Demystifying the Role of Histone Demethylases in Colorectal Cancer: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of CRC Pathogenesis and Signaling Pathways
3. Overview of Mechanisms of Histone Methylation, HDM Classification and Composition
4. LSD Family and CRC
4.1. KDM1A and CRC
4.2. KDM1B and CRC
5. JMJD Family and CRC
5.1. KDM2 Family and CRC
5.2. KDM3 Family and CRC
5.3. KDM4 Family and CRC
5.4. KDM5 Family and CRC
5.5. KDM6 Family and CRC
| References | HDM | Histone Demethylation Sites | Gene Expression Profile | Mechanisms of Action | Impact on CRC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [157] | KDM6A | H3K27me3 | NA | Regulation of E-cadherin expression | Inhibition of CRC cell migration and invasion |
| [158] | KDM6A | H3K27me3 | NA | Regulation of E-cadherin expression | Inhibition of EMT and tumor invasion |
| [159] | KDM6A | NA | Upregulated | Regulation of KIF14 and pAKT expression | Promotion of CRC cell proliferation |
| [27] | KDM6A/B | H3K27me3 | NA | Interruption of oxaliplatin-induced NOTCH signaling | KDM6A/6B depletion enhanced oxaliplatin-induced apoptosis |
| [29] | KDM6A/B | H3K27me3 | NA | Inducing global enhancer reprogramming | KDM6 inhibition attenuated the malignant phenotype of CRC cells, sensitized them to chemotherapy, and suppressed tumor-initiating cells’ properties and stemness-associated gene signatures |
| [160] | KDM6A | H3K27me3 | NA | Mediating CRC stem cell marker gene activation | Mediating CRC stem cell proliferation |
| [161] | KDM6A | NA | NA | Promotion of survival and accumulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells | KDM6A deficiency promoted immune escape and CRC progression |
| [162] | KDM6A | H3K27me3 | Downregulated | Targeting EMP1 and AUTS2 | KDM6A downregulation promoted CRC progression |
| [163] | KDM6A/B | H3K27me3 | NA | Mediating EMT | NA |
| [164] | KDM6A | NA | NA | Enhancement of glycolysis by promoting the binding of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α to the lactate dehydrogenase A promoter | KDM6A deletion promoted CRC progression |
| [166] | KDM6B | NA | NA | Regulation of the EMT and Wnt/b-catenin pathways | Mediating the inhibitory effect of 1,25(OH)2D3 on CRC |
| [167] | KDM6B | H3K27me3 | NA | Increased expression of Th1-type chemokines | Mediating immune evasion in CRC |
| [168] | KDM6B | H3K27me3 | NA | Promoting EPHB4 expression | Promoting proliferation and invasion |
| [169] | KDM6B | H3K27me3 | NA | Upregulation of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase expression | Mediating 5-fluorouracil resistance in CRC |
5.6. KDM7 Family and CRC
5.7. KDM8 Family and CRC
5.8. RIOX1/2 and CRC
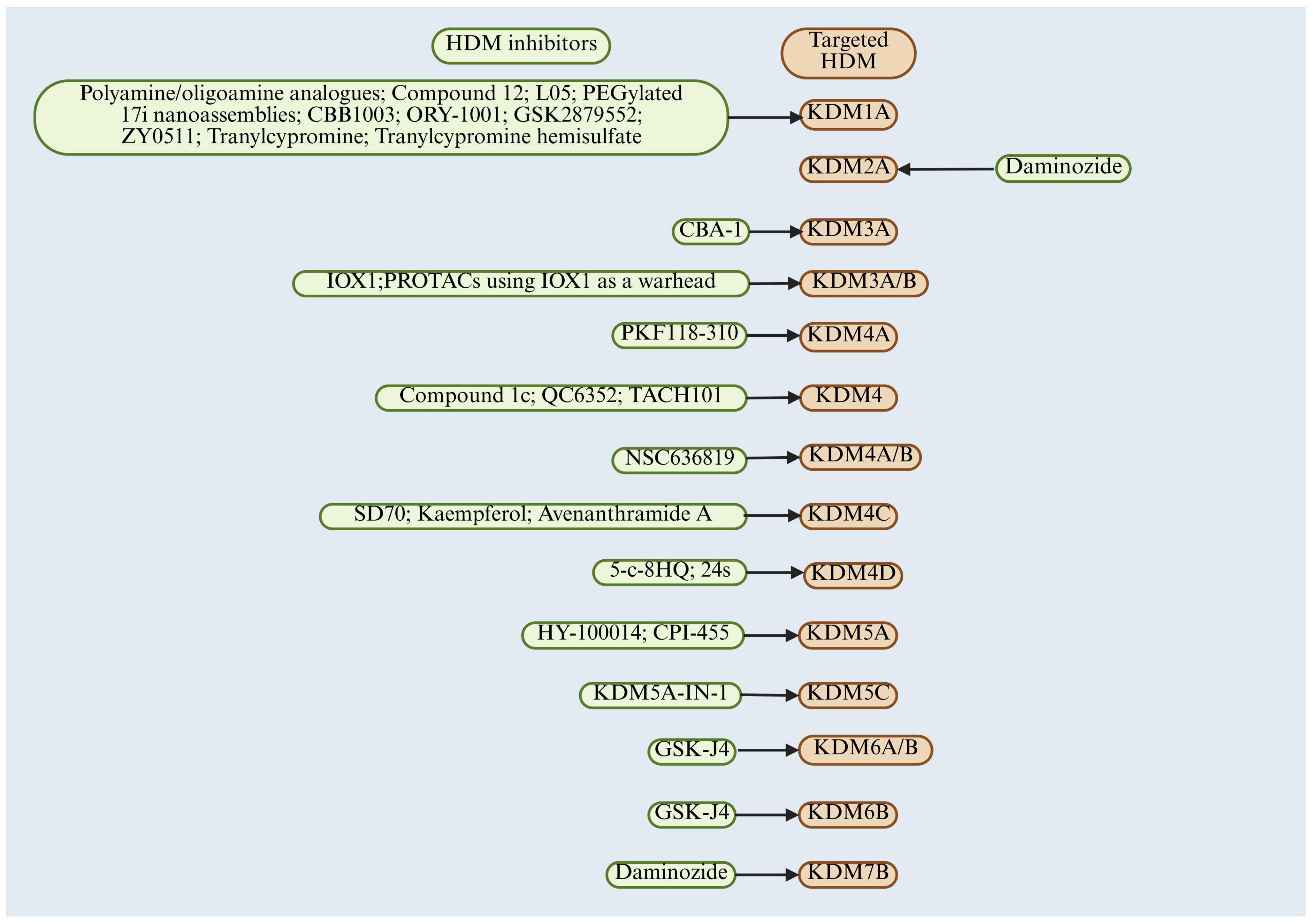
6. Therapeutic Opportunities for Targeting HDM in CRC
6.1. LSD Family Inhibitor and CRC
6.2. JMJD Family Inhibitor and CRC
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Huang, A.; Shi, J.; Sun, Z.; Hong, H.; Gu, J. Epidemiology and early screening strategies for colorectal cancer in China. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2023, 35, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, Y.; Ding, K.; Rudan, I.; Theodoratou, E.; et al. National and subnational incidence, mortality and associated factors of colorectal cancer in China: A systematic analysis and modelling study. J. Glob. Health 2023, 13, 04096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuipers, E.J.; Grady, W.M.; Lieberman, D.; Seufferlein, T.; Sung, J.J.; Boelens, P.G.; Van De Velde, C.J.H.; Watanabe, T. Colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, C.; Yoshino, T.; Ruíz-García, E.; Mostafa, N.; Cann, C.G.; O’Brian, B.; Benny, A.; O Perez, R.; Cremolini, C. Colorectal cancer. Lancet 2024, 404, 294–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolini, A.; Ferrari, P. Involvement of tumor immune microenvironment metabolic reprogramming in colorectal cancer progression, immune escape, and response to immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1353787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, W.M.; Yu, M.; Markowitz, S.D. Epigenetic Alterations in the Gastrointestinal Tract: Current and Emerging Use for Biomarkers of Cancer. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 690–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Ren, C.; Liu, Y.; Lan, H.; Wang, Z. An update on colorectal cancer microenvironment, epigenetic and immunotherapy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 89 Pt A, 107041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, X.; Chakravarti, D.; Shalapour, S.; DePinho, R.A. Genetic and biological hallmarks of colorectal cancer. Genes Dev. 2021, 35, 787–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baretti, M.; Azad, N.S. The role of epigenetic therapies in colorectal cancer. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2018, 42, 530–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Tian, Y.; Deng, Z.; Yang, F.; Chen, E. Epigenetic Alteration in Colorectal Cancer: Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, G.; Hernández-Illán, E.; Moreira, L.; Balaguer, F.; Goel, A. Epigenetics of colorectal cancer: Biomarker and therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteller, M.; Dawson, M.A.; Kadoch, C.; Rassool, F.V.; Jones, P.A.; Baylin, S.B. The Epigenetic Hallmarks of Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2024, 14, 1783–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Song, X.; Xu, D.; Tiek, D.; Goenka, A.; Wu, B.; Sastry, N.; Hu, B.; Cheng, S.-Y. Stem cell programs in cancer initiation, progression, and therapy resistance. Theranostics 2020, 10, 8721–8743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, R.; Pauklin, S. Epigenetic regulation of cancer stem cell formation and maintenance. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 148, 2884–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Lee, Y.-T.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, Y. Targeting epigenetic regulatory machinery to overcome cancer therapy resistance. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 83, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, K.; Jeon, J.; Park, K.; Kim, J. Writing, erasing and reading histone lysine methylations. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambhekar, A.; Dhall, A.; Shi, Y. Roles and regulation of histone methylation in animal development. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.C.; Van Rechem, C.; Whetstine, J.R. Histone lysine methylation dynamics: Establishment, regulation, and biological impact. Mol. Cell 2012, 48, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, M. Histone Demethylation Profiles in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Prognostic Values in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Bioinformatic Analysis. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 3640–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Lin, C.; Zhong, L.L.D.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, G.; Lu, A.; Wu, J.; Bian, Z. Targeting histone methylation for colorectal cancer. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2017, 10, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Peng, K.; Mo, P.; Yu, C. Histone Demethylase JMJD2D: A Novel Player in Colorectal and Hepatocellular Cancers. Cancers 2022, 14, 2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagraba, G.; Yarmohammadi, M.; Javed, A.; Barceló, C.; Rubio-Tomás, T. The Role of LSD1 and LSD2 in Cancers of the Gastrointestinal System: An Update. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, A.; Khoufaf, F.Z.H.; Idrissou, M.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Bignon, Y.-J.; Guy, L.; Bernard-Gallon, D. The Functions of the Demethylase JMJD3 in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Wang, J.; Zeng, W.; Cheng, X.; Liu, L.; Li, W. Lysine-specific histone demethylase 1B (LSD2/KDM1B) represses p53 expression to promote proliferation and inhibit apoptosis in colorectal cancer through LSD2-mediated H3K4me2 demethylation. Aging 2020, 12, 14990–15001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.B.; Na Fu, L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Gao, Q.Y.; Xu, J.; Cao, Z.J.; Chen, Y.X.; Fang, J.Y. Silencing of JMJD2B induces cell apoptosis via mitochondria-mediated and death receptor-mediated pathway activation in colorectal cancer. J. Dig. Dis. 2014, 15, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Sun, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Tao, Y.; Li, C.; et al. Elevating H3K27me3 level sensitizes colorectal cancer to oxaliplatin. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 12, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lan, Z.; Liao, W.; Horner, J.W.; Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Yoshihama, Y.; Jiang, S.; Shim, H.S.; Slotnik, M.; et al. Histone demethylase KDM5D upregulation drives sex differences in colon cancer. Nature 2023, 619, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ying, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, M.; Huang, X.; Jia, M.; Zeng, J.