Biological and Pharmacological Properties of Carbon Monoxide: A General Overview
Abstract
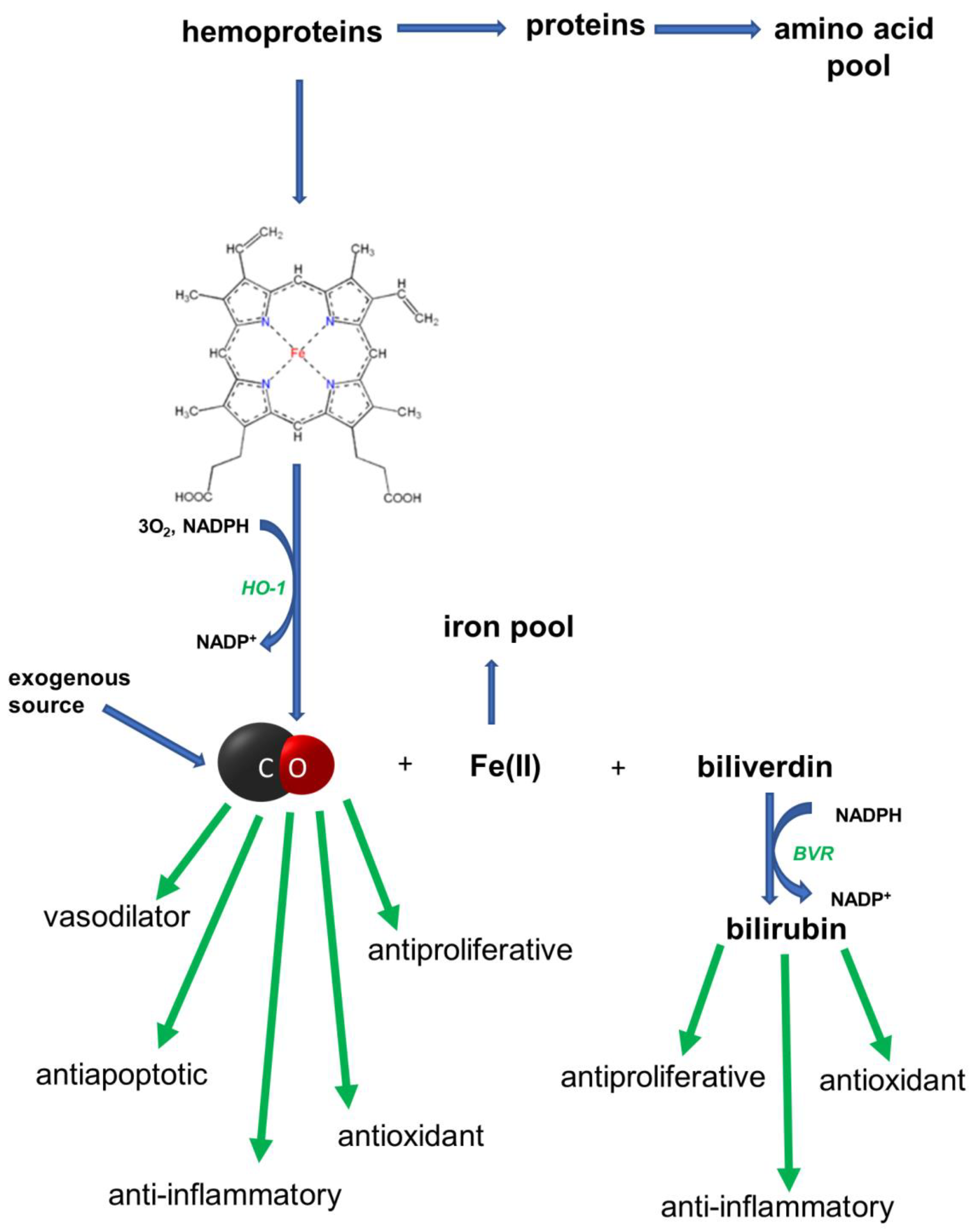
1. Introduction
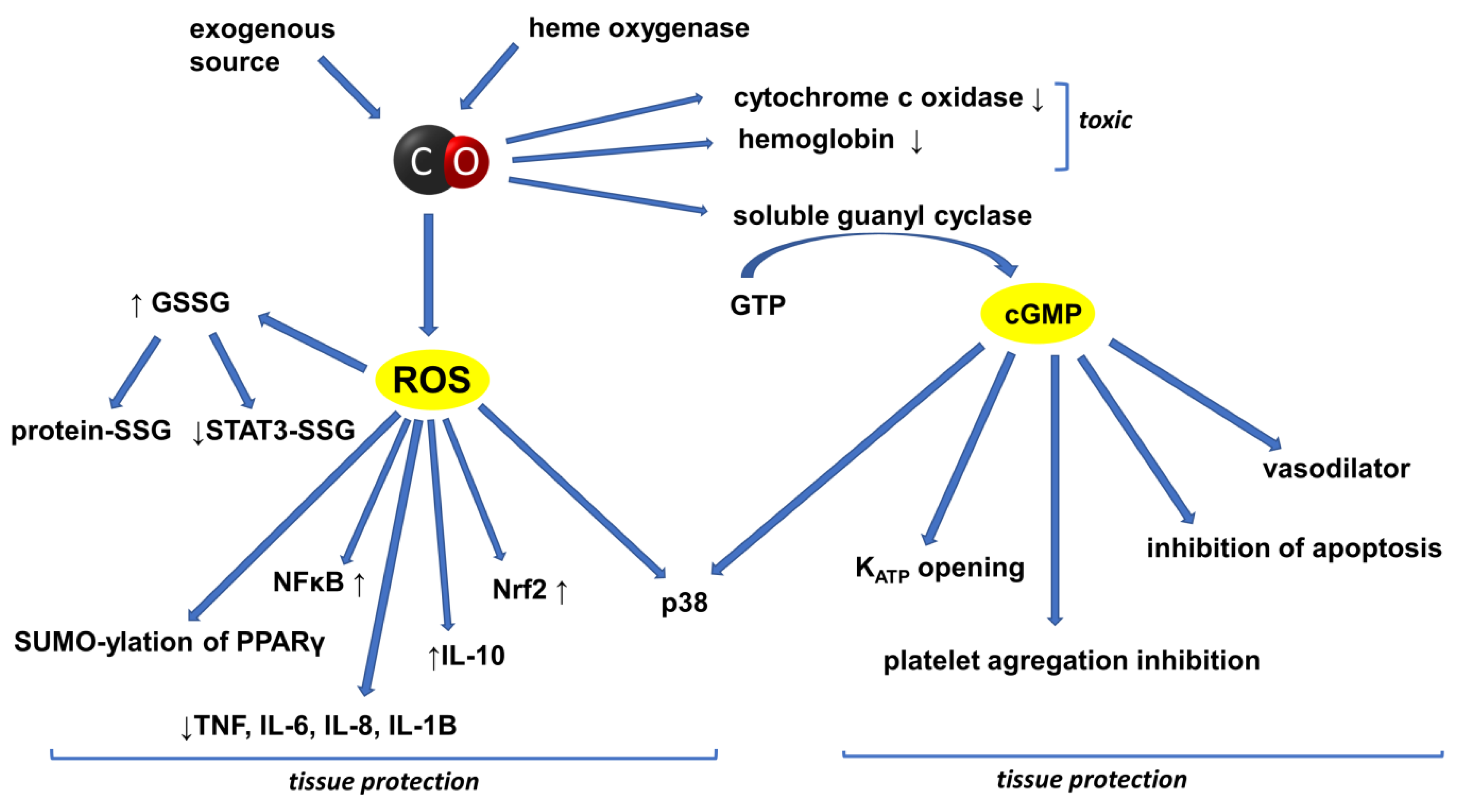
2. CO in the Circulatory System
3. The Effect of CO on the Central Nervous System
4. Inflammation and Cancer: The Role of the HO/CO System
5. The Effect of CO on Metabolic Processes
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sjöstrand, T. The formation of carbon monoxide by the decomposition of haemoglobin in vivo. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1952, 26, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durante, W.; Johnson, F.K.; Johnson, R.A. Role of carbon monoxide in cardiovascular function. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2006, 10, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayer, A.; Zarjou, A.; Agarwal, A.; Stocker, R. Heme oxygenases in cardiovascular health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1449–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryter, S.W.; Choi, A.M. Targeting heme oxygenase-1 and carbon monoxide for therapeutic modulation of inflammation. Transl. Res. 2016, 167, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.Q.; Li, L.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Sun, Y.Y.; Wu, J. Research Progress in Understanding the Relationship Between Heme Oxygenase-1 and Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, W.; Choi, A.M.; Li, C. Carbon monoxide inhibits IL-17-induced IL-6 production through the MAPK pathway in human pulmonary epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2005, 289, L268–L273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.P.; Choi, A.M. A new road to induce heme oxygenase-1 expression by carbon monoxide. Circ. Res. 2007, 101, 862–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kietzmann, T.; Samoylenko, A.; Immenschuh, S. Transcriptional regulation of heme oxygenase-1 gene expression by MAP kinases of the JNK and p38 pathways in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 17927–17936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapora, E.; Jarocka, I. Hemoglobin—Source of reactive oxygen. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2013, 67, 214–220. (In Polish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Omata, Y.; Sakamoto, H.; Higashimoto, Y.; Hara, T.; Sagara, Y.; Noguchi, M. Characterization of rat heme oxygenase-3 gene. Implication of processed pseudogenes derived from heme oxygenase-2 gene. Gene 2004, 336, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, S.; Gilun, P.; Kozioł, K.; Romerowicz-Misielak, M.; Koziorowska-Gilun, M.; Wąsowska, B. Carbon Monoxide (CO) as a Retinal Regulator of Heme Oxygenases-1, and-2 (HO’s) Expression. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maines, M.D. The heme oxygenase system: A regulator of second messenger gases. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1997, 37, 517–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruse, I.; Maines, M.D. Evidence suggesting that the two forms of heme oxygenase are products of different genes. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 3348–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitti, M.; Piras, S.; Marinari, U.M.; Moretta, L.; Pronzato, M.A.; Furfaro, A.L. HO-1 induction in cancer progression: A matter of cell adaptation. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waza, A.A.; Hamid, Z.; Ali, S.; Bhat, S.A.; Bhat, M.A. A review on heme oxygenase-1 induction: Is it a necessary evil. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 67, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bełtowski, J.; Jamroz, A.; Borkowska, E. Heme oxygenase and carbon monoxide in the physiology and pathology of the cardiovascular system. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2004, 58, 83–99. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Jasnos, K.; Magierowski, M.; Kwiecień, S.; Brzozowski, T. Carbon monoxide in human physiology—Its role in the gastrointestinal tract. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2014, 68, 101–109. (In Polish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, S.R. Carbon Monoxide pathophysiology and treatment. In Physiology and Medicine of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy; Neuman, T.S., Thom, S.R., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008; pp. 321–347. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Z.; Wu, L. Carbon monoxide-induced vasorelaxation and the underlying mechanisms. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 121, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evgenov, O.V.; Pacher, P.; Schmidt, P.M.; Haskó, G.; Schmidt, H.H.; Stasch, J.P. NO-independent stimulators and activators of soluble guanylate cyclase: Discovery and therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furchgott, R.F.; Jothianandan, D. Endothelium-dependent and -independent vasodilation involving cyclic GMP: Relaxation induced by nitric oxide, carbon monoxide and light. Blood Vessel 1991, 28, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozma, F.; Johnson, R.A.; Zhang, F.; Yu, C.; Tong, X.; Nasjletti, A. Contribution of endogenous carbon monoxide to regulation of diameter in resistance vessels. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276, R1087–R1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katada, K.; Bihari, A.; Mizuguchi, S.; Yoshida, N.; Yoshikawa, T.; Fraser, D.D.; Potter, R.F.; Cepinskas, G. Carbon monoxide liberated from CO-releasing molecule (CORM-2) attenuates ischemia/reperfusion (I/R)-induced inflammation in the small intestine. Inflammation 2010, 33, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, T. Heme oxygenase and atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 1786–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubos, E.; Handy, D.E.; Loscalzo, J. Role of oxidative stress and nitric oxide in atherothrombosis. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 5323–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlopicki, S.; Olszanecki, R.; Marcinkiewicz, E.; Lomnicka, M.; Motterlini, R. Carbon monoxide released by CORM-3 inhibits human platelets by a mechanism independent of soluble guanylate cyclase. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 71, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryter, S.W.; Alam, J.; Choi, A.M. Heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide: From basic science to therapeutic applications. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 583–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorup, C.; Jones, C.L.; Gross, S.S.; Moore, L.C.; Goligorsky, M.S. Carbon monoxide induces vasodilation and nitric oxide release but suppresses endothelial NOS. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 277, F882–F889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Farrugia, G.; Miller, S.M.; Ferris, C.D.; Snyder, S.H.; Szurszewski, J.H. Carbon monoxide and nitric oxide as coneurotransmitters in the enteric nervous system: Evidence from genomic deletion of biosynthetic enzymes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 1851–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wu, L. The chemical modification of KCa channels by carbon monoxide in vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 8222–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escalante, B.; Sacerdoti, D.; Davidian, M.M.; Laniado-Schwartzman, M.; McGiff, J.C. Chronic treatment with tin normalizes blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension 1991, 17, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndisang, J.F.; Wu, L.; Zhao, W.; Wang, R. Induction of heme oxygenase-1 and stimulation of cGMP production by hemin in aortic tissues from hypertensive rats. Blood 2003, 101, 3893–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndisang, J.F.; Mishra, M. The heme oxygenase system selectively suppresses the proinflammatory macrophage m1 phenotype and potentiates insulin signaling in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 2013, 26, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nath, K.A.; Grande, J.P.; Belcher, J.D.; Garovic, V.D.; Croatt, A.J.; Hillestad, M.L.; Barry, M.A.; Nath, M.C.; Regan, R.F.; Vercellotti, G.M. Antithrombotic effects of heme-degrading and heme-binding proteins. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2020, 318, H671–H681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparkenbaugh, E.M.; Chantrathammachart, P.; Wang, S.; Jonas, W.; Kirchhofer, D.; Gailani, D.; Gruber, A.; Kasthuri, R.; Key, N.S.; Mackman, N.; et al. Excess of heme induces tissue factor-dependent activation of coagulation in mice. Haematologica 2015, 100, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detzel, M.S.; Schmalohr, B.F.; Steinbock, F.; Hopp, M.T.; Ramoji, A.; Paul George, A.A.; Neugebauer, U.; Imhof, D. Revisiting the interaction of heme with hemopexin. Biol. Chem. 2021, 402, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motterlini, R.; Clark, J.E.; Foresti, R.; Sarathchandra, P.; Mann, B.E.; Green, C.J. Carbon monoxide-releasing molecules: Characterization of biochemical and vascular activities. Circ. Res. 2002, 90, E17–E24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramkowski, K.; Mogielnicki, A.; Motterilini, R.; Chłopicki, S.; Buczko, W. Carbon monoxide releasing molecule 3 (CORM-3) inhibits arterial thrombosis in rats. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7 (Suppl. 2), 2149–2157. [Google Scholar]
