Whole Exome Sequencing for the Identification of Mutations in Bone Marrow CD34+Cells in Hodgkin Lymphoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bone Marrow and Blood Sample Collection
2.2. Cell Separation and Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.3. Whole Exome Sequencing
2.4. Variant Calling and Annotation
2.5. Sanger Sequencing Validation
2.6. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Manifestations of cHL Patients
3.2. Whole Exome Sequencing and Pathogenic Mutation Profile of cHL Patients
3.3. Novel Genetic Alterations in cHL Not Otherwise Specified
3.4. Association Between CNN2 and MUC4 Expression Levels and Clinical Features in cHL
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADAM12 | ADAM Metallopeptidase Domain 12 |
| AFAP1L1 | Actin filament-associated protein 1-like 1 |
| B2M | β2 microglobulin |
| BM | Bone marrow |
| cHL | Classical Hodgkin lymphoma |
| CNN2 | Calponin 2 |
| DUOX2 | Dual Oxidase 2 |
| ERK | Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase |
| FBN3 | Fibrillin 3 |
| GNA | G protein subunit alpha |
| GSK3β | Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta |
| GSS | Glutathione synthetase |
| HAVCR2 | Hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 2 |
| HRS | Hodgkin and multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells |
| HLA | Human leukocyte antigen |
| INDEL | Insertion and deletion |
| JAK-STAT | Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| KDR | Kinase insert domain receptor |
| KMT2C | Lysine Methyltransferase 2C |
| LDH | Lactic acid dehydrogenase |
| LRHL | Lymphocyte-rich Hodgkin’s lymphoma |
| LDHL | Lymphocyte-depleted Hodgkin’s lymphoma |
| MAF | Minor allele frequency |
| MCHL | Mixed cellularity Hodgkin’s lymphoma |
| MMP9 | Matrix metalloproteinase-9 |
| MTSS2 | MTSS I-BAR Domain Containing 2 |
| MUC4 | Mucin 4 |
| NCF1 | Neutrophil Cytosolic Factor 1 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| NSHL | Nodular sclerosis Hodgkin’s lymphoma |
| PBMC | Peripheral blood mononuclear cells |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| PD-L | Programmed cell death ligand |
| PI3K/Akt | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B |
| PTPN1 | Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 1 |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| TAMs | Tumor-associated macrophages |
| TCF19 | Transcription Factor 1 |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor beta |
| TNFAIP3 | Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3 |
| TTLL5 | Tubulin tyrosine ligase like 5 |
| VDR | Vitamin D receptor |
