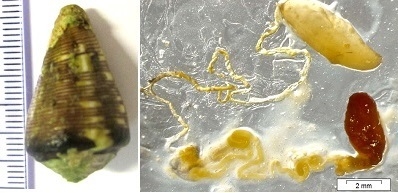
Conopeptides from Cape Verde Conus crotchii
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
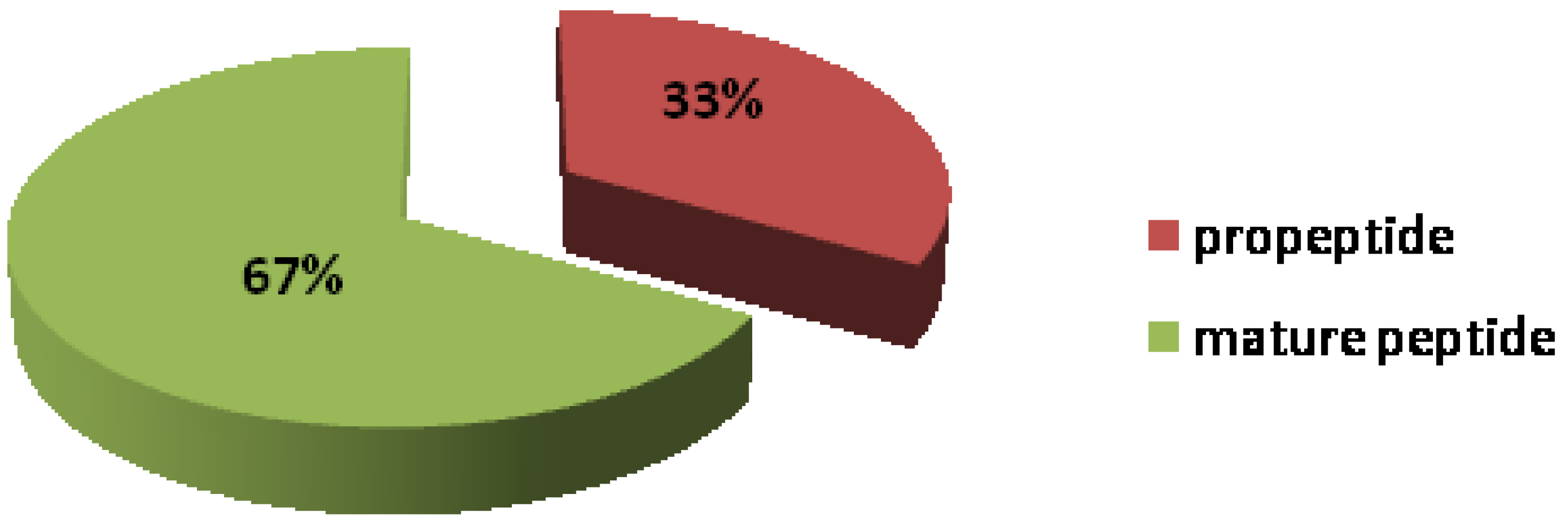
2.1. Peptide Mass Range Distribution
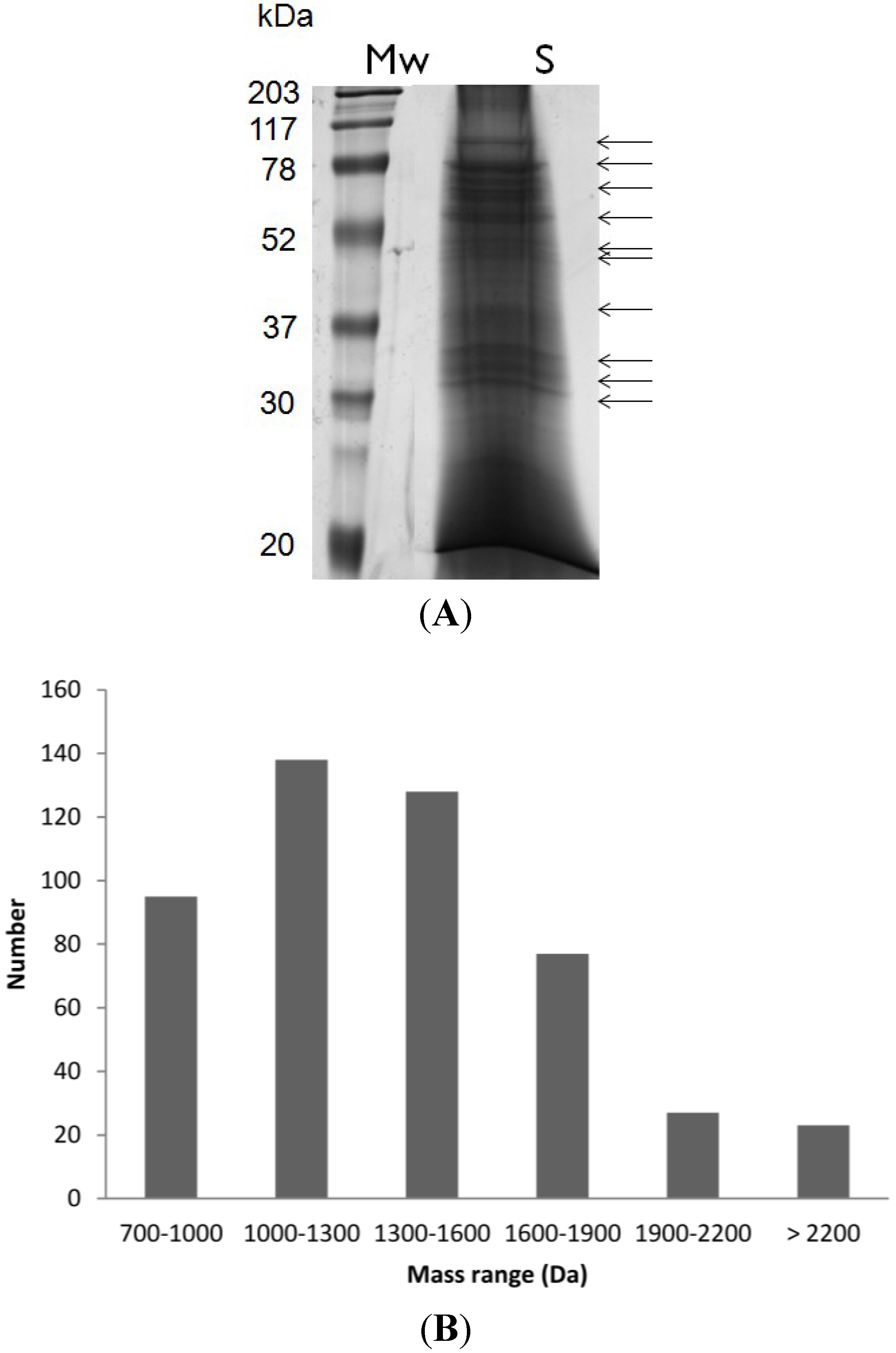
2.2. Peptides Sequence
| Conopeptide | Calculated Mass (Da) | Observed Mass (Da) | Sequence | Cysteine |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1916.99 2042.78 | 1916.90 2042.72 | TKTDDDVPLSSLRDNLK
ECCEDGWCCTAAPLTGR | 4 |
| 2 | 795.44 2232.96 | 795.48 2233.05 | EQHLIR
CCDFVKYVGMNPPADKCR | 3 |
| 3 | 1701.89 2042.73 | 1701.80 2042.69 | LWALMKGPRQCTPK
DAPCDDNNQCCSGLECK | 4 |
| 4 | 2545.05 | 2544.99 | RPECCSDPRCNSTHPELCGGR | 4 |
| 5 | 1076.56 | 1076.57 | IRASEGCRK AVGLIDKMRR KGDRCGTHLCCPGLR | 4 |
| 1158.67 1786.82 | 1158.62 1786.88 | |||
| 6 | 1790.81 1693.79 | 1790.87 1693.80 | FQFLNFCCNEK ILEDIVSTALATCCK | 4 |
| 7 | 1687.88 1970.76 | 1687.88 1970.66 | ASDGGNAAASDLIALTIK GCCSRPPCALSNPDYCG | 4 |
| 8 | 798.32 1790.83 | 798.29 1790.89 | CVGVCF
G EQNKTCCGLTNGRPR | 4 |
| 9 | 2042.76 798.34 | 2042.69 798.32 | SGGACNSHDQCCINFCR KATSTCM | 5 |
| 10 | 1169.51 1190.53 | 1169.55 1190.55 | NFGDTRSCGR RGKPCPCCR | 4 |
| 11 | 966.49 2205.99 | 966.46 2206.08 | KCNRFNK IPNQKCFQHLDDCCSRK | 4 |
| 12 | 985.45 1352.56 | 983.46 1352.59 | RGHGRSCPG NGCTCVYHWR | 3 |
2.3. BLAST Search for Conotoxins
| Conotoxin (Accession) | Protein sequence | E-Value a |
|---|---|---|
| TxVA (P81755.2) |  | 2e-12 |
| im23.3 (D0PX86.1) |  | 7e-21 |
| Ec15a (B0KZ79.1) |  | 3e-28 |
| Ai1.2 (P0CB08.1) |  | 9e-17 |
| Bu2 (P0CY61.1) |  | 7e-30 |
| Ca5.1 (P0C666.1) |  | 4e-22 |
| PnMGMR-02 (Q9BP56.1) |  | 8e-30 |
| VnMSGL-0123 (Q9BP59.1) | 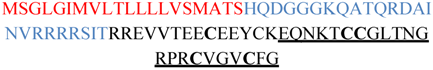 | 2e-15 |
| Eb6.18 (C7T1P1.1) | 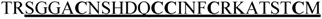 | 2e-19 |
| Leo-O2 (P0C903.1) |  | 1e-12 |
| PVIIA (P56633.2) |  | 7e-20 |
| VxXXB (P0C1W6.2) |  | 2e-14 |
| Name | C. species | Diet | Superfamily | Family | Cys pattern (framework) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ec15a | C. emaciatus | v | O2 | unknown | C-C-CC-C-C-C-C (XV) | [31] |
| Ca5.1 | C. caracteristicus | v | T | unknown | CC-CC (V) | [34] |
| im23.3 | C. imperialis | v | A | unknown | C-C-C-CC-C (XXIII) | [35] |
| Eb6.18 | C. ebraeus | v | O1 | unknown | C-C-CC-C-C (VI/VII) | [36] |
| Leo-O2 | C. leopardus | v | O1 | unknown | C-C-CC-C-C (VI/VII) | [37] |
| VxXXB | C. vexillum | v | D | α | C-CC-C-CC-C-C-C (XX) | [38] |
