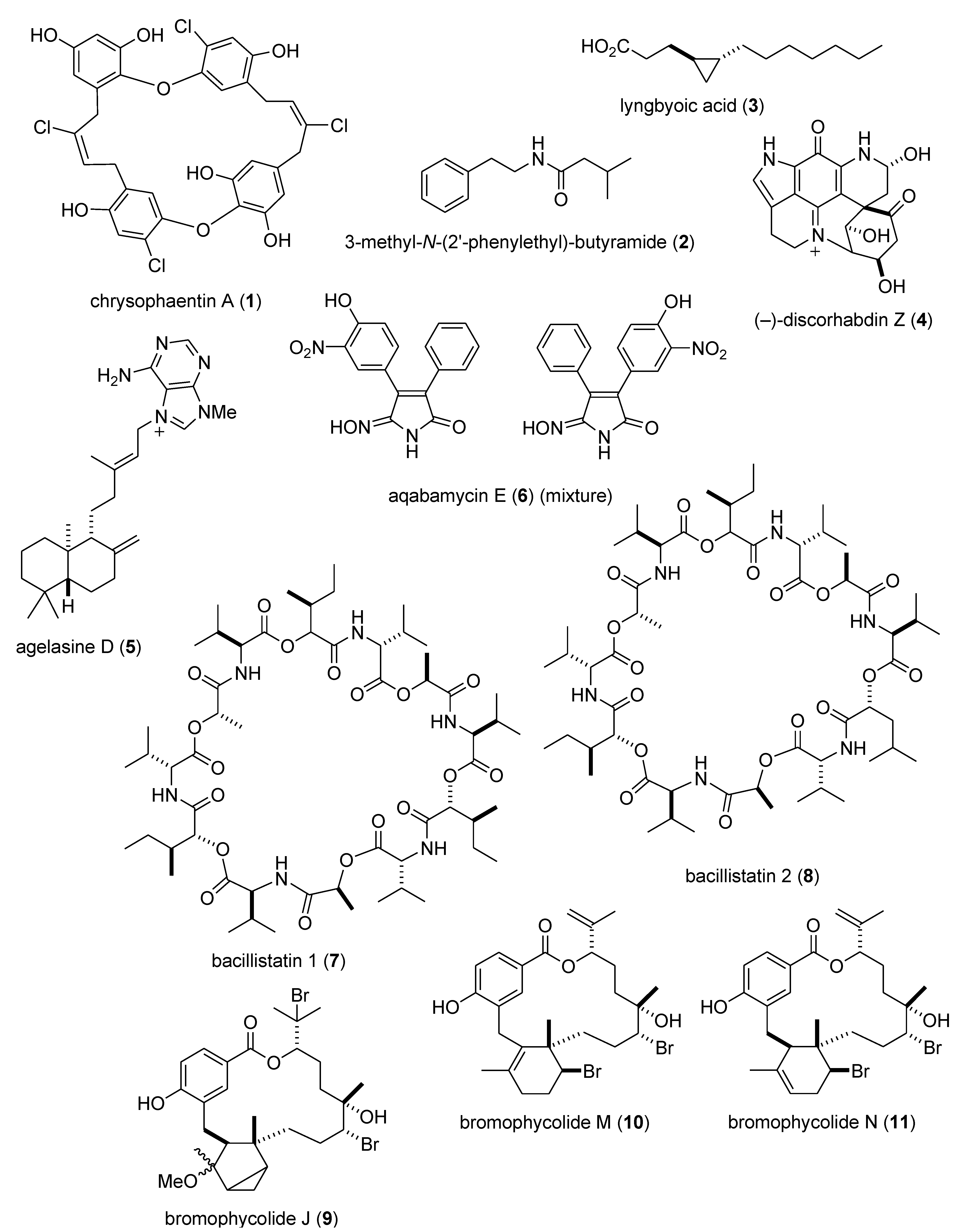
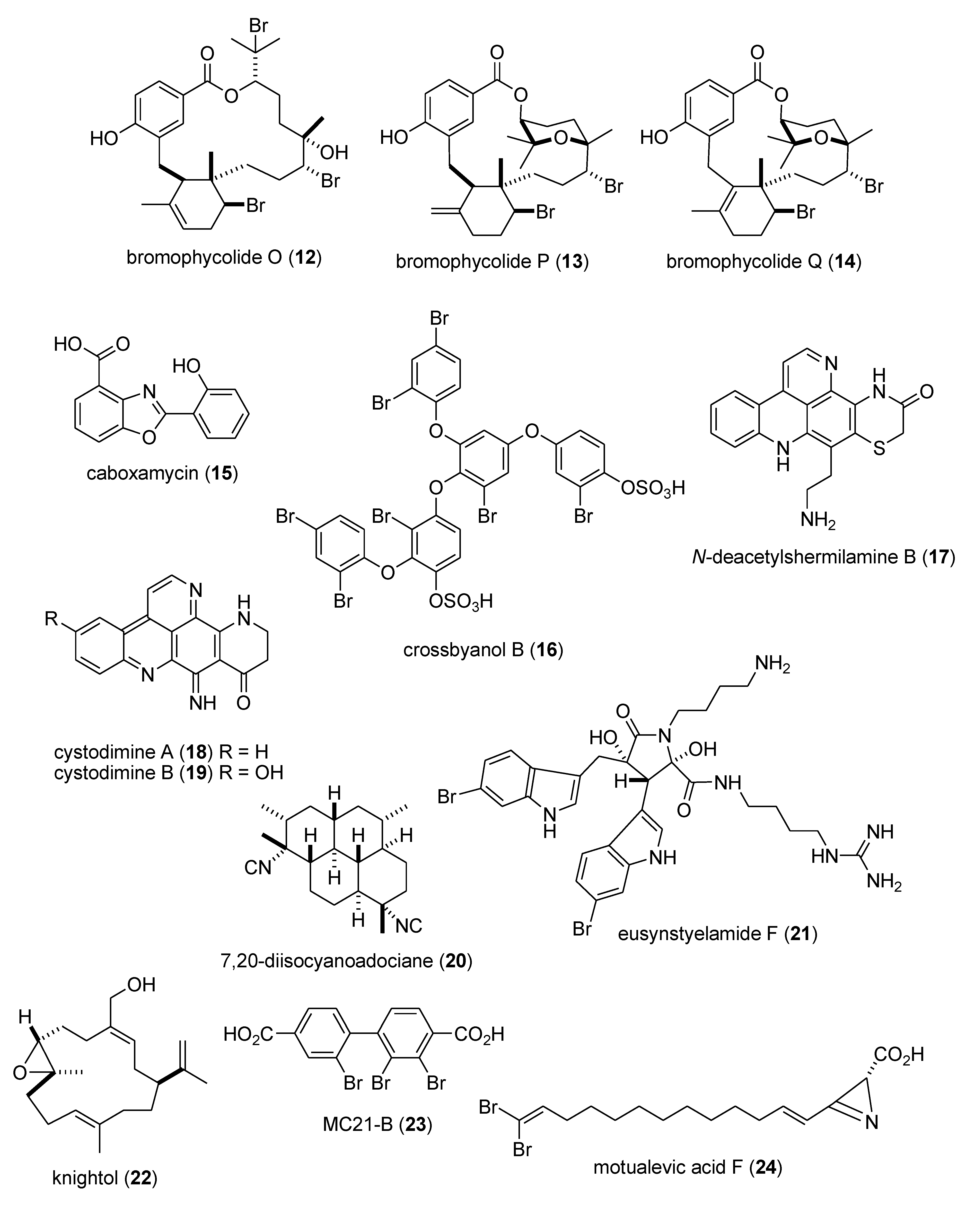
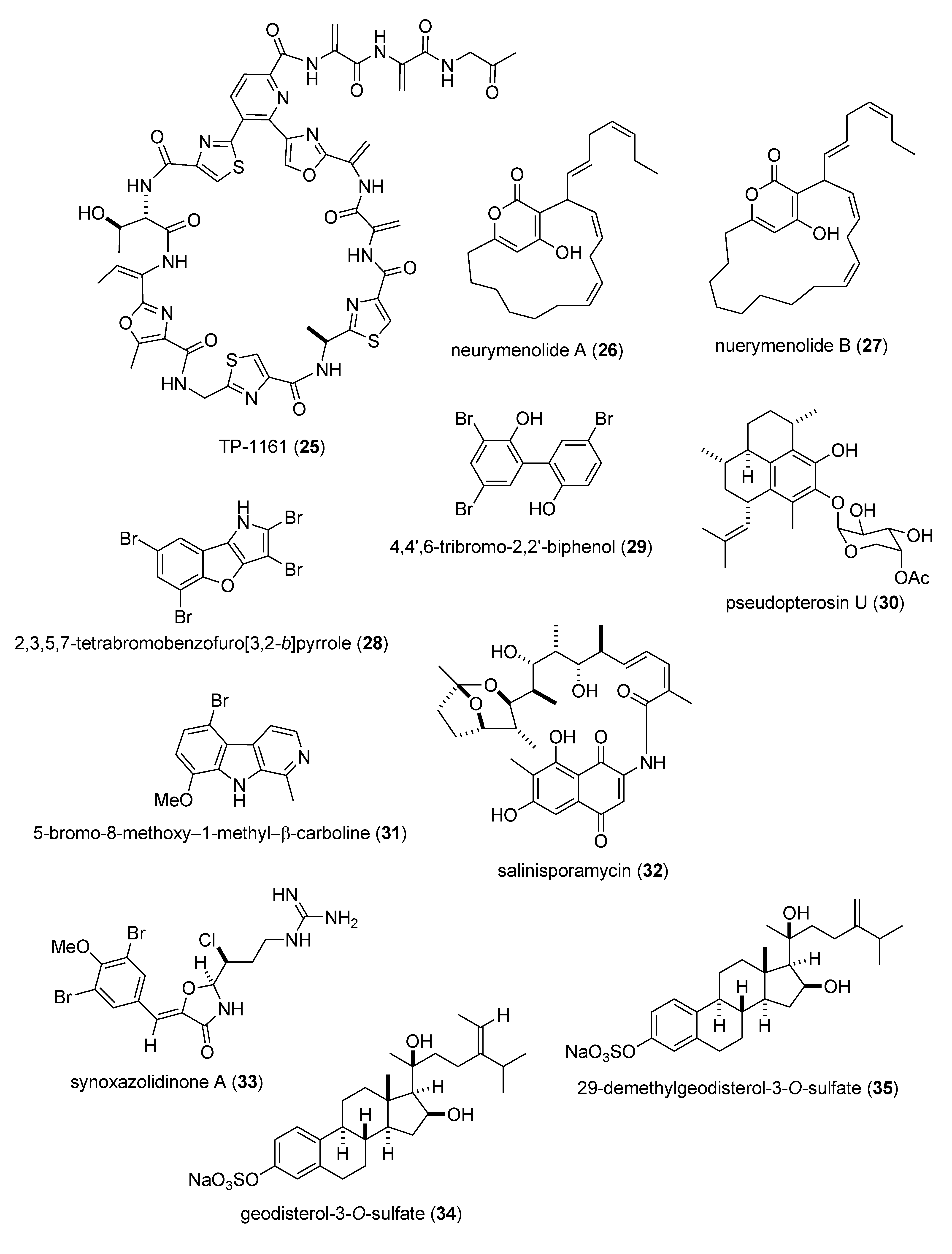
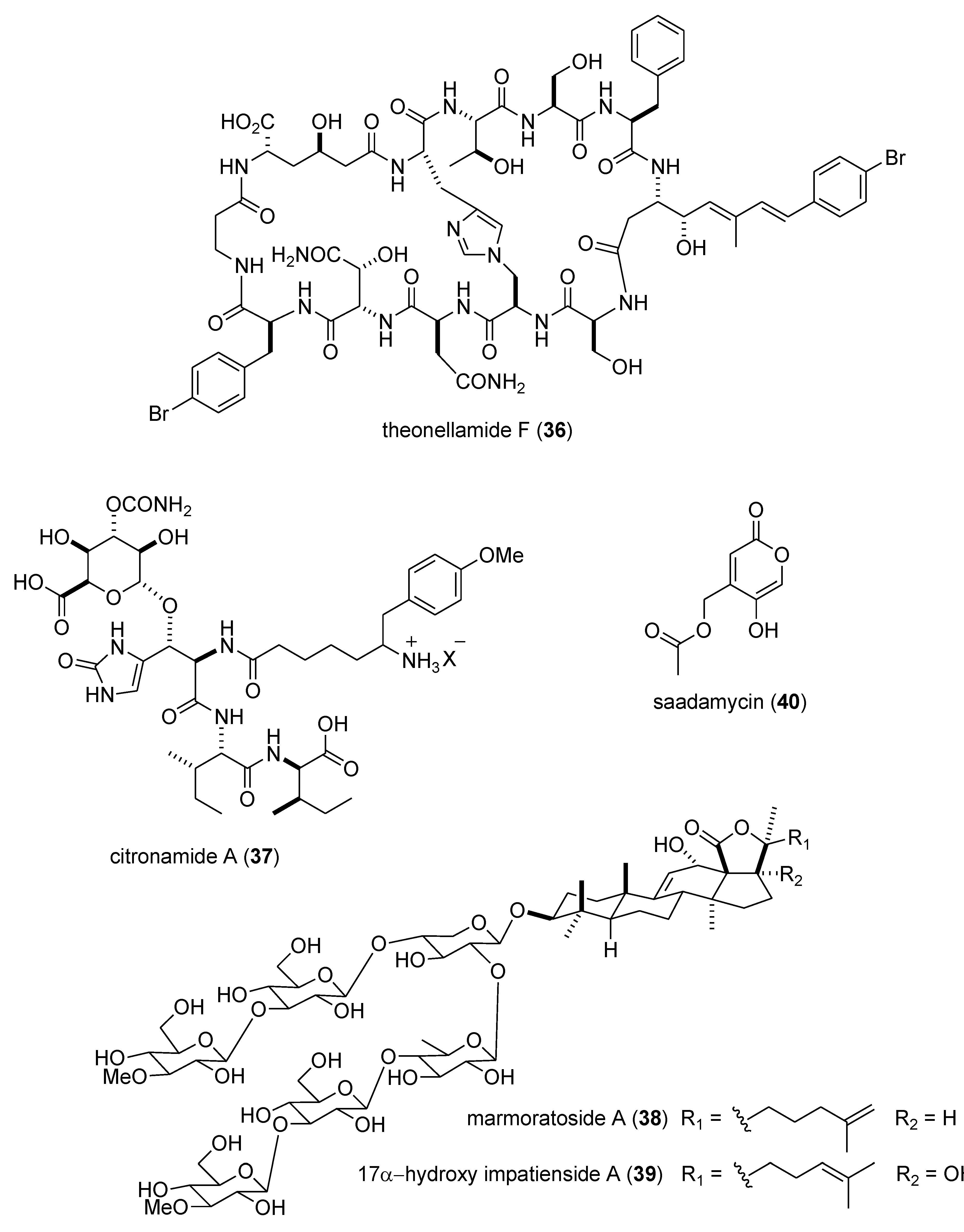
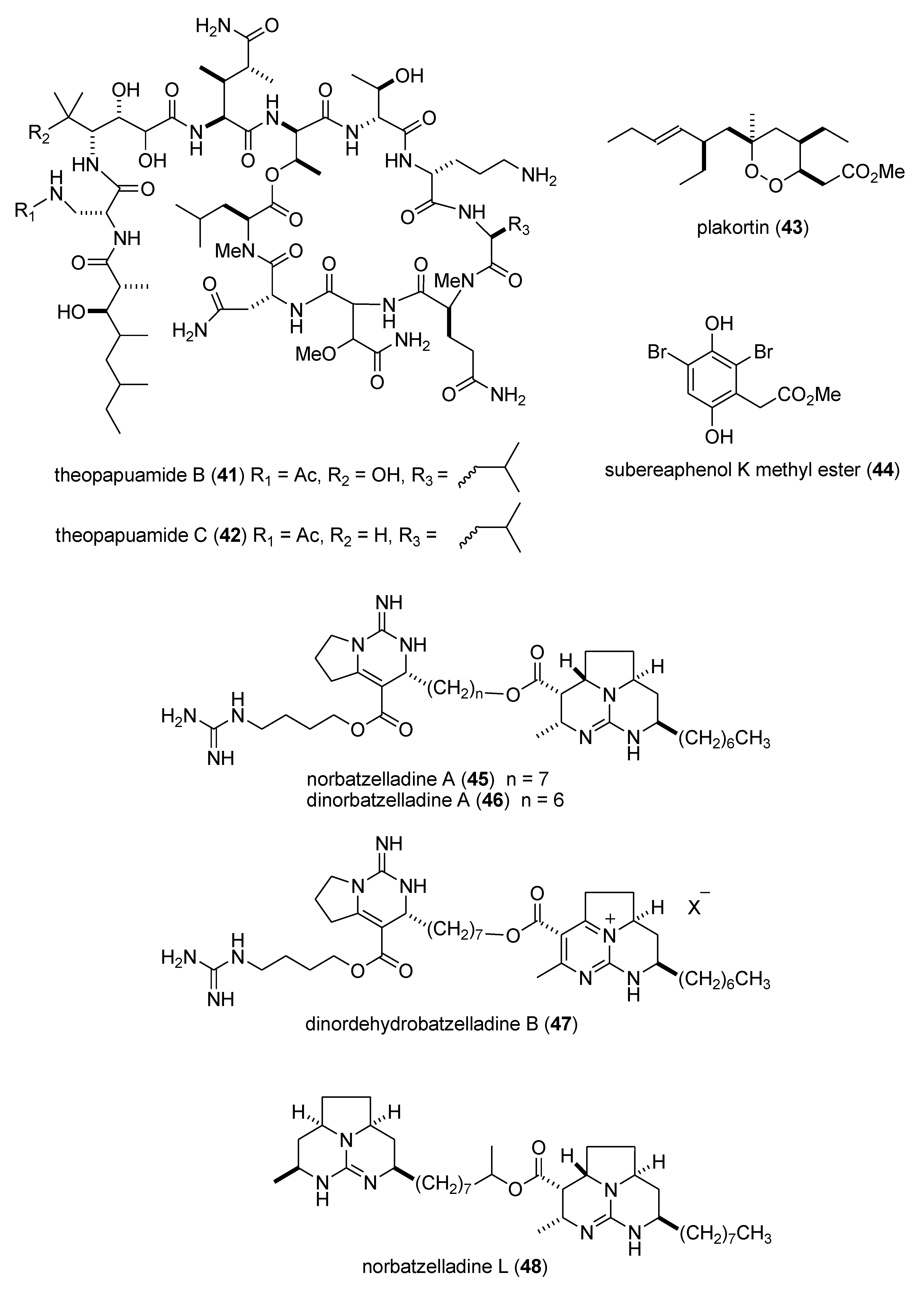
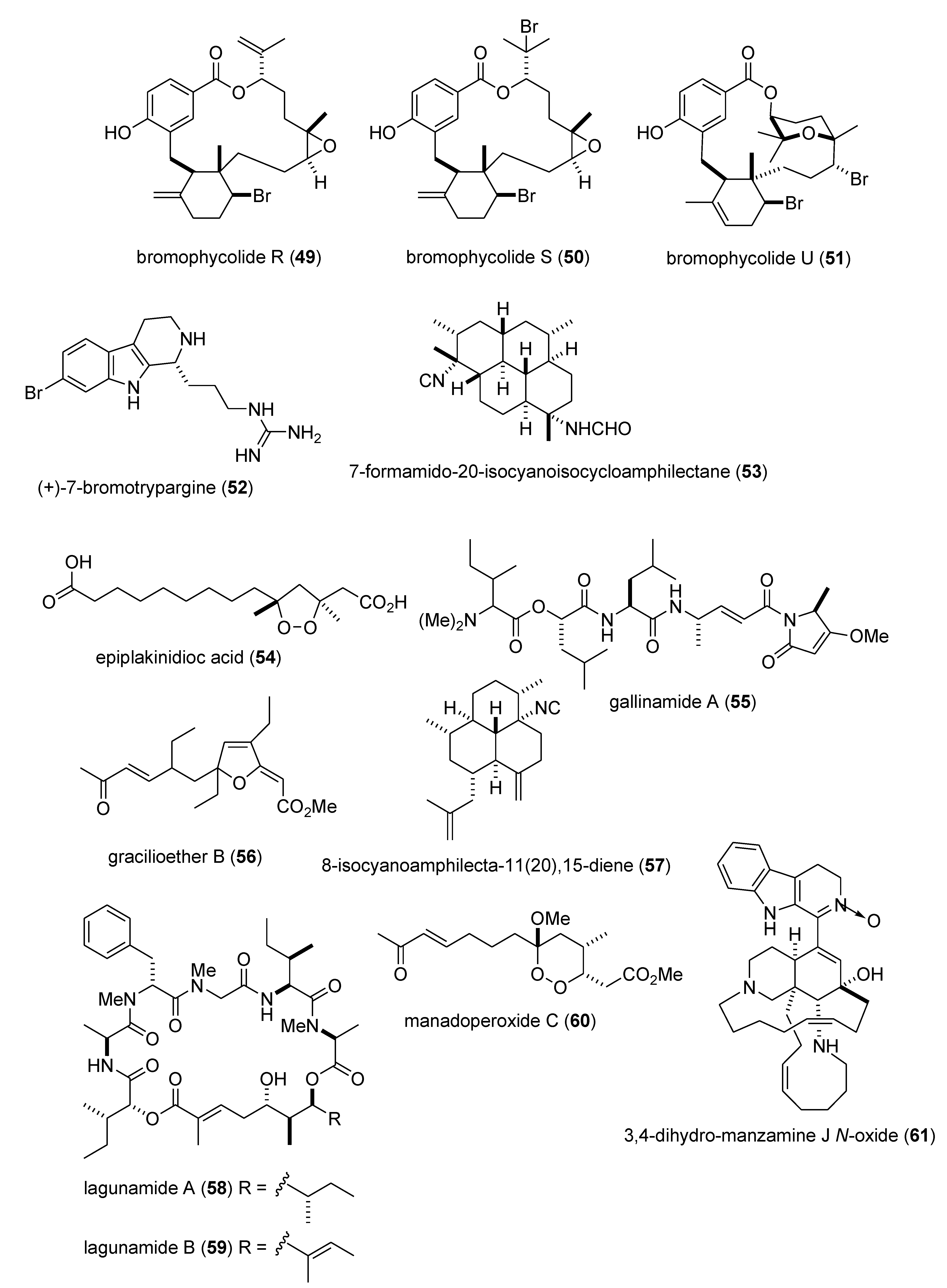
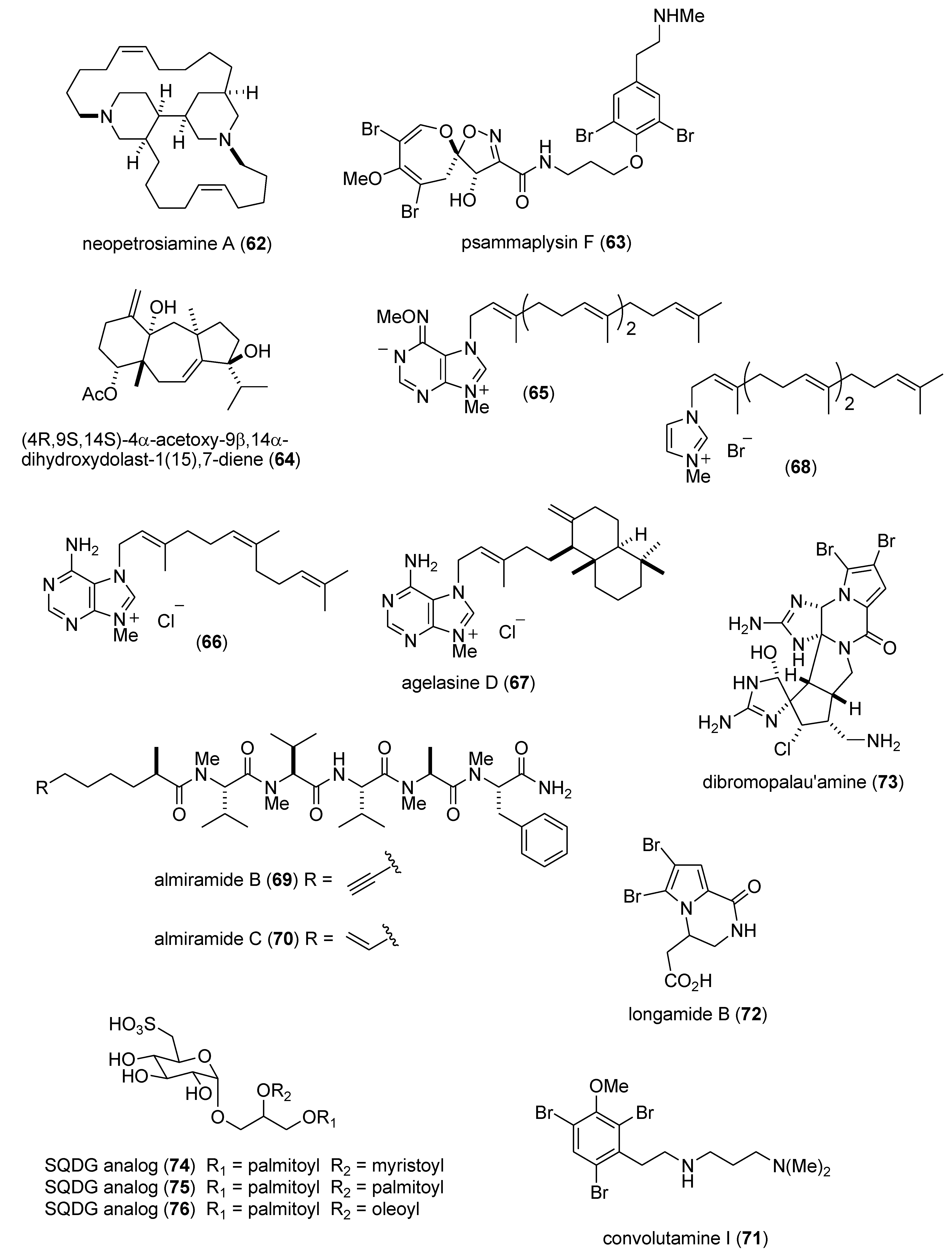
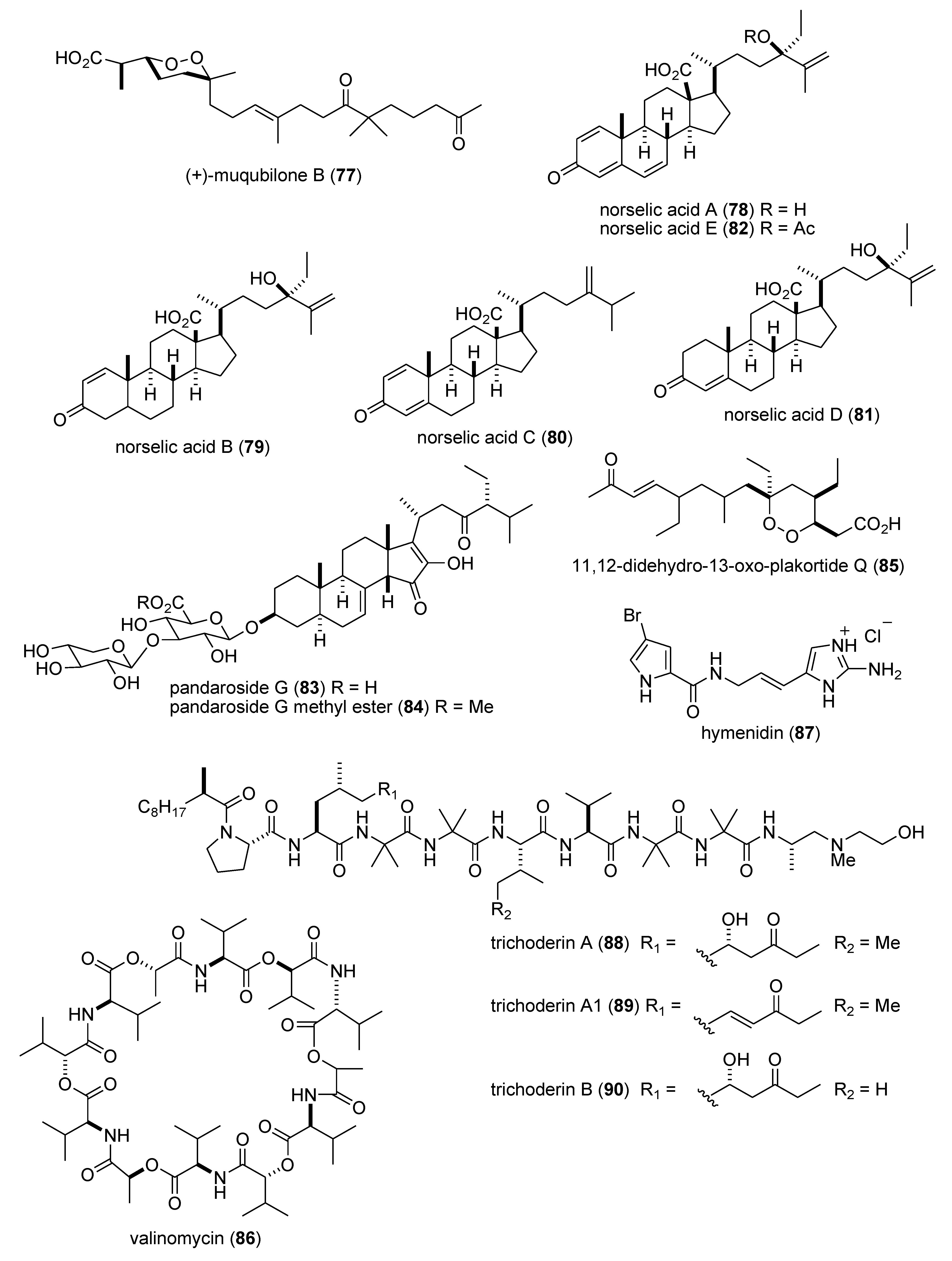
Marine Pharmacology in 2009–2011: Marine Compounds with Antibacterial, Antidiabetic, Antifungal, Anti-Inflammatory, Antiprotozoal, Antituberculosis, and Antiviral Activities; Affecting the Immune and Nervous Systems, and other Miscellaneous Mechanisms of Action †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
3. Marine Compounds with Antidiabetic and Anti-Inflammatory Activity, and Affecting the Immune and Nervous System
| Drug Class | Compound/organism a+ | Chemistry | Pharmacological activity | IC50 b | MMOA c | Country d | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
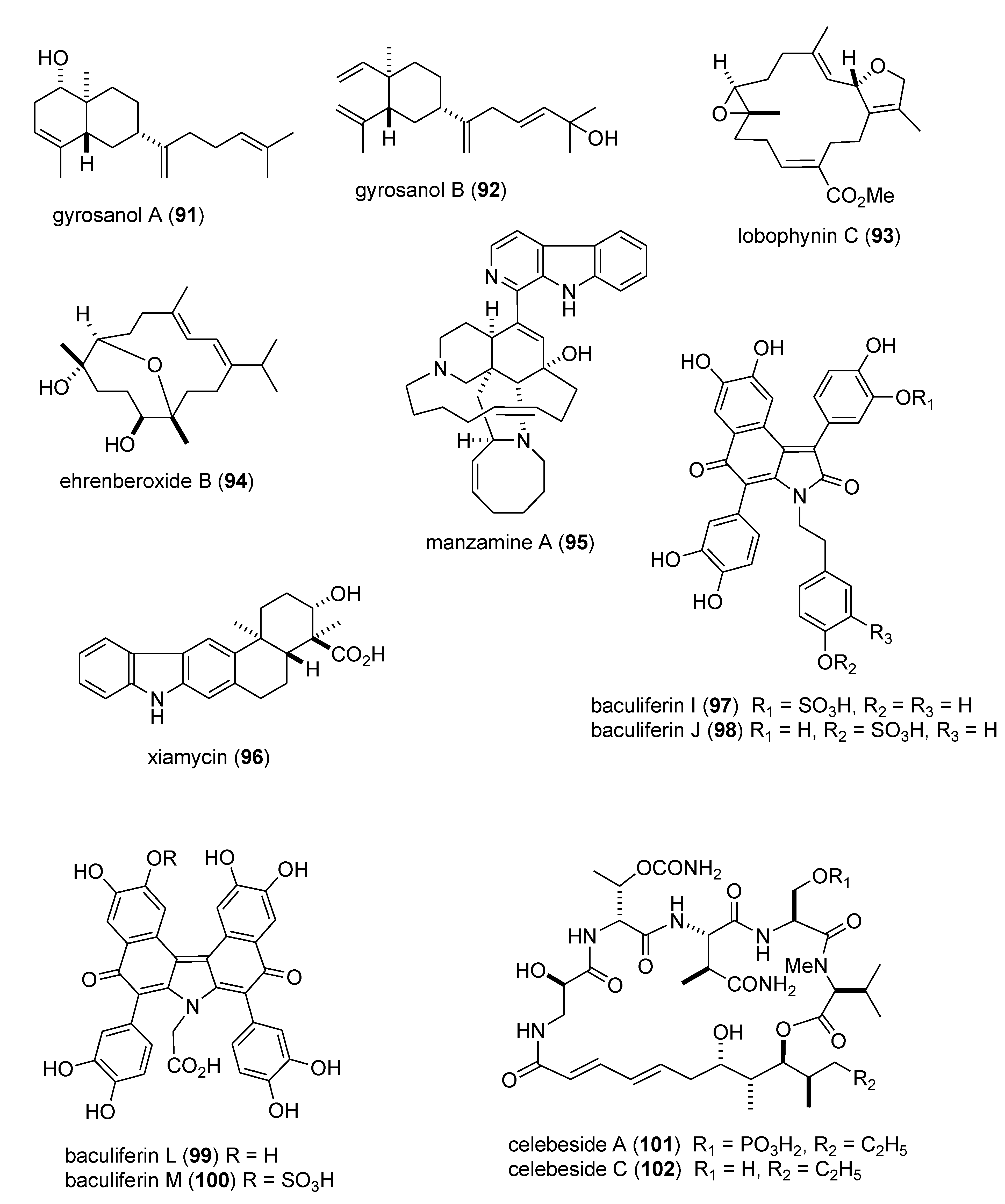
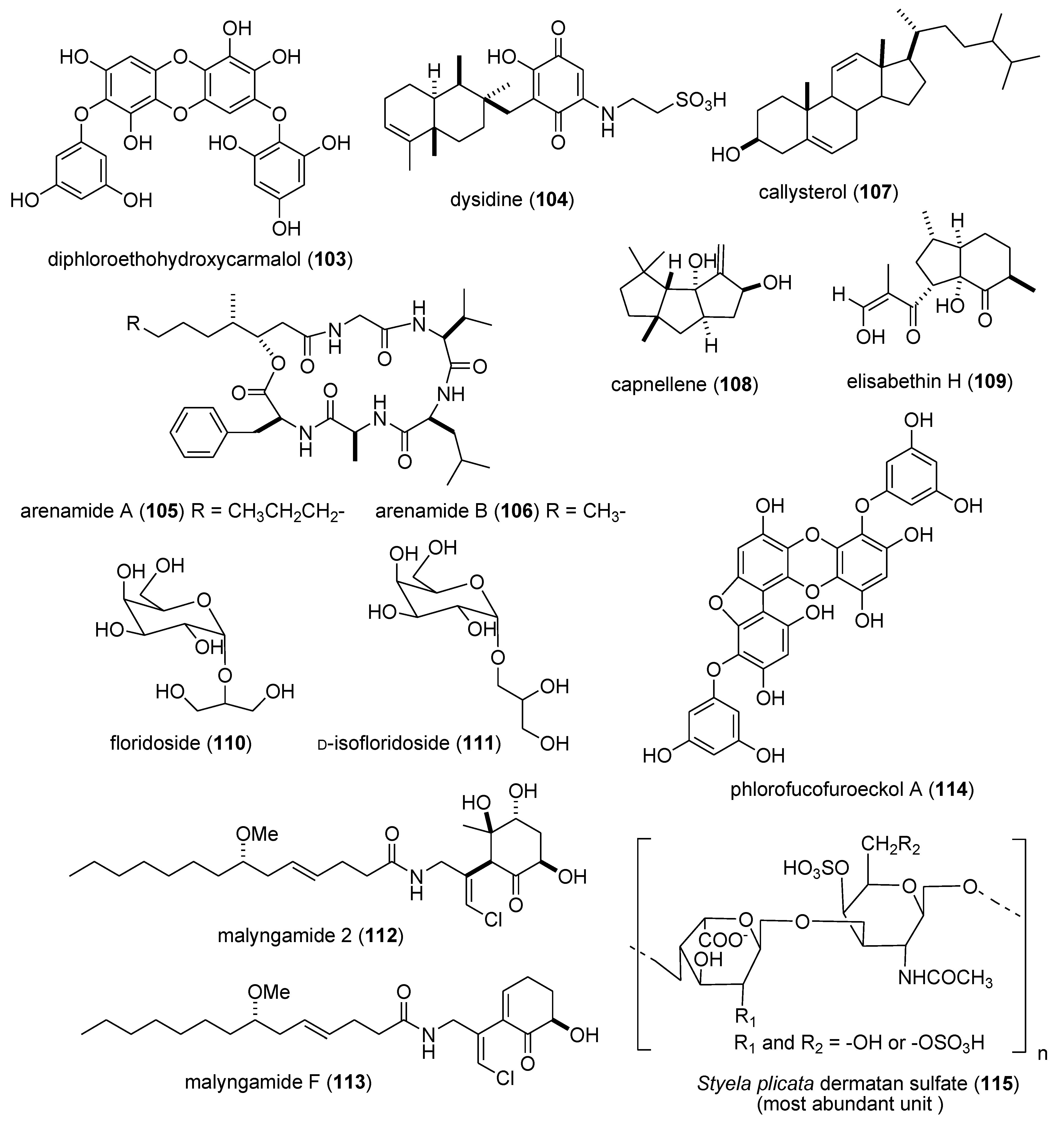
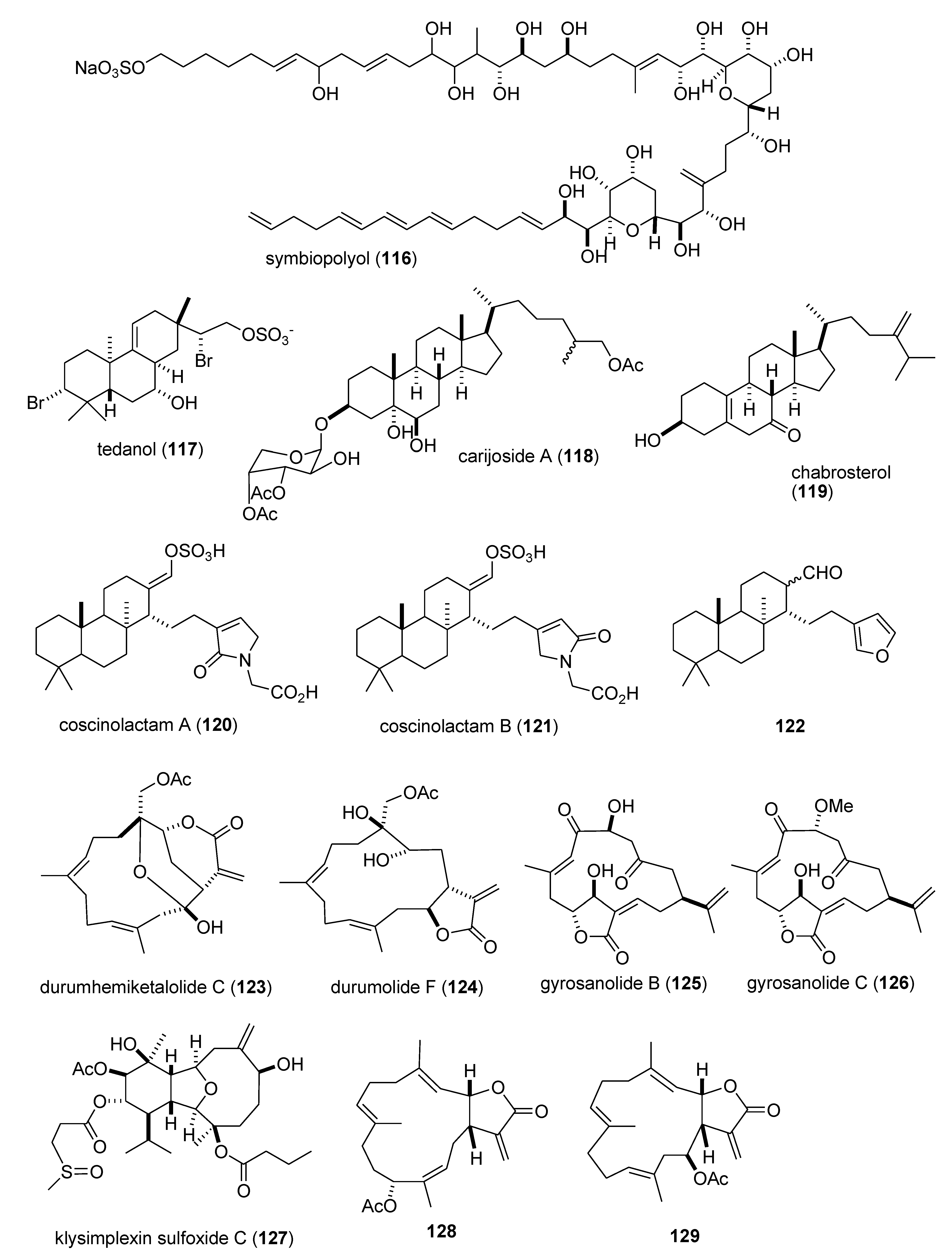
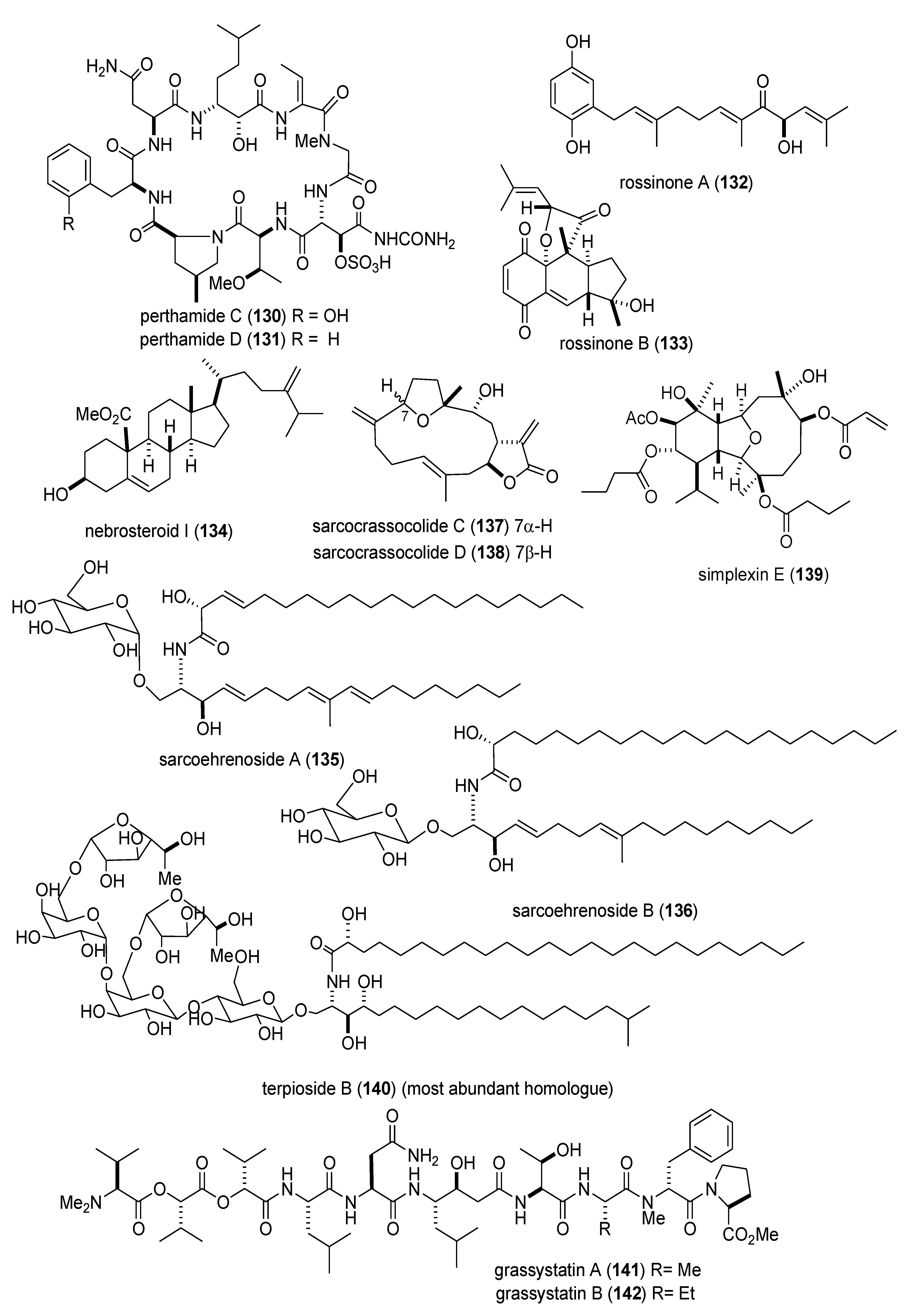
| Antidiabetic | DPHC (103)/alga | Polyketide e | Postprandial hyperglycemia inhibition | 100 mg/kg * | α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibition | S. KOR | [104] |
| Antidiabetic | dysidine (104)/sponge | Terpene f | Insulin signaling and glucose uptake | 6.7 μM | hPTP1b inhibition | CHN | [105,106] |
| Anti-inflammatory | arenamides A & B (105,106)/bacterium | Peptide g | Modulation of LPS-activated murine macrophages in vitro | 3–10 μM * | Nitric oxide and PGE2 inhibition | USA | [107] |
| Anti-inflammatory | callysterol (107)/sponge | Steroid f | Murine hind paw oedema inhibition | ND | TXB2 inhibition | EGY, NLD, USA | [108] |
| Anti-inflammatory | capnellene (108)/soft coral | Terpene f | In vivo inhibition of microglia activation | 10 mg/kg * | iNOS and COX-2 inhibition | TWN | [109] |
| Anti-inflammatory | elisabethin H (109)/soft coral | Terpene f | Modulation of LPS-activated microglia in vitro | 7.0 μM | TXB2 inhibition | USA | [110] |
| Anti-inflammatory | floridosides (110,111)/alga | Glycolipid | Free-radical oxidative stress inhibition | 22–43 μM * | Myeloperoxidase & MMP inhibition | S.KOR & CHN | [111] |
| Anti-inflammatory | malyngamide 2 (112)/bacterium | PKS/NRPS | LPS-activated macrophage in vitro inhibition | 8.0 μM | NO inhibition | PNG, USA | [112] |
| Anti-inflammatory | malyngamide F (113)/bacterium | PKS/NRPS | Macrophages NO release & iNOS expression inhibition | 7.1 μM | MyD88-dependent pathway inhibition | USA | [113] |
| Anti-inflammatory | PFF-A (114)/alga | Polyketide e | LPS-activated macrophage in vitro inhibition | 4.7 μM | iNOS and COX-2 inhibition | S. KOR | [114] |
| Anti-inflammatory | S. plicata dermatan sulfate (115)/ascidian | Polysaccharide h | Colonic inflammation inhibition | 8 mg/kg * | TNF-α, TGF-β, VEGF inhibition | BRA | [115] |
| Anti-inflammatory | symbiopolyol (116)/dinoflagellate | Polyketide e | Lymphocyte adhesion inhibition | 6.6 μM | VCAM-1 expression inhibition | JPN | [116] |
| Anti-inflammatory | tedanol (117)/sponge | Terpene f | Murine hind paw oedema inhibition | 1 mg/kg * | iNOS, COX-1 and COX-2 inhibition | ITA | [117] |
| Anti-inflammatory | carijoside A (118)/coral | Steroid glycoside f | Neutrophil superoxide and elastase inhibition | 1.8–6.8 μg/mL | Undetermined | TWN | [118] |
| Anti-inflammatory | chabrosterol (119)/soft coral | Steroid f | Macrophage COX-2 & iNOS expression inhibition | 10 μM * | Undetermined | TWN | [119] |
| Anti-inflammatory | coscinolactams (120–122)/sponge | Terpene f | Macrophage PGE2 & nitric oxide inhibition | 10 μM * | Undetermined | ITA, ESP, FRA | [120] |
| Anti-inflammatory | durumhemiketalolide C (123)/soft coral | Terpene f | Macrophage COX-2 & iNOS expression inhibition | 10 μM * | Undetermined | TWN | [121] |
| Anti-inflammatory | durumolide F (124)/soft coral | Terpene f | Macrophage COX-2 & iNOS expression inhibition | 10 μM * | Undetermined | TWN | [122] |
| Anti-inflammatory | gyrosanolides B & C (125,126)/soft coral | Terpene f | Macrophage iNOS expression inhibition | 10 μM * | Undetermined | TWN | [123] |
| Anti-inflammatory | klysimplexin sulfoxide (127) soft coral | Terpene f | Macrophage COX-2 & iNOS expression inhibition | 10 μM * | Undetermined | TWN | [124] |
| Anti-inflammatory | L. crassum diterpenes (128,129)/soft coral | Terpene f | Macrophage NO release & iNOS expression inhibition | 3.8–4.0 μM | Undetermined | JPN | [125] |
| Anti-inflammatory | perthamides C & D (130,131)/sponge | Peptideg | Murine hind paw oedema inhibition | 0.3 mg/kg * | Undetermined | FRA, ITA | [126] |
| Anti-inflammatory | rossinones A & B(132,133)/ascidian | Terpene f | Neutrophil superoxide inhibition | 0.8–2.5 μM | Undetermined | MYS, NZL | [127] |
| Anti-inflammatory | nebrosteroid I (134)/soft coral | Steroid f | Macrophage iNOS expression inhibition | 10 μM * | Undetermined | TWN | [128] |
| Anti-inflammatory | sarcoehrenosides A & B (135,136)/soft coral | Glycolipid | Macrophage iNOS expression inhibition | 10 μM * | Undetermined | TWN | [129] |
| Anti-inflammatory | sarcocrassocolides A & B(137,138)/soft coral | Terpene f | Macrophage iNOS expression inhibition | 10 μM * | Undetermined | TWN | [130] |
| Anti-inflammatory | simplexin E (139)/soft coral | Terpene f | Macrophage COX-2 & iNOS expression inhibition | 10 μM * | Undetermined | TWN | [131] |
| Anti-inflammatory | terpioside B (140)/sponge | Glycolipid | Macrophage iNOS expression inhibition | <10 μM * | Undetermined | ITA | [132] |
| Immune system | grassystatins A–C (141–143)/bacterium | Peptide g | T cell antigen presentation inhibition | 10 μM * | Cathepsin E, IL-17 and IFN-γ inhibition | USA | [133] |
| Immune system | callyspongidiol (144) & 14,15-dihydrosiphonodiol (145)/sponge | Polyketide e | Dendritic cell activation | 10 μM * | IL-10 and Ag-presenting activity | DEU, JPN | [134] |
| Immune system | PFF-A (114)/alga | Polyketide e | Basophil IgE receptor inhibition | 25 μM * | Ca2+ influx and degranulation inhibition | S. KOR | [135] |
| Immune system | splenocin B (146)/bacterium | PKS/NRPS | Interleukin 5 and 13 Inhibition | 1.6–1.8 nM | Undetermined | USA | [136] |
| Immune system | HCLPS-1 (147)/clam | Polysaccharide h | In vivo & in vitro T and B cell activation | 20 mg/kg * | Undetermined | CHN | [137] |
| Immune system | yessotoxin (148)/alga | Polyketide(polyether) e | Macrophage phagocytosis inhibition | 1 nM * | TNF-α, MIP-1α & MIP-2 inhibition | ITA | [138] |
| Nervous system | calyculin A (149)/sponge | PKS/NRPS e | Hippocampal neuron neurite retraction | 100 mM * | Dependent on actomyosin activation | JPN | [139] |
| Nervous system | C. olemda purine (150)/sponge | Alkaloid g | Convulsion induction | 4 nm/mouse * | GABAergic transmission inhibition | JPN, USA | [140] |
| Nervous system | hoiamide B (151)/bacterium | Peptide g | Neocortical neuron Ca2+ oscillation inhibition | 79.8 nM | Stimulation of sodium influx | ITA, PNG, USA | [141] |
| Nervous system | palmyrolide A (152)/bacterium | Polyketide e | Neocortical neuron Ca2+ oscillation inhibition | 3.7 µM | Sodium influx inhibition | MEX, USA | [142] |
| Nervous system | xyloketal B (153)/fungus | Polyketide e | Ischemia-induced PC12 cell injury inhibition | 100 µM * | Free radical scavenging | CHN | [143] |
| Nervous system | alotamide (154)/bacterium | PKS/NRPS g | Neocortical neuron Ca2+ oscillation stimulation | 4.18 μM | Undetermined | MEX, USA | [144] |
| Nervous system | (−)-dibromophakellin (155)/sponge | Alkaloid g | Α2B adrenoreceptor agonist | 4.2 µM | Undetermined | AUS | [145] |
| Nervous system | dysideamine (156)/sponge | Terpene e | Hippocampal reactive oxygen species inhibition | 10 µM * | Undetermined | IDN, JPN | [146] |
| Nervous system | ircinialactams (157,158)/sponge | Terpene f | α1 & α3 glycine receptor potentiation | 0.5 µM * | Undetermined | AUS | [147] |
| Nervous system | eusynstyelamides B & C (159,160)/ascidian | Peptide g | Neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibition | 4.3–5.8 µM | Undetermined | AUS | [148] |
| Nervous system | nanolobatolide (161)/soft coral | Terpene f | 6-hydroxy-dopamine neurotoxicity inhibition | 0.1 µM * | Undetermined | TWN | [149] |
| Nervous system | pulicatin A (162)/bacterium | Alkaloid g | Human serotonin 5-HT2B binding | 505 nM ** | Undetermined | PHL, USA | [150] |
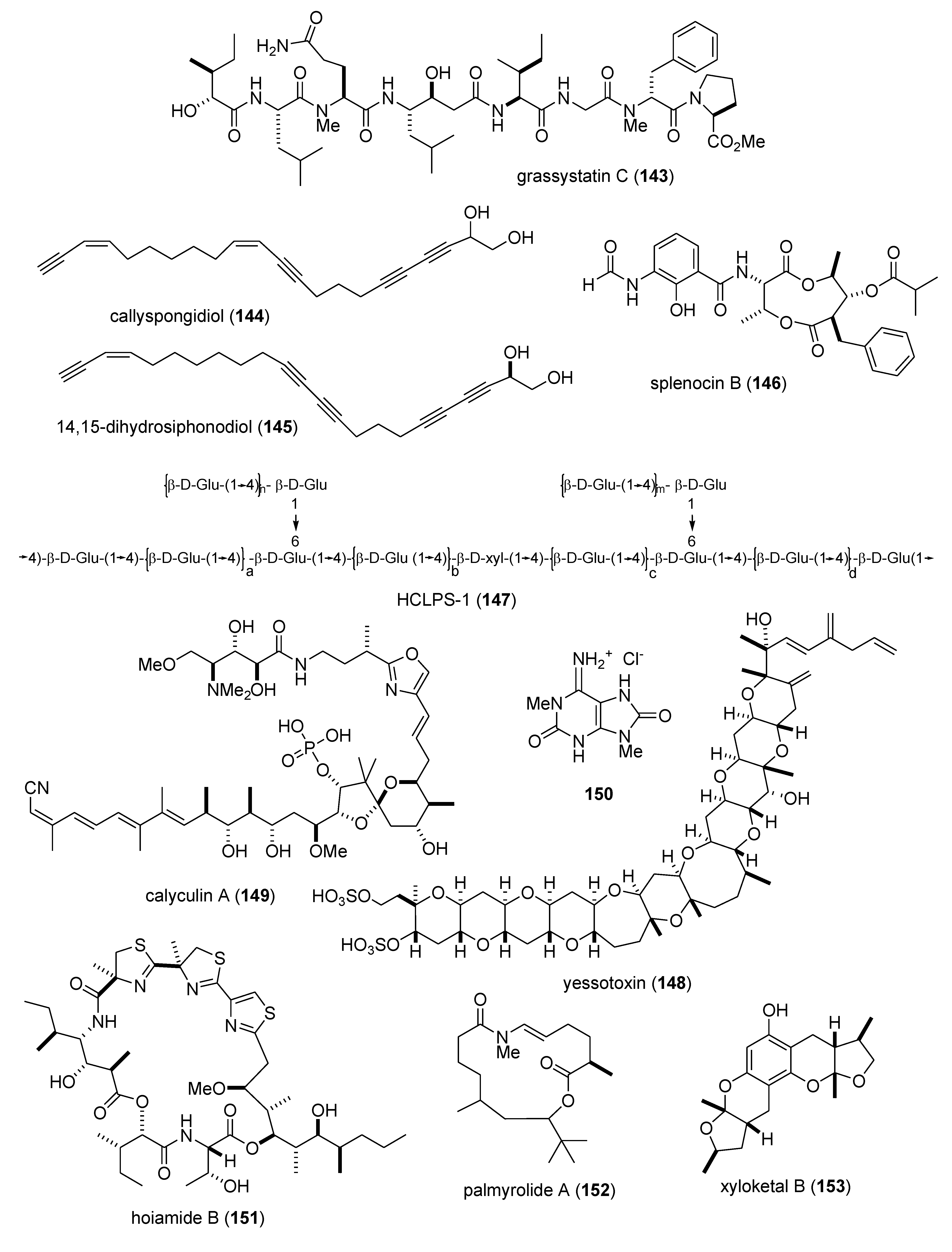
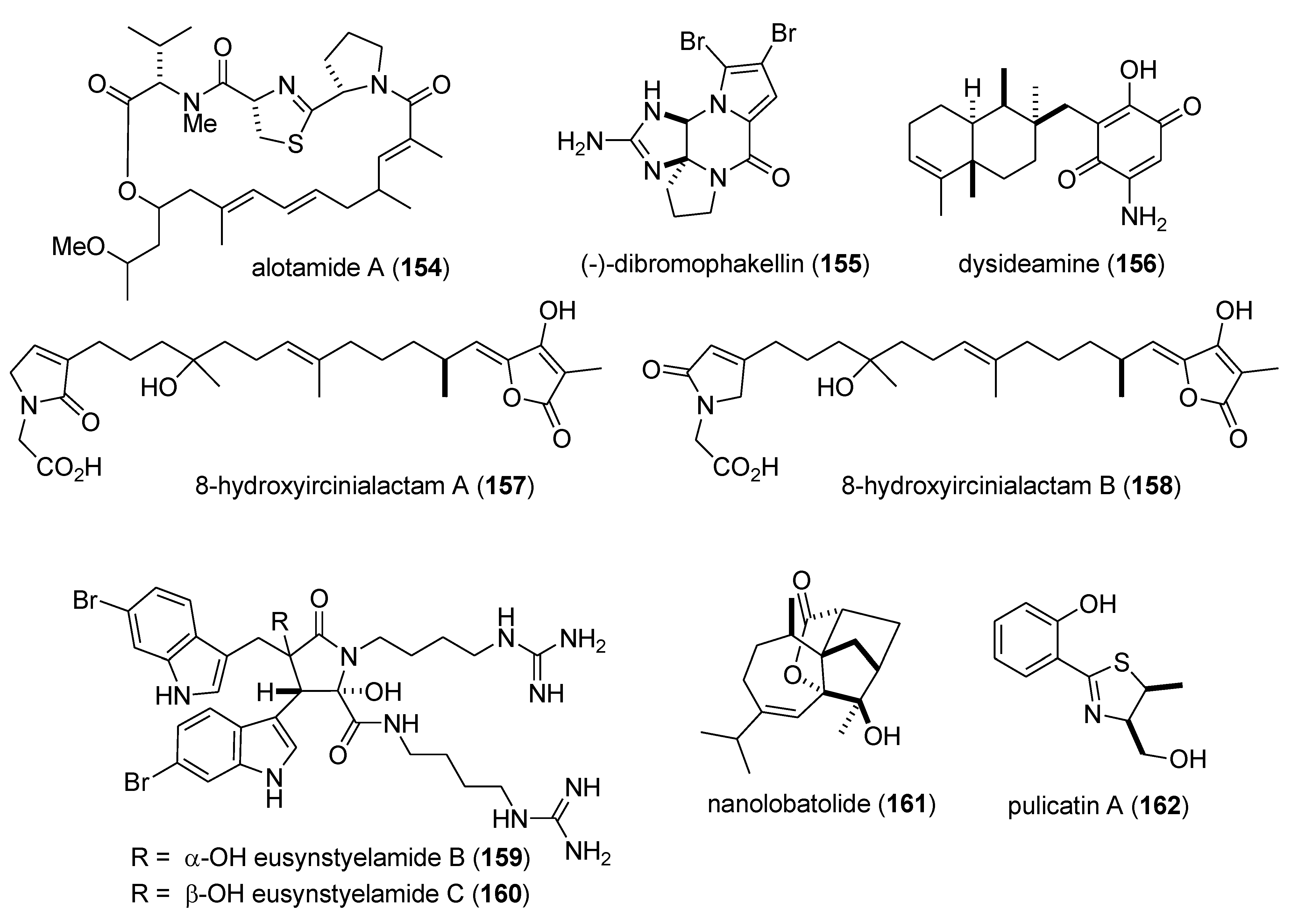
3.1. Antidiabetic Activity
3.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
3.3. Marine Compounds with Activity on the Immune System
3.4. Marine Compounds Affecting the Nervous System
4. Marine Compounds with Miscellaneous Mechanisms of Action
| Compound/Organism a | Chemistry | Pharmacological Activity | IC50 b | MMOA c | Country d | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bisebromoamide (163)/cyanobacterium | Peptide g | In vitro tumor growth inhibition | 0.040 μM | ERK inhibition | JPN | [152] |
| botryllamide I & J (164,165)/ascidian | Shikimate g | Multidrug resistance inhibition | 27–41 μM | ABCG2 transporter inhibition | USA | [153] |
| dysidine (104)/sponge | Terpene f | Insulin pathway activation | 10 μM | Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibition | CHN | [106] |
| E. cava phlorotannins (166,167)/alga | Polyketide e | In vitro antioxidants | DPPH, hydroxyl, peroxyl, & superoxide scavenging | CHN, S. KOR | [154] | |
| fucophlorethols (168,169)/alga | Polyketide e | DPPH radical scavenging | 10–14 μM | Cytochrome P450 CYP1A inhibition | DEU, ISR | [155] |
| GSS (170)/starfish | Peptide g | Oocyte maturation and ovulation | 2 nM | cAMP production | JPN | [156] |
| halichlorine (171)/sponge | Alkaloid (polyketide) g | Inhibition of vascular contractility | 3 μM * | L-type Ca2+ channel inhibition | JPN | [157] |
| hoiamide A (172)/bacterium | Peptide g | Voltage-gated sodium channel activator | 2.3 μM | Sodium channel site 2 activator | USA | [158] |
| hypochromin A & B (173,174)/fungus | Polyketide e | Angiogenesis inhibition | 13 & 50 μM | Tyrosine kinase inhibition | JPN | [159] |