| WES | Whole exome sequencing |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Ruggeri, E.; Frezzato, F.; Mouawad, N.; Pizzi, M.; Scarmozzino, F.; Capasso, G.; Trimarco, V.; Quotti Tubi, L.; Cellini, A.; Cavarretta, C.A.; et al. Protein kinase CK2alpha is overexpressed in classical hodgkin lymphoma, regulates key signaling pathways, PD-L1 and may represent a new target for therapy. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1393485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, S.; Yokote, T.; Hiraoka, N.; Nishiwaki, U.; Hanafusa, T.; Nishimura, Y.; Tsuji, M. Role of mast cells in fibrosis of classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2016, 29, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathas, S.; Hartmann, S.; Kuppers, R. Hodgkin lymphoma: Pathology and biology. Semin. Hematol. 2016, 53, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jachimowicz, R.D.; Pieper, L.; Reinke, S.; Gontarewicz, A.; Plutschow, A.; Haverkamp, H.; Frauenfeld, L.; Fend, F.; Overkamp, M.; Jochims, F.; et al. Whole-slide image analysis of the tumor microenvironment identifies low B-cell content as a predictor of adverse outcome in patients with advanced-stage classical Hodgkin lymphoma treated with BEACOPP. Haematologica 2021, 106, 1684–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahid, U.; Akbar, F.; Amaraneni, A.; Husnain, M.; Chan, O.; Riaz, I.B.; McBride, A.; Iftikhar, A.; Anwer, F. A Review of Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation in Lymphoma. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2017, 12, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadkhoda, D.; Nikoonezhad, M.; Baghestani, A.R.; Parkhideh, S.; Momeni-Varposhti, Z.; Khadem Maboudi, A.A. Prognostic Factors for the Long-Term Survival after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with Hodgkin Lymphoma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2023, 24, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballova, V.; Ladicka, M.; Vranovsky, A.; Lakota, J. Autologous stem cell transplantation with selected CD34+ cells and unmanipulated peripheral blood stem cells in patients with relapsed and refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma: A single centre experience. Neoplasma 2008, 55, 428–436. [Google Scholar]
- Radu, P.; Zurzu, M.; Paic, V.; Bratucu, M.; Garofil, D.; Tigora, A.; Georgescu, V.; Prunoiu, V.; Pasnicu, C.; Popa, F.; et al. CD34-Structure, Functions and Relationship with Cancer Stem Cells. Medicina (Kaunas) 2023, 59, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civin, C.I.; Strauss, L.C.; Brovall, C.; Fackler, M.J.; Schwartz, J.F.; Shaper, J.H. Antigenic analysis of hematopoiesis. III. A hematopoietic progenitor cell surface antigen defined by a monoclonal antibody raised against KG-1a cells. J. Immunol. 1984, 133, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaron, E.M.; Almeida, J.; Lopez-Holgado, N.; Sanchez-Guijo, F.M.; Alberca, M.; Blanco, B.; Sanchez-Abarca, L.I.; Lopez, O.; Perez-Simon, J.A.; San Miguel, J.F.; et al. In leukapheresis products from non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma patients, the immature hematopoietic progenitors show higher CD90 and CD34 antigenic expression. