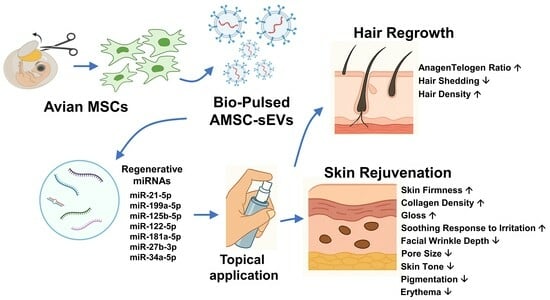
Topical Application of Bio-Pulsed Avian MSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Enhances Hair Regrowth and Skin Rejuvenation: Evidence from Clinical Evaluation and miRNA Profiling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. miRNA Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis
2.3. miRNA Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.4. Clinical Product Application Protocol
- •
- Anagen/telogen (A/T) ratio and telogen follicle percentage (T%), using the Aram Huvis ASW Scalp Analyzer (Aram Huvis Co., Ltd., Seongnam, Republic of Korea) and Motic DM-1802 microscope (MoticEurope; Barcelona, Spain).
- •
- Hair shedding via a standardized 60-stroke comb test, conducted by trained technicians under controlled conditions as previously described [14].
- •
- Hair density analysis using ImageJ software (version 1.54j) (National Institutes of Health; Bethesda, MD, USA), which processed and analyzed grayscale intensity from standardized trichoscopic photographs.
- •
- Subjective evaluations via an 8-item Likert scale questionnaire at Days 30 and 60, assessing hair condition, shedding, texture, and density (Supplementary Table S1).
- •
- Wrinkle depth and pore size: Miravex Antera 3D (Miravex; Dublin, Ireland), which provides high-resolution 3D topographic surface analysis.
- •
