4-Methylenesterols from a Sponge Theonella swinhoei
Abstract
:1. Introduction

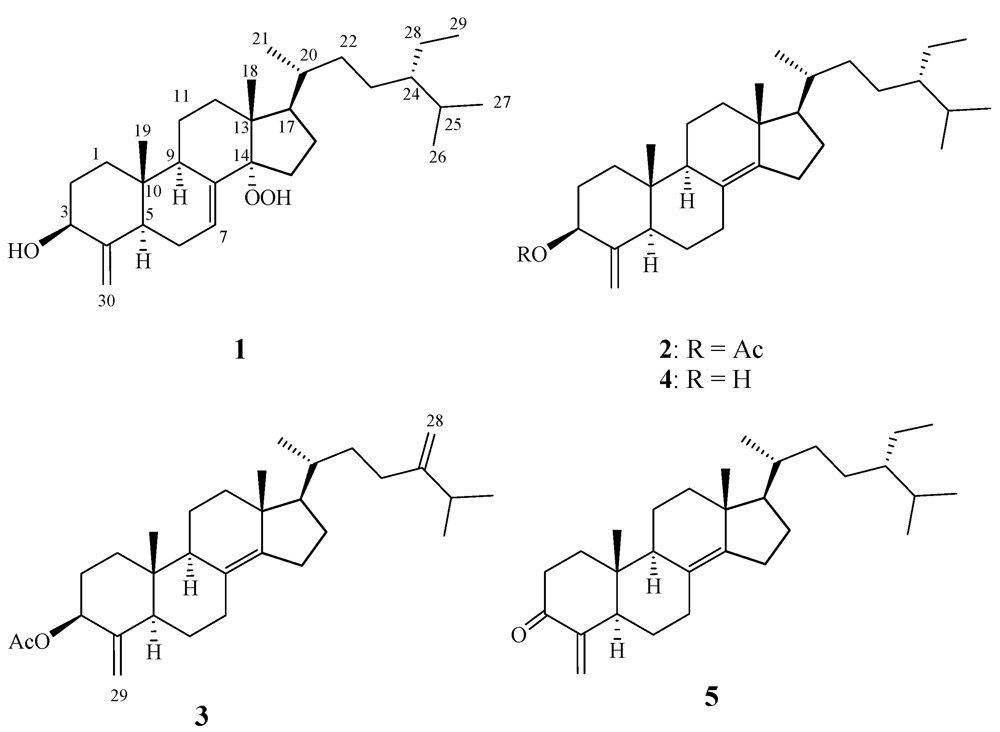
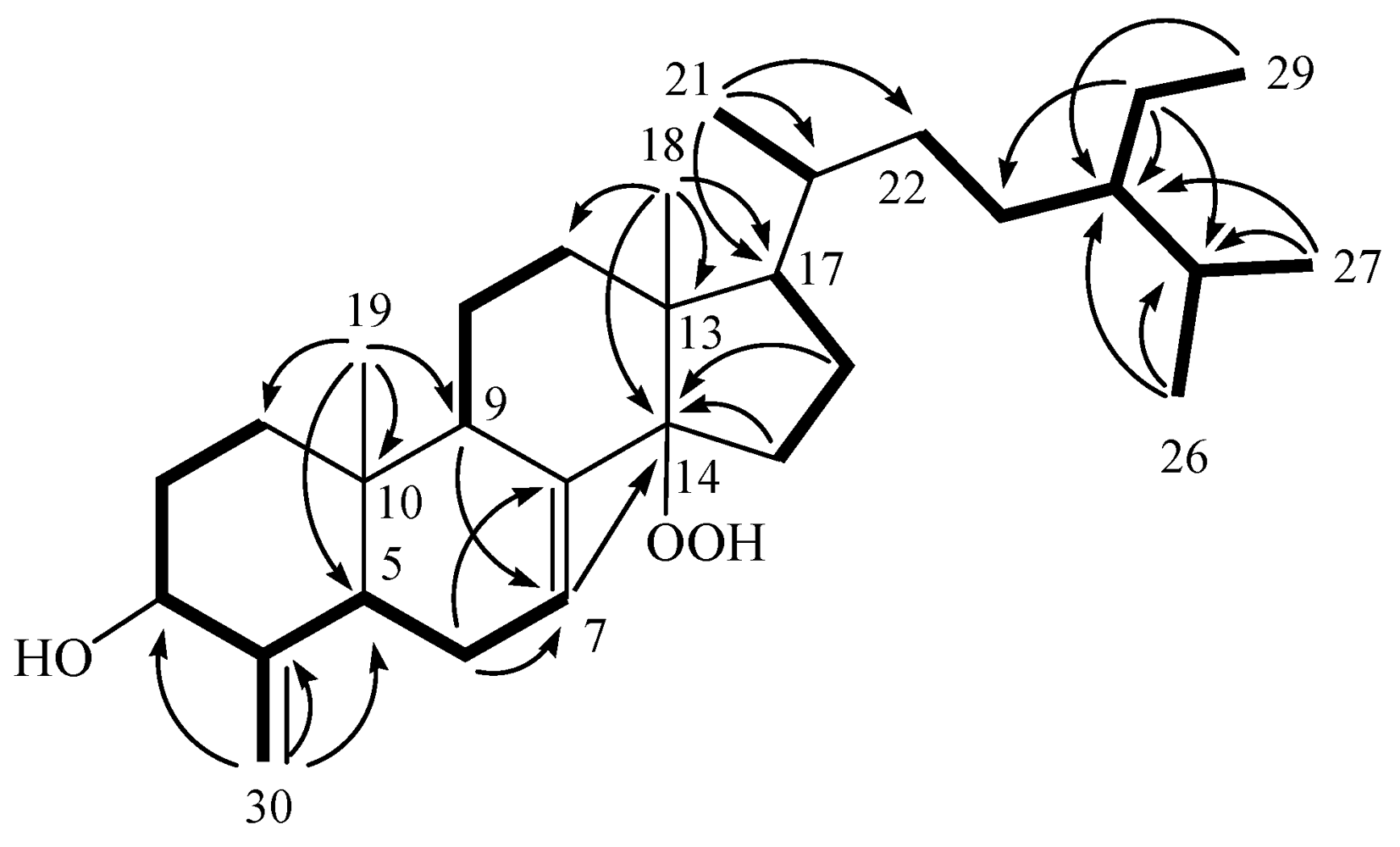
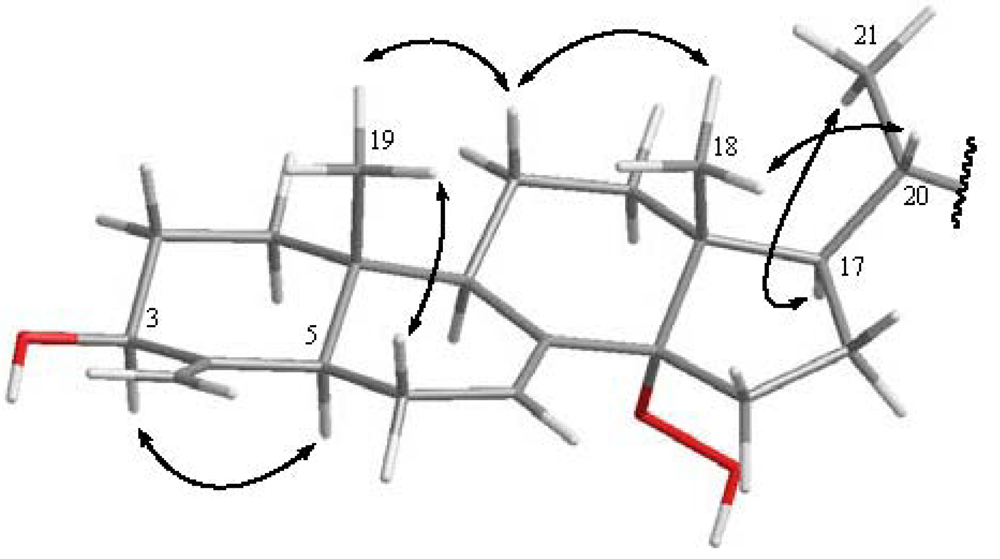
2. Results and Discussion
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH ( J in Hz) a | δC (mult.) b | δH ( J in Hz) a | δC (mult.) b | δH ( J in Hz) a | δC (mult.) b | |
| 1 | 1.39 m; 1.82 m | 37.2 (CH2) | 1.38 m; 1.80 m | 36.5 (CH2) | 1.38 m; 1.79 m | 36.5 (CH2) |
| 2 | 1.42 m; 1.98 m | 32.7 (CH2) | 1.50 m; 1.94 m | 29.6 (CH2) | 1.52 m; 1.94 m | 29.6 (CH2) |
| 3 | 4.01 dd (11.0, 5.0) | 73.2 (CH) | 5.15 dd (12.0, 5.0) | 74.8 (CH) | 5.15 dd (12.0, 5.0) | 74.8 (CH) |
| 4 | 151.9 (C) | 148.0 (C) | 148.0 (C) | |||
| 5 | 1.97 m | 45.1 (CH) | 1.89 d (13.0) | 49.5 (CH) | 1.90 m | 49.5 (CH) |
| 6 | 2.07 m; 2.14 m | 25.1 (CH2) | 1.38 m; 1.84 m | 27.0 (CH2) | 1.40 m; 1.84 m | 27.0 (CH2) |
| 7 | 5.68 d (5.5) | 125.0 (CH) | 2.25 m | 25.8 (CH2) | 2.25 m | 25.8 (CH2) |
| 8 | 135.5 (C) | 125.5 (C) | 125.6 (C) | |||
| 9 | 2.17 m | 45.4 (CH) | 1.80 m | 49.1 (CH) | 1.80 m | 49.1 (CH) |
| 10 | 37.2 (C) | 39.8 (C) | 39.8 (C) | |||
| 11 | 1.47 m; 1.64 m | 20.8 (CH2) | 1.48 m; 1.64 m | 20.4 (CH2) | 1.48 m; 1.64 m | 20.4 (CH2) |
| 12 | 1.62 m; 1.82 m | 30.5 (CH2) | 1.14 m; 1.96 m | 37.3 (CH2) | 1.15 m; 1.96 m | 37.3 (CH2) |
| 13 | 47.3 (C) | 42.7 (C) | 42.8 (C) | |||
| 14 | 98.3 (C) | 143.1 (C) | 143.0 (C) | |||
| 15 | 1.34 m; | 26.9 (CH2) | 1.75 m; | 29.2 (CH2) | 1.77 m; | 29.2 (CH2) |
| 2.06 m | 2.47 dd (13.5, 1.0) | 2.47 d (14.0) | ||||
| 16 | 1.62 m; 2.08 m | 24.8 (CH2) | 1.36 m; 1.60 m | 24.5 (CH2) | 1.36 m; 1.59 m | 24.5 (CH2) |
| 17 | 1.85 m | 50.9 (CH) | 1.16 m | 56.7 (CH) | 1.17 m | 56.7 (CH) |
| 18 | 0.74 s | 17.0 (CH3) | 0.84 s | 18.2 (CH3) | 0.85 s | 18.2 (CH3) |
| 19 | 0.71 s | 13.6 (CH3) | 0.62 s | 13.1 (CH3) | 0.62 s | 13.1 (CH3) |
| 20 | 1.37 m | 36.3 (CH) | 1.46 m | 34.9 (CH) | 1.50 m | 34.4 (CH) |
| 21 | 0.89 d (7.0) | 19.0 (CH3) | 0.95 d (6.5) | 19.2 (CH3) | 0.96 d (6.5) | 19.1 (CH3) |
| 22 | 1.00 m; 1.40 m | 34.0 (CH2) | 1.06 m; 1.41 m | 33.7 (CH2) | 1.24 m; 1.60 m | 34.4 (CH2) |