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2007, 37, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciola, E.; Guglielmo, P.; Cacciola, E.; Stagno, F.; Cacciola, R.R.; Impera, S. CD34 expression in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 1995, 18 (Suppl. 1), 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jona, A.; Szodoray, P.; Illes, A. Immunologic pathomechanism of Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Exp. Hematol. 2013, 41, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santisteban-Espejo, A.; Bernal-Florindo, I.; Montero-Pavon, P.; Perez-Requena, J.; Atienza-Cuevas, L.; Fernandez-Valle, M.D.C.; Villalba-Fernandez, A.; Garcia-Rojo, M. Pathogenic Variants Associated with Epigenetic Control and the NOTCH Pathway Are Frequent in Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, A.; Gloghini, A.; Castagna, L.; Santoro, A.; Carlo-Stella, C. Primary refractory and early-relapsed Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Strategies for therapeutic targeting based on the tumour microenvironment. J. Pathol. 2015, 237, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzel, B.M.; Gerth, M.; Chen, Y.; Wunsche, E.; Facklam, T.; Beck, J.F.; Guntinas-Lichius, O.; Petersen, I. Mutation analysis of tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3 gene in Hodgkin lymphoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2017, 213, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotunno, M.; McMaster, M.L.; Boland, J.; Bass, S.; Zhang, X.; Burdett, L.; Hicks, B.; Ravichandran, S.; Luke, B.T.; Yeager, M.; et al. Whole exome sequencing in families at high risk for Hodgkin lymphoma: Identification of a predisposing mutation in the KDR gene. Haematologica 2016, 101, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, D.; Zander, T.; Diehl, V.; Wolf, J. Genetic instability in Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Ann. Oncol. 2002, 13 (Suppl. 1), 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maura, F.; Ziccheddu, B.; Xiang, J.Z.; Bhinder, B.; Rosiene, J.; Abascal, F.; Maclachlan, K.H.; Eng, K.W.; Uppal, M.; He, F.; et al. Molecular Evolution of Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma Revealed Through Whole-Genome Sequencing of Hodgkin and Reed Sternberg Cells. Blood Cancer Discov. 2023, 4, 208–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnappauf, O.; Heale, L.; Dissanayake, D.; Tsai, W.L.; Gadina, M.; Leto, T.L.; Kastner, D.L.; Malech, H.L.; Kuhns, D.B.; Aksentijevich, I.; et al. Homozygous variant p. Arg90His in NCF1 is associated with early-onset Interferonopathy: A case report. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2021, 19, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Ma, J.; Yao, C.; Ye, Z.; Ding, H.