| mycothiazole (175)/sponge | PKS/NRPS | Angiogenesis inhibition | 10 nM * | Mitochondrial complex 1 inhibition | USA | [160] |
| Mycale sp. metabolites (176,177)/sponge | Polyketide e | Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 inhibition | 7.8–8.6 μM | Mitochondrial electron transport chain inhibition | USA | [161] |
| neocomplanines A & B (178,179)/fireworm | Polyketide e | Murine footpad inflammation | ND | PKC activation | JPN | [162] |
| pateamine A (180)/sponge | PKS/NRPS | Nonsense-mediated mRNA inhibition | 100 nM * | Binding to eukaryotic initiation factor 4AIII | DEU, USA | [163] |
| polytheonamide B (181)/sponge | Peptide g | Cytotoxic mammalian channel formation | 14–29 nM | Selectivity towards Cs + cation | JPN | [164] |
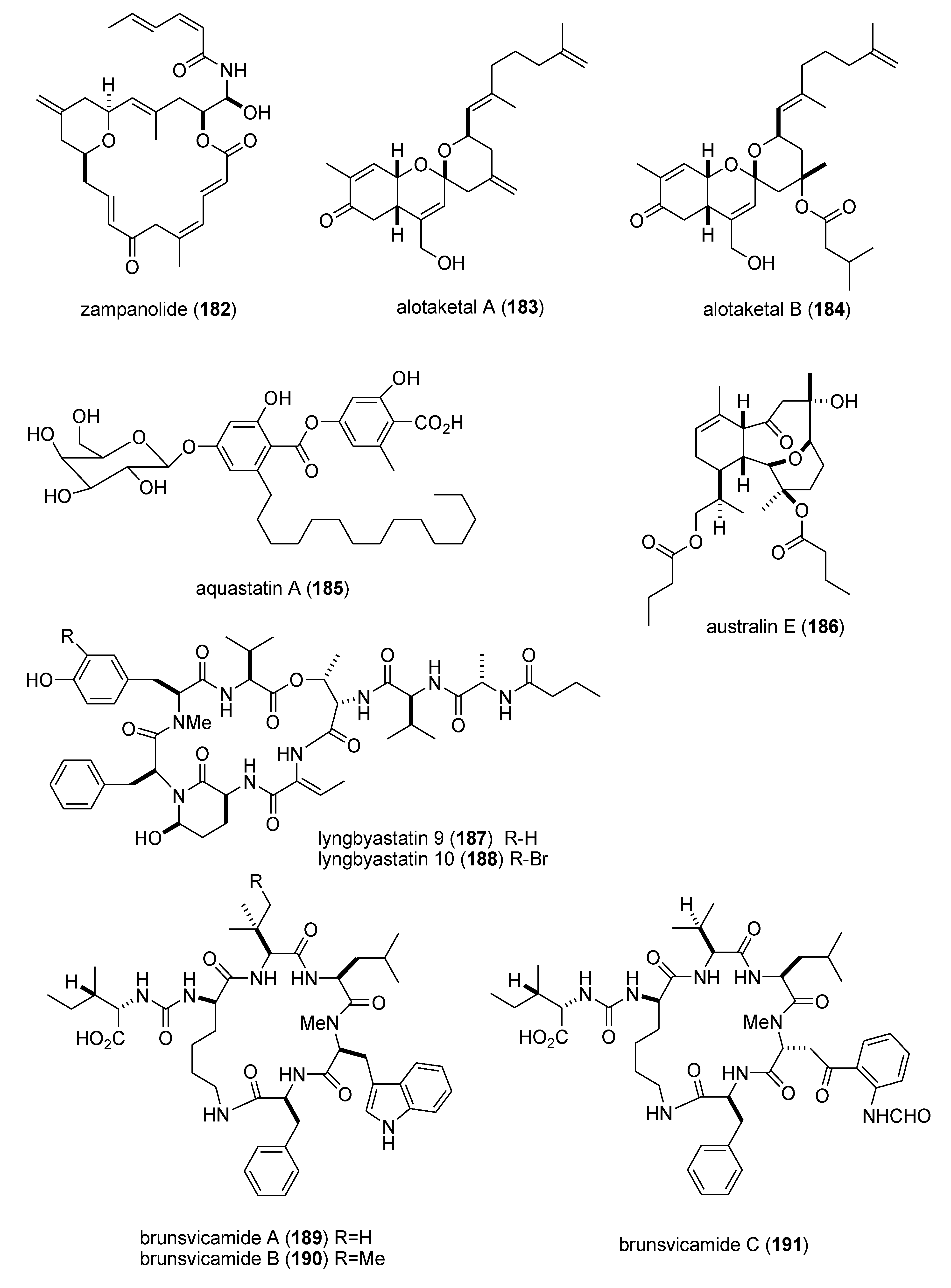
| zampanolide (182)/sponge | Polyketide e | G2/M cell cycle arrest | 8 nM * | Microtubule bundle formation by tubulin polymerization | NZL | [165] |
| alotaketals A & B (183,184)/sponge | Terpene f | cAMP cell signaling activation | 18 & 240 nM | Undetermined | CAN, NLD, PAP | [166] |
| aquastatin (185)/fungus | Polyketide e | Protein phosphatase 1B inhibition | 0.19 μM | Undetermined | S. KOR | [167] |
| australin E (186)/soft coral | Terpene f | Inositol 5-phosphatase SHIP1 activation | >100 μM | Undetermined | CAN | [168] |
| lyngbyastatins 9 & 10 (187,188)/bacterium | Peptide g | Elastase and chymotrypsin inhibition | 0.2–9.3 μM | Undetermined | USA | [169] * |
| brunsvicamides A–C (189–191)/bacterium | Peptide g | Elastase inhibition | 2.0–4.4 μM | Undetermined | DEU | [170] |
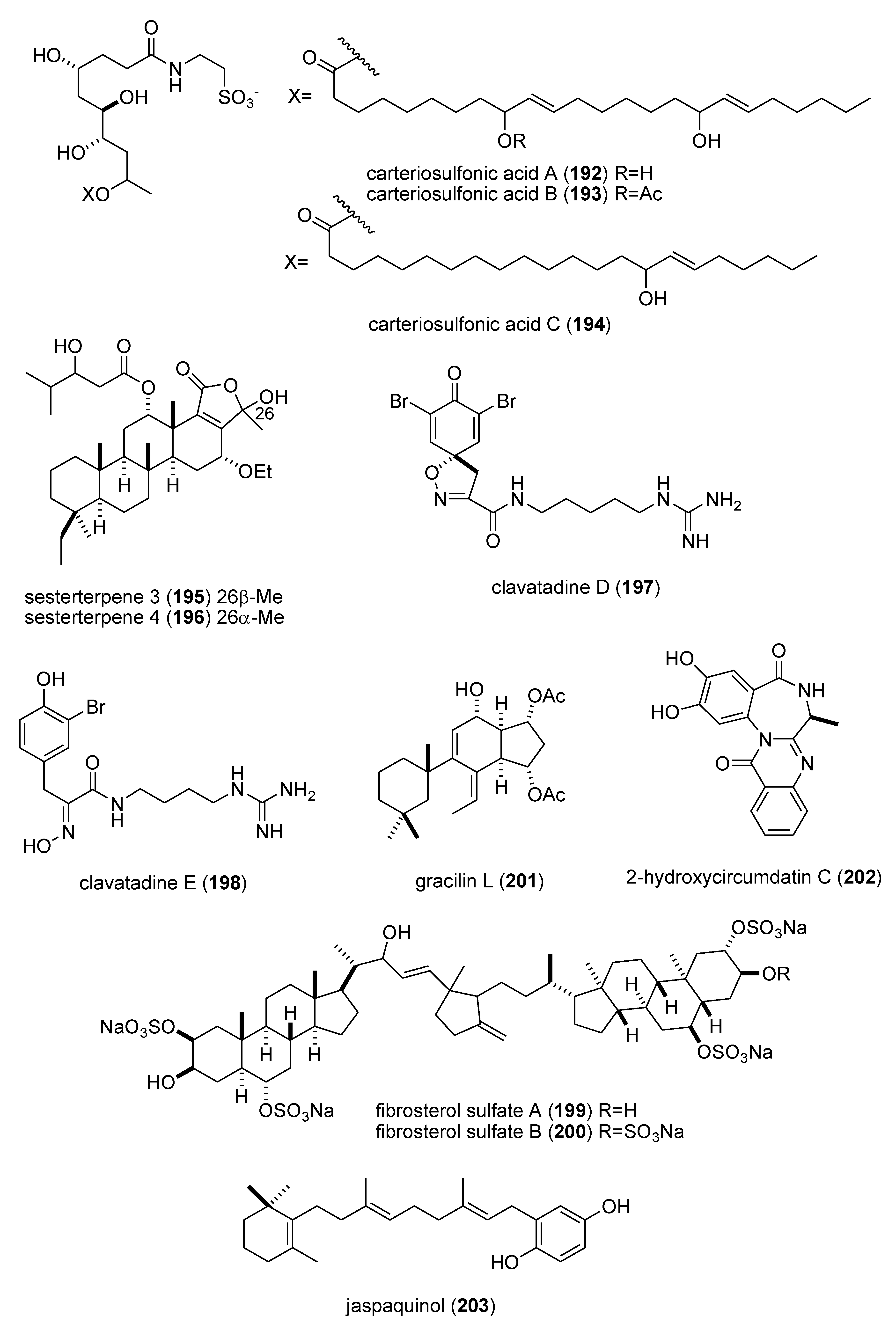
| carteriosulfonic acids A, B & C (192–194)/sponge | Polyketide e | GSK-3β inhibition | 6.8–12.5 µM | Undetermined | SGP, USA | [171] |
| Carteriospongia foliascens sesterterpenoids (195,196)/sponge | Terpene f | Human Ras-converting enzyme inhibition | 4.2 μg/mL * | Undetermined | CAN, IDN,NLD, USA | [172] |
| clavatadines D & E (197,198)/sponge | Shikimate g | Factor XIa inhibition | 222 μM * | Undetermined | AUS | [173] |
| fibrosterol sulfates A & B (199,200)/sponge | Terpene f | Protein Kinase Cζ inhibition | 5.6 & 16.4 µM | Undetermined | PHL, USA | [174] |
| gracilin L (201)/sponge | Terpene f | EGF-R tyrosine kinase inhibition | <100 μM * | Undetermined | GBR, LUX | [175] |
| grassystatins A–C (141–143)/bacterium | Peptide g | cathepsin E inhibition | 0.3–43 nM | Undetermined | USA | [133] |
| 2-hydroxycircumdatin C (202)/fungus | Alkaloid g | DPPH radical scavenging activity | 9.9 µM | Undetermined | CHN | [176] |
| jaspaquinol (203)/sponge | Terpene f | 5-lipoxygenase inhibition | 0.45 µM | Undetermined | USA | [177] |
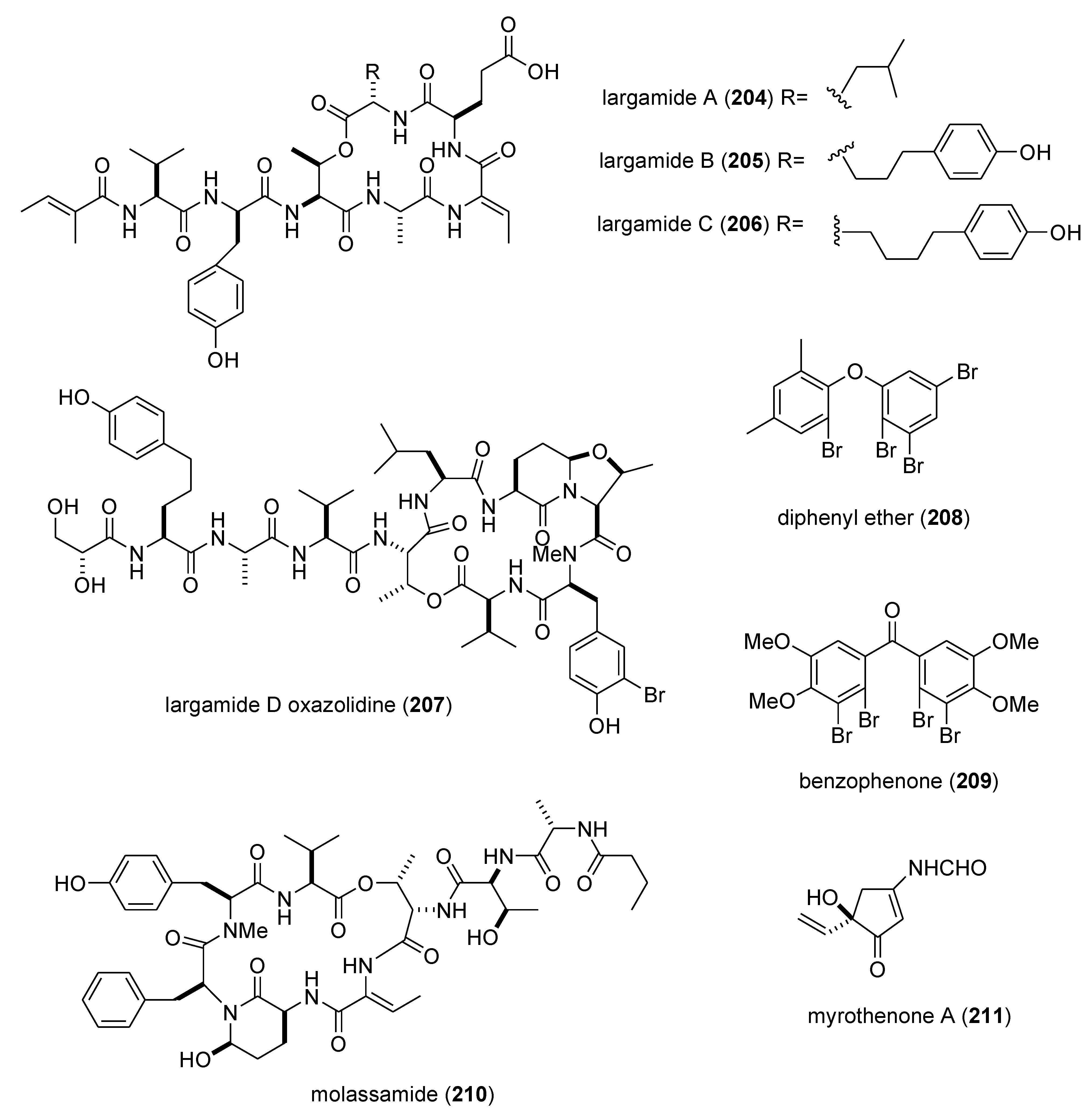
| largamides A–C (204–206)/bacterium | Peptide g | Elastase inhibition | 0.53–1.41 µM | Undetermined | USA | [178] |
| largamide D oxazolidine (207)/bacterium | Peptide g | Elastase and chymotrypsin inhibition | 0.9–1.5 μM | Undetermined | USA | [179] |
| Laurencia similis brominated metabolites (208,209)/alga | Polyketide e | Protein phosphatase 1B inhibition | 2.7–3 μM | Undetermined | CAN, CHN | [180] |
| molassamide (210)/bacterium | Peptide g | Elastase and chymotrypsin inhibition | 0.03 & 0.23 μM | Undetermined | USA | [181] |
| myrothenone A (211)/fungus | Polyketide e | Tyrosinase inhibition | 6.6 μM | Undetermined | S. KOR | [182] |
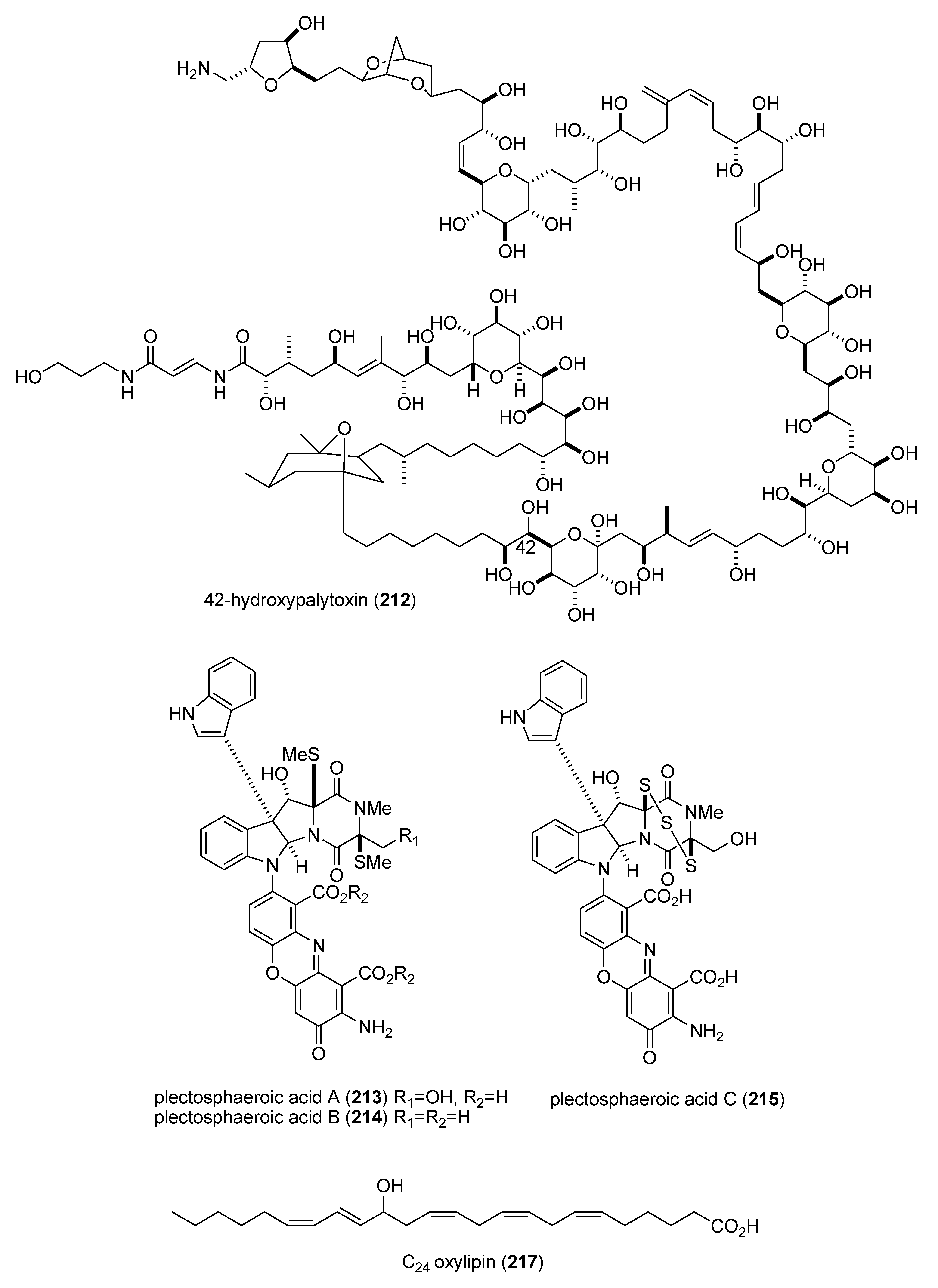
| 42-hydroxy-palytoxin (212)/soft coral | PKS/NRPS | Na+/K+ pump inhibition | 28 ± 7 nM | Undetermined | ITA, USA | [183] |
| plectosphaeroic acids A–C (213–215)/fungus | Alkaloid g | Indoleamine 2, 3 dioxygenase inhibtion | 2 μM * | Undetermined | CAN | [184] |
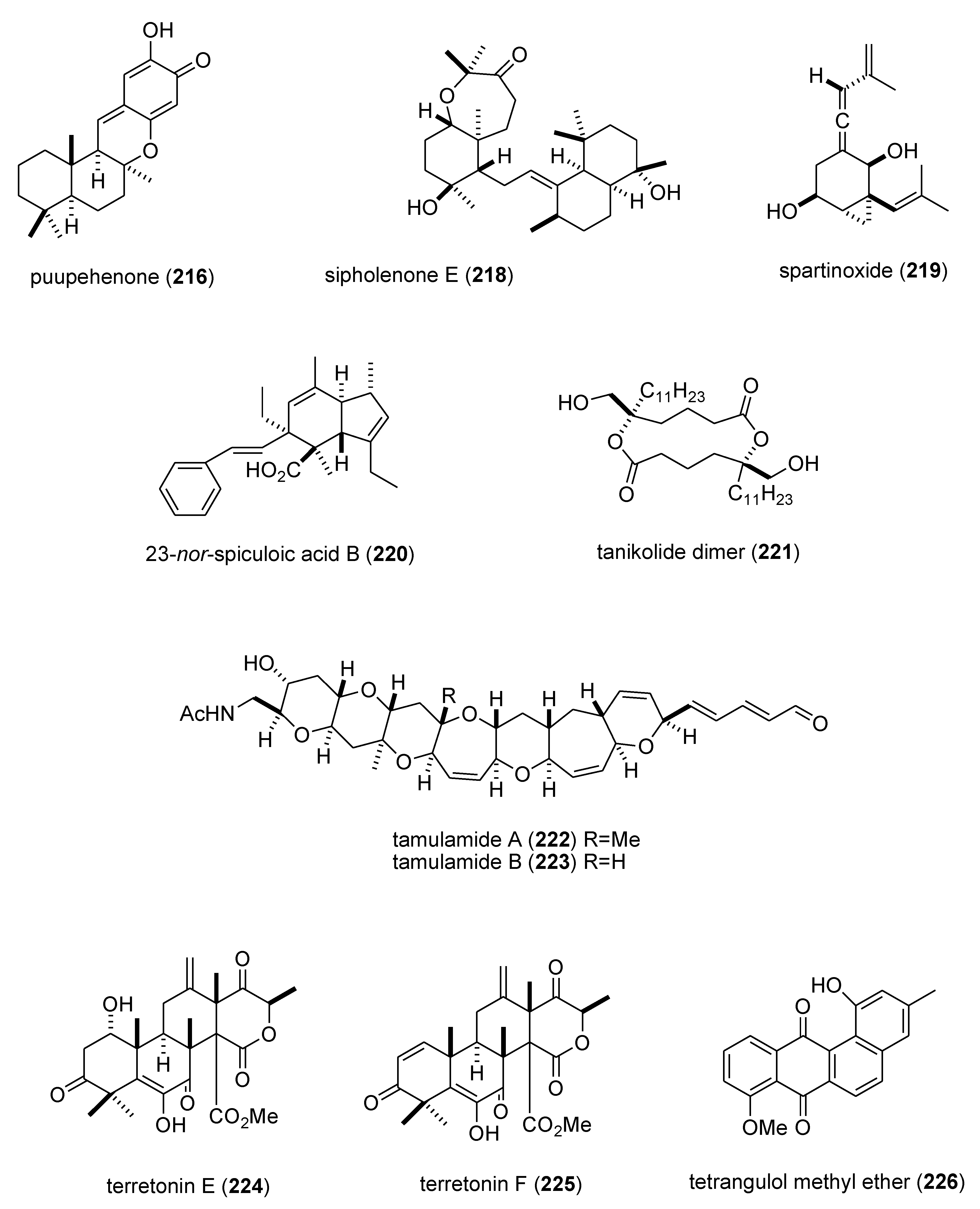
| puupehenone (216)/sponge | Terpene f | 5-lipoxygenase inhibition | 0.68 μM | Undetermined | USA | [177] |
| Sinularia numerosa oxylipin (217)/soft coral | Fatty acid e | Angiogenesis inhibition | 20–40 μM | Undetermined | JPN | [185] |
| sipholenone E (218)/sponge | Terpene f | P-glycoprotein multidrug resistance reversal | 5.7–62 nM | Undetermined | EGY, CHN, USA | [186] |
| spartinoxide (219)/fungus | Terpene f | Human elastase inhibition | 6.5 μM | Undetermined | DEU | [187] |
| 23-nor-spiculoic acid B (220)/sponge | Polyketide e | NFκB inhibition | 0.47 μM | Undetermined | VEN, USA | [188] |
| tanikolide dimer (221)/bacterium | Polyketide e | Human sirtuin type 2 inhibition | 0.176–2.4 μM | Undetermined | DEU, S. KOR, USA | [189] |
| tamulamide A & B (222,223)/dinoflagellate | Polyketide(polyether) e | Brevetoxin-3 binding inhibition | 0.2–2.5 μM | Undetermined | USA | [190] |
| terretonins E & F (224,225)/fungus | Terpene f | NADH oxidase inhibition | 2.9–3.9 μM | Undetermined | ESP, ITA | [191] |
| tetrangulol methyl ether (226)/bacterium | Polyketide e | Quinone reductase-2 inhibition | 0.16 μM | Undetermined | USA | [192] |
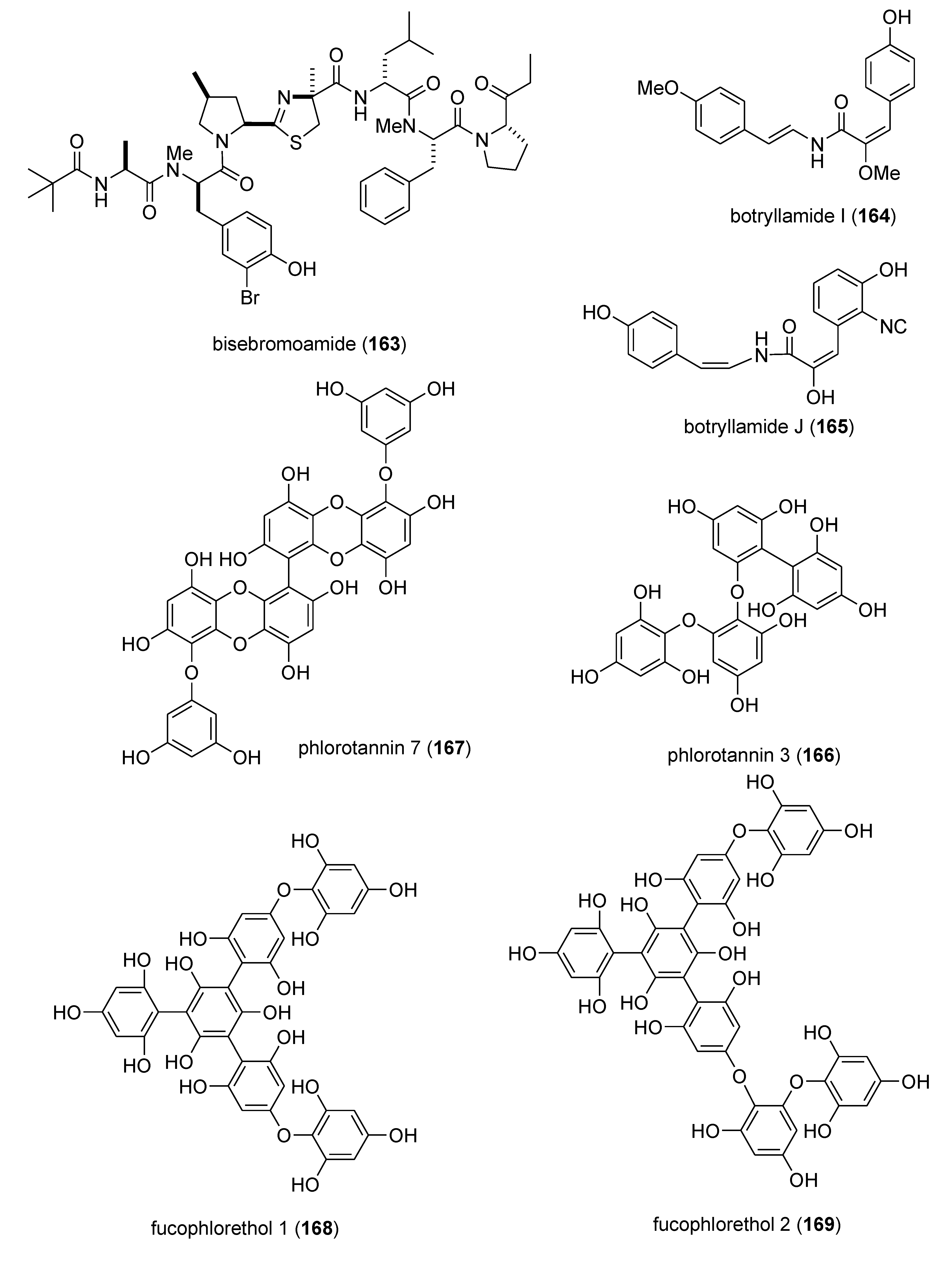
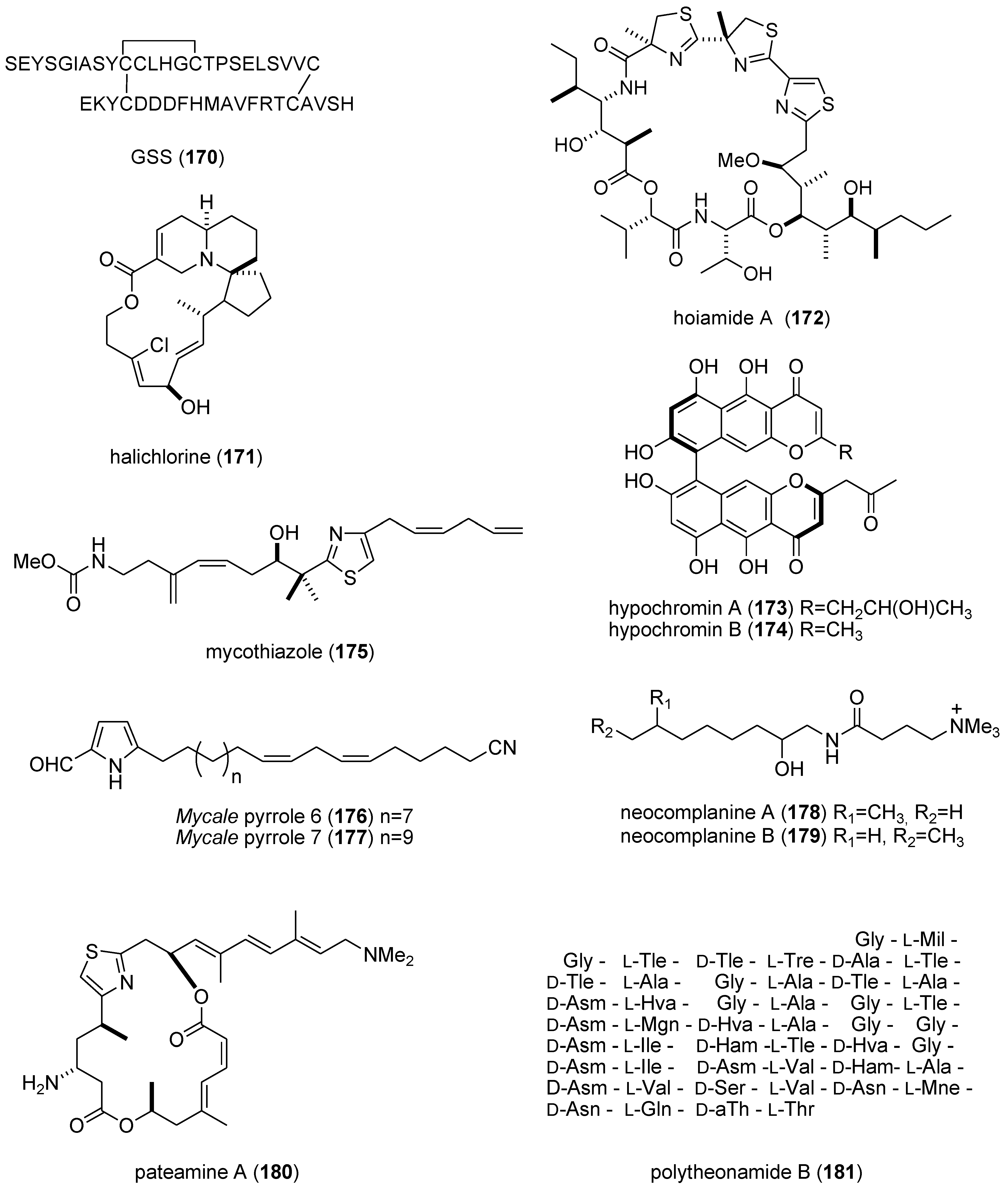
5. Reviews on Marine Pharmacology
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Lehmann, V.K.B. Marine pharmacology in 1998: Marine compounds with antibacterial, anticoagulant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, anthelmintic, antiplatelet, antiprotozoal, and antiviral activities; with actions on the cardiovascular, endocrine, immune, and nervous systems; and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Pharmacologist 2000, 42, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Hamann, M.T. Marine pharmacology in 1999: Compounds with antibacterial, anticoagulant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, anthelmintic, anti-inflammatory, antiplatelet, antiprotozoal and antiviral activities; Affecting the cardiovascular, endocrine, immune, and nervous systems; and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 2002, 132, 315–339. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Hamann, M.T. Marine pharmacology in 2000: Marine compounds with antibacterial, anticoagulant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antiplatelet, antituberculosis, and antiviral activities; Affecting the cardiovascular, immune, and nervous systems and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Mar. Biotechnol. 2004, 6, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Berlinck, R.G.; Hamann, M.T. Marine pharmacology in 2003–4: Marine compounds with anthelmintic, antibacterial, anticoagulant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antiplatelet, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis, and antiviral activities; Affecting the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 2007, 145, 553–581. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Hamann, M.T. Marine pharmacology in 2001–2002: Marine compounds with anthelmintic, antibacterial, anticoagulant, antidiabetic, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antiplatelet, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis, and antiviral activities; Affecting the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 2005, 140, 265–286. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Berlinck, R.G.; Hamann, M.T. Marine pharmacology in 2005–6: Marine compounds with anthelmintic, antibacterial, anticoagulant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis, and antiviral activities; Affecting the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 283–308. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Berlinck, R.G.; Fusetani, N. Marine pharmacology in 2007–8: Marine compounds with antibacterial, anticoagulant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis, and antiviral activities; Affecting the immune and nervous system, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 2011, 153, 191–222. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz, F.J.; Bowden, B.F.; Toth, S.I. Antitumor and Cytotoxic Compounds from Marine Organisms; Attaway, D.H., Zaborsky, O.R., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Schillaci, D.; Arizza, V.; Parrinello, N.; DiStefano, V.; Fanara, S.; Muccilli, V.; Cunsolo, V.; Haagensen, J.J.; Molin, S. Antimicrobial and antistaphylococcal biofilm activity from the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbois, A.P.; Mearns-Spragg, A.; Smith, V.J. A fatty acid from the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum is antibacterial against diverse bacteria including multi-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Mar. Biotechnol. 2009, 11, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.S.; Fidelis, G.P.; Cordeiro, S.L.; Oliveira, R.M.; Sabry, D.A.; Camara, R.B.; Nobre, L.T.; Costa, M.S.; Almeida-Lima, J.; Farias, E.H.; et al. Biological activities of sulfated polysaccharides from tropical seaweeds. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2010, 64, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qi, X.; Sun, H.; Chen, Y.; Guo, S. Chemical characteristic and anticoagulant activity of the sulfated polysaccharide isolated from Monostroma latissimum (Chlorophyta). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2009, 44, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Kahla-Nakbi, A.; Haouas, N.; El, O.A.; Guerbej, H.; Ben, M.K.; Babba, H. Screening of antileishmanial activity from marine sponge extracts collected off the tunisian coast. Parasitol. Res. 2010, 106, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, V.; Srivastava, S.; Kumar, M.S.; Misra, S.; Verma, M.; Misra-Bhattacharya, S. In vitro and in vivo antifilarial potential of marine sponge, Haliclona exigua (Kirkpatrick), against human lymphatic filarial parasite brugia malayi: Antifilarial activity of H. exigua. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 105, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, E.A.; Falshaw, R.; Carnachan, S.M.; Kern, E.R.; Prichard, M.N. Virucidal activity of polysaccharide extracts from four algal species against herpes simplex virus. Antiviral Res. 2009, 83, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, Z.M.; Lahaye, E.; Defer, D.; Douzenel, P.; Perrin, B.; Bourgougnon, N.; Sire, O. Isolation of a sulphated polysaccharide from a recently discovered sponge species (Celtodoryx girardae) and determination of its anti-herpetic activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2009, 44, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellai, A.; Laroche-Clary, A.; Mhadhebi, L.; Robert, J.; Bouraoui, A. Anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative activities of crude extract and its fractions of the defensive secretion from the mediterranean sponge. Spongia officinalis. Drug Dev. Res. 2010, 71, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.K.; Choi, I.; Oh, S.; Park, S.G.; Seo, S.K.