Immunomodulatory Effect of Marine Cembrane-Type Diterpenoids on Dendritic Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Suppression of TNF-α Expression in BMDCs by Cembrane-Type Diterpenoids
2.2. Blocking of Various TLR Agonists-Mediated TNF-α Production in BMDCs by Lobocrassin B
| Compound | Structure | Molecular Weight | CC20 (μM) * |
|---|---|---|---|
| (9E,13E)-5-Acetoxy-6-hydroxy-9,13-dimethyl-3-methylene-3,3a,4,5,6,7,8,11,12,14a-decahydro-2H-cyclotrideca[b]furan-2-one (1) |  | 332.43 | 38 |
| (9E,13E)-5-Acetoxy-6-acetyl-9,13-dimethyl-3-methylene-3,3a,4,5,6,7,8,11,12,14a-decahydro-2H-cyclotrideca[b]furan-2-one (2) | 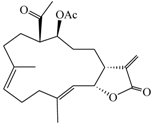 | 374.47 | 33 |
| Lobocrassin B (3) | 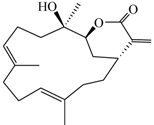 | 318.45 | 39 |
| (−)14-Deoxycrassin (4) | 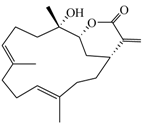 | 318.45 | 26.9 |
| Cembranolide B (5) | 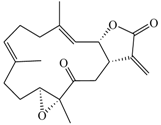 | 330.42 | 36 |
| 13-Acetoxysarcocrassolide (6) | 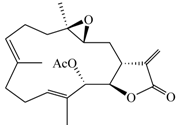 | 374.47 | 4.2 |
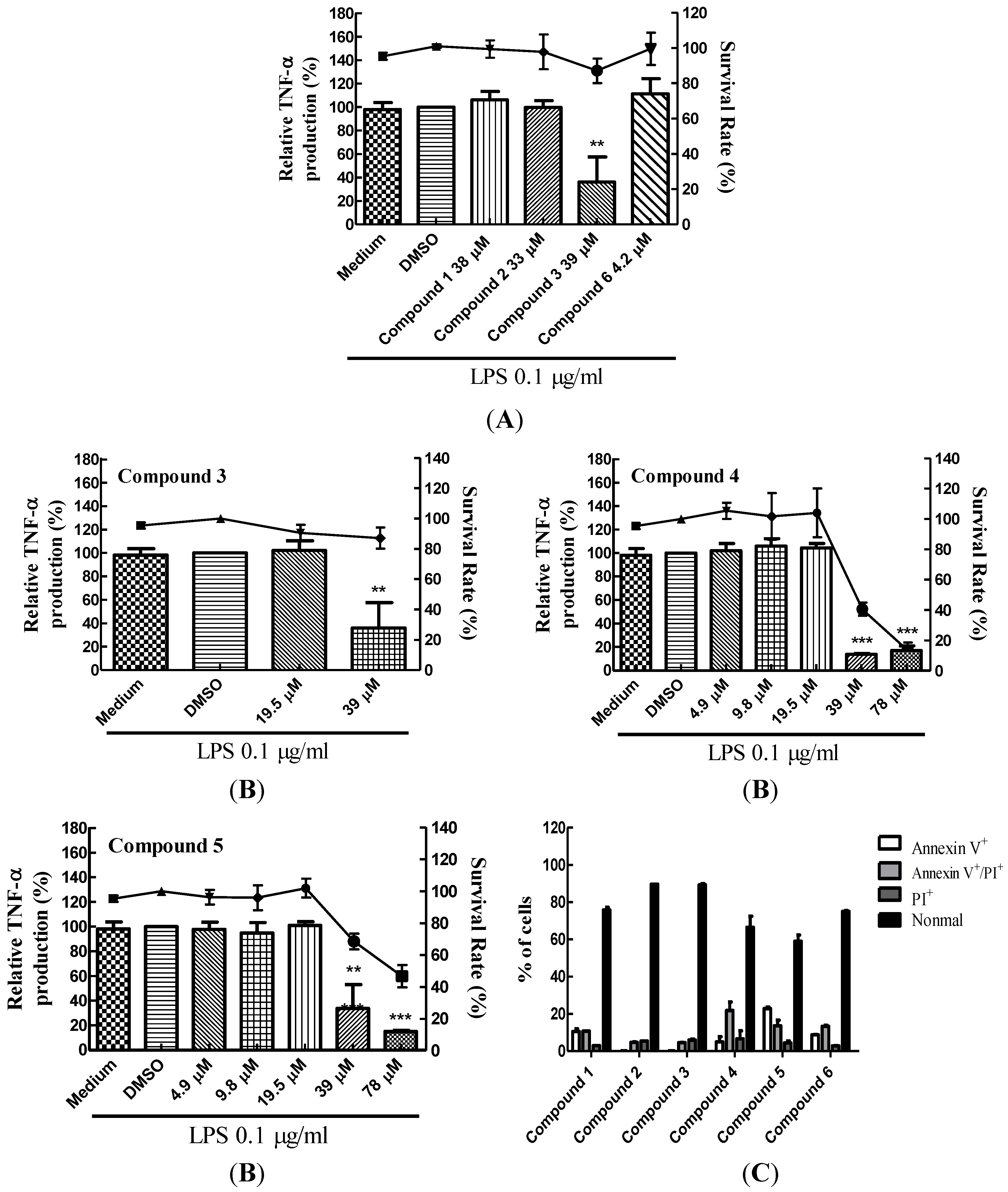
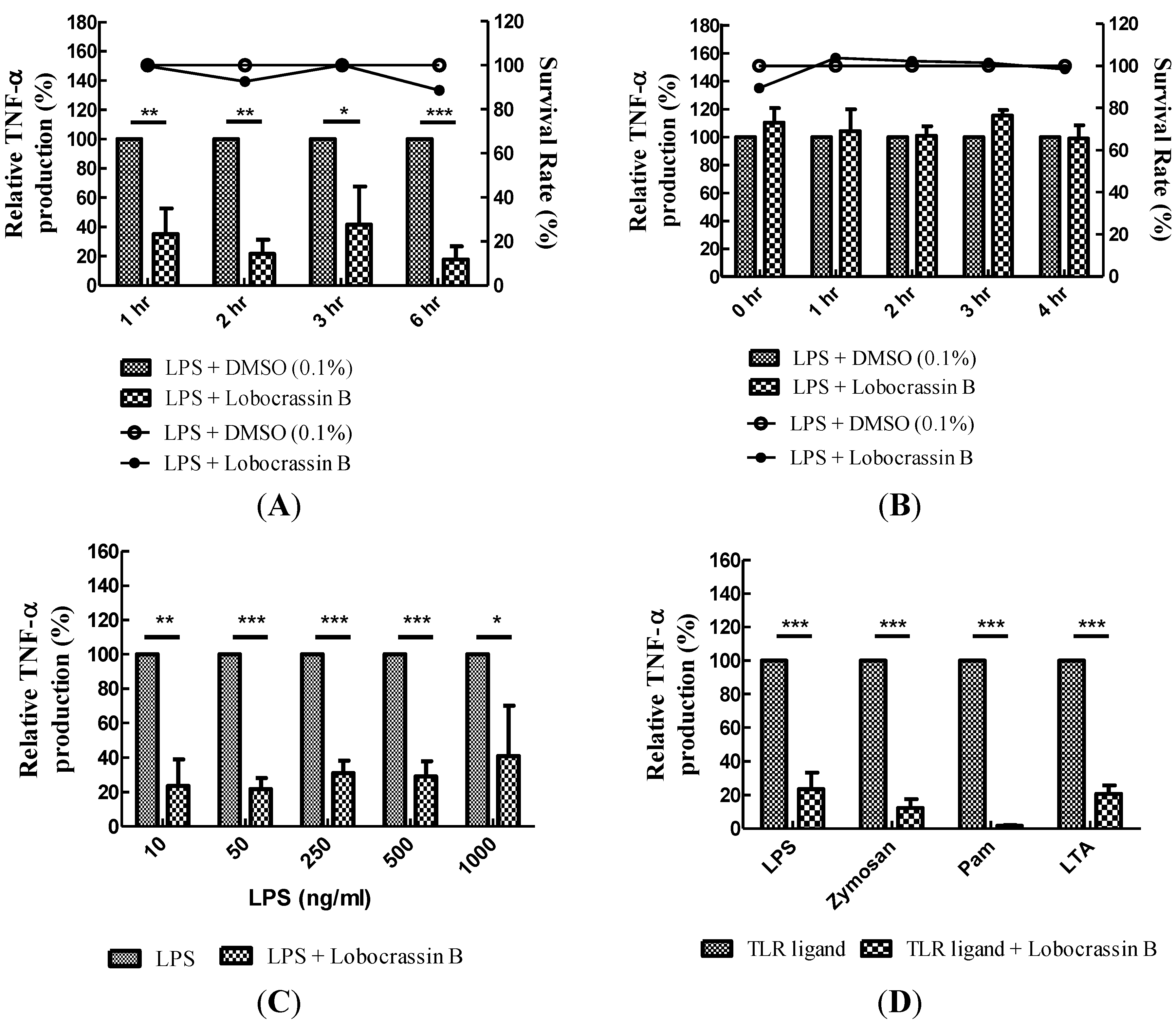
2.3. Dose-Dependent Inhibition of TNF-α Production and NF-κB (p65) Nuclear Translocation by Lobocrassin B

2.4. Attenuation of LPS-Induced DC Maturation and Endocytosis by Lobocrassin B
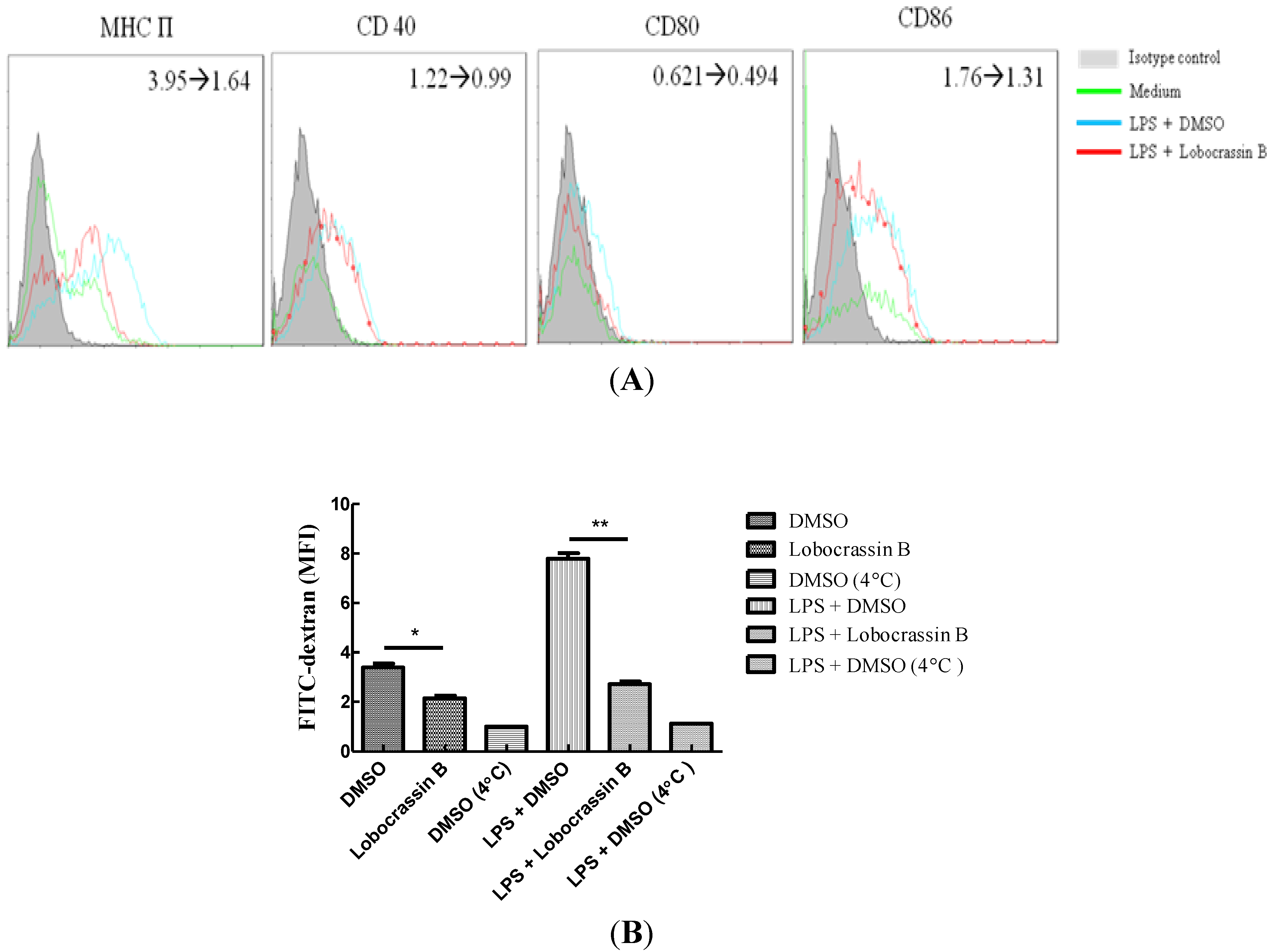
2.5. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Mice and Generation of DCs
3.2. Preparation of Cembrane-Type Diterpenoids
3.3. Cytotoxicity Assay of Cembrane-Type Diterpenoids
3.4. Measurement of TNF-α Production
3.5. High Content Image Analysis of NF-κB Nuclear Translocation
3.6. Assay of DC Maturation and Endocytosis Activity
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Mayer, A.M.; Rodriguez, A.D.; Berlinck, R.G.; Hamann, M.T. Marine pharmacology in 2005–6: Marine compounds with anthelmintic, antibacterial, anticoagulant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis, and antiviral activities; affecting the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 283–308. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, A.M.; Rodriguez, A.D.; Berlinck, R.G.; Fusetani, N. Marine pharmacology in 2007–8: Marine compounds with antibacterial, anticoagulant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antiprotozoal, anti-tuberculosis, and antiviral activities; affecting the immune and nervous system, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 2011, 153, 191–222. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, A.M.; Rodriguez, A.D.; Berlinck, R.G.; Hamann, M.T. Marine pharmacology in 2003–4: Marine compounds with anthelmintic antibacterial, anticoagulant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antiplatelet, antiprotozoal, anti-tuberculosis, and antiviral activities; affecting the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 2007, 145, 553–581. [Google Scholar]
- Hegazy, M.E.; Su, J.H.; Sung, P.J.; Sheu, J.H. Cembranoids with 3,14-ether linkage and a secocembrane with bistetrahydrofuran from the Dongsha Atoll soft coral Lobophytum sp. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.Y.; Su, J.H.; Lu, M.C.; Hwang, T.L.; Wang, W.H.; Chen, J.J.; Sheu, J.H.; Kuo, Y.H.; Weng, C.F.; Fang, L.S.; et al. Lobocrassins A–E: New cembrane-type diterpenoids from the soft coral Lobophytum crassum. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.L.; Su, J.H. Tetrahydrofuran cembranoids from the cultured soft coral Lobophytum crassum. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2526–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.T.; Wang, S.K.; Duh, C.Y. Cembranoids from the Dongsha Atoll soft coral Lobophytum crassum. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2705–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnard, I.; Jhaumeer-Laulloo, S.B.; Bontemps, N.; Banaigs, B.; Aknin, M. New lobane and cembrane diterpenes from two comorian soft corals. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 359–372. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, C.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Yeh, H.C.; Sheu, J.H. Cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory cembranoids from the soft coral Lobophytum crassum. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1819–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanzola, M.; Furuta, T.; Kohno, Y.; Fukumitsu, S.; Yasukochi, S.; Watari, K.; Tanaka, C.; Higuchi, R.; Miyamoto, T. Four new cembrane diterpenes isolated from an Okinawan soft coral Lobophytum crassum with inhibitory effects on nitric oxide production. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 2010, 58, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Quang, T.H.; Ha, T.T.; Minh, C.V.; Kiem, P.V.; Huong, H.T.; Ngan, N.T.; Nhiem, N.X.; Tung, N.H.; Tai, B.H.; Thuy, D.T.; et al. Cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory cembranoids from the Vietnamese soft coral Lobophytum laevigatum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 2625–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhika, P.; Rao, P.R.; Archana, J.; Rao, N.K. Anti-inflammatory activity of a new sphingosine derivative and cembrenoid diterpene (lobohedleolide) isolated from marine soft corals of Sinularia crassa TIXIER-DURIVAULT and Lobophytum species of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 1311–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.Y.; Chen, N.F.; Chen, W.F.; Hung, H.C.; Lee, H.P.; Lin, Y.Y.; Wang, H.M.; Sung, P.J.; Sheu, J.H.; Wen, Z.H. Sinularin from indigenous soft coral attenuates nociceptive responses and spinal neuroinflammation in carrageenan-induced inflammatory rat model. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1899–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, R.M. The dendritic cell system and its role in immunogenicity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1991, 9, 271–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vliet, S.J.; den Dunnen, J.; Gringhuis, S.I.; Geijtenbeek, T.B.; van Kooyk, Y. Innate signaling and regulation of Dendritic cell immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 435–440. [Google Scholar]
- Steinman, R.M.; Inaba, K.; Turley, S.; Pierre, P.; Mellman, I. Antigen capture, processing, and presentation by dendritic cells: recent cell biological studies. Hum. Immunol. 1999, 60, 562–567. [Google Scholar]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. TLR signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 816–825. [Google Scholar]
- Richmond, A. NF-κB, chemokine gene transcription and tumour growth. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, R.M.; Banchereau, J. Taking dendritic cells into medicine. Nature 2007, 449, 419–426. [Google Scholar]
- Galkina, E.; Ley, K. Immune and inflammatory mechanisms of atherosclerosis (*). Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 165–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyoshi, M.K.; He, R.; Kumar, L.; Yoon, J.; Geha, R.S. Cellular and molecular mechanisms in atopic dermatitis. Adv. Immunol. 