Comparison of Physicochemical Characteristics and Anticoagulant Activities of Polysaccharides from Three Sea Cucumbers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Extraction and Purification
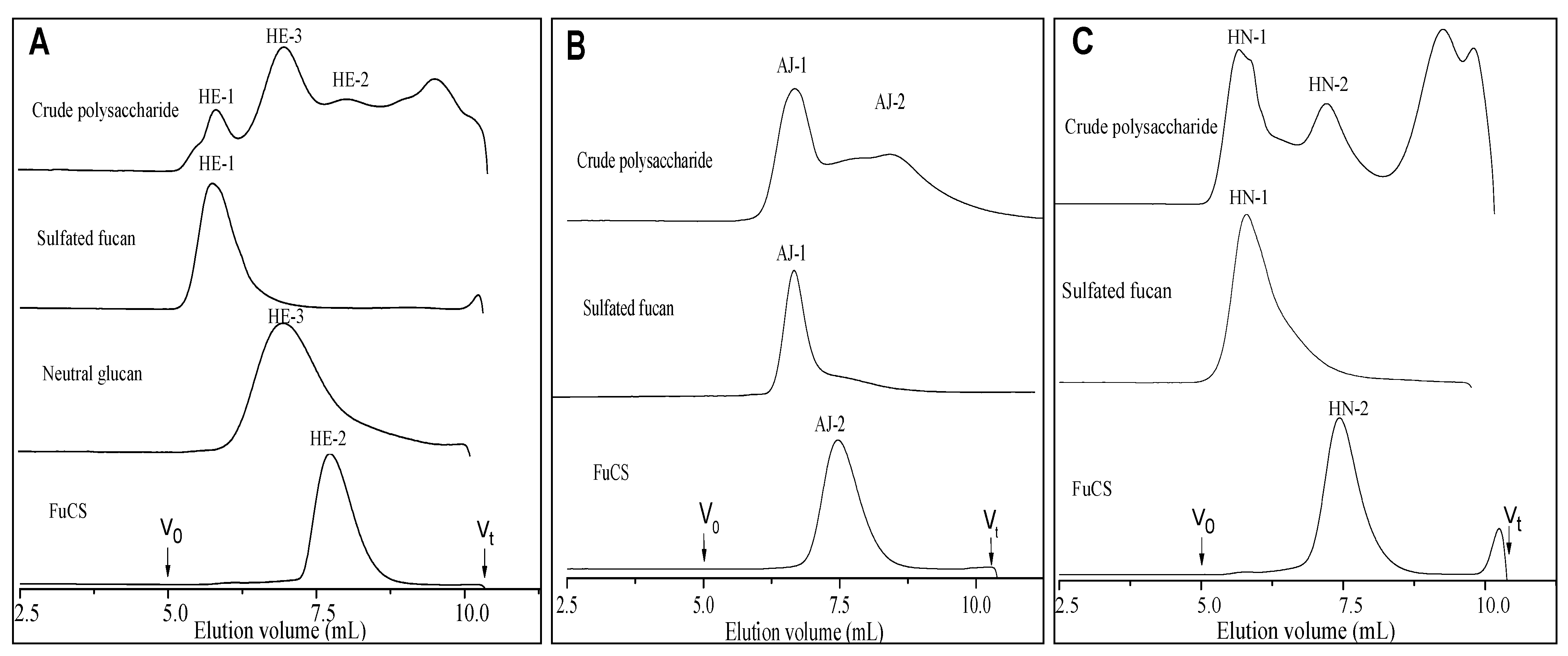
| Samples | Chemical composition (molar ratios) a | Average molecular weight | Specific rotation | [η] | ΚH | ΚK | |||||||
| GlcA | GalNAc | Fuc | Glc | OSO3−/COO− | SO3−/Fuc | Mn | Mw | Mw/Mn | (mL·g−1) | (×10−4) | (×10−4) | ||
| Sulfated fucans | |||||||||||||
| HE-1 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 1.00 | <0.01 | / | 0.53 | 517,900 | 615,500 | 1.19 | −181.4° | 605.6 | 2.12 | −1.49 |
| AJ-1 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 1.00 | <0.01 | / | 0.57 | 225,900 | 419,900 | 1.86 | −181.5° | 208.6 | 1.98 | −2.37 |
| HN-1 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 1.00 | <0.01 | / | 0.51 | 289,400 | 475,800 | 1.64 | −193.4° | 428.0 | 2.56 | −1.63 |
| Fucosylated chondroitin sulfates and a standard polysaccharide | |||||||||||||
| HE-2 | 1 | 1.28 | 0.82 b | <0.01 | 3.50 | ND c | 41,340 | 51,090 | 1.24 | −37.9° | 24.6 | −8.71 | −12.62 |
| AJ-2 | 1 | 1.05 | 1.03 b | <0.01 | 2.96 | ND | 46,760 | 56,820 | 1.22 | −56.2° | 32.5 | −20.95 | −11.50 |
| HN-2 | 1 | 0.96 | 0.82 b | <0.01 | 2.99 | ND | 42,460 | 55,320 | 1.30 | −45.9° | 34.0 | −10.48 | −14.06 |
| Heparin | ND | ND | ND | <0.01 | 2.04 | ND | 20,230 | 26,260 | 1.30 | 48.2° | 24.5 | −11.60 | −15.59 |
| Neutral glucan | |||||||||||||
| HE-3 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 1.00 | / | / | 197,900 | 253,300 | 1.28 | 170.2° | 0.8 | 15397 | 15212 |
2.2. Physicochemical Characteristics