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Li, G.; He, Y.; Li, J.; et al. The NCF1 variant p.R90H aggravates autoimmunity by facilitating the activation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e153619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giefing, M.; Winoto-Morbach, S.; Sosna, J.; Doring, C.; Klapper, W.; Kuppers, R.; Bottcher, S.; Adam, D.; Siebert, R.; Schutze, S. Hodgkin-Reed-Sternberg cells in classical Hodgkin lymphoma show alterations of genes encoding the NADPH oxidase complex and impaired reactive oxygen species synthesis capacity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.O.; Medeiros, J.W.; Albuquerque, G.S.; Valderrama, P.M.; Barbosa, A.H.Q.; de Souza, J.M.; Oliveira, R.S.; Morais, A.L.; Neto, J.; Muniz, M.T.C. Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 as poor prognosis factor for Hodgkin’s lymphoma patients. J. Pediatr. (Rio. J.). 2023, 99, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renne, C.; Benz, A.H.; Hansmann, M.L. Vitamin D3 receptor is highly expressed in Hodgkin’s lymphoma. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Ansari, I.A.; Singh, P.; Dass, J.F. Prediction of functionally significant single nucleotide polymorphisms in PTEN tumor suppressor gene: An in silico approach. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2017, 64, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.M.; Cooper, D.N.; Schuelke, M.; Seelow, D. MutationTaster2: Mutation prediction for the deep-sequencing age. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaser, R.; Adusumalli, S.; Leng, S.N.; Sikic, M.; Ng, P.C. SIFT missense predictions for genomes. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, D.T.; Giang, N.H.; Trang, B.K.; Ngoc, N.T.; Giang, N.V.; Canh, N.X.; Vuong, N.B.; Xuan, N.T. Prevalence of CYLD mutations in Vietnamese patients with polycythemia vera. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2022, 31, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, B.C.; Chen, C.; You, Q.; Chiu, R.; Venkataraman, G.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, X.; Smith, S.M.; He, C.; et al. Alterations of 5-hydroxymethylation in circulating cell-free DNA reflect molecular distinctions of subtypes of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. NPJ Genom. Med. 2021, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaumeyer, B.; Fidai, S.; Sukhanova, M.; Yap, K.L.; Segal, J.; Raca, G.; Stock, W.; McNeer, J.; Lager, A.M.; Gurbuxani, S. MUC4 expression by immunohistochemistry is a specific marker for BCR-ABL1+ and BCR-ABL1-like B-lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2022, 63, 1436–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Cui, Q.; Ge, Y.; Liu, Y. Case report: Mutation evolution in a patient with TdT positive high grade B cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 rearrangements following the treatment of concurrent follicular lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Discov. Oncol. 