Comparative Analysis of the Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Eight Salvia Medicinal Species: Insights into the Deep Phylogeny of Salvia in East Asia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material, DNA Extraction, and Sequencing
2.2. Chloroplast Genome Assembly and Annotation
2.3. Genome Structure and Codon Usage Analysis
2.4. Long and Simple Sequence Repeats Analyses
2.5. Comparative Genomic Analysis
2.6. Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results
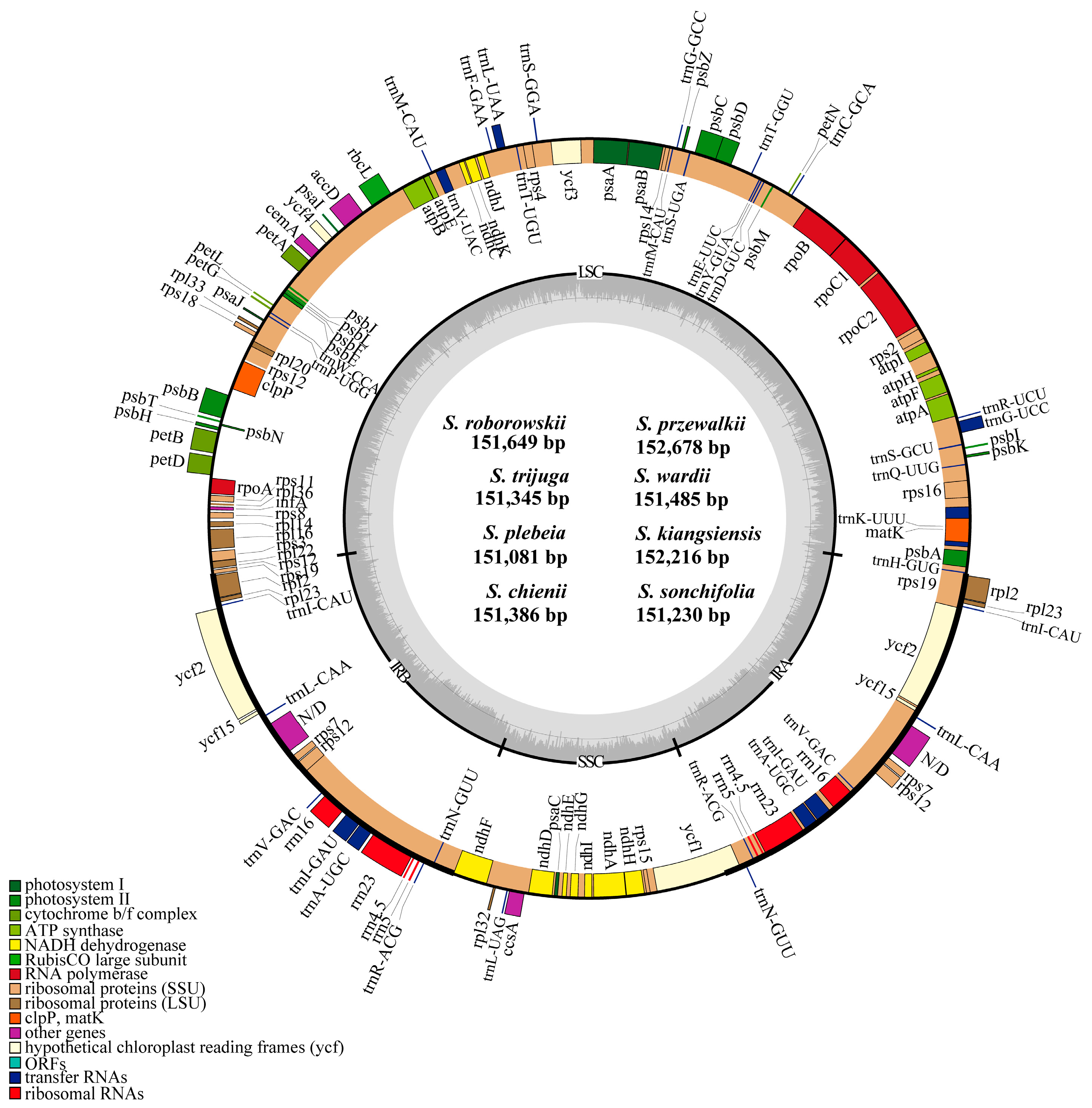
3.1. Size and Structure of Chloroplast Genomes
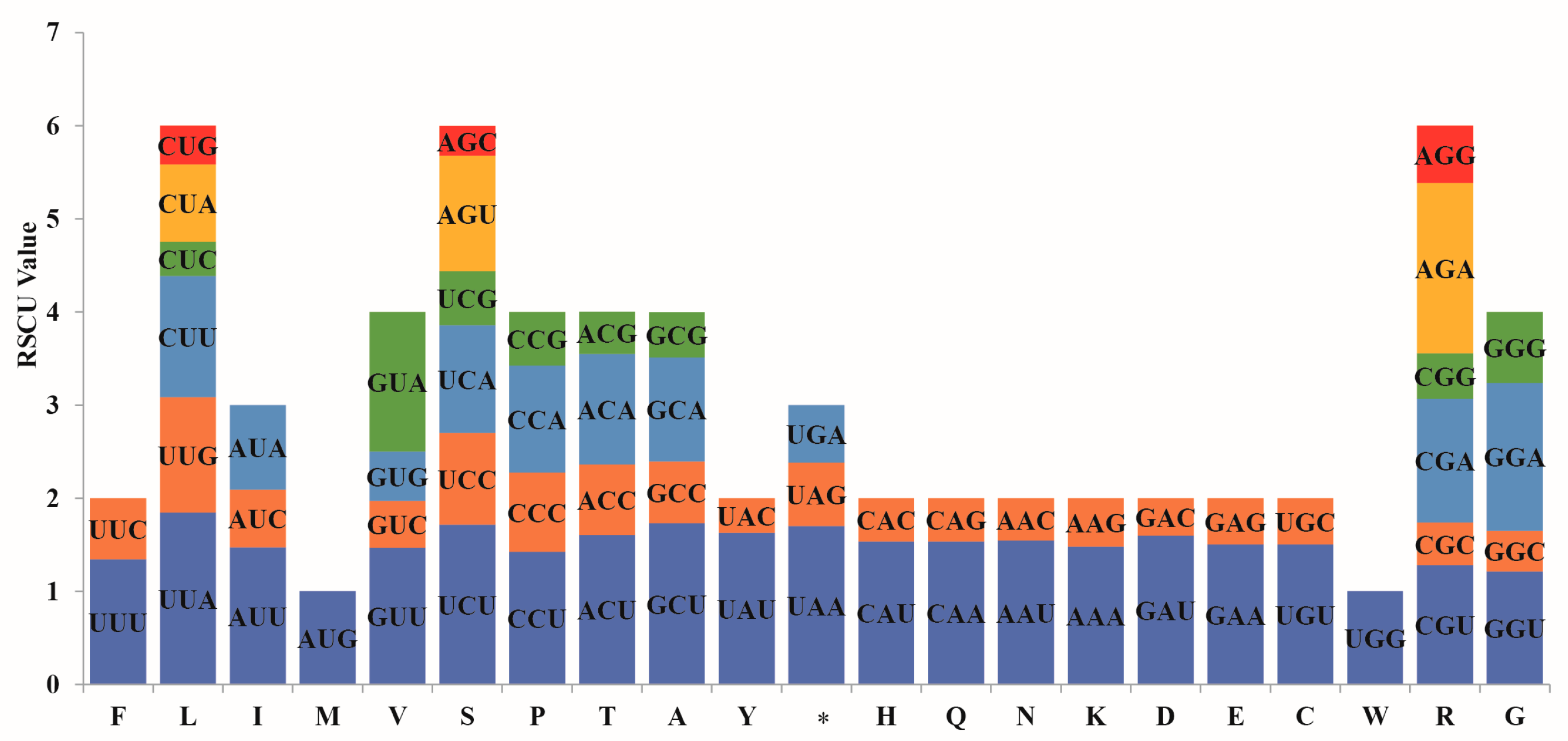
3.2. Codon Usage Preference Analysis
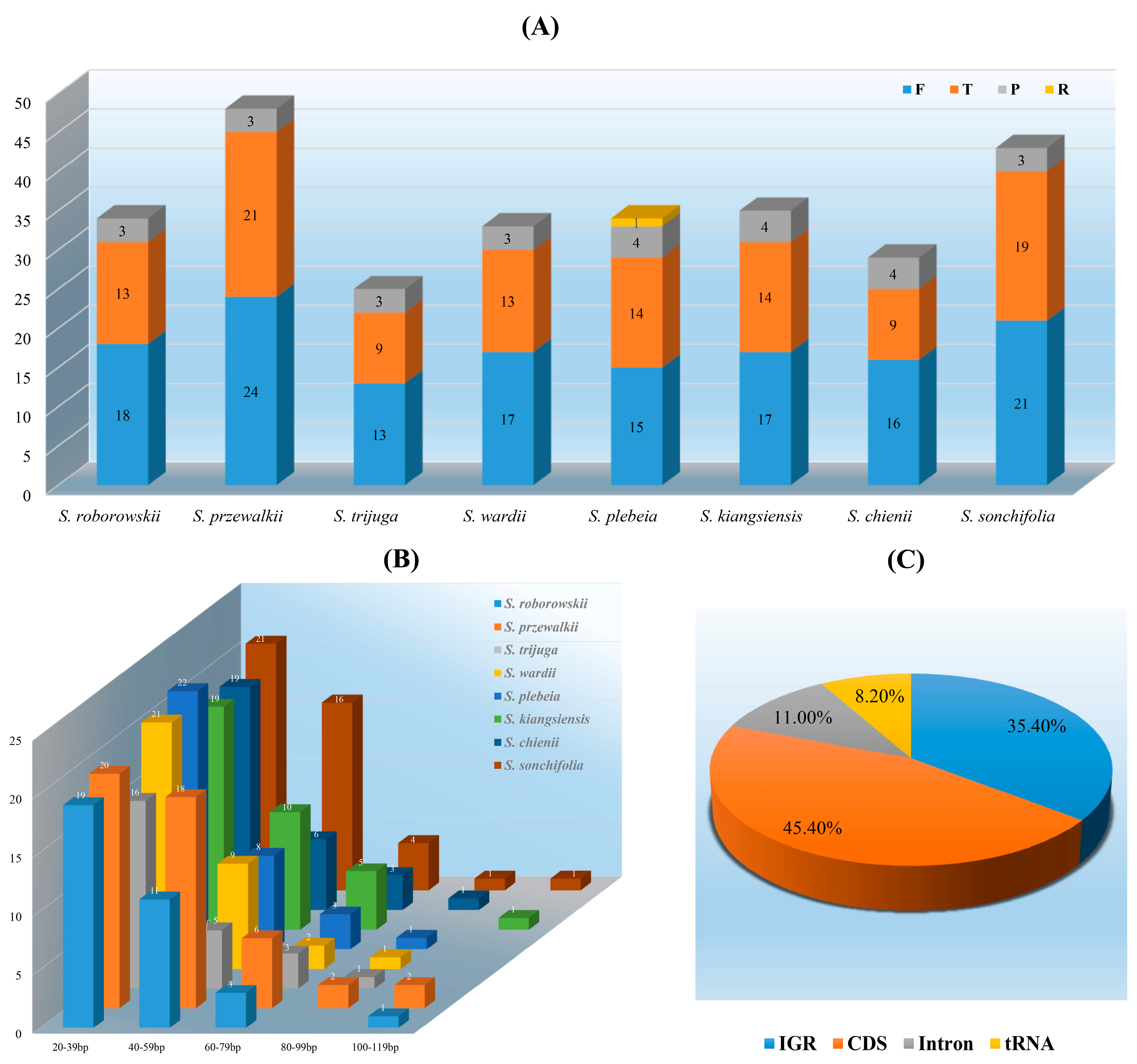
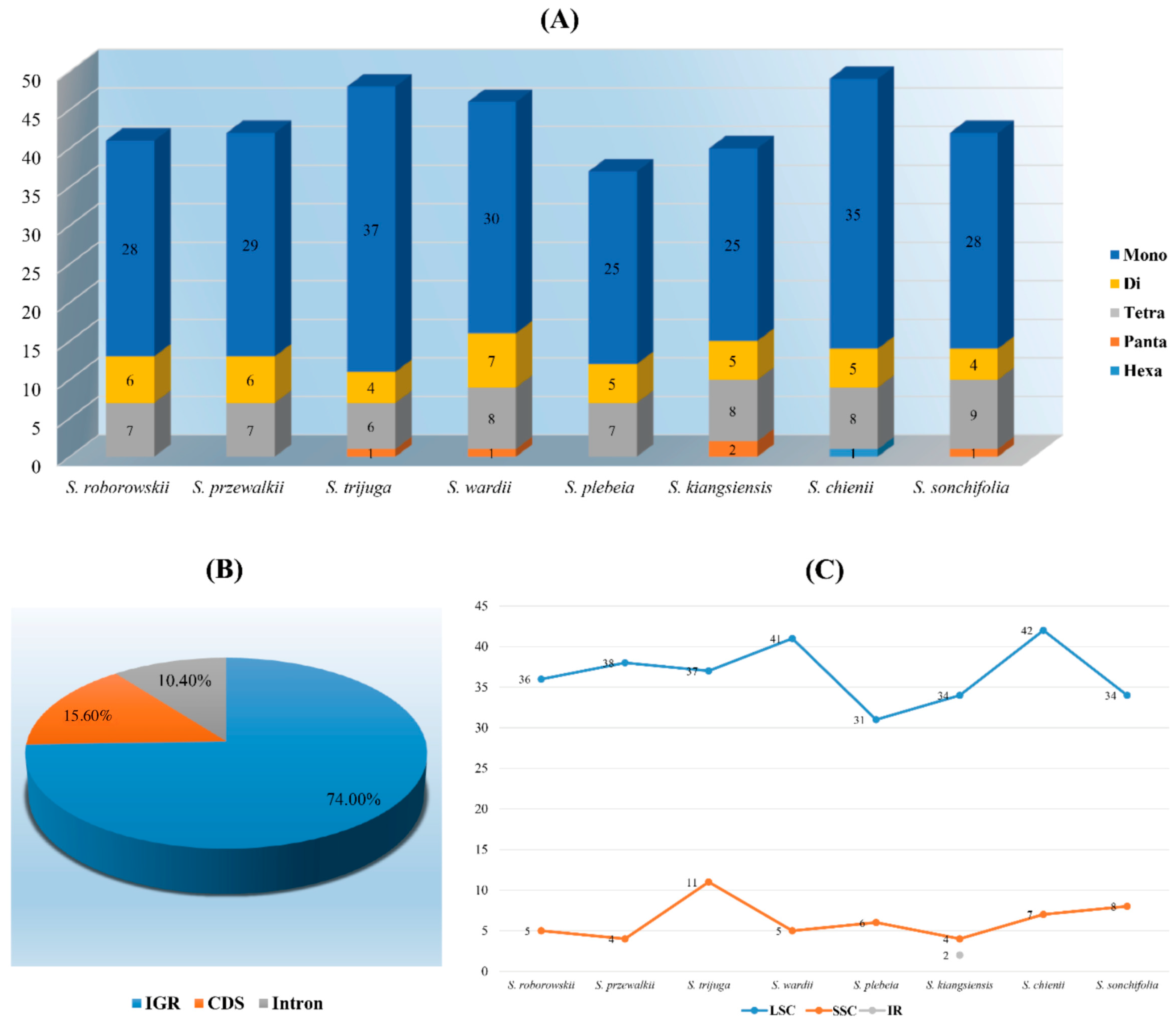
3.3. Long and Simple Sequence Repeats Analyses
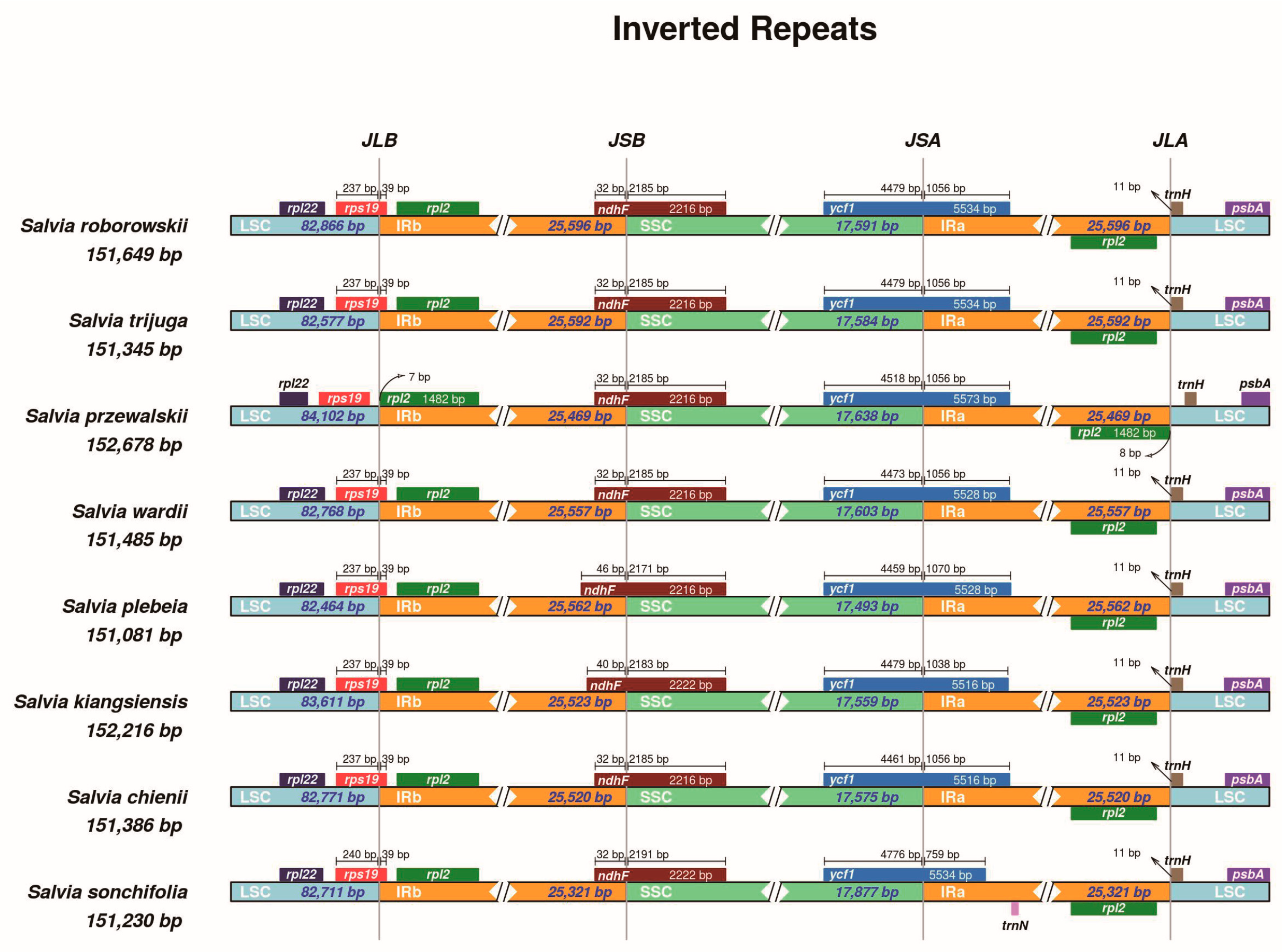
3.4. Inverted Repeat Expansion and Contraction
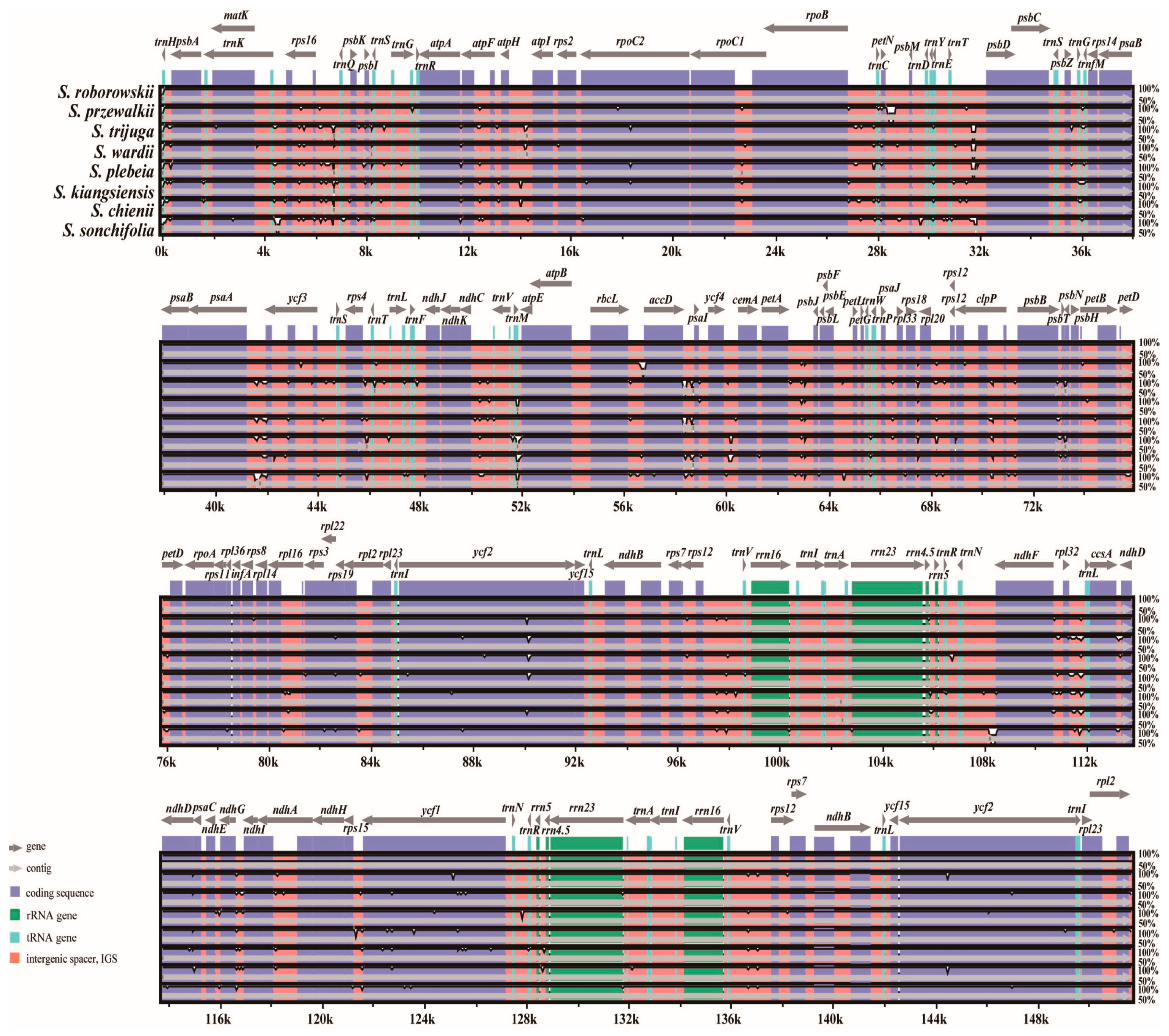
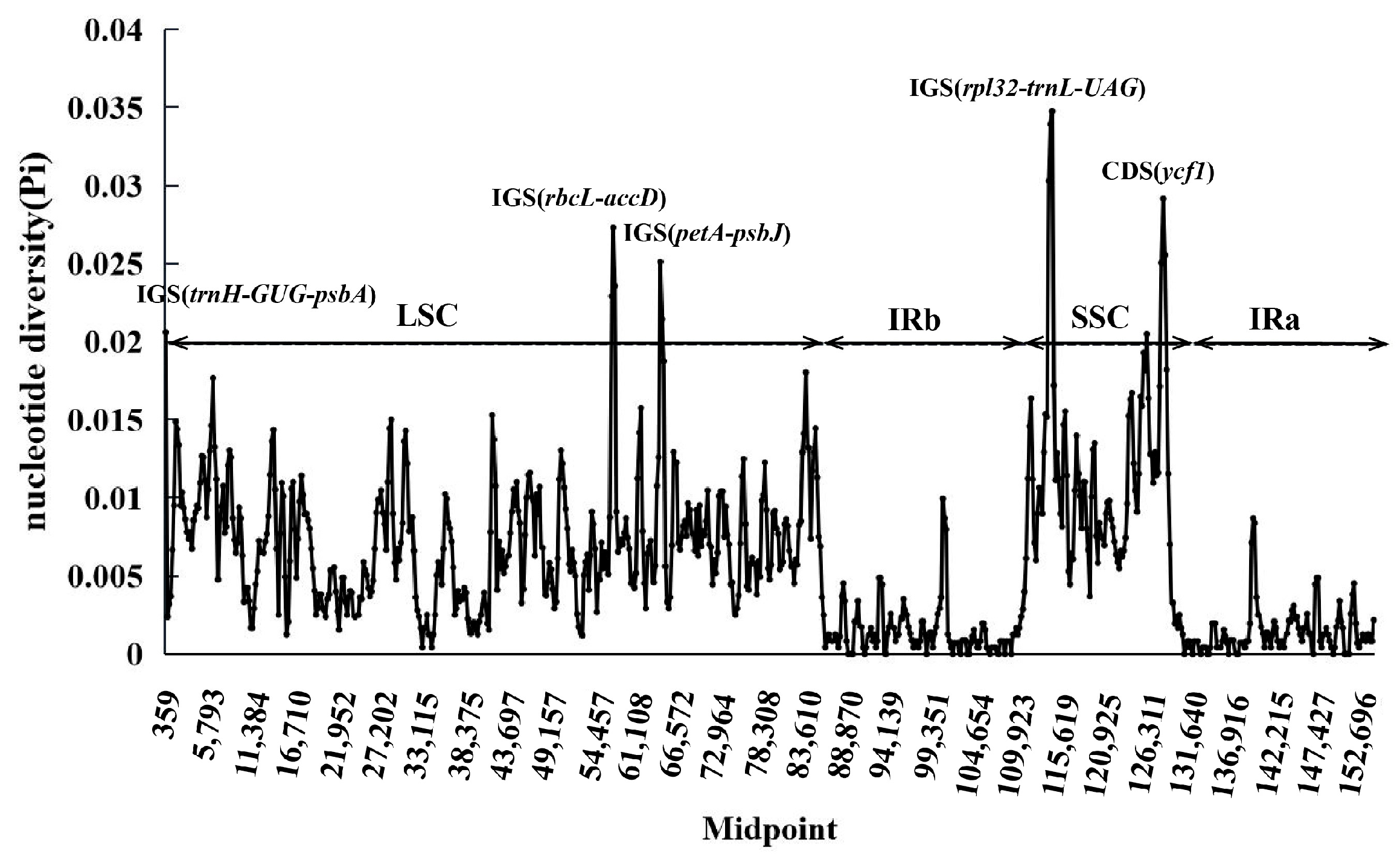
3.5. Comparative Chloroplast Genomic Analysis
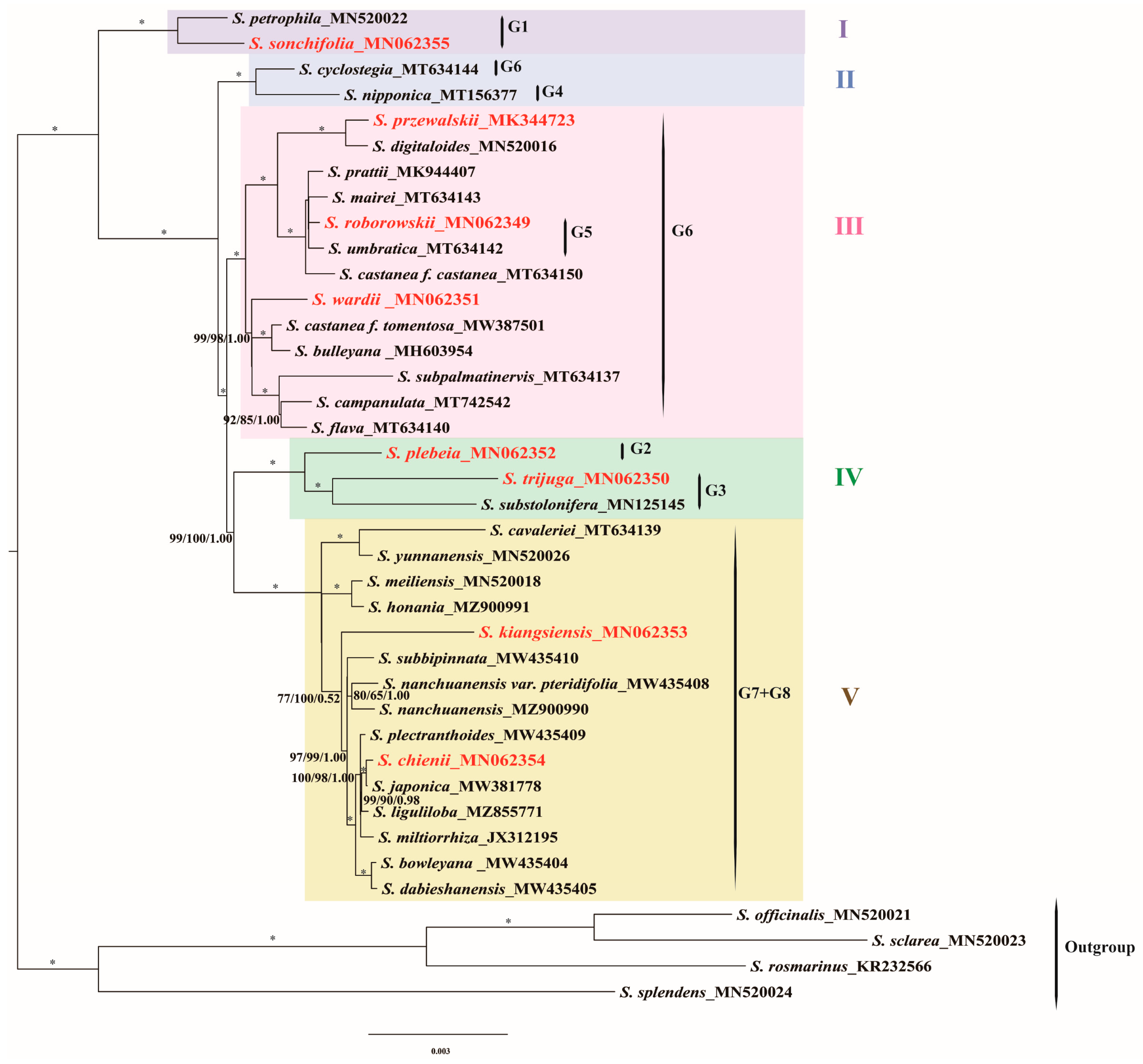
3.6. Phylogenetic Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. Size and Structure of Chloroplast Genomes
4.2. Codon Usage Bias
4.3. LSRs and SSRs Analyses
4.4. Inverted Repeat Expansion and Contraction
4.5. Sequence Divergence and Hypervariable Regions
4.6. Phylogenetic Insights into East Asian Salvia
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LSC | Large single-copy |
| SSC | Small single-copy |
| IR | Inverted repeat sequence |
| GC | Guanine/cytosine content |
| PCG | Protein-coding gene |
| SSRs | Simple sequence repeats |
| LSRs | Long sequence repeats |
| BI | Bayesian inference |
| ML | Maximum likelihood |
| MP | Maximum Parsimony |
| CP | Chloroplast |
| IGR | Intergenic regions |
| PP | Posterior probability |
References
- Daniell, H.; Lin, C.S.; Yu, M.; Chang, W.J. Chloroplast genomes: Diversity, evolution, and applications in genetic engineering. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 134–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicke, S.; Schneeweiss, G.M.; Depamphilis, C.W.; Müller, K.F.; Quandt, D. The evolution of the plastid chromosome in land plants: Gene content, gene order, gene function. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 76, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, R.K.; Cai, Z.; Raubeson, L.A.; Daniell, H.; dePamphilis, C.W.; Leebens-Mack, J.; Müller, K.F.; Guisinger-Bellian, M.; Haberle, R.C.; Hansen, A.K.; et al. Analysis of 81 genes from 64 plastid genomes resolves relationships in angiosperms and identifies genome-scale evolutionary patterns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19369–19374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.D.; Stein, D.B. Conservation of chloroplast genome structure among vascular plants. Curr. Genet. 