| 23 | 1.04 m; 1.34 m | 26.7 (CH2) | 1.04 m; 1.32 m | 26.2 (CH2) | 1.90 m; 2.08 m | 30.8 (CH2) |
| 24 | 0.94 m | 46.0 (CH) | 0.92 m | 46.1 (CH) | 156.9 (C) | |
| 25 | 1.68 m | 29.0 (CH) | 1.68 m | 28.9 (CH) | 2.24 m | 33.8 (CH) |
| 26 | 0.81 d (7.0) | 18.9 (CH3) | 0.82 d (8.5) | 19.0 (CH3) | 1.03 d (7.0) | 21.9 (CH3) |
| 27 | 0.83 d (7.0) | 19.6 (CH3) | 0.83 d (7.0) | 19.5 (CH3) | 1.04 d (7.5) | 22.0 (CH3) |
| 28 | 1.14 m; 1.32 m | 23.0 (CH2) | 1.16 m; 1.32 m | 23.0 (CH2) | 4.67 s; 4.73 s | 105.9 (CH2) |
| 29 | 0.86 t (7.5) | 12.3 (CH3) | 0.86 t (7.5) | 12.3 (CH3) | 4.60 s; 4.89 s | 103.7 (CH2) |
| 30 | 4.74 s; 5.18 s | 103.6 (CH2) | 4.60 s; 4.89 s | 103.7 (CH2) | ||
| 3-OAc | 2.13 s | 21.2 (CH3) | 2.13 s | 21.2 (CH3) | ||
| 170.2 (C) | 170.2 (C) | |||||
| 14-OOH | 6.79 br s | |||||
| Cell Lines | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DLD-1 | T-47D | HCT-116 | MCF-7 | MDA-MB-231 | K562 | Molt 4 | |
| 1 | 12.9 | 12.0 | 6.3 | 11.5 | 11.4 | 4.3 | 6.3 |
| 2 | – c | – c | – c | – c | – c | 13.7 | 17.8 |
| Doxorubicin b | 0.42 | 0.28 | 0.89 | 2.2 | 1.3 | 0.14 | 0.009 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Animal Material
3.3. Extraction and Separation
3.4. Cytotoxicity Testing
3.5. Molecular Mechanics Calculations
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Andavan, G.S.B.; Lemmens-Gruber, R. Cyclodepsipeptides from marine sponges: Natural agents for drug research. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 810–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebada, S.S.; Lin, W.; Proksch, P. Bioactive sesterterpenes and triterpenes from marine sponges: Occurrence and pharmacological significance. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 313–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.G.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 144–222. [Google Scholar]
- Essack, M.; Bajic, V.B.; Archer, J.A.C. Recently confirmed apoptosis-inducing lead compounds isolated from marine sponge of potential relevance in cancer treatment. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1580–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-Y.; Kim, W.-J.; Choi, Y.H. Pectenotoxin-2 from marine sponges: A potential anti-cancer agent—a review. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2176–2187. [Google Scholar]