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, D.S.; Heo, S.J.; Jeon, Y.J.; Je, J.Y.; et al. Anti-asthmatic effect of marine red alga (Laurencia undulata) polyphenolic extracts in a murine model of asthma. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.M.; Rajapakse, N.; Kim, S.K. Anti-inflammatory effect of Ishige okamurae ethanolic extract via Inhibition of NF-kappaB transcription factor in RAW 264. 7 cells. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Frota, M.L.J.; Braganhol, E.; Canedo, A.D.; Klamt, F.; Apel, M.A.; Mothes, B.; Lerner, C.; Battastini, A.M.; Henriques, A.T.; Moreira, J.C. Extracts of marine sponge Polymastia janeirensis induce oxidative cell death through a caspase-9 apoptotic pathway in human U138MG glioma cell line. Investig. New Drugs 2009, 27, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappo, M.; Berkov, S.; Massucco, C.; Di Maria, V.; Bastida, J.; Codina, C.; Avila, C.; Messina, P.; Zupo, V.; Zupo, S. Apoptotic activity of the marine diatom Cocconeis scutellum and eicosapentaenoic acid in BT20 cells. Pharm. Biol. 2011, 50, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Grunewald, N.; Alban, S. Optimized and standardized isolation and structural characterization of anti-inflammatory sulfated polysaccharides from the red alga Delesseria sanguinea (Hudson) lamouroux (ceramiales, delesseriaceae). Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 2998–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Je, J.Y.; Ahn, C.B.; Oh, M.J.; Kang, S.Y. Antioxidant activity of a red seaweed Polysiphonia morrowii extract. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 18, 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini-Filho, J.; Novoa, A.V.; Gonzalez, A.E.; de Andrade-Wartha, E.R.; de O e Silva, A.M.; Pinto, J.R.; Mancini, D.A. Free phenolic acids from the seaweed Halimeda monile with antioxidant effect protecting against liver injury. Z. Naturforsch. C 2009, 64, 657–663. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.H.; Mao, W.J.; Chen, Y.; Guo, S.D.; Li, H.Y.; Qi, X.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Xu, J. Isolation, chemical characteristics and antioxidant properties of the polysaccharides from marine fungus Penicillium sp. F23-2. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 78, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Shi, X.; Song, H.; Zhang, J. In vitro antioxidant activities of acetylated, phosphorylated derivatives of porphyran extracted from Porphyra haitanensis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 78, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badiu, D.L.; Luque, R.; Dumitrescu, E.; Craciun, A.; Dinca, D. Amino acids from Mytilus galloprovincialis (L.) and Rapana venosa molluscs accelerate skin wounds healing via enhancement of dermal and epidermal neoformation. Protein J. 2010, 29, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganthy, N.; Karutha, P.S.; Pandima, D.K. Neuroprotective effect of seaweeds inhabiting south indian coastal area (hare island, gulf of mannar marine biosphere reserve): Cholinesterase inhibitory effect of Hypnea valentiae and Ulva reticulata. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 468, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, A.; Keffer, J.L.; Bifulco, G.; Lloyd, J.R.; Bewley, C.A. Chrysophaentins A–H, antibacterial bisdiarylbutene macrocycles that inhibit the bacterial cell division protein FtsZ. J. Am. Chem Soc. 2010, 132, 9069–9077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teasdale, M.E.; Liu, J.; Wallace, J.; Akhlaghi, F.; Rowley, D.C. Secondary metabolites produced by the marine bacterium Halobacillus salinus that inhibit quorum sensing-controlled phenotypes in gram-negative bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 567–572. [Google Scholar]
- Kwan, J.C.; Meickle, T.; Ladwa, D.; Teplitski, M.; Paul, V.; Luesch, H. Lyngbyoic acid, a “Tagged” fatty acid from a marine cyanobacterium, disrupts quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Biosyst. 2011, 7, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.E.; Na, Z.; Jung, M.; Lee, H.S.; Sim, C.J.; Nahm, K.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J. Discorhabdins from the Korean marine sponge Sceptrella sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertiani, T.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Ortlepp, S.; van Soest, R.W.; de Voogd, N.J.; Wray, V.; Hentschel, U.; Kozytska, S.; Muller, W.E.; Proksch, P. From anti-fouling to biofilm inhibition: New cytotoxic secondary metabolites from two indonesian Agelas sponges. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 1297–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zereini, W.; Fotso Fondja Yao, C.B.; Laatsch, H.; Anke, H. Aqabamycins A–G: Novel nitro maleimides from a marine Vibrio species. I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation and biological activities. J. Antibiot. 2010, 63, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, G.R.; Knight, J.C.; Herald, D.L.; Pettit, R.K.; Hogan, F.; Mukku, V.J.; Hamblin, J.S.; Dodson, M.J.; Chapuis, J.C. Antineoplastic agents. 570. Isolation and structure elucidation of bacillistatins 1 and 2 from a marine Bacillus silvestris. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, A.L.; Stout, E.P.; Lin, A.S.; Prudhomme, J.; Le, R.K.; Fairchild, C.R.; Franzblau, S.G.; Hay, M.E.; Aalbersberg, W.; Kubanek, J. Antimalarial bromophycolides J–Q from the fijian red alga Callophycus serratus. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 2736–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmann, C.; Schneider, K.; Bruntner, C.; Irran, E.; Nicholson, G.; Bull, A.T.; Jones, A.L.; Brown, R.; Stach, J.E.; Goodfellow, M.; et al. Caboxamycin, a new antibiotic of the benzoxazole family produced by the deep-sea strain Streptomyces sp. NTK 937. J. Antibiot. 2009, 62, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Engene, N.; Smith, J.E.; Preskitt, L.B.; Gerwick, W.H. Crossbyanols A–D, toxic brominated polyphenyl ethers from the hawai’ian bloom-forming cyanobacterium Leptolyngbya crossbyana. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontemps, N.; Bry, D.; Lopez-Legentil, S.; Simon-Levert, A.; Long, C.; Banaigs, B. Structures and antimicrobial activities of pyridoacridine alkaloids isolated from different chromotypes of the ascidian Cystodytes dellechiajei. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.D.; McCluskey, A.; Robertson, M.J.; MacGregor, K.A.; Gordon, C.P.; Guenther, J. Anti-malarial, anti-algal, anti-tubercular, anti-bacterial, anti-photosynthetic, and anti-fouling activity of diterpene isonitriles from the tropical marine sponge Cymbastela hooperi. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, M.; Tabudravu, J.N.; Jaspars, M.; Strom, M.B.; Hansen, E.; Andersen, J.H.; Kristiansen, P.E.; Haug, T. The antibacterial ent-eusynstyelamide B and eusynstyelamides D, E, and F from the arctic bryozoan Tegella cf. spitzbergensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tello, E.; Castellanos, L.; Arevalo-Ferro, C.; Duque, C. Cembranoid diterpenes from the caribbean sea whip Eunicea knighti. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isnansetyo, A.; Kamei, Y. Anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) activity of MC21-B, an antibacterial compound produced by the marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas phenolica O-BC30T. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 34, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keffer, J.L.; Plaza, A.; Bewley, C.A. Motualevic acids A–F, antimicrobial Acids from the Sponge Siliquariaspongia sp. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 1087–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, K.; Degnes, K.F.; Kemmler, M.; Bredholt, H.; Fjaervik, E.; Klinkenberg, G.; Sletta, H.; Ellingsen, T.E.; Zotchev, S.B. Production of a new thiopeptide antibiotic, TP-1161, by a marine Nocardiopsis Species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4969–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, E.P.; Hasemeyer, A.P.; Lane, A.L.; Davenport, T.M.; Engel, S.; Hay, M.E.; Fairchild, C.R.; Prudhomme, J.; Le, R.K.; Aalbersberg, W.; et al. Antibacterial neurymenolides from the fijian red alga Neurymenia fraxinifolia. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feher, D.; Barlow, R.; McAtee, J.; Hemscheidt, T.K. Highly brominated antimicrobial metabolites from a marine Pseudoalteromonas sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1963–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, H.; Aristizabal, F.; Duque, C.; Kerr, R. Cytotoxic and antimicrobial activity of pseudopterosins and seco-Pseudopterosins isolated from the octocoral Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae of san andres and providencia islands (Southwest Caribbean Sea). Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Till, M.; Prinsep, M.R. 5-Bromo-8-methoxy-1-methyl-β-carboline, an alkaloid from the New Zealand marine bryozoan Pterocella vesiculosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 796–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, S.; Adachi, K.; Matsuo, Y.; Nukina, M.; Shizuri, Y. Salinisporamycin, a novel metabolite from Salinispora arenicola. J. Antibiot. 2009, 62, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, M.; Strom, M.B.; Svenson, J.; Jaspars, M.; Milne, B.F.; Torfoss, V.; Andersen, J.H.; Hansen, E.; Stensvag, K.; Haug, T. Synoxazolidinones A and B: Novel bioactive alkaloids from the ascidian Synoicum pulmonaria. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 4752–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiGirolamo, J.A.; Li, X.C.; Jacob, M.R.; Clark, A.M.; Ferreira, D. Reversal of fluconazole resistance by sulfated sterols from the marine sponge Topsentia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1524–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, S.; Arita, Y.; Honda, M.; Iwamoto, K.; Matsuyama, A.; Shirai, A.; Kawasaki, H.; Kakeya, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Matsunaga, S.; et al. Marine antifungal theonellamides target 3β-hydroxysterol to activate rho1 signaling. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010, 6, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.R.; Duffy, S.; Avery, V.M. Citronamides A and B, tetrapeptides from the australian sponge Citronia astra. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.H.; Yi, Y.H.; Tang, H.F.; Liu, B.S.; Wang, Z.L.; Sun, G.Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Sun, P. Antifungal triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Bohadschia marmorata. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gendy, M.M.; El-Bondkly, A.M. Production and genetic improvement of a novel antimycotic agent, saadamycin, against dermatophytes and other clinical fungi from endophytic Streptomyces sp. Hedaya 48. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 37, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, A.; Bifulco, G.; Keffer, J.L.; Lloyd, J.R.; Baker, H.L.; Bewley, C.A. Celebesides A-C and theopapuamides B-D, depsipeptides from an indonesian sponge that inhibit HIV-1 entry. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Fattorusso, E.; Romano, A.; Scala, F.; Barone, V.; Cimino, P.; Stendardo, E.; Catalanotti, B.; Persico, M.; Fattorusso, C. Insight into the mechanism of action of plakortins, Simple 1,2-Dioxane antimalarials. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebouvier, N.; Jullian, V.; Desvignes, I.; Maurel, S.; Parenty, A.; Dorin-Semblat, D.; Doerig, C.; Sauvain, M.; Laurent, D. Antiplasmodial activities of homogentisic acid derivative protein kinase inhibitors isolated from a vanuatu marine sponge Pseudoceratina sp. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laville, R.; Thomas, O.P.; Berrue, F.; Marquez, D.; Vacelet, J.; Amade, P. Bioactive guanidine alkaloids from two caribbean marine sponges. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1589–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.S.; Stout, E.P.; Prudhomme, J.; Le, R.K.; Fairchild, C.R.; Franzblau, S.G.; Aalbersberg, W.; Hay, M.E.; Kubanek, J. Bioactive bromophycolides R–U from the Fijian red alga Callophycus serratus. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.A.; Duffy, S.; Avery, V.M.; Camp, D.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Quinn, R.J. (+)-7-bromotrypargine:An antimalarial β-Carboline from the australian marine sponge Ancorina sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 583–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.D.; Lang-Unnasch, N. Diterpene formamides from the tropical marine sponge Cymbastela hooperi and their antimalarial activity in vitro. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Romero, C.; Ortíz, I.; Vicente, J.; Vera, B.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Nam, S.; Jove, R. Bioactive cycloperoxides isolated from the puerto rican sponge Plakortis halichondrioides. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1694–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linington, R.G.; Clark, B.R.; Trimble, E.E.; Almanza, A.; Urena, L.D.; Kyle, D.E.; Gerwick, W.H. Antimalarial peptides from marine cyanobacteria: Isolation and structural elucidation of gallinamide A. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueoka, R.; Nakao, Y.; Kawatsu, S.; Yaegashi, J.; Matsumoto, Y.; Matsunaga, S.; Furihata, K.; van Soest, R.W.; Fusetani, N. Gracilioethers A–C, antimalarial metabolites from the marine sponge Agelas gracilis. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 4203–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanapiromsakul, C.; Plubrukarn, A.; Suwanborirux, K. 8-Isocyanoamphilecta-11(20),15-diene, a new antimalarial isonitrile diterpene from the sponge Ciocalapata sp. Can. J. Chem. 2009, 87, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Puddick, J.; Prinsep, M.R.; Rottmann, M.; Tan, L.T. Lagunamides A and B: Cytotoxic and antimalarial cyclodepsipeptides from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1810–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorusso, C.; Persico, M.; Calcinai, B.; Cerrano, C.; Parapini, S.; Taramelli, D.; Novellino, E.; Romano, A.; Scala, F.; Fattorusso, E.; et al. Manadoperoxides A–D from the indonesian sponge Plakortis cfr. simplex. Further insights on the structure-activity relationships of simple 1,2-dioxane antimalarials. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Kubota, T.; Fromont, J.; Ishiyama, A.; Otoguro, K.; Yamada, H.; Omura, S.; Kobayashi, J. Zamamidine C, 3,4-dihydro-6-hydroxy-10,11-Epoxymanzamine A, and 3,4-Dihydromanzamine J N-oxide, new manzamine alkaloids from sponge Amphimedon sp. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 2313–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Nieves, K.; Rodríguez, A.D. Neopetrosiamine A, biologically active bis-piperidine alkaloid from the caribbean sea sponge Neopetrosia proxima. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 5905–5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Davis, R.A.; Buchanan, M.S.; Duffy, S.; Avery, V.M.; Camp, D.; Quinn, R.J. Antimalarial bromotyrosine derivatives from the australian marine sponge Hyattella sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 985–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, A.O.; Britta, E.A.; Bianco, E.M.; Ueda-Nakamura, T.; Filho, B.P.; Pereira, R.C.; Nakamura, C.V. 4-Acetoxydolastane diterpene from the brazilian brown alga Canistrocarpus cervicornis as antileishmanial agent. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2369–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vik, A.; Proszenyak, A.; Vermeersch, M.; Cos, P.; Maes, L.; Gundersen, L.L. Screening of agelasine D and analogs for inhibitory activity against pathogenic protozoa; Identification of hits for visceral leishmaniasis and chagas disease. Molecules 2009, 14, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, L.M.; Lopez, D.; Vesely, B.A.; Della, T.G.; Gerwick, W.H.; Kyle, D.E.; Linington, R.G. Almiramides A–C: Discovery and development of a new class of leishmaniasis lead compounds. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 4187–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.A.; Sykes, M.; Avery, V.M.; Camp, D.; Quinn, R.J. Convolutamines I and J, antitrypanosomal alkaloids from the bryozoan Amathia tortusa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6615–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, F.; Fattorusso, E.; Menna, M.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Tierney, M.; Kaiser, M.; Tasdemir, D. Bromopyrrole alkaloids as lead compounds against protozoan parasites. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2162–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantillo-Ciau, Z.; Moo-Puc, R.; Quijano, L.; Freile-Pelegrin, Y. The tropical brown alga Lobophora variegata: A source of antiprotozoal compounds. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1292–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, B.K.; Tenney, K.; Ang, K.H.; Abdulla, M.; Arkin, M.; McKerrow, J.H.; Crews, P. The marine sponge Diacarnus bismarckensis as a source of peroxiterpene inhibitors of Trypanosoma brucei, the causative agent of sleeping sickness. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.S.; Mutka, T.; Vesley, B.; Amsler, M.O.; McClintock, J.B.; Amsler, C.D.; Perman, J.A.; Singh, M.P.; Maiese, W.M.; Zaworotko, M.J.; et al. Norselic acids A–E, highly oxidized anti-infective steroids that deter mesograzer predation, from the antarctic sponge Crella sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1842–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regalado, E.L.; Tasdemir, D.; Kaiser, M.; Cachet, N.; Amade, P.; Thomas, O.P. Antiprotozoal steroidal saponins from the marine sponge Pandaros acanthifolium. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1404–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Davis, R.A.; Sykes, M.; Avery, V.M.; Camp, D.; Quinn, R.J. Antitrypanosomal cyclic polyketide peroxides from the australian marine sponge Plakortis sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 716–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel-Elardo, S.M.; Kozytska, S.; Bugni, T.S.; Ireland, C.M.; Moll, H.; Hentschel, U. Anti-parasitic compounds from Streptomyces sp. strains isolated from mediterranean sponges. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, J.; Vera, B.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Rodríguez-Escudero, I.; Raptis, R.G. Euryjanicin A: A new cycloheptapeptide from the caribbean marine sponge Prosuberites laughlini. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 4571–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruksakorn, P.; Arai, M.; Kotoku, N.; Vilcheze, C.; Baughn, A.D.; Moodley, P.; Jacobs, W.R., Jr.; Kobayashi, M. Trichoderins, novel aminolipopeptides from a marine sponge-derived Trichoderma sp., are active against dormant mycobacteria. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3658–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Chuang, C.T.; Wang, S.K.; Wen, Z.H.; Chiou, S.F.; Hsu, C.H.; Dai, C.F.; Duh, C.Y. Antiviral and anti-inflammatory diterpenoids from the soft coral Sinularia gyrosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1184–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Wang, S.K.; Chiou, S.F.; Hsu, C.H.; Dai, C.F.; Chiang, M.Y.; Duh, C.Y. Cembranoids from the octocoral Sarcophyton ehrenbergi. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palem, J.R.; Bedadala, G.R.; El Sayed, K.A.; Hsia, S.C. Manzamine a as a novel inhibitor of herpes simplex virus type-1 replication in cultured corneal cells. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Munch, J.; Goerls, H.; Maier, A.; Fiebig, H.H.; Lin, W.H.; Hertweck, C. Xiamycin, a pentacyclic indolosesquiterpene with selective anti-HIV activity from a bacterial mangrove endophyte. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 6685–6687. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, G.; Li, Z.; Shen, S.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, M.; Bruhn, T.; Bruhn, H.; Morschhauser, J.; Bringmann, G.; et al. Baculiferins A–O, O-Sulfated pyrrole alkaloids with anti-HIV-1 activity, from the chinese marine sponge Iotrochota baculifera. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 5466–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Carbone, M.; Vitale, R.M.; Amodeo, P.; Castelluccio, F.; Sicilia, G.; Mollo, E.; Nappo, M.; Cimino, G.; Guo, Y.W.; et al. Rare casbane diterpenoids from the Hainan soft coral Sinularia depressa. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, K.; Lipton, A.P.; Paulraj, R.; Chakraborty, R.D. Guaiane sesquiterpenes from seaweed Ulva fasciata delile and their antibacterial properties. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 2237–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemami Wangun, H.V.; Wood, A.; Fiorilla, C.; Reed, J.K.; McCarthy, P.J.; Wright, A.E. Gymnochromes E and F, cytotoxic phenanthroperylenequinones from a deep-water crinoid, Holopus rangii. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 712–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondol, M.A.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.A.; Tareq, F.S.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Shin, H.J. Ieodomycins A–D, antimicrobial fatty acids from a marine Bacillus sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1606–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Kondratyuk, T.P.; Tan, G.T.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Chang, L.C. Bioactive sulfated sesterterpene alkaloids and sesterterpene sulfates from the marine sponge Fasciospongia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsebai, M.F.; Kehraus, S.; Lindequist, U.; Sasse, F.; Shaaban, S.; Gutschow, M.; Josten, M.; Sahl, H.G.; König, G.M. Antimicrobial phenalenone derivatives from the marine-derived fungus Coniothyrium cereale. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, P.; Wahidullah, S.; Rodrigues, C.; Souza, L.D. The sponge-associated bacterium Bacillus licheniformis SAB1: A source of antimicrobial compounds. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, Y.; Sueyoshi, M.; Hayashi, K.; Terada, R.; Nozaki, H. The novel anti-Propionibacterium acnes compound, sargafuran, found in the marine brown alga Sargassum macrocarpum. J. Antibiot. 2009, 62, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyrniotopoulos, V.; Vagias, C.; Rahman, M.M.; Gibbons, S.; Roussis, V. Structure and antibacterial activity of brominated diterpenes from the red alga Sphaerococcus coronopifolius. Chem. Biodivers. 2010, 7, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, H.; Kubota, T.; Aoyama, K.; Mikami, Y.; Fromont, J.; Kobayashi, J. Tyrokeradines A and B, new bromotyrosine alkaloids with an imidazolyl-quinolinone moiety from a verongid sponge. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 1337–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Haug, T.; Moe, M.K.; Styrvold, O.B.; Stensvag, K. Centrocins: Isolation and characterization of novel dimeric antimicrobial peptides from the green sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galinier, R.; Roger, E.; Sautiere, P.E.; Aumelas, A.; Banaigs, B.; Mitta, G. Halocyntin and papillosin, two new antimicrobial peptides isolated from hemocytes of the solitary tunicate, Halocynthia papillosa. J. Pept. Sci. 2009, 15, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperstad, S.V.; Haug, T.; Vasskog, T.; Stensvag, K. Hyastatin, a glycine-rich multi-domain antimicrobial peptide isolated from the spider crab (Hyas araneus) hemocytes. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 46, 2604–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.J.; Hwang, J.Y.; Choi, J.I.; Han, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Jeon, Y.J. Diphlorethohydroxycarmalol isolated from Ishige okamurae, a brown alga, a potent α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibitor, alleviates postprandial hyperglycemia in diabetic mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 615, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, X.; Guo, Y.W. A novel sesquiterpene quinone from hainan sponge Dysidea villosa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.W.; Jiang, H.L.; Shen, X. A sesquiterpene quinone, dysidine, from the sponge Dysidea villosa, activates the insulin pathway through inhibition of PTP ases. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2009, 30, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asolkar, R.N.; Freel, K.C.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W.; Kondratyuk, T.P.; Park, E.J.; Pezzuto, J.M. Arenamides A–C, cytotoxic NFκB inhibitors from the marine actinomycete Salinispora arenicola. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 396–402. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, D.T.; Ibrahim, A.K.; Khalifa, S.I.; Mesbah, M.K.; Mayer, A.M.; van Soest, R.W. New anti-inflammatory sterols from the red sea sponges Scalarispongia aqabaensis and Callyspongia siphonella. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Jean, Y.H.; Chen, W.F.; Sung, C.S.; Duh, C.Y.; Huang, S.Y.; Lin, C.S.; Tai, M.H.; Tzeng, S.F.; Wen, Z.H. Capnellene, a natural marine compound derived from soft coral, attenuates chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.P.; Wei, X.; Rodríguez, I.I.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Mayer, A.M.S. New terpenoid constituents of the Southwestern Caribbean sea whip Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae (Bayer) including a unique pentanorditerpene. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 4, 493–502. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.X.; Li, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Qian, Z.J.; Kim, S.K. Inhibitors of oxidation and matrix metalloproteinases, floridoside, and d-isofloridoside from marine red alga Laurencia undulata. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malloy, K.L.; Villa, F.A.; Engene, N.; Matainaho, T.; Gerwick, L.; Gerwick, W.H. Malyngamide 2, an oxidized lipopeptide with nitric oxide inhibiting activity from a papua new guinea marine cyanobacterium. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, F.A.; Lieske, K.; Gerwick, L. Selective MyD88-dependent pathway inhibition by the cyanobacterial natural product malyngamide F acetate. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 629, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.R.; Shin, T.S.; Lee, M.S.; Park, J.Y.; Park, K.E.; Yoon, N.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, J.S.; Jang, B.C.; Byun, D.S.; et al. Isolation and identification of phlorotannins from Ecklonia stolonifera with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 3483–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmiro, C.L.; Castelo-Branco, M.T.; Melim, L.M.; Schanaider, A.; Elia, C.; Madi, K.; Pavao, M.S.; de Souza, H.S. Unfractionated heparin and new heparin analogues from ascidians (chordate-tunicate) ameliorate colitis in rats. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 11267–11278. [Google Scholar]
- Hanif, N.; Ohno, O.; Kitamura, M.; Yamada, K.; Uemura, D. Symbiopolyol, a VCAM-1 inhibitor from a symbiotic dinoflagellate of the jellyfish Mastigias papua. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, V.; Fattorusso, E.; Mangoni, A.; Perinu, C.; Cirino, G.; de Gruttola, G.L.; Roviezzo, F. Tedanol: A potent anti-inflammatory ent-pimarane diterpene from the caribbean sponge Tedania ignis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 7542–7547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Hwang, T.L.; Lin, M.R.; Chen, Y.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Fang, L.S.; Wang, W.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Sung, P.J. Carijoside A, a bioactive sterol glycoside from an octocoral Carijoa sp. (Clavulariidae). Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2014–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Huang, Y.C.; Wen, Z.H.; Chiou, S.F.; Wang, S.K.; Hsu, C.H.; Dai, C.F.; Duh, C.Y. Novel sesquiterpenes and norergosterol from the soft corals Nephthea erecta and Nephthea chabroli. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 802–806. [Google Scholar]
- De Marino, S.; Festa, C.; D’Auria, M.V.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.L.; Petek, S.; Debitus, C.; Andres, R.M.; Terencio, M.C.; Paya, M.; Zampella, A. Coscinolactams A and B: New nitrogen-containing sesterterpenoid from the marine sponge Coscinoderma mathewsi exerting anti-inflammatory Properties. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 2905–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Wen, Z.H.; Wang, S.K.; Chiou, S.F.; Hsu, C.H.; Dai, C.F.; Chiang, M.Y.; Duh, C.Y. Unprecedented hemiketal cembranolides with anti-inflammatory activity from the soft coral Lobophytum durum. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Wen, Z.H.; Wang, S.K.; Chiou, S.F.; Hsu, C.H.; Dai, C.F.; Duh, C.Y. Anti-inflammatory cembranolides from the soft coral Lobophytum durum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 3763–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Chuang, C.T.; Wen, Z.H.; Wang, S.K.; Chiou, S.F.; Hsu, C.H.; Dai, C.F.; Duh, C.Y. Bioactive norditerpenoids from the soft coral Sinularia gyrosa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 3379–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.W.; Chao, C.H.; Su, J.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Sung, P.J.; Sheu, J.H. Anti-inflammatory eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the cultured soft coral Klyxum simplex. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 2363–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanzola, M.; Furuta, T.; Kohno, Y.; Fukumitsu, S.; Yasukochi, S.; Watari, K.; Tanaka, C.; Higuchi, R.; Miyamoto, T. Four new cembrane diterpenes isolated from an okinawan soft coral Lobophytum crassum with inhibitory effects on nitric oxide production. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festa, C.; de Marino, S.; Sepe, V.; Monti, M.C.; Luciano, P.; D’Auria, M.V. Perthamides C and D, two new potent anti-inflammatory cyclopeptides from a solomon lithistid sponge Theonella swinhoei. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 10424–10429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleton, D.R.; Chuen, C.S.; Berridge, M.V.; Webb, V.L.; Copp, B.R. Rossinones A and B, biologically active meroterpenoids from the antarctic ascidian, Aplidium species. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 9195–9198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Huang, Y.C.; Wen, Z.H.; Hsu, C.H.; Wang, S.K.; Dai, C.F.; Duh, C.Y. New 19-oxygenated and 4-methylated steroids from the formosan soft coral Nephthea chabroli. Steroids 2009, 74, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Wen, Z.H.; Chiou, S.F.; Tsai, C.W.; Wang, S.K.; Hsu, C.H.; Dai, C.F.; Chiang, M.Y.; Wang, W.H.; Duh, C.Y. Ceramide and cerebrosides from the octocoral Sarcophyton ehrenbergi. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.Y.; Su, J.H.; Lu, Y.; Wen, Z.H.; Dai, C.F.; Kuo, Y.H.; Sheu, J.H. Cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory cembranoids from the dongsha atoll soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 1936–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.L.; Su, J.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Hsu, C.H.; Chen, B.W.; Dai, C.F.; Kuo, Y.H.; Sheu, J.H. Simplexins A–I, eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the soft coral Klyxum simplex. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 994–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, V.; Fattorusso, E.; Mangoni, A.; Teta, R.; Panza, E.; Ianaro, A. Terpioside B, a difucosyl GSL from the marine sponge Terpios sp. is a potent inhibitor of NO release. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 5310–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, J.C.; Eksioglu, E.A.; Liu, C.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Grassystatins A–C from marine cyanobacteria, potent cathepsin E inhibitors that reduce antigen presentation. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 5732–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, M.; Umeyama, A.; Shoji, N.; Hashimoto, T. Polyacetylenediols regulate the function of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2010, 10, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.Y.; Choi, J.S.; Byun, D.S. Inhibitory effects of phloroglucinol derivatives isolated from Ecklonia stolonifera on FcεRI expression. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 4734–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strangman, W.K.; Kwon, H.C.; Broide, D.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Potent inhibitors of pro-inflammatory cytokine production produced by a marine-derived bacterium. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 2317–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Chemical properties and immunostimulatory activity of a water-soluble polysaccharide from the clam of Hyriopsis cumingii lea. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsi, C.F.; Colombari, B.; Callegari, F.; Todaro, A.M.; Ardizzoni, A.; Rossini, G.P.; Blasi, E.; Peppoloni, S. Yessotoxin inhibits phagocytic activity of macrophages. Toxicon 2010, 55, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inutsuka, A.; Goda, M.; Fujiyoshi, Y. Calyculin A-induced neurite retraction is critically dependent on actomyosin activation but not on polymerization state of microtubules. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 390, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurada, T.; Gill, M.B.; Frausto, S.; Copits, B.; Noguchi, K.; Shimamoto, K.; Swanson, G.T.; Sakai, R. Novel N-methylated 8-oxoisoguanines from pacific sponges with diverse neuroactivities. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 6089–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Pereira, A.R.; Cao, Z.; Shuman, C.F.; Engene, N.; Byrum, T.; Matainaho, T.; Murray, T.F.; Mangoni, A.; Gerwick, W.H. The hoiamides, structurally intriguing neurotoxic lipopeptides from papua new guinea marine cyanobacteria. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1411–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.R.; Cao, Z.; Engene, N.; Soria-Mercado, I.E.; Murray, T.F.; Gerwick, W.H. Palmyrolide A, an unusually stabilized neuroactive macrolide from palmyra atoll cyanobacteria. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 4490–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, L.; Ling, C.; Li, J.; Pang, J.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Liu, J.; Huang, R.; Wang, G.L.; Pei, Z.; et al. Marine compound xyloketal B protects PC12 cells against OGD-induced cell damage. Brain Res. 2009, 1302, 240–247. [Google Scholar]
- Soria-Mercado, I.E.; Pereira, A.; Cao, Z.; Murray, T.F.; Gerwick, W.H. Alotamide A, a novel neuropharmacological agent from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya bouillonii. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 4704–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.A.; Fechner, G.A.; Sykes, M.; Garavelas, A.; Pass, D.M.; Carroll, A.R.; Addepalli, R.; Avery, V.M.; Hooper, J.N.; Quinn, R.J. (−)-Dibromophakellin: An α2B adrenoceptor agonist isolated from the australian marine sponge, Acanthella costata. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 2497–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suna, H.; Arai, M.; Tsubotani, Y.; Hayashi, A.; Setiawan, A.; Kobayashi, M. Dysideamine, a new sesquiterpene aminoquinone, protects hippocampal neuronal cells against iodoacetic acid-induced cell death. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 3968–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balansa, W.; Islam, R.; Fontaine, F.; Piggott, A.M.; Zhang, H.; Webb, T.I.; Gilbert, D.F.; Lynch, J.W.; Capon, R.J. Ircinialactams: Subunit-selective glycine receptor modulators from Australian sponges of the family irciniidae. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 2912–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiolas, D.M.; Bowden, B.F.; Abou-Mansour, E.; Willis, R.H.; Doyle, J.R.; Muirhead, A.N.; Liptrot, C.; Llewellyn, L.E.; Wolff, C.W.; Wright, A.D.; et al. Eusynstyelamides A, B, and C, nNOS inhibitors, from the Ascidian Eusynstyela latericius. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.J.; Wen, Z.H.; Dai, C.F.; Chiang, M.Y.; Sheu, J.H. Nanolobatolide, a new C18 metabolite from the formosan soft coral Sinularia nanolobata. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 5030–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Antemano, R.R.; Hughen, R.W.; Tianero, M.D.; Peraud, O.; Haygood, M.G.; Concepcion, G.P.; Olivera, B.M.; Light, A.; Schmidt, E.W. Pulicatins A–E, neuroactive thiazoline metabolites from cone snail-associated bacteria. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1922–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, V.H.; Nicoll, J.A.; Holmes, C. Microglia in neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teruya, T.; Sasaki, H.; Fukazawa, H.; Suenaga, K. Bisebromoamide, a potent cytotoxic peptide from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya sp.: Isolation, stereostructure, and biological activity. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 5062–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrich, C.J.; Robey, R.W.; Takada, K.; Bokesch, H.R.; Bates, S.E.; Shukla, S.; Ambudkar, S.V.; McMahon, J.B.; Gustafson, K.R. Botryllamides: Natural product inhibitors of ABCG2. ACS Chem. Biol. 2009, 4, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qian, Z.J.; Ryu, B.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, M.M.; Kim, S.K. Chemical components and its antioxidant properties in vitro: An edible marine brown alga, Ecklonia cava. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 1963–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parys, S.; Kehraus, S.; Krick, A.; Glombitza, K.W.; Carmeli, S.; Klimo, K.; Gerhauser, C.; Konig, G.M. In vitro chemopreventive potential of fucophlorethols from the brown alga Fucus vesiculosus L. by anti-oxidant activity and inhibition of selected cytochrome P450 enzymes. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mita, M.; Yoshikuni, M.; Ohno, K.; Shibata, Y.; Paul-Prasanth, B.; Pitchayawasin, S.; Isobe, M.; Nagahama, Y. A relaxin-like peptide purified from radial nerves induces oocyte maturation and ovulation in the starfish, Asterina pectinifera. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9507–9512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubosaka, Y.; Murata, T.; Kinoshita, K.; Yamada, K.; Uemura, D.; Hori, M.; Ozaki, H. Halichlorine is a novel L-type Ca2+ channel inhibitor isolated from the marine sponge Halichondria okadai Kadota. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 628, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.; Cao, Z.; Murray, T.F.; Gerwick, W.H. Hoiamide A, a sodium channel activator of unusual architecture from a consortium of two papua new guinea cyanobacteria. Chem. Biol. 2009, 16, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, Y.; Miki, K.; Suzuki, T.; Nishio, K.; Sugita, T.; Kinoshita, K.; Takahashi, K.; Koyama, K. Antiangiogenic metabolites from a marine-derived fungus, Hypocrea vinosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.B.; Mahdi, F.; Liu, Y.; Coothankandaswamy, V.; Jekabsons, M.B.; Johnson, T.A.; Sashidhara, K.V.; Crews, P.; Nagle, D.G.; Zhou, Y.D. The marine sponge metabolite mycothiazole: A novel prototype mitochondrial complex I inhibitor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 5988–5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.C.; Liu, Y.; Morgan, J.B.; Jekabsons, M.B.; Zhou, Y.D.; Nagle, D.G. Lipophilic 2,5-disubstituted pyrroles from the marine sponge Mycale sp. Inhibit mitochondrial respiration and HIF-1 Activation. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1927–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Tachikawa, Y.; Ohno, O.; Kitamura, M.; Suganuma, M.; Uemura, D. Neocomplanines A and B, a complanine family isolated from the marine fireworm. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Low, W.K.; Xu, J.; Gehring, N.H.; Dietz, H.C.; Romo, D.; Liu, J.O. Inhibition of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay by the natural product pateamine a through eukaryotic initiation factor 4AIII. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 23613–23621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, M.; Shimizu, H.; Muramatsu, I.; Oiki, S.A. Cytotoxic peptide from a marine sponge exhibits ion channel activity through vectorial-insertion into the membrane. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 3995–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, J.J.; Singh, A.J.; Kanakkanthara, A.; Halafihi, T.; Northcote, P.T.; Miller, J.H. Microtubule-stabilizing activity of zampanolide, a potent macrolide isolated from the tongan marine sponge Cacospongia mycofijiensis. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 7328–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forestier, R.; Merchant, C.E.; de Voogd, N.J.; Matainaho, T.; Kieffer, T.J.; Anderson, R.J. Aloketals A and B, sesterterpenoids from the marine sponge Hamigera species that activate the cAMP cell signalings pathway. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 5166–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, C.; Sohn, J.H.; Oh, H.; Kim, B.Y.; Ahn, J.S. Isolation of the protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitory metabolite from the marine-derived fungus Cosmospora sp. SF-5060. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 6095–6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.E.; Amlani, A.; Dewi, A.S.; Patrick, B.O.; van Ofwegen, L.; Mui, A.L.F.; Andersen, R.J. Australin E isolated from the soft coral Cladiella sp. collected in pohnpei activates the inositol 5-phosphatase SHIP1. Aust. J. Chem. 2010, 63, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, B.K.; Parrish, S.M.; Yoshida, W.; Schupp, P.J.; Schils, T.; Williams, P.G. Depsipeptides from a guamanian marine cyanobacterium, Lyngbya bouillonii, with selective inhibition of serine proteases. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 6718–6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisay, M.T.; Hautmann, S.; Mehner, C.; Konig, G.M.; Bajorath, J.; Gutschow, M. Inhibition of human leukocyte elastase by brunsvicamides A–C: Cyanobacterial cyclic peptides. Chem. Med. Chem. 2009, 4, 1425–1429. [Google Scholar]
- McCulloch, M.W.; Bugni, T.S.; Concepcion, G.P.; Coombs, G.S.; Harper, M.K.; Kaur, S.; Mangalindan, G.C.; Mutizwa, M.M.; Veltri, C.A.; Virshup, D.M.; et al. Carteriosulfonic acids A–C, GSK-3β inhibitors from a Carteriospongia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1651–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.E.; Hollander, I.; Feldberg, L.; Frommer, E.; Mallon, R.; Tahir, A.; Van Soest, S.R.; Andersen, R.J. Scalarane-based sesterterpenoid RCE-protease inhibitors isolated from the indonesian marine sponge Carteriospongia foliascens. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1106–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, M.S.; Carroll, A.R.; Wessling, D.; Jobling, M.; Avery, V.M.; Davis, R.A.; Feng, Y.; Hooper, J.N.; Quinn, R.J. Clavatadines C–E, guanidine alkaloids from the australian sponge Suberea clavata. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 973–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitson, E.L.; Bugni, T.S.; Chockalingam, P.S.; Concepcion, G.P.; Feng, X.; Jin, G.; Harper, M.K.; Mangalindan, G.C.; McDonald, L.A.; Ireland, C.M. Fibrosterol sulfates from the philippine sponge Lissodendoryx (Acanthodoryx) fibrosa: Sterol dimers that inhibit PKCzeta. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 5902–5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rateb, M.E.; Houssen, W.E.; Schumacher, M.; Harrison, W.T.; Diederich, M.; Ebel, R.; Jaspars, M. Bioactive diterpene derivatives from the marine sponge Spongionella sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.M.; Li, X.M.; Li, C.Y.; Sun, H.F.; Gan, S.S.; Wang, B.G. Benzodiazepine alkaloids from marine-derived endophytic fungus Aspergillus ochraceus. Helv. Chim. Acta 2009, 92, 1366–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.J.; Hoobler, E.K.; Riener, M.; Loveridge, S.T.; Tenney, K.; Valeriote, F.A.; Holman, T.R.; Crews, P. Using enzyme assays to evaluate the structure and bioactivity of sponge-derived meroterpenes. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1857–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthew, S.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Largamides A–C, tiglic acid-containing cyclodepsipeptides with elastase-inhibitory activity from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya confervoides. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthew, S.; Ratnayake, R.; Becerro, M.A.; Ritson-Williams, R.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Intramolecular modulation of serine protease inhibitor activity in a marine cyanobacterium with antifeedant properties. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1803–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Su, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhu, L.; Wu, X.; Pan, H.; Li, X. Highly brominated metabolites from marine red alga Laurencia similis inhibit protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 7152–7154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekera, S.P.; Miller, M.W.; Kwan, J.C.; Luesch, H.; Paul, V.J. Molassamide, a depsipeptide serine protease inhibitor from the marine cyanobacterium Dichothrix utahensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Leutou, A.S.; Yang, G.; Nenkep, V.N.; Siwe, X.N.; Choi, H.D.; Kang, J.S.; Son, B.W. Bioactive cyclopentenone derivatives from marine isolates of fungi. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2009, 30, 2345–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Dello, I.E.; Fattorusso, E.; Forino, M.; Grauso, L.; Tartaglione, L.; Florio, C.; Lorenzon, P.; de Bortoli, M.; et al. Stereostructure and biological activity of 42-Hydroxy-palytoxin: A new palytoxin analogue from Hawaiian Palythoa subspecies. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2009, 22, 1851–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, G.; Tay, W.; Bottriell, H.; Andersen, S.K.; Mauk, A.G.; Andersen, R.J. Plectosphaeroic Acids A, B, and C, indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase inhibitors produced in culture by a marine isolate of the fungus Plectosphaerella cucumerina. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 2996–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Nakao, Y.; Matsunaga, S.; Oikawa, T.; Imahara, Y.; Fusetani, N. A new antiangiogenic C24 oxylipin from the soft coral Sinularia numerosa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 2181–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Abraham, I.; Carvalho, P.; Kuang, Y.H.; Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.; Avery, M.A.; Chen, Z.S.; El Sayed, K.A. Sipholane triterpenoids: Chemistry, reversal of ABCB1/P-Glycoprotein-Mediated multidrug resistance, and pharmacophore modeling. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsebai, M.F.; Kehraus, S.; Gutschow, M.; Konig, G.M. Spartinoxide, a new enantiomer of A82775C with inhibitory activity toward HLE from the marine-derived fungus Phaeosphaeria spartinae. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Ankisetty, S.; Gochfeld, D.J.; Diaz, M.C.; Khan, S.I.; Slattery, M. Chemical constituents of the deep reef caribbean sponges Plakortis angulospiculatus and Plakortis halichondrioides and their anti-inflammatory activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1494–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.; Andrianasolo, E.H.; Shin, W.K.; Goeger, D.E.; Yokochi, A.; Schemies, J.; Jung, M.; France, D.; Cornell-Kennon, S.; Lee, E.; et al. Structural and synthetic investigations of tanikolide dimer, a SIRT2 selective inhibitor, and tanikolide seco-acid from the madagascar marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 5267–5275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truxal, L.T.; Bourdelais, A.J.; Jacocks, H.; Abraham, W.M.; Baden, D.G. Characterization of tamulamides A and B, polyethers isolated from the marine dinoflagellate Karenia brevis. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Gresa, M.P.; Cabedo, N.; Gonzalez-Mas, M.C.; Ciavatta, M.L.; Avila, C.; Primo, J. Terretonins E and F, inhibitors of the mitochondrial respiratory chain from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus insuetus. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1348–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Jermihov, K.; Nam, S.J.; Sturdy, M.; Maloney, K.; Qiu, X.; Chadwick, L.R.; Main, M.; Chen, S.N.; Mesecar, A.D.; Farnsworth, N.R.; Pauli, G.F.; Fenical, W.; Pezzuto, J.M.; van Breemen, R.B. Screening natural products for inhibitors of quinone reductase-2 using ultrafiltration LC-MS. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, J.C.; Taori, K.; Paul, V.; Luesch, H. Lyngbyastatins 8–10, elastase inhibitors with cyclic depsipeptide scaffolds isolated from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya semiplena. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, K.B.; Mayer, A.M. A renaissance in marine pharmacology: From preclinical curiosity to clinical reality. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Kitamura, M.; Uemura, D. Biologically active marine natural products. Heterocycles 2009, 78, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinski, T.F.; Dalisay, D.S.; Lievens, S.L.; Saludes, J.P. Drug development from marine natural products. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusetani, N. Biotechnological potential of marine natural products. Pure Appl. Chem. 2010, 82, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.T.; Fenical, W. Pharmaceuticals from marine natural products: Surge or Ebb? Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 777–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rae, I.D. Marine pharmacology in Australia. The roche research institute at dee why, new South Wales, 1974–81. Aust. J. Chem. 2010, 63, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.M.; Glaser, K.B.; Cuevas, C.; Jacobs, R.S.; Kem, W.; Little, R.D.; McIntosh, J.M.; Newman, D.J.; Potts, B.C.; Shuster, D.E. The odyssey of marine pharmaceuticals: A current pipeline perspective. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 31, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.R.; Kavlekar, D.P.; LokaBharathi, P.A. Marine drugs from sponge-microbe association—A review. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1417–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Tiwari, S.P.; Rai, A.K.; Mohapatra, T.M. Cyanobacteria: An emerging source for drug discovery. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y. Mining invertebrate natural products for future therapeutic treasure. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar]