1986, 10, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.J.; Dhingra, A.; Soltis, P.S.; Shaw, R.; Farmerie, W.G.; Folta, K.M.; Soltis, D.E. Rapid and accurate pyrosequencing of angiosperm plastid genomes for phylogenetic analyses. Am. J. Bot. 2010, 97, 1062–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.B.; Sytsma, K.J.; Treutlein, J.; Wink, M. Salvia (Lamiaceae) is not monophyletic: Implications for the systematics, radiation, and ecological specialization of Salvia and tribe Mentheae. Am. J. Bot. 2004, 91, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Bian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y. Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge): A prospective healing sage for cardiovascular diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhumaliyeva, G.; Zhussupova, A.; Zhusupova, G.E.; Błońska-Sikora, E.; Cerreto, A.; Omirbekova, N.; Zhunusbayeva, Z.; Gemejiyeva, N.; Ramazanova, M.; Wrzosek, M.; et al. Natural compounds of Salvia L. genus and molecular mechanism of their biological activity. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, I.; Mohammed, F.S.; Lekesiz, Ö.; Sevindik, E.; Özbas Gerçeker, F.; Sevindik, M. Pharmacological and nutritional properties: Genus Salvia. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. 2023, 11, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y. Salvia. In Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae; Wu, C.Y., Ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1977; Volume 66, pp. 70–196. [Google Scholar]
- Murata, G.; Yamazaki, T. Salvia. In Flora of Japan; Kodansha: Tokyo, Japan, 1993; Volume IIIa, pp. 302–307. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Li, M.; Yuan, Q.; Cui, Z.; Huang, L.; Xiao, P. Phylogenetic relationships of Salvia (Lamiaceae) in China: Evidence from DNA sequence datasets. J. Syst. Evol. 2013, 51, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.X.; Atsuko, T.; Drew, B.T.; Soltis, D.E.; Soltis, P.S.; Peng, H.; Xiang, C.L. Phylogeny and staminal evolution of Salvia (Lamiaceae, Nepetoideae) in East Asia. Ann. Bot. 2018, 122, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenks, A.A.; Walker, J.B.; Kim, S.C. Phylogeny of New World Salvia subgenus Calosphace (Lamiaceae) based on cpDNA (psbA-trnH) and nrDNA (ITS) sequence data. J. Plant Res. 2013, 14, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Drew, B.T.; Chen, Y.; Hu, G.; Li, B.; Xiang, C. The chloroplast genome of Salvia: Genomic characterization and phylogenetic analysis. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2020, 181, 812–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ma, P.F.; Li, H.T.; Hu, G.X.; Li, D.Z. Comparative plastomic analysis and insights into the phylogeny of Salvia (Lamiaceae). Plant Divers. 