- Skin firmness and collagen density: Cortex DermaLab Combo (Cortex Technology; Aalborg, Denmark), which combines suction-based elastometry and high-frequency ultrasound imaging (20 MHz) for real-time evaluation of dermal structural properties. Firmness values were derived from the skin’s retraction time post-suction, while collagen density was measured by echo intensity across dermal layers.
- •
- Melanin and erythema indices: CK Mexameter® MX18 (Courage + Khazaka Electronic GmbH; Köln, Germany), which employs a tristimulus light source and two specific narrow-band wavelengths (red and green) to assess the concentration of melanin and hemoglobin in the epidermis and superficial dermis. Measurements were recorded in triplicate at each timepoint, and average values were analyzed.
- •
- Gloss and radiance: Zehntner ZGM1120 Glossmeter (Zehntner GmbH Testing Instruments; Sissach, Switzerland) evaluated at a 60° incident angle, providing objective gloss units for surface reflectivity.
- •
- UV spot and pigmentation: CK VisioFace RD (Courage + Khazaka Electronic GmbH; Köln, Germany) used for full-face imaging and quantification of UV-induced pigmentation and spot scores.
- •
- Subjective evaluations via an 8-item Likert scale questionnaire at Days 14 and 28 (Supplementary Table S2).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Study Design and Inclusion Criteria
2.7. Use of Generative AI in Study Preparation
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Characterization of Bio-Pulsed AMSC-sEVs
3.2. Hair Regeneration Outcomes
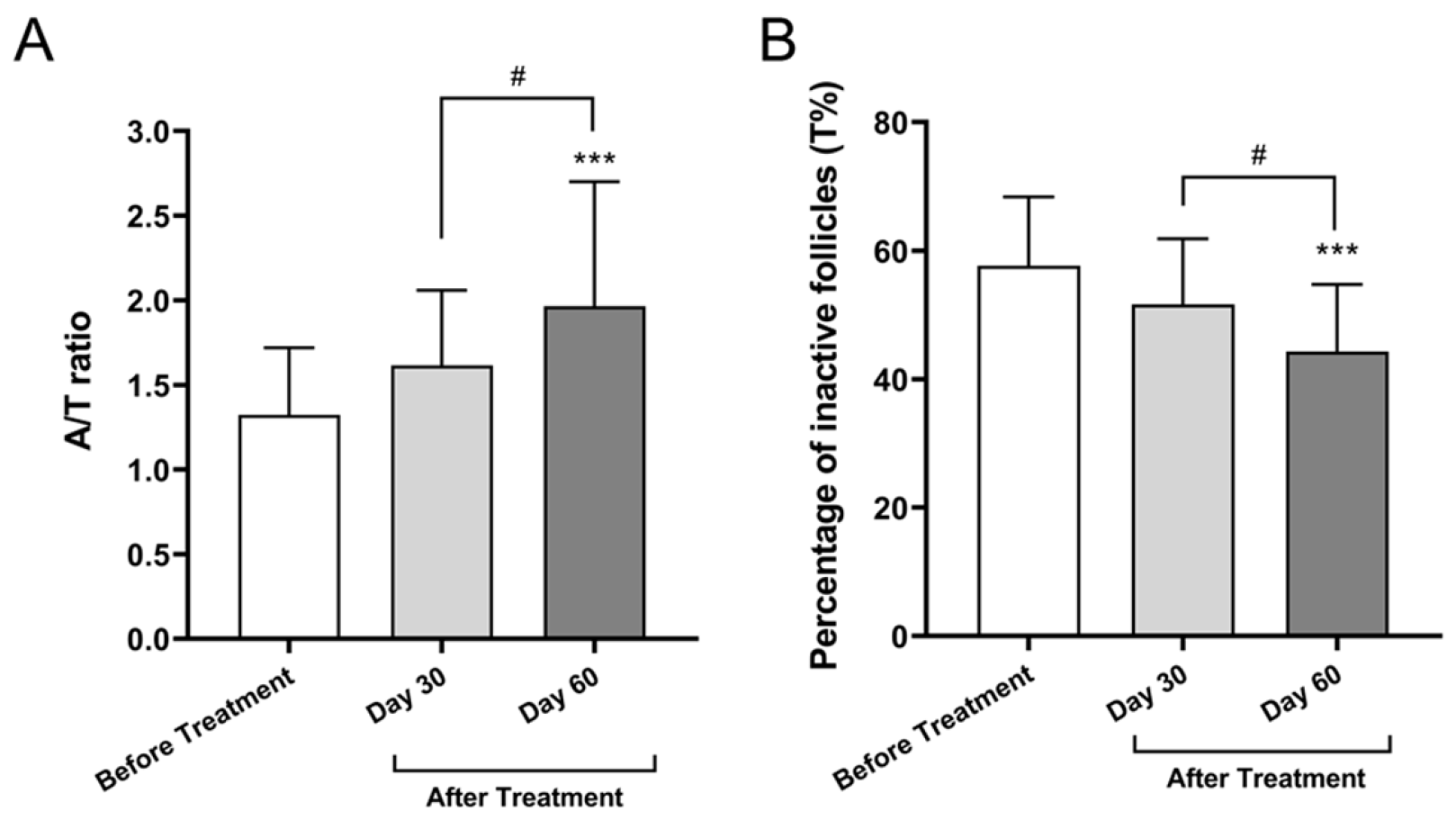
3.2.1. Anagen-to-Telogen (A/T) Ratio
3.2.2. Percentage of Inactive (Telogen) Follicles (T%)