2024, 15, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Katib, A.M.; Ebrahim, A.S.; Kandouz, M.; Zaiem, F.; Raufi, A.; Ebrahim, S.; Mohamed, A.; Emara, N.; Gabali, A.M. Isolation and characterization of a CD34(+) sub-clone in B-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voso, M.T.; Hohaus, S.; Moos, M.; Haas, R. Lack of t(14;18) polymerase chain reaction-positive cells in highly purified CD34+ cells and their CD19 subsets in patients with follicular lymphoma. Blood 1997, 89, 3763–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossakowska, A.E.; Urbanski, S.J.; Janowska-Wieczorek, A. Matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors—Expression, role and regulation in human malignant non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Leuk. Lymphoma 2000, 39, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumilina, E.; Nurbaeva, M.K.; Yang, W.; Schmid, E.; Szteyn, K.; Russo, A.; Heise, N.; Leibrock, C.; Xuan, N.T.; Faggio, C.; et al. Altered regulation of cytosolic Ca(2)(+) concentration in dendritic cells from klotho hypomorphic mice. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2013, 305, C70–C77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, P.; Singh, A.P.; Batra, S.K. Structure, evolution, and biology of the MUC4 mucin. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 966–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhao, P.; Liu, K.; Kong, D.L. Ectopic expression of CNN2 of colon cancer promotes cell migration. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, M.; Jepson, S.; Arango, M.E.; Carothers Carraway, C.A.; Carraway, K.L. Muc4/sialomucin complex, an intramembrane modulator of ErbB2/HER2/Neu, potentiates primary tumor growth and suppresses apoptosis in a xenotransplanted tumor. Oncogene 2001, 20, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, A.; Parrinello, N.L.; Vetro, C.; Chiarenza, A.; Cerchione, C.; Ippolito, M.; Palumbo, G.A.; Di Raimondo, F. Prognostic meaning of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and lymphocyte to monocyte ration (LMR) in newly diagnosed Hodgkin lymphoma patients treated upfront with a PET-2 based strategy. Ann. Hematol. 2018, 97, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straus, D.J.; Gaynor, J.J.; Myers, J.; Merke, D.P.; Caravelli, J.; Chapman, D.; Yahalom, J.; Clarkson, B.D. Prognostic factors among 185 adults with newly diagnosed advanced Hodgkin’s disease treated with alternating potentially noncross-resistant chemotherapy and intermediate-dose radiation therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 1990, 8, 1173–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Sevilla, J.J.; Salar, A. Recent