pH-Dependent Solution Structure and Activity of a Reduced Form of the Host-Defense Peptide Myticin C (Myt C) from the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
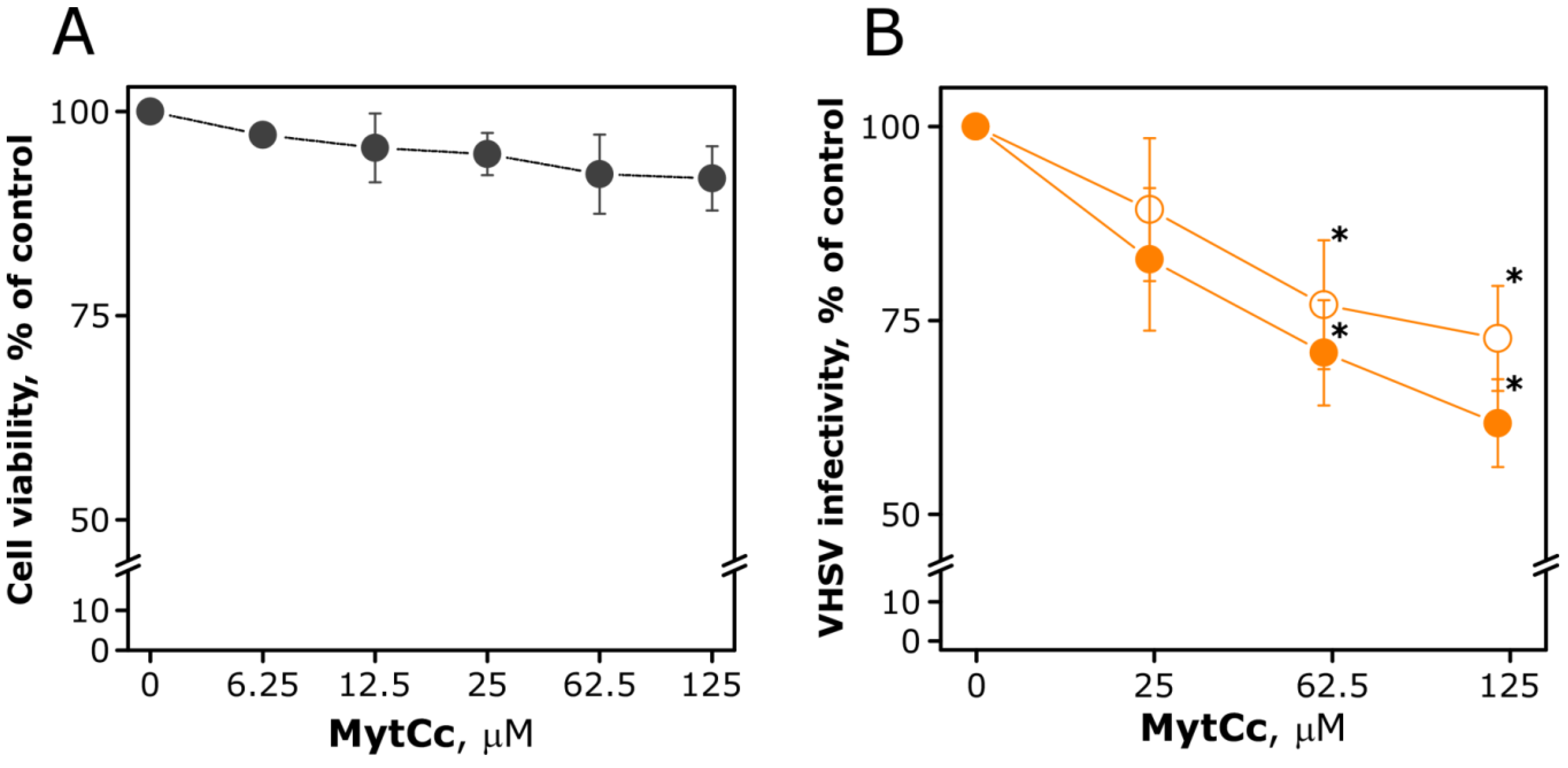
2. Results
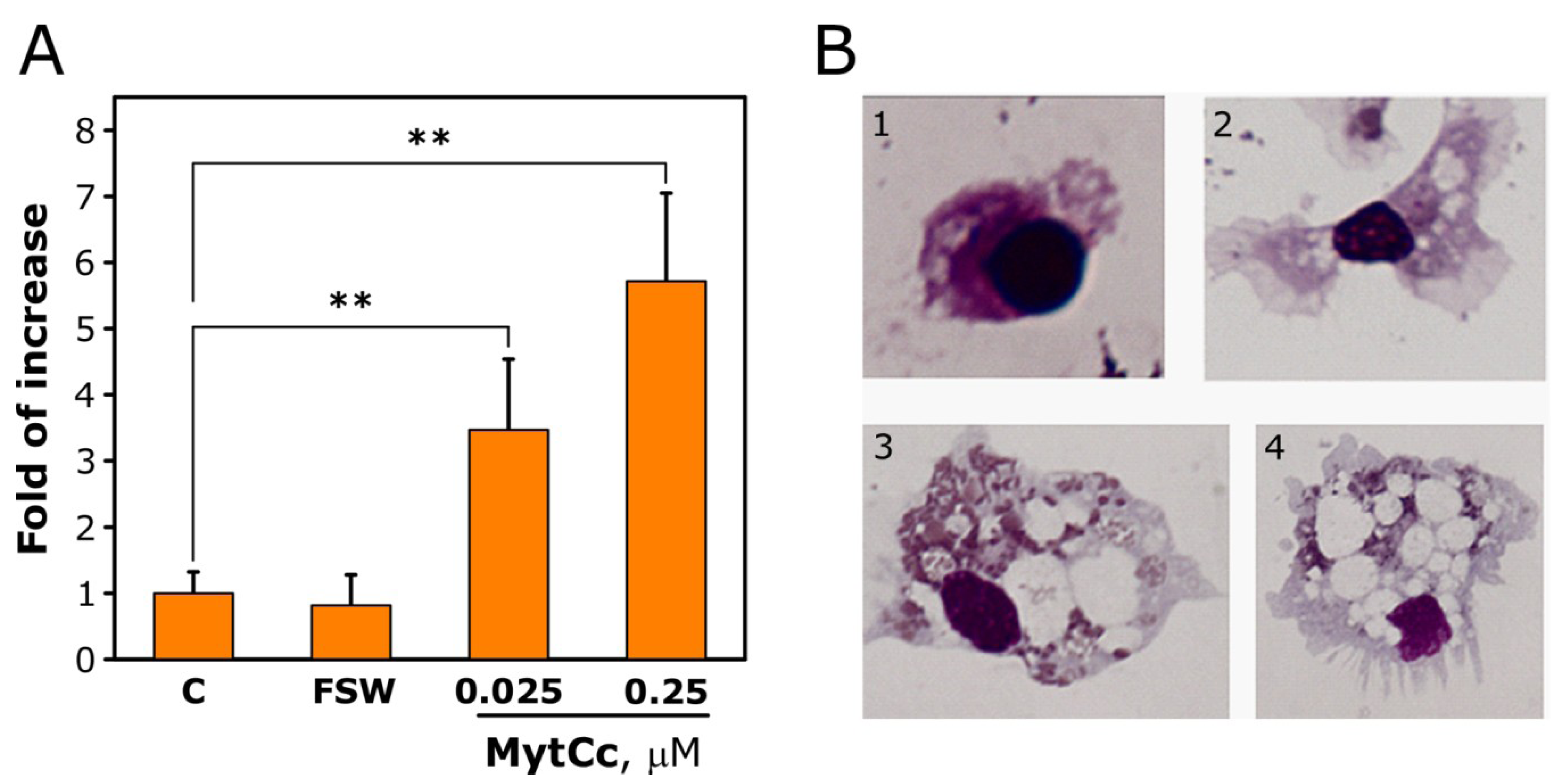
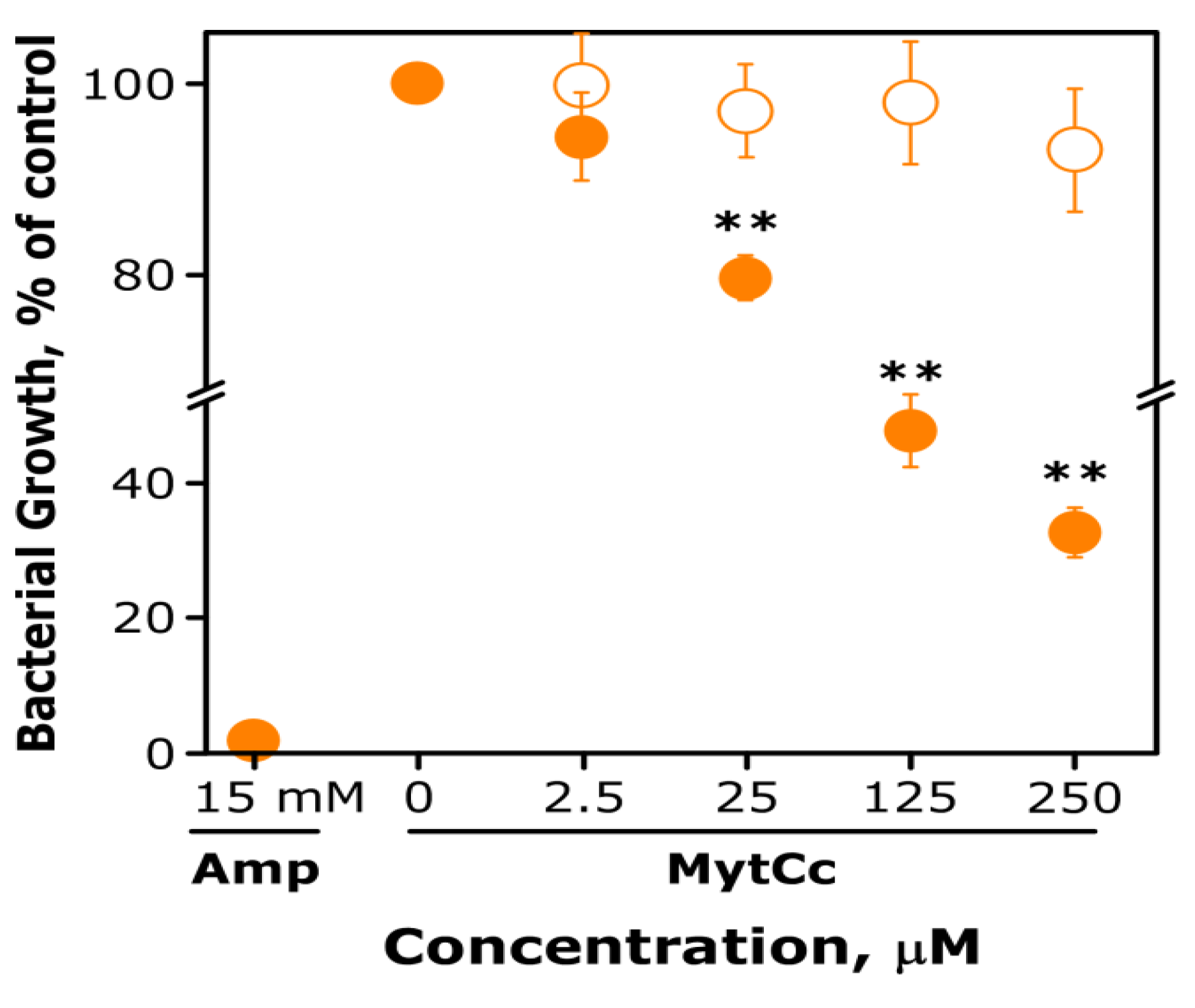
2.2. Chemotactic Properties of Synthetic Red-MytCc at Neutral pH
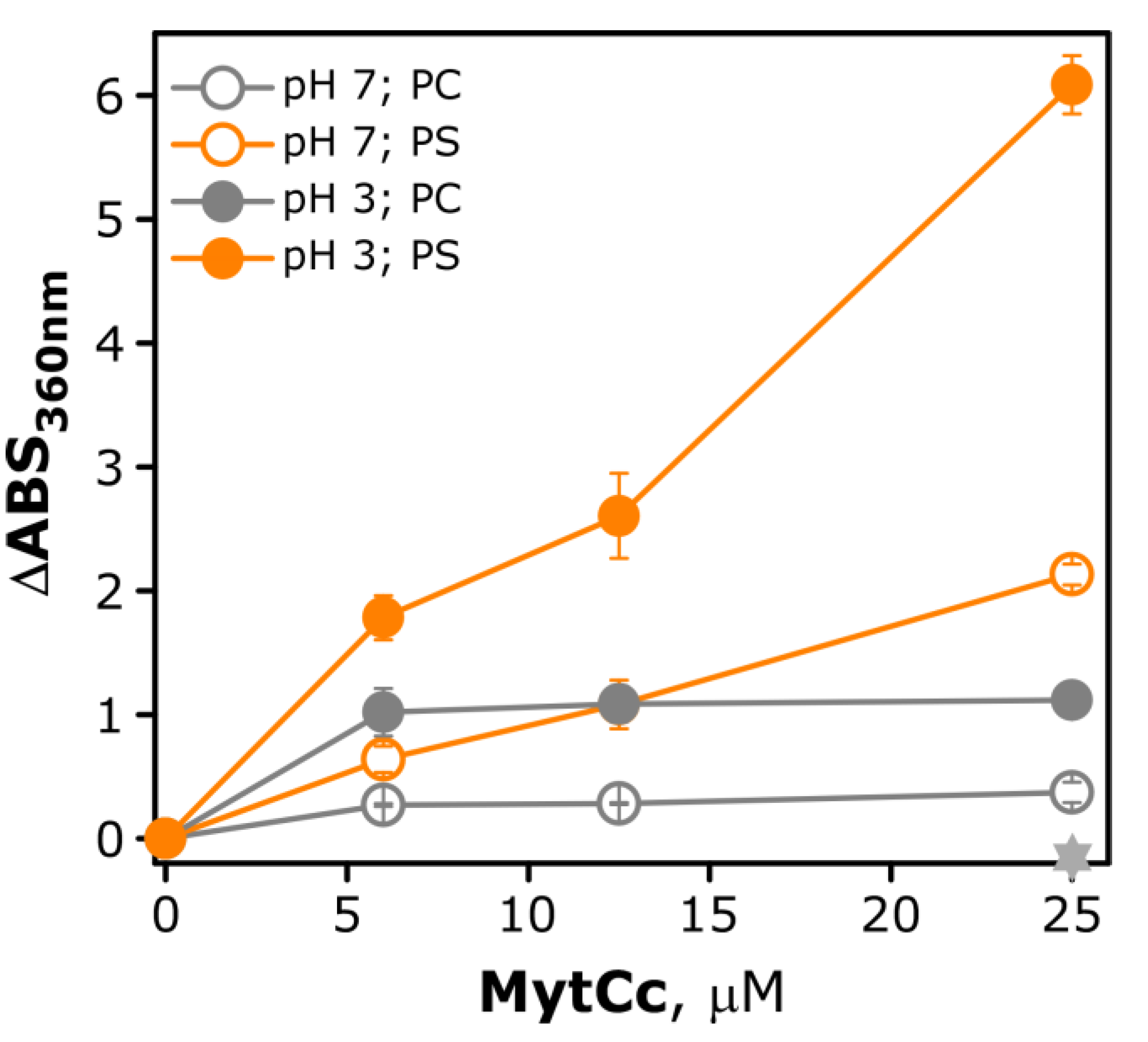
2.3. pH-Dependence Membrane Destabilization Induced by the Red-MytCc Peptide
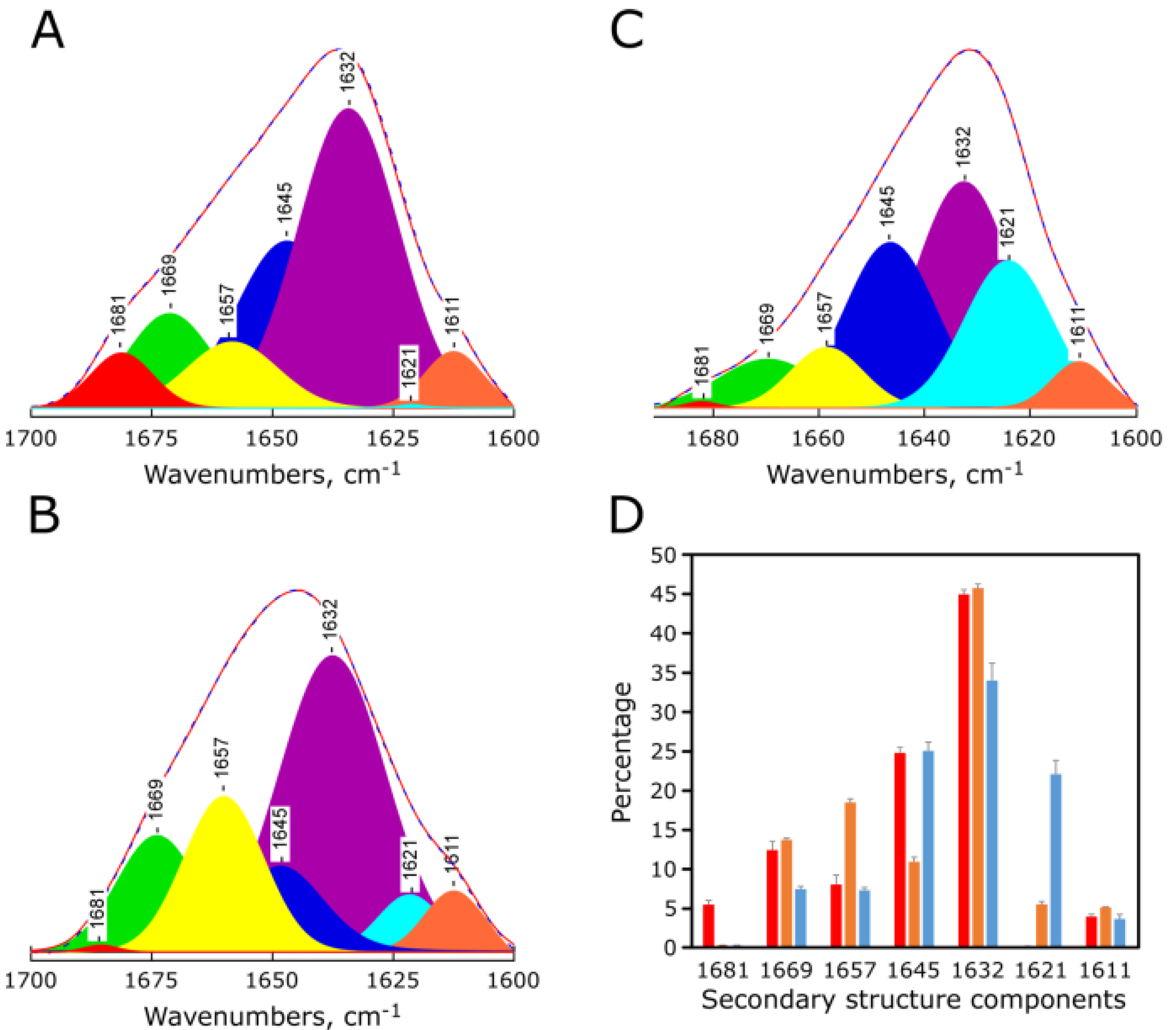
2.4. pH-Dependent Secondary Structure of Synthetic Red-MytCc
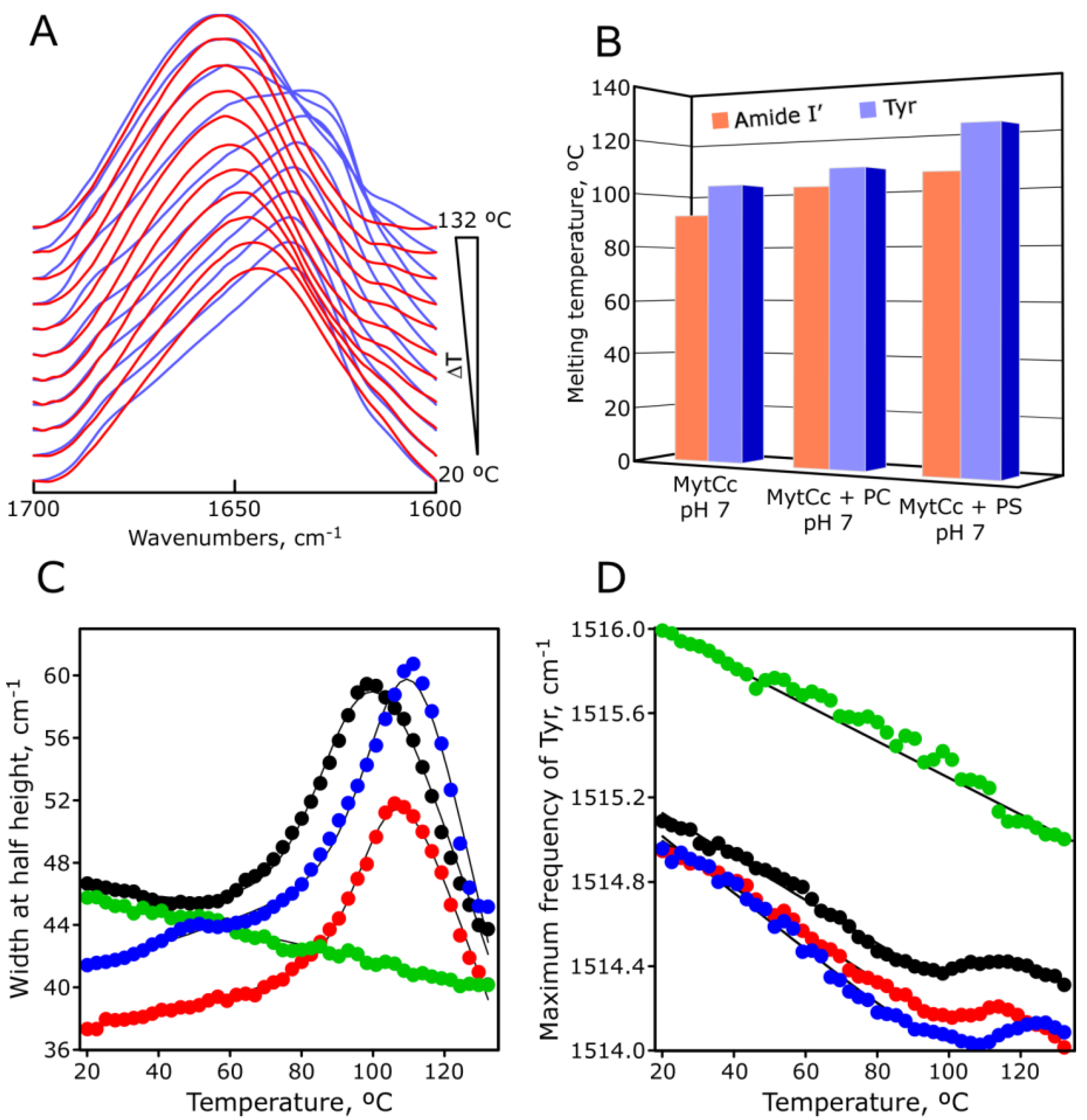
2.5. pH-Dependent Thermal Stability of Synthetic Red-MytCc
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Cultures and Virus
4.3. Bactericidal Assay of Synthetic Myt C
4.4. In Vitro Cell Viability Assays
4.5. Viral Infectivity Assays
4.6. Chemotaxis Assays
4.7. Lipid Vesicle Preparation
4.8. Vesicle Aggregation Assay
4.9. FTIR Measurements
4.10. Sigmoidal Data Fitting Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Afacan, N.J.; Yeung, A.T.; Pena, O.M.; Hancock, R.E. Therapeutic potential of host defense peptides in antibiotic-resistant infections. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, A.; Ortega-Villaizan, M.; Chico, V.; Brocal, I.; Perez, L.; Coll, J.M.; Estepa, A. Antimicrobial peptides as model molecules for the development of novel antiviral agents in aquaculture. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, R.E.; Sahl, H.G. Antimicrobial and host-defense peptides as new anti-infective therapeutic strategies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zasloff, M. Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 2002, 415, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero-Gonzalez, A.J.; Magalhaes, B.S.; Garcia-Villarino, M.; Lopez-Abarrategui, C.; Sousa, D.A.; Dias, S.C.; Franco, O.L. Antimicrobial peptides from marine invertebrates as a new frontier for microbial infection control. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 1320–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, S.; Donnelly, S.; Robinson, M.W.; Dalton, J.P.; Thivierge, K. Defense peptides secreted by helminth pathogens: Antimicrobial and/or immunomodulator molecules? Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 269. [Google Scholar]
- Brocal, I.; Falco, A.; Mas, V.; Rocha, A.; Perez, L.; Coll, J.M.; Estepa, A. Stable expression of bioactive recombinant pleurocidin in a fish cell line. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 72, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.M.; Dios, S.; Alonso-Gutierrez, J.; Romero, A.; Novoa, B.; Figueras, A. Evidence of high individual diversity on myticin C in mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2009, 33, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallavicini, A.; Costa Mdel, M.; Gestal, C.; Dreos, R.; Figueras, A.; Venier, P.; Novoa, B. High sequence variability of myticin transcripts in hemocytes of immune-stimulated mussels suggests ancient host-pathogen interactions. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balseiro, P.; Falco, A.; Romero, A.; Dios, S.; Martinez-Lopez, A.; Figueras, A.; Estepa, A.; Novoa, B. Mytilus galloprovincialis myticin C: A chemotactic molecule with antiviral activity and immunoregulatory properties. PLoS One 2011, 6, e23140. [Google Scholar]
- Vera, M.; Martinez, P.; Poisa-Beiro, L.; Figueras, A.; Novoa, B. Genomic organization, molecular diversification, and evolution of antimicrobial peptide myticin-C genes in the mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis). PLoS One 2011, 6, e24041. [Google Scholar]
- Govorin, I. Role of bivalves in the depuration of seawaters contaminated by bacteria. Russ. J. Mar. Biol. 2000, 26, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkbeck, T.H.; McHenery, J.G. Degradation of bacteria by Mytilus edulis. Mar. Biol. 1982, 72, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Casado, E.; Estepa, A.; Coll, J.M. A comparative review on European-farmed finfish RNA viruses and their vaccines. Vaccine 2011, 29, 2657–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susi, H. Infrared spectroscopy—Conformation. Methods Enzymol. 1972, 26, 455–472. [Google Scholar]
