A Trifluoromethyl Quinazoline Compound Regulates the Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition of Prostatic Hyperplasia Cells by Inhibiting the Secretion of TGF-β1 in Stromal Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Compounds and Cell Culture
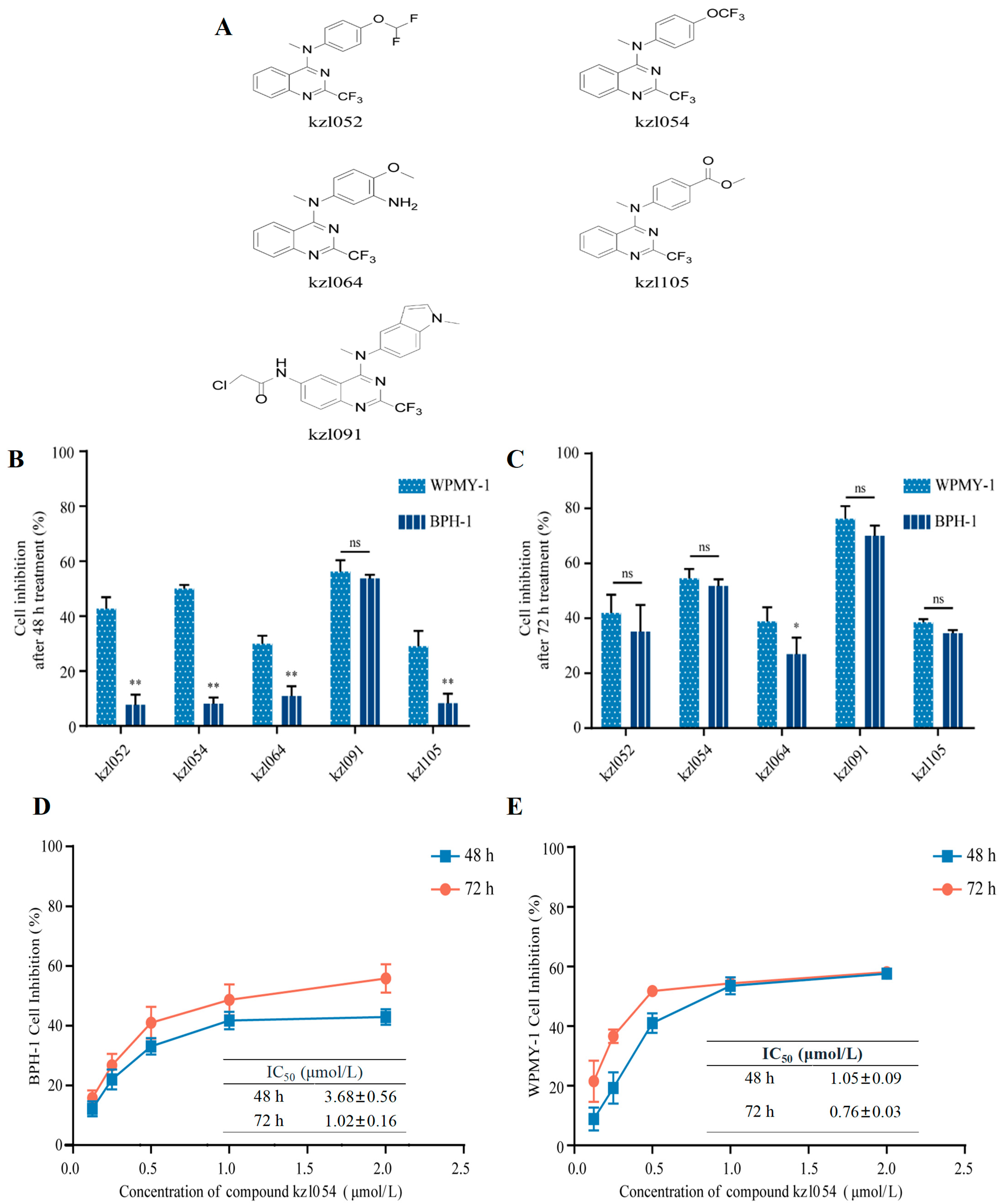
2.2. MTT Assay for Cell Proliferation
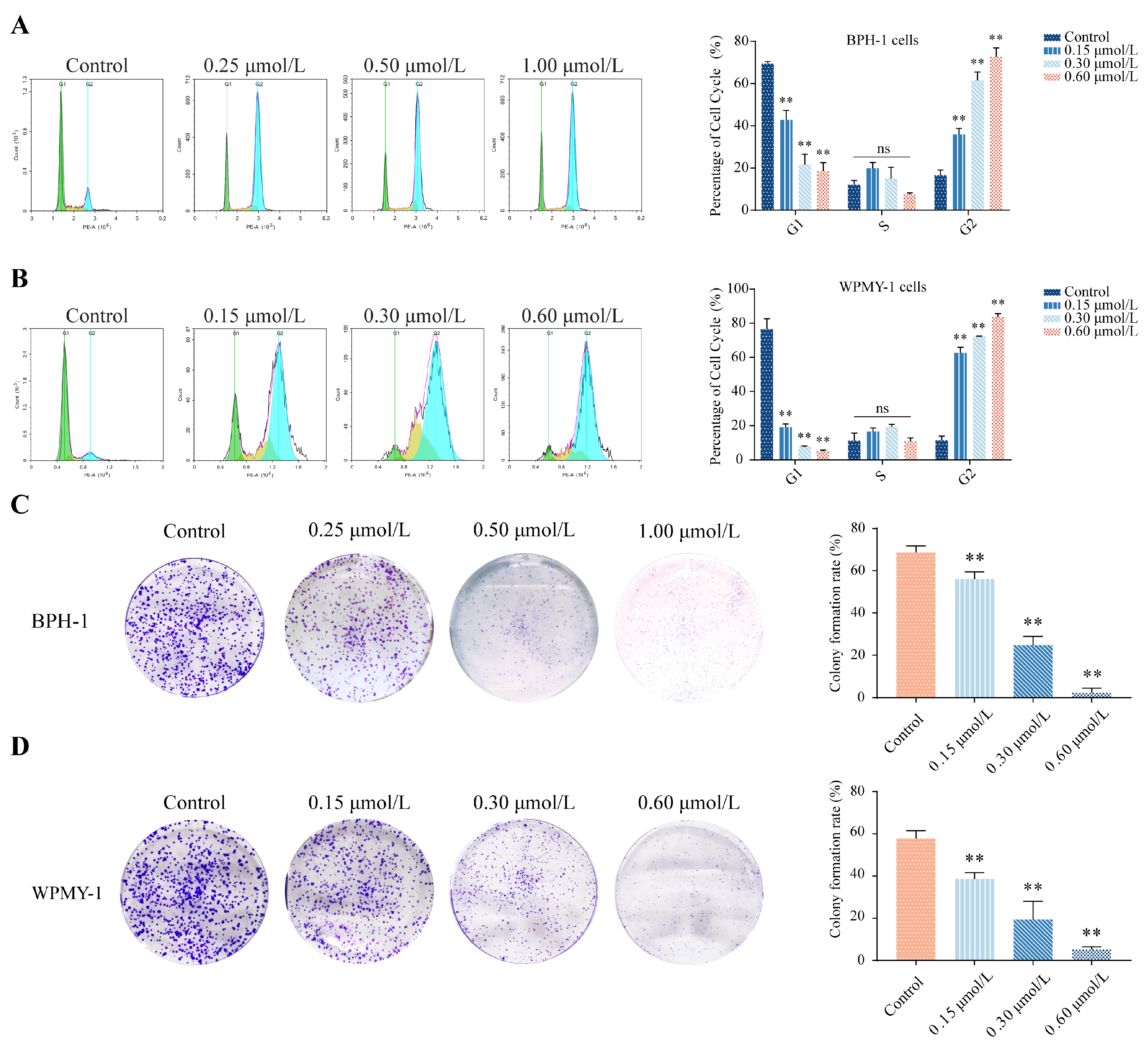
2.3. Flow Cytometry for Cell Cycle and Apoptosis Detection
2.4. Colony Formation Assay
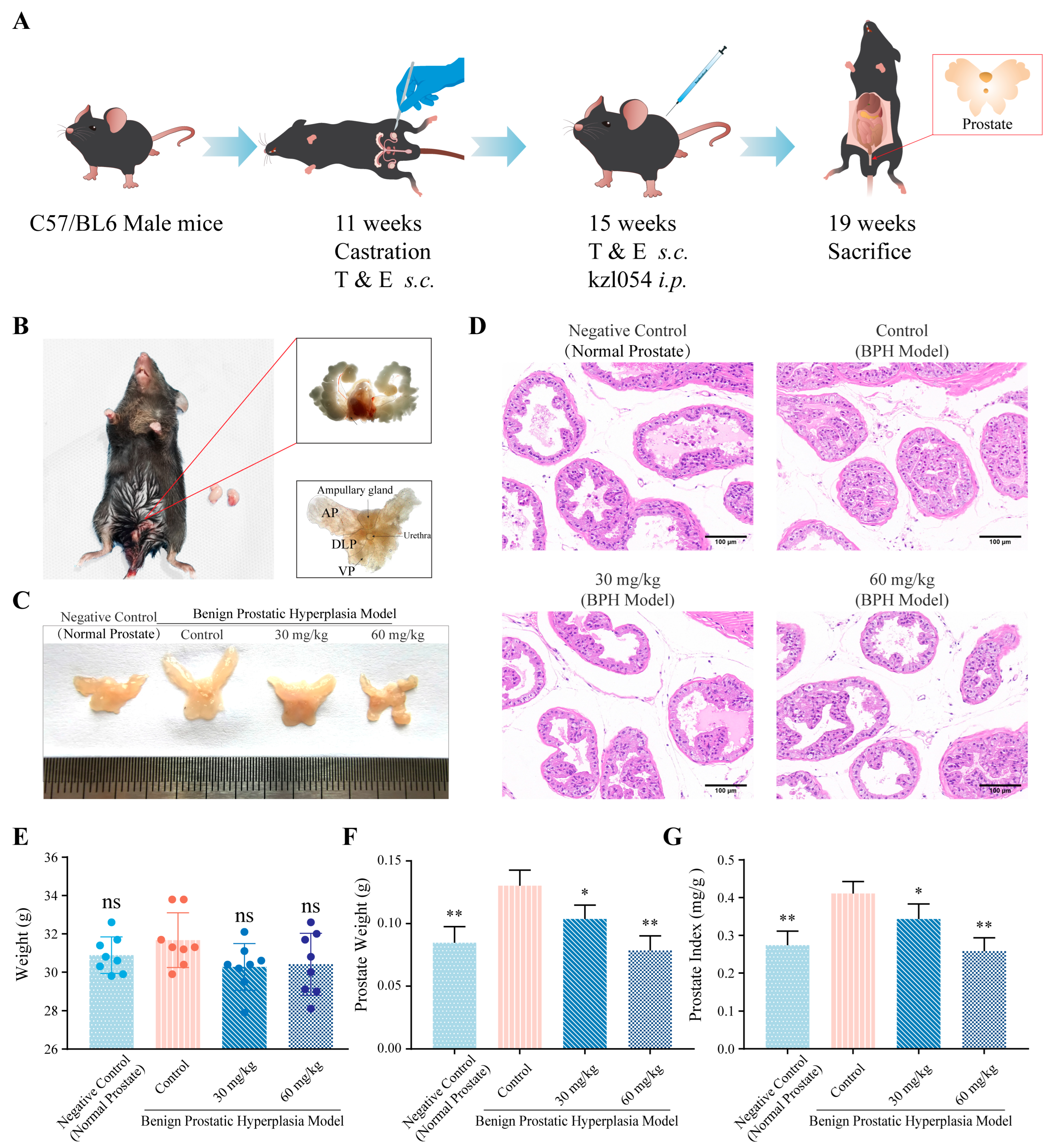
2.5. Establishment of Prostatic Hyperplasia Model
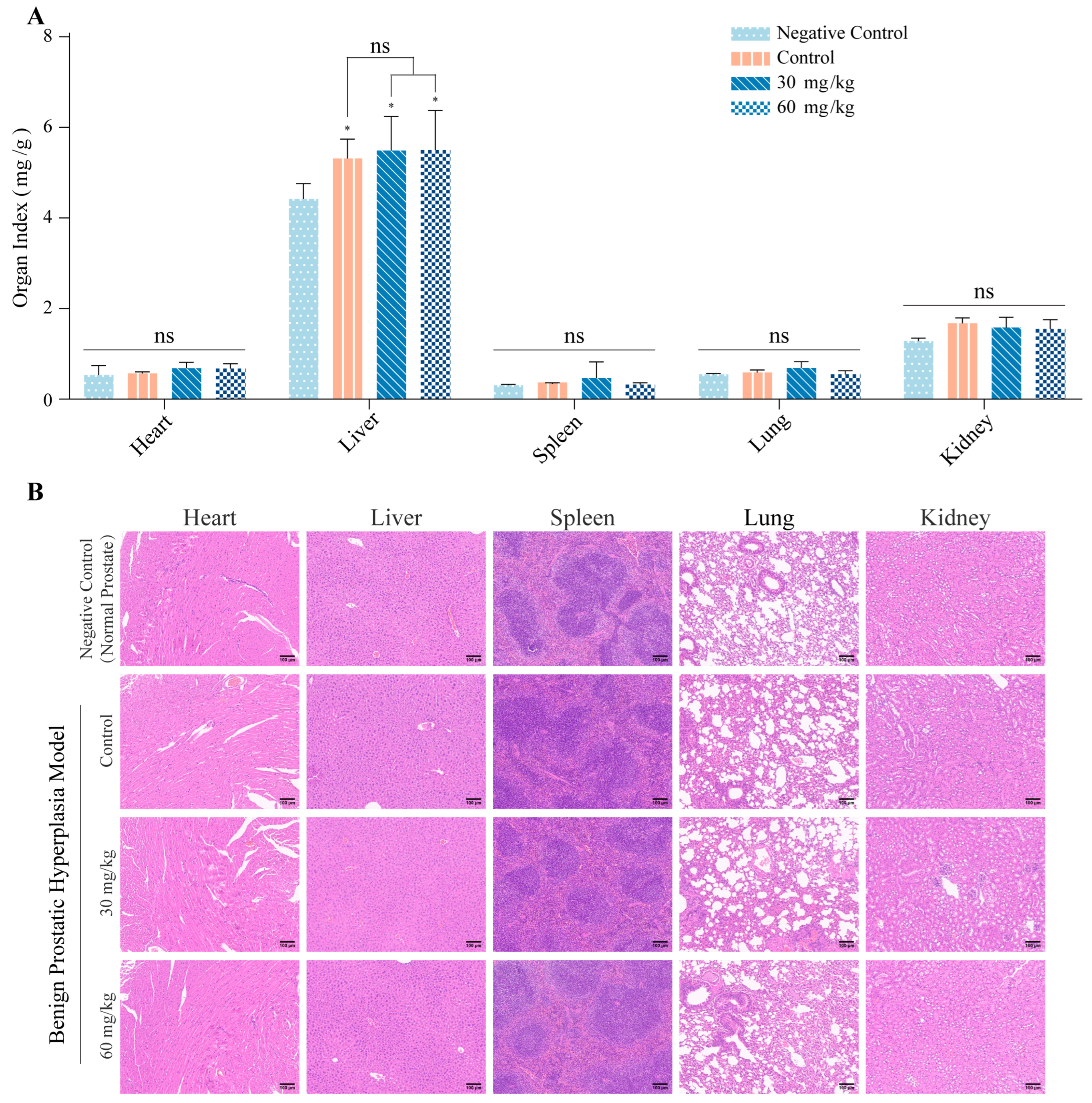
2.6. Animal Experiments
2.7. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
2.8. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Staining
2.9. Immunofluorescence (IF) Staining
2.10. Western Blotting
2.11. ELISA Detection
2.12. Target Prediction
2.13. Molecular Docking
2.14. Microtubule Binding Site Assay
2.15. EBI Competitive Binding Assay
2.16. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. kzl054 Inhibits the Cell Growth of BPH-1 and WPMY-1 Cells In Vitro
3.2. kzl054 Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Inhibits Colony Formation in BPH-1 and WPMY-1 Cells
3.3. kzl054 Suppresses Prostate Hyperplasia in C57BL/6J Mice
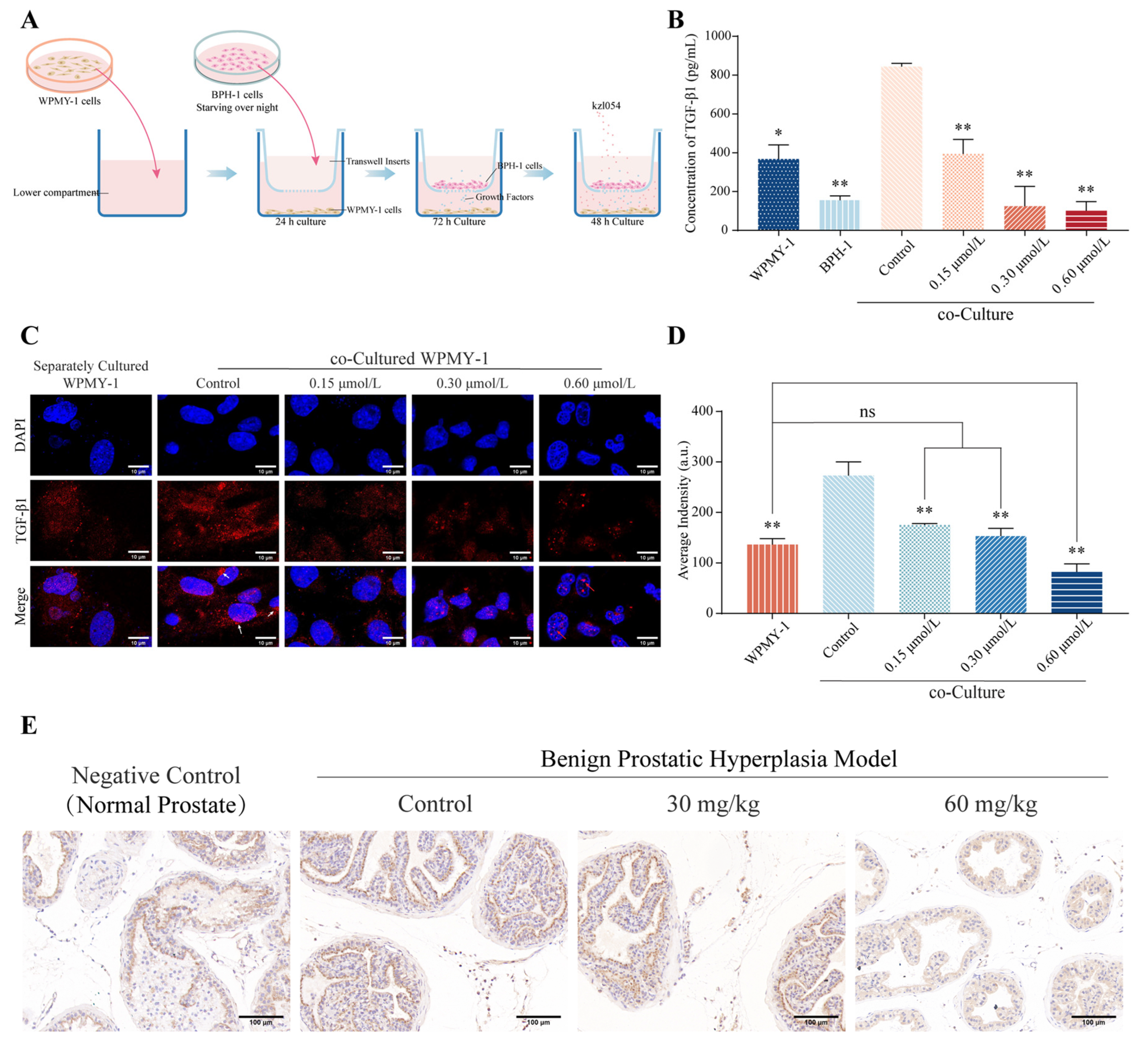
3.4. kzl054 Inhibits TGF-β1 Secretion in Co-Cultured WPMY-1 Cells
| Compounds | IC50/L-02 (μmol/L) | IC50/HepG2 (μmol/L) | Selective Index (SI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 48 h | 72 h | 48 h | 72 h | 48 h | 72 h | |
| kzl054 | 7.50 ± 0.18 | 3.50 ± 0.13 | 0.69 ± 0.27 | 0.36 ± 0.05 | 10.9 ** | 9.72 ** |
| kzl091 | 4.93 ± 0.48 | 3.33 ± 0.09 | 1.02 ± 0.11 | 0.66 ± 0.01 | 4.83 | 5.04 |
| Groups | Growth Factors (pg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGF-1 | TGF-β1 | EGF | VEGF | |
| BPH-1 | NA | 155.13 ± 18.35 ** | NA | NA |
