Gypenosides Alleviate Hyperglycemia by Regulating Gut Microbiota Metabolites and Intestinal Permeability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Compounds and Reagents
2.2. Extract Preparation and Qualitative and Quantitative Analyses of Gps
2.3. Animal Models and Treatments
2.4. Blood Biochemical Tests
2.5. Histological Staining
2.6. Immunohistochemistry of Colon Tissues
2.7. 16S rDNA Sequencing Analysis
2.8. SCFA Analysis
2.9. BA Analysis
2.10. Western Blotting
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Components of Gps Measured by UPLC-ESI-Q/TOF-MS/MS
3.2. Quantitative Analysis of Key Chemical Markers
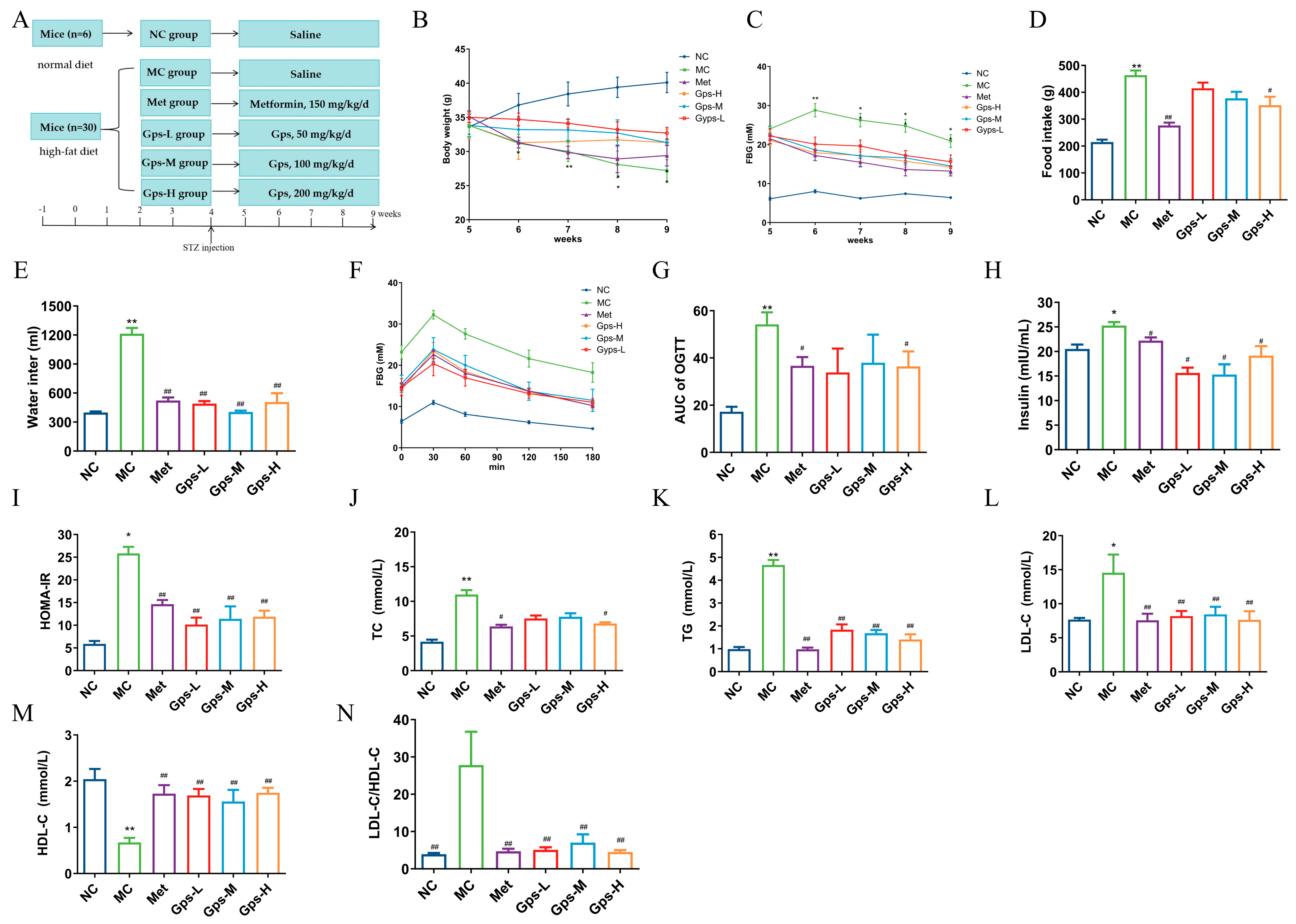
3.3. Gps Exhibit Metabolic Protective Effects in HFD/STZ-Induced Diabetic Mice
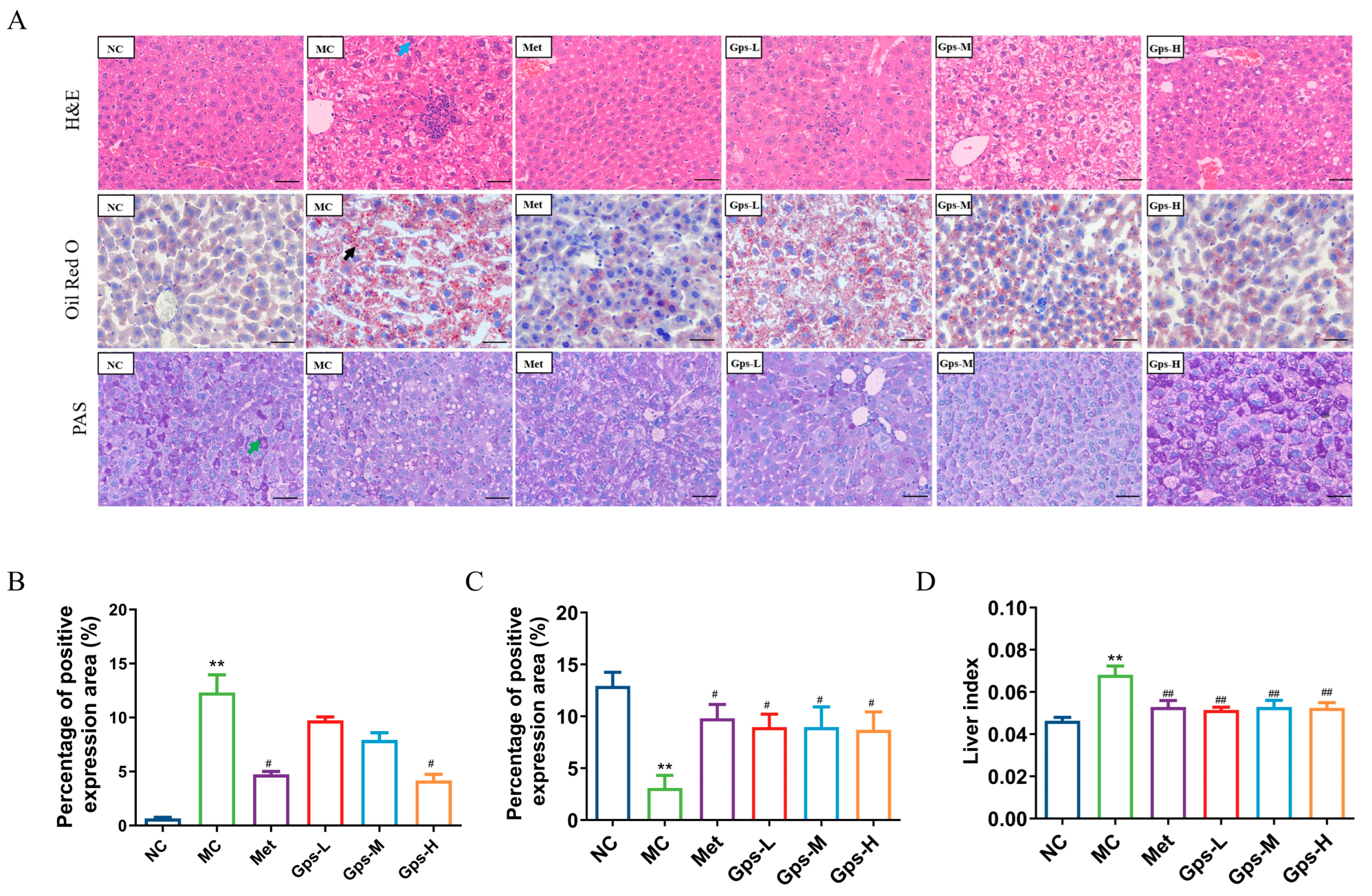
3.4. Gps Alleviate Liver Histology of HFD/STZ Mice
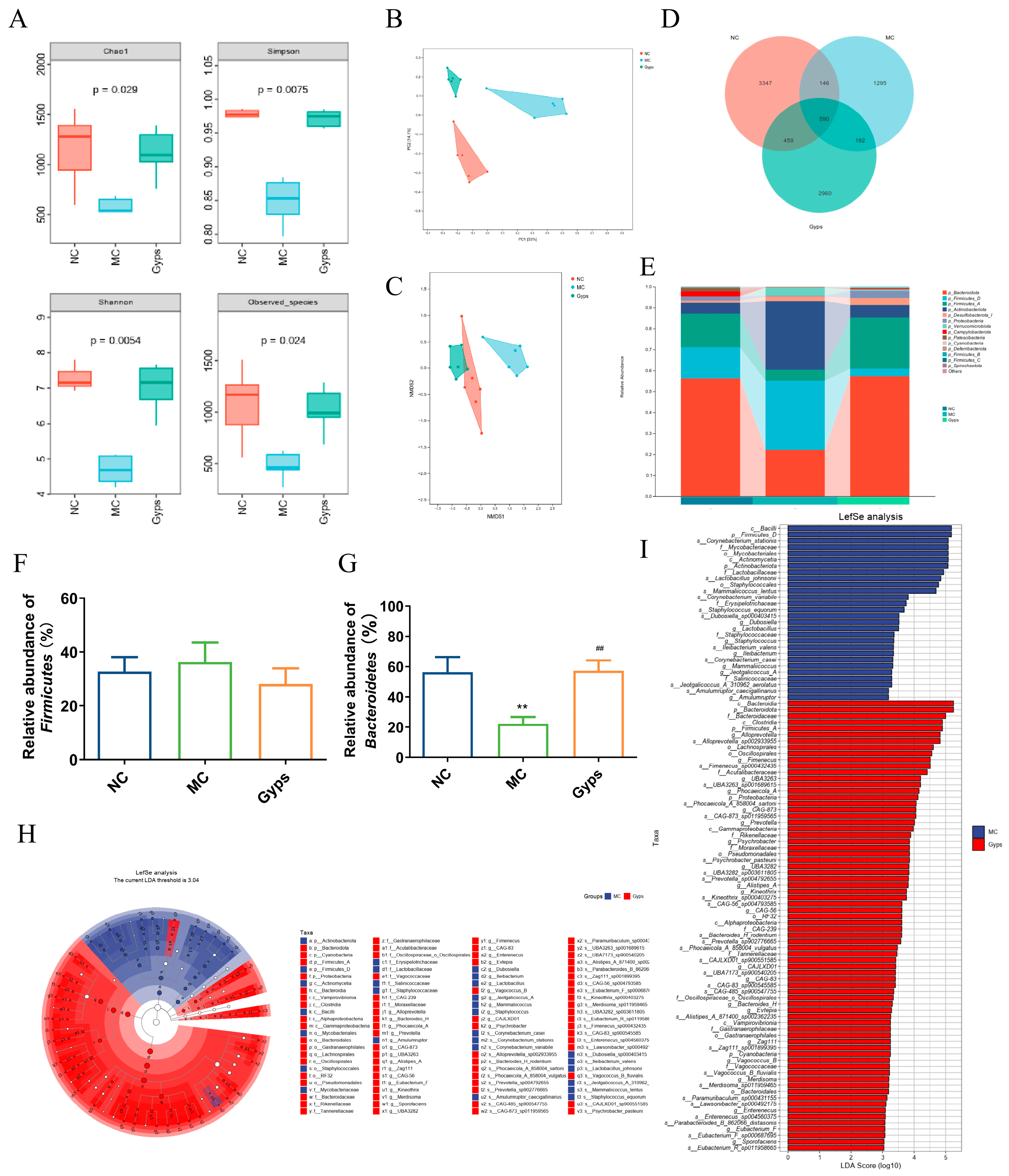
3.5. Gps Modulate Gut Microbiota Composition in T2DM Mice
3.6. Gps Inhibit Inflammation and Alleviate Gut Barrier Damage
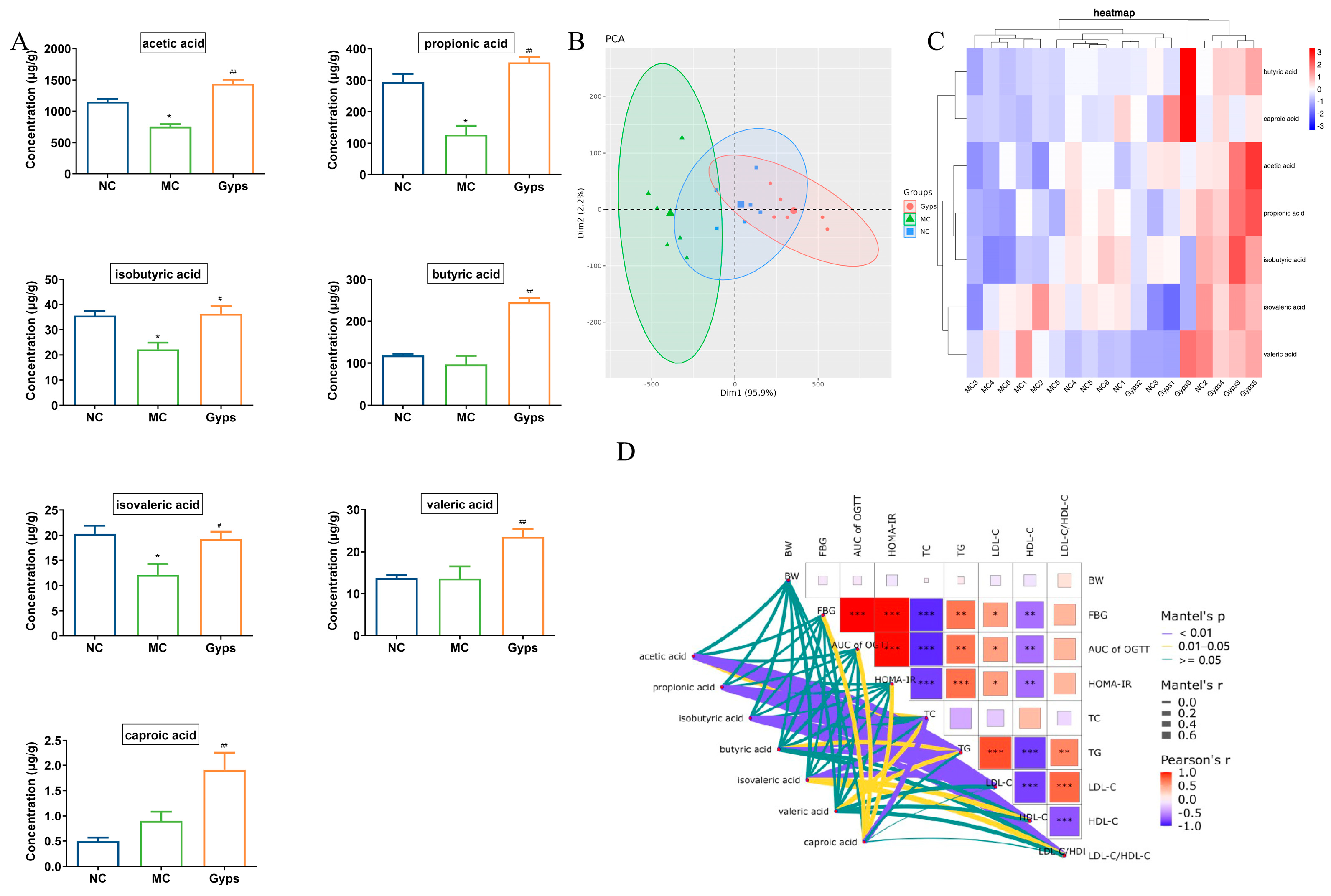
3.7. Gps Increase SCFA Production in T2DM Mice
3.8. Gps Improve BA Dysregulation in T2DM Mice
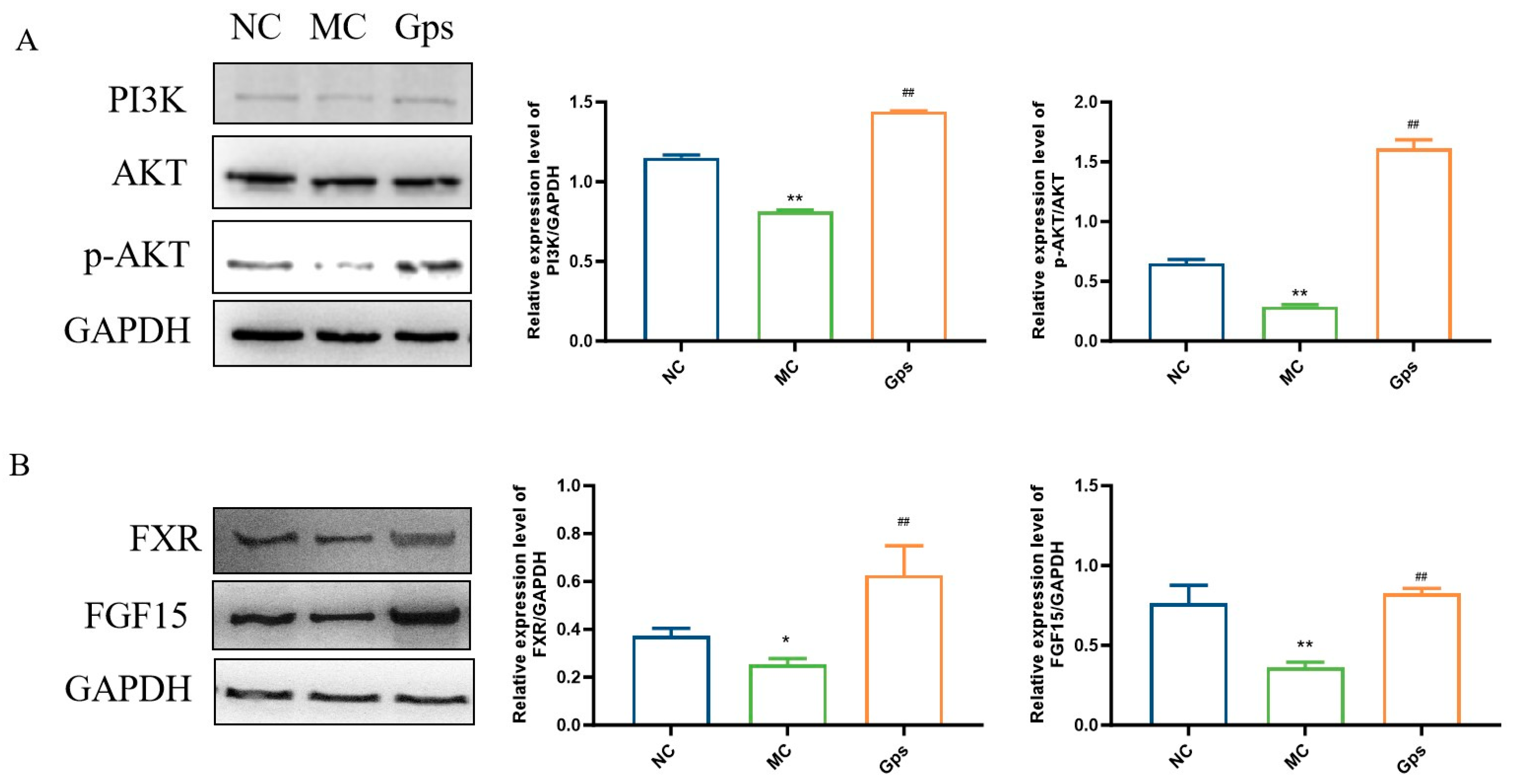
3.9. Effects of Gps on Regulating Signal Pathways Involved in Insulin and BA Metabolism
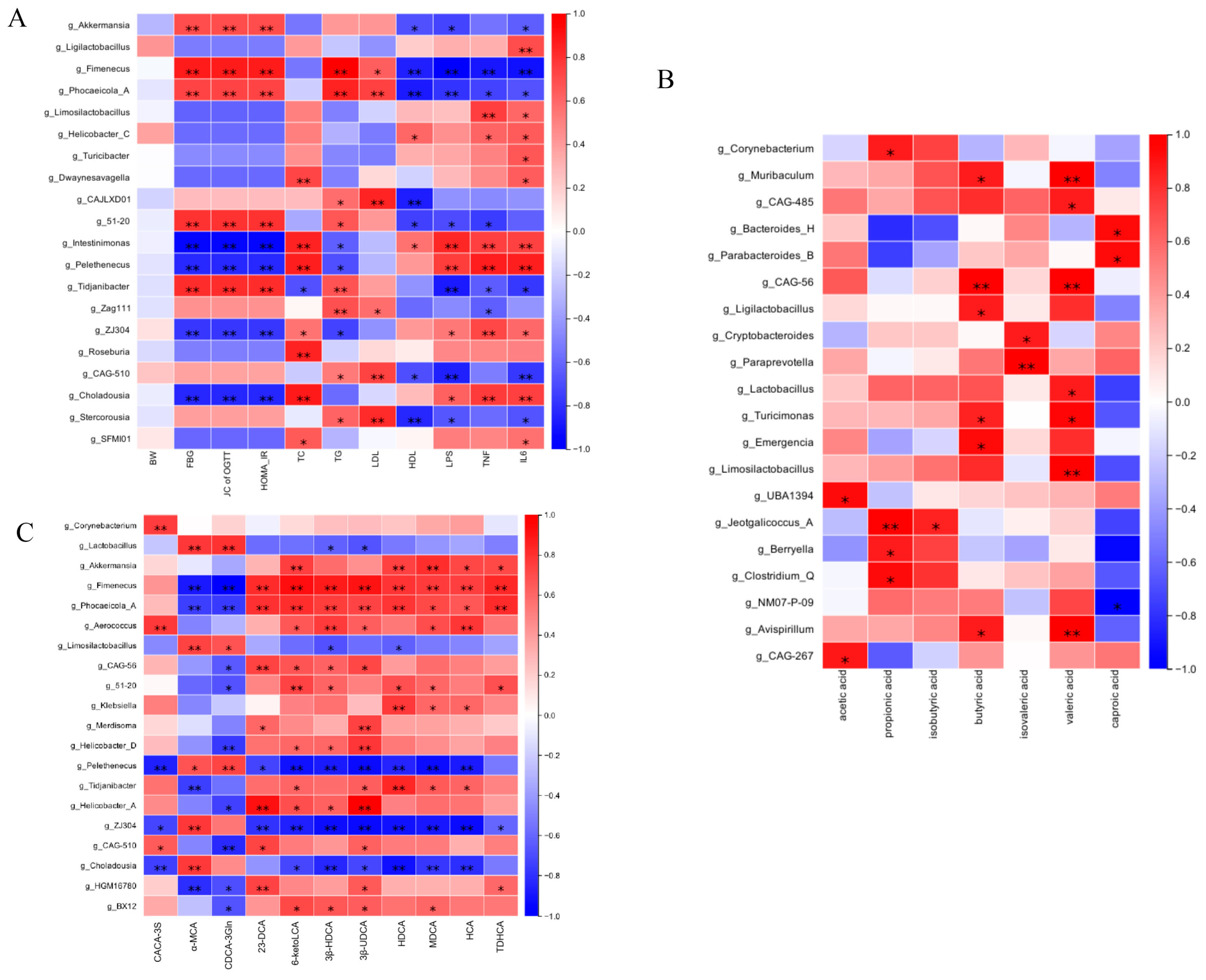
3.10. Correlation Analysis Between Gut Microbial Communities and Metabolic Parameters (SCFAs and BAs)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| Gps | Gypenosides |
| BW | Body weight |
| STZ | Streptozotocin |
| HFD | High-fat diet |
| FBG | Fasting blood glucose |
| OGTT | Oral glucose tolerance test |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| TG | Total triglyceride |
| LDL-C | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| PCoA | Principal coordinates analysis |
| NMDS | Non-metric multidimensional scaling |
| OTU | Operational taxonomic unit |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| ZO-1 | Zonula occludens-1 |
| MOD | Mean optical density |
| SCFAs | Short-chain fatty acid |
| BAs | Bile acids |
| FXR | Farnesoid X receptor |
References