- Susi, H.; Timasheff, S.N.; Stevens, L. Infrared spectra and protein conformations in aqueous solutions. I. The amide I band in H2O and D2O solutions. J. Biol. Chem. 1967, 242, 5460–5466. [Google Scholar]
- Surewicz, W.K.; Mantsch, H.H. New insight into protein secondary structure from resolution-enhanced infrared spectra. Biochim. Biophy. Acta 1988, 952, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encinar, J.A.; Mallo, G.V.; Mizyrycki, C.; Giono, L.; Gonzalez-Ros, J.M.; Rico, M.; Canepa, E.; Moreno, S.; Neira, J.L.; Iovanna, J.L. Human p8 is a HMG-I/Y-like protein with DNA binding activity enhanced by phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 2742–2751. [Google Scholar]
- Arrondo, J.L.; Castresana, J.; Valpuesta, J.M.; Goni, F.M. Structure and thermal denaturation of crystalline and noncrystalline cytochrome oxidase as studied by infrared spectroscopy. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 11650–11655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, H.; Mantsch, H.H. Ribonuclease A revisited: Infrared spectroscopic evidence for lack of native-like secondary structures in the thermally denatured state. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 13651–13655. [Google Scholar]
- Aneiros, A.; Garateix, A. Bioactive peptides from marine sources: Pharmacological properties and isolation procedures. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 803, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitta, G.; Hubert, F.; Noel, T.; Roch, P. Myticin, a novel cysteine-rich antimicrobial peptide isolated from haemocytes and plasma of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 265, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, B.O.; Stange, E.F.; Wehkamp, J. Waking the wimp: Redox-modulation activates human beta-defensin 1. Gut Microbes 2011, 2, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, B.O.; Wu, Z.; Nuding, S.; Groscurth, S.; Marcinowski, M.; Beisner, J.; Buchner, J.; Schaller, M.; Stange, E.F.; Wehkamp, J. Reduction of disulphide bonds unmasks potent antimicrobial activity of human beta-defensin 1. Nature 2011, 469, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitta, G.; Hubert, F.; Dyrynda, E.A.; Boudry, P.; Roch, P. Mytilin B and MGD2, two antimicrobial peptides of marine mussels: Gene structure and expression analysis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2000, 24, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitta, G.; Vandenbulcke, F.; Hubert, F.; Salzet, M.; Roch, P. Involvement of mytilins in mussel antimicrobial defense. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 12954–12962. [Google Scholar]
