Diagnostic Value of Serum sST2 and MicroRNA-29a in Ovarian Cancer: A Dual-Biomarker Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| miRNA | Micro RNA |
| CA-125 | Cancer Antigen 125 |
| IL-33 | Interleukin-33 |
| ST2 | Suppression of Tumorigenicity 2 |
| sST2 | Soluble ST2 |
| EOC | Epithelial over cancer |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| AUC | Area under curve |
References
- Kumar, V.; Gupta, S.; Varma, K.; Sachan, M. microRNA as Biomarker in Ovarian Cancer Management: Advantages and Challenges. DNA Cell Biol. 2020, 39, 2103–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.T. Towards Prevention of Ovarian Cancer. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2018, 18, 522–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.; Liu, Y.; Yin, H.; Huang, K.; Pu, X.L.; Zhu, Z.X. Identifying Factors Contributing to Delayed Diagnosis of Ovarian Cancer: A Comprehensive Analysis. Int. J. Womens Health 2024, 16, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matulonis, U.A.; Sood, A.K.; Fallowfield, L.; Howitt, B.E.; Sehouli, J.; Karlan, B.Y. Ovarian Cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, D.P.; Vanderhyden, B.C. Ovarian Cancer and the Evolution of Subtype Classifications Using Transcriptional Profiling. Biol. Reprod. 2019, 101, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayson, G.J.; Kohn, E.C.; Kitchener, H.C.; Ledermann, J.A. Ovarian Cancer. Lancet 2014, 384, 1376–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.T.; Ani, O.A.; Ani, F.-A. Epidemiology and Risk Factors for Ovarian Cancer. Menopause Rev. 2023, 22, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Shao, F.; Tian, Y.; Chen, S. Genomic and Clinical Insights into Ovarian Cancer: Subtype-Specific Alterations and Predictors of Metastasis and Relapse. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratner, E.; Lu, L.; Boeke, M.; Barnett, R.; Nallur, S.; Chin, L.J.; Pelletier, C.; Blitzblau, R.; Tassi, R.; Paranjape, T.; et al. A KRAS-Variant in Ovarian Cancer Acts as a Genetic Marker of Cancer Risk. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6509–6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmsen, M.G.; Hermens, R.P.M.G.; Prins, J.B.; Hoogerbrugge, N.; de Hullu, J.A. How medical choices influence quality of life of women carrying a BRCA mutation. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2015, 96, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charkhchi, P.; Cybulski, C.; Gronwald, J.; Wong, F.O.; Narod, S.A.; Akbari, M.R. CA125 and Ovarian Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Cancers 2020, 12, 3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, I.J.; Menon, U. Progress and challenges in screening for early detection of ovarian cancer. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2004, 3, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.J.; Bonfrer, J.M.; Kulpa, J.; Rustin, G.J.S.; Soletormos, G.; Torre, G.C.; Tuxen, M.; Zwirner, M. CA125 in ovarian cancer: European Group on Tumor Markers guidelines for clinical use. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2005, 15, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, H.M.A.; Novianti, P.W.; Pradjatmo, H.; Haryana, S.M. MicroRNA-Mediated Approaches in Ovarian Cancer Therapy. Oncol. Lett. 2024, 28, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Allen, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, M.A.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Ferdin, J.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs in body fluids--the mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etheridge, A.; Lee, I.; Hood, L.; Galas, D.; Wang, K. Extracellular microRNA: A new source of biomarkers. Mutat. Res. 2011, 717, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samad, M.A.; Ahmad, I.; Asghar, M.N.; Suhail, M.; Rehan, M.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Alsolami, K.; Akhter, M.S.; Ahmad, A.; Tabrez, S. MicroRNAs: From Bench to Bedside Applications as Breast Cancer Therapeutics. Semin. Oncol. 2025, 52, 152386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari Basir, S.; Adeli, K. MicroRNAs: Critical Regulators of mRNA Traffic and Translational Control with Promising Biotech and Therapeutic Applications. Iran J. Biotechnol. 2013, 11, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tili, E.; Michaille, J.J.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNAs Play a Central Role in Molecular Dysfunctions Linking Inflammation with Cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 253, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C.M. The Role of MicroRNAs in Human Cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. The Role of miRNA in Ovarian Cancer: An Overview. Reprod. Sci. 2022, 29, 2760–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asl, E.R.; Sarabandi, S.; Shademan, B.; Dalvandi, K.; Sheikhansari, G.; Nourazarian, A. MicroRNA Targeting: A Novel Therapeutic Intervention for Ovarian Cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2023, 35, 101519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Tian, C.; Zhang, Y. MiRNA-29a Serves as a Promising Diagnostic Biomarker in Children with Temporal Lobe Epilepsy and Regulates Seizure-Induced Cell Death and Inflammation. Epileptic Disord. 2022, 24, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemoto, R.; Jinnin, M.; Wang, Z.; Kudo, H.; Inoue, K.; Nakayama, W.; Ichihara, A.; Igata, T.; Kajihara, I.; Fukushima, S.; et al. Hair miR-29a Levels Are Decreased in Patients with Scleroderma. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 22, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Xia, F.; Yang, A.X.; Qian, J.X.; Zhao, H.; Tao, W.-Y. Effect of lncRNA-MIAT on Kidney Injury in Sepsis Rats via Regulating miR-29a Expression. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 10942–10949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imir, N.G. MicroRNA-29a Plays a Prominent Role in PRIMA-1Met-Induced Apoptosis in Ovarian Cancer Cells. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2020, 72, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Ling, W.; Ruan, Z. TAM-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Containing microRNA-29a-3p Explain the Deterioration of Ovarian Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 25, 468–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condrat, C.E.; Thompson, D.C.; Barbu, M.G.; Bugnar, O.L.; Boboc, A.; Cretoiu, D.; Suciu, N.; Cretoiu, S.M.; Voinea, S.C. miRNAs as Biomarkers in Disease: Latest Findings Regarding Their Role in Diagnosis and Prognosis. Cells 2020, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, G.; Wu, J.H.; Jiang, C.P. Roles of miR-29 in Cancer (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.X.; Luo, M.; Qiu, L.W.; He, Y.L.; Wang, X.F. Prognostic Implications of microRNA-100 and Its Functional Roles in Human Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 27, 1238–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.P. IL-33: An Alarmin Cytokine with Crucial Roles in Innate Immunity, Inflammation and Allergy. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 31, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, W.J.; Vu, V.P.; Krebs, P. IL-33 biology in cancer: An update and future perspectives. Cytokine 2022, 157, 155961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, F.; Li, M.; Yu, J.M.; Yang, S.-Y.; Zou, L.; Yang, G.-J.; Zhang, L.-L. IL-33/ST2 Axis in Diverse Diseases: Regulatory Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1533335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, K.E.; Porte, J.; Kelly, A.; Wallace, W.A.; Huntington, C.E.; Overed-Sayer, C.L.; Cohen, E.S.; Jenkins, R.G.; John, A.E. The IL-33:ST2 Axis Is Unlikely to Play a Central Fibrogenic Role in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Jin, X.; Li, C.; Wen, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, R. Roles of IL-33 in the Pathogenesis of Cardiac Disorders. Exp. Biol. Med. 2023, 248, 2167–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, S.; Hegde, U.; Acharya, A.B. The Clinicopathological Implications of Serum IL-33 and sST2 as Cancer Biomarkers: A Narrative Review. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2025, 15, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.; Barbour, M.; Hou, K.; Gao, C.; Cao, S.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Mu, R.; Jiang, H.-R. Interleukin-33 Predicts Poor Prognosis and Promotes Ovarian Cancer Growth via ERK and JNK Pathways. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, N.L.; Gilchrist, D.S.; Akbar, M.; Reilly, J.H.; Kerr, S.C.; Campbell, A.L.; Murrell, G.A.C.; Liew, F.Y.; Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; McInnes, I.B. MicroRNA-29a Regulates IL-33-Mediated Tissue Remodelling in Tendon Disease. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumeliotis, S.; Schurgers, J.; Tsalikakis, D.G.; D’Arrigo, G.; Gori, M.; Pitino, A.; Leonardis, D.; Tripepi, G.; Liakopoulos, V. ROC Curve Analysis: A Useful Statistic Multi-Tool in Nephrology Research. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2024, 56, 2651–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metz, C.E. Basic Principles of ROC Analysis. Semin. Nucl. Med. 1978, 8, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, P.A.; Williams, J.A.; Martini, J.F.; Motzer, R.J.; Valota, O.; Buller, R.E. Receiver Operating Characteristic Analysis of Efficacy Biomarkers in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Future Oncol. 2016, 12, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, D.; Mallery, P. IBM SPSS Statistics 19 Step by Step: A Simple Guide and Reference, 12th ed.; Pearson Higher Education: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kossaï, M.; Leary, A.; Scoazec, A.J.; Genestie, C. Ovarian Cancer: A Heterogeneous Disease. Pathobiology 2018, 85, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, H.R. Ovarian Cancer. CA Cancer J. Clin. 1986, 36, 149–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, P.M.; Jordan, S.J. Epidemiology of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2017, 41, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, J.R.; Rosen, B.; Moody, J.; Pal, T.; Fan, I.; Shaw, P.A.; Risch, H.A.; Sellers, T.A.; Sun, P.; Narod, S.A. Long-Term Ovarian Cancer Survival Associated with Mutation in BRCA1 or BRCA2. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colangelo, T.; Fucci, A.; Votino, C.; Sabatino, L.; Pancione, M.; Laudanna, C.; Binaschi, M.; Bigioni, M.; Maggi, C.A.; Parente, D.; et al. MicroRNA-130b Promotes Tumor Development and Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 1086–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Yuan, Y.; Xie, L.; Ran, P.; Xiang, X.; Huang, Q.; Qi, G.; Guo, X.; Xiao, C.; Zheng, S. miRNA-320a Inhibits Tumor Proliferation and Invasion by Targeting c-Myc in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignotti, E.; Calza, S.; Tassi, R.A.; Zanotti, L.; Bandiera, E.; Sartori, E.; Odicino, F.E.; Ravaggi, A.; Todeschini, P.; Romani, C. Identification of Stably Expressed Reference Small Non-Coding RNAs for microRNA Quantification in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Carcinoma Tissues. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 2341–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, D.D.; Yan, W.; Sha, H.H.; Zhao, J.H.; Yang, S.-J.; Zhang, H.-D.; Hou, J.-C.; Xu, H.-Z.; et al. MiR-29a: A Potential Therapeutic Target and Promising Biomarker in Tumors. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20171265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, M.; Huang, L.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Jiang, J.; Jiang, X.X. microRNA-29a Repressed Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Progression by Directly Targeting SIRT1. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2017, 10, 4411–4420. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Mao, H.L.; Zhao, X.R.; Li, Y.; Liu, P.S. MiR-29c-3p, a Target miRNA of LINC01296, Accelerates Tumor Malignancy: Therapeutic Potential of a LINC01296/miR-29c-3p Axis in Ovarian Cancer. J. Ovarian Res. 2020, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resnick, K.E.; Alder, H.; Hagan, J.P.; Richardson, D.L.; Croce, C.M.; Cohn, D.E. Detection of Differentially Expressed microRNAs from Serum of Ovarian Cancer Patients Using a Novel Real-Time PCR Platform. Gynecol. Oncol. 2009, 112, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Wan, S.; Qiao, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. MiR-29 Promotes Ovarian Carcinoma Cell Proliferation through the PTEN Pathway. Eur. J. Gynaecol. Oncol. 2020, 41, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Imran, M.; Ahsan, H. Biomarkers as Biomedical Bioindicators: Approaches and Techniques for the Detection, Analysis, and Validation of Novel Biomarkers of Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Xu, O.; Sha, R.; Bao, T.T.; Xi, X.; Guo, G. MicroRNA-29a Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Arrests Cell Cycle by Modulating p16 Methylation in Cervical Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, S.; Karabegović, I.; Ikram, M.A.; Ahmad, S.; Ghanbari, M. Plasma circulating microRNAs associated with blood-based immune markers: A population-based study. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2023, 215, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, E.M.; Mohammed, E.H.H.; Darwish, A.M.A. Evaluation of Serum Soluble ST2 as a Diagnostic Biomarker for Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolism. Hematol. Transfus. Cell Ther. 2025, 47, 103740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimoto, M.; Koshikawa, N.; Morinaga, T.; Tamamori-Adachi, M.; Takatori, A.; Takenaga, K. Downregulation of sST2, a Decoy Receptor for Interleukin-33, Enhances Subcutaneous Tumor Growth in Murine Pancreatic Cancer Cells. FEBS Open Bio 2025, 15, 2031–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaga, K.; Akimoto, M.; Koshikawa, N.; Nagase, H. Cancer Cell-Derived Interleukin-33 Decoy Receptor sST2 Enhances Orthotopic Tumor Growth in a Murine Pancreatic Cancer Model. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergis, D.; Kassis, V.; Radeke, H.H. High Plasma sST2 Levels in Gastric Cancer and Their Association with Metastatic Disease. Cancer Biomark. 2016, 16, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergis, D.; Kassis, V.; Ranglack, A.; Koeberle, V.; Piiper, A.; Kronenberger, B.; Radeke, H.H. High Serum Levels of the Interleukin-33 Receptor Soluble ST2 as a Negative Prognostic Factor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Transl. Oncol. 2013, 6, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Piao, L.; Wang, S.; Yue, Y. Role of the IL-33/ST2 Receptor Axis in Ovarian Cancer Progression. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, A.; Matsumoro, K.; Matsuda, A. Type 2 Cytokine-Induced microRNA-29s Suppress Both Soluble ST2 Release and IFNAR1 Expression in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Authorea 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Jiang, J.; Jia, J.; Zhou, X. Recent Advances in Exosomal miRNA Biosensing for Liquid Biopsy. Molecules 2022, 27, 7145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Luo, G.; Yi, T.; Wang, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, X.; Guo, X. Diagnostic Value of Urinary-to-Serum Human Epididymis Protein 4 Ratio in Ovarian Cancer. Biomed. Rep. 2017, 7, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klisic, A.; Ahmad, R.; Daka, B.; Sindhu, S. Cardiometabolic Diseases in Postmenopausal Women. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1514913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, V.; Kose, V.; Somalwar, S.; Dwidmuthe, K.S.; Rao, S.; Raman, V., Jr.; Rao, S., Jr. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Association with Menopausal Symptoms in Post-Menopausal Women: A Scoping Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e39069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccardi, M.; Myhre, P.L.; Zelniker, T.A.; Metra, M.; Januzzi, J.L.; Inciardi, R.M. Soluble ST2 in Heart failure: A clinical role beyond B-Type natriuretic peptide. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis 2023, 10, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosroshahi, P.A.; Ashayeri, H.; Ghanbari, M.; Malek, A.; Farhang, S.; Haghi, M. Downregulation of miR-29a as a possible diagnostic biomarker for schizophrenia. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepe, M.S.; Etzioni, R.; Feng, Z.; Potter, J.D.; Thompson, M.L.; Thornquist, M.; Winget, M.; Yasui, Y. Phases of Biomarker Development for Early Detection of Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanash, S.M.; Pitteri, S.J.; Faca, V.M. Mining the plasma proteome for cancer biomarkers. Nature 2008, 452, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Patients | n, % |