| WPMY-1 | NA | 367.53 ± 59.27 * | NA | NA |
| Co-cultured control | NA | 743.63 ± 14.10 | NA | NA |
| Co-culture (0.15 μmol/L) | NA | 394.17 ± 61.01 ** | NA | NA |
| Co-culture (0.30 μmol/L) | NA | 124.53 ± 83.88 ** | NA | NA |
| Co-culture (0.60 μmol/L) | NA | 101.00 ± 38.99 ** | NA | NA |
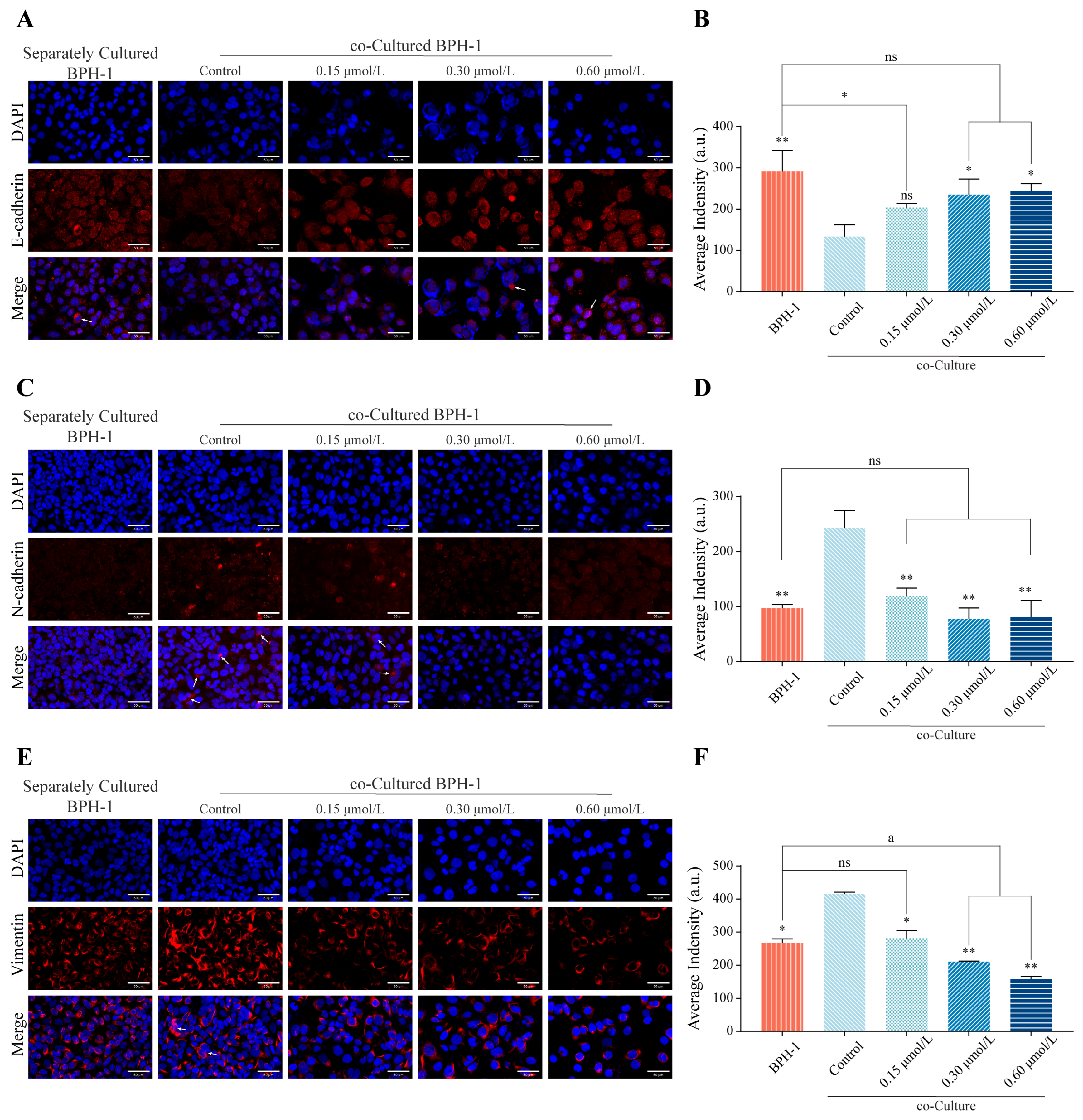
3.5. kzl054 Inhibits EMT in Co-Cultured BPH-1 Cells
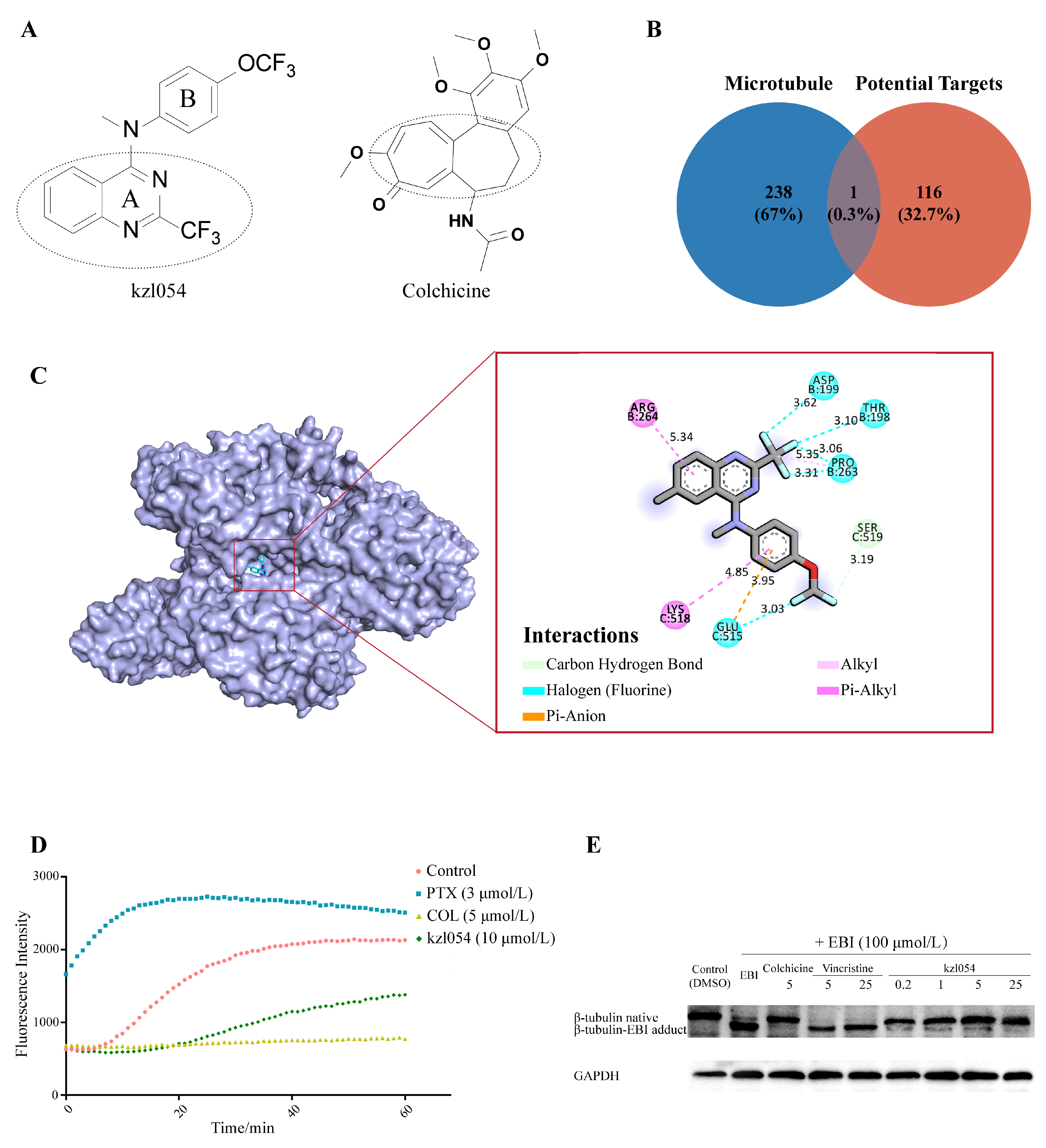
3.6. kzl054 Inhibited Microtubule Polymerization by Targeting β-Tubulin
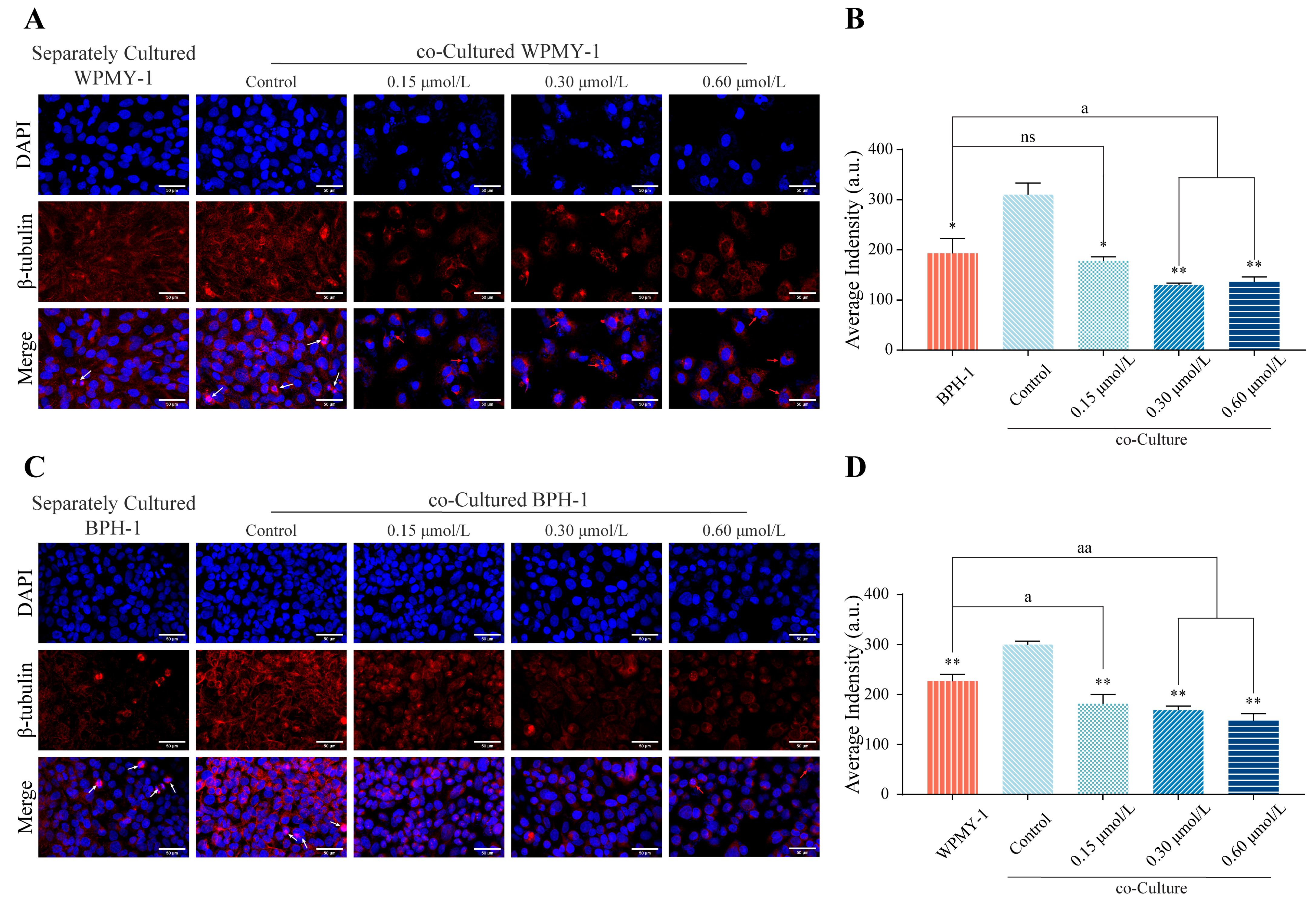
3.7. kzl054 Inhibits β-Tubulin Expression and Localization in Co-Cultured WPMY-1 and BPH-1 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Madersbacher, S.; Sampson, N.; Culig, Z. Pathophysiology of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Benign Prostatic Enlargement: A Mini-Review. Gerontology 2019, 65, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okeke, C.J.; Ojewola, R.W.; Odo, C.; Oyibo, U.E.; Obi, A.O.; Nnadozie, U.U. Urological Surgeries in a West African Teaching Hospital. J. West Afr. Coll. Surg. 2023, 13, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante Hernández, S.; Gómez Rivas, J.; Moreno Sierra, J. Benign prostatic hyperplasia. Med. Clin. 2024, 163, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannarella, R.; Condorelli, R.A.; Barbagallo, F.; La Vignera, S.; Calogero, A.E. Endocrinology of the Aging Prostate: Current Concepts. Front. Endocrinol 2021, 12, 554078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insausti, I.; Sáez de Ocáriz, A.; Galbete, A.; Capdevila, F.; Solchaga, S.; Giral, P.; Bilhim, T.; Isaacson, A.; Urtasun, F.; Napal, S. Randomized Comparison of Prostatic Artery Embolization versus Transurethral Resection of the Prostate for Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2020, 31, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, J.Y.; Patel, A.S.; Ramasamy, R. Minimizing