Abstract
The structures, names, bioactivities and references of 105 natural products obtained from gorgonian corals belonging to the family Plexauridae with an Indo-Pacific distribution are described in this review. All compounds mentioned in this review were obtained from gorgonian corals belonging to the genera Astrogorgia, Bebryce, Echinomuricea, Euplexaura and Menella.
1. Introduction
Over the past thirty-four years, 105 natural products have been reported from gorgonian corals belonging to the genera Astrogorgia, Bebryce, Echinomuricea, Euplexaura and Menella with an Indo-Pacific distribution, all belonging to the family Plexauridae (Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Gorgonacea) [1]. This review summarizes the structures, names, bioactivities and references of all compounds in tabular form.
2. Natural Products from Gorgonian Corals Belonging to the Family Plexauridae
2.1. Genus Astrogorgia
Astrogorgia sp.
A novel 9,10-secosterol, astrogorgiadiol (1), and a new eunicellin-based diterpenoid, astrogorgin (2), along with a known eunicellin, ophirin (3), were isolated from the gorgonian Astrogorgia sp., collected at Okino-shima Island off Shikoku, Japan [2] (Table 1). The structures of new metabolites 1 and 2 were established by spectroscopic methods and by comparison of the spectral data with those of related analogs. Compounds 1–3 were found to display activity to inhibit cell division of the fertilized eggs of the starfish Asterina pectinifera.

Table 1.
The natural products from Astrogorgia sp.
| Structure | No. | Name | Biological Activity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 1 | Astrogorgiadiol | Inhibited cell division of fertilized starfish (Asterina pectinifera) eggs at a concentration of 50 μg/mL. IC50 (ALK, Aurora-B, AXL, FAK, IGF1-R, MEK1 wt, MET wt, SRC, VEGF-R2) = 7.6, 25.1, 16.9, 13.2, 2.8, 48.9, 78.0, 1.9, 4.4 μM. | [2,3] |
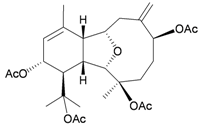 | 2 | Astrogorgin | Eunicellins 2 and 3 inhibited cell division of fertilized starfish (Asterina pectinifera) eggs at a concentration of 10 μg/mL. | [2] |
 | 3 | Ophirin | [2] |
Furthermore, twenty-one 9,10-secosterols, including thirteen new metabolites, astrogorgols A–M (4–16), along with eight known compounds, calicoferols A–C (17–19), E (20), G (21), I (22), 24-exomethylenecalicoferol E (23), and astrogorgiadiol (1) and a new steroid, astrogorgol N (24), were isolated from the gorgonian Astrogorgia sp. collected from the inner coral reef in Beibuwan Bay, Guangxi province, China [3] (Table 2). The structures of new sterols 4–16 and 24 were determined by spectroscopic methods and by comparison of their spectral and physical data with those reported in the literature. Secosterols 1, 9, 17, 18 and 23 showed inhibitory effects against a series of protein kinases. The structures of calicoferols B (18) [3,4], C (19), E (20) [3,5] and I (22) [3,6] that are shown in reference 3 should be revised as presented in the original literature.