| TxVA | C. textile | m | T | є | CC-CC (V) | [39] |
| Ai1.2 | C. ammairalis | m | A | α | CC-C-C (I) | [31] |
| PnMGMR-02 | C. pennaceus | m | A | α | CC-C-C (I) | [31] |
| VnMSGL-0123 | C. ventricosus | m | O3 | unknown | C-C-CC-C-C (VI/VII) | [31] |
| Bu2 | C. bullatus | p | O1 | unknown | C-C-CC-C-C (VI/VII) | [40] |
| PVIIA | C. purpurascens | p | O1 | κ | C-C-CC-C-C (VI/VII) | [41] |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cone Snail Specimen and Venom Extraction
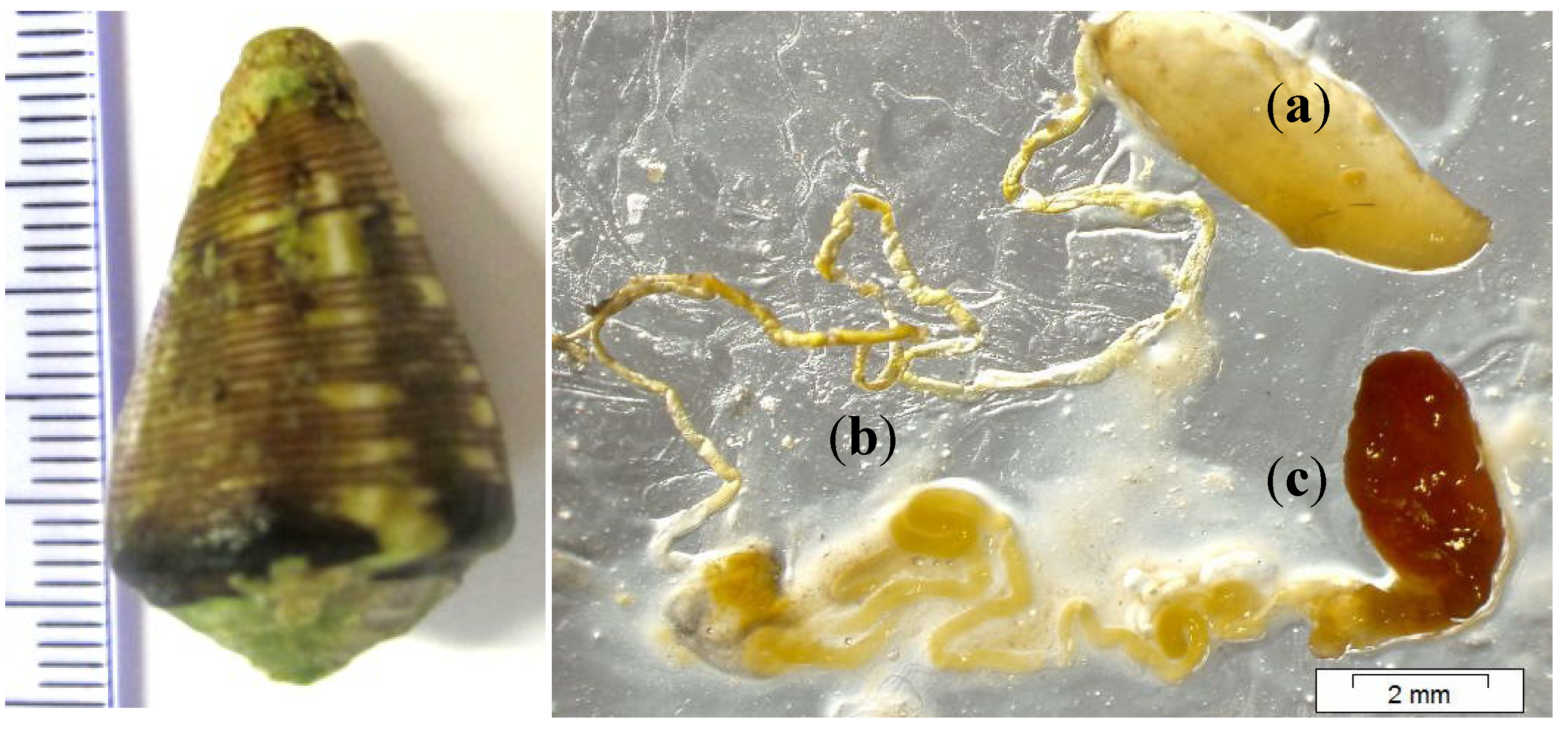
3.2. Sample Fractionation, SDS-PAGE
3.3. Protein Reduction, Alkylation and Trypsin Digestion
3.4. MALDI-TOF-MS Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dobson, R.; Collodoro, M.; Gilles, N.; Turtoi, A.; de Pauw, E.; Quinton, L. Secretion and maturation of conotoxins in the venom ducts of Conus textile. Toxicon 2012, 60, 1370–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, B.M. Conus venom peptides: Reflections from the biology of clades and species. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2002, 33, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlau, H.; Olivera, B.M. Conus venoms: A rich source of novel ion channel-targeted peptides. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 41–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, B.M. Conus venom peptides, receptor and ion channel targets, and drug design: 50 million years of neuropharmacology. Mol. Biol. Cell 1997, 8, 2101–2109. [Google Scholar]
- Kauferstein, S.; Porth, C.; Kendel, Y.; Wunder, C.; Nicke, A.; Kordis, D.; Favreau, P.; Koua, D.; Stöcklin, R.; Mebs, D. Venomic study on cone snails (Conus spp.) from South Africa. Toxicon 2011, 57, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J. Remarkable inter- and intra-species complexity of conotoxins revealed by LC/MS. Peptides 2009, 30, 1222–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favreau, P.; Stöcklin, R. Marine snail venoms: Use and trends in receptor and channel neuropharmacology. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, B.M.; Cruz, L.J. Conotoxins, in retrospect. Toxicon 2001, 39, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcintosh, J.M.; Santos, A.D.; Olivera, B.M. Conus peptides targeted to specific nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes. Peptides 1999, 68, 59–88. [Google Scholar]
