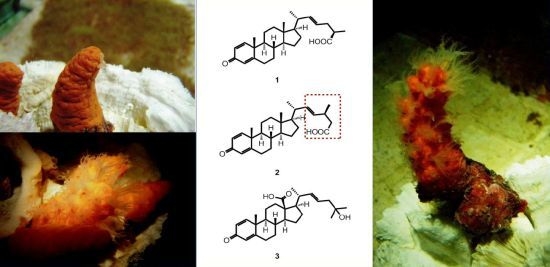
Steroidal Carboxylic Acids from Soft Coral Paraminabea acronocephala
Abstract
:1. Introduction
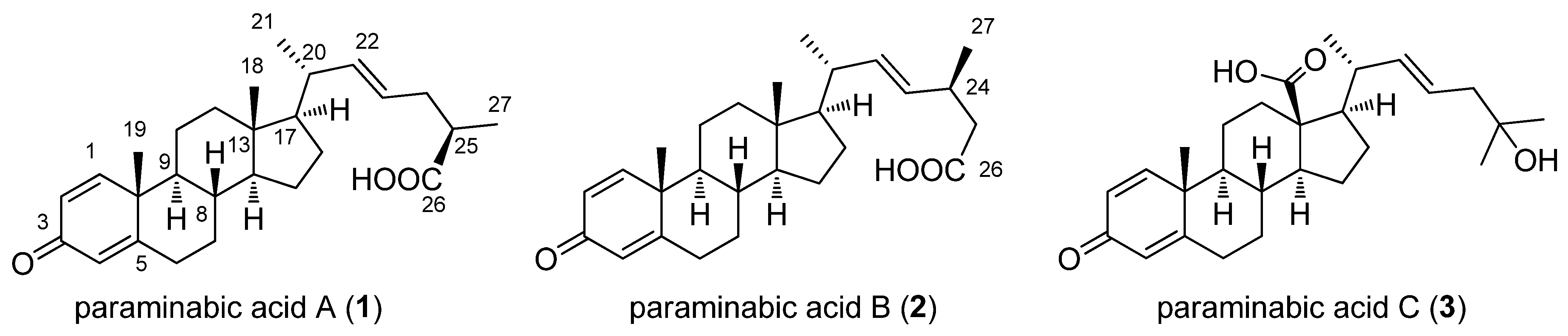
2. Results and Discussion
| Position | 1 a, δC, mult. | 2 a, δC, mult. | 3 a, δC, mult. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 156.1, CH | 156.1, CH | 155.9, CH |
| 2 | 127.4, CH | 127.4, CH | 127.5, CH |
| 3 | 186.5, C | 186.5, C | 186.5, C |
| 4 | 123.8, CH | 123.7, CH | 123.8, CH |
| 5 | 169.5, C | 169.6, C | 169.3, C |
| 6 | 32.9, CH2 | 32.9, CH2 | 32.7, CH2 |
| 7 | 33.7, CH2 | 33.7, CH2 | 33.4, CH2 |
| 8 | 35.5, CH | 35.5, CH | 37.1, CH |
| 9 | 52.4, CH | 52.4, CH | 52.4, CH |
| 10 | 43.6, C | 43.6, C | 43.6, C |
| 11 | 22.8, CH2 | 22.8, CH2 | 24.6, CH2 |
| 12 | 39.3, CH2 | 39.3, CH2 | 35.1, CH2 |
| 13 | 42.6, C | 42.5, C | 55.8, C |
| 14 | 55.6, CH2 | 55.5, CH2 | 55.7, CH2 |
| 15 | 24.4, CH2 | 24.3, CH2 | 25.0, CH2 |
| 16 | 28.4, CH2 | 28.3, CH2 | 25.3, CH2 |
| 17 | 55.5, CH | 55.5, CH | 55.3, CH |
| 18 | 12.2, CH3 | 12.2, CH3 | 176.8, C b |
| 19 | 18.7, CH3 | 18.7, CH3 | 18.7, CH3 |
| 20 | 40.0, CH | 39.9, CH | 38.4, CH |
| 21 | 20.6, CH3 | 20.6, CH3 | 22.0, CH3 |
| 22 | 139.6, CH | 136.1, CH | 136.7, CH |
| 23 | 123.8, CH | 131.3, CH | 124.8, CH |
| 24 | 36.4, CH2 | 33.7, CH | 46.8, CH2 |
| 25 | 39.3, CH | 41.6, CH2 b | 71.7, C |
| 26 | 180.6, C b | 176.9, C b | 27.6, CH3 |
| 27 | 16.3, CH3 b | 20.6, CH3 | 30.5, CH3 |
| # | 1, δH (J in Hz) a | 2, δH (J in Hz) a | 3, δH (J in Hz) a |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7.06, d (10.0) | 7.06, d (10.0) | 7.03, d (10.0) |
| 2 | 6.23, dd (10.0, 1.6) | 6.24, d (10.0) | 6.23, d (10.0) |
| 4 | 6.07, s | 6.07, s | 6.07, s |
| 6 | a: 2.45, m | a: 2.46, td (13.6, 4.4) | a: 2.46, td (13.4, 4.4) |
| b: 2.35, m | b: 2.35, m | b: 2.35, m | |
| 7 | a: 1.93, m | a: 1.93, m | a: 2.04, m |
| b: 1.02, m | b: 1.02, m | b: 1.07, m | |
| 8 | 1.60, m | 1.59, m | 1.69, m |