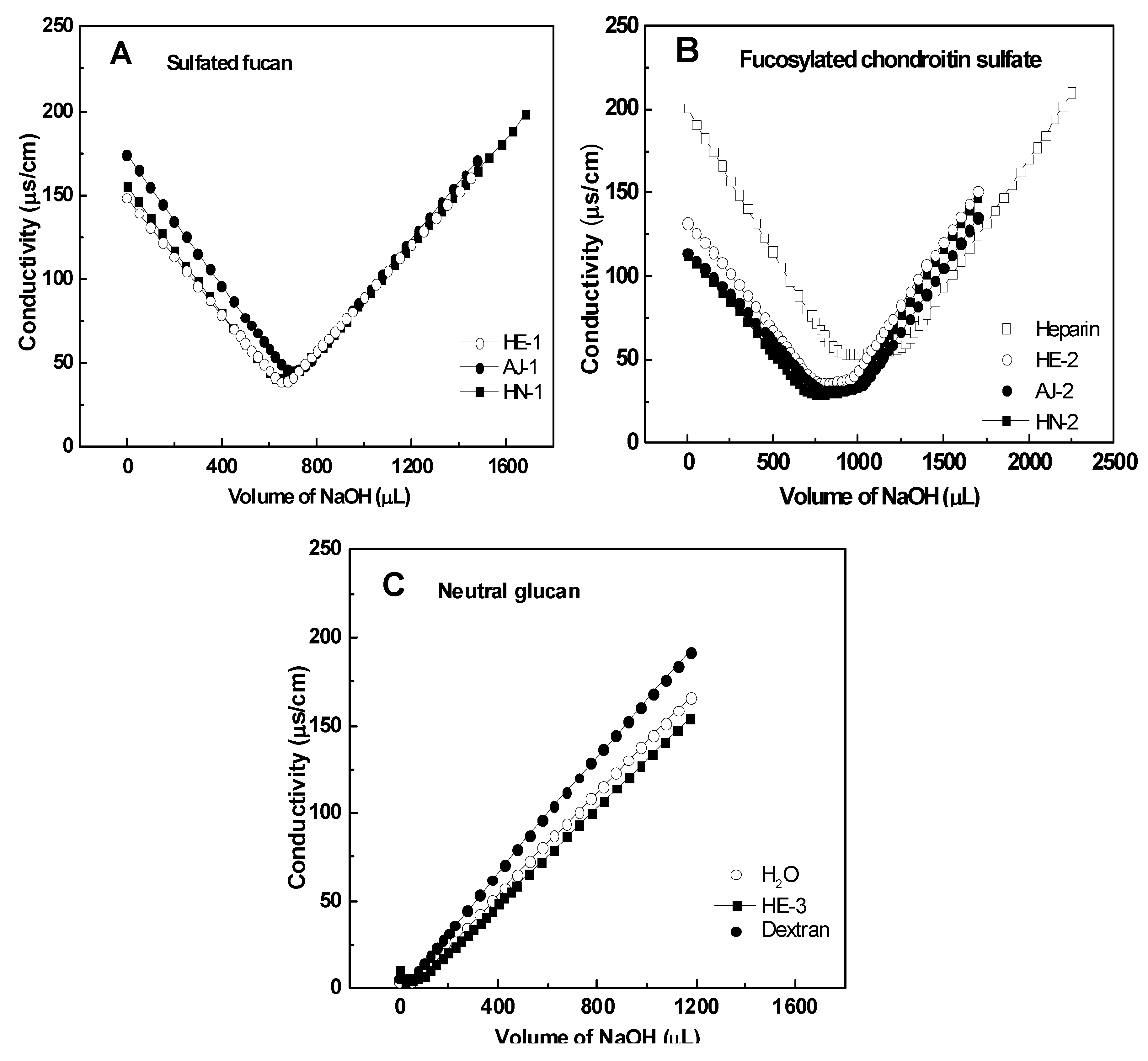
2.2.1. Chemical Composition and Analysis of Sulfate and Carboxyl Groups
2.2.2. Specific Optical Rotation
2.2.3. Molecular Weight and Molecular Weight Distribution
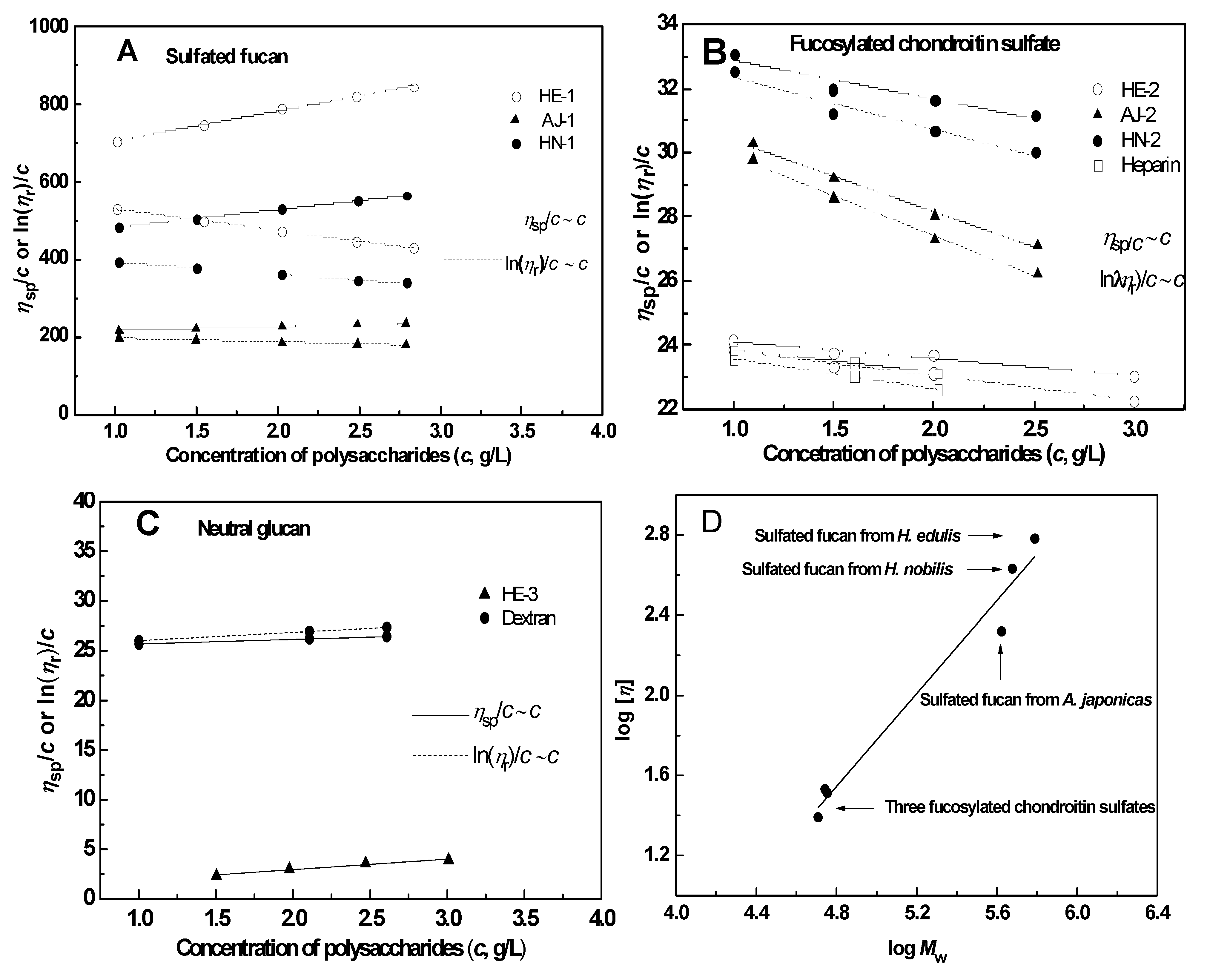
2.2.4. Intrinsic Viscosity


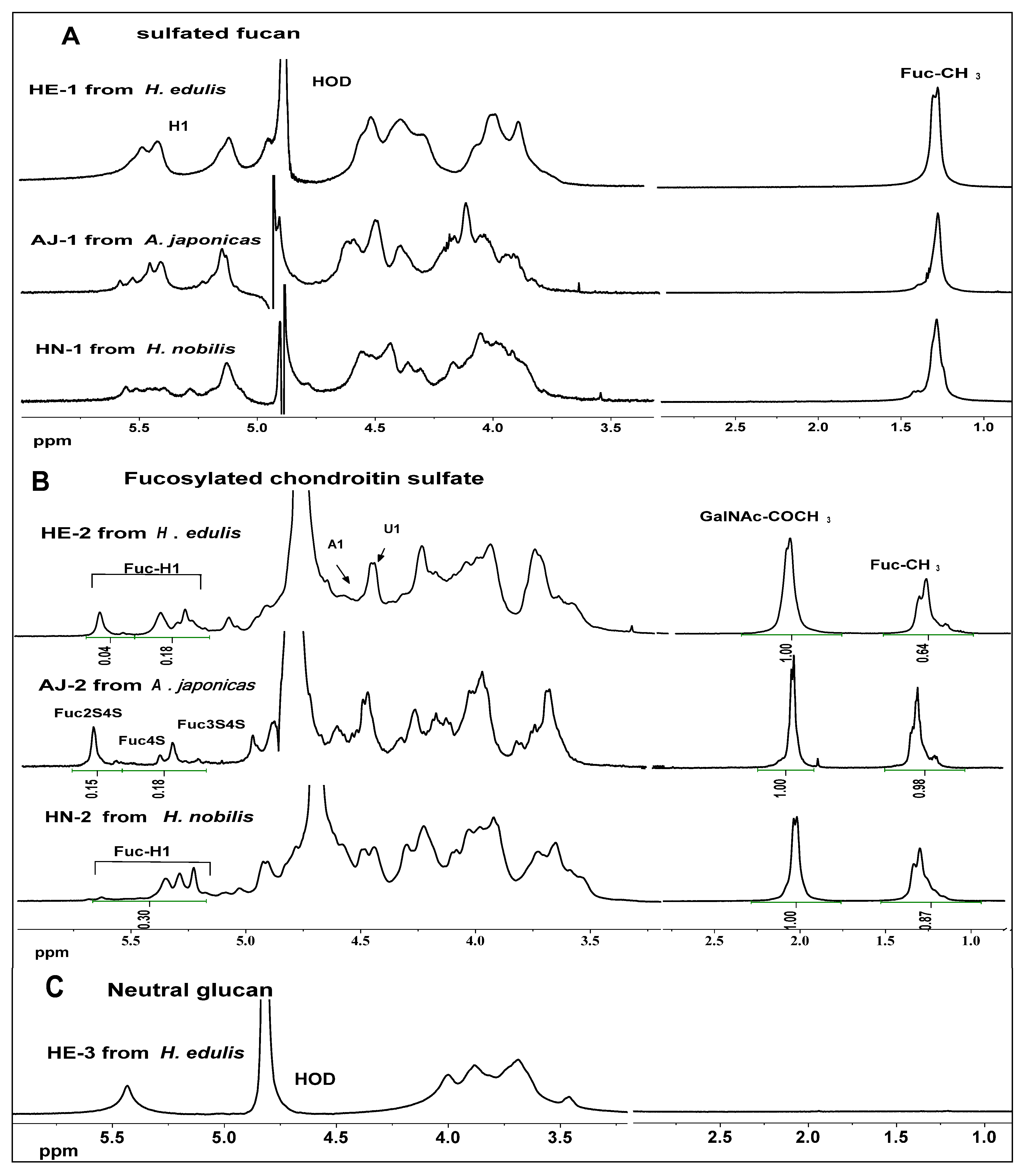
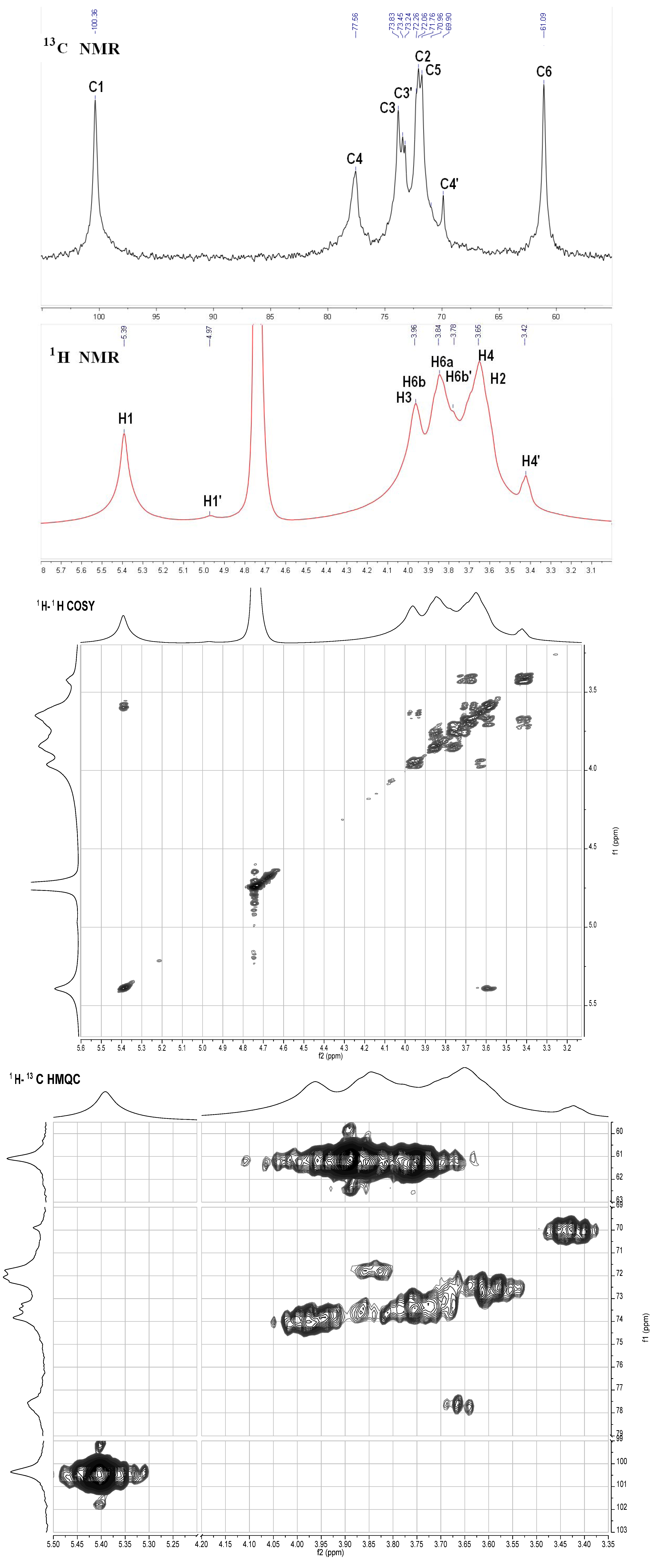
2.3. NMR Analysis
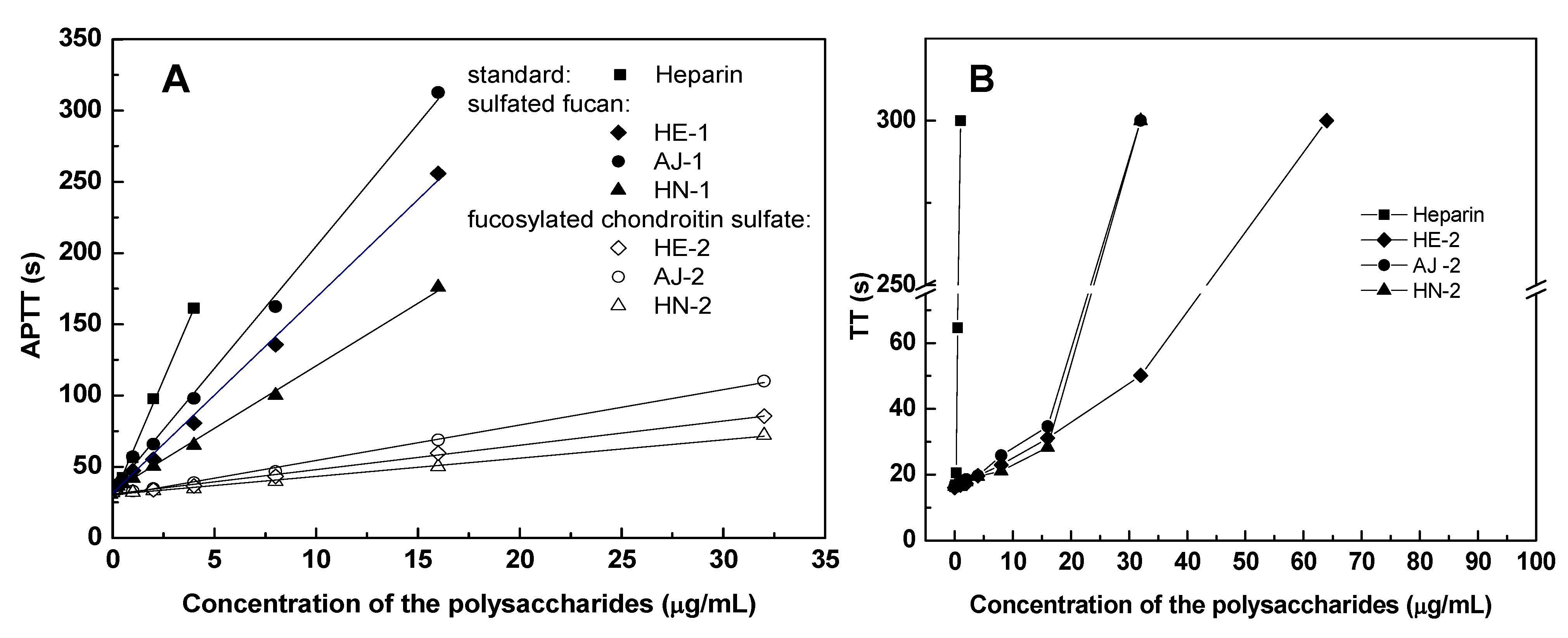
2.4. Anticoagulant Activity
| Samples | Sources | APTT a | TT a | PT a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| μg/mL | U/mg | μg/mL | U/mg | μg/mL | U/mg | ||
| Sulfated fucans | |||||||
| HE-1 | Holothuria edulis | 18.71 | 13 | >128 | <1 | >1000 | <1 |
| AJ-1 | Apostichopus japonicas | 13.30 | 19 | >128 | <1 | >1000 | <1 |
| HN-1 | Holothuria nobilis | 26.59 | 9 | >128 | <1 | >1000 | <1 |
| Fucosylated chondroitin sulfates | |||||||
| HE-2 | Holothuria edulis | 2.86 | 89 | 16.03 | 6 | >1000 | <1 |
| AJ-2 | Apostichopus japonicas | 2.20 | 116 | 14.20 | 7 | >1000 | <1 |
| HN-2 | Holothuria nobilis | 4.33 | 59 | 22.66 | 4 | >1000 | <1 |
| Neutral glucan | |||||||
| HE-3 | Holothuria edulis | >1000 | <1 | >1000 | <1 | >1000 | <1 |
| Standard glycosaminoglycan | |||||||
| Heparin | Porcine intestine | 1.20 | 212 | 0.45 | 212 | 24 | 212 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Extraction and Purification of Polysaccharides
3.2. NMR Analysis
3.3. Chemical Composition Analysis
3.4. Analysis of Molecular Weight
3.5. Specific Rotation
3.6. Measurement of Intrinsic Viscosity
3.7. Anticoagulant Action Measured by APTT, PT and TT
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Material
