Marine Cyclotripeptide X-13 Promotes Angiogenesis in Zebrafish and Human Endothelial Cells via PI3K/Akt/eNOS Signaling Pathways
Abstract
:Abbreviations
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| Akt | alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase |
| eNOS | endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| HUVEC | human umbilical vein endothelial cells |
1. Introduction
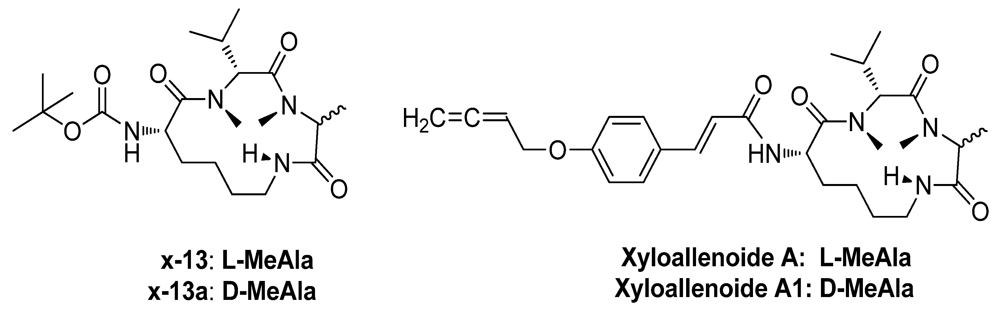
2. Results and Discussion
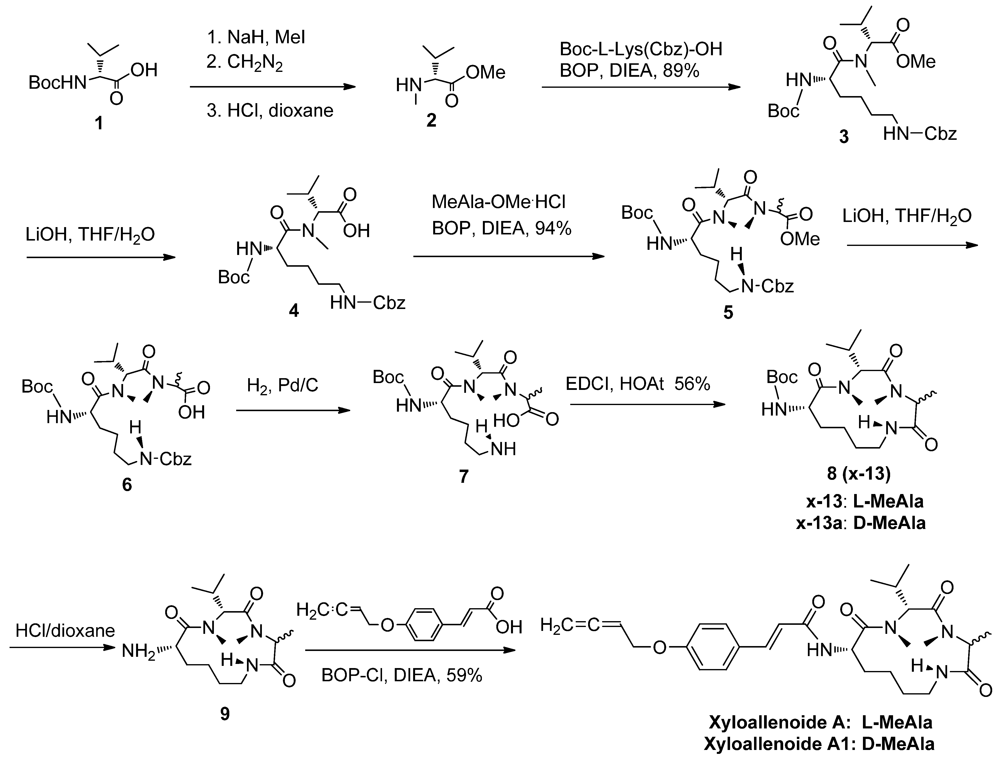
2.1. The Synthesis of Marine Cyclotripeptide X-13 and Xyloallenoide A
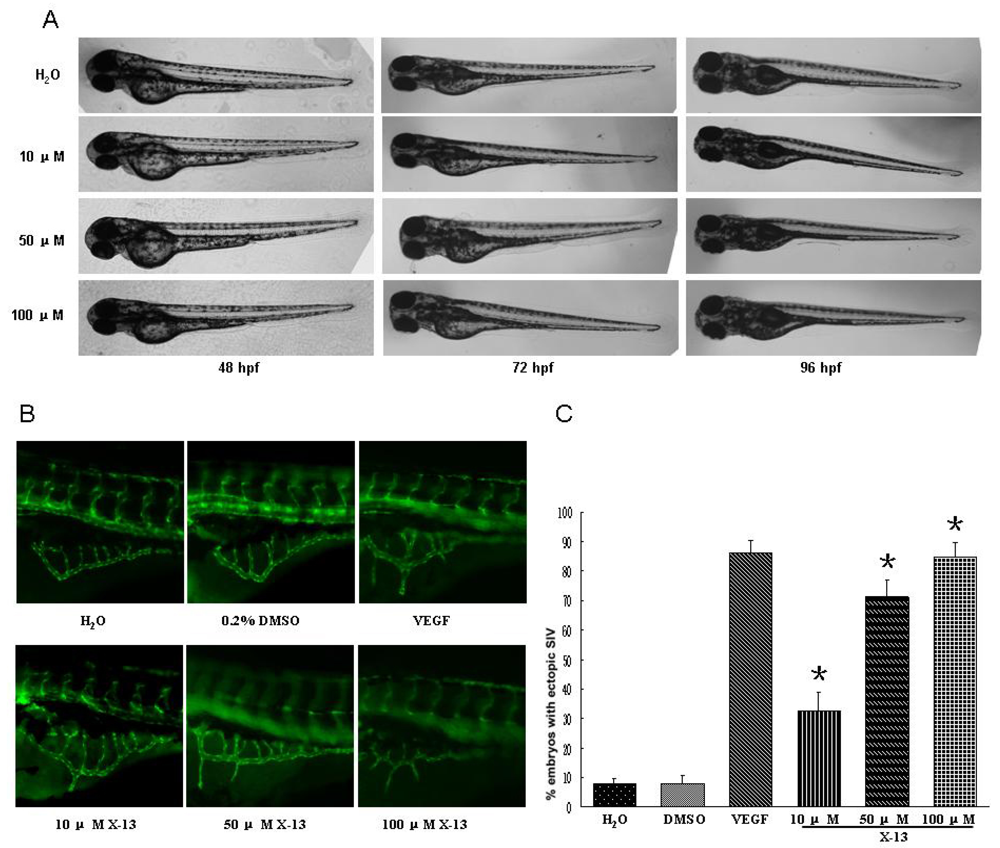
2.2. Angiogenic Activity in Zebrafish Angiogenesis Screen
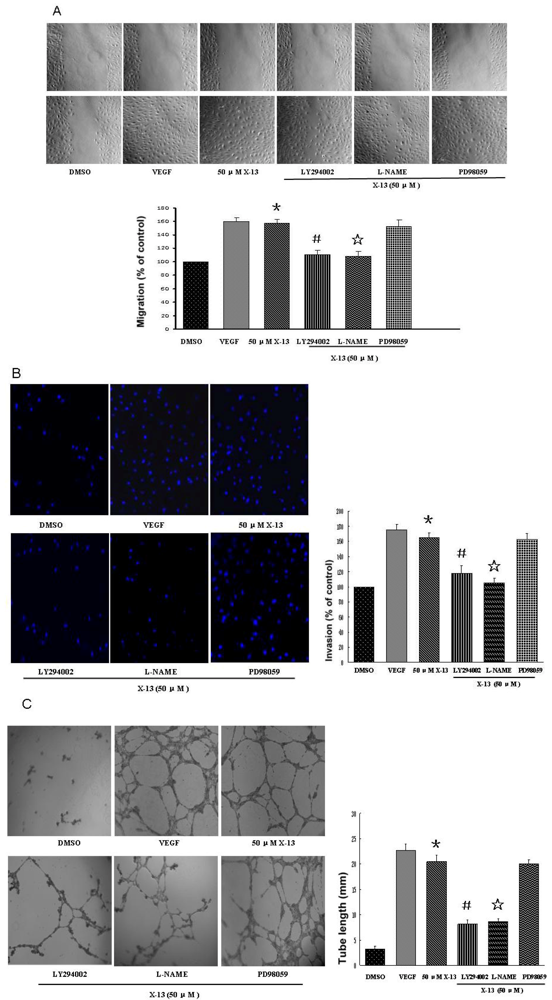
2.3. In Vitro Angiogenesis in Mammalian Endothelial Cells
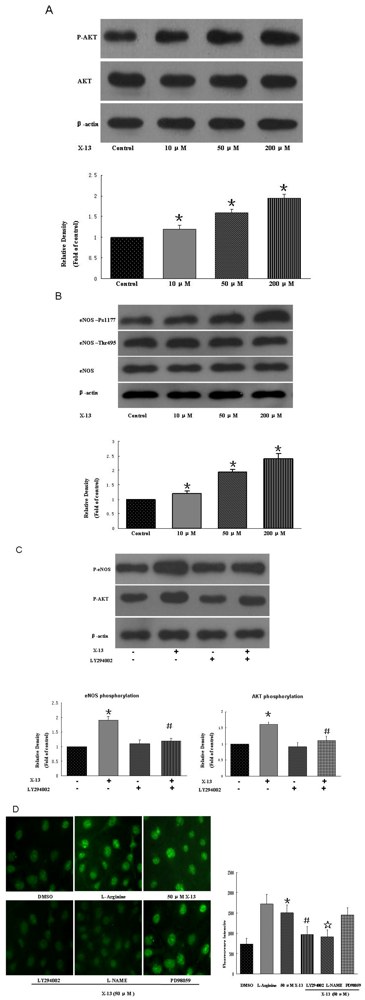
2.4. PI3K/Akt/eNOS Activities in HUVECs
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Preparation of Reagents and Cell Culture
3.2. Angiogenesis in Zebrafish Embryos
3.3. Cell Invasion, Migration and Tube Formation
3.4. Western Immunoblot Analysis
3.5. Measurement of NO Generation in HUVECs
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Xiang, Q.; Pei, Z.; Liu, X.; Lu, B.; Chen, L.; Wang, G.; Pang, J.; Lin, Y. Design and synthesis of novel xyloketal derivatives and their vasorelaxing activities in rat thoracic aorta and angiogenic activities in zebrafish angiogenesis screen. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 4642–4653. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Wu, X.; Feng, S.; Jiang, G.; Zhu, S.; Vrijmoed, L.L.P.; Jones, E.B.G. A novel N-cinnamoylcyclopeptide containing an allenic ether from the fungus Xylaria sp. (strain #2508) from the South China Sea. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 449–451. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Pei, Z.; Xu, Z.; Pang, J.; Wang, S.; Lu, X.; Huang, R.; Wang, G.; Li, J. Preparation and Application of a Marine Cyclic Peptide. Patent CN 201010512692.X, 23 February 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Mao, W.; She, Z.; Li, C.; Yang, D.; Lin, Y.; Fu, L. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 12 allenic aromatic ethers. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 2785–2788. [Google Scholar]
- Auerbach, R.; Lewis, R.; Shinners, B.; Kubai, L.; Akhtar, N. Angiogenesis assays: A critical overview. Clin. Chem. 2003, 49, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morello, F.; Perino, A.; Hirsch, E. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase signallingn in the vascular system. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 82, 261–271. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, K.H.; Alex, D.; Lam, I.K.; Tsui, S.K.; Yang, Z.F.; Lee, S.M. Nobiletin, a polymethoxylated flavonoid from citrus, shows anti-angiogenic activity in a zebrafish in vivo model and HUVEC in vitro model. J. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 112, 3313–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunath, M.; Wong, Y.; Muhamma, F.; Ge, R. Pharmacologically induced angiogenesis in transgenic zebrafish. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 378, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, H.; Lin, H.; Lao, S.; Gao, J.; Hong, S.; Leong, C.; Yue, P.; Kwan, Y.; Leung, A.; Wang, Y.; Lee, S. The angiogenic effects of Angelica sinensis extract on HUVEC in vitro and zebrafish in vivo. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 103, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Wan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, G.; Lin, H.; Seto, S.; Kwan, Y.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lee, S. Angiogenic effect of saponin extract from Panax notoginseng on HUVECs in vitro and zebrafish in vivo. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Malak, N.; Mofarrahi, M.; Mayaki, D.; Khachigian, L.; Hussain, S. Early growth response-1 regulates angiopoietin-1-induced endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, R.; Chen, V.; Lee, C.; Chao, J. Structural elements of kallistatin required for inhibition of angiogenesis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2003, 284, C1604–C1613. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, W.; Wang, M.; Moore, P.; Jin, H.; Yao, T.; Zhu, Y. The novel proangiogenic effect of hydrogen sulfide is dependent on Akt phosphorylation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 76, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, H.; Urano, Y.; Kikuchi, K.; Hirata, Y.; Nagano, T. Fluorescent indicators for imaging nitric oxide production. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1999, 38, 3209–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, X.-L.; Xu, Z.-L.; Yao, X.-L.; Su, F.-J.; Ye, C.-H.; Li, J.; Lin, Y.-C.; Wang, G.-L.; Zeng, J.-S.; Huang, R.-X.; et al. Marine Cyclotripeptide X-13 Promotes Angiogenesis in Zebrafish and Human Endothelial Cells via PI3K/Akt/eNOS Signaling Pathways. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1307-1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10061307
Lu X-L, Xu Z-L, Yao X-L, Su F-J, Ye C-H, Li J, Lin Y-C, Wang G-L, Zeng J-S, Huang R-X, et al. Marine Cyclotripeptide X-13 Promotes Angiogenesis in Zebrafish and Human Endothelial Cells via PI3K/Akt/eNOS Signaling Pathways. Marine Drugs. 2012; 10(6):1307-1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10061307
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Xi-Lin, Zhong-Liang Xu, Xiao-Li Yao, Feng-Juan Su, Cheng-Hui Ye, Jing Li, Yong-Cheng Lin, Guang-Lei Wang, Jin-Sheng Zeng, Ru-Xun Huang, and et al. 2012. "Marine Cyclotripeptide X-13 Promotes Angiogenesis in Zebrafish and Human Endothelial Cells via PI3K/Akt/eNOS Signaling Pathways" Marine Drugs 10, no. 6: 1307-1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10061307
APA StyleLu, X.-L., Xu, Z.-L., Yao, X.-L., Su, F.-J., Ye, C.-H., Li, J., Lin, Y.-C., Wang, G.-L., Zeng, J.-S., Huang, R.-X., Ou, J.-S., Sun, H.-S., Wang, L.-P., Pang, J.-Y., & Pei, Z. (2012). Marine Cyclotripeptide X-13 Promotes Angiogenesis in Zebrafish and Human Endothelial Cells via PI3K/Akt/eNOS Signaling Pathways. Marine Drugs, 10(6), 1307-1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10061307