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; et al. Targeted inhibition of KDM6 histone demethylases eradicates tumor-initiating cells via enhancer reprogramming in colorectal cancer. Theranostics 2020, 10, 10016–10030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Han, Y.; Ouyang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Wu, X.; Yang, L.; Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J.; et al. Kaempferol inhibits colorectal cancer metastasis through circ_0000345 mediated JMJD2C/β-catenin signalling pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 128, 155261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhuang, S.; Hong, Y.; Yang, L.; Guo, P.; Mo, P.; Peng, K.; Li, W.; Xiao, N.; Yu, C. Demethylase JMJD2D induces PD-L1 expression to promote colorectal cancer immune escape by enhancing IFNGR1-STAT3-IRF1 signaling. Oncogene 2022, 41, 1421–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Adolph, T.E.; Gerner, R.R.; Moschen, A.R. The Intestinal Microbiota in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 954–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Singh, J.K.; Wunnava, A.; Al-Obeed, O.; Abdulla, M.; Srivastava, S.K. Emerging trends in colorectal cancer: Dysregulated signaling pathways (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 47, 4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M.; Greten, F.R. The inflammatory pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Zein, M.; Boukhdoud, M.; Shammaa, H.; Mouslem, H.; El Ayoubi, L.M.; Iratni, R.; Issa, K.; Khachab, M.; Assi, H.I.; Sahebkar, A.; et al. Immunotherapy and immunoevasion of colorectal cancer. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Sun, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, P.; Chen, F.; Chen, H.; Xia, D.; Xu, E.; Lai, M.; Wu, Y.; et al. Mutations of key driver genes in colorectal cancer progression and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilar, E.; Gruber, S.B. Microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer—The stable evidence. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 7, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, H.; Yin, Y.; Jia, S.; Luo, X. Colorectal cancer: Metabolic interactions reshape the tumor microenvironment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wu, C. The Role of the Tumor Microenvironment and Treatment Strategies in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 792691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.C.; Yu, J. Gut microbiota in colorectal cancer development and therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 429–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.H.; Yu, J. Gut microbiota in colorectal cancer: Mechanisms of action and clinical applications. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 690–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Geng, S.; Luo, H.; Wang, W.; Mo, Y.-Q.; Luo, Q.; Wang, L.; Song, G.-B.; Sheng, J.-P.; Xu, B. Signaling pathways involved in colorectal cancer: Pathogenesis and targeted therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiphrakpam, P.D.; Rajappa, S.J.; Krishnan, M.; Batra, R.; Murthy, S.S.; Are, C. Colorectal cancer: Review of signaling pathways and associated therapeutic strategies. J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 127, 1277–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Ming, T.; Tang, S.; Ren, S.; Yang, H.; Liu, M.; Tao, Q.; Xu, H. Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer: Pathogenic role and therapeutic target. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, F.; Avan, A.; Hashemy, S.I.; Hassanian, S.M. Role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling regulatory microRNAs in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.K.; Choi, E.-J. Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2010, 1802, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, C.; Miricescu, D.; Stanescu-Spinu, I.-I.; Nica, R.I.; Greabu, M.; Totan, A.R.; Jinga, M. Growth Factors, PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK Signaling Pathways in Colorectal Cancer Pathogenesis: Where Are We Now? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, S.; Nandi, S.; Nayak, A. Unraveling the complexities of colorectal cancer and its promising therapies—An updated review. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 143 Pt 1, 113325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, A.; Khazaei, M.; Hasanzadeh, M.; ShahidSales, S.; Mashhad, M.J.; Farazestanian, M.; Sadeghnia, H.R.; Rezayi, M.; Maftouh, M.; Hassanian, S.M.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Targeting PI3K/AKT Pathway in Treatment of Colorectal Cancer: Rational and Progress. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 2460–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiphrakpam, P.D.; Are, C. PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway as a Target for Colorectal Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Huang, D. Targeting the JAK-STAT pathway in colorectal cancer: Mechanisms, clinical implications, and therapeutic potential. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1507621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldner, M.J.; Neurath, M.F. TGFβ and the Tumor Microenvironment in Colorectal Cancer. Cells 2023, 12, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, M.; Pirozzi, M.; Miceli, C.C.; Cocule, M.; Caraglia, M.; Boccellino, M.; Vitale, P.; De Falco, V.; Farese, S.; Zotta, A.; et al. TGF-β Modulated Pathways in Colorectal Cancer: New Potential Therapeutic Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinson, K.E.; George, D.C.; Fender, A.W.; Bertrand, F.E.; Sigounas, G. The Notch pathway in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 1835–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brisset, M.; Mehlen, P.; Meurette, O.; Hollande, F. Notch receptor/ligand diversity: Contribution to colorectal cancer stem cell heterogeneity. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1231416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, A.; Sharma, A.K.; Damodaran, C. A Review on Notch Signaling and Colorectal Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, S.; Esfahani, A.T.; Sarpash, S.; Vakili, F.; Zafarjafarzadeh, N.; Mashaollahi, A.; Pardakhtchi, A.; Nazemalhosseini-Mojarad, E. Hippo Signaling Pathway in Colorectal Cancer: Modulation by Various Signals and Therapeutic Potential. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2024, 2024, 5767535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhu, X.; Liu, W.; Ruan, T.; Tao, K. Hedgehog signaling pathway in colorectal cancer: Function, mechanism, and therapy. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 3249–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, N.; Gerling, M. Hedgehog Signaling in Colorectal Cancer: All in the Stroma? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.-L.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Deng, B.; Zhu, B.-S.; Cao, T.; Li, Y.-K.; Xiao, J.; Han, Q.; Wu, Q. Colorectal cancer (CRC) as a multifactorial disease and its causal correlations with multiple signaling pathways. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20200265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunaka, Y.; Furukawa, A.; Nishimura, Y. Histone tail network and modulation in a nucleosome. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2022, 75, 102436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, F.; Miller, K.M. Histone methylation and the DNA damage response. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2019, 780, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; DesMarais, T.L.; Tong, Z.; Yao, Y.; Costa, M. Oxidative stress alters global histone modification and DNA methylation. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 82, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, E.L.; Shi, Y. Histone methylation: A dynamic mark in health, disease and inheritance. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.G.; Tsukada, Y.-I. The discovery of histone demethylases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a017947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noce, B.; Di Bello, E.; Fioravanti, R.; Mai, A. LSD1 inhibitors for cancer treatment: Focus on multi-target agents and compounds in clinical trials. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1120911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Park, J.-W.; Chun, Y.-S. Jumonji histone demethylases as emerging therapeutic targets. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 105, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipp, F.V. Crosstalk between epigenetics and metabolism—Yin and Yang of histone demethylases and methyltransferases in cancer. Briefings Funct. Genom. 