Table 2.
The natural products from Astrogorgia sp.
| Structure | No. | Name | Biological Activity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 4 | Astrogorgol A (R1 = H, R2 = SC1) | [3] | |
| 5 | Astrogorgol B (R1 = H, R2 = SC2) | [3] | ||
| 6 | Astrogorgol C (R1 = OH, R2 = SC1) | [3] | ||
| 7 | Astrogorgol D (R1 = OH, R2 = SC3) | [3] | ||
| 17 | Calicoferol A (R1 = H, R2 = SC3) | IC50 (ALK, AXL, FAK, | [3] | |
| IGF1-R, MET wt, SRC, | ||||
| VEGF-R2) = 4.2, 14.7, 9.9, 2.4, | ||||
| 47.6, 2.2, 4.6 μM. | ||||
| 20 | Calicoferol E (R1 = H, R2 = SC5) | [3,5] | ||
| 22 | Calicoferol I (R1 = OH, R2 = SC5) | [3,6] | ||
| 23 | 24-Exomethylenecalicoferol E | IC50 (ALK, AXL, FAK, | [3] | |
| (R1 = H, R2 = SC4) | IGF1-R, MET wt, SRC, | |||
| VEGF-R2) = 4.4, 20.2, 10.7, | ||||
| 2.3, 27.5, 1.5, 4.9 μM. | ||||
 | 8 | Astrogorgol E (R1 = H, R2 = SC1, R3 = β-OH) | [3] | |
| 9 | Astrogorgol F (R1 = H, R2 = SC3, R3 = β-OH) | IC50 (ALK, | [3] | |
| Aurora-B, AXL, | ||||
| FAK, IGF1-R, MET | ||||
| wt, SRC, VEGF-R2) | ||||
| = 9.3, 38.1, 21.9, | ||||
| 16.9, 3.2, 34.0, 2.4, | ||||
| 5.0 μM | ||||
| 10 | Astrogorgol G (R1 = H, R2 = SC5, R3 = β-OH) | [3] | ||
| 11 | Astrogorgol H (R1 = H, R2 = SC3, R3 = α-OH) | [3] | ||
| 12 | Astrogorgol I (R1 = H, R2 = SC2, R3 = α-OH) | [3] | ||
| 13 | Astrogorgol J (R1 = H, R2 = SC6, R3 = α-OH) | [3] | ||
| 14 | Astrogorgol K (R1 = H, R2 = SC7, R3 = α-OH) | [3] | ||
| 15 | Astrogorgol L (R1 = OH, R2 = SC3, R3 = α-OH) | [3] | ||
| 16 | Astrogorgol M (R1 = OH, R2 = SC4, R3 = α-OH) | [3] | ||
| 18 | Calicoferol B (R1 = OH, R2 = SC5, R3 = α-OH) | IC50 (ALK, AXL, | [3,4] | |
| FAK, IGF1-R, MET | ||||
| wt, SRC, VEGF-R2) | ||||
| = 4.7, 32.6, 9.6, 2.5, | ||||
| 71.5, 2.2, 6.0 μM. | ||||
| 19 | Calicoferol C (R1 = H, R2 = SC4, R3 = α-OH) | [3,5] | ||
| 21 | Calicoferol G (R1 = H, R2 = SC8, R3 = α-OH) | [3] | ||
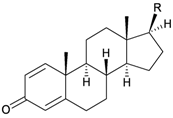 | 24 | Astrogorgol N (R = SC7) | [3] | |
 | ||||
2.2. Genus Bebryce
2.2.1. Bebryce grandicalyx
In 1998, a new unstable sesquiterpene, bebryazulene (25), with a guaiane skeleton, was isolated from the gorgonian coral B. grandicalyx, collected at the Prevoyante Reef, Lagoon of Mayotte, Comoros Islands, Indian Ocean [7] (Table 3). The structure of guaiane 25 was assigned by spectroscopic methods. This metabolite was labile and reacted with 4-phenyl-3H-1,2,4-triazoline-3,5-dione to yield a triazolinedione adduct.

Table 3.
The natural product from B. grandicalyx.
| Structure | No. | Name | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 25 | Bebryazulene | [7] |
2.2.2. Bebryce indica
B. indica, a gorgonian species collected off the coast of Sanya, Hainan province, China, was found to contain a new steroidal glycoside, bebrycoside (26) [8] (Table 4). The main structure of 26 was determined by spectral data analysis, although the stereochemistry of the C-25 chiral carbon was not determined. Bebrycoside (26) is the first steroidal glycoside to be isolated from the genus Bebryce.

Table 4.
The natural product from B. indica.
| Structure | No. | Name | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
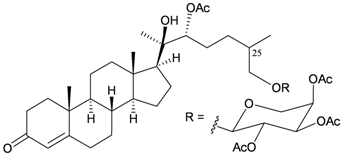 | 26 | Bebrycoside | [8] |
2.2.3. Bebryce sp.
Bebryceoid A (27), a new trihydroxysteroid, was isolated from gorgonian Bebryce sp., collected off the coast of Pingtung, southern Taiwan [9] (Table 5). The structure of steroid 27 was assigned by spectroscopic methods. Bebryceoid A (27) exhibited weak cytotoxicity toward P388D1 and DLD-1 tumor cells.

Table 5.
The natural product from Bebryce sp.
| Structure | No. | Name | Biological Activity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 27 | Bebryceoid A | ED50 (P388D1, DLD-1, CCRF-CEM, HL-60) = 18.5, 7.2, >40, >40 μg/mL | [9] |
2.3. Genus Echinomuricea
Echinomuricea sp.
Two sesquiterpenoids, including new natural product (7S,10R)-(+)-10,11-epoxycurcuphenol (28) and known metabolite (+)-curcuphenol (29) [10], along with a new labdane-type diterpenoid, echinolabdane A (30), a new sterol, 6-epi-yonarasterol B (31) [11], a new clerodane-type diterpenoid, echinoclerodane A (32) [12] and a new halimane-type diterpenoid, echinohalimane A (33) [13], were isolated from the gorgonian coral Echinomuricea sp., collected off the coast of southern Taiwan (Table 6). The structures of metabolites 28–33 were elucidated by spectroscopic methods. Echinolabdane A (30) possesses a novel tetracyclic skeleton with an oxepane ring joined to an α,β-unsaturated-γ-lactone ring by a hemiketal moiety [11]. Echinolabdane A (30), echinoclerodane A (32) and echinohalimane A (33) are the first labdane-, clerodane- and halimane-type diterpenoids to be obtained from marine organisms belonging to the phylum Cnidaria, respectively [11,12,13].