|---|---|
| Family history of cancer | |
| Yes | 9 (39.1%) |
| No | 14 (60.9%) |
| Menopause | |
| Yes | 16 (69.6%) |
| No | 7 (30.4%) |
| Metastasis | |
| Yes | 7 (30.4%) |
| No | 16 (69.6%) |
| Stage | |
| I | 6 (26.1%) |
| II | 5 (21.7%) |
| III | 8 (34.8%) |
| IV | 4 (17.4%) |
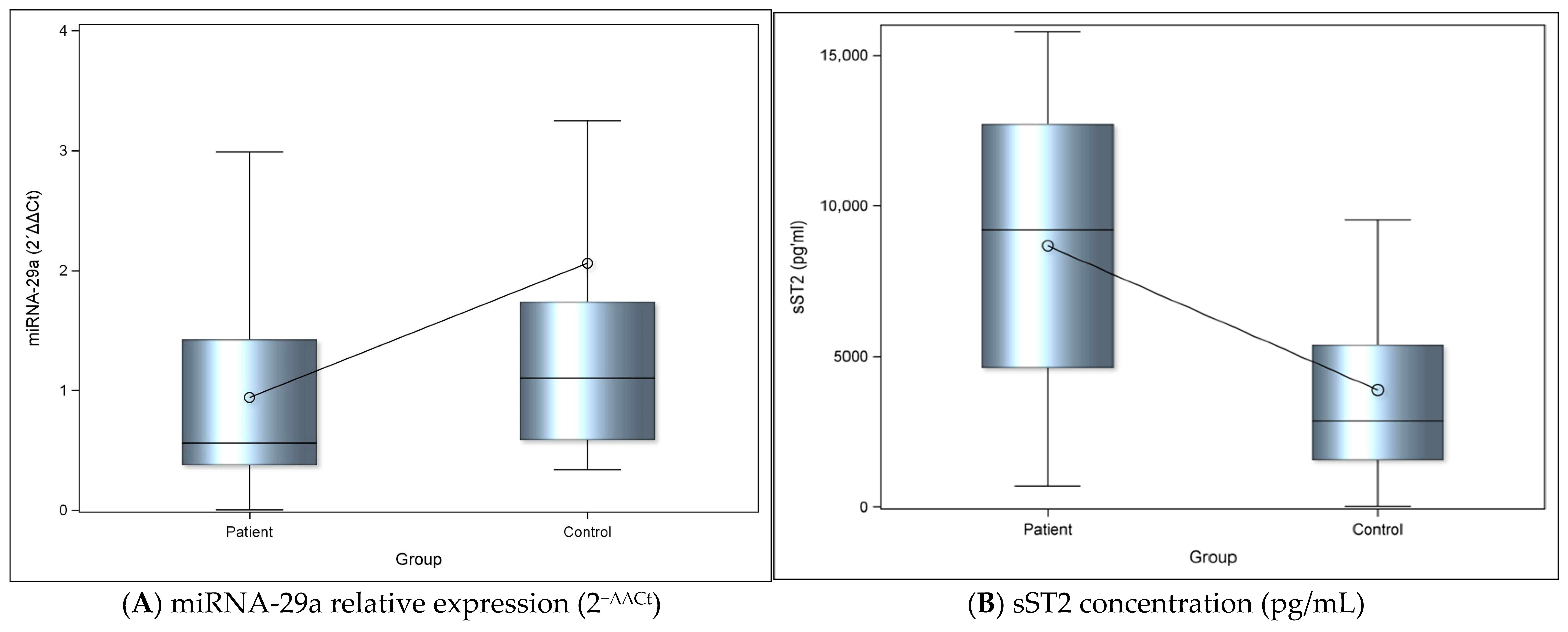
| Group | Patient (N = 23) | Control (N = 22) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
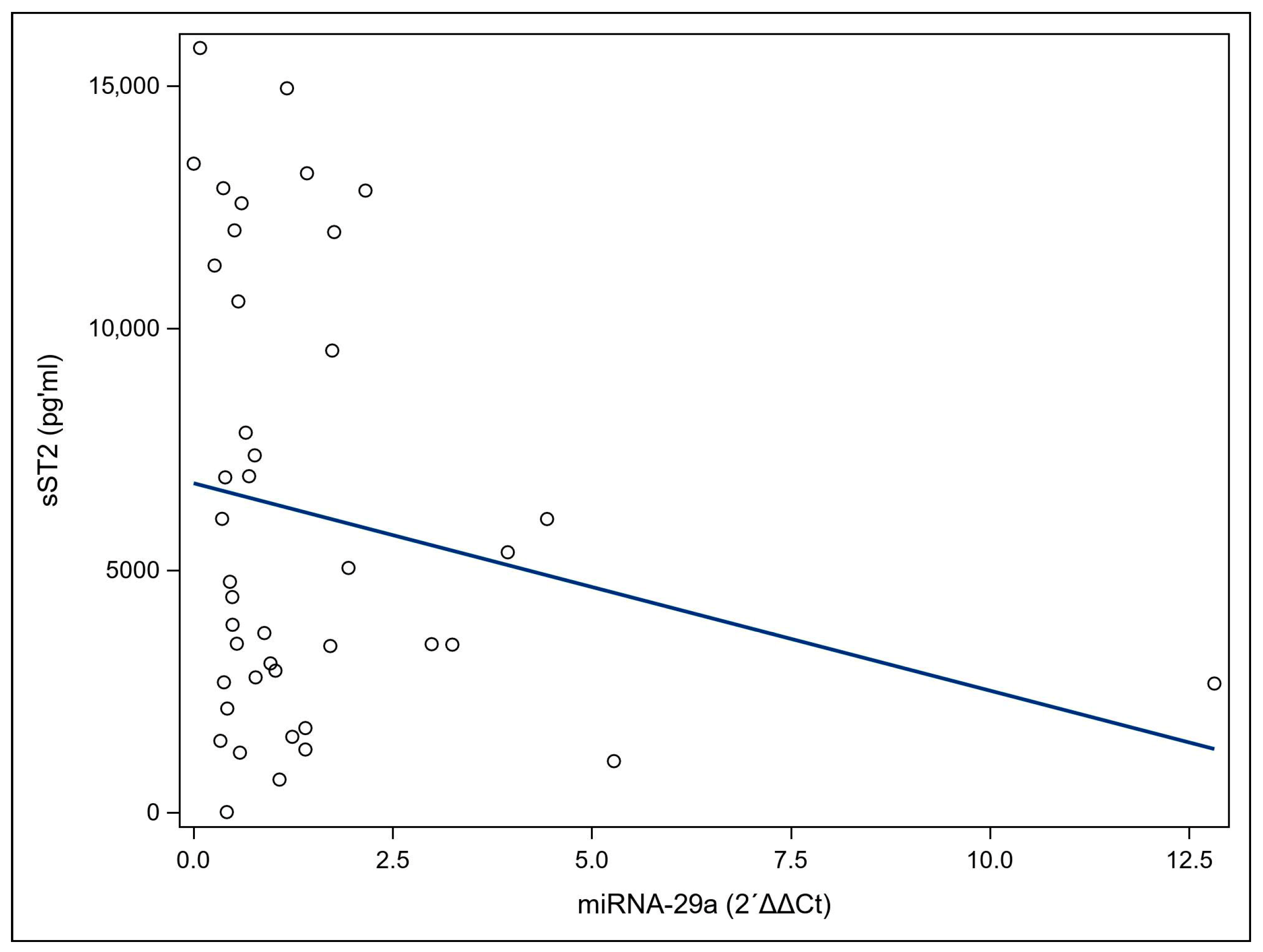
| miRNA-29a 2−ΔΔCt Mean (SD) Median (Range) | 0.0410 * | ||
| 0.9 (0.92) | 2.1 (2.78) | ||
| 0.6 (0.03, 3.4) | 1.1 (0.3, 12.8) | ||
| sST2 (pg/mL) Mean (SD) Median | 0.0003 * | ||
| 8669.0 (4421.20) | 3880.3 (3412.20) | ||
| 9198.3 | 2862.4 |
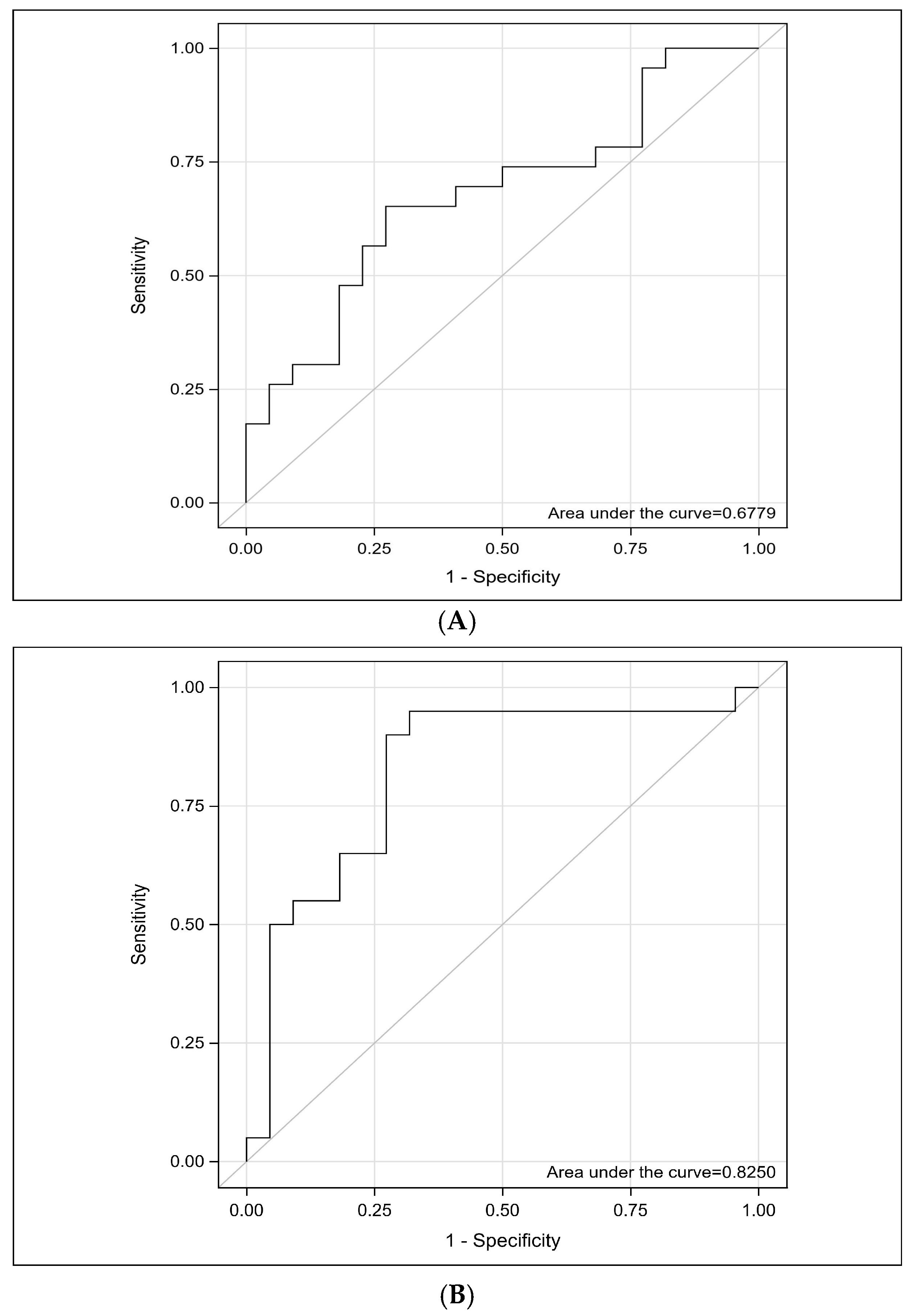
| AUC | SE | 95%CI | p | Cut Off | Sensitivity | Specificity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miRNA-29a | 0.6779 | 0.0815 | 0.5180 | 0.8377 | 0.0270 | 0.6552 | 0.65217 | 0.72727 |
| sST2 | 0.8250 | 0.0690 | 0.6890 | 0.9610 | 0.0001 | 3479.4 | 0.95 | 0.68182 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Akdeniz, F.T.; Barut, Z.; Avsar, O.; Bakırezer, S.D.; Attar, R.; Isbir, T. Diagnostic Value of Serum sST2 and MicroRNA-29a in Ovarian Cancer: A Dual-Biomarker Pilot Study. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2026, 48, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb48010113
Akdeniz FT, Barut Z, Avsar O, Bakırezer SD, Attar R, Isbir T. Diagnostic Value of Serum sST2 and MicroRNA-29a in Ovarian Cancer: A Dual-Biomarker Pilot Study. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2026; 48(1):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb48010113
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkdeniz, Fatma Tuba, Zerrin Barut, Orcun Avsar, Selvi Duman Bakırezer, Rukset Attar, and Turgay Isbir. 2026. "Diagnostic Value of Serum sST2 and MicroRNA-29a in Ovarian Cancer: A Dual-Biomarker Pilot Study" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 48, no. 1: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb48010113
APA StyleAkdeniz, F. T., Barut, Z., Avsar, O., Bakırezer, S. D., Attar, R., & Isbir, T. (2026). Diagnostic Value of Serum sST2 and MicroRNA-29a in Ovarian Cancer: A Dual-Biomarker Pilot Study. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 48(1), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb48010113