2021, 43, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.J.; Yu, W.B.; Yang, J.B.; Song, Y.; de Pamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.S.; Li, D.Z. GetOrganelle: A fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 241–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.J.; Moore, M.J.; Li, D.Z.; Yi T., S. PGA: A software package for rapid, accurate, and flexible batch annotation of plastomes. Plant Methods 2019, 15, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, T.M.; Eddy, S.R. tRNAscan-SE: A program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic. Acids Res. 1997, 25, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohse, M.; Drechsel, O.; Kahlau, S.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW): A suite of tools for generating physical maps of plastid and mitochondrial genomes and visualizing expression data sets. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2013, 41, W575–W581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633_4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic. Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W273–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Cheon, K.; Yoo, K.; Lee, H.; Cho, K.; Suh, J.; Kim, S.; Nam, J.; Sohn, H.; Kim, Y. Complete chloroplast genome sequences and comparative analysis of Chenopodium quinoa and C. album. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1696–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swofford, D.L. PAUP*: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (and Other Methods), Version 4.0b10; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Li, Y.; Meng, F.; Duan, Y.; Sun, M.; Yang, S.; Liu, H. Analysis of chloroplast genome characteristics and codon usage bias in 14 species of Annonaceae. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2024, 24, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Pei, Y.; Cui, N.; Zhao, G.P.; Hou, M.M.; Chen, Y.Y.; Li, X.W. Comparative and phylogenetic analysis of complete chloroplast genome sequences of Salvia regarding its worldwide distribution. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14268–14282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Y.; Yang, J.X.; Li, H.K.; Zhao, H.S. Chloroplast genomes of two species of Cypripedium: Expanded genome size and proliferation of AT-biased repeat sequences. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 609729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Wang, W.; Huang, Q.; Fan, R.; Wang, X.; Feng, P.; Zhao, G.; Bian, S.; Ren, H.; Chang, Y. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Dryopteris fragrans (L.) Schott and the repeat structures against the thermal environment. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 166351–166362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Zhao, W.; Xin, Y.; Shen, W.; Wang, F.; Li, Q.; Tu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Z.; Xin, P. Characteristics of the complete chloroplast genome of Pourthiaea (Rosaceae) and its comparative analysis. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, G.; Liu, C. Comparative genomics of Eight complete chloroplast genomes of Phyllostachys species. Forests 2024, 15, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Wang, Z.S.; Zhang, J.G. The complete chloroplast genomic landscape and phylogenetic analyses of Populus alba L. J. For. Res. 2020, 31, 1875–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.L.; Yu, J.J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Wang, S.Z. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Rhododendron fortunei: Structural comparative and phylogenetic analysis in the Ericaceae family. Bot. Serbica 2023, 47, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Song, J.; Gao, H.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, J.; Pang, X.; Yao, H.; Sun, C.; Li, X.; Li, C.; et al. The Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequence of the Medicinal Plant Salvia miltiorrhiza. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ping, H.; Ding, Y.; Hu, S.; Bi, G.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Guo, L.; et al. Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Salvia leucantha (Lamiaceae). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2021, 6, 3406–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Yang, H.; Zeng, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, J.; Sun, S.; Wang, B.; Liu, C. Comparative genomics and phylogenetic analysis of the chloroplast genomes in three medicinal Salvia species for bioexploration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Feng, M. Analysis of the codon usage bias pattern in the chloroplast genomes of Chloranthus species (Chloranthaceae). Genes 2025, 16, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; He, L.; Li, Z.; Yuan, B.; Fang, F.; Wang, M.; Li, A.; Liu, C.; He, M.; et al. Comparative chloroplast genomics and codon usage bias analysis in Hevea Genus. Genes 2025, 16, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Chen, Z.; He, L.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Du, G.; Shi, C.; Wang, S. Comparative chloroplast genome analysis of wax gourd (Benincasa hispida) with three Benincaseae species, revealing evolutionary dynamic patterns and phylogenetic implications. Genes 2022, 13, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Gong, W.; Li, Y. Comparative analysis of the codon usage pattern in the chloroplast genomes of Gnetales species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Wu, J.; Fan, C.; Luo, Y.; Liu, J.; Deng, Z.J.; Li, Q. Comparative analysis of codon usage bias in the chloroplast genomes of eighteen Ampelopsideae species (Vitaceae). BMC Genom. Data 2024, 25, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Wang, L.; Ma, W.; Xu, J. A comparative study of complete chloroplast genome for the genus Salvia. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Wang, L.; Lei, J.; Duan, B.; Ma, W.; Xiao, S.; Qi, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shen, X.; et al. A comparative analysis of the chloroplast genomes of Four Salvia medicinal plants. Engineering 2019, 5, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniell, H.; Lee, S.; Grevich, J.; Saski, C.; Quesada-Vargas, T.; Guda, C.; Tomkins, J.; Jansen, R. Complete chloroplast genome sequences of Solanum bulbocastanum, Solanum lycopersicum and comparative analyses with other Solanaceae genomes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 112, 1503–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solórzano, S.; Chincoya, D.A.; Sanchez-Flores, A.; Estrada, K.; Díaz-Velásquez, C.E.; González-Rodríguez, A.; Vaca-Paniagua, F.; Dávila, P.; Arias, S. De Novo assembly discovered novel structures in genome of plastids and revealed divergent inverted repeats in Mammillaria (Cactaceae, Caryophyllales). Plants 2019, 8, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, D.; Shanker, A. Identification of simple sequence repeats in chloroplast genomes of Magnoliids through bioinformatics approach. Interdiscip. Sci. Comput. Life Sci. 2016, 8, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Li, S.; Bi, C.; Hao, Z.; Sun, C.; Ye, N. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of a major economic species, Ziziphus jujuba (Rhamnaceae). Curr. Genet. 2017, 63, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Tang, P.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H. The first complete chloroplast genome sequences in Actinidiaceae: Genome structure and comparative analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.J.; Chen, S.F.; Xie, L.; Wang, L.; Feng, Y.Y.; Lv, T.; Fang, Y.M.; Ding, H. The complete chloroplast genomes of three hamamelidaceae species: Comparative and phylogenetic analyses. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e8637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Li, Z.; Xie, D.; Gui, L.; Peng, C.; Wen, J.; He, X. Plastomes of eight Ligusticum species: Characterization, genome evolution, and phylogenetic relationships. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.M.; Li, M.J.; He, S.T.; Li, Z.; Wen, F.; Tan, K.; Bai, X.X.; Hu, G.X. Comparative chloroplast genomes analysis of nine Primulina (Gesneriaceae) rare species, from karst region of southwest China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30256–30272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Zou, L.; Yao, C. Comparison of chloroplast genomes and phylogenomics in the Ficus sarmentosa complex (Moraceae). PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0279849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.W.; Nie, L.P.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Z.C.; Wang, Y.; He, C.N.; Song, J.Y.; Yao, H. Comparative and phylogenetic analyses of the chloroplast genomes of species of Paeoniaceae. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14643–14659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, F. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Fagus longipetiolata Seemen (Fagaceae): Genome structure, adaptive evolution, and phylogenetic relationships. Life 2022, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, D.; Yaradua, S.; Albokhari, E.; Abba, A. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Barleria prionitis, comparative chloroplast genomics and phylogenetic relationships among Acanthoideae. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.; Lickey, E.; Schilling, E.; Small, R. Comparison of whole chloroplast genome sequences to choose noncoding regions for phylogenetic studies in angiosperms: The tortoise and the hare III. Am. J. Bot. 2007, 94, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.; Shaw, J.; Shafer, H.; Leonard, O.; Kovach, M.; Schorr, M.; Morris, A. Chloroplast DNA sequence utility for the lowest phylogenetic and phylogeographic inferences in angiosperms: The tortoise and the hare IV. Am. J. Bot. 2014, 101, 1987–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Song, W.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, C.; Wang, S. Complete chloroplast genomes of four Atalantia (Rutaceae) species: Insights into comparative analysis, phylogenetic relationships, and divergence time estimation. Plant Syst. Evol. 2023, 309, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Liu, C.; Yang, X.; Li, M.; Liu, L.; Jia, K.; Li, W. Comparative and phylogenetic analysis of the chloroplast genomes of four wild species of the genus Prunus. Genes 2025, 16, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Landis, J.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, H. Comparative analysis of chloroplast genome structure and molecular dating in Myrtales. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, T.; Geng, Y.F.; Xiang, C.L.; Zhao, F.; Wang, M.; Gu, L.; Hu, G.X. Chloroplast genome of Salvia Sect. Drymosphace: Comparative and phylogenetic analysis. Diversity 2022, 14, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Sample Locality | Voucher | Genbank Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salvia bowleyana | Fujian | 131 | MW435404 |
| Salvia bulleyana | na | na | MH603954 |
| Salvia campanulata | na | na | MT742542 |
| Salvia castanea f. castanea | na | 11CS3534 | MT634150 |
| Salvia castanea f.tomentosa | na | na | MW387501 |
| Salvia cavaleriei | na | 10CS1700 | MT634139 |
| Salvia chienii | Anhui | Hu0071 | MN062354 |
| Salvia cyclostegia | na | HP8813 | MT634144 |
| Salvia dabieshanensis | Anhui | 165 | MW435405 |
| Salvia digitaloides | Yunnan | 1292 | MN520016 |
| Salvia flava | na | 11CS3465 | MT634140 |
| Salvia honania | na | na | MZ900991 |
| Salvia japonica | na | na | MW381778 |
| Salvia kiangsiensis | Jiangxi | Hu0062 | MN062353 |
| Salvia liguliloba | na | na | MZ855771 |
| Salvia mairei | na | HP8366 | MT634143 |
| Salvia meiliensis | Anhui | GX Hu 0089 | MN520018 |
| Salvia miltiorrhiza | na | na | JX312195 |
| Salvia nanchuanensis | na | na | MZ900990 |
| Salvia nanchuanensis var. pteridifolia | Guangxi | 615 | MW435408 |
| Salvia nipponica | na | na | MT156377 |
