Research Progress on the Regulatory Mechanism of the Waxy Gene in Rice Starch Synthesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
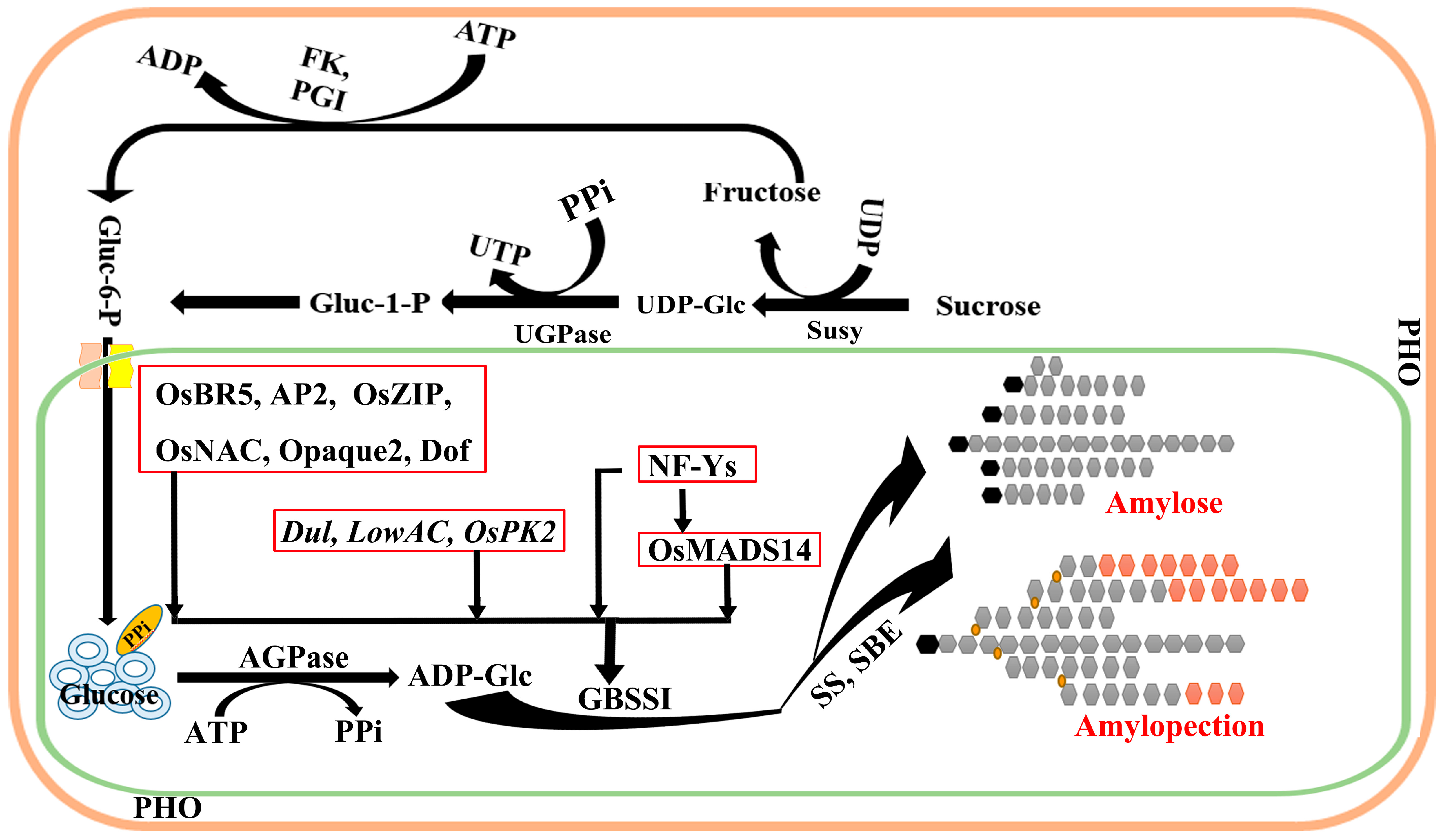
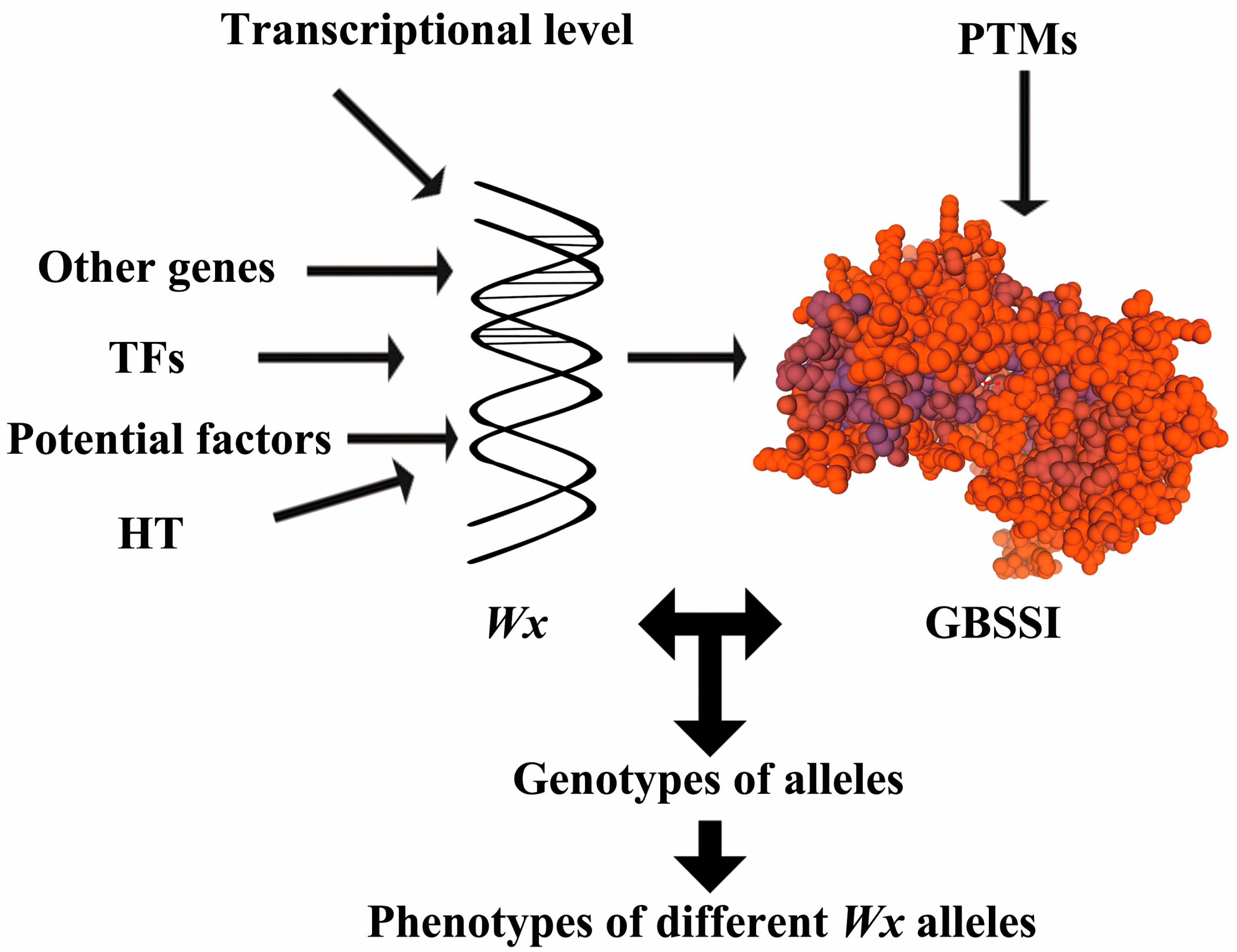
2. Transcriptional Level Differences Affect Wx Gene Function
2.1. Regulation of Transposons Affects the Function of the Wx Gene
2.2. Different Binding Sites Affect the Transcriptional Ratio of Wx Gene
2.3. Influence of AGPLs on the Function of the Wx Gene
2.4. Effect of SS on the Functional Regulation of the Wx Gene
2.5. Transcription Factors Affect the Functional Regulation of the Wx Gene
2.6. Effects of Other Genes on the Function of Wx
3. The Function Regulation of Wx Due to Post-Translational Modification of Protein
4. Additional Factors Affect the Functional Regulation of Wx
5. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGPase | ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase |
| PHO | Phosphorylases |
| PTST | Protein targeting to starch |
| GBSS | Granule-bound starch synthase |
| SS | Starch synthase |
| SBE | Starch branching enzyme |
| Susy | Sucrose synthase |
| UDPG | Uridine diphosphate glucose |
| AAC | Apparent amylose content |
| ADPG | ADP-glucose |
| RNAi | RNA interference |
References
- Jeon, J.S.; Ryoo, N.; Hahn, T.R.; Walia, H.; Nakamura, Y. Starch biosynthesis in cereal endosperm. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 48, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannah, L.C.; James, M. The complexities of starch biosynthesis in cereal endosperms. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2008, 19, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetlow, I.J.; Emes, M.J. Starch biosynthesis in the developing endosperms of grasses and cereals. Agronomy 2017, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Sun, H.; Qiao, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Z.; Wei, X.; Yang, J.; Yuan, Q.; et al. Cell-free chemoenzymatic starch synthesis from carbon dioxide. Science 2021, 373, 1523–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, H.; Shibahara, K.; Tokunaga, T.; Nishi, A.; Tasaki, M.; Hwang, S.K.; Okita, T.W.; Kaneko, N.; Fujita, N.; Yoshida, M.; et al. Mutation of the plastidial alpha-glucan phosphorylase gene in rice affects the synthesis and structure of starch in the endosperm. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 1833–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Peng, Y.; Mao, B.; Lv, Q.; Yuan, D.; Liu, X. Allelic variations of the Wx locus in cultivated rice and their use in the development of hybrid rice in China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zi, Y.; Ding, J.F.; Song, J.M.; Humphreys, G.; Peng, Y.X.; Li, C.Y.; Zhu, X.K.; Guo, W.S. Grain yield, starch content and activities of key enzymes of waxy and non-waxy wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4548. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, Y.; Umemoto, T.; Takahata, Y.; Komae, K.; Amano, E.; Satoh, H. Changes in structure of starch and enzyme activities affected by sugary mutations in developing rice endosperm. Possible role of starch debranching enzyme (R-enzyme) in amylopectin biosynthesis. Physiol. Plant 2010, 97, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, J.; Chen, S.; Fan, X.; Li, Q.; Lu, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, H.; Yi, C.; Tang, S.; et al. Wxlv, the ancestral allele of rice Waxy gene. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, A.M.; Morell, M.K.; James, M.G.; Ball, S.G. Recent progress toward understanding biosynthesis of the amylopectin crystal. Plant Physiol. 2000, 122, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M.; Denyer, A.K.; Martin, C. The synthesis of the starch granule. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1997, 48, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Xia, D.; Zhao, D.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Wu, B.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, G.; Xiao, J.; et al. The origin of Wxla provides new insights into the improvement of grain quality in rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, Y.; Hirano, H.Y.; Nishimura, M. Evolutionary significance of differential regulation at the wx locus of rice. In Rice Genetics II; IRRI: Los Baños, Philippines, 2015; pp. 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Sano, Y.; Katsumata, M.; Okuno, K. Genetic studies of speciation in cultivated rice. 5. Inter- and intraspecific differentiation in the waxy gene expression of rice. Euphytica 1986, 35, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bligh, H.; Larkin, P.D.; Roach, P.S.; Jones, C.A.; Fu, H.; Park, W.D. Use of alternate splice sites in granule-bound starch synthase mRNA from low-amylose rice varieties. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 38, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Xing, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Hong, M.M. Aberrant splicing of intron 1 leads to the heterogeneous 5′ UTR and decreased expression of waxy gene in rice cultivars of intermediate amylose content. Plant J. 2010, 14, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.C.; Yu, X.Q.; Xing, Y.Z.; Xu, C.G.; Luo, L.J.; Zhang, Q.J. The main effects, epistatic effects and environmental interactions of QTLs on the cooking and eating quality of rice in a doubled-haploid line population. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 110, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, H.Y.; Eiguchi, M.; Sano, Y. A single base change altered the regulation of the Waxy gene at the posttranscriptional level during the domestication of rice. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1998, 15, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isshiki, M.; Morino, K.; Nakajima, M.; Okagaki, R.J.; Wessler, S.R.; Izawa, T.; Shimamoto, K. A naturally occurring functional allele of the rice waxy locus has a GT to TT mutation at the 5′ splice site of the first intron. Plant J. 1998, 15, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inukai, T.; Sako, A.; Hirano, H.Y.; Sano, Y. Analysis of intragenic recombination at wx in rice: Correlation between the molecular and genetic maps within the locus. Genome 2000, 43, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Zheng, F.Q.; Shen, G.Z.; Gao, J.P.; Snustad, D.P.; Li, M.G.; Zhang, J.L.; Hong, M.M. The amylose content in rice endosperm is related to the post-transcriptional regulation of the waxy gene. Plant J. 1995, 7, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathepha, P. Unearthed new indel in the Waxy gene in glutinous rice landraces from Thailand. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 24, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroyuki, S.; Yasuhiro, S.; Makoto, S.; Tokio, I. Molecular characterization of Wx-mq, a novel mutant gene for low-amylose content in endosperm of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Breed. Sci. 2002, 52, 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Ma, X.; Liu, S.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Ren, Y.; Dong, H.; Chen, L.; et al. Identification and characterization of a novel Waxy allele from a Yunnan rice landrace. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 71, 609–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, K.M.; Genetics, M.D. Molecular evidence on the origin and evolution of glutinous rice. Genetics 2002, 162, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, I.; Aikawa, M.; Hirano, H.Y.; Sano, Y. Altered tissue-specific expression at the Wx gene of the opaque mutants in rice. Euphytica 1999, 105, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, N.M.; Mcclung, A.M.; Larkin, P.D.; Bligh, H.F.J.; Jones, C.A.; Park, W.D.J.T.; Genetics, A. Microsatellites and a single-nucleotide polymorphism differentiate apparentamylose classes in an extended pedigree of US rice germ plasm. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1997, 94, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, S.G.; van de Wal, M.H.; Visser, R.G.F. Progress in understanding the biosynthesis of amylose. Trends Plant Sci. 1998, 3, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, A.; Levin, I.; Oguz, I.; Petreikov, M.; Bar, M. ADPglucose pyrophosphorylase activity and starch accumulation in immature tomato fruit: The effect of a Lycopersicon hirsutum-derived introgression encoding for the large subunit. Plant Sci. 2000, 152, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okita, T. Is there an alternative pathway for starch synthesis? Plant Physiol. 1992, 100, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetlow, I.J.; Morell, M.K.; Emes, M.J. Recent developments in understanding the regulation of starch metabolism in higher plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 2131–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Ballicora, M.A.; Preiss, J.; Geiger, J.H. Crystal structure of potato tuber ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballicora, M.A.; Dubay, J.R.; Devillers, C.H.; Preiss, J. Resurrecting the ancestral enzymatic role of a modulatory subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, G.; Anna, K.; Axel, T. Redox regulation of carbon storage and partitioning in response to light and sugars. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, T.; Niiyama, H.; Sasahara, T. Cloning of cDNA for UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase and the expression of mRNA in rice endosperm. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 105, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, T.; Ohdan, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Terao, T. Expression profiling of genes related to starch synthesis in rice leaf sheaths during the heading period. Physiol. Plant. 