3.2.3. Hair Shedding and Density
3.2.4. Subjective Satisfaction
3.3. Skin Rejuvenation Outcomes
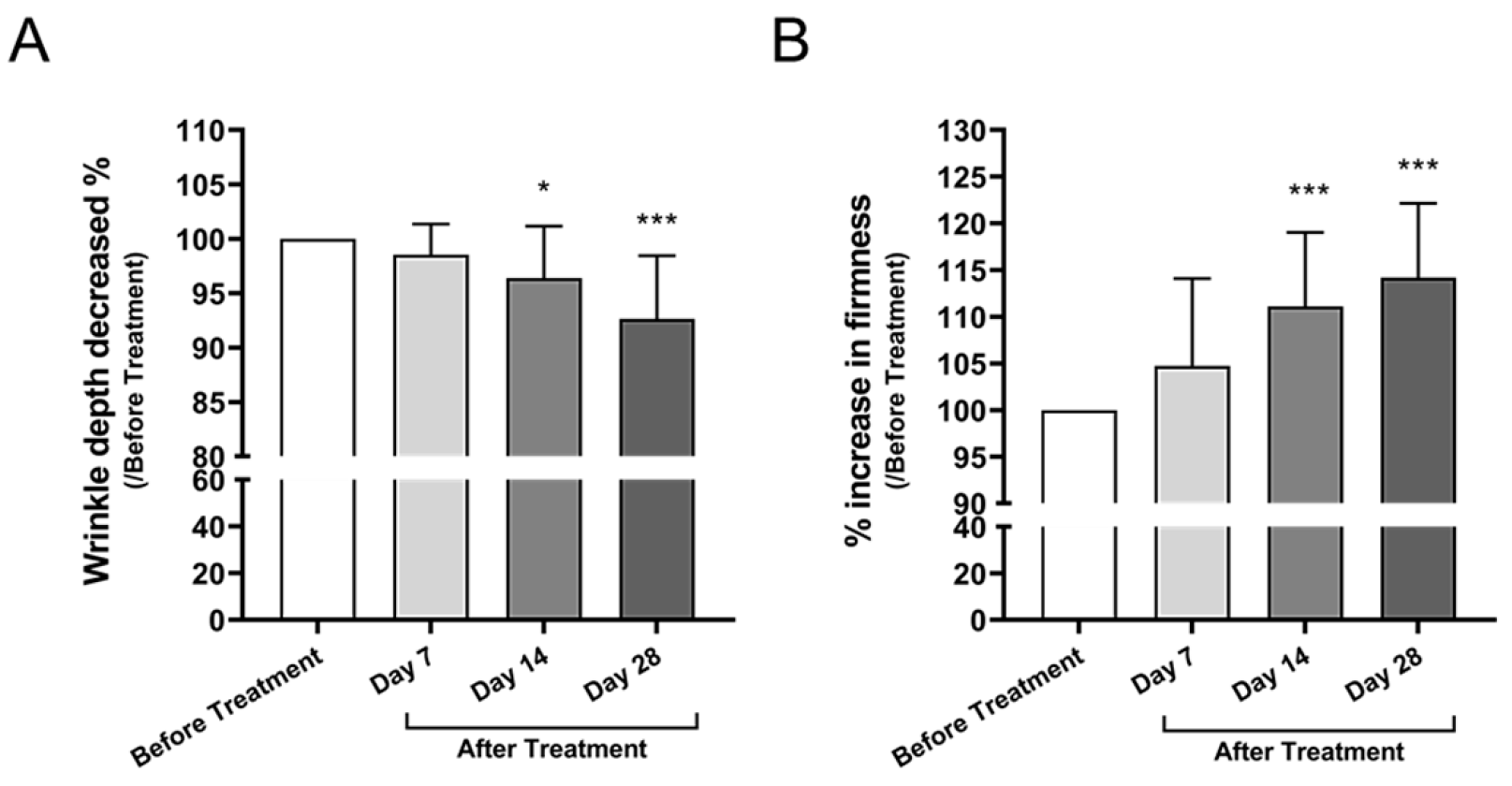
3.3.1. Facial Wrinkle Depth and Skin Firmness
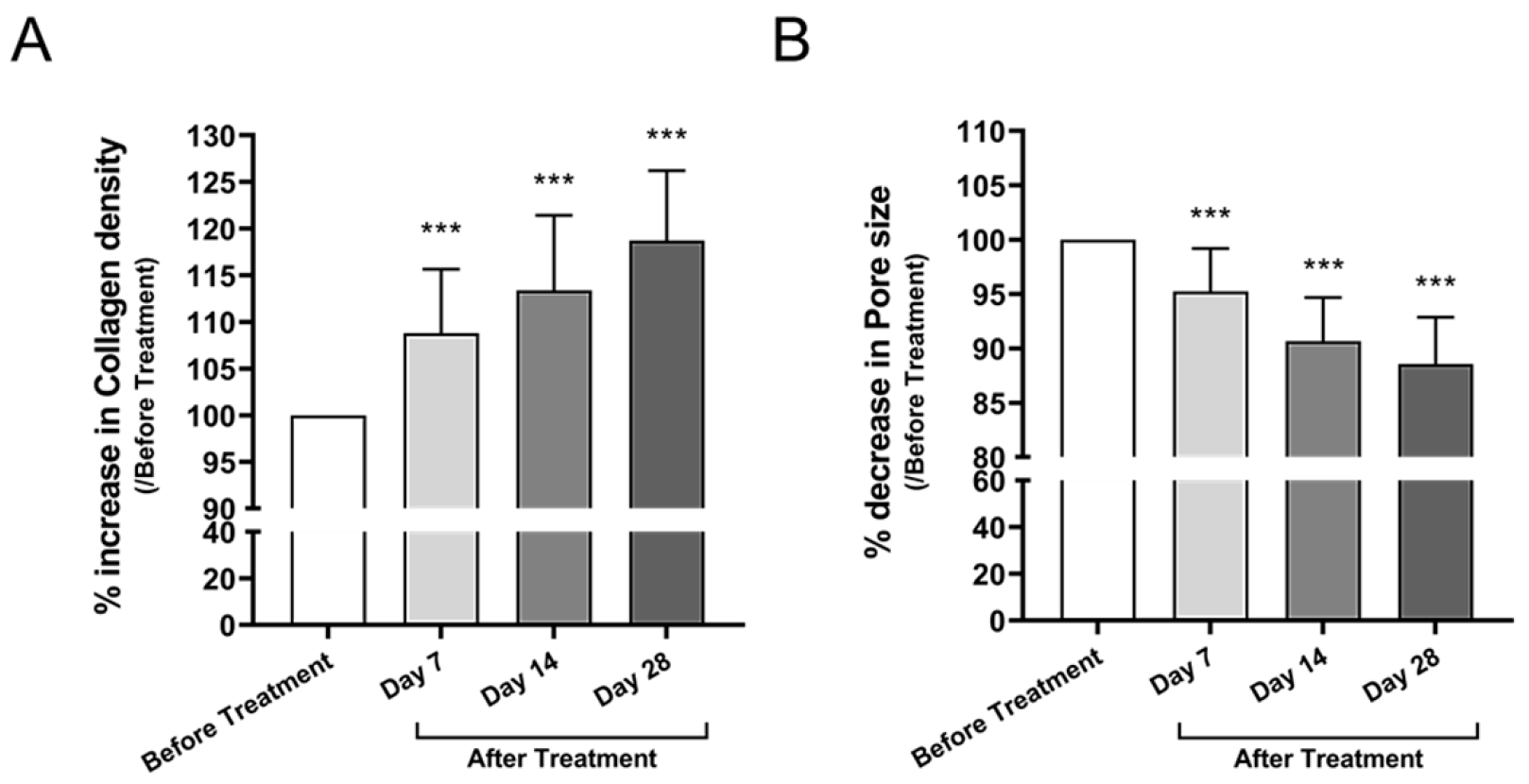
3.3.2. Collagen Density and Pore Size
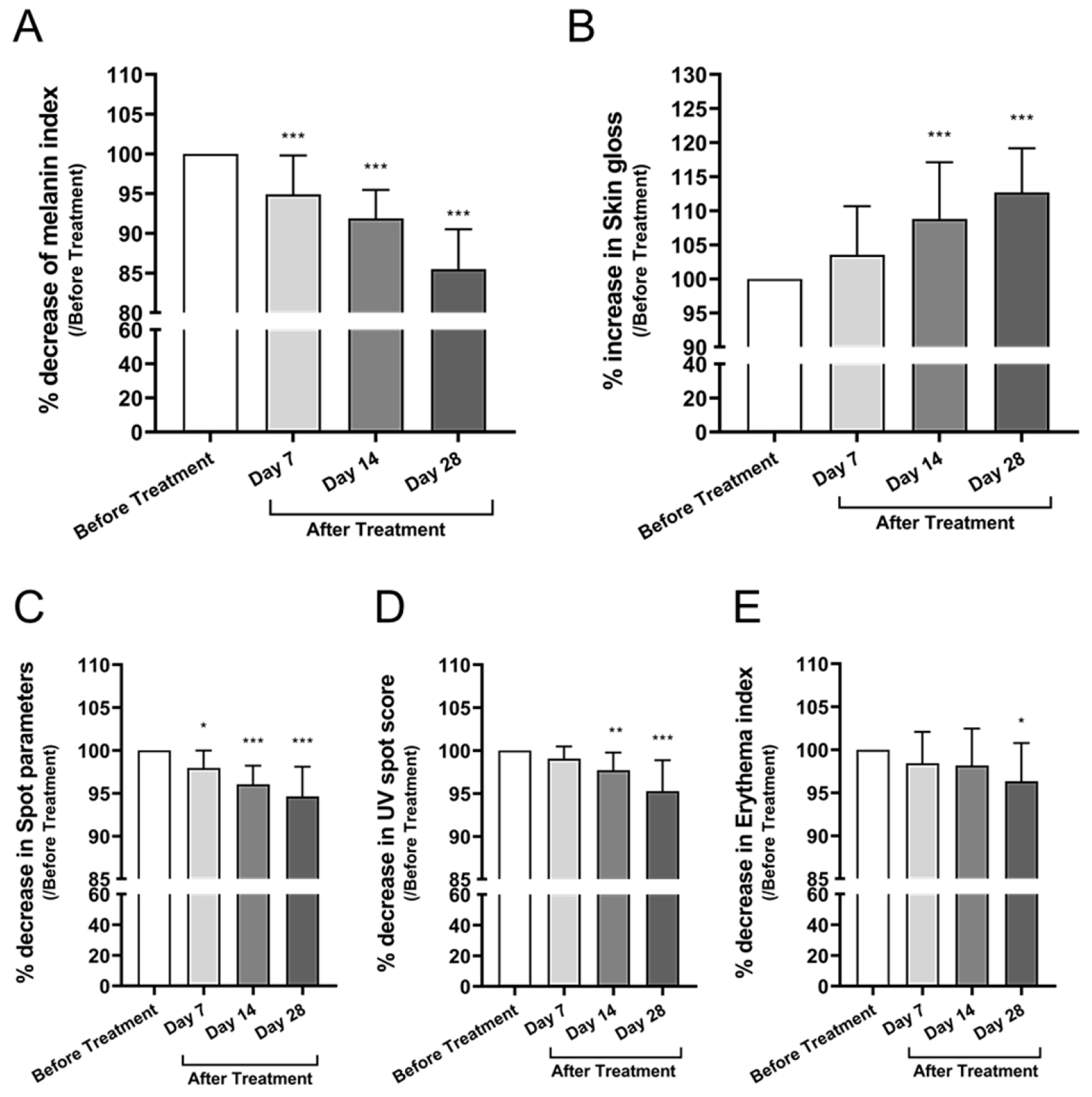
3.3.3. Skin Tone, Pigmentation, Gloss, and Erythema
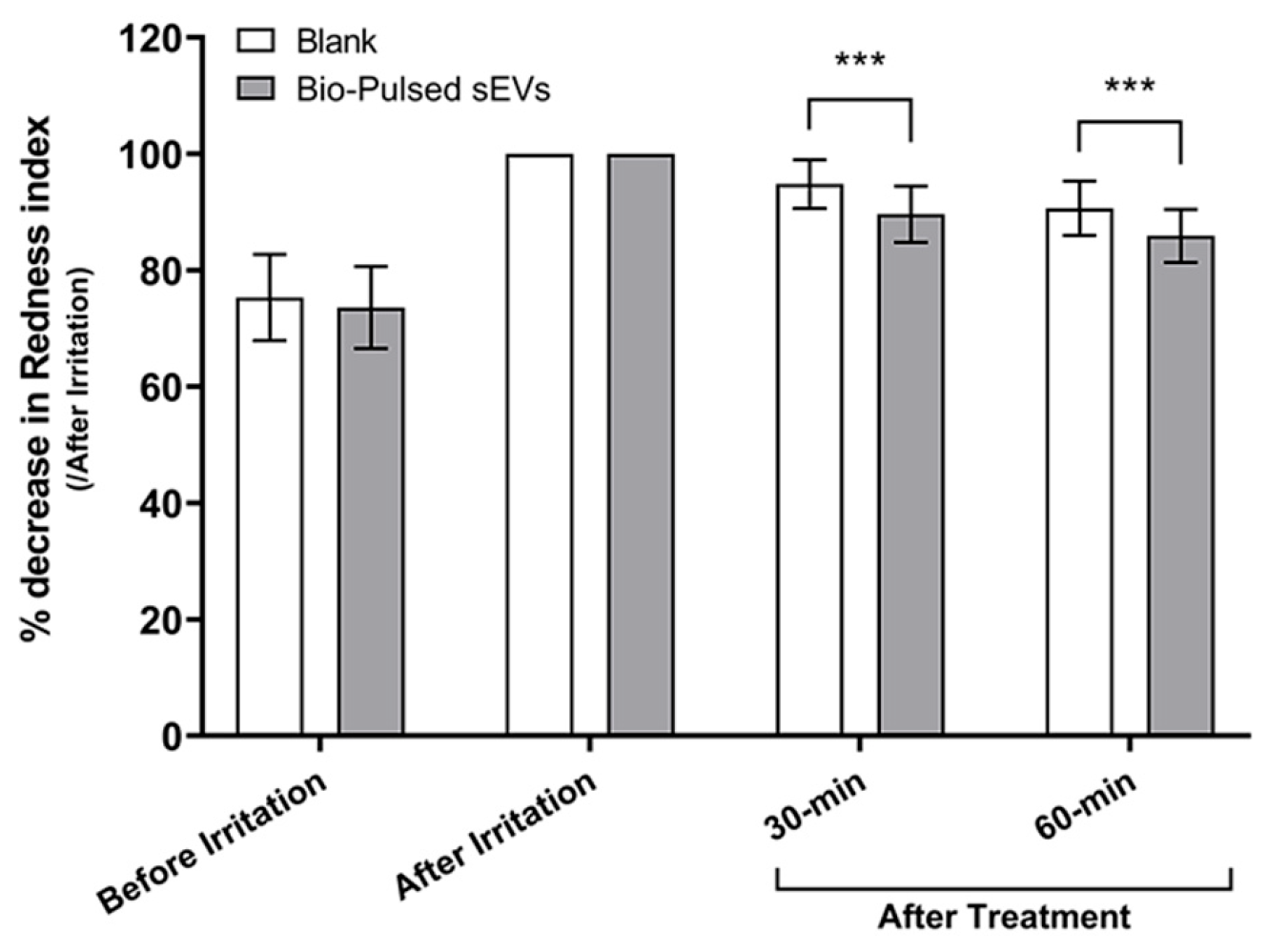
3.3.4. Soothing Response to Irritation
3.3.5. Consumer Perception
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Bio-Pulsed AMSC-sEVs | Bio-Pulsed avian mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles |
| miRNAs | microRNAs |
| MMPs | matrix metalloproteinases |
| CI | confidence interval |
References
- Jung, H.; Jung, Y.; Seo, J.; Bae, Y.; Kim, H.S.; Jeong, W. Roles of extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stem cells in regeneration. Mol. Cells 2024, 47, 100151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadh, M.J.; Ramirez-Coronel, A.A.; Saini, R.S.; Arias-Gonzales, J.L.; Amin, A.H.; Gavilan, J.C.O.; Sârbu, I. Advances in mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-based therapy and their extracellular vesicles for skin wound healing. Hum. Cell 2023, 36, 1253–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muraca, M.; Piccoli, M.; Franzin, C.; Tolomeo, A.M.; Jurga, M.; Pozzobon, M.; Perilongo, G. Diverging Concepts and Novel Perspectives in Regenerative Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haykal, D.; Wyles, S.; Garibyan, L.; Cartier, H.; Gold, M. Exosomes in Cosmetic Dermatology: A Review of Benefits and Challenges. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2025, 24, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kose, O.; Botsali, A.; Caliskan, E. The role of exosomes in skin diseases. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 3219–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, H.; Siwakoti, P.; Qu, X.; Ye, P.; He, Y.; Kumeria, T.; et al. Microneedle-mediated hypoxic extracellular vesicle-encapsulated selenium nanoparticles delivery to treat androgenetic alopecia. J. Control. Release 2025, 381, 113597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdez-Zertuche, J.A.; Ramirez-Marin, H.A.; Tosti, A. Efficacy, safety and tolerability of drugs for alopecia: A comprehensive review. Expert. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2025, 21, 347–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trigo, C.M.; Rodrigues, J.S.; Camoes, S.P.; Sola, S.; Miranda, J.P. Mesenchymal stem cell secretome for regenerative medicine: Where do we stand? J. Adv. Res. 2025, 70, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shieh, J.S.; Chin, Y.T.; Chiu, H.C.; Hsieh, Y.Y.; Cheng, H.R.; Gu, H.; Chang, F.W. Bio-Pulsed Stimulation Effectively Improves the Production of Avian Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles That Enhance the Bioactivity of Skin Fibroblasts and Hair Follicle Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Pang, Y.; He, Q.; Song, Z.; Xie, X.; Zeng, J.; Guo, J. Exosome-derived microRNAs: Emerging players in vitiligo. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1419660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Vincenzo, M.; Diotallevi, F.; Piccirillo, S.; Carnevale, G.; Offidani, A.; Campanati, A.; Orciani, M. miRNAs, Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Major Neoplastic and Inflammatory Skin Diseases: A Page Being Written: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toutfaire, M.; Bauwens, E.; Debacq-Chainiaux, F. The impact of cellular senescence in skin ageing: A notion of mosaic and therapeutic strategies. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 142, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di, V.D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrügger, U. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasko, C.A.; Mackley, C.L.; Sperling, L.C.; Mauger, D.; Miller, J.J. Standardizing the 60-second hair count. Arch. Dermatol. 2008, 144, 759–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, P. Autologous Cellular Method Using Micrografts of Human Adipose Tissue Derived Follicle Stem Cells in Androgenic Alopecia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Liu, P.; Wei, J.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Li, R.; Yao, J. Cell Therapy for Androgenetic Alopecia: Elixir or Trick? Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2023, 19, 1785–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schur, N.; Samman, L.; Shah, M.; Dukharan, V.; Stegura, C.; Broughton, L.; Schlesinger, T. Exosomes: Historical Evolution and Emerging Roles in Dermatology. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2025, 24, e16769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiest, E.F.; Zubair, A.C. Generation of Current Good Manufacturing Practices-Grade Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Using Automated Bioreactors. Biology 2025, 14, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, A.; Rai, D. Global requirements for manufacturing and validation of clinical grade extracellular vesicles. J. Liq. Biopsy. 2024, 6, 100278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
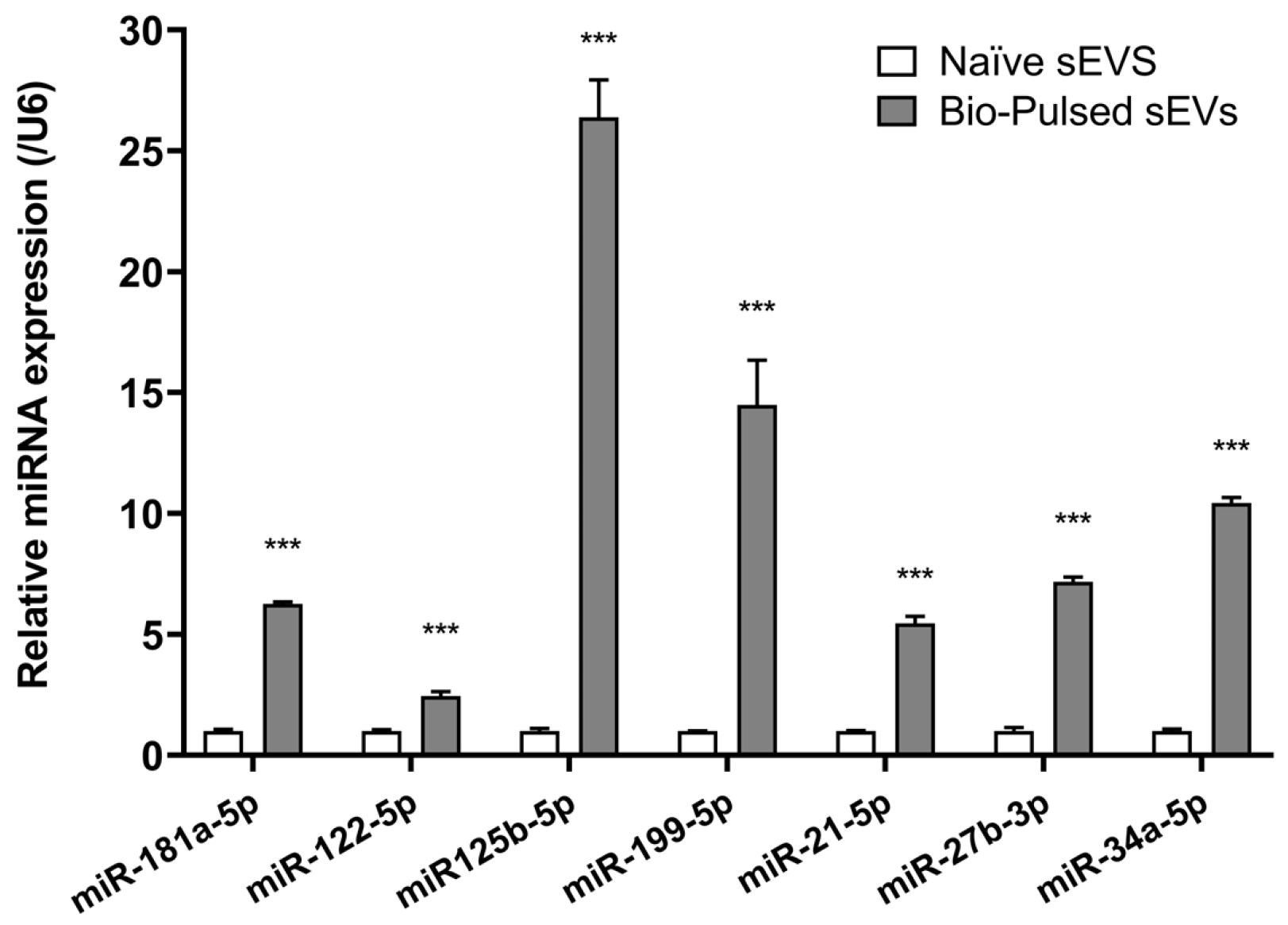

| DEMs | Reads of miRNAs | Log2FC | Regulation | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naïve AMSC-sEVs | Bio-Pulsed AMSC-sEVs | ||||
| gga-miR-181a-5p | 15,304 | 98,713 | 2.6893 | Up | <0.001 |
| gga-miR-122-5p | 1177 | 19,767 | 4.0699 | Up | <0.001 |
| gga-miR-125b-5p | 25,640 | 1,759,371 | 6.1005 | Up | <0.001 |
| gga-miR-199-5p | 925 | 59,526 | 6.0079 | Up | <0.001 |
| gga-miR-21-5p | 210,645 | 1,423,493 | 3.9758 | Up | <0.001 |
| gga-miR-27b-3p | 7915 | 68,897 | 3.1218 | Up | <0.001 |
| gga-miR-34a-5p | 1091 | 191,776 | 7.4576 | Up | <0.001 |
| Evaluation Item | Mean Satisfaction Score | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 30 | Score ≥ 4.0 (%) | Day 60 | Score ≥ 4.0 (%) | |
| Reduced hair shedding | 4.3 ± 0.66 | 90% | 4.3 ± 0.61 | 93% |
| Increased hair volume | 3.8 ± 0.83 | 77% | 3.9 ± 0.69 | 87% |
| New hair growth | 4.3 ± 0.66 | 90% | 4.6 ± 0.49 | 100% |