2017, 16, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Bruick, R.K. JMJD6 is a histone arginine demethylase. Science 2007, 318, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wysocka, J.; Sayegh, J.; Lee, Y.-H.; Perlin, J.R.; Leonelli, L.; Sonbuchner, L.S.; McDonald, C.H.; Cook, R.G.; Dou, Y.; et al. Human PAD4 regulates histone arginine methylation levels via demethylimination. Science 2004, 306, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jing, L.; Li, M.; He, L.; Guo, Z. Regulation of histone arginine methylation/demethylation by methylase and demethylase (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 3963–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webby, C.J.; Wolf, A.; Gromak, N.; Dreger, M.; Kramer, H.; Kessler, B.; Nielsen, M.L.; Schmitz, C.; Butler, D.S.; Yates, J.R.; et al. Jmjd6 catalyses lysyl-hydroxylation of U2AF65, a protein associated with RNA splicing. Science 2009, 325, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuthbert, G.L.; Daujat, S.; Snowden, A.W.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Hagiwara, T.; Yamada, M.; Schneider, R.; Gregory, P.D.; Tempst, P.; Bannister, A.J.; et al. Histone deimination antagonizes arginine methylation. Cell 2004, 118, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnici, J.; Oueini, R.; Salah, E.; Johansson, C.; Schofield, C.J.; Kawamura, A. The catalytic domains of all human KDM5 JmjC demethylases catalyse N-methyl arginine demethylation. FEBS Lett. 2023, 597, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, J.; Wang, F.; He, L.; Huangyang, P.; Liang, J.; Si, W.; Yan, R.; Han, X.; Liu, S.; Gui, B.; et al. JMJD6 promotes colon carcinogenesis through negative regulation of p53 by hydroxylation. PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, e1001819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Liu, B.-L.; Cui, J.-P.; Li, S.-Q. Livin promotes colon cancer progression by regulation of H2A.XY39ph via JMJD6. Life Sci. 2019, 234, 116788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Højfeldt, J.W.; Agger, K.; Helin, K. Histone lysine demethylases as targets for anticancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 917–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, W.; Jianxin, X.; Weiqi, H.; Siyuan, C.; Huashan, S. JMJD family proteins in cancer and inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Shin, S.; Janknecht, R. The small members of the JMJD protein family: Enzymatic jewels or jinxes? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2019, 1871, 406–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Ramírez, R.; Gutiérrez-Angulo, M.; Peregrina-Sandoval, J.; Moreno-Ortiz, J.M.; Franco-Topete, R.A.; Cerda-Camacho, F.d.J.; Ayala-Madrigal, M.d.l.L. Somatic deletion of KDM1A/LSD1 gene is associated to advanced colorectal cancer stages. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 73, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayami, S.; Kelly, J.D.; Cho, H.; Yoshimatsu, M.; Unoki, M.; Tsunoda, T.; Field, H.I.; Neal, D.E.; Yamaue, H.; Ponder, B.A.; et al. Overexpression of LSD1 contributes to human carcinogenesis through chromatin regulation in various cancers. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Du, Z.; Ravasz, M.; Dong, B.; Wang, Z.; Ewing, R.M. A Protein Interaction between β-Catenin and Dnmt1 Regulates Wnt Signaling and DNA Methylation in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Hanigan, C.L.; Wu, Y.; Wang, W.; Park, B.H.; Woster, P.M.; Casero, R.A. Loss of LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) suppresses growth and alters gene expression of human colon cancer cells in a p53- and DNMT1(DNA methyltransferase 1)-independent manner. Biochem. J. 2013, 449, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, D.; Zhongmin, Z.; Guoqing, L.; Sheng, L.; Yi, Z.; Jing, W.; Liang, Z. Positive expression of LSD1 and negative expression of E-cadherin correlate with metastasis and poor prognosis of colon cancer. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 1581–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Xia, Y.; Liao, G.-Q.; Pan, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, Z.-S. LSD1-mediated epigenetic modification contributes to proliferation and metastasis of colon cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 994–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Li, S.; Song, W.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Han, Y.; Zhang, X.; Miao, S.; Du, R.; et al. Lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1/KDM1A) contributes to colorectal tumorigenesis via activation of the Wnt/Β-Catenin pathway by down-regulating dickkopf-1 (DKK1). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, J.; Ding, J.; Wang, Z.; Du, J.; Wu, C. Knocking down LSD1 inhibits the stemness features of colorectal cancer stem cells. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, e9230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-C.; Liu, Y.-S.; Tseng, K.-C.; Yang, T.-S.; Yeh, C.-Y.; You, J.-F.; Hung, H.-Y.; Chen, S.-J.; Chen, H.-C. CBB1003, a lysine-specific demethylase 1 inhibitor, suppresses colorectal cancer cells growth through down-regulation of leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptor 5 expression. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 141, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antona, A.; Leo, G.; Favero, F.; Varalda, M.; Venetucci, J.; Faletti, S.; Todaro, M.; Mazzucco, E.; Soligo, E.; Saglietti, C.; et al. Targeting lysine-specific demethylase 1 (KDM1A/LSD1) impairs colorectal cancer tumorigenesis by affecting cancer cells stemness, motility, and differentiation. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Xie, M.; Lian, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, P.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, K. Long noncoding RNA HOXA-AS2 represses P21 and KLF2 expression transcription by binding with EZH2, LSD1 in colorectal cancer. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, e288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zou, Y.; Luo, B.; Liu, Q.; Cao, X. Upregulated long noncoding RNAs LINC02163 and FEZF1-AS1 exert oncogenic roles in colorectal cancer. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2021, 32, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, C.; Xia, R.; Gong, H.; Yang, P.; Chen, T.; Wu, D.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, J.; et al. The pseudogene derived from long non-coding RNA DUXAP10 promotes colorectal cancer cell growth through epigenetically silencing of p21 and PTEN. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ma, X.; Bian, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, Q. LINC00586 Represses ASXL1 Expression Thus Inducing Epithelial-To-Mesenchymal Transition of Colorectal Cancer Cells Through LSD1-Mediated H3K4me2 Demethylation. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 887822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, X.; Huang, H.; Qiu, X.; Ding, Z.; Feng, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhuo, H.; Hou, J.; Zhao, J.; Cai, W.; et al. Targeting posttranslational modifications of RIOK1 inhibits the progression of colorectal and gastric cancers. eLife 2018, 7, e29511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Z.; Tang, Q.; Zhou, X. MiR-137-3p Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Cell Migration by Regulating a KDM1A-Dependent Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 66, 2272–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tao, L.; Zuo, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Qian, X.; Lin, Y.; Jie, H.; Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; et al. ZY0511, a novel, potent and selective LSD1 inhibitor, exhibits anticancer activity against solid tumors via the DDIT4/mTOR pathway. Cancer Lett. 2019, 454, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Zhang, H.; Tan, S.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Li, Q.; Cen, X.; Yang, S.; et al. Synergistic antitumor effect of 5-fluorouracil with the novel LSD1 inhibitor ZY0511 in colorectal cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920937428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qian, X.; Lin, Y.; Tao, L.; Zuo, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S.; Cen, X.; Zhao, Y. Lipidomic profiling reveals lipid regulation by a novel LSD1 inhibitor treatment. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 46, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-S.; Liu, H.-Y.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, H.-L.; Liu, M.