2010, 128, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Hwang, S.K.; Han, M.; Eom, J.S.; Kang, H.G.; Han, Y.; Choi, S.B.; Cho, M.H.; Bhoo, S.H.; An, G.; et al. Identification of the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase isoforms essential for starch synthesis in the leaf and seed endosperm of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol. Biol. 2007, 65, 531–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akihiro, T.; Mizuno, K.; Fujimura, T. Gene expression of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase and starch contents in rice cultured cells are cooperatively regulated by sucrose and ABA. Plant Cell Physiol. 2005, 46, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohdan, T.; Francisco, P.B., Jr.; Sawada, T.; Hirose, T.; Terao, T.; Satoh, H.; Nakamura, Y. Expression profiling of genes involved in starch synthesis in sink and source organs of rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 3229–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.M.; Kuo, Y.H.; Sheu, G.; Sheu, Y.J.; Liu, L.F. Metabolic derepression of alpha-amylase gene expression in suspension-cultured cells of rice. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 21131–21137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Liu, X.; Yin, J.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Hui, L.; Li, S.; Li, L. Activity and expression of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase during rhizome formation in lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.). Bot. Stud. 2016, 57, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.Q.; Xiong, F.; Gu, Y.Y.; Gu, G.J. Changes in the activities of enzymes involved in starch synthesis and accumulation in caryopsis of transgenic rice with antisense Wx gene. Zhi Wu Sheng LI Yu Fen Zi Sheng Wu Xue Xue Bao 2006, 32, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Denyer, K.; Hylton, C.M.; Jenner, C.F.; Smith, A.M. Identification of multiple isoforms of soluble and granule-bound starch synthase in developing wheat endosperm. Planta 1995, 196, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, R.; Nakajima, M.; Isshiki, M.; Okagaki, R.J.; Wessler, S.R.; Shimamoto, K. Antisense waxy genes with highly active promoters effectively suppress waxy gene expression in transgenic rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2000, 41, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, J.; Lloyd, J.R.; Tomlinson, K.; Barber, L.; Edwards, A.; Wang, T.L.; Martin, C.; Smith, A.M. Mutations in the gene encoding starch synthase II profoundly alter amylopectin structure in pea embryos. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemoto, T.; Yano, M.; Satoh, H.; Shomura, A.; Nakamura, Y. Mapping of a gene responsible for the difference in amylopectin structure between japonica-type and indica-type rice varieties. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 104, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Wanat, J.; Stinard, P.; James, M.; Myers, A.M. Characterization of dull1, a maize gene coding for a novel starch synthase. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanashiro, I.; Itoh, K.; Kuratomi, Y.; Yamazaki, M.; Igarashi, T.; Matsugasako, J.; Takeda, Y. Granule-bound starch synthase I is responsible for biosynthesis of extra-long unit chains of amylopectin in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2008, 49, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radchuk, V.V.; Borisjuk, L.; Sreenivasulu, N.; Merx, K.; Mock, H.P.; Rolletschek, H.; Wobus, U.; Weschke, W. Spatiotemporal profiling of starch biosynthesis and degradation in the developing barley grain. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, M.G.; Denyer, K.; Myers, A.M. Starch synthesis in the cereal endosperm. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2003, 6, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryoo, N.; Yu, C.; Park, C.S.; Baik, M.Y.; Park, I.M.; Cho, M.H.; Bhoo, S.H.; An, G.; Hahn, T.R.; Jeon, J.S. Knockout of a starch synthase gene OsSSIIIa/Flo5 causes white-core floury endosperm in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep. 2007, 26, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Gasic, K.; Sun, F.; Xu, M.; Korban, S.S. A gene encoding starch branching enzyme I (SBEI) in apple (Malusxdomestica, Rosaceae) and its phylogenetic relationship to Sbe genes from other angiosperms. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 43, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.I.; Lee, Y.K.; Chung, W.I.; Lee, I.H.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, W.M.; Ezura, H.; Lee, S.P.; Kim, I.J. Modification of sugar composition in strawberry fruit by antisense suppression of an ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase. Mol. Breed. 2006, 17, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Hucl, P.; Chibbar, R.N. Isolation, characterization and expression analysis of starch synthase I from wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Genome 2001, 161, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibbar, R.N.; Baga, M. Genetic Modification of Primary Metabolism: Carbohydrates; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 449–459. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, N.; Kubo, A.; Suh, D.; Wong, K.; Jane, J.; Ozawa, K.; Takaiwa, F.; Inaba, Y.; Nakamura, Y. Antisense inhibition of isoamylase alters the structure of amylopectin and the physicochemical properties of starch in rice endosperm. Plant Cell Physiol. 2003, 44, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.; Nelson, O.E.J. A debranching enzyme deficiency in endosperms of the sugary-1 mutants of maize. Plant Physiol. 1984, 74, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Szydlowski, N.; Delvallé, D.; D’Hulst, C.; James, M.G.; Myers, A.M. Overlapping functions of the starch synthases SSII and SSIII in amylopectin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Biol. 2008, 23, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, R.A.; Jenner, H.; Carrangis, L.; Fahy, B.; Fincher, G.B.; Hylton, C.; Laurie, D.A.; Parker, M.; Waite, D.; Van, W.S.; et al. Starch granule initiation and growth are altered in barley mutants that lack isoamylase activity. Plant J. 2010, 31, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeman, S.C.; Umemoto, T.; Lue, W.L.; Au-Yeung, P.; Martin, C.; Smith, A.M.; Chen, J. A mutant of Arabidopsis lacking a chloroplastic isoamylase accumulates both starch and phytoglycogen. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 1699–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cao, Z.Z.; Pan, G.; Wang, F.B.; Wei, K.S.; Zhao-Wei, L.I.; Shi, C.H.; Geng, W.; Cheng, F.M. Effect of high temperature on the expressions of genes encoding starch synthesis enzymes in developing rice endosperms. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 642–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geigenberger, P.; Stitt, M. Diurnal changes in sucrose, nucleotides, starch synthesis and AGPS transcript in growing potato tubers that are suppressed by decreased expression of sucrose phosphate synthase. Plant J. 2010, 23, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, Y.; Maekawa, M.; Kikuchl, H. Temperature effects on the Wx protein level and amylose content in the endosperm of rice. J. Hered. 1985, 76, 221–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Guiltinan, M.J.; Thompson, D.B. Mutation of the maize sbe1a and ae genes alters morphology and physical behavior of wx-type endosperm starch granules. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 2619–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, M.; Zhong, M.; Fan, X.; Gu, M.; Liu, Q. Waxy rice soluble starch synthase I: Allelic variation, expression, function, and interaction with. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 13, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Satoh, H. Biochemical and genetic analysis of the effects of amylose-extender mutation in rice endosperm. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tanaka, N.; Fujita, N.; Nishi, A.; Satoh, H.; Nakamura, Y. The structure of starch can be manipulated by changing the expression levels of starch branching enzyme IIb in rice endosperm. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2004, 2, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, N.; Rui, S.; Hayashi, A.; Kodama, M.; Itoh, R.; Aihara, S.; Nakamura, Y. Starch biosynthesis in rice endosperm requires the presence of either starch synthase I or IIIa. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 4819–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crofts, N.; Sugimoto, K.; Oitome, N.F.; Nakamura, Y.; Fujita, N. Differences in specificity and compensatory functions among three major starch synthases determine the structure of amylopectin in rice endosperm. Plant Mol. Biol. 2017, 94, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, N.; Yoshida, M.; Kondo, T.; Saito, K.; Utsumi, Y.; Tokunaga, T.; Nishi, A.; Satoh, H.; Park, J.H.; Jane, J.L.; et al. Characterization of SSIIIa-deficient mutants of rice: The function of SSIIIa and pleiotropic effects by SSIIIa deficiency in the rice endosperm. Plant Physiol. 2007, 144, 2009–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buléon, A.; Gallant, D.J.; Bouchet, B.; Mouille, G.; D’Hulst, C.; Kossmann, J.; Ball, S. Starches from A to C: Chlamydomonas reinhardtii as a model microbial system to investigate the biosynthesis of the plant amylopectin crystal. Plant Physiol. 1997, 115, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delrue, B.; Fontaine, T.; Routier, F.; Decq, A.; Wieruszeski, J.M.; Koornhuyse, N.V.D.; Maddelein, M.L.; Fournet, B.; Ball, S. Waxy chlamydomonas reinhardtii: Monocellular algal mutants defective in amylose biosynthesis and granule-bound starch synthase activity accumulate a structurally modified amylopectin. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 3612–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Wal, M.; d’Hulst, C.; Vincken, J.P.; Buléon, A.; Visser, R.; Ball, S. Amylose is synthesized in vitro by extension of and cleavage from amylopectin. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 22232–22240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crofts, N.; Domon, A.; Miura, S.; Hosaka, Y.; Oitome, N.; Itoh, A.; Noge, K.; Fujita, N. Starch synthases SSIIa and GBSSI control starch structure but do not determine starch granule morphology in the absence of SSIIIa and SSIVb. Plant Mol. Biol. 2021, 108, 379–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.; Smith, A.M. Starch biosynthesis. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 971–985. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Mizuno, K.; Kimura, K.; Arai, Y.; Kawasaki, T.; Baba, T. Starch branching enzymes from immature rice seeds. J. Biochem. 1992, 112, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Takeichi, T.; Kawaguchi, K.; Yamanouchi, H. Purification of two forms of starch branching enzyme (Q-enzyme) from developing rice endosperm. Physiol. Plant. 1992, 84, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okagaki, R.J.; Wessler, S.R. Comparison of non-mutant and mutant waxy genes in rice and maize. Genetics 1989, 120, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Melander, M.; Pojmark, P.; Larsson, H.K.; Bülow, L.; Hofvander, P. Targeted gene suppression by RNA interference: An efficient method for production of high-amylose potato lines. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 123, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sestili, F.; Janni, M.; Doherty, A.; Botticella, E.; D’Ovidio, R.; Masci, S.; Jones, H.D.; Lafiandra, D. Increasing the amylose content of durum wheat through silencing of the SBEIIa genes. Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 144. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Cai, X.L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Hong, M.M. An interaction between a MYC protein and an EREBP protein is involved in transcriptional regulation of the rice Wx gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 47803–47811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brust, H.; Orzechowski, S.; Fettke, J.; Steup, M. Starch synthesizing reactions and paths: In vitro and in vivo studies. J. Appl. Glycosci. 2013, 60, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goren, A.; Ashlock, D.; Tetlow, I.J. Starch formation inside plastids of higher plants. Protoplasma 2018, 255, 1855–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, M.; Hamada, T.; Kitahara, K.; Kim, S.H.; Shimada, T. Increase of amylose content of sweetpotato starch by inhibition of sbeii. Plant Biotchnol. 2010, 23, 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; He, K.; Tang, X.; Li, Z.; Lv, L.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. An Arabidopsis transcriptional regulatory map reveals distinct functional and evolutionary features of novel transcription factors. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 1767–1773, Correction in Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 37, 3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.F.; Xue, H.W. Coexpression analysis identifies Rice Starch Regulator1, a rice AP2/EREBP family transcription factor, as a novel rice starch biosynthesis regulator. Plant Physiol. 2010, 154, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Xu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Q.Q.; Cai, X.L. OsbZIP58, a basic leucine zipper transcription factor, regulates starch biosynthesis in rice endosperm. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 11, 3453–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Kumar, P.; Sharma, M.; Tuli, R.; Dhaliwal, H.S.; Chaudhury, A.; Roy, J. Expression patterns of genes involved in starch biosynthesis during seed development in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum). Mol. Breed. 2015, 35, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Xie, S.; Xiao, Q.; Wei, B.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Long, T.; Li, Y.; et al. Sucrose and ABA regulate starch biosynthesis in maize through a novel transcription factor, ZmEREB156. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, S.; Wei, H.; Milne, J.; Page, G.P.; Somerville, C.R. Identification of genes required for cellulose synthesis by regression analysis of public microarray data sets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 8633–8638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Dong, J.; Ji, C.; Wu, Y.; Messing, J. NAC-type transcription factors regulate accumulation of starch and protein in maize seeds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 27590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, S. A maize NAC transcription factor, ZmNAC34, negatively regulates starch synthesis in rice. Plant Cell Rep. 2019, 38, 1473–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, D.; Yan, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Qian, Q.; Li, J. Du1, encoding a novel pro- protein, regulates starch biosynthesis through affecting the splicing of Wxb pre-mRNAs in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol. Biol. 2007, 65, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, H.; Ito, H.; Shimada, T.; Kang, D.J.; Hamada, S. A novel rice dull gene, LowAC1, encodes an RNA recognition motif protein affecting Waxy pre-mRNA splicing. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 162, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, M.; Zhou, W.; Dong, Q.; Jiang, H.; Cheng, B. The DOF-domain transcription factor ZmDOF36 positively regulates starch synthesis in transgenic maize. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, C. The rice LEC1-like transcription factor OsNF-YB9 interacts with SPK, an endosperm specific sucrose synthase protein kinase, and functions in seed development. Plant J. 2021, 106, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Yang, J.; Messing, J.; Wu, Y. Maize endosperm-specific transcription factors O2 and PBF network the regulation of protein and starch synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10842–10847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Qi, W.; Lv, Y.; Yan, S.; Xu, L.; Yang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Song, R. Opaque11 is a central hub of the regulatory network for maize endosperm development and nutrient metabolism. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 375–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Li, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhu, D.; Yu, J. ZmDof3, a maize endosperm-specific Dof protein gene, regulates starch accumulation and aleurone development in maize endosperm. Plant Mol. Biol. 2017, 93, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botticella, E.; Sestili, F.; Sparla, F.; Moscatello, S.; Marri, L.; Cuesta-Seijo, J.A.; Falini, G.; Battistelli, A.; Trost, P.; Lafiandra, D. Combining mutations at genes encoding key enzymes involved in starch synthesis affects the amylose content, carbohydrate allocation and hardness in the wheat grain. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 1723–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Yamamori, M.; Hirano, H.; Hidaka, S.; Nagamine, T. Production of waxy (Amylose-Free) Wheats. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1995, 248, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrinten, P.L.; Nakamura, T. Wheat granule-bound starch synthase I and II are encoded by separate genes that are expressed in different tissues. Plant Physiol. 2000, 122, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemoto-Kuno, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Nakamura, S.; Satoh, H.; Ohtsubo, K. Soluble starch synthase I effects differences in amylopectin structure between indica and japonica rice varieties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 9234–9240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araki, E.; Miura, H.; Sawada, S. Differential effects of the null alleles at the three Wx loci on the starch-pasting properties of wheat. Genetics 2000, 100, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, C.; Caballero, L.; Yamamori, M.; Alvarez, J.B. Molecular characterization of a new waxy allele with partial expression in spelt wheat. Planta 2012, 235, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, H.; Sugawara, A. Dosage effects of the three Wx genes on amylose synthesis in wheat endosperm. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1996, 93, 1066–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamori, M.; Quynh, N. Differential effects of Wx-A1, -B1 and -D1 protein deficiencies on apparent amylose content and starch pasting properties in common wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2000, 100, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamori, M.; Guzmán, C. SNPs and an insertion sequence in five Wx-A1 alleles as factors for variant Wx-A1 protein in wheat. Euphytica 2013, 192, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, P.V.; Maeda, T.; Morita, N. Waxy and high-amylose wheat starches and flours-characteristics, functionality and application. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, C.; Alvarez, J. Wheat waxy proteins: Polymorphism, molecular characterization and effects on starch properties. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2016, 129, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patron, N.J.; Smith, A.M.; Fahy, B.F.; Hylton, C.M.; Naldrett, M.J.; Rossnagel, B.G.; Denyer, K. The altered pattern of amylose accumulation in the endosperm of low-amylose barley cultivars is attributable to a single mutant allele of granule-bound starch synthase i with a deletion in the 5′-non-coding region1. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; He, Y.; Sretenovic, S.; Liu, S.; Cheng, Y.; Han, Y.; Liu, G.