Sexual Dysfunction in BPH Surgery. Curr. Sex. Health Rep. 2019, 11, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottaiano, N.; Shelton, T.; Sanekommu, G.; Benson, C.R. Surgical Complications in the Management of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Treatment. Curr. Urol. Rep. 2022, 23, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, D.S. Effects of an alpha-1d adrenoreceptor antagonist (naftopidil) on bladder dysfunction after radiotherapy in female rats. Int. Urogynecology J. 2021, 32, 2747–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robitaille, J.; Langlois, V.S. Consequences of steroid-5alpha-reductase deficiency and inhibition in vertebrates. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 290, 113400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahtamouni, L.; Alzghoul, A.; Alderfer, S.; Sun, J.; Ahram, M.; Prasad, A.; Bamburg, J. The role of activated androgen receptor in cofilin phospho-regulation depends on the molecular subtype of TNBC cell line and actin assembly dynamics. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0279746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uleri, A.; Nicolas Cornu, J.; Gobbo, A.; Herrmann, T.R.W.; De Nunzio, C.; Hashim, H.; Baboudjian, M. Association of 5α-Reductase Inhibitors with Depression and Suicide: A Mini Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. Focus 2024, 10, 751–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winograd, J.; Venishetty, N.; Codelia-Anjum, A.; Bhojani, N.; Elterman, D.; Zorn, K.C.; Te, A.; Chughtai, B. Emerging drugs for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia: A 2023 update. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2024, 29, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wu, L.; Zhao, S.; Xia, S.J.; Pan, L.; Chen, M.; Zhu, Y.P.; Jiang, J.T.; Shi, F. Upregulation of FGF7 Induced Intravesical Prostatic Protrusion of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia via the ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway. Gerontology 2023, 69, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodamoradi, P.; Amniattalab, A.; Alizadeh, S. Overexpression of GDNF and FGF-1 in Canine Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Evidence for a Pathogenetic Role of Neural Growth Factor. J. Comp. Pathol. 2021, 182, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Q.; He, W.; Liu, D.; Yin, J.; Ye, L.; Chen, P.; Xu, D.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Zeng, G.; et al. M2a macrophage can rescue proliferation and gene expression of benign prostate hyperplasia epithelial and stroma cells from insulin-like growth factor 1 knockdown. Prostate 2021, 81, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisberg, M.; Hanai J-i Sugimoto, H.; Mammoto, T.; Charytan, D.; Strutz, F.; Kalluri, R. BMP-7 counteracts TGF-β1–induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and reverses chronic renal injury. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tu, B.; Wang, Z.; Shao, Z.; Fu, C.; Hua, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Sun, H.; Mao, C.; et al. Doxazosin Attenuates Development of Testosterone Propionate-induced Prostate Growth by regulating TGF-β/Smad Signaling Pathway, Prostate-specific Antigen Expression and Reversing Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition in Mice and Stroma Cells. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2025, 17, e18761429315125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Rong, N.; Liu, M.; Xu, C.; Xiong, Q.; Lei, Y. The exosome-like vesicles derived from androgen exposed-prostate stromal cells promote epithelial cells proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2021, 411, 115384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, X.F.; Morris-Natschke, S.L.; Liu, Y.Q.; Guo, X.; Xu, X.S.; Goto, M.; Li, J.C.; Yang, G.Z.; Lee, K.H. Biologically active quinoline and quinazoline alkaloids part I. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 775–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ballard, P.; Yates, J.W.; Yang, Z.; Kim, D.W.; Yang, J.C.; Cantarini, M.; Pickup, K.; Jordan, A.; Hickey, M.; Grist, M.; et al. Preclinical Comparison of Osimertinib with Other EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Brain Metastases Models, and Early Evidence of Clinical Brain Metastases Activity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 5130–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogentoft, C.; Ericsson, O.; Kvist, M.; Danielsson, B.; Akerman, B. Studies on the medicinal chemistry of oxoquinazolines. X. Synthesis and local anaesthetic properties of some 4-oxoquinazolines unsubstituted in the 2-position. Acta. Pharm. Suec. 1971, 8, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luan, M.Z.; Zhang, X.F.; Yang, Y.; Meng, Q.G.; Hou, G.G. Anti-inflammatory activity of fluorine-substituted benzo[h]quinazoline-2-amine derivatives as NF-κB inhibitors. Bioorganic Chem. 2023, 132, 106360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Huang, P.; Yan, Z.; Shi, X.; Tang, X.; Yang, J.; Jin, C. Self-Catalyzed Phototandem Perfluoroalkylation/Cyclization of Unactivated Alkenes: Synthesis of Perfluoroalkyl-Substituted Quinazolinones. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, J.; Rathinasamy, K. Microtubules and Cell Division: Potential Pharmacological Targets in Cancer Therapy. Curr. Drug Targets 2023, 24, 889–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laisne, M.C.; Michallet, S.; Lafanechère, L. Characterization of Microtubule Destabilizing Drugs: A Quantitative Cell-Based Assay That Bridges the Gap between Tubulin Based- and Cytotoxicity Assays. Cancers 2021, 13, 5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudimchuk, N.B.; McIntosh, J.R. Regulation of microtubule dynamics, mechanics and function through the growing tip. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 777–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.H.; Koch, P.D.; Luan, H.H.; Tu, H.C.; Shimada, K.; Ngan, I.; Ventura, R.; Jiang, R.; Mitchison, T.J. Colchicine acts selectively in the liver to induce hepatokines that inhibit myeloid cell activation. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, E.; Jeong, J.; Lee, J.; Keum, S.; Hwang, Y.E.; Choi, J.H.; Rhee, S. Casein kinase 2 promotes the TGF-β-induced activation of α-tubulin acetyltransferase 1 in fibroblasts cultured on a soft matrix. BMB Rep. 2022, 55, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, B.K.; Chatterjee, A.; Kondaiah, P.; Gundiah, N. Substrate Stiffness Modulates TGF-β Activation and ECM-Associated Gene Expression in Fibroblasts. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Yu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, K.; Peng, X.; Xu, G.; Chen, C.; Meng, X.; Zeng, X.; Wu, H.; et al. Discovery of novel quinazoline derivatives containing trifluoromethyl against cell proliferation by targeting werner helicase. Mol. Divers. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Su, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, D.; Shen, L.; Wang, H.; Wen, J.; Hu, H.; Zheng, R. The effect of acupuncture on oestrogen receptors in rats with benign prostatic hyperplasia. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2023, 234, 106402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-Y.; Cai, Y.; Hu, X.; Li, F.; Qian, X.-H.; Xia, L.-Y.; Gao, B.; Wu, L.; Xie, W.-Z.; Gu, J.