Marine Compounds with Therapeutic Potential in Gram-Negative Sepsis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
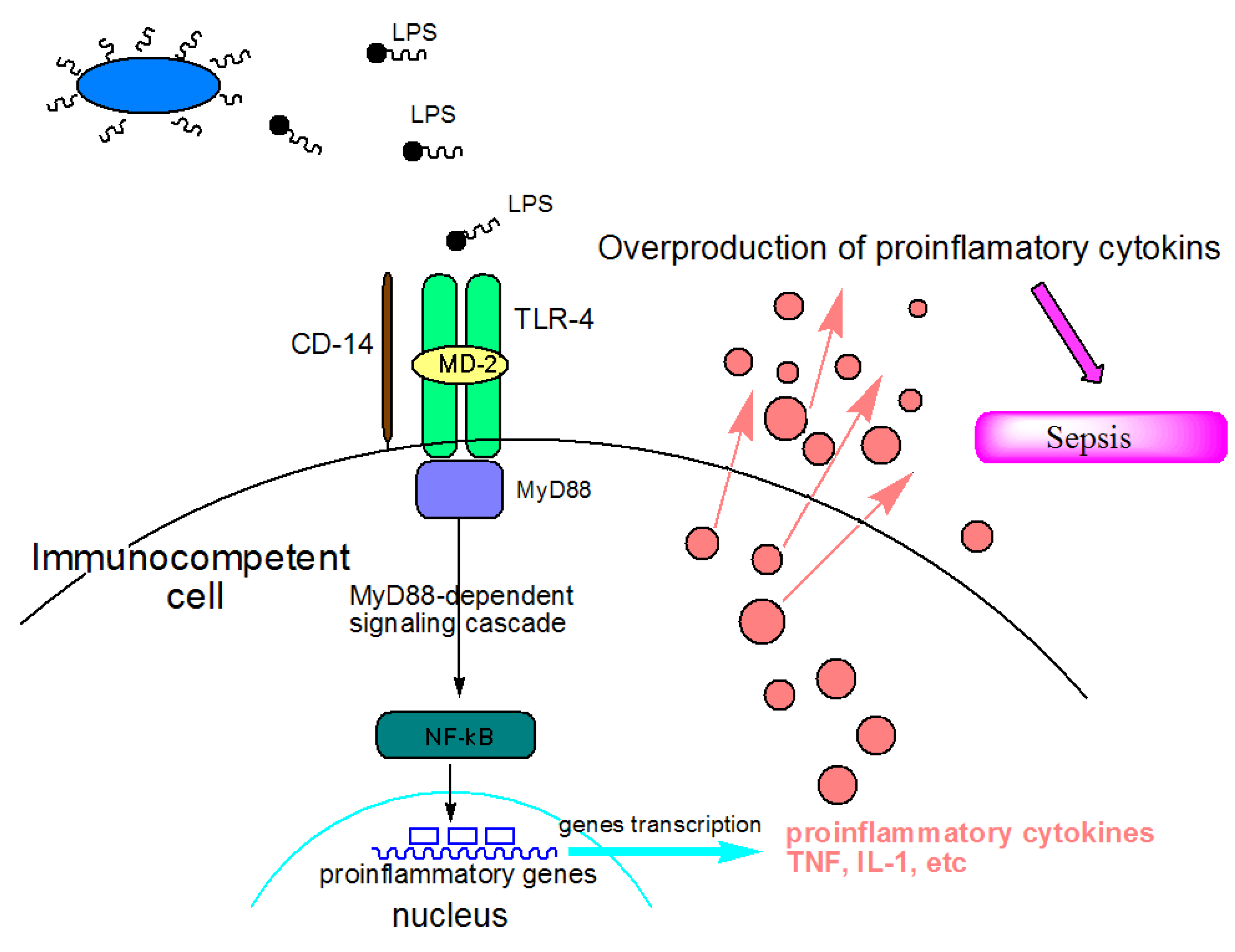
2. Lipid A, Chitosan and Carrageenan—Marine Compounds with Antiendotoxic Potential
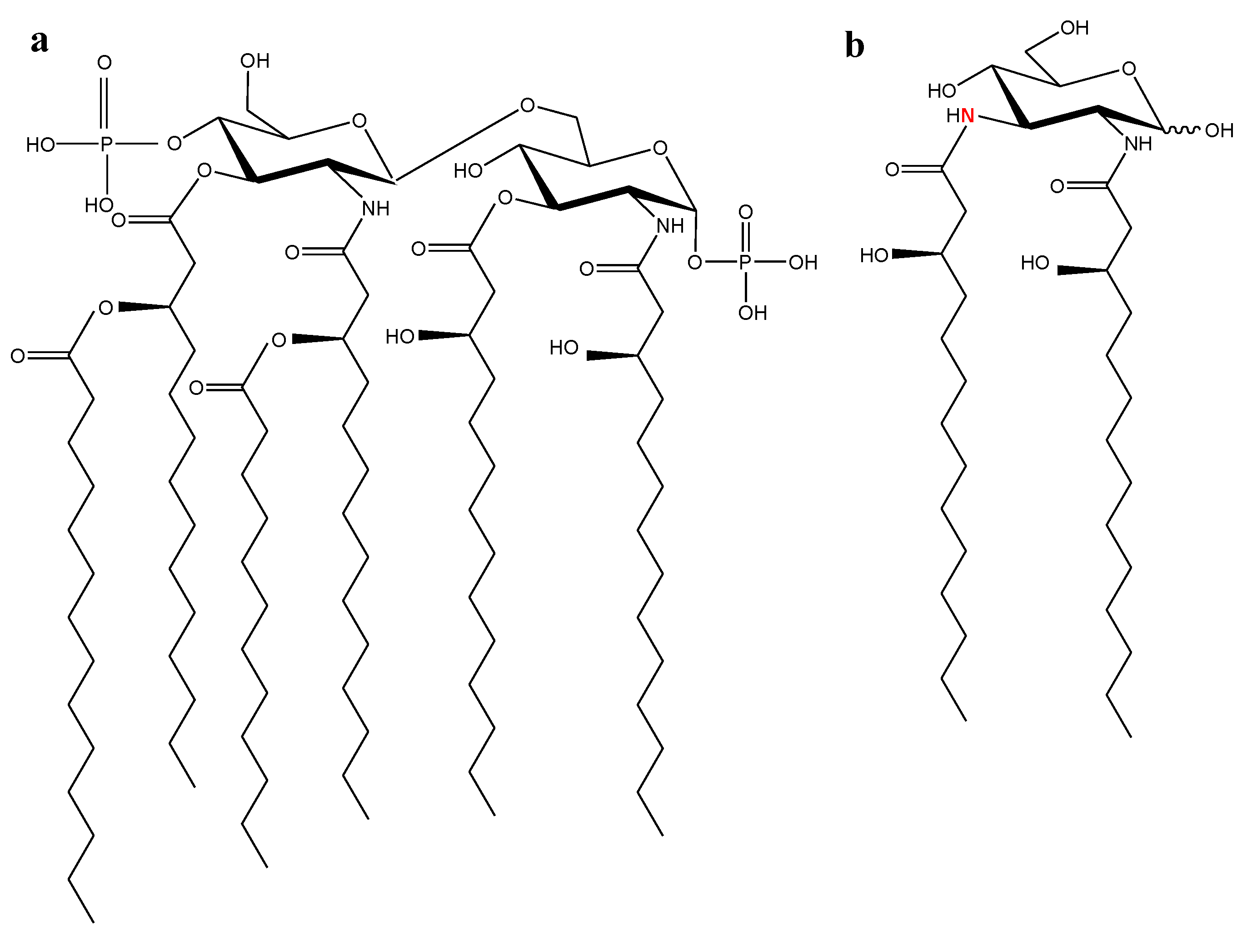
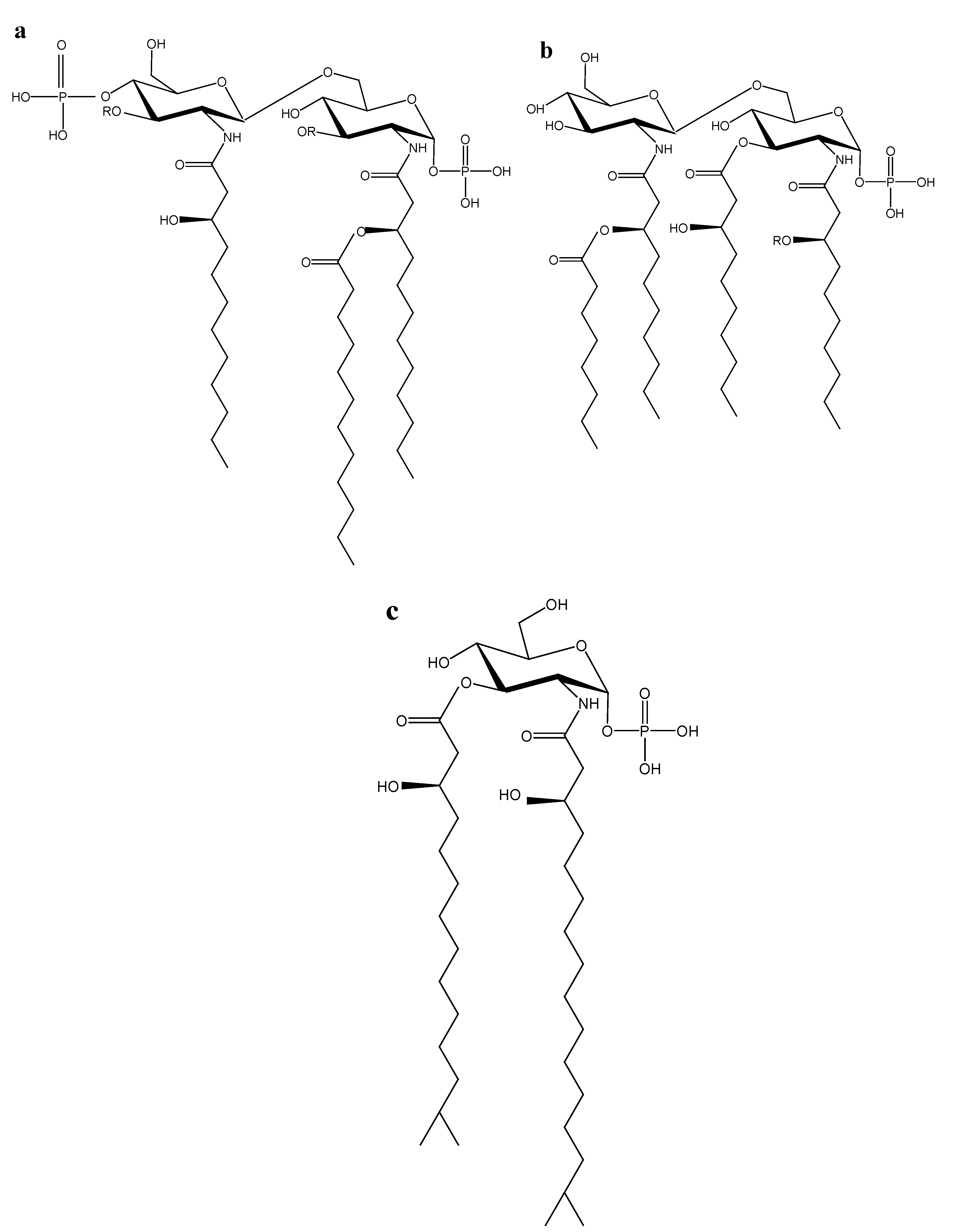
2.1. Marine Lipid A Potential Endotoxin Antagonists
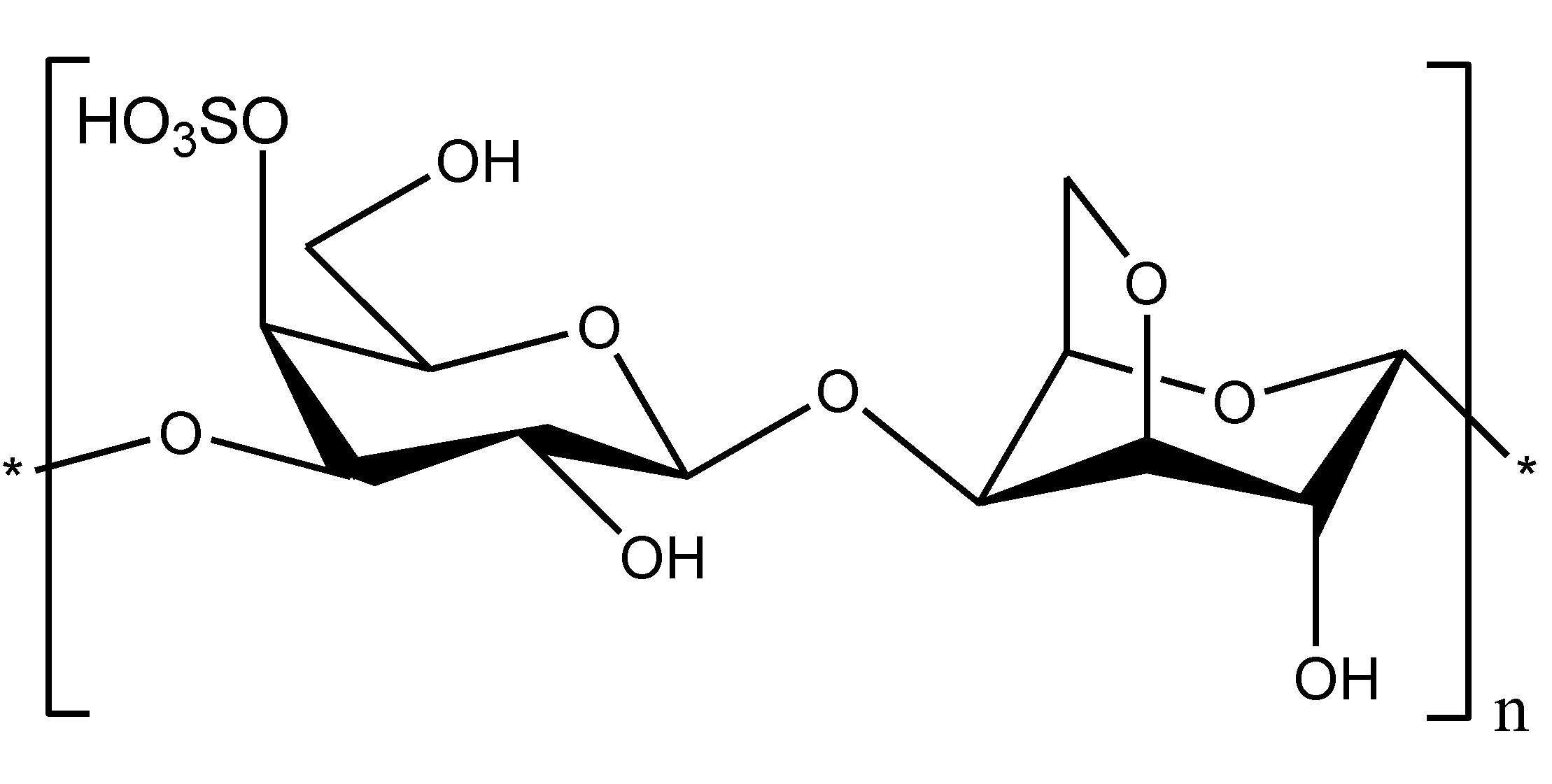
2.2. Chitosan as an LPS Binding and Endotoxin Neutralizing Agent

2.3. Chitosan and Carrageenan as Auxiliary Agents for Sepsis Therapy
3. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Cohen, J. The immunopathogenesis of sepsis. Nature 2002, 420, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Amersfoort, E.S.; van Berkel, T.J.; Kuiper, J. Receptors, mediators, and mechanisms involved in bacterial sepsis and septic shock. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 379–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, L.D.; Christ, W.J.; Rossignol, D.P. Inhibition of endotoxin response by synthetic TLR4 antagonists. Curr. Topics Med. Chem. 2004, 4, 1147–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietschel, E.T.; Kirikae, T.; Schade, F.U.; Mamat, U.; Schmidt, G.; Loppnow, H.; Ulmer, A.J.; Zahinger, U.; Seydel, U.; Di Padova, F.; et al. Bacterial endotoxin: Molecular relationships of structure to activity and fuction. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Imoto, M.; Kusumoto, S.; Shiba, T.; Naoki, H.; Iwashita, T.; Rietschel, E.T.; Wollenweber, H.-W.; Galanos, C.; Luderitz, O. Chemical structure of Escherichia coli lipid A: Linkage site of acyl groups in the disaccharide backbone. Tetrahedron Lett. 1983, 24, 4017–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roppel, J.; Mayer, H.; Weckesser, J. Identification of a 2,3-diamino-2,3-dideoxyhexose in the lipid A component of lipopolysaccharides of Rhodopseudomonas viridis and Rhodopseudomonaspalustris. Carbohydr. Res. 1975, 40, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, N.; Takayama, K.; Kurtz, R. Diphosphoryl lipid A obtained from nontoxic lipopolysaccharide of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides is on endotoxin antagonist in mice. Infect. Immun. 1991, 59, 441–444. [Google Scholar]
