Astaxanthin Suppresses MPP+-Induced Oxidative Damage in PC12 Cells through a Sp1/NR1 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Cell Viability after MPP+-Induced Toxicity in PC12 Cells
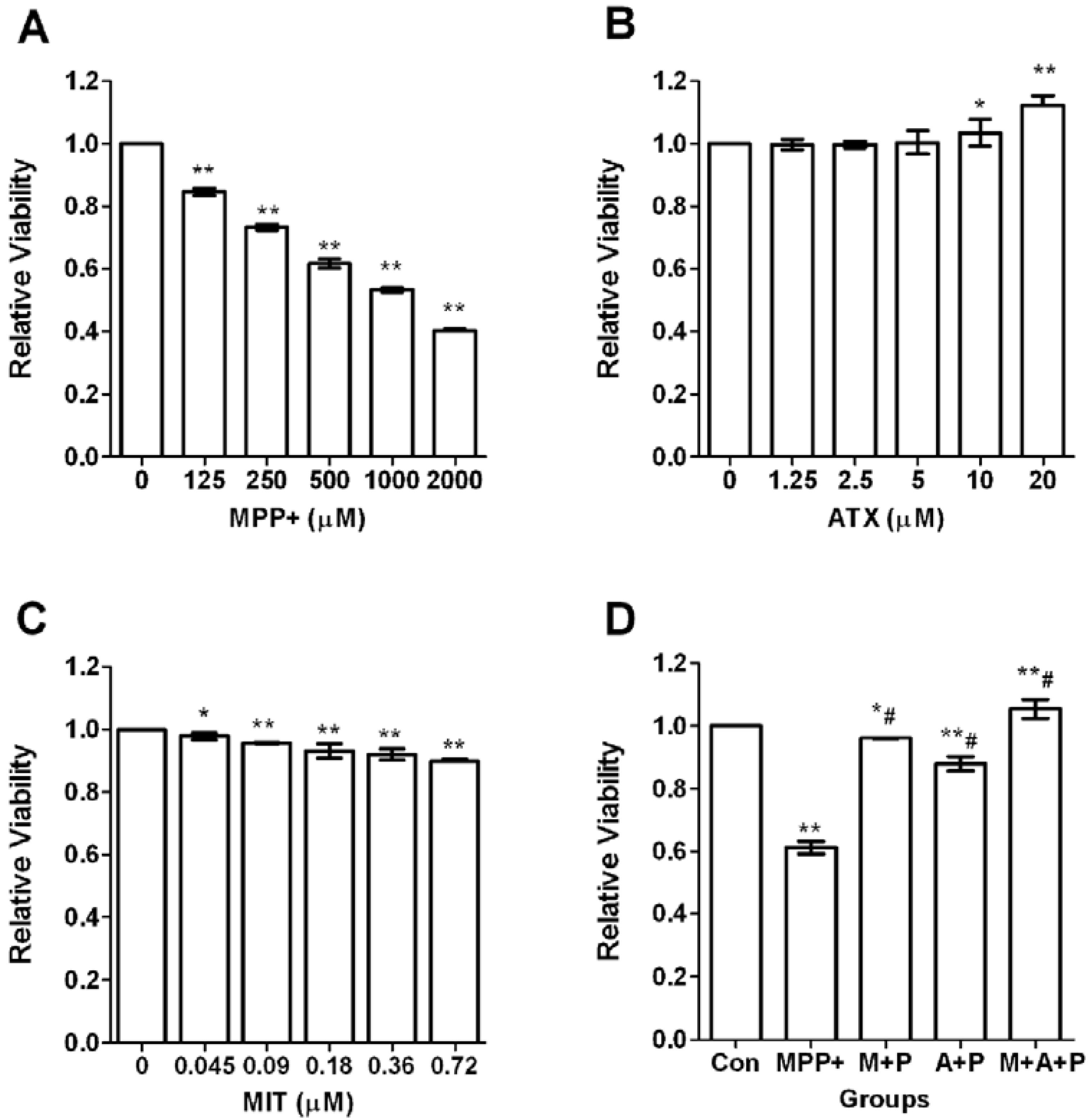
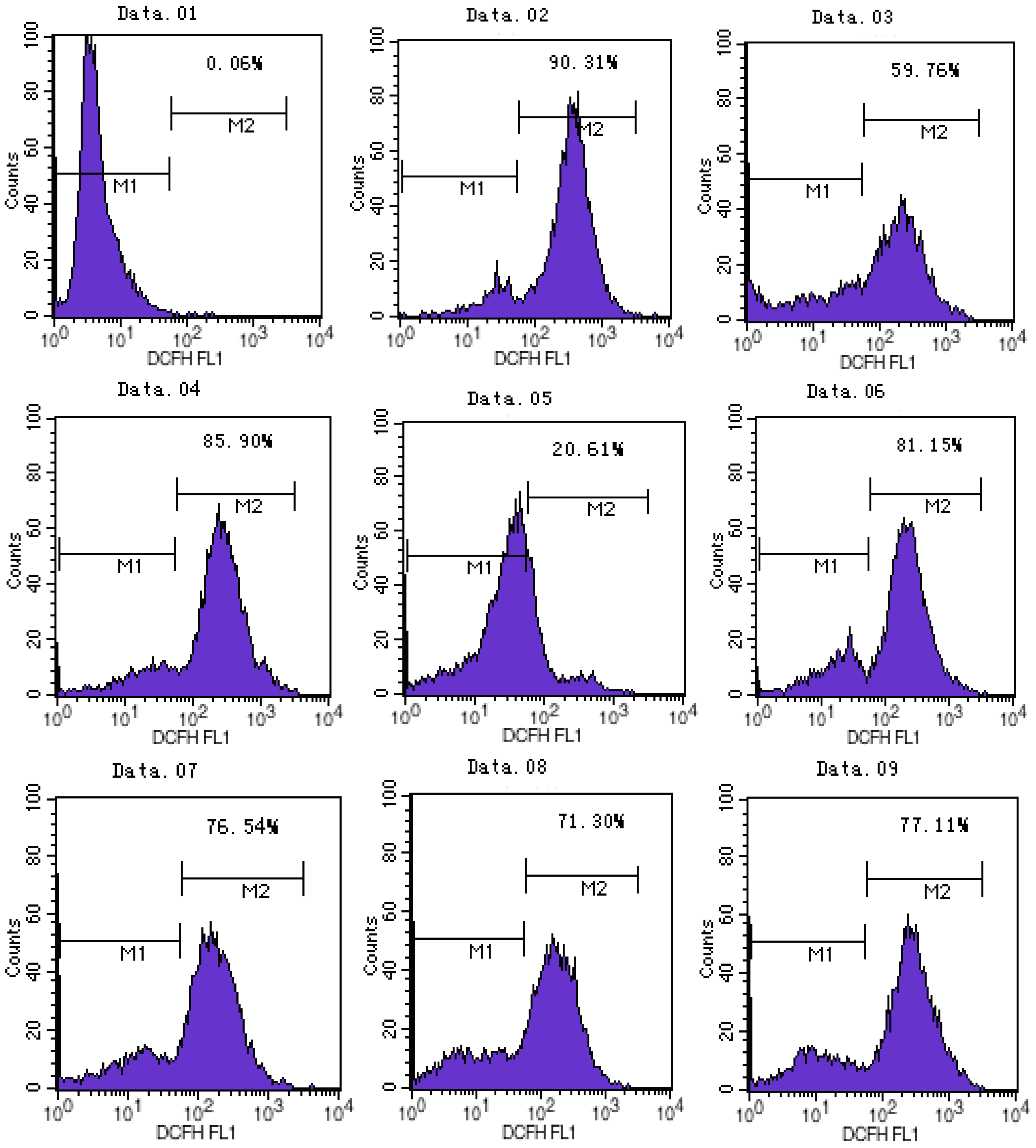
2.2. ATX/MIT Protect against MPP+-Induced Toxicity in PC12 Cells by Reducing ROS
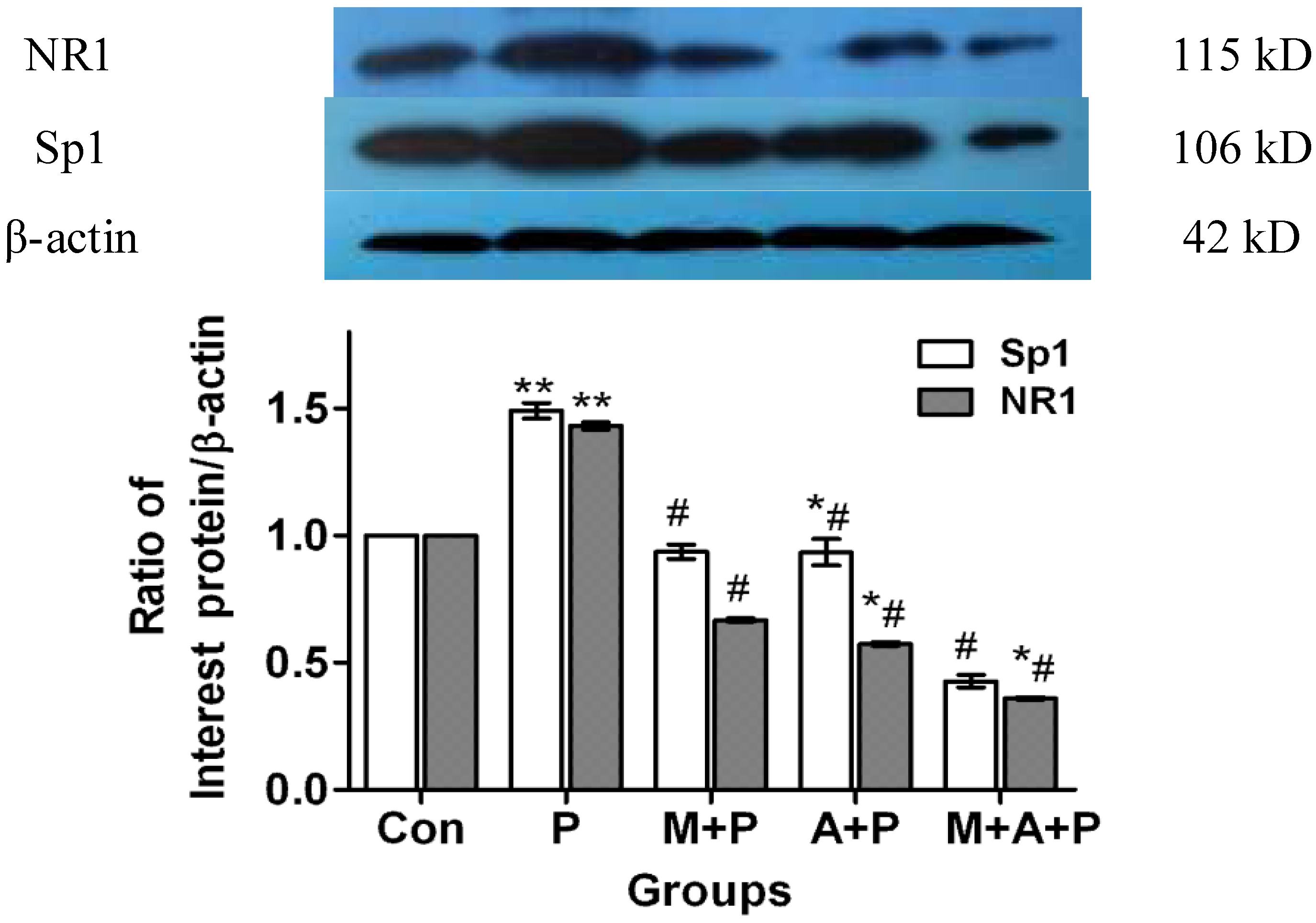
2.3. The Expression Level of Protein Sp1 and NR1
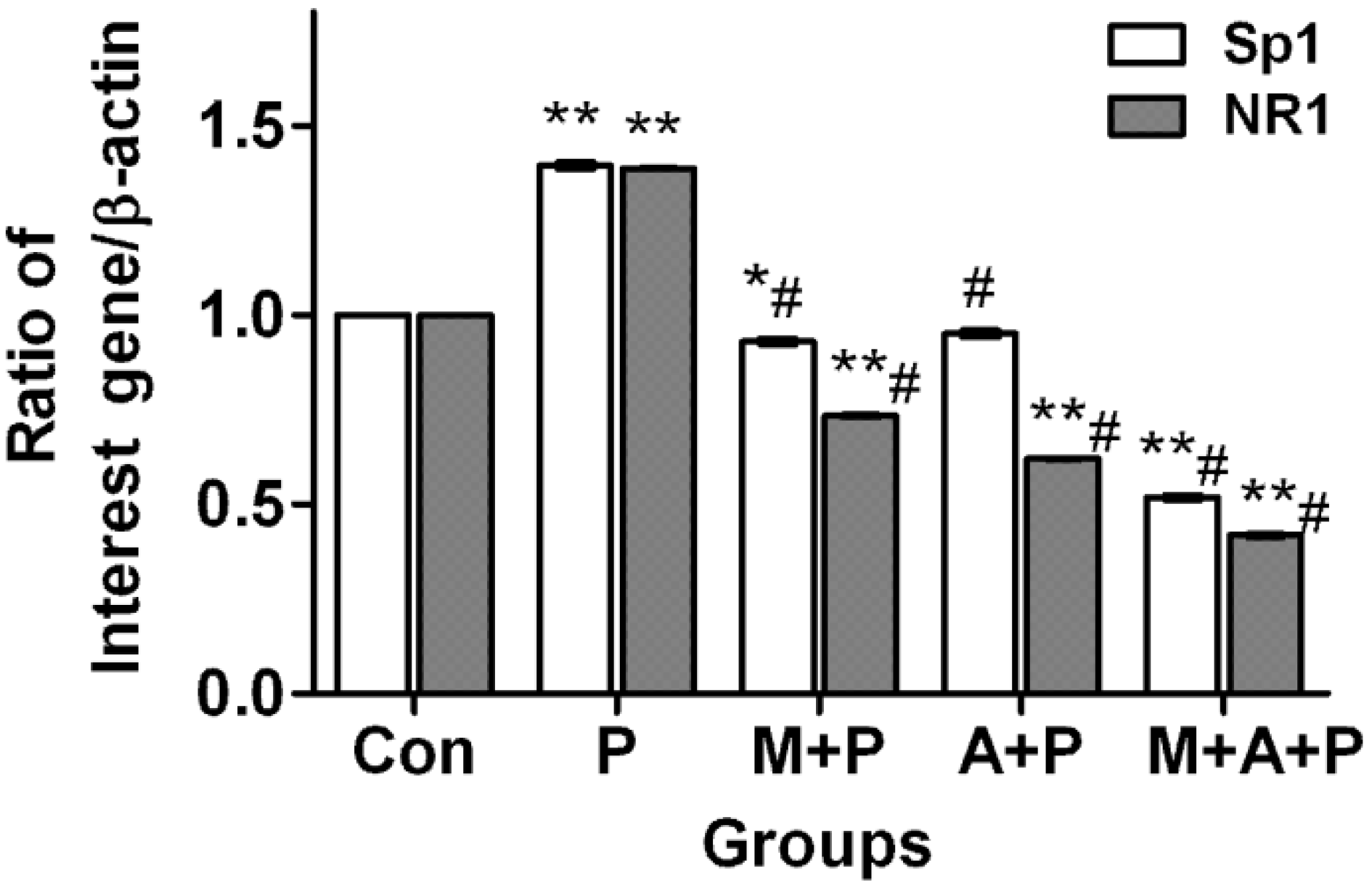
2.4. The Expression Level of Sp1 and NR1 mRNA
2.5. Localization of Sp1 and NR1 Protein, and Possible Nuclear Transfer of Sp1 in PC12 Cells
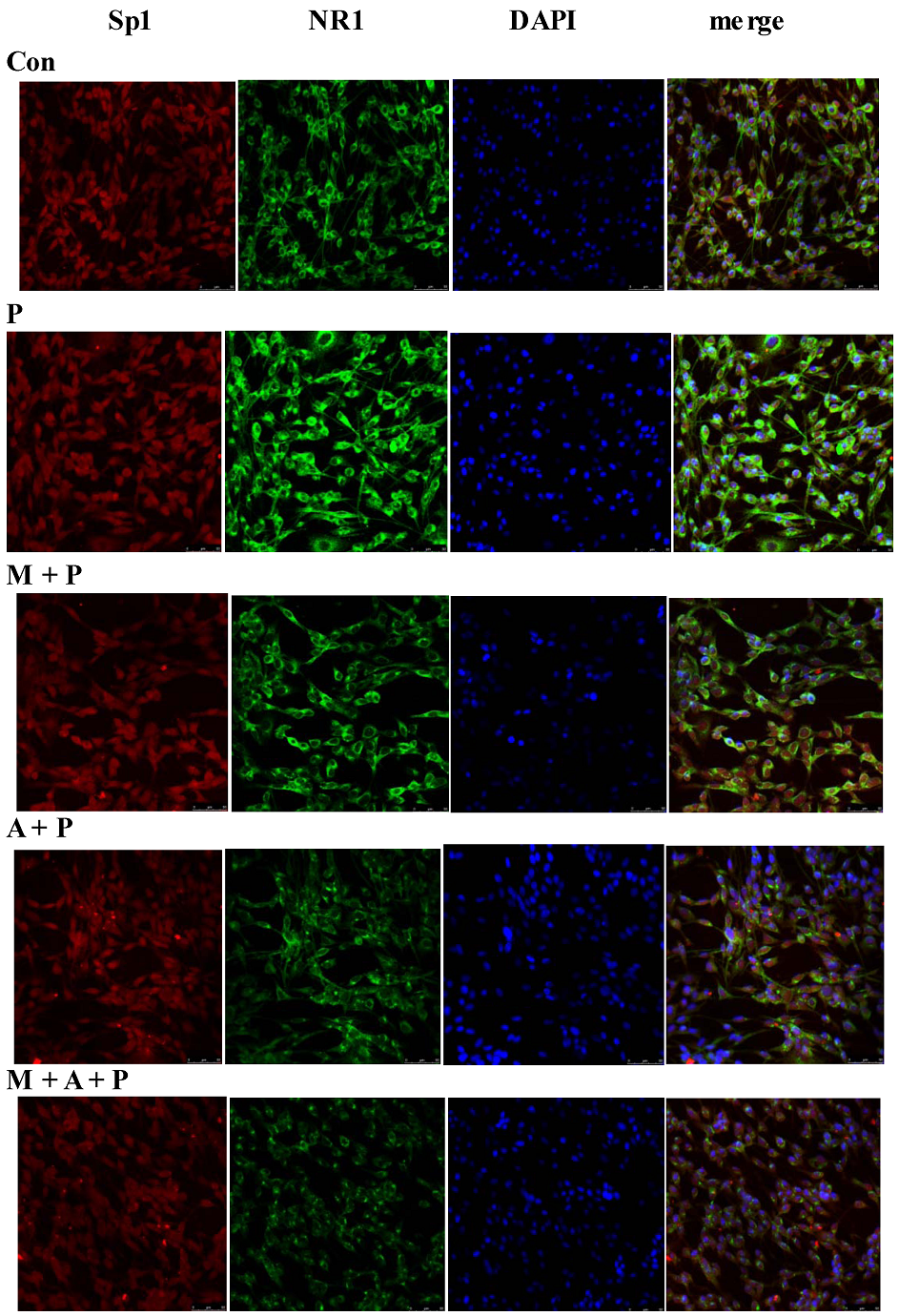
2.6. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Cell Culture
3.3. MTT Assay to Evaluate Survival Cells
3.4. ROS Test
3.5. Immunoblot Analysis
3.6. RNA Isolation and Real-Time PCR
3.7. Cell Immunofluorescence Technique
3.8. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Conflict of Interest
Authors’ Contributions
Acknowledgments
References
- Hou, R.R.; Chen, J.Z.; Chen, H.; Kang, X.G.; Li, M.G.; Wang, B.R. Neuroprotective effects of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) on paraquat-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2008, 32, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Sun, X.; Kang, X. Tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside attenuates MPP+-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells by inhibiting ROS generation and modulating JNK activation. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 483, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, P.; Olanow, C.W. Understanding cell death in Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 1998, 44, 72–84. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, Y.; Tsuji, S.; Satoh, A.; Ishikura, M.; Shirasawa, T.; Shimizu, T. Protective effects of astaxanthin on 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. J. Neurochem. 2008, 107, 1730–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Kuo, C.C.; Chou, J.; Delvolve, A.; Jackson, S.N.; Post, J.; Woods, A.S.; Hoffer, B.J.; Wang, Y.; Harvey, B.K. Astaxanthin reduces ischemic brain injury in adult rats. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 1958–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Osawa, T. Astaxanthin Protects Neuronal Cells against Oxidative Damage and Is a Potent Candidate for Brain Food. In Food Factors for Health Promotion; Yoshikawa, T., Ed.; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2009; Volume 61, pp. 178–191. [Google Scholar]
- Hota, S.K.; Prasad, D.; Ilavazhagan, G.; Singh, S.B. Oxidative-Stress-induced alterations in Sp factors mediate transcriptional regulation of the NR1 subunit in hippocampus during hypoxia. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awobuluyi, M.; Vazhappilly, R.; Sucher, N.J. Translational activity of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunit NR1 mRNA in PC12 cells. Neurosignals 2003, 12, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterton, J.E.; Awobuluyi, M.; Premkumar, L.S.; Takahashi, H.; Talantova, M.; Shin, Y.; Cui, J.; Tu, S.; Sevarino, K.A.; Nakanishi, N.; et al. Excitatory glycine receptors con-taining the NR3 family of NMDA receptor subunits. Nature 2002, 415, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kosaras, B.; Aleyasin, H.; Han, J.A.; Park, D.S.; Ratan, R.R.; Kowall, N.W.; Ferrante, R.J.; Lee, S.W.; Ryu, H. Role of cyclooxygenase-2 induction by transcription factor Sp1 and Sp3 in neuronal oxidative and DNA damage response. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 2375–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, F.; Paule, M.G.; Slikker, W., Jr. Anesthetic-induced oxidative stress and potential protection. Sci. World J. 2010, 10, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Chan, S.L.; Haughey, N.; Lee, W.T.; Mattson, M.P. Selective and biphasic effect of the membrane lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxy-2,3-nonenal on N-methyl-d-aspartate channels. J. Neurochem. 2001, 78, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazhappilly, R.; Wee, K.S.; Sucher, N.J.; Low, C.M. A non-muscle myosin II motor links NR1 to retrograde trafficking and proteasomal degradation in PC12 cells. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 56, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langston, J.W.; Irwin, I.; Langston, E.B.; Forno, L.S. 1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP+): Identification of a metabolite of MPTP, a toxin selective to the substantia nigra. Neurosci. Lett. 1984, 48, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleagraharan, N.; Ponnusamy, K. Neuroprotective effect of Centella asiatica extract (CAE) on experimentally induced parkinsonism in aged Sprague-Dawley rats. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 35, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiueh, C.C.; Krishna, G.; Tulsi, P.; Obata, T.; Lang, K.; Huang, S.J.; Murphy, D.L. Intracranial microdialysis of salicylic acid to detect hydroxyl radical generation through dopamine autooxidation in the caudate nucleus: Effects of MPP+. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1992, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shi, L.; Xie, Y.; Ma, C.; Li, W.; Su, X.; Huang, S.; Chen, R.; Zhu, Z.; Mao, Z.; Han, Y.; Li, M. SP600125, a new JNK inhibitor, protects dopaminergic neurons in the MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 48, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, E.; Rotilio, D.; di Matteo, V.; di Giulio, C.; Cacchio, M.; Algeri, S. A review of specific dietary antioxidants and the effects on biochemical mechanisms related to neurodegenerative processes. Neurobiol. Aging 2002, 23, 719–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harish, G.; Venkateshappa, C.; Mythri, R.B.; Dubey, S.K.; Mishra, K.; Singh, N.; Vali, S.; Bharath, M.M. Bioconjugates of curcumin display improved protection against glutathione depletion mediated oxidative stress in a dopaminergic neuronal cell line: Implications for Parkinson’s disease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 2631–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.C.; Mong, M.C.; Yin, M.C. Antioxidative and anti-inflammatory neuroprotective effects of astaxanthin and canthaxanthin in nerve growth factor differentiated PC12 cells. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, H225–H231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.M.; Asoh, S.; Hiranuma, H.; Ohsawa, I.; Iio, K.; Satou, A.; Ishikura, M.; Ohta, S. Astaxanthin protects mitochondrial redox state and functional integrity against oxidative stress. J. Nutr. Biochen. 2010, 21, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraiz, T.; Guillén, H. Inhibition of the bioactivation of the neurotoxin MPTP by antioxidants, redox agents and monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispo, J.A.; Piché, M.; Ansell, D.R.; Eibl, J.K.; Tai, I.T.; Kumar, A.; Ross, G.M.; Tai, T.C. Protective effects of methyl gallate on H2O2-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 393, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Kim, C.S.; Lee, Y.J. Astaxanthin protects against MPTP/MPP+-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and ROS production in vivo and in vitro. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.P.; Liu, S.Y.; Sun, H.; Wu, X.M.; Li, J.J.; Zhu, L. Neuroprotective effect of astaxanthin on H(2)O(2)-induced neurotoxicity in vitro and on focal cerebral ischemia in vivo. Brain Res. 2010, 1360, 40–48. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, H.Y.; Ji, S.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Shin, J.S.; Cheong, H.T.; Kim, J.T.; Park, I.C.; Kong, H.S.; Park, C.K.; et al. Antioxidative effects of astaxanthin against nitric oxide-induced oxidative stress on cell viability and gene expression in bovine oviduct epithelial cell and the developmental competence of bovine IVM/IVF embryos. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2010, 45, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Q.; Sun, X.B.; Xu, Y.X.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Zhu, C.Q. Astaxanthin upregulates heme oxygenase-1 expression through ERK1/2 pathway and its protective effect against beta-amyloid-induced cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. Brain Res. 2010, 1360, 159–167. [Google Scholar]
- Dasari, A.; Bartholomew, J.N.; Volonte, D.; Galbiati, F. Oxidative stress induces premature senescence by stimulating caveolin-1 gene transcription through p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase/Sp1-mediated activation of two GC-rich promoter elements. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 10805–10814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betzen, C.; White, R.; Zehendner, C.M.; Pietrowski, E.; Bender, B.; Luhmann, H.J.; Kuhlmann, C.R. Oxidative stress upregulates the NMDA receptor on cerebrovascular endothelium. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller-Burke, D.; Koehler, R.C.; Martin, L.J. Rapid NMDA receptor phosphorylation and oxidative stress precede striatal neurodegeneration after hypoxic ischemia in newborn piglets and are attenuated with hypothermia. Int.J. Dev. Neurosci. 2008, 26, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hota, S.K.; Barhwal, K.; Sinqh, S.B.; Sairam, M.; Ilavazhagan, G. NR1 and GluR2 expression mediates excitotoxicity in chronic hypobaric hypoxia. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 1142–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Kwon, K.H. Neuroprotective effects of astaxanthin in oxygen-glucose deprivation in SH-SY5Y cells and global cerebral ischemia in rat. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2010, 47, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Chyun, J.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Line, L.L.; Chew, B.P. Astaxanthin decreased oxidative stress and inflammation and enhanced immune response in humans. Nutr. Metab. (Lond.) 2010, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.W.; Ho, P.W.; Zhang, W.Y.; Liu, H.F.; Kwok, K.H.; Yiu, D.C.; Chan, K.H.; Kung, M.H.; Ramsden, D.B.; Ho, S.L. Transcriptional regulation of UCP4 by NF-kappaB and its role in mediating protection against MPP+ toxicity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountain, S.J.; Cheonq, A.; Li, J.; Dondas, N.Y.; Zeng, F.; Wood, I.C.; Beech, D.J. K(v)1.5 potassium channel gene regulation by Sp1 transcription factor and oxidative stress. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 293, H2719–H2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleiman, S.F.; Lanqley, B.C.; Basso, M.; Berlin, J.; Xia, L.; Payappilly, J.B.; Kharel, M.K.; Guo, H.; Marsh, J.L.; Thompson, L.M.; et al. Mithramycin is a gene-selective Sp1 inhibitor that identifies a biological intersection between cancer and neurodegeneration. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 6858–6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, P.M.; Abramson, R.D.; Watson, R.; Gelfand, D.H. Detection of specific polymerase chain reaction product by utilizing the 5′----3′ exonuclease activity of Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 7276–7280. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(2-Delta Delta C(T)). Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Huang, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, X. Astaxanthin protects against MPP+-induced oxidative stress in PC12 cells via the HO-1/NOX2 axis. BMC Neurosci. 2012, 13, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, Q.; Zhang, X.; Huang, B.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, X. Astaxanthin Suppresses MPP+-Induced Oxidative Damage in PC12 Cells through a Sp1/NR1 Signaling Pathway. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1019-1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11041019
Ye Q, Zhang X, Huang B, Zhu Y, Chen X. Astaxanthin Suppresses MPP+-Induced Oxidative Damage in PC12 Cells through a Sp1/NR1 Signaling Pathway. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(4):1019-1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11041019
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Qinyong, Xiaodong Zhang, Bixia Huang, Yuangui Zhu, and Xiaochun Chen. 2013. "Astaxanthin Suppresses MPP+-Induced Oxidative Damage in PC12 Cells through a Sp1/NR1 Signaling Pathway" Marine Drugs 11, no. 4: 1019-1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11041019
APA StyleYe, Q., Zhang, X., Huang, B., Zhu, Y., & Chen, X. (2013). Astaxanthin Suppresses MPP+-Induced Oxidative Damage in PC12 Cells through a Sp1/NR1 Signaling Pathway. Marine Drugs, 11(4), 1019-1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11041019