-M.; et al. P. gingivalis in oral-prostate axis exacerbates benign prostatic hyperplasia via IL-6/IL-6R pathway. Mil. Med. Res. 2024, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Tang, J.; Yin, G.; Long, Z.; He, L.; Zhou, C.; Luo, L.; Qi, L.; Wang, L. Animal models of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2021, 24, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Huang, D.; Su, X.; Yang, R.; Shao, C.; Jiang, J.; Li, J.; Wu, J. Sildenafil citrate induces prostatic hyperplasia in BPH model rats and aged rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2024, 493, 117147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, C.; Gu, M.; Zhan, M.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Z. LncRNA DIO3OS regulated by TGF-β1 and resveratrol enhances epithelial mesenchymal transition of benign prostatic hyperplasia epithelial cells and proliferation of prostate stromal cells. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2021, 10, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janus, P.; Kuś, P.; Jaksik, R.; Vydra, N.; Toma-Jonik, A.; Gramatyka, M.; Kurpas, M.; Kimmel, M.; Widłak, W. Transcriptional responses to direct and indirect TGFβ1 stimulation in cancerous and noncancerous mammary epithelial cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeschke, A.; Jacobi, A.; Lawrence, M.G.; Risbridger, G.P.; Frydenberg, M.; Williams, E.D.; Vela, I.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Bray, L.J.; Taubenberger, A. Cancer-associated fibroblasts of the prostate promote a compliant and more invasive phenotype in benign prostate epithelial cells. Mater. Today Bio 2020, 8, 100073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitoun, O.A.; Farhat, A.M.; Mohamed, M.A.; Hamad, M.R.; Aramini, B.; Haider, K.H. Management of benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH) by combinatorial approach using alpha-1-adrenergic antagonists and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 883, 