Table 6.
The natural products from Echinomuricea sp.
| Structure | No. | Name | Biological Activity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 28 | (7 S,10R)-(+)-10,11-Epoxycurcuphenol | Showed inhibitory effects on the generation of superoxide anions (inhibition rate 35.3%) and the release of elastase (inhibition rate 38.8%) at a concentration of 10 μg/mL. | [10] |
 | 29 | (+)-Curcuphenol | Showed inhibitory effects on the generation of superoxide anion (inhibition rate 36.9%) and the release of elastase (inhibition rate 83.6%) at a concentration of 10 μg/mL. ED50 (DLD-1, CCRF-CEM) = 12.5, 11.8 μg/mL. | [10] |
 | 30 | Echinolabdane A | Not active in terms of inhibition of the generation of superoxide anions (inhibition rate 2.5%) or the release of elastase (inhibition rate 1.8%) at a concentration of 10 μg/mL. IC50 (HL-60) = 19.1 μg/mL. | [11] |
 | 31 | 6- epi-Yonarasterol B | Showed significant inhibitory effects on the generation of superoxide anions (IC50 = 3.0 μg/mL) and the release of elastase (IC50 = 1.1 μg/mL). | [11] |
 | 32 | Echinoclerodane A | Showed inhibitory effects on the generation of superoxide anions (inhibition rate 68.6%) and the release of elastase (inhibition rate 35.4%) at a concentration of 10 μg/mL. IC50 (K562, MOLT-4, HL-60, DLD-1, LoVo, DU-145) = 37.1, 13.2, 14.9, 23.4, 21.7, 53.9 μg/mL. | [12] |
 | 33 | Echinohalimane A | Showed a significant inhibitory effect on the release of elastase (IC50 = 0.4 μg/mL).IC50 (K562, MOLT-4, HL-60, DLD-1, LoVo) = 6.3, 2.1, 2.1, 1.0, 0.6 μg/mL. | [13] |
In biological activity experiments, sesquiterpenoid 29 displayed a significant inhibitory effect on the release of elastase by human neutrophils. This compound also exhibited weak cytotoxicity toward DLD-1 and CCRF-CEM tumor cells [9]. Steroid 31 displayed significant inhibitory effects on the generation of superoxide anions and the release of elastase by human neutrophils [11]. Clerodane 32 exhibited weak cytotoxicity toward MOLT-4 and HL-60 tumor cells and displayed a significant inhibitory effect on the generation of superoxide anions by human neutrophils [12]. Halimane 33 exhibited cytotoxicity toward K562, MOLT-4, HL-60, DLD-1 and LoVo tumor cells and displayed a significant inhibitory effect on the release of elastase by human neutrophils [13].
2.4. Genus Euplexaura
2.4.1. Euplexaura anastomosans
Four new steroids of the cholestane class, anastomosacetals A–D (34–37), were obtained from the gorgonian coral E. anastomosans, collected off the shore of Keomun Island, South Sea Korea [14] (Table 7). The structures of steroids 34–37 were determined by spectroscopic methods, and these four compounds are the first examples of marine steroids possessing an unusual hemiacetal linkage formed by oxidation of the C-21 methyl group.
In addition, seven new moritoside class farnesylhydroquinone glycosides, euplexides A–G (38–44), were isolated from E. anastomosans [15,16] (Table 7). The structures of glycosides 38–44, including their absolute stereochemistry, were elucidated by spectroscopic and chemical methods. Compounds 38–44 exhibited moderate cytotoxicity and antioxidant activity as well as an inhibitory effect against PLA2.

Table 7.
The natural products from E. anastomosans.
| Structure | No. | Name | Biological Activity | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 34 | Anastomosacetal A | Steroids 34–37 were not toxic to P-388 cells or brine-shrimp larva. | [14] | ||
| 35 | Anastomosacetal B (4,5-dihydro) | [14] | ||||
| 36 | Anastomosacetal C (1,2-dihydro) | [14] | ||||
| 37 | Anastomosacetal D (1,2,4,5-tetrahydro) | [14] | ||||
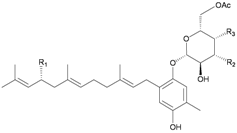 | 38 | Euplexide A (R1 = OH, R2 = R3 = OAc) | Glycosides 38–40, 43, 44 exhibited cytotoxicity toward K462 cells (IC50 = 2.6, 3.1, 5.2, 8.7, 11.3 μg/mL). Glycosides 38–40 displayed antioxidant activity of 3.4, 3.6 and 3.5 times, respectively, that of superoxide dismutase (SOD) at a concentration of 10 μg/300 μL. Glycosides 38, 39, 43, 44 exhibited 52, 71, 47 and 58%, respectively, inhibition of PLA2 at a concentration of 50 μg/mL. | [15] | ||
| 39 | Euplexide B (R1 = R2 = R3 = OAc) | [15] | ||||
| 40 | Euplexide C (R1 = H, R2 = R3 = OAc) | [15] | ||||
| 43 | Euplexide F (R1 = H, R2 = OH, R3 = OAc) | [16] | ||||
| 44 | Euplexide G (R1 = H, R2 = OAc, R3 = OH) | [16] | ||||
 | 41 | Euplexide D | IC50 (K462) = 8.1 μg/mL. | [15] | ||
 | 42 | Euplexide E | IC50 (K462) = 9.4 μg/mL. Displayed antioxidant activity of 3.1 times that of superoxide dismutase (SOD) at a concentration of 10 μg/300 μL. | [15] | ||
2.4.2. Euplexaura erecta
A prostaglandin derivative, PGF2α (45), was isolated from the gorgonian coral E. erecta collected at Shimoda, Sagami Bay, Japan [17] (Table 8), and this compound was proven to be the active component in E. erecta. This finding is the first demonstration that gorgonian corals containing prostaglandins are not limited to species in the Caribbean area.
Furthermore, a bluish-violet oil, guaiazulene (46), was isolated from E. erecta collected at Enoshima Island, Kanagawa, Japan [18] (Table 8). The structure of guaiazulene (46) from E. erecta was determined by spectroscopic methods and by comparison of the spectral data with those of reported data. This is the first isolation of guaiazulene from an animal, and this compound showed mild antimicrobial activity [18].