-Y. TSPAN8 promotes colorectal cancer cell growth and migration in LSD1-dependent manner. Life Sci. 2020, 241, 117114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.A.; Policastro, R.A.; Sriramkumar, S.; Lai, T.; Huntington, T.D.; Ladaika, C.A.; Kim, D.; Hao, C.; Zentner, G.E.; O’Hagan, H.M. LSD1 and Aberrant DNA Methylation Mediate Persistence of Enteroendocrine Progenitors That Support BRAF-Mutant Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 3791–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladaika, C.A.; Ghobashi, A.H.; Boulton, W.C.; Miller, S.A.; O’hagan, H.M. LSD1 and CoREST2 Potentiate STAT3 Activity to Promote Enteroendocrine Cell Differentiation in Mucinous Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res. 2024, 85, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldani, C.; De Simone, G.; Polidoro, M.A.; Morabito, A.; Franceschini, B.; Colombo, F.S.; Anselmo, A.; Milana, F.; Lleo, A.; Torzilli, G.; et al. Riboflavin-LSD1 axis participates in the in vivo tumor-associated macrophage morphology in human colorectal liver metastases. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2024, 73, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.-L.; Du, C.; Liu, H.; Pei, L.; Qin, L.; Jia, M.; Wang, H. Lysine-specific demethylase 2A expression is associated with cell growth and cyclin D1 expression in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2018, 33, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, C.; Ye, N.-Y.; Wang, Y.-B. LncRNA LINC01278 accelerates colorectal cancer progression via miR-134-5p/KDM2A axis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 10526–10534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Meng, J.; Su, R.; Shen, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, W.; Du, J.; Zhu, S.; Li, P.; et al. SP1-mediated up-regulation of lncRNA TUG1 underlines an oncogenic property in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Yano, H.; Ogasawara, S.; Yoshioka, S.-I.; Imamura, H.; Okamoto, K.; Tsuneoka, M. Mild Glucose Starvation Induces KDM2A-Mediated H3K36me2 Demethylation through AMPK To Reduce rRNA Transcription and Cell Proliferation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 35, 4170–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-K.; Merrick, K.A.; Kong, Y.W.; Izrael-Tomasevic, A.; Eng, G.; Handly, E.D.; Patterson, J.C.; Cannell, I.G.; Suarez-Lopez, L.; Hosios, A.M.; et al. An RNA damage response network mediates the lethality of 5-FU in colorectal cancer. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharopoulou, N.; Tsapara, A.; Kallergi, G.; Schmid, E.; Alkahtani, S.; Alarifi, S.; Tsichlis, P.N.; Kampranis, S.C.; Stournaras, C. The Epigenetic Factor KDM2B Regulates EMT and Small GTPases in Colon Tumor Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.I.; Zuo, X.; Shureiqi, I. 15-Lipoxygenase-1 as a tumor suppressor gene in colon cancer: Is the verdict in? Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2011, 30, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Zuo, X.; Jaoude, J.; Mao, F.; Colby, J.; Shureiqi, I. ALOX15 as a suppressor of inflammation and cancer: Lost in the link. Prostagland. Other Lipid Mediat. 2017, 132, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Morris, J.S.; Shureiqi, I. Chromatin modification requirements for 15-lipoxygenase-1 transcriptional reactivation in colon cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 31341–31347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, M.; Yamamoto, H.; Takemasa, I.; Mimori, K.; Hemmi, H.; Mizushima, T.; Ikeda, M.; Sekimoto, M.; Matsuura, N.; Doki, Y.; et al. Jumonji domain containing 1A is a novel prognostic marker for colorectal cancer: In vivo identification from hypoxic tumor cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 4636–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padi, S.K.; Zhang, Q.; Rustum, Y.M.; Morrison, C.; Guo, B. MicroRNA-627 mediates the epigenetic mechanisms of vitamin D to suppress proliferation of human colorectal cancer cells and growth of xenograft tumors in mice. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yu, B.; Deng, P.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, Y.; Kevork, K.; Ramadoss, S.; Ding, X.; Li, X.; Wang, C.-Y. KDM3 epigenetically controls tumorigenic potentials of human colorectal cancer stem cells through Wnt/β-catenin signalling. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, K.; Su, G.; Ji, J.; Yang, X.; Miao, M.; Mo, P.; Li, M.; Xu, J.; Li, W.; Yu, C. Histone demethylase JMJD1A promotes colorectal cancer growth and metastasis by enhancing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 10606–10619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Oh, S.; Song, H.; Shin, S.; Zhang, B.; Freeman, W.M.; Janknecht, R. A potential common role of the Jumonji C domain-containing 1A histone demethylase and chromatin remodeler ATRX in promoting colon cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 6652–6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liang, T.; Zhangsun, W. KDM3A is associated with tumor metastasis and modulates colorectal cancer cell migration and invasion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 126, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-Y.; Long, Q.-Y.; Tang, S.-B.; Xiao, Q.; Gao, C.; Zhao, Q.-Y.; Li, Q.-L.; Ye, M.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.-Y.; et al. Histone demethylase KDM3A is required for enhancer activation of hippo target genes in colorectal cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 2349–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.R.; Zeng, C.; Chen, Y. MiR-22-3p regulates the proliferation, migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by directly targeting KDM3A through the Hippo pathway. Histol. Histopathol. 2022, 37, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Liu, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Song, C.; Zhang, T.; Liu, M.; et al. Acetylation of PHF5A Modulates Stress Responses and Colorectal Carcinogenesis through Alternative Splicing-Mediated Upregulation of KDM3A. Mol. Cell 2019, 74, 1250–1263.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Li, X.; Oh, S.; Zhang, B.; Freeman, W.M.; Shin, S.; Janknecht, R. Opposite Roles of the JMJD1A Interaction Partners MDFI and MDFIC in Colorectal Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Song, H.; Freeman, W.M.; Shin, S.; Janknecht, R. Cooperation between ETS transcription factor ETV1 and histone demethylase JMJD1A in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 57, 1319–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Jiang, H.; Kellogg, C.M.; Oh, S.; Janknecht, R. Promotion of colorectal cancer by transcription factor BHLHE40 involves upregulation of ADAM19 and KLF7. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1122238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, P.; Liu, Y.; Ji, T.; Liu, X.; Yao, S.; Cheng, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Xiao, Z.; et al. An epigenetic role for PRL-3 as a regulator of H3K9 methylation in colorectal cancer. Gut 2013, 62, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Aihemaiti, M.; Zhang, X.; Qu, H.; Sun, Q.-L.; He, Q.-S.; Yu, W.-B. Downregulation of histone demethylase JMJD1C inhibits colorectal cancer metastasis through targeting ATF2. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 852–865. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.; Shin, S.; Berry, W.L.; Oh, S.; Janknecht, R. The JMJD2A demethylase regulates apoptosis and proliferation in colon cancer cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 113, 1368–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.-Y.; Wang, F.; Cui, S.-X.; Gao, Z.-H.; Qu, X.-J. CXCR7/CXCR4 heterodimer-induced histone demethylation: A new mechanism of colorectal tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2019, 38, 1560–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Chen, L.; Yang, J.; Ye, T.; Chen, Y.; Fang, J. HIF-1α-induced histone demethylase JMJD2B contributes to the malignant phenotype of colorectal cancer cells via an epigenetic mechanism. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1664–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Fu, L.; Kong, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z.; Ma, X.; Akiyama, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fang, J. Jumonji domain-containing protein 2B silencing induces DNA damage response via STAT3 pathway in colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1014–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Deng, W.-W.; Hu, Q.; Liu, Z.-R.; Chen, Q.-H.; Wang, W.-X.; Zhang, H.-G.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y.-L.; Zhang, X.-K. KDM4B promotes DNA damage response via STAT3 signaling and is a target of CREB in colorectal cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 449, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.-N.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Tan, J.; Xu, J.; Gao, Q.-Y.; Chen, Y.-X.; Fang, J.