- Bunnell, E.; Lynn, M.; Habet, K.; Neumann, A.; Perdomo, C.A.; Friedhoff, L.T.; Rogers, S.L.; Parrillo, J.E. A lipid A analog, E5531, blocks the endotoxin response in human volunteers with experimental endotoxemia. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 28, 2713–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribi, E. Beneficial modification of the endotoxin molecule. J. Biol. Response Mod. 1984, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, K.; Yung, Y.C.; Fukushima, A.; Saiki, I.; Takahashi, T.A.; Fujihara, M.; Tonooka, S.; Azuma, I. A novel synthetic lipid A analog with low endotoxicity, DT-5461, prevents lethal endotoxemia. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 2859–2866. [Google Scholar]
- Raetz, C.R.H.; Reynolds, C.M.; Trent, M.S.; Bishop, R.E. Lipid A modification systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007, 76, 295–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahringer, U.; Linder, B.; Rietschel, E.T. Molecular structure of lipid, the endotoxic center of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 1994, 50, 211–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiRienzo, J.M.; MacLeod, R.A. Composition of the fractions separated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the lipopolysaccharide of a marine bacterium. J. Bacteriol. 1978, 136, 158–167. [Google Scholar]
- Moule, A.L.; Wilkinson, S.G. Composition of lipopolysaccharides grom Alteromonas putrefaciens (Shewanella putrefaciens). J. Gen. Microbiol. 1989, 135, 163–173. [Google Scholar]
- Corsaro, M.M.; Piaz, F.D.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M. Lipid A structure of Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis TAC 125: Use of electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of fatty acid distribution. J. Mass Spectrom. 