- Essack, M.; Bajic, V.B.; Archer, J.C. Conotoxins that confer therapeutic possibilities. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1244–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, B.M. Conus peptides: Biodiversity-based discovery and exogenomics. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 31173–31177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Zhangsun, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Xie, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X. Identification and molecular diversity of T-superfamily conotoxins from Conus lividus and Conus litteratus. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2006, 68, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Yang, S.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, P. New conotoxin SO-3 targeting N-type voltage-sensitive calcium channels. Mar. Drugs 1995, 4, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violette, A.; Leonardi, A.; Piquemal, D.; Terrat, Y.; Biass, D. Recruitment of glycosyl hydrolase proteins in a cone snail venomous arsenal: Further insights into biomolecular features of Conus venoms. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 258–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, B.M. Conus Snail Venom Peptides. In Handbook of Biologically Active peptides; Kastin, A.J., Ed.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 381–388. [Google Scholar]
- Biass, D.; Dutertre, S.; Gerbault, A.; Menou, J.-L.; Offord, R.; Favreau, P.; Stöcklin, R. Comparative proteomic study of the venom of the piscivorous cone snail Conus consors. J. Proteomics 2009, 72, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowski, J.A.; Kelley, W.P.; Sweedler, J.V.; Gilly, W.F.; Schulz, J.R. Intraspecific variation of venom injected by fish-hunting Conus snails. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 2873–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, R.L.; Castilho, R.; Rüber, L.; Zardoya, R. Patterns of cladogenesis in the venomous marine gastropod genus Conus from the Cape Verde islands. Syst. Biol. 2005, 54, 634–650. [Google Scholar]
- Kaas, Q.; Westermann, J.-C.; Craik, D.J. Conopeptide characterization and classifications: An analysis using ConoServer. Toxicon 2010, 55, 1491–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biass, D.; Križaj, I.; Leonardi, A.; Dutertre, S. Peptidomics and proteomics of Conus consors cone snail venom. Comp. Gen. Pharmacol. 2009, 72, 37592. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Haegen, A.; Peigneur, S.; Dyubankova, N.; Möller, C.; Marí, F.; Diego-García, E.; Naudé, R.; Lescrinier, E.; Herdewijn, P.; Tytgat, J. Pc16a, the first characterized peptide from Conus pictus venom, shows a novel disulfide connectivity. Peptides 2012, 34, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaas, Q.; Yu, R.; Jin, A.H.; Dutertre, S.; Craik, D.J. ConoServer: Updated content, knowledge, and discovery tools in the conopeptide database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D325–D330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczek, O.; Bulaj, G.; Olivera, B.M. Conotoxins and the posttranslational modification of secreted gene products. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 3067–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannu, N.S.; Hemby, S.E. De novo protein sequence analysis of Macaca mulatta. BMC Genomics 2007, 8, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standing, K. Peptide and protein de novo sequencing by mass spectrometry. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2003, 13, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechi, S.; Chait, B.T. Modification of cysteine residues by alkylation. A tool in peptide mapping and protein identification. Peptides 1998, 70, 5150–5158. [Google Scholar]
- Jakubowski, J.A.; Sweedler, J.V. Sequencing and mass profiling highly modified conotoxins using global reduction/alkylation followed by mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 6541–6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, W.R. Disulfide structures of highly bridged peptides: A new strategy for analysis. Protein Sci. 1993, 2, 1732–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, M.B.; López-Vera, E.; Heimer de la Cotera, E.P.; Falcón, A.; Olivera, B.M.; Maillo, M. I-Conotoxins in vermivorous species of the West Atlantic: Peptide sr11a from Conus spurius. Peptides 2007, 28, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilly, W.F.; Richmond, T.A.; Duda, T.F.; Elliger, C.; Lebaric, Z.; Schulz, J.; Bingham, J.P.; Sweedler, J.V. A diverse family of novel peptide toxins from an unusual cone snail, Conus californicus. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Zhangsun, D.; Feng, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Hu, Y. Diversity of the O-superfamily conotoxins from Conus miles. J. Peptide Sci. 2007, 13, 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.; Ye, M.; Wang, Y.; Shao, X.; Yuan, D.; Liu, J.; Hawrot, E.; Wang, C.; Chi, C. A new subfamily of conotoxins belonging to the A-superfamily. Peptides 2010, 31, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Wu, X.; Han, Y.; Yuan, D.; Chi, C.; Wang, C. Identification of six novel T-1 conotoxins from Conus pulicarius by molecular cloning. Peptides 2007, 28, 2116–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puillandre, N.; Koua, D.; Favreau, P.; Olivera, B.M.; Stöcklin, R. Molecular phylogeny, classification and evolution of conopeptides. J. Mol. Evol. 2012, 74, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, T.F.; Chang, D.; Lewis, B.D.; Lee, T. Geographic variation in venom allelic composition and diets of the widespread predatory marine gastropod Conus ebraeus. PLoS One 2009, 4, e6245. [Google Scholar]
- Remigio, E.A.; Duda, T.F. Evolution of ecological specialization and venom of a predatory marine gastropod. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 1156–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughnan, M.; Nicke, A.; Jones, A.; Schroeder, C.I.; Nevin, S.T.; Adams, D.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Lewis, R.J. Identification of a novel class of nicotinic receptor antagonists: Dimeric conotoxins VxXIIA, VxXIIB, and VxXIIC from Conus vexillum. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 24745–24755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, C.S.; Steel, D.; Jacobsen, R.B.; Lirazan, M.B.; Cruz, L.J.; Hooper, D.; Shetty, R.; DelaCruz, R.C.; Nielsen, J.S.; Zhou, L.M.; et al. The T-superfamily of conotoxins. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 30664–30671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Bandyopadhyay, P.K.; Olivera, B.M.; Yandell, M. Characterization of the Conus bullatus genome and its venom-duct transcriptome. BMC Genomics 2011, 12, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Shon, K.; Stocker, M.; Terlau, H.; Stu, W.; Jacobsen, R.; Walker, C.; Grilley, M.; Watkins, M.; Hillyard, D.R.; Gray, W.R.; et al. κ-Conotoxin PVIIA is a peptide inhibiting the shaker K+ channel. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhoff, V.; Arold, N.; Taube, D.; Ehrhardt, W. Improved staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels including isoelectric focusing gels with clear background at nanogram sensitivity using Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 and R-250. Electrophoresis 1988, 9, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalume, D.E.; Stenflo, J.; Czerwiec, E.; Hambe, B.; Furie, B.C.; Furie, B.; Roepstorff, P. Structure determination of two conotoxins from Conus textile by a combination of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and biochemical methods. JMS 2000, 35, 145–156. [Google Scholar]