-Y. Role of JMJD2B in colon cancer cell survival under glucose-deprived conditions and the underlying mechanisms. Oncogene 2018, 37, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Lan, J.; Wang, G.; Guo, K.; Han, C.; Li, X.; Hu, J.; Cao, Z.; Luo, X. KDM4B facilitates colorectal cancer growth and glucose metabolism by stimulating TRAF6-mediated AKT activation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Wang, H.-L.; Yang, J.; Liu, Q.-Q.; Li, C.-M.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Fu, L.-N.; Gao, Q.-Y.; Chen, Y.-X.; Fang, J.-Y. JMJD2B-induced amino acid alterations enhance the survival of colorectal cancer cells under glucose-deprivation via autophagy. Theranostics 2020, 10, 5763–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, W.L.; Kim, T.-D.; Janknecht, R. Stimulation of β-catenin and colon cancer cell growth by the KDM4B histone demethylase. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, G.; Li, X.; Tao, D.; Hu, J.; Luo, X. KDM4B plays an important role in mitochondrial apoptosis by upregulating HAX1 expression in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 57866–57877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.-Q.; Li, C.-M.; Fu, L.-N.; Wang, H.-L.; Tan, J.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Sun, D.-F.; Gao, Q.-Y.; Chen, Y.-X.; Fang, J.-Y. Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis induces the stemness in colorectal cancer via upregulating histone demethylase JMJD2B. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1788900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, J.; Feng, Y.; Xu, Y. Activation of TC10-Like Transcription by Lysine Demethylase KDM4B in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 617549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Tateishi, K.; Kudo, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Isagawa, T.; Nagae, G.; Nakatsuka, T.; Asaoka, Y.; Ijichi, H.; Hirata, Y.; et al. Histone demethylase KDM4C regulates sphere formation by mediating the cross talk between Wnt and Notch pathways in colonic cancer cells. Carcinog. 2013, 34, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, R.; Song, Q.; Zhang, C.; Jia, R.; Han, Z.; Zhou, L.; Sui, H.; Liu, X.; Zhu, H.; et al. JMJD2C promotes colorectal cancer metastasis via regulating histone methylation of MALAT1 promoter and enhancing β-catenin signaling pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, T.-T.; Lin, C.-C.; Jiang, J.-K.; Yang, S.-H.; Teng, H.-W.; Yang, M.-H. Harnessing stemness and PD-L1 expression by AT-rich interaction domain-containing protein 3B in colorectal cancer. Theranostics 2020, 10, 6095–6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, M.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, H.; Qiu, T.; Liang, L. Exosomal circPABPC1 promotes colorectal cancer liver metastases by regulating HMGA2 in the nucleus and BMP4/ADAM19 in the cytoplasm. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, R.; Dou, Z.; Li, N.; Fan, X.; Amin, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, P. Avenanthramide A potentiates Bim-mediated antineoplastic properties of 5-fluorouracil via targeting KDM4C/MIR17HG/GSK-3β negative feedback loop in colorectal cancer. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 14, 5321–5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Kou, L.; Yu, L.; Bai, C.; Li, M.; Mo, P.; Li, W.; Yu, C. Histone Demethylase JMJD2D Interacts with β-Catenin to Induce Transcription and Activate Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation and Tumor Growth in Mice. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1112–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, K.; Zhuo, M.; Li, M.; Chen, Q.; Mo, P.; Yu, C. Histone demethylase JMJD2D activates HIF1 signaling pathway via multiple mechanisms to promote colorectal cancer glycolysis and progression. Oncogene 2020, 39, 7076–7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, M.; Chen, W.; Shang, S.; Guo, P.; Peng, K.; Li, M.; Mo, P.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, X.; Li, W.; et al. Inflammation-induced JMJD2D promotes colitis recovery and colon tumorigenesis by activating Hedgehog signaling. Oncogene 2020, 39, 3336–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evensen, N.A.; Li, Y.; Kuscu, C.; Liu, J.; Cathcart, J.; Banach, A.; Zhang, Q.; Li, E.; Joshi, S.; Yang, J.; et al. Hypoxia promotes colon cancer dissemination through up-regulation of cell migration-inducing protein (CEMIP). Oncotarget 2015, 6, 20723–20739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Ye, Z.; Wu, W.; Zhao, K.; Cheng, G.; Xu, L.; Gan, L.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Z. lncRNA NEAT1 facilitates the progression of colorectal cancer via the KDM5A/Cul4A and Wnt signaling pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2021, 59, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, M. Long non-coding RNA tumor protein 73 antisense RNA 1 influences an interaction between lysine demethylase 5A and promoter of tumor protein 73 to enhance the malignancy of colorectal cancer. Hum. Cell 2022, 35, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, K.; Haraguchi, N.; Kano, Y.; Kagawa, Y.; Konno, M.; Nishikawa, S.; Hamabe, A.; Hasegawa, S.; Ogawa, H.; Fukusumi, T.; et al. Depletion of JARID1B induces cellular senescence in human colorectal cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Xiao, F.; Hao, H.; Hua, F.; Luo, Z.; Huang, Z.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. JARID1B promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and Wnt/β-catenin signaling via decreasing CDX2 level. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Li, S.; Yue, M.; Li, C.; Kang, Z. Lysine demethylase 5B suppresses CC chemokine ligand 14 to promote progression of colorectal cancer through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Life Sci. 2021, 264, 118726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Yang, G.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Guo, S.; Cao, B. KDM5c inhibits multidrug resistance of colon cancer cell line by down-regulating ABCC1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 1205–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, M.; Xu, X.; Zeng, K.; Liu, X.; Pan, B.; Li, C.; Sun, L.; Qin, J.; Xu, T.; et al. METTL14-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of SOX4 mRNA inhibits tumor metastasis in colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Li, L.; Gu, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhou, L.; Cheng, X.; Jiang, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, W.; et al. Lysine demethylase 5C inhibits transcription of prefoldin subunit 5 to activate c-Myc signal transduction and colorectal cancer progression. Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Gao, N. KDM5D inhibits the transcriptional activation of FKBP4 by suppressing the expression of E2F1 in colorectal cancer in males. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 194, 114814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, J.; Meng, L.; Kong, L.; Lu, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W. The epigenetic downregulation of LncGHRLOS mediated by RNA m6A methylase ZCCHC4 promotes colorectal cancer tumorigenesis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, L.; Cao, Q.; Cui, X.; Li, F.; Liang, H.; Xue, B.; Shi, H. Epigenetic regulation of E-cadherin expression by the histone demethylase UTX in colon cancer cells. Med. Oncol. 2016, 33, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Du, G.; Li, H.; Yu, X.; Huang, Y. Loss of TET1 facilitates DLD1 colon cancer cell migration via H3K27me3-mediated down-regulation of E-cadherin. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Cai, W.; Cheng, J.; Lu, P.; Ma, S.; Chen, C.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; Hu, P.; et al. The histone H3 lysine-27 demethylase UTX plays a critical role in colorectal cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Zhou, W.; Du, J.; Zhou, J.; Wu, D.; Zhao, M.; Yang, L.; Hao, A. PCGF1 promotes epigenetic activation of stemness markers and colorectal cancer stem cell enrichment. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Su, J.; Lin, S.; Chen, T.; Gao, W.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Wei, D.; Hu, Z.; Gao, C.; et al. Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase Is a Metabolic Immune Checkpoint for UTX-deficient Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology 2023, 164, 1165–1179.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Chen, M.; Li, Q.; Wang, K.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Fu, G.; Shan, Z.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Y.; et al. CUL4B-DDB1-COP1-mediated UTX downregulation promotes colorectal cancer progression. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Rani, H.; Mahesh, Y.; Jolly, M.K.; Dixit, J.; Mahadevan, V. Loss of p53 epigenetically modulates epithelial to mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 43, 101848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhao, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, M.; Xiao, M.; Zhu, K.; Niu, W.; Dai, Y. Inactivation of KDM6A promotes the progression of colorectal cancer by enhancing the glycolysis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, R.; Sakamoto, Y.; Nakagawa, S.; Miyake, K.; Izumi, D.; Kosumi, K.; Taki, K.; Higashi, T.; Imamura, Y.; Ishimoto, T.; et al. The Prognostic Significance of Histone Lysine Demethylase JMJD3/KDM6B in Colorectal Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.; Barbáchano, A.; Silva, J.; Bonilla, F.; Campbell, M.J.; Muñoz, A.; Larriba, M.J. KDM6B/JMJD3 histone demethylase is induced by vitamin D and modulates its effects in colon cancer cells. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 4655–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarsheth, N.; Peng, D.; Kryczek, I.; Wu, K.; Li, W.; Zhao, E.; Zhao, L.; Wei, S.; Frankel, T.; Vatan, L.; et al. PRC2 Epigenetically Silences Th1-Type Chemokines to Suppress Effector T-Cell Trafficking in Colon Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.; Jia, X.; Shi, N.; Xie, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Ma, F.; Liu, H.; Wang, A.; Cheng, X.; et al. Notch signaling promotes serrated neoplasia pathway in colorectal cancer through epigenetic modification of EPHB2 and EPHB4. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 6129–6141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.-K.; Wu, X.-F.; Tan, M.-Y.; Liang, W.-S.; Yang, Y.-M.; Chu, Z.-Z.; Xu, R.; Li, K.-Q.; Cheng, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; et al. Activation of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 (S1PR2) upregulates dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) expression in colon cancer cells. J. Adv. Res. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Shi, Y.; Han, Q.; Dai, G. Histone demethylase PHF8 accelerates the progression of colorectal cancer and can be regulated by miR-488 in vitro. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 4437–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Zhang, M. hnRNPA2B1 drives colorectal cancer progression via the circCDYL/EIF4A3/PHF8 axis. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2025, 41, e12943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Sui, M.; Liu, J.; Chen, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dang, C.; et al. Genome-wide CRISPR screening identifies PHF8 as an effective therapeutic target for KRAS- or BRAF-mutant colorectal cancers. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2025, 44, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-H.; Park, J.-W.; Sung, H.-S.; Choi, Y.-J.; Kim, W.H.; Lee, H.S.; Chung, H.-J.; Shin, H.-W.; Cho, C.-H.; Kim, T.-Y.; et al. PHF2 histone demethylase acts as a tumor suppressor in association with p53 in cancer. Oncogene 2015, 34, 2897–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Huang, Q.; Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, Y. JMJD5 is a potential oncogene for colon carcinogenesis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 6482–6489. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nishizawa, Y.; Nishida, N.; Konno, M.; Kawamoto, K.; Asai, A.; Koseki, J.; Takahashi, H.; Haraguchi, N.; Nishimura, J.; Hata, T.; et al. Clinical Significance of Histone Demethylase NO66 in Invasive Colorectal Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 24, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teye, K.; Tsuneoka, M.; Arima, N.; Koda, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Ueta, Y.; Shirouzu, K.; Kimura, H. Increased expression of a Myc target gene Mina53 in human colon cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujino, S.; Kinugasa, T.; Sudo, T.; Mizobe, T.; Yoshida, T.; Yoshida, N.; Ohchi, T.; Tajiri, K.; Yuge, K.; Nagasu, S.; et al. Mina53 nuclear localization is an important indicator of prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer after adjuvant chemotherapy. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Greene, E.; Stewart, T.M.; Goodwin, A.C.; Baylin, S.B.; Woster, P.M.; Casero, R.A. Inhibition of lysine-specific demethylase 1 by polyamine analogues results in reexpression of aberrantly silenced genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8023–8028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Stewart, T.M.; Wu, Y.; Baylin, S.B.; Marton, L.J.; Perkins, B.; Jones, R.J.; Woster, P.M.; Casero, R.A. Novel oligoamine analogues inhibit lysine-specific demethylase 1 and induce reexpression of epigenetically silenced genes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 7217–7228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorna, V.; Theisen, E.R.; Stephens, B.; Warner, S.L.; Bearss, D.J.; Vankayalapati, H.; Sharma, S. High-throughput virtual screening identifies novel N′-(1-phenylethylidene)-benzohydrazides as potent, specific, and reversible LSD1 inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9496–9508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, R.; Wang, Y. Identification of selective and reversible LSD1 inhibitors with anti-metastasis activity by high-throughput docking. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, J. Carrier-free supramolecular nanoassemblies of pure LSD1 inhibitor for effective anti-tumor therapy. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 1012882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sviripa, V.M.; Xie, Y.; Yu, T.; Haney, M.G.; Blackburn, J.S.; Adeniran, C.A.; Zhan, C.-G.; Watt, D.S.; Liu, C. Epigenetic Regulation of Wnt Signaling by Carboxamide-Substituted Benzhydryl Amines that Function as Histone Demethylase Inhibitors. iScience 2020, 23, 101795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyle, R.G.; Wang, H.; Cen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. IOX1 Suppresses Wnt Target Gene Transcription and Colorectal Cancer Tumorigenesis through Inhibition of KDM3 Histone Demethylases. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, S.U.; Pagare, P.P.; Ma, H.; Hoyle, R.G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Novel PROTAC probes targeting KDM3 degradation to eliminate colorectal cancer stem cells through inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. RSC Med. Chem. 2024, 15, 3746–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franci, G.; Sarno, F.; Nebbioso, A.; Altucci, L. Identification and characterization of PKF118-310 as a KDM4A inhibitor. Epigenetics 2017, 12, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, D.H.; Choi, Y.-S.; Jeong, J.-H.; Kwon, S.H. Benzo[b]tellurophenes as a Potential Histone H3 Lysine 9 Demethylase (KDM4) Inhibitor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.K.; Bonaldi, T.; Cuomo, A.; Del Rosario, J.R.; Hosfield, D.J.; Kanouni, T.; Kao, S.-C.; Lai, C.; Lobo, N.A.; Matuszkiewicz, J.; et al. Design of KDM4 Inhibitors with Antiproliferative Effects in Cancer Models. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Q.; Wang, T.; Yang, W.; Fan, Y.; Yu, C.; Xiang, R.; Yang, S. Discovery of a potent and selective inhibitor of histone lysine demethylase KDM4D. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 223, 113662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandhasin, C.; Dang, V.; Perabo, F.; Del Rosario, J.; Chen, Y.K.; Filvaroff, E.; Stafford, J.A.; Clarke, M. TACH101, a first-in-class pan-inhibitor of KDM4 histone demethylase. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2023, 34, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Xiao, C.; Fan, T.; Deng, Z.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; He, J. Targeting LSD1 in cancer: Molecular elucidation and recent advances. Cancer Lett. 2024, 598, 217093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
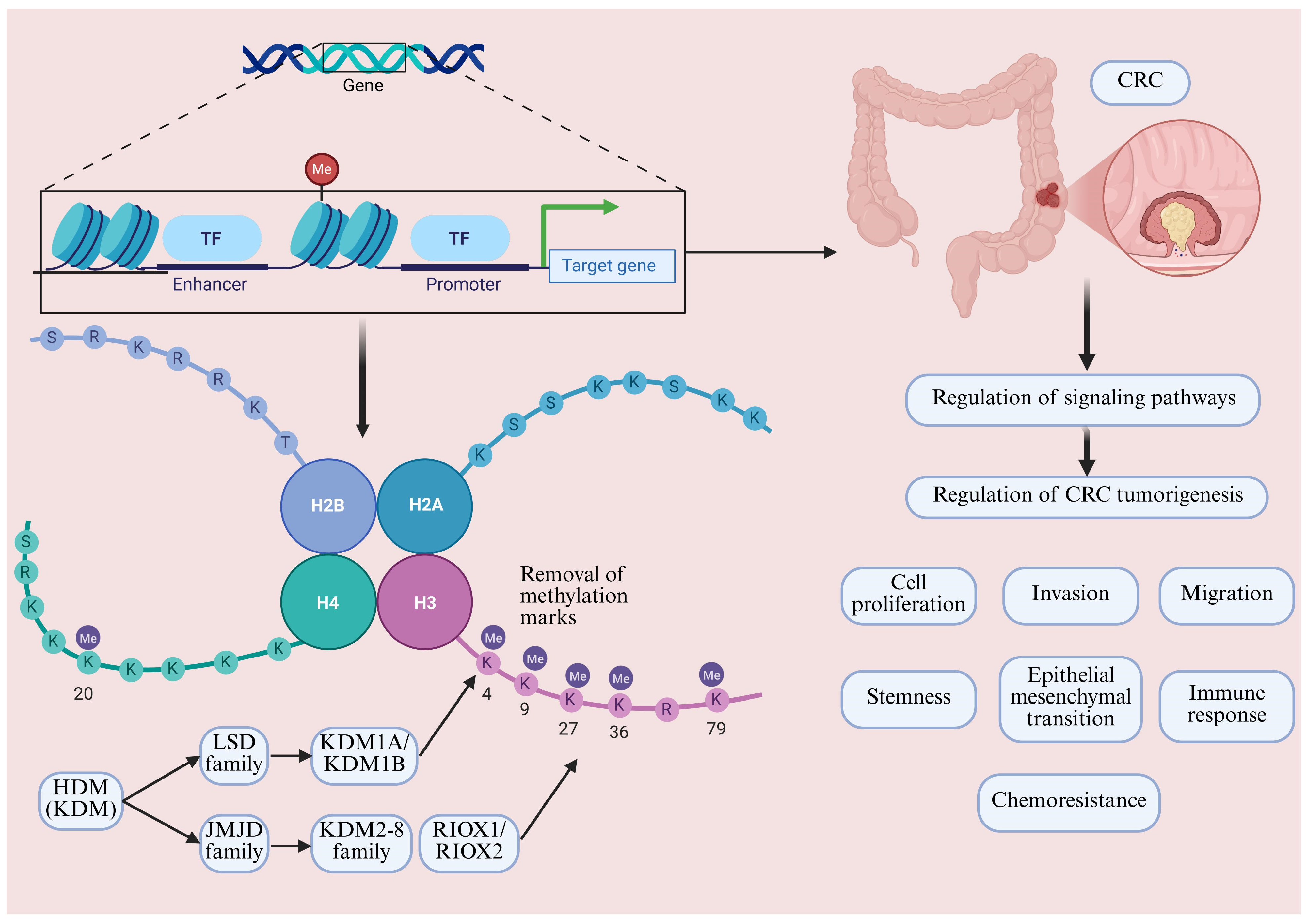

| HDM | Aliases | Histone Substrates |
|---|---|---|
| Confirmed activity | ||
| KDM1A | LSD1, AOF2, BHC110 | H3K4me1/2; H3K9me1/2 |
| KDM1B | LSD2, AOF1 | H3K4me1/2 |
| KDM2A | JHDM1A, FBXL11 | H3K36me1/2 |
| KDM2B | JHDM1B, FBXL10 | H3K36me2; H3K4me3; H3K79me2/3 |
| KDM3A | JMJD1A, JHDM2A, TSGA | H3K9me1/2 |
| KDM3B | JMJD1B | H3K9me1/2/3 |
| KDM4A | JMJD2A, JHDM3A | H3K9me2/3; H3K36me2/3; H1.4K26me2/3 |
| KDM4B | JMJD2B, JHDM3B | H3K9me2/3; H3K36me2/3; H1.4K26me2/3 |
| KDM4C | JMJD2C, JHDM3C, GASC1 | H3K9me2/3; H3K36me2/3; H1.4K26me2/3 |
| KDM4D | JMJD2D, JHDM3D | H3K9me2/3 |
| KDM5A | JARID1A, RBP2 | H3K4me2/3 |
| KDM5B | JARID1B, PLU1 | H3K4me2/3 |
| KDM5C | JARID1C, SMCX | H3K4me2/3 |
| KDM5D | JARID1D, SMCY | H3K4me2/3 |
| KDM6A | UTX | H3K27me2/3 |
| KDM6B | JMJD3 | H3K27me2/3 |
| KDM7A | KIAA1718, JHDM1D | H3K9me1/2; H3K27me1/2 |
| KDM7B | PHF8, JHDM1F | H3K9me1/2; H3K27me2; H4K20me1 |
| RIOX1 | NO66, MAPJD, C14orf169 | H3K4me2/3; H3K36me2/3 |