| 9 | 1.04, m | 1.03, m | 1.10, m |
| 11 | 1.67, m | 1.67, m | 1.85, m |
| 1.69, m | |||
| 12 | a: 2.00, m | a: 1.99, m | a: 2.66, br d (14.0) |
| b: 1.18, m | b: 1.17, m | b: 1.03, m | |
| 14 | 1.12, m | 1.11, m | 1.30, m |
| 15 | a: 1.55, m | a: 1.52, m | a: 1.91, m |
| b: 1.08, m | b: 1.02, m | b: 1.66, m | |
| 16 | a: 1.65, m | a: 1.62, m | a: 1.78, m |
| b: 1.22, m | b: 1.20, m | b: 1.70, m | |
| 17 | 0.99, m | 0.99, m | 1.62, m |
| 18 | 0.74, s | 0.74, s | |
| 19 | 1.23, s | 1.23, s | 1.15, s |
| 20 | 2.03, m | 2.00, m | 2.36, m |
| 21 | 0.99, d (6.8) | 0.98, d (6.4) | 1.05, d (6.4) |
| 22 | 5.27–5.30 b | 5.23–5.26 b | 5.39 dd (15.2, 8.8) |
| 23 | 5.27–5.30 b | 5.23–5.26 b | 5.48, ddd (15.2, 8.8, 5.2) |
| 24 | a: 2.33, m | 2.59, m | 2.18, dd (14.0, 5.2) |
| b: 2.10, m | 2.11, dd (14.0, 8.8) | ||
| 25 | 2.49, m | 2.30, d (7.2) | |
| 26 | 1.25, s | ||
| 27 | 1.15, d (7.2) | 1.03, d (6.4) | 1.25, s |
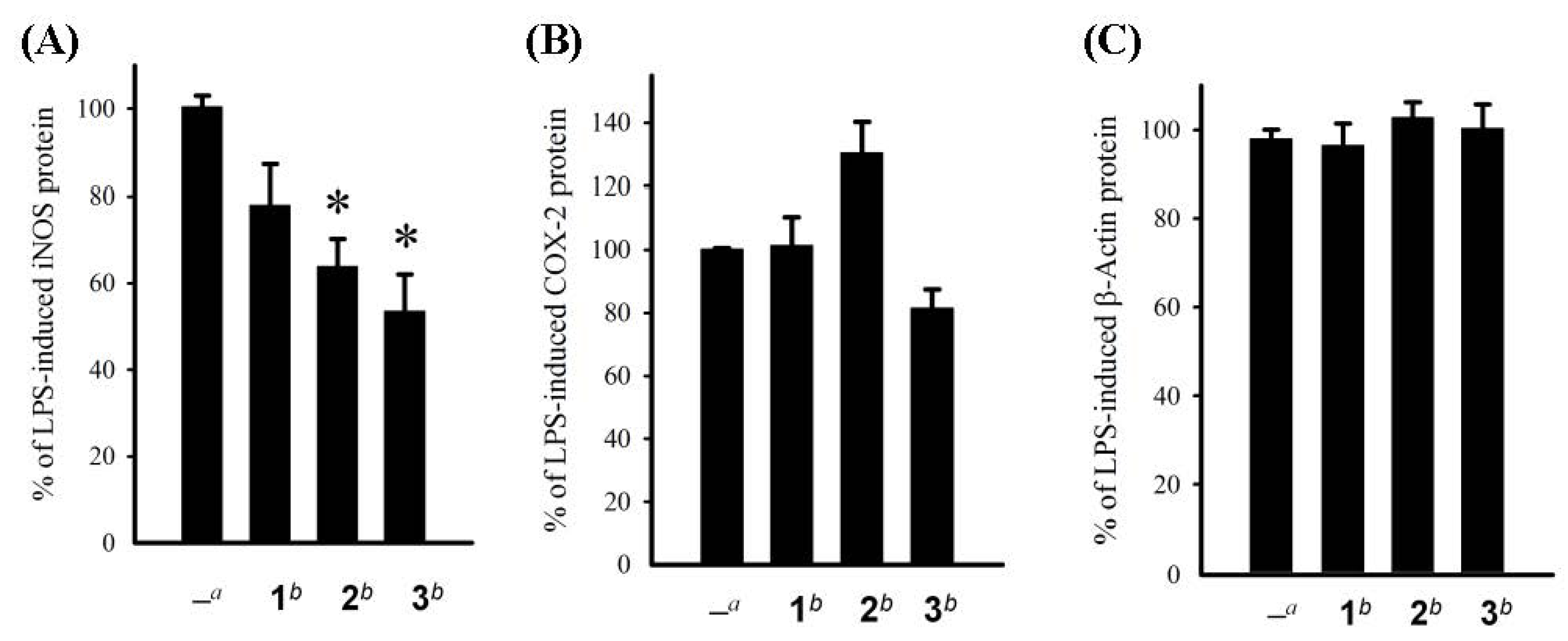
| Compound | Cell lines IC50 (μg/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hep G2 | Hep 3B | MDA-MB-231 | MCF-7 | A549 | |
| 1 | 15.21 | – | 19.66 | – | – |
| 2 | 19.77 | – | – | – | – |
| 3 | 13.57 | 2.83 | 2.25 | 2.23 | 2.05 |
| doxorubicin | 0.31 | 0.40 | 1.32 | 0.68 | 1.33 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Animal Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
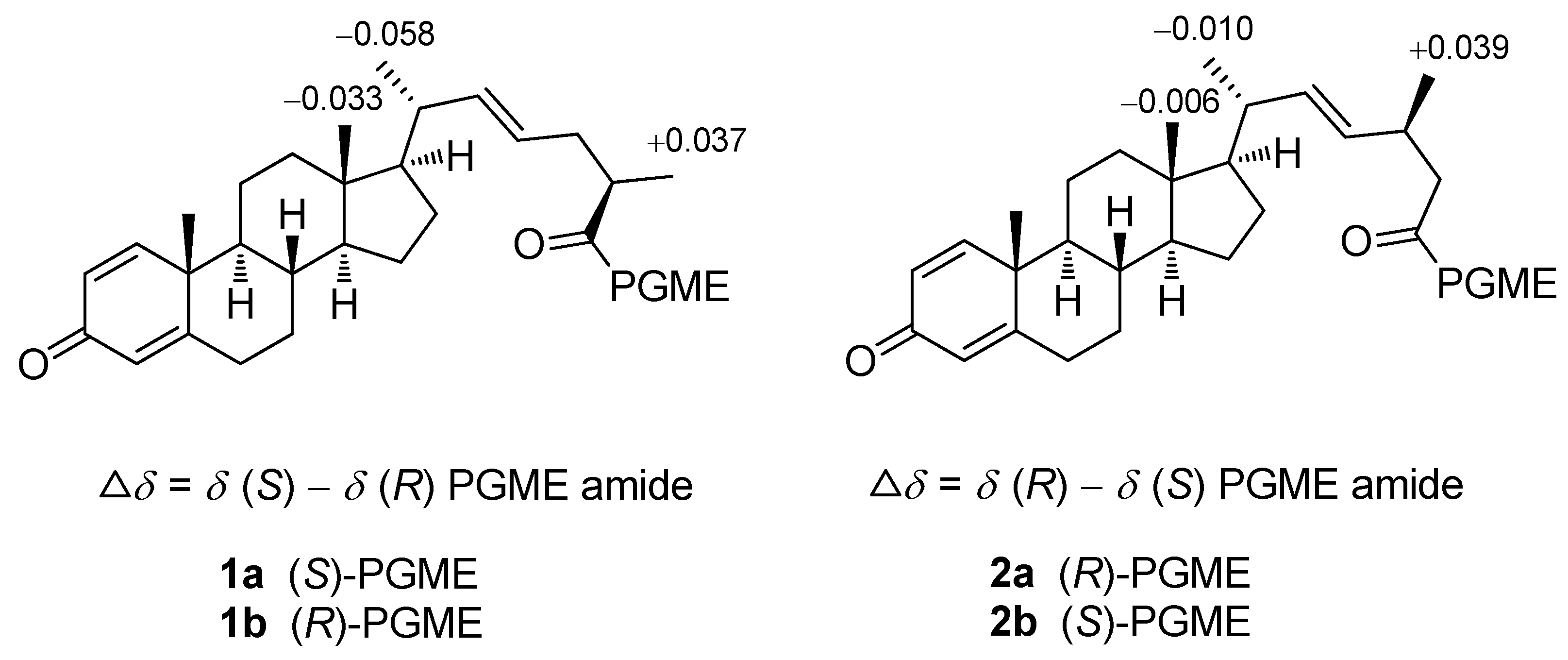
3.4. Preparation of (S) and (R)-PGME amides of 1 and 2
3.5. Cytotoxicity Testing
3.6. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Assay
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Chao, C.-H.; Chou, K.-J.; Wen, Z.-H.; Wang, G.-H.; Wu, Y.-C.; Dai, C.-F.; Sheu, J.-H. Paraminabeolides A–F, cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory marine withanolides from the soft coral Paraminabea acronocephala. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Ksebati, M.B.; Schmitz, F.J. Minabeolides: A group of withanolides from a soft coral, Minabea sp. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 3926–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.-N.; Park, E.K.; Nikolic, D.; Santarsiero, B.D.; Mesecar, A.D.; Vigo, J.S.; Graham, J.G.; Cabieses, F.; van Breemen, R.B.; Fong, H.H.S.; et al. Activity-guided isolation of novel norwithanolides from Deprea subtriflora with potential cancer chemopreventive activity. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 2350–2361. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Lee, J.S.; Nakazawa, T.; Ukai, K.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Wewengkang, D.S.; Rotinsulu, H.; Kobayashi, H.; Tsukamoto, S.; Namikoshi, M. (25S)-Cholesten-26-oic acid derivatives from an Indonesian soft coral Minabea sp. Steroids 2009, 74, 758–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.-H.; Wen, Z.-H.; Chen, I.-M.; Su, J.-H.; Huang, H.-C.; Chiang, M.Y.; Sheu, J.-H. Anti-inflammatory steroids from the octocoral Dendronephthya griffini. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 3554–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, Y.; Kusumi, T. New chiral anisotropic reagents for determining the absolute configurationof carboxylic acids. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 1853–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabuuchi, T.; Kusumi, T. Phenylglycine methyl ester, a useful tool for absolute configuration determination of various chiral carboxylic acids. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, M.C.; Scudiero, D.A.; Monks, A.; Hursey, M.L.; Czerwinski, M.J.; Fine, D.L.; Abbott, B.J.; Mayo, J.G.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Boyd, M.R. Feasibility of drug screening with panels of human tumor cell lines using a microculture tetrazolium assay. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 589–601. [Google Scholar]