2009, 102, 135–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Munro, M.H.; Northcote, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 196–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.H.; Ahmed, A.F.; Sung, P.J.; Chao, C.H.; Kuo, Y.H.; Sheu, J.H. Manaarenolides A–I, diterpenoids from the soft coral Sinularia manaarensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.Y.; Su, J.H.; Lu, Y.; Wen, Z.H.; Dai, C.F.; Kuo, Y.H.; Sheu, J.H. Cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory cembranoids from the Dongsha Atoll soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 1936–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.Y.; Lu, Y.; Su, J.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Dai, C.F.; Kuo, Y.H.; Sheu, J.H. Bioactive cembranoids from the dongsha atoll soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.H.; Wen, Z.H. Bioactive cembrane-based diterpenoids from the soft coral Sinularia triangular. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.A.; Gustafson, K.R.; Boyd, M.R. HIV-Inhibitory cembrane derivatives from a Philippines collection of the soft coral Lobophytum species. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 531–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthee, G.F.; Konig, G.M.; Wright, A.D. Three new diterpenes from the marine soft coral Lobophytum crassum. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tello, E.; Castellanos, L.; Arevalo-Ferro, C.; Duque, C. Cembranoid diterpenes from the Caribbean sea whip Eunicea knighti. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Lin, Y.F.; Wen, Z.H.; Su, J.H.; Kuo, Y.H.; Chiang, M.Y.; Sheu, J.H. Anti-inflammatory cembranoids from the soft corals Sinularia querciformis and Sinularia granosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1754–1759. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Su, J.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Kuo, Y.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Hsu, C.H.; Sheu, J.H. Cembranoids from the soft corals Sinularia granosa and Sinularia querciformis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 2010, 58, 464–466. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.Y.; Yu, Y.L.; Cheng, W.C.; OuYang, C.N.; Fu, E.; Chu, C.L. Immunosuppressive effect of quercetin on dendritic cell activation and function. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 6815–6821. [Google Scholar]
- Cella, M.; Engering, A.; Pinet, V.; Pieters, J.; Lanzavecchia, A. Inflammatory stimuli induce accumulation of MHC class II complexes on dendritic cells. Nature 1997, 388, 782–787. [Google Scholar]