| Controversial activity | ||
| KDM3C | JMJD1C | H3K9me1/2 |
| KDM4E | JMJD2E | H3K9me2/3 |
| KDM6C | UTY | H3K27me2/3 |
| KDM7C | PHF2, JHDM1E | H3K9me2 |
| KDM8 | JMJD5 | H3K36me2 |
| RIOX2 | MINA, Mdig, NO52; MINA53 | H3K9me3; H3K36me3 |
| JMJD6 | PTDSR, KIAA0585 | H3R2me2; H4R3me2 |
| References | HDM | Histone Demethylation Sites | Gene Expression Profile | Mechanisms of Action | Impact on CRC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [83] | KDM1A | NA | NA | Increased expression of target genes | KDM1A deletion led to reduced cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo |
| [84] | KDM1A | NA | Upregulated | Negative correlation with E-cadherin expression | Positively correlated with lymph node and distant metastases among CRC patients |
| [85] | KDM1A | H3K4me2 | Upregulated | Downregulation of E-cadherin expression | Inhibition of KDM1A impaired proliferation and invasiveness and induced apoptosis in colon cancer cells |
| [86] | KDM1A | NA | Upregulated | Activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway through downregulation of the pathway antagonist DKK1 | KDM1A knockout led to lower tumorigenicity of CRC cells in vivo and in vitro |
| [87] | KDM1A | NA | NA | NA | KDM1A knockdown impaired stemness of CD133+ CRC cells |
| [88] | KDM1A | NA | Upregulated | KDM1A inhibitor treatment downregulated LGR5 levels and inactivated the Wnt/β-catenin pathway | KDM1A inhibitor treatment inhibited CRC cell proliferation and colony formation |
| [89] | KDM1A | NA | Upregulated | CSC stemness maintenance, cytoskeletal remodeling and altered mitochondrial function | Inhibition of KDM1A impaired migration and invasion of CRC cells |
| [90] | KDM1A | H3K4me2 | NA | Inhibition of P21 and Krüppel-like factor 2 expression by binding to the lncRNA HOXA-AS2 | Promotion of CRC cell proliferation |
| [91] | KDM1A | H3K4me2 | NA | Interaction with lncRNA FEZF1-AS1 and inhibition of Krüppel-like factor 2 expression | Influence on CRC cell proliferation |
| [92] | KDM1A | H3K4me2 | NA | Silencing of p21 and PTEN expression by binding to lncRNA DUXAP1 | Promotion of CRC cell growth and reduction in apoptosis |
| [93] | KDM1A | H3K4me2 | NA | Silencing of ASXL1 expression by LINC00586 recruitment to the ASXL1 promoter | Inhibition of CRC cell viability, migration, EMT, and in vivo tumorigenesis |
| [94] | KDM1A | NA | NA | Increased stability of RIOK1 | Influencing tumor growth and metastasis |
| [95] | KDM1A | H3K4me2 | Upregulated | Suppression of EMT | Promotion of CRC cell invasiveness |
| [96] | KDM1A | H3K4me1/2 | NA | KDM1A inhibition increased expression of the mTORC1 suppressor DNA Damage Inducible Transcript 4 | Inhibition of KDM1A suppressed CRC cell proliferation |
| [97] | KDM1A | NA | Upregulated | Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and DNA synthesis pathways | KDM1A inhibition enhanced the anticancer effect of 5-fluorouracil |
| [98] | KDM1A | NA | NA | Altered lipid metabolism | NA |
| [99] | KDM1A | H3K9me2 | Upregulated | Upregulation of tetraspanin 8 expression to promote EMT | Promotion of CRC cell proliferation and migration |
| [100] | KDM1A | NA | NA | KDM1A deletion blocked enteroendocrine cell progenitor cell formation | KDM1A deficiency reduced tumor growth and metastasis |
| [101] | KDM1A | NA | NA | Enhancement of the enteroendocrine cell specification regulator STAT3 chromatin binding | Influence on primary tumor growth and lung metastasis |
| [102] | KDM1A | NA | NA | Reprogramming tumor-associated macrophage subtypes | NA |
| [25] | KDM1B | H3K4me2 | Upregulated | Inhibition of p53 activity | Promotion of CRC cell proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis |
| References | HDM | Histone Demethylation Sites | Gene Expression Profile | Mechanisms of Action | Impact on CRC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [111] | KDM3A | H3K9me2 | NA | Transcriptional activation of 15-LOX-1 | NA |
| [112] | KDM3A | NA | Upregulated | NA | KDM3A deletion inhibited CRC cell proliferation and invasion |
| [113] | KDM3A | H3K9me2 | NA | Mediating the anti-tumor activity of vitamin D as a direct target of miR-627 | Downregulation of KDM3A suppressed proliferative factor expression and xenograft tumor growth |
| [114] | KDM3A/B | H3K9me2 | NA | Promotion of Wnt target gene transcription | KDM3 depletion inhibited tumorigenic growth and chemoresistance in CSCs |
| [115] | KDM3A | H3K9me2 | Upregulated | Enhancement of Wnt/β-catenin signaling | Promotion of CRC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion |
| [116] | KDM3A | H3K9me2 | Upregulated | Upregulation of ATRX expression | Downregulation of KDM3A inhibited clonogenic activity in CRC cells |
| [117] | KDM3A | NA | Upregulated | Regulation of EMT and matrix metalloproteinase | Promotion of CRC cell migration and invasion |
| [118] | KDM3A | H3K9me2 | NA | Positive regulators of hippo target genes | KDM3A depletion led to impaired growth and migration of CRC cells |
| [119] | KDM3A | NA | Upregulated | Regulation of the HIPPO signaling pathway as a target of miR-22-3p | Promotion of proliferation, invasion and migration of CRC cells |
| [120] | KDM3A | H3K9me2 | NA | Promoted stress resistance in CRC cells | Promotion of colon carcinogenesis |
| [121] | KDM3A | NA | NA | Binding to MDFI domain-containing and MDFI domain-containing to influence transcription of several genes | Promotion of CRC cells growth in vitro |
| [122] | KDM3A | NA | NA | Binding to ETV1 to co-regulate FOXQ1 | Driving colorectal tumorigenesis |
| [123] | KDM3A | NA | NA | Co-control of BHLHE40 transcription with ETV1 and KDM4A to upregulate KLF7 and ADAM19 | NA |
| [124] | KDM3B | H3K9me3 | Downregulated | NA | May function as a tumor suppressor |
| [125] | KDM3C | H3K9me2 | Upregulated | Regulation of ATF2 expression | Silencing of KDM3C suppressed CRC migration and invasion in vitro and in vivo |
| References | HDM | Histone Demethylation Sites | Gene Expression Profile | Mechanisms of Action | Impact on CRC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [126] | KDM4A | H3K9me3 | NA | Recruited with p53 to the promoter of p21 | KDM4A depletion induced proliferation reduction and apoptosis in CRC cells |
| [127] | KDM4A | H3K9me3 and H3K36me3 | Upregulated | Induction of transcription of inflammatory factors and oncogenes | Inhibition of KDM4A prevented CRC |
| [128] | KDM4B | H3K9me3 | Upregulated | Upregulation of hypoxia-inducible genes | Promoting malignant phenotypes in CRC cells |
| [129] | KDM4B | H3K9me3 | NA | Regulation of the DNA damage response | Mediation in cancer cell survival and tumor growth |
| [130] | KDM4B | NA | Upregulated | Promoting DNA damage response through STAT3 signaling | KDM4B silencing sensitized tumor cells to irradiation |
| [131] | KDM4B | H3K9me3 | Upregulated | Upregulation of glucose transporter 1 to regulate glucose uptake | KDM4B knockdown impaired colon cancer cell viability |
| [132] | KDM4B | NA | Upregulated | Regulation of glucose transporter 1 expression through the AKT signaling pathway to promote glucose uptake and ATP production | Promotion of CRC proliferation |
| [133] | KDM4B | H3K9me3 | NA | Inhibiting autophagy and reducing intracellular levels of specific amino acids in CRC cells by regulating light chain 3 beta | Downregulation of KDM4B inhibited CRC cell survival |
| [134] | KDM4B | NA | Upregulated | Promoting β-catenin-mediated gene transcription | Promoting CRC cell growth and clone formation |
| [26] | KDM4B | NA | NA | Regulation of mitochondria and death receptor-related pathways | KDM4B silencing induced apoptosis |
| [135] | KDM4B | H3K9me3 | Upregulated | Activation of HCLS1-associated protein X-1 transcription to mediate mitochondrial apoptosis | Inhibition of KDM4B promoted CRC cell apoptosis |
| [136] | KDM4B | H3K9me3 | NA | Upregulation of Nanog homeobox expression | Modulation of CSC properties |
| [137] | KDM4B | H3K9me2/3 | Upregulated | Interact with ETS-related gene 1 to activate TC10-like transcription | KDM4B knockdown attenuated CRC cell migration and invasion |
| [138] | KDM4C | NA | Upregulated | Mediating β-catenin-dependent transcription of Jagged-1 | KDM4C knockdown eliminated colonosphere formation from CRC cells |
| [139] | KDM4C | H3K9me3 and H3K36me3 | Upregulated | Upregulation of MALAT1 and enhancement of β-catenin signaling pathway activity | Promoting CRC metastasis in vitro and in vivo |
| [140] | KDM4C | H3K9me3 | NA | Activation of Notch target genes, intestinal stem cell genes and PD-L1 | Promoting stem cell-like properties and immune escape in CRC cells |
| [141] | KDM4C | H3K9me3 | Upregulated | Initiation of high mobility group AT-hook 2 transcription | Regulating EMT and cancer metastasis |
| [30] | KDM4C | NA | NA | Promoting β-catenin signaling | Regulation of CRC metastasis |
| [142] | KDM4C | H3K9me3 | Upregulated | Regulation of MIR17HG transcription | Mediating the CRC chemotherapy response |