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Q.; Zheng, X.; et al. CRISPR-BETS: A base editing design tool for generating stop codons. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 20, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Fang, Y.; Liu, F.; Qin, B.; Li, R. Development of soft rice lines by regulating amylose content via editing the 5′UTR of the Wx gene. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 10, 10517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Liu, T.; Ma, X.; Wang, B.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, X.; Yang, B.; Zhao, Z.; Zhu, Q.; et al. Quantitative regulation of Waxy expression by CRISPR/Cas9-based promoter and 5′ UTR-intron editing improves grain quality in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 2385–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Hui, Z.; Botella, J.R.; Zhu, J.K. Generation of new glutinous rice by CRISPR/Cas9-targeted mutagenesis of the Waxy gene in elite rice varieties. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2018, 60, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isshiki, M.; Nakajima, M.; Satoh, H.; Shimamoto, K. dull: Rice mutants with tissue-specific effects on the splicing of the waxy pre-mRNA. Plant J. 2010, 23, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Jiang, Q.T.; Zhao, Q.Z.; Zhao, S.; Lan, X.J.; Dai, S.F.; Lu, Z.X.; Liu, C.; Wei, Y.M.; Zheng, Y.L. Characterization and expression analysis of waxy alleles in barley accessions. Genetica 2013, 141, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isshiki, M.; Matsuda, Y.; Takasaki, A.; Wong, H.L.; Satoh, H.; Shimamoto, K. Du3, a mRNA cap-binding protein gene, regulates amylose content in Japonica rice seeds. Plant Tissue Cult. Lett. 2008, 25, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felker, F.C.; Peterson, D.M.; Nelson, O.E. Anatomy of immature grains of eight maternal effect shrunken endosperm barley mutants. Am. J. Bot. 1985, 72, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetlow, I.J.; Beisel, K.G.; Cameron, S.; Makhmoudova, A.; Liu, F.; Bresolin, N.S.; Wait, R.; Emes, M.J. Analysis of protein complexes in wheat amyloplasts reveals functional interactions among starch biosynthetic enzymes. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 1878–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Ono, M.; Utsumi, C.; Steup, M. Functional interaction between plastidial starch phosphorylase and starch branching enzymes from rice during the synthesis of branched maltodextrins. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012, 53, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friso, G.; Wijk, K.J. Post-translational protein modifications in plant metabolism. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 1469–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, L.D.; Gevaert, K.; Smet, I.D. Protein Language: Post-Translational Modifications Talking to Each Other. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 1068–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinders, J.; Sickmann, A. State-of-the-art in phosphoproteomics. Proteomics 2005, 5, 4052–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spoel, S.H. Orchestrating the proteome with post-translational modifications. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 4499–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Xu, J.; He, Y.; Yang, K.Y.; Mordorski, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S. Phosphorylation of an ERF transcription factor by Arabidopsis MPK3/MPK6 regulates plant defense gene induction and fungal resistance. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 1126–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wei, Z.; Wang, X. Post-translational control of ABA signalling: The roles of protein phosphorylation and ubiquitination. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Bao, J.; Wang, Y.; Yao, J.; Gui, Y.; Hu, W.; Zhu, J.; Zeng, M.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y. Post-domestication selection in the maize starch pathway. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Li, Y.; Zheng, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, H.; Qi, P.; Deng, M.; Ma, J.; et al. The impact of GBSSI inactivation on starch structure and functionality in EMS-induced mutant lines of wheat. BMC Genom. 2025, 26, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Johnson, J.W.; Graybosch, R.A.; Gaines, C.S. Physicochemical properties and end-use quality of wheat starch as a function of waxy protein alleles. J. Cereal Sci. 2003, 37, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Seung, D.; Guzmán, C.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Tang, H.; Qi, P.; et al. Reducing amylose content in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) using a novel Wx-D1 null allele generated by chemical mutagenesis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2025, 105, 2332–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, S.G.; Khound, R.; Santra, D.K. Phenotypic diversity for morpho-agronomic traits in the US proso millet (Panicum miliaceum L.) core collection. Crop Sci. 2024, 64, 2599–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, H.V.; Denyer, K.; Packman, L.C.; Jones, M.K.; Howe, C.J. Molecular basis of the waxy endosperm starch phenotype in broomcorn millet (Panicum miliaceum L.). Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 1478–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Crop | Allele Gene | Genetic Variation Loci in Wx Gene | Endosperm Phenotype |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rice | Wxa | G at Int1–1 and T at Exon-10 | High amylose content |