Table 8.
The natural products from E. erecta.
| Structure | No. | Name | Biological Activity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 45 | PGF2α | Contracting activity towards isolated guinea-pig ileum strips. | [17] |
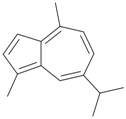 | 46 | Guaiazulene | Showed mild activity against fungi, gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. | [18] |
2.4.3. Euplexaura flava
Four new unnamed fatty acid derivatives 47–50, which contain a butenolide moiety, were isolated from the gorgonian coral E. flava, collected at the coral reef of Ishigaki Island, Okinawa, Japan. The structures of butenolides 47–50 were elucidated by spectroscopic and chemical methods [19] (Table 9).

Table 9.
The natural products from E. flava.
| Structure | No. | Name | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
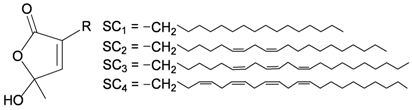 | 47 | R = SC1 | [19] |
| 48 | R = SC2 | [19] | |
| 49 | R = SC3 | [19] | |
| 50 | R = SC4 | [19] |
2.4.4. Euplexaura nuttingi
Six new tetraprenylated purine alkaloids, nuttingins A–F (51–56), were isolated together with five new compounds, malonganenones D–H (57–61), and three known metabolites, malonganenones A–C (62–64), from the gorgonian coral E. nuttingi collected in Uvinage, Pemba Island, Tanzania. The structures of compounds 51–64 were elucidated by interpretation of spectral data [20] (Table 10). Mixtures of nuttingins A and B (51 and 52), C–E (53–55), malonganenones D and E (57 and 58), and F and G (59 and 60) have been found to inhibit growth of K562 and UT7 tumor cells. Nuttingins A–E (51–55) and malonganenones D–H (57–61) induce apoptosis in transformed mammalian cells [20].

Table 10.
The natural products from E. nuttingi.
| Structure | No. | Name | Biological Activity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 51 | Nuttingin A (R = SC1) | Compounds 51–55 and 57–61 induce apoptosis in transformed mammalian cells at a concentration of 1.25 μg/mL. Mixtures of compounds 51 and 52 displayed inhibitory activity on the proliferation of UT7 and K562 cell lines, although they were approximately 3-fold less potent than mixtures of compounds 53–55. | [20] |
| 52 | Nuttingin B (R = SC3) | [20] | ||
 | 53 | Nuttingin C (R = SC1) | Mixtures of compounds 53–55 induced 50% inhibition of cell growth in UT7 cells and 30% in K562 cells after 48 h of exposure at a concentration of 0.4 μg/mL. | [20] |
| 54 | Nuttingin D (R = SC2) | [20] | ||
| 55 | Nuttingin E (R = SC3) | [20] | ||
 | 56 | Nuttingin F (R = SC2) | [20] | |
 | 57 | Malonganenone D (R = SC1) | Mixtures of compounds 57 and 58 displayed inhibitory activity on the proliferation of UT7 and K562 cell lines, although they were approximately 3-fold less potent than mixtures of compounds 53–55. | [20] |
| 58 | Malonganenone E (R = SC2) | [20] | ||
| 62 | Malonganenone A (R = SC3) | [20] | ||
 | 59 | Malonganenone F (R = SC1) | Mixtures of compounds 59 and 60 displayed inhibitory activity on the proliferation of UT7 and K562 cell lines, although they were approximately 3-fold less potent than mixtures of compounds 53–55. | [20] |
| 60 | Malonganenone G (R = SC2) | [20] | ||
| 63 | Malonganenone B (R = SC3) | [20] | ||
 | 61 | Malonganenone H (R = SC2) | [20] | |
| 64 | Malonganenone C (R = SC3) | [20] | ||
 | ||||
2.4.5. Euplexaura sp.
Moritoside (65), a new hydroquinone glycoside derivative was isolated from the gorgonian Euplexaura sp., collected near Morito beach in the Gulf of Sagami, Japan. The structure of glycoside 65 was determined by spectroscopic and chemical methods [21] (Table 11). This is the first example of the occurrence of D-altrose in natural products, and this compound inhibits the first cell division of fertilized starfish (Asterina pectinifera) eggs.