- Laport, M.S.; Santos, O.C.S.; Muricy, G. Marine sponges: Potential sources of new antimicrobial drugs. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2009, 10, 86–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, S.; Kaur, M.; Minneman, K.P. Antiviral lead compounds from marine sponges. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2619–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kho, E.; Imagawa, D.K.; Rohmer, M.; Kashman, Y.; Djerassi, C. Sterols in marine invertebrates. 22. Isolation and structure elucidation of conicasterol and theonellasterol, two new 4-methylene sterols from the Red Sea sponges Theonella conica and Theonella swinhoei. J. Org. Chem. 1981, 46, 1836–1839. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, A.; Faulkner, D.J. 7α-Hydroxytheonellasterol, a cytotoxic 4-methylene sterol from the Philippines sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Kawazoe, K.; Katori, T.; Kitagawa, I. Marine natural products. XXX. Two new 3-keto-4-methylene steroids, theonellasterone and conicasteone, and bistheonellasterone, from the Okinawan marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1992, 40, 1773–1778. [Google Scholar]
- Inouye, Y.; Sugo, Y.; Kusumi, T.; Fusetani, N. Structure and absolute sterochemistry of bisconicasterone from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Chem. Lett. 1994, 23, 419–420. [Google Scholar]
- Sugo, Y.; Inouye, Y.; Nakayama, N. Structures of nine oxygenated 4-methylene sterols from Hachijo marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Steroids 1995, 60, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeyama, A.; Shoji, N.; Enoki, M.; Arihara, S. Swinhosterols A–C, 4-methylene secosteroids from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Yi, Y.H.; Lin, H.W. Oxygenated 4-methylidene sterols from the South China Sea sponge Theonella swinhoei. Helv. Chim. Acta 2010, 93, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar]