| Salvia petrophila | Guizhou | GX Hu 0292 | MN520022 |
| Salvia plebeia | Guangxi | Hu0024 | MN062352 |
| Salvia plectranthoides | Yunnan | 6 | MW435409 |
| Salvia prattii | na | na | MK944407 |
| Salvia przewalskii | Yunnan | HGW-00807 | MK344723 |
| Salvia roborowskii | Gansu | FW11193 | MN062349 |
| Salvia sonchifolia | Yunnan | 269 | MN062355 |
| Salvia subbipinnata | Zhejiang | YJX-04 | MW435410 |
| Salvia subpalmatinervis | na | YangQE1866 | MT634137 |
| Salvia substolonifera | na | na | MN125145 |
| Salvia trijuga | Yunnan | D576 | MN062350 |
| Salvia umbratica | na | 10CS2479 | MT634142 |
| Salvia wardii | Tibet | 3270 | MN062351 |
| Salvia yunnanensis | Yunnan | GX Hu QT001 | MN520026 |
| Salvia officinalis | na | na | MN520021 |
| Salvia sclarea | na | na | MN520023 |
| Salvia splendens | na | na | MN520024 |
| Salvia rosmarinus | na | na | KR232566 |
| Characteristics | Salvia roborowskii | Salvia przewalskii | Salvia trijuga | Salviawardii | Salvia plebeia | Salvia kiangsiensis | Salviachienii | Salvia sonchifolia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genome size (bp) | 151,649 | 152,678 | 151,345 | 151,485 | 151,081 | 152,216 | 151,386 | 151,230 |
| LSC size (bp) | 82,866 | 83,912 | 82,577 | 82,768 | 82,464 | 83,611 | 82,771 | 82,711 |
| IR size (bp) | 25,596 | 25,564 | 25,592 | 25,557 | 25,562 | 25,523 | 25,520 | 25,321 |
| SSC size (bp) | 17,591 | 17,638 | 17,584 | 17,603 | 17,493 | 17,559 | 17,575 | 17,877 |
| Total number of genes | 132 | 132 | 132 | 132 | 132 | 132 | 132 | 132 |
| Protein encoding | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 |
| tRNA genes | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| rRNA genes | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| duplicated genes | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| pseudogenes | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| GC content (%) | 38.0 | 38.0 | 37.9 | 38.0 | 38.0 | 38.1 | 38.0 | 38.1 |
| GC content of LSC (%) | 36.1 | 36.2 | 36.0 | 36.1 | 36.1 | 36.3 | 36.1 | 36.2 |
| GC content of IR (%) | 43.1 | 43.1 | 43.1 | 43.1 | 43.1 | 43.1 | 43.1 | 43.2 |
| GC content of SSC (%) | 31.9 | 31.9 | 31.7 | 31.9 | 32.0 | 32.0 | 32.0 | 32.0 |
| Category | Gene Type | Gene |
|---|---|---|
| Self-replication | rRNA | rrn16(2×), rrn23(2×), rrn4.5(2×), rrn5(2×) |
| tRNA | trnI-CAU(2×), trnL-CAA(2×), trnV-GAC(2×), * trnI-GAU(2×), * trnA-UGC(2×), trnR-ACG(2×), trnN-GUU(2×), trnL-UAG, trnP-UGG, trnW-CCA, trnM-CAU, * trnV-UAC, trnF-GAA, * trnL-UAA, trnT-UGU, trnS-GGA, trnfM-CAU, trnG-GCC, trnS-UGA, trnT-GGU, trnE-UUC, trnY-GUA, trnD-GUC, trnC-GCA, trnR-UCU, * trnG-UCC, trnS-GCU, trnQ-UUG, * trnK-UUU, trnH-GUG | |
| Small subunit of ribosome | rps2, rps3, rps4, rps7(2×), rps8, rps11, ** rps12(2×), rps14, rps15, * rps16, rps18, rps19 | |
| Large subunit of ribosome | * rpl2(2×), rpl14, * rpl16, rpl20, rpl22, rpl23(2×), rpl32, rpl33, rpl36 | |