Advances in the Genetic of MALT Lymphomas. Cancers 2021, 14, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayden, T.; Sepulveda, F.E.; Khuong-Quang, D.A.; Pratt, J.; Valera, E.T.; Garrigue, A.; Kelso, S.; Sicheri, F.; Mikael, L.G.; Hamel, N.; et al. Germline HAVCR2 mutations altering TIM-3 characterize subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphomas with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytic syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1650–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moonla, C.; Polprasert, C.; Komvilaisak, P.; Rattanathammethee, T.; Kongkiatkamon, S.; Wudhikarn, K.; Kobbuaklee, S.; Boonyabaramee, P.; Tangcheewinsirikul, N.; Pakakasama, S.; et al. Germline HAVCR2 mutations and their relation to the clinical spectrum of subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: Results from a multicenter study and meta-analysis. Haematologica 2023, 108, 2743–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velissari, A.; Vassilakopoulos, T.P.; Angelopoulou, M.K.; Korkolopoulou, P.; Bamias, G.; Daikos, G.; Konstantopoulos, K.; Siakantaris, M. Genetic polymorphisms and risk of MALT lymphoma in Greek population. Curr. Res. Transl. Med. 2022, 70, 103330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Xin, S.; Wan, Z.; Dong, H.; Liu, L.; Fan, Z.; Li, T.; Peng, F.; Xiong, Y.; Han, Y. TCF19 promotes cell proliferation and tumor formation in lung cancer by activating the Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 45, 101978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.Y.; Wei, F. TGF-beta: An active participant in the immune and metabolic microenvironment of multiple myeloma: TGF-beta in the microenvironment of multiple myeloma. Ann. Hematol. 2024, 103, 4351–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
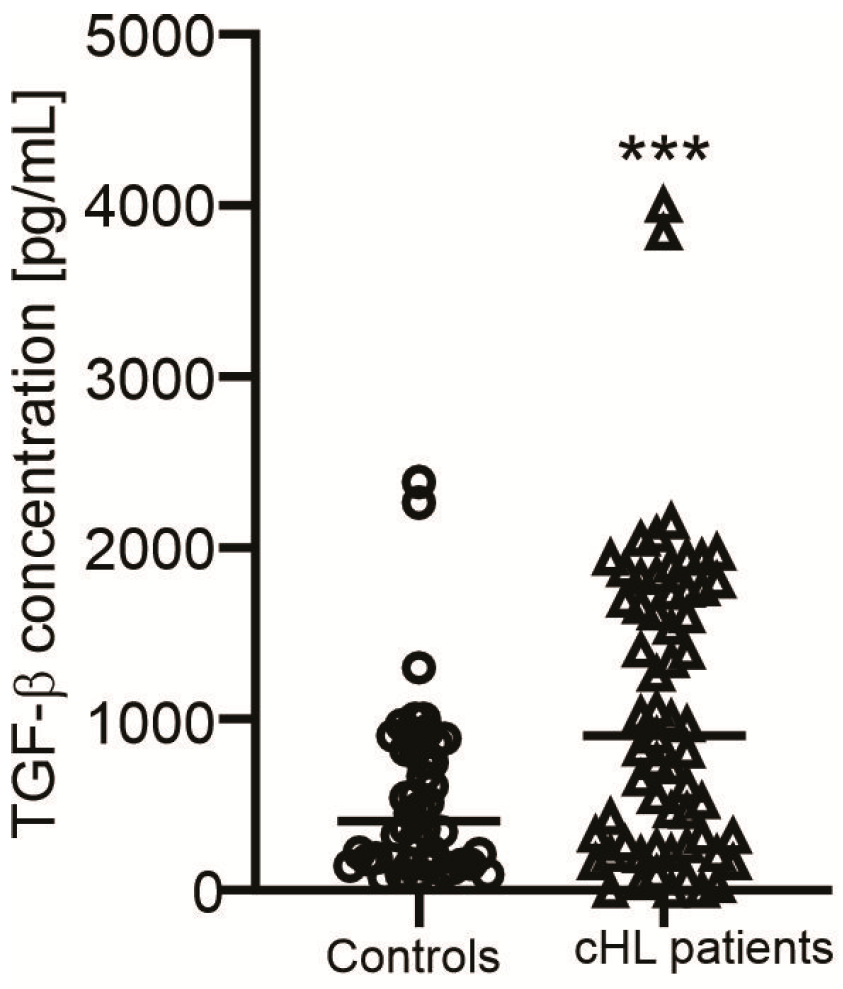
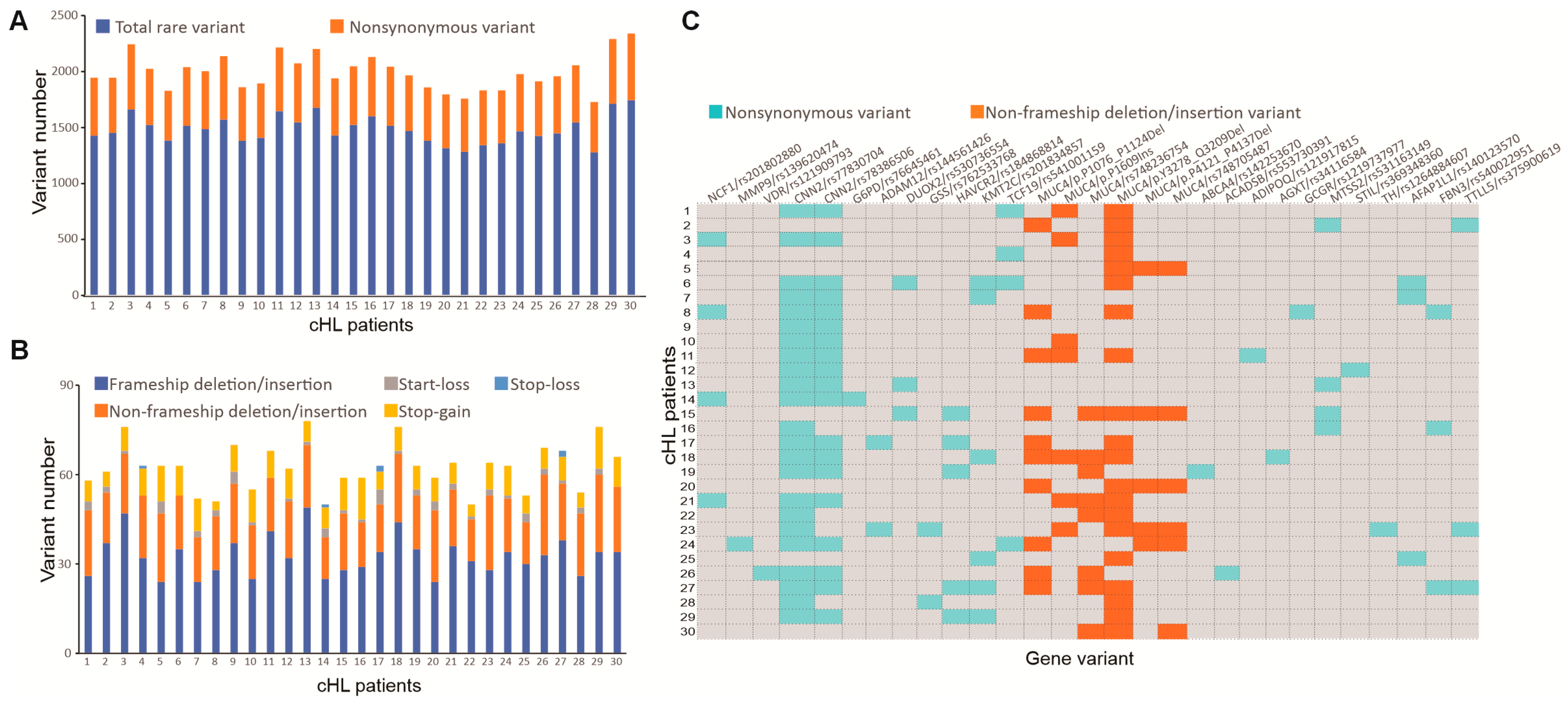

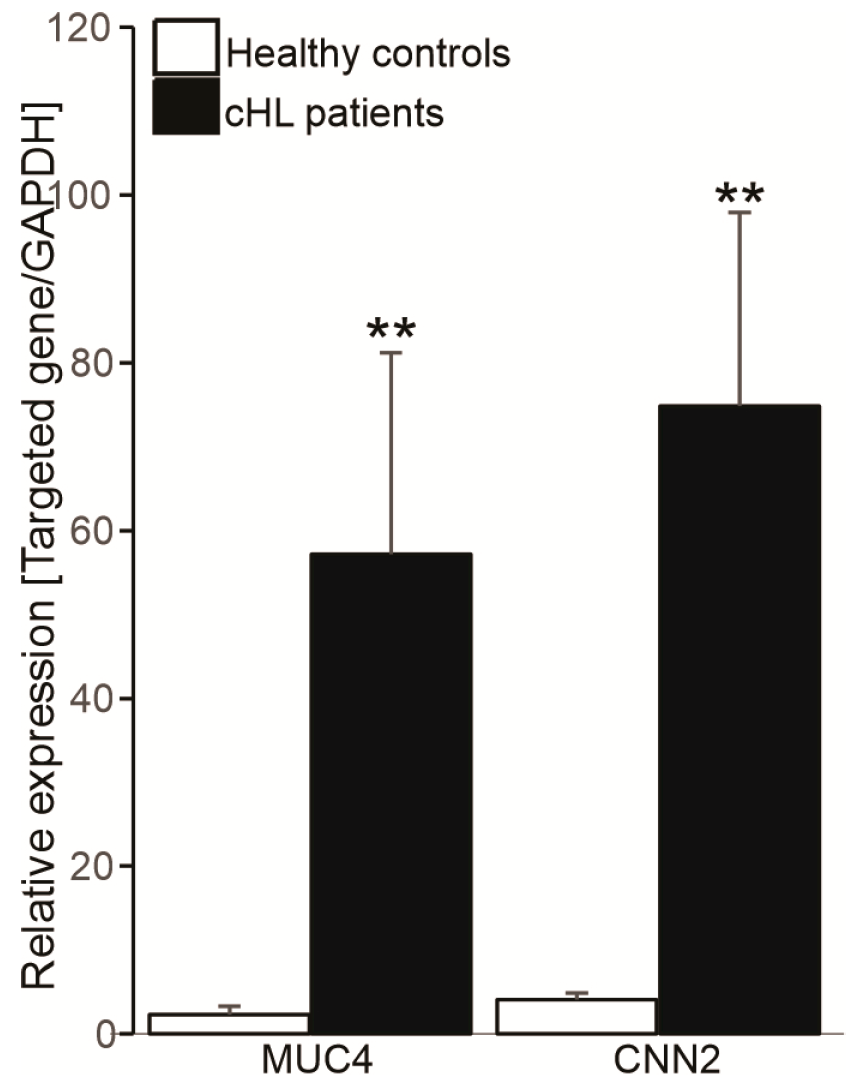
| Characteristics | Normal Value | NSHL (n = 31) | MCHL (n = 21) | LRHL (n = 7) | LDHL (n = 1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 31.17 ± 10.05 | 33.14 ± 15.04 | 52 ± 20.45 | 76 | |
| Sex, Female (n. %) | 13 (40.63) | 12 (54.55) | 1 (14.29) | 0 | |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 3.3–6.6 | 4.67 ± 1.59 | 4.5 ± 1.11 | 5.3 ± 1.37 | 4.6 |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 3.9–5.6 | 5.1 ± 1.48 | 4.78 ± 1.05 | 4.74 ± 0.93 | 6.7 |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 50–110 | 72.64 ± 15.1 | 71.82 ± 12.57 | 82.28 ± 19.3 | 73 |
| Uric acid (µmol/L) | < 420 | 338.39 ± 76.7 | 327.03 ± 76.96 | 303.87 ± 96.48 | 139 |
| Total bilirubin (µmol/L) | 0–21 | 9.45 ± 6.57 | 9.79 ± 3.69 | 8.83 ± 4.78 | 153.8 |
| Direct bilirubin (µmol/L) | 0–7 | 2.3 ± 2.36 | 2.88 ± 1.84 | 3.28 ± 2.76 | 88.7 |