- Laaroussi, H.; Bakour, M.; Ousaaid, D.; Aboulghazi, A.; Ferreira-Santos, P.; Genisheva, Z.; Teixeira, J.-A.; Lyoussi, B. Effect of antioxidant-rich propolis and bee pollen extracts against d-glucose induced type 2 diabetes in rats. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138 Pt B, 109802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Luo, J.; Bao, Y. Effects of polygonatum sibiricum saponin on hyperglycemia, gut microbiota composition and metabolic profiles in type 2 diabetes mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 143, 112155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, H.-T.; Chang, K.-C.; Li, C.-Y.; Wu, J.-S. Risks of cardiovascular diseases associated with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and other antidiabetic drugs in patients with type 2 diabetes: A nation-wide longitudinal study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrientos-Avalos, J.-R.; Morel-Cerda, E.-C.; Felix-Tellez, F.-A.; Vidrio-Huerta, B.-E.; Aceves-Ayala, A.-R.; Flores-Rendon, A.-R.; Velarde-Ruiz, V.-J. Gastrointestinal adverse effects of old and new antidiabetics: How do we deal with them in real life? Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. 2024, 89, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolkepli, H.; Widodo, R.-T.; Mahmood, S.; Salim, N.; Awang, K.; Ahmad, N.; Othman, R. A review on the delivery of plant-based antidiabetic agents using nanocarriers: Current status and their role in combatting hyperglycaemia. Polymers 2022, 14, 2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, D.; Rao, C.; Xue, S.; Lei, J. Purification, characterization and neuroprotective effects of a polysaccharide from gynostemma pentaphyllum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 122, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Lin, Z.; Shao, K.; Fang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y. Jiaogulan tea (gpostemma pentaphyllum) potentiates the antidiabetic effect of white tea via the ampk and pi3k pathways in c57bl/6 mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 4339–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Gao, X.; Huang, D.; Xu, X.; Shen, J. The potential of gynostemma pentaphyllum in the treatment of hyperlipidemia and its interaction with the lox1-pi3k-akt-enos pathway. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 8000–8012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-C.; Lu, K.-W.; Tsai, M.-L.; Hsu, S.-C.; Kuo, C.-L.; Yang, J.-S.; Hsia, T.-C.; Yu, C.-S.; Chou, S.-T.; Kao, M.-C.; et al. Gypenosides induced g0/g1 arrest via chk2 and apoptosis through endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondria-dependent pathways in human tongue cancer scc-4 cells. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, J.; Kang, Y.-J.; Jeon, S.-M.; Jung, U.-J.; Lee, M.-K.; Song, H.; Choi, M.S. Potential hypoglycemic effect of an ethanol extract of gynostemma pentaphyllum in c57bl/ksj-db/db mice. J. Med. Food 2008, 11, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-J.; Zhao, T.-T.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, C.-K.; Hwang, B.-Y.; Lee, K.-E.; Lee, M.-K. Ethanol extract from gynostemma pentaphyllum ameliorates dopaminergic neuronal cell death in transgenic mice expressing mutant a53t human alpha-synuclein. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Seaton, S.-C.; Ndousse-Fetter, S.; Adhikari, A.-A.; Dibenedetto, N.; Mina, A.-I.; Banks, A.-S.; Bry, L.; Devlin, A.-S. A selective gut bacterial bile salt hydrolase alters host metabolism. Elife 2018, 7, 37182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Zhao, M.; Qi, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, N.; Liu, Z.; Bian, Y. Hypoglycemic effect of gynostemma pentaphyllum saponins by enhancing the nrf2 signaling pathway in stz-inducing diabetic rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2016, 39, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.-B.; Xie, P.; Guo, M.; Li, F.-F.; Xiao, M.-Y.; Qi, Y.-S.; Pei, W.-J.; Luo, H.-T.; Gu, Y.-L.; Piao, X.-L. Protective effect of heat-processed gynostemma pentaphyllum on high fat diet-induced glucose metabolic disorders mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1215150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iatcu, O.