- Angawi, R.F.; Calcinai, B.; Cerrano, C.; Dien, H.A.; Fattorusso, E.; Scala, F.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Dehydroconicasterol and aurantoic acid, a chlorinated polyene derivative, from the indonesian sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 2195–2198. [Google Scholar]
- De Marino, S.; Sepe, V.; D’Auria, M.V.; Bifulco, G.; Renga, B.; Petek, S.; Fiorucci, S.; Zampella, A. Towards new ligands of nuclear receptors. Discovery of malaitasterol A, an unique bis-secosterol from marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 4856–4862. [Google Scholar]
- De Marino, S.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Chini, M.G.; Bifulco, G.; Renga, B.; D’Amore, C.; Fiorucci, S.; Debitus, C.; Zampella, A. Theonellasterols and conicasterols from Theonella swinhoei. Novel marine natural ligands for human nuclear receptors. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3065–3075. [Google Scholar]
- De Marino, S.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Chini, M.G.; Bifulco, G.; D’Amore, C.; Renga, B.; Mencarelli, A.; Petek, S.; Fiorucci, S.; Zampella, A. 4-Methylenesterols from Theonella swinhoei sponge are natural pregnane-X-receptor agonists and farnesoid-X-receptor antagonists thatmodulate innate immunity. Steroids 2012, 77, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, V.; Ummarino, R.; D’Auria, M.V.; Chini, M.G.; Bifulco, G.; Renga, B.; D’Amore, C.; Debitus, C.; Fiorucci, S.; Zampella, A. Conicasterol E, a small heterodimer partner sparing farnesoid X receptor modulator endowed with a pregnane X receptor agonistic activity, from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 84–93. [Google Scholar]
- Chini, M.G.; Jones, C.R.; Zampella, A.; D’Auria, M.V.; Renga, B.; Fiorucci, S.; Butts, C.P.; Bifulco, G. Quantitative NMR-derived interproton distances combined with quantum mechanical calculations of 13C chemical shifts in the stereochemical determination of conicasterol F, a nuclear receptor ligand from Theonella swinhoei. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar]