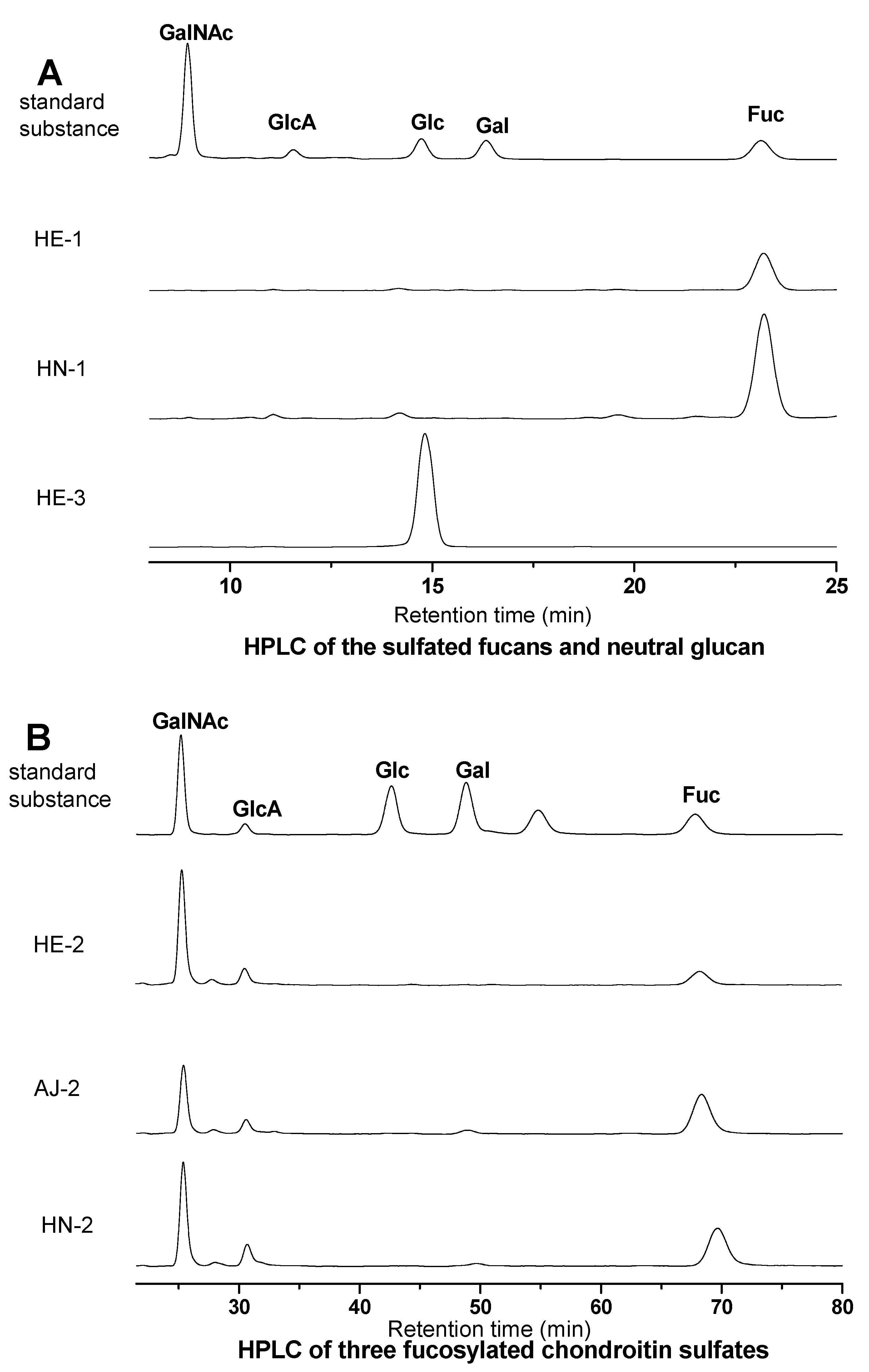
S1. Qualitative Analysis of Monosaccharide Composition of the Sea Cucumber Polysaccharide Samples by HPLC
S1.1. Materials
S1.2. Methods
S1.2.1. Hydrolysis and PMP Labeling
S1.2.2. HPLC Analysis
S1.3. Results
S2. NMR Analysis Results of the Neutral Glucan from the Sea Cucumber H. Edulis
Acknowledgements
References
- Streiff, M.B.; Bockenstedt, P.L.; Cataland, S.R.; Chesney, C.; Eby, C.; Fanikos, J.; Fogarty, P.F.; Gao, S.W.; Grcia-Aguilar, J.; Goldhaber, S.Z.; et al. Venous thromboembolic disease. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2011, 9, 714–777. [Google Scholar]
- Mourão, P.A.S.; Pereira, M.S. Searching for alternatives to heparin: Sulfated fucans from marine invertebrates. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 1999, 9, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glauser, B.F.; Pereira, M.S.; Monteiro, R.Q.; Mourão, P.A.S. Serpin-independent anticoagulant activity of a fucosylated chondroitin sulfate. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 100, 420–428. [Google Scholar]
- Bordbar, S.; Anwar, F.; Saari, N. High-value components and bioactives from sea cucumbers for functional foods—A review. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1761–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomin, V.H. Fucanomics and galactanomics: Marine distribution, medicinal impact, conceptions, and challenges. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 793–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomin, V.H.; Mourão, P.A.S. Structure, biology, evolution and medical importance of sulfated fucans and galactans. Glycobiology 2008, 18, 1016–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyue, Y.; Sheehan, J.P. Fucosylated chondroitin sulfate inhibits plasma thrombin generation via targeting of the factor IXa heparin-binding exosite. Blood 2009, 114, 3092–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, R.J.; Mourão, P.A.S. Fucosylated chondroitin sulfate as a new oral antithrombotic agent. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 96, 822–829. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, F.R.; Pereira, M.S.; Foguel, D.; Mourão, P.A.S. Antithrombin-mediated anticoagulant activity of sulfated polysaccharides. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 20824–20835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.Y.; Xu, S.M.; Zhao, J.H.; Kang, H.; Ding, H. Physicochemical characteristics and anticoagulant activities of low molecular weight fractions by free radical depolymerization of a fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from sea cucumber Thelenota ananas. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, T.; Aizu, Y.; Nagumo, T. Influence of sulfate content and molecular weight of a fucan sulfate from the brown seaweed Ecklonia kurome on its antithrombin activity. Thromb. Res. 1991, 64, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroun-Bouhedja, F.; Ellouali, M.; Sinquin, C.; Boisson-Vidal, C. Relationship between sulfate groups and biological activities of fucans. Thromb. Res. 2000, 100, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.Y.; Huang, R.; Wen, D.D.; Gao, N.; He, J.B.; Li, Z.; Zhao, J.H. Structure and effect of sulfated fucose branches on anticoagulant activity of the fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from sea cucumber Thelenota ananas. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Wu, M.Y.; Liu, S.; Lian, W.; Li, Z.; Zhao, J.H. Preparation and characterization of O-acylatedfucosylated chondroitin sulfate from sea cucumber. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1647–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.-C.; Vieira, R.P.; Mourão, P.A.S.; Mulloy, B. A sulfated α-L-fucan from sea cucumber. Carbohydr. Res. 1994, 255, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariya, Y.; Mulloy, B.; Imai, K.; Tominaga, A.; Kaneko, T.; Asari, A.; Suzuki, K.; Masuda, H.; Kyogashima, M.; Ishii, T. Isolation and partial characterization of fucan sulfates from the body wall of sea cucumber Stichopus japonicus and their ability to inhibit osteoclastogenesis. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourão, P.A.S.; Pereira, M.S.; Pavão, M.S.G.; Mulloy, B.; Tollefsen, D.M.; Mowinckel, M.C.; Abildgaard, U. Structure and anticoagulant activity of a fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from echinoderm: Sulfated fucose branches on the polysaccharide account for its high anticoagulant action. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 23973–23984. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, K.; Minami, Y.; Nemoto, H.; Numata, K.; Yamanaka, E. Structure of DHG, a depolymerizedglycosaminoglycan from sea cucumber Stichopus japonicus. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 4959–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.G.; Xue, C.H.; Yin, L.A.; Tang, Q.J.; Yu, G.L.; Chai, W.G. Comparison of structures and anticoagulant activities of fucosylated chondroitin sulfates from different sea cucumbers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariya, Y.; Watabe, S.; Hashimoto, K.; Yoshida, K. Occurrence of chondroitin sulfate E in glycosaminoglycan isolated from the body wall of sea cucumber Stichopus japonicus. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 5081–5085. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, R.P.; Mulloy, B.; Mourão, P.A.S. Structure of a fucose-branched chondroitin sulfate from sea cucumber: Evidence for the presence of 3-O-sulfo-β-D-glucuronosyl residues. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 13530–13536. [Google Scholar]
- Casu, B.; Gennaro, U. A conductimetric method for the determination of sulphate and carboxyl groups in heparin and other mucopolysaccharides. Carbohydr. Res. 1975, 39, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, T.; Hattori, M.; Sakabe, M.; Haginaka, J. Determination of the molecular mass of new L-fucose-containing glycosaminoglycan and its distribution by high-performance gel-permeation chromatography with laser light-scattering detection. Anal. Sci. 2001, 17, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.Y.; Xu, S.M.; Zhao, J.H.; Kang, H.; Ding, H. Preparation and characterization of molecular weight fractions of glycosaminoglycan from sea cucumber Thelenota ananas using free radical depolymerization. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasteson, A. Properties of fractionated chondroitinsulphate from ox nasal septa. Biochem. J. 1971, 122, 477–485. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.F.; Li, J.H.; Yang, D.Y.; Pan, Y.J.; Wan, H.T. A neuroprotective polysaccharide from Hyriopsis cumingii. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1489–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourão, P.A.S.; Boisson-Vidal, C.; Tapon-Bretaudiere, J.; Drouet, B.; Bros, A.; Fischer, A. Inactivation of thrombin by a fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from echinoderm. Thromb. Res. 2001, 102, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.S.; Mulloy, B.; Mourão, P.A.S. Structure and anticoagulant activity of sulfated fucans: Comparison between the regular, repetitive, and linear fucans from echinoderms with the more heterogeneous and branched polymers from brown algae. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 7656–7667. [Google Scholar]
- Blumenkrantz, N.; Asboe-Hansen, G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal. Biochem. 1973, 54, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondle, C.J.; Morgan, W.T.J. The determination of glucosamine and galactosamine. Biochem. J. 1955, 61, 586–589. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission, Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; People’s Medical Publishing: Beijing, China, 2005; Volume II, Appendix VI E A–48.
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission, Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; People’s Medical Publishing: Beijing, China, 2005; Volume II, Appendix VI G A–48.
- Fu, D.T.; O’Neill, R.A. Monosaccharide composition analysis of oligosaccharides and glycoproteins by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 1995, 227, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.T.; Zopf, D. Analysis of sialyllactoses in blood and urine by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 1999, 269, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, L.; Wu, M.; Xu, L.; Lian, W.; Xiang, J.; Lu, F.; Gao, N.; Xiao, C.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J. Comparison of Physicochemical Characteristics and Anticoagulant Activities of Polysaccharides from Three Sea Cucumbers. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 399-417. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11020399
Luo L, Wu M, Xu L, Lian W, Xiang J, Lu F, Gao N, Xiao C, Wang S, Zhao J. Comparison of Physicochemical Characteristics and Anticoagulant Activities of Polysaccharides from Three Sea Cucumbers. Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(2):399-417. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11020399
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Lan, Mingyi Wu, Li Xu, Wu Lian, Jingying Xiang, Feng Lu, Na Gao, Chuang Xiao, Shengmin Wang, and Jinhua Zhao. 2013. "Comparison of Physicochemical Characteristics and Anticoagulant Activities of Polysaccharides from Three Sea Cucumbers" Marine Drugs 11, no. 2: 399-417. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11020399
APA StyleLuo, L., Wu, M., Xu, L., Lian, W., Xiang, J., Lu, F., Gao, N., Xiao, C., Wang, S., & Zhao, J. (2013). Comparison of Physicochemical Characteristics and Anticoagulant Activities of Polysaccharides from Three Sea Cucumbers. Marine Drugs, 11(2), 399-417. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11020399