2002, 37, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasikova, I.N.; Kapustina, N.V.; Svetashev, V.I.; Gorshkova, R.P.; Tomshich, S.V.; Nazarenko, E.L.; Komandrova, N.A.; Ivanova, E.P.; Gorshkova, N.M.; Romanenko, L.A.; et al. Chemical characterization of lipid A from some marine Proteobacteria. Biochemistry (Mosc.) 2001, 66, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Krasikova, I.N.; Kapustina, N.V.; Isakov, V.V.; Gorshkova, N.M.; Solov’eva, T.F. Elucidation of structure of lipid A from the marine Gram-negative bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis ATCC 14393T. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2004, 30, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, A.S.; Krasikova, I.N.; Anastyuk, S.D.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Solov’eva, T.F. Structure of lipid A from the marine Gram-negative bacterium Pseudoalteromonas nigrifaciens IAM 13010T. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2007, 43, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapustina, N.V.; Krasikova, I.N.; Isakov, V.V.; Gorshkova, N.M.; Solov’eva, T.F. Structure of lipid A from the lipopolysaccharide of marine γ-Proteobacterium Marinomonas vaga ATCC 27119T. Biochemistry (Mosc.) 2004, 69, C.407–C.412. [Google Scholar]
- Krasikova, I.N.; Kapustina, N.V.; Isakov, V.V.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Gorshkova, N.M.; Solov’eva, T.F. Detailed structure of lipid A from lipopolysaccharide from the marine proteobacterium Marinomonas vaga ATCC 27119T. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 2895–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobeva, E.V.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Isakov, V.V.; Krasikova, I.N.; Solov’eva, T.F. The structure of uncommon lipid A from the marine bacterium Marinomonas communis ATCC 27118T. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2005, 31, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobeva, E.V.; Krasikova, I.N.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Nedashkovskaya, O.I.; Solov’eva, T.F. An unusual lipid A from a marine bacterium Chryseobacterium scophtalmum CIP 104199T. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2006, 32, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutler, B.; Milsark, I.W.; Cerami, A.C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science 1985, 229, 869–871. [Google Scholar]