-C.; Hamamah, S.; Covasa, M. Harnessing prebiotics to improve type 2 diabetes outcomes. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koliada, A.; Syzenko, G.; Moseiko, V.; Budovska, L.; Puchkov, K.; Perederiy, V.; Gavalko, Y.; Dorofeyev, A.; Romanenko, M.; Tkach, S.; et al. Association between body mass index and firmicutes/bacteroidetes ratio in an adult ukrainian population. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Besten, G.; van Eunen, K.; Groen, A.-K.; Venema, K.; Reijngoud, D.-J.; Bakker, B.-M. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2325–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noureldein, M.-H.; Bitar, S.; Youssef, N.; Azar, S.; Eid, A.-A. Butyrate modulates diabetes-linked gut dysbiosis: Epigenetic and mechanistic modifications. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2020, 64, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, W.; Zhan, L.; Hou, S.; Zhao, C.; Bi, T.; Lu, X. Fecal microbiota transplantation alters the susceptibility of obese rats to type 2 diabetes mellitus. Aging 2020, 12, 17480–17502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lv, B.; Liu, N.; Tao, S.; Dou, J.; Li, J.; Deng, R.; Yang, X.; Jiang, G. The mechanism of bile acid metabolism regulating lipid metabolism and inflammatory response in t2dm through the gut-liver axis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Meng, X.; Xue, Y.; Mao, M.; Liu, Y.; Tian, X.; Sui, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, P. Bile acids-gut microbiota crosstalk contributes to the improvement of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1027212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.-Y.; Yue, S.-R.; Tan, Y.-Y.; Tang, N.; Xu, Y.-S.; Zhang, B.-J.; Mao, Y.-J.; Xue, Z.-S.; Lu, A.-P.; Liu, B.-C.; et al. Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract alleviates NASH in mice: Exploration of inflammation and gut microbiota. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Liu, C.-S.; Hu, Y.-N.; Luo, Z.-Y.; Chen, F.-L.; Yuan, L.-X.; Tan, X.-M. Coix seed polysaccharides alleviate type 2 diabetes mellitus via gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids activation of igf1/pi3k/akt signaling. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150 Pt A, 110717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.; Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H.; Cao, W. Impact of schisandrachinensis bee pollen on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and gut microbiota in high fat diet induced obese mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, C.; Werner, P.; Worthmann, A.; Wegner, K.; Todter, K.; Scheja, L.; Rohn, S.; Heeren, J.; Fischer, M. A liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry-based method for the simultaneous determination of hydroxy sterols and bile acids. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1371, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Bian, X.; Wu, W.; Lv, L.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Q.; Shi, D.; Fang, D.; et al. Protective effect of lactobacillus salivarius li01 on thioacetamide-induced acute liver injury and hyperammonaemia. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 1860–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Ding, L.; Tang, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, T. Baicalin protects against hypertension-associated intestinal barrier impairment in part through enhanced microbial production of short-chain fatty acids. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Su, H.; Wang, H.; Lu, F.; Nie, K.; Wang, Z.; Huang, W.; Dong, H. The effect and mechanism of jiao-tai-wan in the treatment of diabetes mellitus with depression based on network pharmacology and experimental analysis. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, H.; Xiang, D.; Xiao, S.; Xiao, J.; Shen, W.; Hu, P.; Ren, H.; Peng, M. Dynamics of the gut-liver axis in rats with varying fibrosis severity. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 3390–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lu, P.-X.; Liang, H.-Z.; Zheng, W.; Chen, X.-J.; Zhang, J.; Song, J.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y.