| Wxb | T at Int1–1 and C at Exon-10 | Low amylose content | |
| Wxlv | G at Int1–1 and C at Exon-10 | High amylose content | |
| Wxin | A single nucleotide polymorphism in exon-6 | Intermediate-type | |
| Wxmw/la | A single A to C substitution on exon-6 | Low AC | |
| Wxop/hp | G in intron-1 | Very low AC | |
| Wxin | A single nucleotide polymorphism in exon-6 | Intermediate-type | |
| Wxlv | G at Int1–1 and C at Exon10 | High amylose content | |
| Wxop/hp | G in intron-1 | Very low AC | |
| Wxmp | T in Int1–1 and A at Exon4–53 | Very low AC | |
| wx | 23 bp duplication inserted in exon-2 | Very low or no AC | |
| Maize | wx-m1 | 409 bp insertion in exon-9 | – |
| wx-B2 | 128 bp insertion in Exon-11 | Waxy | |
| wx-C34 | Deletion | Waxy | |
| Wheat | Wx-A1 | Wild type | Non-waxy |
| Wx-B1b | Complete deletion | Waxy | |
| Wx-A1b | Deletion of 23 bp in the second exon–intron junction | Waxy | |
| Sorghum | wxa | 4 kb large insertion in exon-3 | Waxy |
| wxb | Missense mutation | Waxy | |
| Cassava | Wx | A single base substitution in exon-11 | Non-waxy |
| wx | A single base deletion in exon-6 | Waxy | |
| Barley | Wx-CDC | 397 bp deletion and a 193 bp insertion | Waxy |
| Wx-Bowman | 11 bp insertion in the promoter region | Non-waxy | |
| Foxtail millet | Type I | Wild type | Non-waxy |
| Type II (TSI-1) | 343 bp insertion in intron-1 | Non-waxy | |
| Type III (TSI-6) | 4050 bp insertion in intron-1 | Low-amylose | |
| Barnyard millet | EeWx1 | Wild type | Non-waxy |
| EeWx2 | Wild type | Non-waxy | |
| Proso millet | WxLC | Wild type | Non-waxy |
| WxS−15 | 15-bp deletion in exon-10 | Waxy | |
| Job’s tears | EeWx | 275-bp deletion in exons 10–11 | Waxy |
| Amaranths | Type Ia | A single nucleotide polymorphism on exons-1 and -6 | Non-waxy |
| Type IIIa | A single nucleotide polymorphism on exons-1 and -6 | Waxy |
| Enzymes | Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Gene Symbols | Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Gene Symbols | Maize (Zea mays L.) Gene Symbols |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADPG pyrophosphorylase (AGPase, EC 2.7.7.27) | OsAGPL1 | TaAGPL1 | ZmAGPL1 |
| OsAGPL2 | TaAGPL2 | ZmAGPL2 | |
| OsAGPL3 | / | ZmAGPL3 | |
| OsAGPL4 | / | ZmAGPL4 | |
| OsAGPS1 | TaAGPS1 | ZmAGPS1 | |
| OsAGPS2 a/b | TaAGPS2 a/b | ZmAGPS2 a/b | |
| Granule-bound starch synthase (GBSS, EC 2.4.1.21) | OsGBSSI | TaGBSSI | ZmGBSSI |
| OsGBSSII a/b | TaGBSSII | ZmGBSSII a/b | |
| Soluble starch synthase (SS, EC 2.4.1.21) | OsSSI | TaSSI | ZmSSI |
| OsSSII a/b/c | TaSSII a/b | ZmSSII a/b/c | |
| OsSSIII a/b | TaSSIII a/b | ZmSSIII a/b | |
| OsSSIV a/b | / | ZmSSIV | |
| Starch branching enzyme (SBE, EC 2.4.1.18) | OsSBEI | TaSBEI | ZmSBEI |
| OsSBEII a/b | TaBEII a/b | ZmBEII a/b | |
| OsSBEIII | TaBEIII | ZmBEIII | |
| Starch/a-glucan phosphorylase (PHO, EC 2.4.1.1) | OsPHOL | TaPHOH | ZmPHOH |
| Protein targeting to starch (PTST) | OsGBP | TaBGC1 | GPM177 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, F.; Song, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, P.; Yu, Y.; Dong, M.; Xie, Y.; Yuan, C.; Zhu, Y.; Qiao, Z. Research Progress on the Regulatory Mechanism of the Waxy Gene in Rice Starch Synthesis. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090678
Chen F, Song Y, Jiang Y, Cao P, Yu Y, Dong M, Xie Y, Yuan C, Zhu Y, Qiao Z. Research Progress on the Regulatory Mechanism of the Waxy Gene in Rice Starch Synthesis. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(9):678. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090678
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Fei, Yunsheng Song, Yi Jiang, Penghui Cao, Yajie Yu, Minghui Dong, Yulin Xie, Caiyong Yuan, Yongliang Zhu, and Zhongying Qiao. 2025. "Research Progress on the Regulatory Mechanism of the Waxy Gene in Rice Starch Synthesis" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 9: 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090678
APA StyleChen, F., Song, Y., Jiang, Y., Cao, P., Yu, Y., Dong, M., Xie, Y., Yuan, C., Zhu, Y., & Qiao, Z. (2025). Research Progress on the Regulatory Mechanism of the Waxy Gene in Rice Starch Synthesis. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(9), 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47090678