- Vorobeva, E.V.; Krasikova, I.N.; Solov’eva, T.F. Influence of lipopolysaccharides and lipids A from some marine bacteria on spontaneous and Escherichia coli LPS-induced TNF-α release from peripheral human blood cells. Biochemistry (Mosc.) 2006, 71, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christ, W.J.; Asano, O.; Robidoux, A.L.C.; Perez, M.; Wang, Y.A.; Dubuc, G.R.; Gavin, W.E.; Hawkins, L.D.; Mcguinness, P.D.; Mullarkey, M.A.; et al. E5531, a pure endotoxin antagonist of high potency. Science 1995, 268, 80–83. [Google Scholar]
- Kean, T.; Thanou, M. Biodegradation, biodistribution and toxicity of chitosan. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, K.; Nishimura, S.; Nishi, N.; Saiki, I.; Tokura, S.; Azuma, I. Immunologic activity of chitin and its derivatives. Vaccine 1984, 2, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Il’ina, A.V.; Varlamov, V.P. Chitosan-Based polyelectrolyte complexes: A review. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2005, 41, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anspach, F.B. Endotoxin removal by affinity sorbents. J. Biochem. Biophys. Meth. 2001, 49, 665–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Chen, X.G.; Xing, K.; Park, H.J. Antimicrobial properties of chitosan and mode of action: A state of the art review. Int. J. Food Microbiol 2010, 144, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurgens, G.; Muller, M.; Gardiel, P.; Koch, M.N.J.; Nakakubo, H.; Blume, A.; Brandenburg, K. Investigation into the interaction of recombinant human serum albumin with Re—Lipopolysaccharide and lipid A. J. Endotoxin Res. 2002, 8, 115–126. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, M.; Giorard, R.; Cazenave, P. Interaction of NK-lysine, a peptide produced by cytolytic lymphocytes, with endotoxin. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 201–205. [Google Scholar]