- Foresti, R.; Hammad, J.; Clark, J.E.; Johnson, R.A.; Mann, B.E.; Friebe, A.; Green, C.J.; Motterlini, R. Vasoactive properties of CORM-3, a novel water-soluble carbon monoxide-releasing molecule. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 142, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motterlini, R.; Mann, B.E.; Johnson, T.R.; Clark, J.E.; Foresti, R.; Green, C.J. Bioactivity and pharmacological actions of carbon monoxide-releasing molecules. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2003, 9, 2525–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.E.; Naughton, P.; Shurey, S.; Green, C.J.; Johnson, T.R.; Mann, B.E.; Foresti, R.; Motterlini, R. Cardioprotective actions by a water-soluble carbon monoxide-releasing molecule. Circ. Res. 2003, 93, e2–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Stein, A.B.; Wu, W.J.; Tan, W.; Zhu, X.; Li, Q.H.; Dawn, B.; Motterlini, R.; Bolli, R. Administration of a CO-Releasing Molecule at the Time of Reperfusion Reduces Infarct Size In Vivo. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2004, 286, H1649–H1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberto, R.; Ortner, K.; Wheatley, N.; Schibli, R.; Schubiger, A.P. Synthesis and properties of boranocarbonate: A convenient in situ CO source for the aqueous preparation of [(99m)Tc(OH(2))3(CO)3]+. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 3135–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motterlini, R.; Sawle, P.; Hammad, J.; Bains, S.; Alberto, R.; Foresti, R.; Green, C.J. CORM-A1: A new pharmacologically active carbon monoxide-releasing molecule. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 284–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczara, P.; Sitek, B.; Przyborowski, K.; Kurpinska, A.; Kus, K.; Stojak, M.; Chlopicki, S. Antiplatelet effect of carbon monoxide is mediated by NAD+ and ATP depletion. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 2376–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Chamberlain, J.; Alfaidi, M.; Hughes, M.; Alizadeh, T.; Casbolt, H.; Evans, P.; Mann, B.; Motterlini, R.; Francis, S.; et al. Carbon Monoxide Releasing Molecule A1 Reduces Myocardial Damage After Acute Myocardial Infarction in a Porcine Model. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2021, 78, e656–e661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettenmann, H.; Hanisch, U.K.; Noda, M.; Verkhratsky, A. Physiology of microglia. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 461–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, K.; Kohsaka, S. Functional roles of microglia in the brain. Neurosci. Res. 1993, 17, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias-Pedroso, D.; Ramalho, J.S.; Sardão, V.A.; Jones, J.G.; Romão, C.C.; Oliveira, P.J.; Vieira, H.L.A. Carbon Monoxide-Neuroglobin Axis Targeting Metabolism against Inflammation in BV-2 Microglial Cells. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 916–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, N.L.; Paiva, I.; Bravo, J.; Queiroga, C.S.F.; Melo, B.F.; Conde, S.V.; Romão, C.C.; Summavielle, T.; Vieira, H.L.A. Carbon Monoxide Modulation of Microglia-Neuron Communication: Anti-Neuroinflammatory and Neurotrophic Role. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 872–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeynalov, E.; Doré, S. Low doses of carbon monoxide protect against experimental focal brain ischemia. Neurotox. Res. 2009, 15, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahian, N.; Yoshiura, M.; Maines, M.D. Overexpression of heme oxygenase-1 is neuroprotective in a model of permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in transgenic mice. J. Neurochem. 1999, 72, 1187–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, H.L.; Queiroga, C.S.; Alves, P.M. Pre-conditioning induced by carbon monoxide provides neuronal protection against apoptosis. J. Neurochem. 2008, 107, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biermann, J.; Lagrèze, W.A.; Dimitriu, C.; Stoykow, C.; Goebel, U. Preconditioning with inhalative carbon monoxide protects rat retinal ganglion cells from ischemia/reperfusion injury. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 3784–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulbrich, F.; Hagmann, C.; Buerkle, H.; Romao, C.C.; Schallner, N.; Goebel, U.; Biermann, J. The Carbon monoxide releasing molecule ALF-186 mediates anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects via the soluble guanylate cyclase ß1 in rats’ retinal ganglion cells after ischemia and reperfusion injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, Q.L.; Wang, G.Z.; Deng, T.Z.; Chen, R.; Liu, M.H.; Wang, S.W. The protective roles of mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channels during hypoxia-ischemia-reperfusion in brain. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 49, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuckerbraun, B.S.; Chin, B.Y.; Bilban, M.; d’Avila, J.C.; Rao, J.; Billiar, T.R.; Otterbein, L.E. Carbon monoxide signals via inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase and generation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilban, M.; Bach, F.H.; Otterbein, S.L.; Ifedigbo, E.; d’Avila, J.C.; Esterbauer, H.; Chin, B.Y.; Usheva, A.; Robson, S.C.; Wagner, O.; et al. Carbon monoxide orchestrates a protective response through PPARγ. Immunity 2006, 24, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Loughran, P.A.; Rao, J.; Billiar, T.R.; Zuckerbraun, B.S. Carbon monoxide activates NF-κB via ROS generation and Akt pathways to protect against cell death of hepatocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 295, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Yang, C.C.; Hsiao, L.D.; Yang, C.M. Carbon Monoxide Releasing Molecule-3 Enhances Heme Oxygenase-1 Induction via ROS-Dependent FoxO1 and Nrf2 in Brain Astrocytes. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 5521196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabluchanskiy, A.; Sawle, P.; Homer-Vanniasinkam, S.; Green, C.J.; Foresti, R.; Motterlini, R. CORM-3, a carbon monoxide-releasing molecule, alters the inflammatory response and reduces brain damage in a rat model of hemorrhagic stroke. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Stone, C.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, C.; Yin, X.; Meng, R. CORM-2 inhibits intracerebral hemorrhage-mediated inflammation. Neurol. Res. 2021, 43, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.C.; Huang, Y.T.; Hsieh, C.W.; Yang, P.M.; Wung, B.S. Carbon monoxide induces heme oxygenase-1 to modulate STAT3 activation in endothelial cells via S-glutathionylation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thériault, P.; ElAli, A.; Rivest, S. The dynamics of monocytes and microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2015, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Simone, A.; Naldi, M.; Tedesco, D.; Milelli, A.; Bartolini, M.; Davani, L.; Widera, D.; Dallas, M.L.; Andrisano, V. Investigating in Vitro Amyloid Peptide 1–42 Aggregation: Impact of Higher Molecular Weight Stable Adducts. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 12308–12318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hettiarachchi, N.; Dallas, M.; Al-Owais, M.; Griffiths, H.; Hooper, N.; Scragg, J.; Boyle, J.; Peers, C. Heme oxygenase-1 protects against Alzheimer’s amyloid-beta(1–42)-induced toxicity via carbon monoxide production. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahan, V.L. Neuroprotective, neurotherapeutic, and neurometabolic effects of carbon monoxide. Med. Gas Res. 2012, 2, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Zhao, Y.; Lee, C.W.; Ganguli, M. Smoking, death, and Alzheimer disease: A case of competing risks. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2012, 26, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chora, A.A.; Fontoura, P.; Cunha, A.; Pais, T.F.; Cardoso, S.; Ho, P.P.; Lee, L.Y.; Sobel, R.A.; Steinman, L.; Soares, M.P. Heme oxygenase-1 and carbon monoxide suppress autoimmune neuroinflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasik, Z.; Skotnicki, P.; Nowak-Sadzikowska, J.; Kulpa, J.K. C-reactive protein in cancer patients. Nowotw. J. Oncol. 2008, 58, 441–446. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Persing, D.H.; Prendergast, F.G. Infection, immunity, and cancer. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 1999, 123, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrington, F.D.; Carmody, R.J.; Goodyear, C.S. Modulation of NF-κB Signaling as a Therapeutic Target in Autoimmunity. J. Biomol. Screen. 