- Dupuy, J.W.; Bonami, J.R.; Roch, P. A synthetic antibacterial peptide from Mytilus galloprovincialis reduces mortality due to white spot syndrome virus in palaemonid shrimp. J. Fish. Dis. 2004, 27, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitta, G.; Vandenbulcke, F.; Hubert, F.; Roch, P. Mussel defensins are synthesised and processed in granulocytes then released into the plasma after bacterial challenge. J. Cell. Sci. 1999, 112, 4233–4242. [Google Scholar]
- Braff, M.H.; di Nardo, A.; Gallo, R.L. Keratinocytes store the antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin in lamellar bodies. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.W. Action of antimicrobial peptides: Two-state model. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 8347–8352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Maier, E.; Benz, R.; Hancock, R.E. Mechanism of interaction of different classes of cationic antimicrobial peptides with planar bilayers and with the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 7235–7242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Rozek, A.; Hancock, R.E. Interaction of cationic antimicrobial peptides with model membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 35714–35722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.H.; Cho, Y.; Lehrer, R.I. Styelins, broad-spectrum antimicrobial peptides from the solitary tunicate, Styela clava. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B 1997, 118, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, K. Why and how are peptide-lipid interactions utilized for self-defense? Magainins and tachyplesins as archetypes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1462, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, S.C.; Choi do, Y.; Seo, C.H.; Hahm, K.S.; Park, Y. Effect of acidic pH on antibacterial action of peptide isolated from Korean pen shell (Atrina pectinata). J. Peptide Sci. 2011, 17, 353–357. [Google Scholar]
- Kyaw, A.; Maung, U.K.; Toe, T. Determination of inorganic phosphate with molybdate and Triton X-100 without reduction. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 145, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijan, N.; Sulimanovic, D.; Bearzotti, M.; Mizinic, D.; Zwillenberg, L.O.; Chilmonczyk, S.; Vautherot, J.F.; de Kinkelin, P. Some properties of the Epithelioma papulosum cyprini (EPC) cell line from carp Cyprinus carpio. Ann. Inst. Pasteur. Virol. 1983, 134, 207–220. [Google Scholar]
- JAMBW Chapter 3.1.6. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.org/JaMBW/3/1/6/index.html (accessed on 3 January 2013).