-X.; Zhang, T.; et al. An effective and high-throughput sample preparation method involving demalonylation followed by an ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography-charged aerosol detector for analyzing gypenoside xlix and gypenoside a in gynostemma longipes. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 230, 115393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Pan, B.; Tian, T.; Su, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Lv, S.; Zhang, Z. Baihu renshen decoction ameliorates type 2 diabetes mellitus in rats through affecting gut microbiota enhancing gut permeability and inhibiting tlr4/nf-kappab-mediated inflammatory response. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1051962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.-S.; Wang, J.; Yannie, P.-J.; Sandhu, Y.-K.; Korzun, W.-J.; Ghosh, S. Dietary supplementation with galactooligosaccharides attenuates high-fat, high-cholesterol diet-induced glucose intolerance and disruption of colonic mucin layer in c57bl/6 mice and reduces atherosclerosis in ldlr-/- mice. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zeng, R.; Gou, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Nhamdriel, T.; Fan, G. The total alkaloids of berberidis cortex alleviate type 2 diabetes mellitus by regulating gut microbiota, inflammation and liver gluconeogenesis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 337 Pt 3, 118957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Tang, C.; Hu, G.; Gao, Z. Targeting gut microbiota as a therapeutic target in T2DM: A review of multi-target interactions of probiotics, prebiotics, postbiotics, and synbiotics with the intestinal barrier. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 210, 107483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Shi, M.; Guo, G.; Xing, J.; Liu, Z.; Song, F.; Liu, S. In-depth investigation of the therapeutic effect of tribulus terrestris l. On type 2 diabetes based on intestinal microbiota and feces metabolomics. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 325, 117815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, X.; Ke, J.; Hou, X.; Shen, G.; Li, S.; Chen, H.; Cui, Q.; Yu, J.; Luo, Q.; et al. Chayote pectin regulates blood glucose through the gut-liver axis: Gut microbes/scfas/foxo1 signaling pathways. Food Res. Int. 2025, 202, 115706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, F.-Z.; Nelson, E.; Chu, P.-Y.; Horlock, D.; Fiedler, A.; Ziemann, M.; Tan, J.-K.; Kuruppu, S.; Rajapakse, N.-W.; El-Osta, A.; et al. High-fiber diet and acetate supplementation change the gut microbiota and prevent the development of hypertension and heart failure in hypertensive mice. Circulation 2017, 135, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Shan, S.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, G. Neohesperidin mitigates high-fat-diet-induced colitis in vivo by modulating gut microbiota and enhancing scfas synthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Long, H.; Muhindo, E.-M.; Liu, R.; Sui, W.; Li, Q.; Zhang, M. Lactobacillus rhamnosus lra05 ameliorate hyperglycemia through a regulating glucagon-mediated signaling pathway and gut microbiota in type 2 diabetic mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 8797–8806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Chen, B.; Jin, W.; Wang, M.; Chen, X.; Jian, M.; Sun, L.; Piao, C. Bile acids as a key target: Traditional chinese medicine for precision management of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus through the gut microbiota-bile acids axis. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1481270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Liu, X.; Song, G.; Peng, W.; Sun, X.; Fang, W.; Qi, W. Imbalance of bile acids metabolism mediated by gut microbiota contributed to metabolic disorders in diabetic model mice. Biology 2025, 14, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.; Huang, F.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, W.; Wang, S.; Li, M.; Han, X.; Ge, K.; Qu, C.; et al. A dysregulated bile acid-gut microbiota axis contributes to obesity susceptibility. Ebiomedicine 2020, 55, 102766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzolo, D.; Buckley, K.; Kong, B.; Zhan, L.; Shen, J.; Stofan, M.; Brinker, A.; Goedken, M.; Buckley, B.; Guo, G.