2016, 21, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, W.C. Regulation of immune responses by NF-kappa B/Rel transcription factor. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 143–146, Erratum in J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skórka, K.; Giannopoulos, K. The structure and the role of NF-κB proteins and their significance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Acta Haematol. Pol. 2012, 43, 54–62. (In Polish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Stark, G.R. NFkappaB-dependent signaling pathways. Exp. Hematol. 2002, 30, 285–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marok, R.; Winyard, P.G.; Coumbe, A.; Kus, M.L.; Gaffney, K.; Blades, S.; Mapp, P.I.; Morris, C.J.; Blake, D.R.; Kaltschmidt, C.; et al. Activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB in human inflamed synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 1996, 39, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Boyle, D.L.; Manning, A.M.; Firestein, G.S. AP-1 and NF-kappaB regulation in rheumatoid arthritis and murine collagen-induced arthritis. Autoimmunity 1998, 28, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagone, P.; Mangano, K.; Mammana, S.; Cavalli, E.; Di Marco, R.; Barcellona, M.L.; Salvatorelli, L.; Magro, G.; Nicoletti, F. Carbon monoxide-releasing molecule-A1 (CORM-A1) improves clinical signs of experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis (EAU) in rats. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 157, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahl, H.L. Activators and target genes of Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6853–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Guttridge, D.C.; Mayo, M.W.; Baldwin, A.S., Jr. NF-kappaB induces expression of the Bcl-2 homologue A1/Bfl-1 to preferentially suppress chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Mol. Cell Biol. 1999, 19, 5923–5929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Józkowicz, A.; Waś, H.; Dulak, J. Heme oxygenase-1 in tumors: Is it a false friend? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2007, 9, 2099–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waś, H.; Cichon, T.; Smolarczyk, R.; Rudnicka, D.; Stopa, M.; Chevalier, C.; Leger, J.J.; Lackowska, B.; Grochot, A.; Bojkowska, K.; et al. Overexpression of heme oxygenase-1 in murine melanoma: Increased proliferation and viability of tumor cells, decreased survival of mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 2181–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, B.; Yin, Y.; Chen, G.; Wang, W.; Gao, X.; Wang, P.; Zhou, H. Overexpressions of HO-1/HO-1G143H in C57/B6J mice affect melanoma B16F10 lung metastases rather than change the survival rate of mice-bearing tumours. Exp. Biol. Med. 2013, 238, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castruccio Castracani, C.; Longhitano, L.; Distefano, A.; Di Rosa, M.; Pittalà, V.; Lupo, G.; Caruso, M.; Corona, D.; Tibullo, D.; Li Volti, G. Heme Oxygenase-1 and Carbon Monoxide Regulate Growth and Progression in Glioblastoma Cells. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 2436–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchinetti, M.M. Heme-Oxygenase-1. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2020, 32, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, K.; Sasahira, T.; Ohmori, H.; Fujii, K.; Kuniyasu, H. Inhibition of heme oxygenase-1 by zinc protoporphyrin IX reduces tumor growth of LL/2 lung cancer in C57BL mice. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, S.C.; Hansen, S.G.; Ruhl, R.A.; Raggo, C.M.; DeFilippis, V.R.; Greenspan, D.; Früh, K.; Moses, A.V. Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) induces heme oxygenase-1 expression and activity in KSHV-infected endothelial cells. Blood 2004, 103, 3465–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucha, O.; Podkalicka, P.; Mikulski, M.; Barwacz, S.; Andrysiak, K.; Biela, A.; Mieczkowski, M.; Kachamakova-Trojanowska, N.; Ryszawy, D.; Białas, A.; et al. Development and characterization of a new inhibitor of heme oxygenase activity for cancer treatment. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 671, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.; Shaeii, A.E.; Zervos, E.E.; Rosemurgy, A.S. In Vitro and In Vivo matrix metalloproteinase production by pancreatic cancer cells and by distant organs. Int. J. Surg. Investig. 2000, 1, 459–465. [Google Scholar]