| DNA-dependent RNA polymerase | rpoA, rpoB, * rpoC1, rpoC2 | |
| Genes for photosynthesis | NADH dehydrogenase | * ndhA, * ndhB(2×), ndhC, ndhD, ndhE, ndhF, ndhG, ndhH, ndhI, ndhJ, ndhK |
| Photosystem I | psaA, psaB, psaC, psaI, psaJ | |
| Photosystem II | psbA, psbB, psbC, psbD, psbE, psbF, psbH, psbI, psbJ, psbK, psbL, psbM, psbN, psbT, psbZ | |
| Cytochrome b/f complex | petA, * petB, * petD, petG, petL, petN | |
| ATP synthase | atpA, atpB, atpE, * atpF, atpH, atpI | |
| Large subunit of rubisco | rbcL | |
| Other genes | Maturase | matK |
| Translational initiation factor | infA | |
| Protease | ** clpP | |
| Envelope membrane protein | cemA | |
| Acetyl-CoA-carboxylase subunit | accD | |
| c-type cytochrome synthesis | ccsA | |
| Component of TIC complex | ycf1 | |
| Unknown | Open reading frame (ORF, ycf) | ycf2(2×), ** ycf3, ycf4, ycf15(2×) |
| No. | Size (bp) | Units | Type | Location Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 41 | TACAGAACCGTACATGAGATTTTCACCTCATACGGCTCCTC | F | IGR (rps12, trnV-GAC), ndhA (intron) |
| 2 | 30 | A(G)CGGAAAGAGAGGGATTCGAACCCTCGGTA | P | trnS-GCU (tRNA), trnS-GGA (tRNA) |
| 3 | 30 | CATTGTTCAAA(C)TCTTTGACAACAC(T)GAAAAA | F | IGR (rrn4.5, rrn5) |
| 4 | 30 | AC(A)GATGCGGGTTCGATTCCCGCTAC(T)CCGCT(C) | F | trnG-UCC (tRNA), trnG-GCC (tRNA) |
| 5 | 30 | TTTCTTTTTGTCC(G)AAG(C)TCACTTCT(C)TTTTTT | F | ycf2 (CDS) |
| 6 | 55 | TTTGTCTAAGCCACTTCGTTTCTTTTTGTCCAAGTCACTTCTTTTTTTGTCCAAG | T | ycf2 (CDS) |
| 7 | 68 | TTTTTGTCCAAGTCACTTCTTTTTTTGTCCAAGTTGCTTTTCTTTTTGTCGAACTCACTTCCTTTTTT | T | ycf2 (CDS) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Xiang, C.; Yang, M. Comparative Analysis of the Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Eight Salvia Medicinal Species: Insights into the Deep Phylogeny of Salvia in East Asia. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070493
Du Y, Luo Y, Wang Y, Li J, Xiang C, Yang M. Comparative Analysis of the Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Eight Salvia Medicinal Species: Insights into the Deep Phylogeny of Salvia in East Asia. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(7):493. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070493
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Yan, Yang Luo, Yuanyuan Wang, Jiaxin Li, Chunlei Xiang, and Meiqing Yang. 2025. "Comparative Analysis of the Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Eight Salvia Medicinal Species: Insights into the Deep Phylogeny of Salvia in East Asia" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 7: 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070493
APA StyleDu, Y., Luo, Y., Wang, Y., Li, J., Xiang, C., & Yang, M. (2025). Comparative Analysis of the Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Eight Salvia Medicinal Species: Insights into the Deep Phylogeny of Salvia in East Asia. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(7), 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47070493