- DeKinkelin, P.; LeBerre, M. Isolament d’un rhabdovirus pathogéne de la truite fario (Salmo trutta, L.1766). C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 1977, 284, 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Basurco, B.; Coll, J.M. Spanish isolates and reference strains of viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus shown similar protein size patterns. Bull. Eur. Ass. Fish. Pathol. 1989, 9, 92–95. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo, G.; Estepa, A.; Coll, J.M. Fast neutralization/immunoperoxidase assay for viral haemorrhagic septicaemia with anti-nucleoprotein monoclonal antibody. J. Virol. Methods 1996, 58, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mas, V.; Perez, L.; Encinar, J.A.; Pastor, M.T.; Rocha, A.; Perez-Paya, E.; Ferrer-Montiel, A.; Gonzalez Ros, J.M.; Estepa, A.; Coll, J.M. Salmonid viral haemorrhagic septicaemia virus: Fusion-related enhancement of virus infectivity by peptides derived from viral glycoprotein G or a combinatorial library. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 2671–2681. [Google Scholar]
- Falco, A.; Mas, V.; Tafalla, C.; Perez, L.; Coll, J.M.; Estepa, A. Dual antiviral activity of human alpha-defensin-1 against viral haemorrhagic septicaemia rhabdovirus (VHSV): Inactivation of virus particles and induction of a type I interferon-related response. Antivir. Res. 2007, 76, 111–123. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz, F.; Coll, J.M. Detection of viral haemorrhagic septicemia virus by direct immunoperoxidase with selected anti-nucleoprotein monoclonal antibody. Bull. Eur. Ass. Fish. Pathol. 1992, 12, 116–119. [Google Scholar]
- Nuñez, E.; Fernandez, A.M.; Estepa, A.; Gonzalez-Ros, J.M.; Gavilanes, F.; Coll, J.M. Phospholipid interactions of a peptide from the fusion-related domain of the glycoprotein of VHSV, a fish rhabdovirus. Virology 1998, 243, 322–330. [Google Scholar]
- Bhushan, A.; McNamee, M.G. Correlation of phospholipid structure with functional effects on the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. A modulatory role for phosphatidic acid. Biophys. J. 1993, 64, 716–723. [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn, R.; Mantsch, H.H. Fourier Transform Infrared Studies of Lipid-Protein Interactions. In Progress in Protein-Lipid Interactions; Watts, A., DePoint, A., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publisher, B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 103–146. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Martinez-Lopez, A.; Encinar, J.A.; Medina-Gali, R.M.; Balseiro, P.; Garcia-Valtanen, P.; Figueras, A.; Novoa, B.; Estepa, A. pH-Dependent Solution Structure and Activity of a Reduced Form of the Host-Defense Peptide Myticin C (Myt C) from the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2328-2346. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11072328
Martinez-Lopez A, Encinar JA, Medina-Gali RM, Balseiro P, Garcia-Valtanen P, Figueras A, Novoa B, Estepa A. pH-Dependent Solution Structure and Activity of a Reduced Form of the Host-Defense Peptide Myticin C (Myt C) from the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(7):2328-2346. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11072328
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartinez-Lopez, Alicia, Jose Antonio Encinar, Regla Maria Medina-Gali, Pablo Balseiro, Pablo Garcia-Valtanen, Antonio Figueras, Beatriz Novoa, and Amparo Estepa. 2013. "pH-Dependent Solution Structure and Activity of a Reduced Form of the Host-Defense Peptide Myticin C (Myt C) from the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis" Marine Drugs 11, no. 7: 2328-2346. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11072328
APA StyleMartinez-Lopez, A., Encinar, J. A., Medina-Gali, R. M., Balseiro, P., Garcia-Valtanen, P., Figueras, A., Novoa, B., & Estepa, A. (2013). pH-Dependent Solution Structure and Activity of a Reduced Form of the Host-Defense Peptide Myticin C (Myt C) from the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Marine Drugs, 11(7), 2328-2346. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11072328