| Strengthened hair roots | 4.0 ± 0.61 | 83% | 4.2 ± 0.73 | 83% |
| More active and healthier scalp | 4.1 ± 0.51 | 93% | 4.4 ± 0.57 | 97% |
| Reduced scalp sensitivity and itchiness | 4.3 ± 0.66 | 90% | 4.5 ± 0.57 | 97% |
| Reduced scalp oiliness | 4.3 ± 0.61 | 93% | 4.5 ± 0.57 | 97% |
| Hair appears fuller and more elastic | 3.5 ± 0.63 | 60% | 4.2 ± 0.90 | 90% |
| Evaluation Item | Mean Satisfaction Score | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 14 | Score ≥ 4.0 (%) | Day 28 | Score ≥ 4.0 (%) | |
| Reduce facial wrinkles and fine lines | 3.8 ± 0.44 | 75% | 4.2 ± 0.77 | 80% |
| Improved skin firmness | 4.0 ± 0.56 | 85% | 4.0 ± 0.21 | 85% |
| Improved skin elasticity | 4.4 ± 0.49 | 100% | 4.4 ± 0.49 | 100% |
| Improve enlarged pores | 4.0 ± 0.86 | 65% | 4.0 ± 0.76 | 70% |
| Brighten skin tone | 4.0 ± 0.56 | 85% | 4.4 ± 0.68 | 90% |
| Improve skin gloss | 4.0 ± 0.60 | 80% | 4.2 ± 0.77 | 80% |
| Improve uneven skin tone | 3.6 ± 0.60 | 55% | 4.4 ± 0.68 | 90% |
| Reduce facial spots | 3.6 ± 0.51 | 55% | 4.0 ± 0.76 | 70% |
| Reduce sensitive erythema on face | 3.8 ± 0.64 | 65% | 4.0 ± 0.51 | 85% |
| Overall skin quality improvement | 4.2 ± 0.75 | 80% | 4.2 ± 0.77 | 80% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shieh, J.-S.; Chin, Y.-T.; Yeh, T.-T.; Guo, J.J.; Chang, F.-W.; Cheng, H.-R.; Hsu, H.-H.; Huang, W.-L.; Huang, H.-H.; Hsieh, Y.-Y.; et al. Topical Application of Bio-Pulsed Avian MSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Enhances Hair Regrowth and Skin Rejuvenation: Evidence from Clinical Evaluation and miRNA Profiling. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070539