| Indirect bilirubin (µmol/L) | ≤12.7 | 7.02 ± 2.16 | 7.4 ± 3.26 | 7.46 ± 3.04 | 65.1 |
| Total protein (g/L) | 60–80 | 78.62 ± 6.92 | 80.1 ± 6.87 | 85.08 ± 12.59 | 58.3 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 35–52 | 39.3 ± 4.73 | 39.16 ± 5.57 | 38.07 ± 7.7 | 33.6 |
| Globulin (g/L) | 20–35 | 39.8 ± 6.97 | 41.89 ± 8.56 | 56.7 ± 23.19 | 24.7 |
| Ferritin (ng/mL) | 10–300 | 598.26 ± 579.89 | 792.19 ± 794.59 | 888.07 ± 585.78 | 2.4 |
| AST (GOT) (U/L) | 5–40 | 23.7 ± 13.42 | 23.09 ± 14.49 | 30.13 ± 15.92 | 68 |
| ALT (GPT) (U/L) | 7–55 | 34.25 ± 36.06 | 26.11 ± 23.64 | 62.88 ± 49.5 | 55 |
| LDH (U/L) | 0–247 | 325.75 ± 147.53 | 369.32 ± 289.88 | 337.89 ± 268.22 | 297 |
| β2 microglobulin (mg/L) | 0.8–2.4 | 1.97 ± 0.72 | 2.88 ± 1.63 | 4.52 ± 3.64 | 6.02 |
| Erythrocytes (1012 cells/L) | 4.2–5.9 | 4.74 ± 0.52 | 4.55 ± 0.95 | 4.4 ± 0.84 | 2.31 |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 130–180 | 127.77 ± 23.38 | 122.10 ± 23.91 | 127 ± 23.38 | 75 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 42–52 | 40.4 ± 3.85 | 37.8 ± 6.65 | 39 ± 7.24 | 22.9 |
| WBC count (×109/L) | 5–14.5 | 12.16 ± 4.77 | 11.63 ± 5.8 | 14.7 ± 6.6 | 1.31 |
| Neutrophil count (×109/L) | 1.6–7.5 | 9.37 ± 4.52 | 8.15 ± 4.96 | 8.89 ± 6.82 | 0.73 |
| Lymphocyte count (×109/L) | 0.9–3.4 | 1.67 ± 0.56 | 1.67 ± 0.88 | 3.95 ± 5.39 | 0.432 |
| Monocyte count (×109/L) | 0–1.2 | 0.69 ± 0.35 | 0.89 ± 0.36 | 0.7 ± 0.18 | 0.144 |
| Eosinophil count (×109/L) | 0–0.8 | 0.29 ± 0.22 | 0.29 ± 0.29 | 1.32 ± 0.36 | 0 |
| Basophil count (×109/L) | 0–0.3 | 0.07 ± 0.07 | 0.07 ± 0.076 | 0.12 ± 0.15 | 0 |
| Platelet count (×109/L) | 150–400 | 364.84 ± 97.21 | 352.62 ± 124 | 310.29 ± 127.88 | 107 |
| Gene Name | dbSNP ID | Type of Variant | Transcription | Locus | Nucleotide Change | Amino Acid Change | Variant Allele Frequency (%) | Scores of SIFT/PolyPhen2/LRT/MutationTaster/MutationAssessor/FATHMM | SIFT/PolyPhen2/LRT/MutationTaster/MutationAssessor/FATHMM | ExAC/1000 Genome (Frequency) | ClinVar | Alpha Fold Database (Model Confidence) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hodgkin lymphoma-associated gene | ||||||||||||
| NCF1 | rs201802880 | Missense | NM_000265.7 | Exon 4 | c.269G>A | p.R90H | 13.33 | 0.029/0.786/0.629/1/3.335/0.866 | D/P/D/D/M/D | 0.0011/0 | USV | Very high |
| MMP9 | rs139620474 | Missense | NM_004994.3 | Exon 2 | c.150C>T | p.R51C | 3.33 | 0.002/1/0.523/1/4.025/0.417 | D/D/D/D/H/T | 0.000019/0 | Likely pathogenic | Very high |
| VDR | rs121909793 | Missense | NM_000376.3 | Exon 4 | c.239G>A | p.R80Q | 3.33 | 0.012/0.996/0.629/1/4.895/0.985 | D/D/D/A/H/D | 0.00004/0 | Pathogenic | Very high |
| Lymphoma- and/or leukemia-related gene | ||||||||||||
| CNN2 | rs77830704 | Missense | NM_004368.4 | Exon 7 | c.787G>A | p.G263S | 76.67 | 0.001/0.991/0.843/1/2.12/0.952 | D/D/D/D/M/D | 0.0001/0 | Pathogenic | Low |