Table 11.
The natural product from Euplexaura sp.
| Structure | No. | Name | Biological Activity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 65 | Moritoside | Inhibits the first cell division of fertilized starfish (Asterina pectinifera) eggs at a concentration of 1 μg/mL. | [21] |
2.5. Genus Menella
2.5.1. Menella spinifera
The gorgonian M. spinifera collected off the South China Sea was found to contain six known compounds, including batyl alcohol (66) [22,23], picolinic acid N-methyl betaine (67) [23,24], n-hexadecanol (68) [23], 3β-hydroxy-5α-pregnane-20-one (69) [23], 9H-purin-6-amino-N-9-dimethyl (70) [23] and thymidine (71) [23] (Table 12). The structures of compounds 66–71 were elucidated by spectroscopic methods.

Table 12.
The natural products from M. spinifera.
| Structure | No. | Name | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
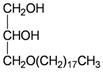 | 66 | Batyl alcohol | [22,23] |
 | 67 | Picolinic acid N-methyl betaine | [23,24] |
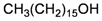 | 68 | n-Hexadecanol | [23] |
 | 69 | 3β-Hydroxy-5α-pregnane-20-one | [23] |
 | 70 | 9 H-Purin-6-amino-N-9-dimethyl | [23] |
 | 71 | Thymidine | [23] |
2.5.2. Menella verrucosa
Four new highly-oxygenated guaiane lactones, menverins A–D (72–75) [25], and two new polyoxygenated steroids, menellsteroids A (76) and B (77) [26] (Table 13), were isolated from the gorgonian M. verrucosa, collected along the coast of Xiaodong Hai, Hainan province, China. The structures of metabolites 72–77 were established by spectroscopic methods. In a later study, menellsteroid A (76) was found to exhibit modest anti-inflammatory inhibition of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced nitric oxide (NO) production in RAW264.7 macrophages [27].

Table 13.
The natural products from M. verrucosa.
| Structure | No. | Name | Biological Activity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 72 | Menverin A (R1 = α-H, R2 = β-OH, R3 = α-methyl) | [25] | |
| 73 | Menverin B (R1 = α-H, R2 = β-methyl, R3 = α-OH) | [25] | ||
| 74 | Menverin C (R1 = α-OH, R2 = β-OH, R3 = α-methyl) | [25] | ||
| 75 | Menverin D (R1 = R2 = β-OH, R3 = α-methyl) | [25] | ||
 | 76 | Menellsteroid A (22,23-dihydro) | Exhibited a modest inhibitory effect with an IC50 of 33.9 μM compared to the positive control aminoguanidine, with an IC50 = 25.0 μM. | [26,27] |
| 77 | Menellsteroid B | [26] |
2.5.3. Menella sp.
Li et al., isolated four new highly-oxygenated guaiane lactones, 1-epimenverin B (78), menverin F (79), 1-deoxymenverin F (80) and menverin G (81), along with two known guaiane analogs, menverins B (73) and C (74), from the gorgonian Menella sp., collected off the Lingshui Bay, Hainan province, China [28] (Table 14). The structures of new guaianes 78–81 were elucidated by spectroscopic methods and by comparison with those of known analogs.

Table 14.
The natural products from Menella sp.
| Structure | No. | Name | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 78 | 1-Epimenverin B | [28] |
 | 79 | Menverin F (R = α-OH) | [28] |
| 80 | 1-Deoxymenverin F (R = α-H) | [28] | |
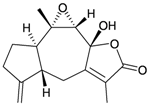 | 81 | Menverin G | [28] |
A chemical investigation of the gorgonian Menella sp., collected off Meishan Island, Hainan province, China, resulted in a novel highly-oxygenated racemate with a C8 skeleton, menellin A (82), a new tetrahydroxysteroid, menellsteroid C (83), a new natural product, 1β,3β,5α-trihydroxy-cholestan-6-one (84) and seven known compounds, menellsteroid A (76), cholestan-3β,5α,6β-triol (85), cholestan-1β,3β,5α,6β-tetrol (86), nephalsterol (87), cholestan-3β-5-en-6-one (88) and junceellolides B (89) and D (90) [27] (Table 15). The structures of the above compounds were elucidated by spectroscopic methods and by comparison of the spectral data with those of known analogs. The structure, including the relative stereochemistry, of menellin A (82) was further confirmed by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. As already reported for menellsteroid A (76), menellin A (82) exhibited modest anti-inflammatory inhibition of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced nitric oxide (NO) production in RAW264.7 macrophages.
Seven pregnane steroids, 3α-hydroxy-5β-pregnan-20-one (91), 3β-hydroxy-5α-pregnan-20-one (92), 3β-hydroxy-pregnan-5-en-20-one (93), 5β-pregnan-3,20-dione (94), 5α-pregnan-3,20-dione (95), pregnan-4-en-3,20-dione (96) and pregnan-1,4-dien-3,20-one (97), were isolated from the gorgonian Menella sp., collected off Meishan Island, Sanya Bay, Hainan province, China [29] (Table 16). The structures of steroids 91–97 were elucidated by spectroscopic methods and by comparison with those of known analogs. The NMR data of steroid 97 are reported for the first time in this study.