Shieh J-S, Chin Y-T, Yeh T-T, Guo JJ, Chang F-W, Cheng H-R, Hsu H-H, Huang W-L, Huang H-H, Hsieh Y-Y, et al. Topical Application of Bio-Pulsed Avian MSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Enhances Hair Regrowth and Skin Rejuvenation: Evidence from Clinical Evaluation and miRNA Profiling. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(7):539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070539
Chicago/Turabian StyleShieh, Ju-Sheng, Yu-Tang Chin, Tsu-Te Yeh, Jiong Jiong Guo, Fung-Wei Chang, Hui-Rong Cheng, Hung-Han Hsu, Wei-Lun Huang, Han-Hsiang Huang, Ya-Yu Hsieh, and et al. 2025. "Topical Application of Bio-Pulsed Avian MSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Enhances Hair Regrowth and Skin Rejuvenation: Evidence from Clinical Evaluation and miRNA Profiling" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 7: 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070539
APA StyleShieh, J.-S., Chin, Y.-T., Yeh, T.-T., Guo, J. J., Chang, F.-W., Cheng, H.-R., Hsu, H.-H., Huang, W.-L., Huang, H.-H., Hsieh, Y.-Y., Chiang, C.-P., & Wang, S.-C. (2025). Topical Application of Bio-Pulsed Avian MSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Enhances Hair Regrowth and Skin Rejuvenation: Evidence from Clinical Evaluation and miRNA Profiling. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(7), 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070539