- Egeblad, M.; Werb, Z. New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kołomecki, K.; Stępień, H.; Narębski, J.M. Matrix metalloproteinase serum levels in surgically treated adrenal tumours. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 1999, 22, 63. [Google Scholar]
- Wysocka, A.; Gizinski, S.; Lechowski, R. Matrix metalloproteinases—Their structure and function. Życie Weter. 2014, 89, 223–227. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Laronha, H.; Caldeira, J. Structure and Function of Human Matrix Metalloproteinases. Cells 2020, 9, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, S.; Mita, S.; Okabe, A.; Abe, M.; Ogawa, M. Prediction of radiosensitivity in human esophageal squamous cell carcinomas with heme oxygenase-1: A clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study. Oncol. Rep. 2001, 8, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandini, N.A.; Alonso, E.N.; Fermento, M.E.; Mascaró, M.; Abba, M.C.; Coló, G.P.; Arévalo, J.; Ferronato, M.J.; Guevara, J.A.; Núñez, M.; et al. Heme Oxygenase-1 Has an Antitumor Role in Breast Cancer. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2019, 30, 2030–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.; Yoon, S.H.; Choe, E.Y.; Cho, S.H.; Woo, C.H.; Rho, J.Y.; Kim, J.H. PMA-induced up-regulation of MMP-9 is regulated by a PKCa-NF-nB cascade in human lungepithelial cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2007, 39, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.W.; Shen, S.C.; Hou, W.C.; Yang, L.Y.; Chen, Y.C. Heme oxygenase-1 inhibits breast cancer invasion via suppressing the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 1195–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.C.; Fukui, H.; Imai, Y.; Sekikawa, A.; Kimura, T.; Yamagishi, H.; Yoshitake, N.; Pohle, T.; Domschke, W.; Fujimori, T. Colonic expression of heme oxygenase-1 is associated with a better long-term survival in patients with colorectal cancer. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 42, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, M.H.; Yanagawa, T.; Iwasa, S.; Tabuchi, K.; Onizawa, K.; Bannai, S.; Toyooka, H.; Yoshida, H. Heme oxygenase-1 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma as involved in lymph node metastasis. Cancer Lett. 1999, 138, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu Hoang, K.N.; Anstee, J.E.; Arnold, J.N. The Diverse Roles of Heme Oxygenase-1 in Tumor Progression. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 658315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otterbein, L.E.; Bach, F.H.; Alam, J.; Soares, M.; Lu, H.T.; Wysk, M.; Davis, R.J.; Flavell, R.A.; Choi, A.M. Carbon monoxide has anti-inflammatory effects involving the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.G.; Pan, K.; Hao, Y.; Yip, C.Y.; Ko, W.H. Anti-inflammatory action of HO-1/CO in human bronchial epithelium in response to cationic polypeptide challenge. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 105, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, T.Y.; Siu, Y.T.; Schlitt, H.J.; Fan, S.T. Heme oxygenase-1-derived carbon monoxide stimulates adenosine triphosphate generation in human hepatocyte. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 336, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haschemi, A.; Chin, B.Y.; Jeitler, M.; Esterbauer, H.; Wagner, O.; Bilban, M.; Otterbein, L.E. Carbon monoxide induced PPARγ SUMOylation and UCP2 block inflammatory gene expression in macrophages. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.Y.; Chung, J.; Joe, Y.; Pae, H.O.; Chang, K.C.; Cho, G.J.; Ryter, S.W.; Chung, H.T. Pretreatment with CO-releasing molecules suppresses hepcidin expression during inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum stress through inhibition of the STAT3 and CREBH pathways. Blood 2012, 119, 2523–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourti, M.; Jiang, W.G.; Cai, J. Aspects of Carbon Monoxide in Form of CO-Releasing Molecules Used in Cancer Treatment: More Light on the Way. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 9326454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Qin, H.; Nakamura, H.; Tsukigawa, K.; Shin, T.; Maeda, H. Carbon monoxide, generated by heme oxygenase-1, mediates the enhanced permeability and retention effect in solid tumors. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Józkowicz, A.; Huk, I.; Nigisch, A.; Weigel, G.; Dietrich, W.; Motterlini, R.; Dulak, J. Heme oxygenase and angiogenic activity of endothelial cells: Stimulation by carbon monoxide and inhibition by tin protoporphyrin-IX. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2003, 5, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulak, J.; Deshane, J.; Józkowicz, A.; Agarwal, A. Heme oxygenase-1 and carbon monoxide in vascular pathobiology: Focus on angiogenesis. Circulation 2008, 117, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Hewett, P.W.; Fujisawa, T.; Sissaoui, S.; Cai, M.; Gueron, G.; Al-Ani, B.; Cudmore, M.; Ahmed, S.F.; Wong, M.K.; et al. Carbon monoxide inhibits sprouting angiogenesis and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 phosphorylation. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 113, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vítek, L.; Gbelcová, H.; Muchová, L.; Váňová, K.; Zelenka, J.; Koníčková, R.; Suk, J.; Zadinova, M.; Knejzlík, Z.; Ahmad, S.; et al. Antiproliferative effects of carbon monoxide on pancreatic cancer. Dig. Liver Dis. 2014, 46, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrando, M.; Gueron, G.; Elguero, B.; Giudice, J.; Salles, A.; Leskow, F.C.; Jares-Erijman, E.A.; Colombo, L.; Meiss, R.; Navone, N.; et al. Heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1) challenges the angiogenic switch in prostate cancer. Angiogenesis 2011, 14, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, C.S.; Schmitt, S.; Dou, Q.P.; Kodanko, J.J. Synthesis, characterization, and reactivity of the stable iron carbonyl complex [Fe(CO)(N4Py)](ClO4)2: Photoactivated carbon monoxide release, growth inhibitory activity, and peptide ligation. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 5336–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Bai, Z.; Zhao, Q.; He, D.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, B. Syntheses and anti-cancer activity of CO-releasing molecules with targeting galactose receptors. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 8115–8129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Ho, C.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Hsu, C.C.; Lin, H.J.; Tian, Y.F.; Wang, J.J.; Guo, H.R. Impact of carbon monoxide poisoning on the risk of breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Iacono, L.; Boczkowski, J.; Zini, R.; Salouage, I.; Berdeaux, A.; Motterlini, R.; Morin, D.A. Carbon monoxide-releasing molecule (CORM-3) uncouples mitochondrial respiration and modulates the production of reactive oxygen species. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 1556–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.; Salouage, I.; Berdeaux, A.; Motterlini, R.; Morin, D. CORM-3, a water soluble CO-releasing molecule, uncouples mitochondrial respiration via interaction with the phosphate carrier. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1837, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.D.; Xu, R.; Reynolds, M.F.; Garcia, M.L.; Heinemann, S.H.; Hoshi, T. Haem can bind to and inhibit mammalian calcium-dependent Slo1 BK channels. Nature 2003, 425, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczara, P.; Motterlini, R.; Rosen, G.M.; Augustynek, B.; Bednarczyk, P.; Szewczyk, A.; Foresti, R.; Chlopicki, S. Carbon monoxide released by CORM-401 uncouples mitochondrial respiration and inhibits glycolysis in endothelial cells: A role for mitoBKCa channels. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1847, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, I.; Cheung, E.C.; Vousden, K.H. Control of glycolysis through regulation of PFK1: Old friends and recent additions. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2011, 76, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Takano, N.; Ishiwata, K.; Ohmura, M.; Nagahata, Y.; Matsuura, T.; Kamata, A.; Sakamoto, K.; Nakanishi, T.; Kubo, A.; et al. Reduced methylation of PFKFB3 in cancer cells shunts glucose towards the pentose phosphate pathway. Nat. Commun. 2014, 17, 3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hishiki, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Morikawa, T.; Kubo, A.; Kajimura, M.; Suematsu, M. Carbon monoxide: Impact on remethylation/transsulfuration metabolism and its pathophysiologic implications. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 90, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabil, O.; Weeks, C.L.; Carballal, S.; Gherasim, C.; Alvarez, B.; Spiro, T.G.; Banerjee, R. Reversible heme-dependent regulation of human cystathionine β-synthase by a flavoprotein oxidoreductase. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 8261–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, S.H.; Mann, B.E.; Meijer, A.J.; Adams, H.; Sawle, P.; Scapens, D.; Motterlini, R. [MnCO)4{S2CNMe(CH2CO2H)}], a new water-soluble CO-releasing molecule. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 4230–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, M.; Stahl, W.; Brenneisen, P.; Reichert, A.S.; Stucki, D. Carbon monoxide releasing molecule 401 (CORM-401) modulates phase I metabolism of xenobiotics. Toxicol. In Vitro 2019, 59, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Minokoshi, Y.; Ito, Y.; Waki, H.; Uchida, S.; Yamashita, S.; Noda, M.; Kita, S.; Ueki, K.; et al. Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammatory pathways and insulin action. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2003, 27, S53–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, J.H.M.; Giacca, A. Role of c-Jun N-terminal Kinase (JNK) in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Cells 2020, 9, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zick, Y. Role of Ser/Thr kinases in the uncoupling of insulin signaling. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2003, 27, S56–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braud, L.; Pini, M.; Muchova, L.; Manin, S.; Kitagishi, H.; Sawaki, D.; Czibik, G.; Ternacle, J.; Derumeaux, G.; Foresti, R.; et al. Carbon monoxide-induced metabolic switch in adipocytes improves insulin resistance in obese mice. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e123485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosick, P.A.; AlAmodi, A.A.; Hankins, M.W.; Stec, D.E. Chronic treatment with a carbon monoxide releasing molecule reverses dietary induced obesity in mice. Adipocyte 2015, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosick, P.A.; AlAmodi, A.A.; Storm, M.V.; Gousset, M.U.; Pruett, B.E.; Gray, W., 3rd; Stout, J.; Stec, D.E. Chronic carbon monoxide treatment attenuates development of obesity and remodels adipocytes in mice fed a high-fat diet. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Zhang, Q.; Joe, Y.; Kim, S.K.; Uddin, M.J.; Rhew, H.; Kim, T.; Ryter, S.W.; Chung, H.T. Carbon monoxide-releasing molecules reverse leptin resistance induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 304, E780–E788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosick, P.A.; Ahmed, E.K.; Gousset, M.U.; Granger, J.P.; Stec, D.E. Inhalation of carbon monoxide is ineffective as a long-term therapy to reduce obesity in mice fed a high fat diet. BMC Obes. 2014, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joe, Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.J.; Park, J.; Chen, Y.; Park, H.J.; Jekal, S.J.; Ryter, S.W.; Kim, U.H.; Chung, H.T. FGF21 induced by carbon monoxide mediates metabolic homeostasis via the PERK/ATF4 pathway. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 2630–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabetes, Fact Sheet No. 312, Media Centre, World Health Organization. 2011. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes (accessed on 31 August 2011).
- WHO. The Top 10 Causes of Death; Fact Sheet No. 310; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 9 December 2020).
- Nikolic, I.; Saksida, T.; Mangano, K.; Vujicic, M.; Stojanovic, I.; Nicoletti, F.; Stosic-Grujicic, S. Pharmacological application of carbon monoxide ameliorates islet-directed autoimmunity in mice via anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulak, J.; Józkowicz, A. Carbon monoxide—A “new” gaseous modulator of gene expression. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2003, 50, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bilska-Wilkosz, A.; Górny, M.; Iciek, M. Biological and Pharmacological Properties of Carbon Monoxide: A General Overview. Oxygen 2022, 2, 130-151. https://doi.org/10.3390/oxygen2020012
Bilska-Wilkosz A, Górny M, Iciek M. Biological and Pharmacological Properties of Carbon Monoxide: A General Overview. Oxygen. 2022; 2(2):130-151. https://doi.org/10.3390/oxygen2020012
Chicago/Turabian StyleBilska-Wilkosz, Anna, Magdalena Górny, and Małgorzata Iciek. 2022. "Biological and Pharmacological Properties of Carbon Monoxide: A General Overview" Oxygen 2, no. 2: 130-151. https://doi.org/10.3390/oxygen2020012
APA StyleBilska-Wilkosz, A., Górny, M., & Iciek, M. (2022). Biological and Pharmacological Properties of Carbon Monoxide: A General Overview. Oxygen, 2(2), 130-151. https://doi.org/10.3390/oxygen2020012