Table 15.
The natural products from Menella sp.
| Structure | No. | Name | Biological Activity | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
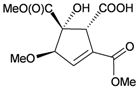 | 82 | Menellin A | Exhibited a modest inhibitory effect (IC50 = 71.3 μM) compared to the positive control aminoguanidine (IC50 = 25.0 μM). There were no obvious scavenging effects for compounds 76 and 82–90 on the antioxidant capacity in a radical DPPH free-radical assay. | [27] | ||
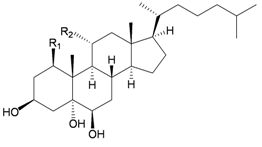 | 83 | Menellsteroid C (R1 = H, R2 = OH) | [27] | |||
| 85 | Cholestan-3β,5α,6β-triol (R1 = R2 = H) | [27] | ||||
| 86 | Cholestan-1β,3β,5α,6β-tetrol (R1 = OH, R2 = H) | [27] | ||||
 | 84 | Menellsteroid D (1β,3β,5α-trihydroxycholestan-6-one) | [27] | |||
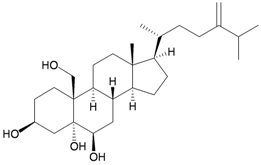 | 87 | Nephalsterol | [27] | |||
 | 88 | Cholestan-3β-5-en-6-one | [27] | |||
 | 89 | Junceellolide B | [27] | |||
 | 90 | Junceellolide D | [27] | |||

Table 16.
The natural products from Menella sp.
| Structure | No. | Name | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
 | 91 | 3α-Hydroxy-5β-pregnan-20-one (R1 = α-OH, R2 = β-H) | [29] |
| 92 | 3β-Hydroxy-5α-pregnan-20-one (R1 = β-OH, R2 = α-H) | [29] | |
 | 93 | 3β-Hydroxy-pregnan-5-en-20-one | [29] |
 | 94 | 5β-Pregnan-3,20-dione (R = β-H) | [29] |
| 95 | 5α-Pregnan-3,20-dione (R = α-H) | [29] | |
 | 96 | Pregnan-4-en-3,20-dione (1,2-dihydro) | [29] |
| 97 | Pregnan-1,4-dien-3,20-dione | [29] |
Eight sesquiterpenoids, including seven new compounds, (–)-hydroxylindestrenolide (98) [30], menelloides A–E (99–103) [31,32,33] and (+)-chloranthalactone B (104) [31], along with a known metabolite, seco-germacrane anhydride (105) [34] (Table 17), were isolated from the Formosan gorgonian Menella sp., collected by trawling off the coast of southern Taiwan. (–)-Hydroxy-lindestrenolide (98) and (+)-chloranthalactone B (104) were proven to be enantiomers of the known sesquiterpenoids (+)-hydroxylindestrenolide and chloranthalactone B, respectively [30,31]. Menelloide A (99) was found to possess a new carbon skeleton [31]. Seco-germacrane anhydride (105) was a known metabolite and there have been no reports of seco-germacrane anhydride (105) being obtained from any marine organism previously [34]. Several of these compounds displayed inhibitory effects on the generation of superoxide anions and the release of elastase by human neutrophils.