-L. Bile acid homeostasis in a cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase and sterol 27-hydroxylase double knockout mouse model. Hepatology 2019, 70, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, L.; Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; Wen, X.; Yang, J. Simiao wan modulates the gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism during improving type 2 diabetes mellitus in mice. Phytomedicine 2022, 104, 154264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Compound | Content (%) | Regression Equation | Linear Range (mg/mL) | Correlation Coefficient, r | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gp XLIX | 5.34–5.45 | Y = 64,757X − 13,585 | 0.02876–15 | 0.9999 |
| 2 | Gp A | 10.14–10.36 | Y = 86,806X + 9016.5 | 0.02876–15 | 0.9999 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Liu, X.-F.; Yang, K.; Yu, L.-L.; Liu, S.-J.; Wang, N.-N.; Chen, Y.-M.; Hu, Y.-Q.; Qin, B. Gypenosides Alleviate Hyperglycemia by Regulating Gut Microbiota Metabolites and Intestinal Permeability. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070515
Wang R, Liu X-F, Yang K, Yu L-L, Liu S-J, Wang N-N, Chen Y-M, Hu Y-Q, Qin B. Gypenosides Alleviate Hyperglycemia by Regulating Gut Microbiota Metabolites and Intestinal Permeability. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(7):515. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070515
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Rong, Xue-Feng Liu, Kuan Yang, Li-Li Yu, Shao-Jing Liu, Na-Na Wang, Yun-Mei Chen, Ya-Qi Hu, and Bei Qin. 2025. "Gypenosides Alleviate Hyperglycemia by Regulating Gut Microbiota Metabolites and Intestinal Permeability" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 7: 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070515
APA StyleWang, R., Liu, X.-F., Yang, K., Yu, L.-L., Liu, S.-J., Wang, N.-N., Chen, Y.-M., Hu, Y.-Q., & Qin, B. (2025). Gypenosides Alleviate Hyperglycemia by Regulating Gut Microbiota Metabolites and Intestinal Permeability. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(7), 515. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070515