- Zugasti-Cruz, A.; Aguilar, M.B.; Falcón, A.; Olivera, B.M.; Heimer de la Cotera, E.P. Two new 4-Cys conotoxins (framework 14) of the vermivorous snail Conus austini from the Gulf of Mexico with activity in the central nervous system of mice. Peptides 2008, 29, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padliya, N.D.; Wood, T.D. Improved peptide mass fingerprinting matches via optimized sample preparation in MALDI mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 627, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, C.; di Francesco, L.; Oliverio, M.; Palazzo, P.; Massilia, G.R.; Ascenzi, P.; Polticelli, F.; Schininà, M.E. Conus ventricosus venom peptides profiling by HPLC-MS: A new insight in the intraspecific variation. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puerto, M.; Campos, A.; Prieto, A.; Cameán, A.; de Almeida, A.M.; Coelho, A.V.; Vasconcelos, V. Differential protein expression in two bivalve species; Mytilus galloprovincialis and Corbicula fluminea; exposed to Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii cells. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 101, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Neves, J.; Campos, A.; Osório, H.; Antunes, A.; Vasconcelos, V. Conopeptides from Cape Verde Conus crotchii. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2203-2215. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11062203
Neves J, Campos A, Osório H, Antunes A, Vasconcelos V. Conopeptides from Cape Verde Conus crotchii. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(6):2203-2215. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11062203
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeves, Jorge, Alexandre Campos, Hugo Osório, Agostinho Antunes, and Vitor Vasconcelos. 2013. "Conopeptides from Cape Verde Conus crotchii" Marine Drugs 11, no. 6: 2203-2215. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11062203
APA StyleNeves, J., Campos, A., Osório, H., Antunes, A., & Vasconcelos, V. (2013). Conopeptides from Cape Verde Conus crotchii. Marine Drugs, 11(6), 2203-2215. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11062203