Table 17.
The natural products from Menella sp.
| Structure | No. | Name | Biological Activity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 98 | (–)-Hydroxylindestrenolide | Displayed a weak inhibitory effect on the generation of superoxide anions (inhibition rate 13.4%) at a concentration of 10 μg/mL. | [30] |
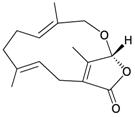 | 99 | Menelloide A | Displayed a weak inhibitory effect on the generation of superoxide anions (27.6%) at a concentration of 10 μg/mL. | [31] |
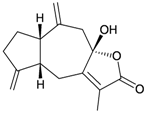 | 100 | Menelloide B | Not active in terms of inhibition of the generation of superoxide anions (inhibition rate 2.9%) and the release of elastase (inhibition rate 0.7%) at a concentration of 10 μg/mL. | [31] |
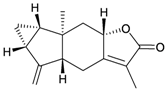 | 101 | Menelloide C | [32] | |
 | 102 | Menelloide D | Displayed a weak inhibitory effect on the release of elastase (inhibition rate 10.5%) at a concentration of 10 μg/mL. | [32] |
 | 103 | Menelloide E | Displayed weak inhibitory effects on the generation of superoxide anions (inhibition rate 19.9%) and the release of elastase (inhibition rate 27.0%) at a concentration of 10 μg/mL. | [33] |
 | 104 | (+)-Chloranthalactone B | Displayed a weak inhibitory effect on the generation of superoxide anions (inhibition rate 16.5%), but was not active in terms of inhibition of the release of elastase (inhibition rate 6.6%) at a concentration of 10 μg/mL. | [31] |
 | 105 | Seco-germacrane anhydride | [34] |
3. Conclusions
The search for bioactive natural products from marine organisms has been remarkably successful, and octocorals have been proven to be rich sources of natural products with potential biomedical application [35,36,37]. In particular, the data reported in this review indicate that terpenoid and steroid derivatives represent the major chemical classes occurring in Indo-Pacific octocoral species belonging to the family Plexauridae. Among the 105 isolated metabolites, in fact, 49 compounds are terpenoid analogs (46.7%) and 45 compounds are steroid metabolites (42.9%). These compounds continue to attract attention owing to their structural novelty, complexity and interesting bioactivities.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Dong Hwa University; the National Museum of Marine Biology and Aquarium (Grant No. 10120022); the Division of Marine Biotechnology, Asia-Pacific Ocean Research Center, National Sun Yat-sen University, (Grant No. 00C-0302-05); the Department of Health, Executive Yuan, Taiwan (Grant No. DOH101-TD-C-111-002); and the National Science Council (Grant No. NSC 101-2325-B-291-001, 100-2325-B-291-001, 101-2320-B-291-001-MY3 and 98-2320-B-291-001-MY3), Taiwan, awarded to Yang-Chang Wu and Ping-Jyun Sung.
References
- Fabricius, K.; Alderslade, P. Soft Corals and Sea Fans: A Comprehensive Guide to the Tropical Shallow-Water Genera of the Central-West Pacific, the Indian Ocean and the Red Sea, 1st ed; Australian Institute of Marine Science: Queensland, Australia, 2001; pp. 59–60, 190–213. [Google Scholar]
- Fusetani, N.; Nagata, H.; Hirota, H.; Tsuyuki, T. Astrogorgiadiol and astrogorgin, inhibitors of cell division in fertilized starfish eggs, from a gorgonian Astrogorgia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989, 30, 7079–7082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D.; Yu, S.; van Ofwegen, L.; Totzke, F.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. 9,10-Secosteroids, protein kinase inhibitors from the Chinese gorgonian Astrogorgia sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6873–6880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, M.; Yamada, K.; Kotsuki, H.; Shibata, K. Calicoferols A and B, two novel secosterols possessing brine-shrimp lethality from the gorgonian Calicogorgia sp. Chem. Lett. 1991, 20, 427–430. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, Y.; Shin, J.; Song, J.-I. New secosteroids from an undescribed gorgonian of the genus Muricella. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Cho, K.W.; Chung, H.; Lee, H.-S.; Shin, J. New secosteroids from a gorgonian of the genus Muricella. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 1441–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aknin, M.; Rudi, A.; Kashman, Y.; Gaydou, E.M. Bebryazulene, a new guaiane metabolite from the Indian Ocean gorgonian coral, Bebryce grandicalyx. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 1286–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Qi, S.-H.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, Z.-H.; Li, Q.-X. Bebrycoside, a new steroidal glycoside from the Chinese gorgonian coral Bebryce indica. Pharmazie 2007, 62, 154–155. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, P.-J.; Liu, C.-Y. New 3β,5α,6β-trihydroxysteroids from the octocorals Bebryce sp. (Plexauridae) and Carijoa sp. (Clavulariidae). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 1240–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.-M.; Hwang, T.-L.; Wang, W.-H.; Fang, L.-S.; Sung, P.-J. Curcuphenol derivatives from the gorgonian Echinomuricea sp. Heterocycles 2009, 78, 2595–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.-M.; Hong, P.-H.; Su, J.-H.; Hwang, T.-L.; Lu, M.-C.; Fang, L.-S.; Wu, Y.-C.; Li, J.-J.; Chen, J.-J.; Wang, W.-H.; Sung, P.-J. Bioactive compounds from a gorgonian coral Echinomuricea sp. (Plexauridae). Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-H.; Chung, H.-M.; Hwang, T.-L.; Lu, M.-C.; Wen, Z.-H.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Wang, W.-H.; Sung, P.-J. Echinoclerodane A: A new bioactive clerodane-type diterpenoid from a gorgonian coral Echinomuricea sp. Molecules 2012, 17, 9443–9450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.-M.; Hu, L.-C.; Yen, W.-H.; Su, J.-H.; Lu, M.-C.; Hwang, T.-L.; Wang, W.-H.; Sung, P.-J. Echinohalimane A, a bioactive halimane-type diterpenoid from a formosan gorgonian Echinomuricea sp. (Plexauridae). Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2246–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Rho, J.