| CNN2 | rs78386506 | Missense | NM_004368.4 | Exon 7 | c.797G>A | p.R266Q | 63.33 | 0/0.42/0.627/0.991/1.995/0.915 | D/B/D/D/M/D | 0.000085/0 | Pathogenic | Low |
| G6PD | rs76645461 | Missense | NM_001360016.2 | Exon 3 | c.143T>C | p.I48T | 3.33 | 1/0.985/0.843/1/1.365/0.982 | T/D/D/D/L/D | 0.000011/0.000265 | Likely pathogenic | Very high |
| ADAM12 | rs144561426 | Missense | NM_001288973.2 | Exon 9 | c.854T>C | pD285G | 6.67 | 0.054/1/0.843/1/1.975/0.634 | T/D/D/D/M/T | 0.0001/0 | USV | Very high |
| DUOX2 | rs530736554 | Missense | NM_001363711.2 | Exon 12 | c.1295G>A | p.R432H | 10 | 0.038/0.933/0.629/1/2.75/0.842 | D/P/D/D/M/D | 0.0000676/0.000998 | USV | Very high |
| GSS | rs762533768 | Missense | NM_000178.4 | Exon 5 | c.383A>G | p.Y128C | 6.67 | 0.001/1/0.629/1/3.74/0.96 | D/D/D/D/H/D | 0.000004/0 | USV | Very high |
| HAVCR2 | rs184868814 | Missense | NM_032782.5 | Exon 2 | c.245A>G | p.Y82C | 16.67 | 0/1/0.505/1/3.765/0.668 | D/D/D/D/H/T | 0.0038/0.00619 | USV | High |
| KMT2C | rs201834857 | Missense | NM_170606.3 | Exon 8 | c.1042G>A | p.D348N | 20 | 0.027/1/0.438/1/2.62/0.988 | D/D/U/D/M/D | 0.0003/0 | USV | High |
| TCF19 | rs541001159 | Missense | NM_007109.2 | Exon 3 | c.755A>G | p.R252G | 13.33 | 0.009/0.998/0.629/0.626/2.47/0.278 | D/D/D/D/M/T | 0.0001/0.000799 | USV | Very high |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trang, P.T.H.; Trang, D.T.; Huong, P.T.; Nhat, P.V.; Sopjani, M.; Giang, N.H.; Canh, N.X.; Giang, N.V.; Nam, N.T.; Vuong, N.B.; et al. Whole Exome Sequencing for the Identification of Mutations in Bone Marrow CD34+Cells in Hodgkin Lymphoma. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110880
Trang PTH, Trang DT, Huong PT, Nhat PV, Sopjani M, Giang NH, Canh NX, Giang NV, Nam NT, Vuong NB, et al. Whole Exome Sequencing for the Identification of Mutations in Bone Marrow CD34+Cells in Hodgkin Lymphoma. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(11):880. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110880
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrang, Phan Thi Hoai, Do Thi Trang, Pham Thi Huong, Pham Viet Nhat, Mentor Sopjani, Nguyen Hoang Giang, Nguyen Xuan Canh, Nguyen Van Giang, Nguyen Trung Nam, Nguyen Ba Vuong, and et al. 2025. "Whole Exome Sequencing for the Identification of Mutations in Bone Marrow CD34+Cells in Hodgkin Lymphoma" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 11: 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110880
APA StyleTrang, P. T. H., Trang, D. T., Huong, P. T., Nhat, P. V., Sopjani, M., Giang, N. H., Canh, N. X., Giang, N. V., Nam, N. T., Vuong, N. B., Binh, V. D., & Xuan, N. T. (2025). Whole Exome Sequencing for the Identification of Mutations in Bone Marrow CD34+Cells in Hodgkin Lymphoma. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(11), 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47110880