- Renga, B.; Mencarelli, A.; D’Amore, C.; Cipriani, S.; D’Auria, M.V.; Sepe, V.; Chini, M.G.; Monti, M.C.; Bifulco, G.; Zampella, A.; Fiorucci, S. Discovery that theonellasterol a marine sponge sterol is a highly selective FXR antagonist that protects against liver injury in cholestasis. PloS One 2012, 7, e30443. [Google Scholar]
- Alley, M.C.; Scudiero, D.A.; Monks, A.; Hursey, M.L.; Czerwinski, M.J.; Fine, D.L.; Abbott, B.J.; Mayo, J.G.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Boyd, M.R. Feasibility of drug screening with panels of human tumor cell lines using a microculturetetrazolium assay. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 589–601. [Google Scholar]
- Scudiero, D.A.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Paull, K.D.; Monks, A.; Tierney, S.; Nofziger, T.H.; Currens, M.J.; Seniff, D.; Boyd, M.R. Evaluation of a soluble tetrazolium/formazan assay for cell growth and drug sensitivity in culture using human and other tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 4827–4833. [Google Scholar]
- Chem3D Ultra, version 9.0.1; CambridgeSoft Corporation: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005.
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
Supplementary Files
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, J.-K.; Chiang, C.-Y.; Lu, M.-C.; Chang, W.-B.; Su, J.-H. 4-Methylenesterols from a Sponge Theonella swinhoei. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1536-1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10071536
Guo J-K, Chiang C-Y, Lu M-C, Chang W-B, Su J-H. 4-Methylenesterols from a Sponge Theonella swinhoei. Marine Drugs. 2012; 10(7):1536-1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10071536
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Jheng-Kun, Ching-Ying Chiang, Mei-Chin Lu, Wen-Been Chang, and Jui-Hsin Su. 2012. "4-Methylenesterols from a Sponge Theonella swinhoei" Marine Drugs 10, no. 7: 1536-1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10071536
APA StyleGuo, J.-K., Chiang, C.-Y., Lu, M.-C., Chang, W.-B., & Su, J.-H. (2012). 4-Methylenesterols from a Sponge Theonella swinhoei. Marine Drugs, 10(7), 1536-1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10071536