-R.; Cho, K.W.; Shin, J. Isolation of new steroidal hemiacetals from the gorgonian Euplexaura anastomosans. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Seo, Y.; Cho, K.W.; Moon, S.-S.; Cho, Y.J. Euplexides A–E: Novel farnesylhydroquinone glycosides from the gorgonian Euplexaura anastomosans. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 1853–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Rho, J.-R.; Cho, K.W.; Shin, J. New farnesylhydroquinone glycosides from the gorgonian Euplexaura anastomosans. Nat. Prod. Lett. 2001, 15, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komoda, Y.; Kanayasu, T.; Ishikawa, M. Prostaglandin F2α from the Japanese coastal gorgonian, Euplexaura erecta. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1979, 27, 2491–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusetani, N.; Matsunaga, S.; Konosu, S. Bioactive marine metabolites I. Isolation of guaiazulene from the gorgonian Euplexaura erecta. Experientia 1981, 37, 680–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, H.; Tsukitani, Y.; Nakanishi, H.; Shimizu, I.; Saitoh, S.; Iguchi, K.; Yamada, Y. New butenolides from the gorgonian Euplexaura flava (Nutting). Chem. Lett. 1982, 11, 233–236. [Google Scholar]
- Sorek, H.; Rudi, A.; Benayahu, Y.; Ben-Califa, N.; Neumann, D.; Kashman, Y. Nuttingins A–F and malonganenones D–H, tetraprenylated alkaloids from the Tanzanian gorgonian Euplexaura nuttingi. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusetani, N.; Yasukawa, K.; Matsunaga, S.; Hashimoto, K. Bioactive marine metabolites XII. Moritoside, an inhibitor of the development of starfish embryo, from the gorgonian Euplexaura sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1985, 26, 6449–6452. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, S.; Peng, S.; Li, F.; Tan, X.; Chen, J. A study on chemical constituents of South China Sea gorgonian Menella spinifera Kukenthal (I). Guangzhou Chem. 1993, 18(4), 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, S.; Li, F.; Peng, S.; Rao, Z.; Wu, H.; Xu, J. Chemical constituents of the South China Sea gorgonian Menella spinifera Kukenthal. Chin. J. Appl. Chem. 1997, 14(5), 80–82. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Deng, S.; Rao, Z.; Wu, H.; Xu, J. Studies on chemical constituents of South China Sea gorgonian Menella spinifera Kukenthal (II). Guangzhou Chem. 1996, 21(3), 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, Y.-W.; Mollo, E.; Cimino, G. Menverins A–D, new highly oxygenated guaiane lactones from Hainan gorgonian Menella verrucosa (Brundin). Helv. Chim. Acta 2004, 87, 2919–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, H.; Ding, Y.; Gavagnin, M.; Mollo, E.; Cimino, G.; Guo, Y.-W. Three new polyoxygenated steroids from two species of the South China Sea gorgonian Muricella flexuosa and Menella verrucosa Brundin. Helv. Chim. Acta 2006, 89, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.-Y.; Sun, J.-F.; Tang, L.-Y.; Yang, X.-W.; Li, Y.-Q.; Huang, H.; Zhou, X.-F.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y. A novel cyclopentene derivative and a polyhydroxylated steroid from a South China Sea gorgonian Menella sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 1391–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, C.-Y.; Huang, H.; Mollo, E.; Cimino, G.; Guo, Y.-W. Further highly oxygenated guaiane lactones from the South China Sea gorgonian Menella sp. Helv. Chim. Acta 2008, 91, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.-Y.; Hu, J.; Huang, H.; Lei, H.; Chen, X.-Q.; Li, Y.-Q.; Sun, J.-F.; Dong, G.; Liu, Y.-H.; Liu, X.-D. Pregnane steroids from a gorgonian Menella sp. in South China Sea. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2011, 30, 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Kao, S.-Y.; Chang, Y.-C.; Su, J.-H.; Lu, M.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Sheu, J.-H.; Wen, Z.-H.; Wang, W.-H.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Hwang, T.-L.; et al. (–)-Hydroxylindestrenolide, a new sesquiterpenoid from a gorgonian coral Menella sp. (Plexauridae). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 59, 1048–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, S.-Y.; Su, J.-H.; Hwang, T.-L.; Sheu, J.-H.; Su, Y.-D.; Lin, C.-S.; Chang, Y.-C.; Wang, W.-H.; Fang, L.-S.; Sung, P.-J. Discovery of novel sesquiterpenoids from a gorgonian Menella sp. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 7311–7315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, S.-Y.; Su, J.-H.; Hwang, T.-L.; Sheu, J.-H.; Wen, Z.-H.; Wu, Y.-C.; Sung, P.-J. Menelloides C and D, new sesquiterpenoids from the gorgonian coral Menella sp. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1534–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Kao, C.-Y.; Kao, S.-Y.; Chang, C.-H.; Su, J.-H.; Hwang, T.-L.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Wen, Z.-H.; Sung, P.-J. Terpenoids from the octocorals Menella sp. (Plexauridae) and Lobophytum crassum (Alcyonacea). Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, P.-J.; Kao, S.-Y.; Kao, C.-Y.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Su, Y.-D. Seco-germacrane anhydride: Occurrence of a sesquiterpene lactone in the gorgonian coral Menella sp. (Plexauridae). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2012, 40, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.; Peixe, L.; Gomes, N.C.M.; Calado, R. Cnidarians as a source of new marine bioactive compounds—An overview of the last decade and future steps for bioprospecting. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1860–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.G.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 144–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrue, F.; Kerr, R.G. Diterpenes from gorgonian corals. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 681–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samples Availability: Available from the authors.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).