- Davydova, V.N.; Naberezhnykh, G.A.; Yermak, I.M.; Gorbach, V.I.; Solov’eva, T.F. Determination of binding constants of lipopolysaccharides of different structure with chitosan. Biochemistry (Mosc.) 2006, 71, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yermak, I.M.; Davidova, V.N.; Gorbach, V.I.; Luk’yanov, P.A.; Solov’eva, T.F.; Ulmer, A.J.; Buwitt-Beckmann, U.; Rietschel, E.T.; Ovodov, Y.S. Forming and immunological properties of some lipopolysaccharide-chitosan complexes. Biochimie 2006, 88, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydel, U.; Hawkins, L.; Schromm, A.B.; Heine, H.; Scheel, O.; Koch, M.H.; Brandenburg, K. The generalized endotoxic principle. Eur. J. Immunol. 2003, 33, 1586–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.G. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides—Themes and variations. Prog. Lipid Res. 1996, 35, 283–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naberezhnykh, G.A.; Gorbach, V.I.; Likhatskaya, G.N.; Davidova, V.N.; Solov’eva, T.F. Interaction of N-acylated chitosans with lipopolysaccharide. Biochemistry (Mosc.) 2008, 73, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydova, V.N.; Yermak, I.M.; Gorbach, V.I.; Krasikova, I.N.; Solov’eva, T.F. Interaction of bacterial endotoxins with chitosan. Effect of endotoxin structure, chitosan molecular mass, and ionic strength of the solution on the formation of the complex. Biochemistry (Mosc.) 2000, 65, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar]
- David, S.A.; Silverstein, R.; Amura, C.R.; Kielian, T.; Morrison, D.C. Lipopolyamines: Novel antiendotoxin compounds that reduce mortality in experimental sepsis caused by Gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 912–919. [Google Scholar]
- Millera, K.A.; Kumarb, E.V.K.S.; Wooda, S.J.; Cromera, J.R.; Dattab, A.; David, S.A. Lipopolysaccharide sequestrants: Structural correlates of activity and toxicity in novel acylhomospermines. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 2589–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naberezhnykh, G.A.; Gorbach, V.I.; Likhatskaya, G.N.; Bratskaya, S.Yu.; Solov’eva, T.F. Interaction of N-acylated and N-alkylated chitosans included in liposomes with lipopolysaccharide of Gram-negative bacteria. Biochemistry (Mosc.) 2013, 78, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, R.I. Hemoglobin enhances the binding of bacterial endotoxin to human endothelial cells. Thromb. Haemost. 1996, 76, 258–262. [Google Scholar]