- Ardeshna, K.M.; Pizzey, A.R.; Devereux, S.; Khwaja, A. The PI3 kinase, p38 SAP kinase, and NF-κB signal transduction pathways are involved in the survival and maturation of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Blood 2000, 96, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Watts, C.; West, M.A.; Zaru, R. TLR signalling regulated antigen presentation in dendritic cells. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2010, 22, 124–130. [Google Scholar]
- Folmer, F.; Jaspars, M.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Marine natural products as targeted modulators of the transcription factor NF-κB. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 603–617. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, I.K.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, H.S.; Kwon, H.J. Streptochlorin, a marine natural product, inhibits NF-κB activation and suppresses angiogenesis in vitro. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 17, 1338–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Terracciano, S.; Aquino, M.; Rodriquez, M.; Monti, M.C.; Casapullo, A.; Riccio, R.; Gomez-Paloma, L. Chemistry and biology of anti-inflammatory marine natural products: molecules interfering with cyclooxygenase, NF-κB and other unidentified targets. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 1947–1969. [Google Scholar]
- Folmer, F.; Jaspars, M.; Solano, G.; Cristofanon, S.; Henry, E.; Tabudravu, J.; Black, K.; Green, D.H.; Kupper, F.C.; Aalbersberg, W.; et al. The inhibition of TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation by marine natural products. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 592–606. [Google Scholar]
- Bowie, A.; O’Neill, L.A. Oxidative stress and nuclear factor-kappaB activation: A reassessment of the evidence in the light of recent discoveries. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 59, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, C.L.; Lowell, C.A. The Lyn tyrosine kinase differentially regulates dendritic cell generation and maturation. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 2880–2889. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, M.C.; Hwang, S.L.; Chang, F.R.; Chen, Y.H.; Chang, T.T.; Hung, C.S.; Wang, C.L.; Chu, Y.H.; Pan, S.H.; Wu, Y.C. Immunostimulatory effect of Antrodia camphorata extract on functional maturation of dendritic cells. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Iguchi, K.; Kikuchi, H.; Tsukitani, Y.; Horiai, H.; Shibayama, F. Studies on marine natural products. IV The stereochemistry of 13-membered carbocyclic cembranolide diterpenes from the soft coral Lobophytum pauciflorum (Ehrenberg). Tetrahedron Lett. 1980, 21, 3911–3914. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, T.; Ding, Y.; Deng, Z.; van Ofwegen, L.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Sinulaflexiolides A–K, cembrane-type diterpenoids from the chinese soft coral Sinularia flexibilis. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumi, T.; Ohtani, I.; Inouye, Y.; Kakisawa, H. Absolute configurations of cytotoxic marine cembranolides; Consideration of mosher’s method. Tetrahedron Lett. 1988, 29, 4731–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duh, C.Y.; Wang, S.K.; Chung, S.G.; Chou, G.C.; Dai, C.F. Cytotoxic cembrenolides and steroids from the formosan soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1634–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.-Y.; Lu, M.-C.; Su, J.-H.; Chu, C.-L.; Shiuan, D.; Weng, C.-F.; Sung, P.-J.; Huang, K.-J. Immunomodulatory Effect of Marine Cembrane-Type Diterpenoids on Dendritic Cells. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1336-1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11041336
Lin C-Y, Lu M-C, Su J-H, Chu C-L, Shiuan D, Weng C-F, Sung P-J, Huang K-J. Immunomodulatory Effect of Marine Cembrane-Type Diterpenoids on Dendritic Cells. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(4):1336-1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11041336
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Ching-Yen, Mei-Chin Lu, Jui-Hsin Su, Ching-Liang Chu, David Shiuan, Ching-Feng Weng, Ping-Jyun Sung, and Kao-Jean Huang. 2013. "Immunomodulatory Effect of Marine Cembrane-Type Diterpenoids on Dendritic Cells" Marine Drugs 11, no. 4: 1336-1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11041336
APA StyleLin, C.-Y., Lu, M.-C., Su, J.-H., Chu, C.-L., Shiuan, D., Weng, C.-F., Sung, P.-J., & Huang, K.-J. (2013). Immunomodulatory Effect of Marine Cembrane-Type Diterpenoids on Dendritic Cells. Marine Drugs, 11(4), 1336-1350. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11041336