- Kingston, D.G. Modern natural products drug discovery and its relevance to biodiversity conservation. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 496–511. [Google Scholar]
- Ebada, S.S.; Proksch, P. Chemical and pharmacological significance of natural guanidines from marine invertebrates. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaser, R.; Luesch, H. Marine natural products: A new wave of drugs? Future Med. Chem. 2011, 3, 1475–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.C.; Fenical, W. Antibacterials from the Sea. Chem. Eur J. 2010, 16, 12512–12525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, A.L.; Hill, R.T.; Place, A.R.; Hamann, M.T. The expanding role of marine microbes in pharmaceutical development. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Cao, X.; Liu, X.; Jiao, B. Marine microbes-derived anti-bacterial agents. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 1077–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero-Gonzalez, A.J.; Magalhaes, B.S.; Garcia-Villarino, M.; Lopez-Abarrategui, C.; Sousa, D.A.; Dias, S.C.; Franco, O.L. Antimicrobial peptides from marine invertebrates as a new frontier for microbial infection control. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 1320–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, H.; Austin, B.; Mitchell, W.J.; Morris, P.C.; Jamieson, D.J.; Adams, D.R.; Spragg, A.M.; Schweizer, M. Novel anti-infective compounds from marine bacteria. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 498–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.J.; Desbois, A.P.; Dyrynda, E.A. Conventional and unconventional antimicrobials from fish, marine invertebrates and micro-algae. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1213–1262. [Google Scholar]
- Sagar, S.; Kaur, M.; Minneman, K.P. Antiviral lead compounds from marine sponges. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2619–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.S.; Kim, S.K. Potential anti-HIV agents from marine resources: An overview. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2871–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuhara-Bell, J.; Lu, Y. Marine compounds and their antiviral activities. Antiviral Res. 2010, 86, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.S.; Ngo, D.H.; Ta, Q.V.; Kim, S.K. Marine organisms as a therapeutic source against herpes simplex virus infection. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 44, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, K.R.; Tenney, K.; Crews, P. The structural diversity and promise of antiparasitic marine invertebrate-derived small molecules. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempone, A.G.; de Oliveira, M.; Berlinck, R.G. Current approaches to discover marine antileishmanial natural products. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashforth, E.J.; Fu, C.; Liu, X.; Dai, H.; Song, F.; Guo, H.; Zhang, L. Bioprospecting for antituberculosis leads from microbial metabolites. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 1709–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peach, K.C.; Linington, R.G. New innovations for an old infection: Antimalarial lead discovery from marine natural products during the period 2003–2008. Future Med. Chem. 2009, 1, 593–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gademann, K.; Kobylinska, J. Antimalarial natural products of marine and freshwater origin. Chem. Rec. 2009, 9, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorusso, E.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Marine antimalarials. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 130–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, F.A.; Gerwick, L. Marine natural product drug discovery: Leads for treatment of inflammation, cancer, infections, and neurological disorders. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2010, 32, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, F.; Jaspars, M.; Schumacher, M.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Marine natural products targeting phospholipases A2. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1793–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrue, F.; McCulloch, M.W.; Kerr, R.G. Marine diterpene glycosides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6702–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaswir, I.; Monsur, H.A. Anti-inflammatory compounds of macro algae origin: A review. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 7146–7154. [Google Scholar]
- Wijesekara, I.; Kim, S.K. Angiotensin-I-converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitors from marine resources: Prospects in the pharmaceutical industry. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1080–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halai, R.; Craik, D.J. Conotoxins: Natural product drug leads. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanowska-Karamyan, A.J.; Hamann, M.T. Marine indole alkaloids: Potential new drug leads for the control of depression and anxiety. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4489–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichert, R.W.; Olivera, B.M. Natural products and ion channel pharmacology. Future Med. Chem. 2010, 2, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangestuti, R.; Kim, S.K. Neuroprotective effects of marine algae. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, N.L.; Craik, D.J. Conopeptides as novel options for pain management. Drugs Future 2011, 36, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Muttenthaler, M.; Akondi, K.B.; Alewood, P.F. Structure-activity studies on alpha-conotoxins. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 4226–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerholm, A.E.; Habrant, D.; Koskinen, A.M. Calyculins and related marine natural products as serine-threonine protein phosphatase PP1 and PP2A inhibitors and total syntheses of calyculin A, B, and C. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 122–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, F.; Jaspars, M.; Solano, G.; Cristofanon, S.; Henry, E.; Tabudravu, J.; Black, K.; Green, D.H.; Küpper, F.C.; Aalbersberg, W.; et al. The inhibition of TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation by marine natural products. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 592–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skropeta, D.; Pastro, N.; Zivanovic, A. Kinase inhibitors from marine sponges. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2131–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senter, P.D.; Sievers, E.L. The discovery and development of brentuximab vedotin for use in relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma and systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Global Marine Pharmaceutical Pipeline. Available online: http://marinepharmacology.midwestern.edu/ (accessed on 3 June 2013).
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Mayer, A.M.S.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Fusetani, N. Marine Pharmacology in 2009–2011: Marine Compounds with Antibacterial, Antidiabetic, Antifungal, Anti-Inflammatory, Antiprotozoal, Antituberculosis, and Antiviral Activities; Affecting the Immune and Nervous Systems, and other Miscellaneous Mechanisms of Action. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2510-2573. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11072510
Mayer AMS, Rodríguez AD, Taglialatela-Scafati O, Fusetani N. Marine Pharmacology in 2009–2011: Marine Compounds with Antibacterial, Antidiabetic, Antifungal, Anti-Inflammatory, Antiprotozoal, Antituberculosis, and Antiviral Activities; Affecting the Immune and Nervous Systems, and other Miscellaneous Mechanisms of Action. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(7):2510-2573. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11072510
Chicago/Turabian StyleMayer, Alejandro M. S., Abimael D. Rodríguez, Orazio Taglialatela-Scafati, and Nobuhiro Fusetani. 2013. "Marine Pharmacology in 2009–2011: Marine Compounds with Antibacterial, Antidiabetic, Antifungal, Anti-Inflammatory, Antiprotozoal, Antituberculosis, and Antiviral Activities; Affecting the Immune and Nervous Systems, and other Miscellaneous Mechanisms of Action" Marine Drugs 11, no. 7: 2510-2573. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11072510
APA StyleMayer, A. M. S., Rodríguez, A. D., Taglialatela-Scafati, O., & Fusetani, N. (2013). Marine Pharmacology in 2009–2011: Marine Compounds with Antibacterial, Antidiabetic, Antifungal, Anti-Inflammatory, Antiprotozoal, Antituberculosis, and Antiviral Activities; Affecting the Immune and Nervous Systems, and other Miscellaneous Mechanisms of Action. Marine Drugs, 11(7), 2510-2573. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11072510