| [143] | KDM4D | H3K9me3 | Upregulated | Interacting with β-catenin to activate transcription of its target genes | KDM4D knockdown reduced CRC cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and xenograft tumor formation |
| [144] | KDM4D | H3K9me3 | NA | Enhancement of glycolysis by activating the hypoxia-inducible factor 1 signaling pathway | KDM4D knockdown inhibited CRC cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and xenograft growth and metastasis |
| [145] | KDM4D | H3K9me3 | Upregulated | Interacting with Gli2 to promote expression of Hedgehog target genes | KDM4D knockdown inhibited CRC growth and metastasis |
| [31] | KDM4D | H3K9me3 | Upregulated | Enhanced STAT3- Interferon regulatory factor 1 signaling and promoted PD-L1 expression | Promoting CRC immune escape |
| References | HDM | Histone Demethylation Sites | Gene Expression Profile | Mechanisms of Action | Impact on CRC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [146] | KDM5A | H3K4me3 | Upregulated | Upregulation of cell migration-inducing protein expression | Mediating CRC cell migration |
| [147] | KDM5A | H3K4me3 | NA | Inhibition of cullin 4A expression | KDM5A downregulation mediated malignant behavior in CRC cells |
| [148] | KDM5A | H3K4me3 | NA | Interact with TP73-AS1 to affect TP73 transcription | Mediating malignant behavior in CRC |
| [149] | KDM5B | H3K4me3 | Upregulated | Induction of cellular senescence | KDM5B depletion led to loss of epithelial differentiation and inhibition of CRC cell growth |
| [150] | KDM5B | H3K4me3 | Upregulated | Promoting Wnt/β-catenin signaling by reducing Caudal Type Homeobox 2 levels | Promoting CRC cell proliferation |
| [151] | KDM5B | H3K4me3 | Upregulated | Inhibition of CC chemokine ligand 14 and Wnt/β-catenin activation | Promoting CRC cell proliferation and invasiveness |
| [152] | KDM5C | H3K4me3 | NA | Downregulation of ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily C Member 1 expression | Promotion of multidrug resistance |
| [153] | KDM5C | H3K4me3 | Upregulated | Inhibition of methyltransferase-like 14 transcription | Mediating CRC cell migration, invasion and metastasis |
| [154] | KDM5C | H3K4me3 | Upregulated | Inhibition of prefoldin subunit 5 transcription to enhance the transcriptional activity of c-Myc | KDM5C knockdown inhibited malignant behavior of CRC cells |
| [155] | KDM5D | H3K4me3 | Downregulated | Inhibition of FKBP Prolyl Isomerase 4 transcription by inhibiting E2F transcription factor 1 expression | KDM5D overexpression inhibited CRC growth and metastasis in vitro and in vivo |
| [28] | KDM5D | H3K4me2/3 | Upregulated | Disruption of cancer cell adhesion properties and tumor immunity | Mediating sex differences in KRAS mutant CRC |
| [156] | KDM5D | NA | Downregulated | NA | Direct control of CRC cell proliferation, migration and invasion |
| References | HDM Inhibitors | Targeted HDM | Histone Demethylation Sites | Mechanisms of Action | Impact on CRC | IC50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [178] | Polyamine analogs | KDM1A | H3K4me2 | Induction of re-expression of multiple abnormally silenced genes | NA | 1 μM |
| [179] | Oligoamine analogs | KDM1A | H3K4me1/2 | Induction of re-expression of multiple abnormally silenced genes | Inhibition of tumor growth in vitro and in vivo | 5 μM |
| [180] | Compound 12 | KDM1A | H3K9me2 | NA | Inhibition of HCT-116 cell proliferation in vitro | 0.013 μM |
| [181] | L05 | KDM1A | H3K4me1/2 | NA | Inhibition of CRC cell migration | 0.21 μM |
| [182] | PEGylated 17i nanoassemblies | KDM1A | NA | NA | Improved anti-tumor effects in vivo | 0.065 μM |
| [88] | CBB1003 | KDM1A | No changes in global methylation levels | Downregulation of LGR5 levels and inactivation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway | Inhibits CRC cell proliferation and colony formation | 250.4 μM |
| [89] | ORY-1001 and GSK2879552 | KDM1A | NA | NA | Reduced cell migration | NA |
| [96] | ZY0511 | KDM1A | H3K4me1/2 | Increased expression of the mTORC1 suppressor DNA Damage Inducible Transcript 4 | Inhibition of CRC cell proliferation | 1.7 nM |
| [97] | ZY0511 | KDM1A | NA | Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and DNA synthesis pathways | Inhibition of CRC cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo | 1.4 nM |
| [98] | ZY0511 | KDM1A | NA | Profoundly altered lipid metabolism in CRC cells | NA | 1.7 nM |
| [95] | Tranylcypromine | KDM1A | H3K4me2 | Suppression of EMT | Reduced migration and invasion of CRC cells | NA |
| [99] | Tranylcypromine hemisulfate | KDM1A | H3K9me2 | Downregulation of tetraspanin 8 expression to inhibit EMT | Inhibition of CRC cell proliferation and migration | NA |
| References | HDM Inhibitors | Targeted HDM | Histone Demethylation Sites | Mechanisms of Action | Impact on CRC | IC50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [107] | Daminozide | KDM2A | NA | Enhancement of nascent RNA transcription and 5-fluorouridine toxicity | Promotion of CRC cell death | NA |
| [183] | CBA-1 | KDM3A | H3K9me2 | Suppression of Wnt target genes | Inhibition of CRC cell proliferation in vitro | NA |
| [184] | IOX1 | KDM3A/B | H3K9me2/3 | Inhibition of Wnt target gene transcription | Inhibition of CRC tumorigenesis | NA |
| [185] | PROTACs using IOX1 as a warhead | KDM3A/B | NA | Inhibition of Wnt signaling | Elimination of colorectal CSCs and inhibition of tumor growth | 8.9 μM |
| [186] | PKF118-310 | KDM4A | H3K9me2/3 | Impacts the cell cycle and induces apoptosis | Inhibition of CRC cell proliferation | 10 μM |
| [187] | Benzo[b]tellurophenes (compound 1c) | KDM4 | H3K9me3 | NA | Induction of colon cancer cell death | 30.24 μM |
| [188] | QC6352 | KDM4 | H3K36me3 | NA | Inhibition of CRC cell viability | 13 nM |
| [140] | SD70; NSC636819 | KDM4C; KDM4A/B | H3K9me3 | Inhibition of ARID3B-induced target gene expression | Reversed CRC stem cell-like features | NA |
| [30] | Kaempferol | KDM4C | NA | Direct interaction with HNRNPK and HNRNPL to inhibit circ_0000345-mediated KDM4C/β-catenin signaling | Inhibits CRC cell migration | 49.02/66.04 μM |
| [142] | Avenanthramide A | KDM4C | H3K9me3 | Impairment of KDM4C/MIR17HG/GSK-3β negative feedback loop | Enhancing the therapeutic effect of 5-fluorouracil in CRC | NA |
| [145] | 5-c-8HQ | KDM4D | H3K9me3 | Inhibition of the Hedgehog signaling pathway | Inhibition of CRC cell proliferation and tumorigenesis | NA |
| [31] | 5-c-8HQ | KDM4D | H3K9me3 | Reduced PD-L1 expression by inhibiting interferon gamma receptor 1-STAT3-interferon regulatory factor 1 signaling | Enhancing the anti-tumor efficacy of PD-L1 antibodies | NA |
| [189] | 24s | KDM4D | H3K9me3 | NA | Inhibition of CRC cell proliferation and migration | 0.023 μM |
| [190] | TACH101 | KDM4 | H3K36me3 | NA | Inhibition of CRC cell proliferation and suppression of tumor growth in vivo | 0.0004 (homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence)/0.085 (immunoblot) μM |
| [148] | HY-100014 | KDM5A | H3K4me3 | Impact on KDM5A enrichment at the TP73 promoter | NA | NA |
| [147] | CPI-455 | KDM5A | H3K4me3 | Promotion of cullin 4A expression | NA | 10 nM |
| [153] | KDM5A-IN-1 | KDM5C | H3K4me3 | Promotion of methyltransferase-like 14 expression | NA | 55 nM |
| [27] | GSK-J4 | KDM6A/B | H3K27me3 | Interruption of oxaliplatin-induced NOTCH signaling | Enhanced oxaliplatin-induced apoptosis in CRC | NA |
| [29] | GSK-J4 | KDM6A/B | H3K27me3 | Induction of global enhancer reprogramming | Attenuated malignant phenotype, increased chemosensitivity, and suppressed tumor-initiating cells and stemness-associated gene signatures | 0.75–21.41 µM |
| [167] | GSK-J4 | KDM6B | H3K27me3 | Reduced C-X-C Motif Ligand 9 and 10 | Reduced anti-tumor immunity | NA |
| [172] | Daminozide | KDM7B | H3K9me2 (and reduced H3K4me3) | Reduced expression of oncogenes KRAS, BRAF and c-Myc | Inhibition of CRC cell proliferation | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Huang, M.; Tian, X.; Huang, X. Demystifying the Role of Histone Demethylases in Colorectal Cancer: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040267
Liu Y, Huang M, Tian X, Huang X. Demystifying the Role of Histone Demethylases in Colorectal Cancer: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(4):267. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040267
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yuanbin, Min Huang, Xia Tian, and Xiaodong Huang. 2025. "Demystifying the Role of Histone Demethylases in Colorectal Cancer: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 4: 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040267
APA StyleLiu, Y., Huang, M., Tian, X., & Huang, X. (2025). Demystifying the Role of Histone Demethylases in Colorectal Cancer: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(4), 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040267