173301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Latour, C.D.; Olawore, O.; Pate, V.; Friedlander, D.F.; Stürmer, T.; Jonsson Funk, M.; Jensen, B.C. Cardiovascular Outcomes of α-Blockers vs 5-α Reductase Inhibitors for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2343299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Zhang, D.; Yu, G.; Cheng, S.; Xu, B.; Yu, J.; Liu, J.; Luo, H. A Trifluoromethyl Quinazoline Compound Regulates the Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition of Prostatic Hyperplasia Cells by Inhibiting the Secretion of TGF-β1 in Stromal Cells. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47121057
Chen L, Zhang D, Yu G, Cheng S, Xu B, Yu J, Liu J, Luo H. A Trifluoromethyl Quinazoline Compound Regulates the Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition of Prostatic Hyperplasia Cells by Inhibiting the Secretion of TGF-β1 in Stromal Cells. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(12):1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47121057
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Lu, Di Zhang, Gang Yu, Sha Cheng, Bixue Xu, Jia Yu, Jiming Liu, and Heng Luo. 2025. "A Trifluoromethyl Quinazoline Compound Regulates the Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition of Prostatic Hyperplasia Cells by Inhibiting the Secretion of TGF-β1 in Stromal Cells" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 12: 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47121057
APA StyleChen, L., Zhang, D., Yu, G., Cheng, S., Xu, B., Yu, J., Liu, J., & Luo, H. (2025). A Trifluoromethyl Quinazoline Compound Regulates the Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition of Prostatic Hyperplasia Cells by Inhibiting the Secretion of TGF-β1 in Stromal Cells. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(12), 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47121057