- Jean, Y.-H.; Chen, W.-F.; Sung, C.-S.; Duh, C.-Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Lin, C.-S.; Tai, M.-H.; Tzeng, S.-F.; Wen, Z.-H. Capnellene, a natural marine compound derived from soft coral, attenuates chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.-H.; Chao, C.-H.; Sheu, J.-H. A neuroprotective sulfone of marine origin and the in vivo anti-inflammatory activity of an analogue. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 5998–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finamore, E.; Minale, L.; Riccio, R.; Rinaldo, G.; Zollo, F. Novel marine polyhydroxylated steroids from the starfish Myxoderma platyacanthum. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar]
- Sarma, N.S.; Krishna, M.S.; Pasha, S.G.; Prakasa Rao, T.S.; Venkateswarlu, Y.; Parameswaran, P.S. Marine metabolites: The sterols of soft coral. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 2803–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samples Availability: Not available.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chao, C.-H.; Wu, Y.-C.; Wen, Z.-H.; Sheu, J.-H. Steroidal Carboxylic Acids from Soft Coral Paraminabea acronocephala . Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 136-145. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11010136
Chao C-H, Wu Y-C, Wen Z-H, Sheu J-H. Steroidal Carboxylic Acids from Soft Coral Paraminabea acronocephala . Marine Drugs. 2013; 11(1):136-145. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11010136
Chicago/Turabian StyleChao, Chih-Hua, Yang-Chang Wu, Zhi-Hong Wen, and Jyh-Horng Sheu. 2013. "Steroidal Carboxylic Acids from Soft Coral Paraminabea acronocephala " Marine Drugs 11, no. 1: 136-145. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11010136
APA StyleChao, C.-H., Wu, Y.-C., Wen, Z.-H., & Sheu, J.-H. (2013). Steroidal Carboxylic Acids from Soft Coral Paraminabea acronocephala . Marine Drugs, 11(1), 136-145. https://doi.org/10.3390/md11010136