- Tapping, R.I.; Akashi, S.; Miyake, K.; Godowski, P.J.; Tobias, P.S. Toll-like receptor 4, but not Toll-like receptor 2, is a signaling receptor for Escherichia and Salmonella lipopolysaccharides. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 5780–5787. [Google Scholar]
- Otterlei, M.; Varum, K.M.; Ryan, L.; Espevik, T. Characterization of binding and TNF-α-inducing ability of chitosans on monocytes: The involvement of CD 14. Vaccine 1994, 12, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.A. Management of sepsis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 1699–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yermak, I.M.; Khotimchenko, Y.S. Chemical Properties, Biological Activities and Applications of Carrageenan from Red Algae. In Recent Advances in Marine Biotechnology; Fingerman, M., Nagabhushanam, R., Eds.; Science Publisher Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 3, pp. 207–255. [Google Scholar]
- Döcke, W.D.; Randow, F.; Styrhe, U.; Krausch, D.; Asadullah, K.; Reinke, P.; Volk, H.-D.; Kox, W. Monocyte deactivation in septic patients: Restoration by INF-γ treatment. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 678–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanushko, L.A.; Solov’eva, T.F.; Zaporozhets, T.S.; Lukyanov, P.A.; Gorbach, V.I.; Besednova, N.N. Comparative study of immunomodulating properties of chitosan and its derivatives. Med. Immunol. (Russ.) 2007, 9, 397–404. [Google Scholar]
- Yermak, I.M.; Barabanova, A.O.; Aminin, D.L.; Davydova, V.N.; Sokolova, E.V.; Solov’eva, T.F.; Kim, Y.H.; Shin, K.S. Effects of structural peculiarities of carrageenans on their immunomodulatory and anticoagulant activities. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakova, A.M.; Astrina, O.S.; Bakhtina, Yu.A.; Maleev, V.V.; Barabanova, A.O.; Yermak, I.M. Possibility of correction of functional state of human trombocytes with natural polysaccharides in patients with alimentary toxic infections and in experimental endotoxinamia. Infektsionnye Bolezn. (Russ.) 2005, 3, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- Yermak, I.M.; Barabanova, A.O.; Kukarskikh, T.A.; Solovyova, T.F.; Bogdanovich, R.N.; Polyakova, A.M.; Astrina, O.S.; Maleev, V.V. Natural polysaccharide carrageenan inhibits toxic effect of Gram-negative bacterial endotoxins. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2006, 141, 191–193. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanushko, L.A.; Soloviova, T.F; Zaporozhets, T.S.; Somova, L.M.; Gorbatch, V.I. Antibacterial and antitoxic properties of chitosan and its derivatives. Pac. Med. J. (Russ.) 2009, 3, 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Khasina, E.I.; Sgrebneva, M.N.; Yermak, I.M.; Maleev, V.V. Effect of carrageenan on the non-specific resistance of mice with LPS-induced endotoxemia. J. Microbiol. Epidemiol. Immunol. (Russ.) 2007, 2, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Khasina, E.I.; Sgrebneva, M.N.; Yermak, I.M; Gorbach, V.I. Chitosan and unspecific resistance. Bull. FEB RAS (Russ.) 2005, 1, 62–71. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Solov'eva, T.; Davydova, V.; Krasikova, I.; Yermak, I. Marine Compounds with Therapeutic Potential in Gram-Negative Sepsis. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2216-2229. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11062216
Solov'eva T, Davydova V, Krasikova I, Yermak I. Marine Compounds with Therapeutic Potential in Gram-Negative Sepsis. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(6):2216-2229. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11062216
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolov'eva, Tamara, Viktoria Davydova, Inna Krasikova, and Irina Yermak. 2013. "Marine Compounds with Therapeutic Potential in Gram-Negative Sepsis" Marine Drugs 11, no. 6: 2216-2229. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11062216
APA StyleSolov'eva, T., Davydova, V., Krasikova, I., & Yermak, I. (2013). Marine Compounds with Therapeutic Potential in Gram-Negative Sepsis. Marine Drugs, 11(6), 2216-2229. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11062216



