Obesity Alters the microRNA Expression Profile Related to Metabolic Disorders in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells: Preliminary Results
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Study Participants
2.3. Biochemical Tests
2.4. RNA Extraction and miRNA Detection
2.5. Cross-Validation Procedure
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
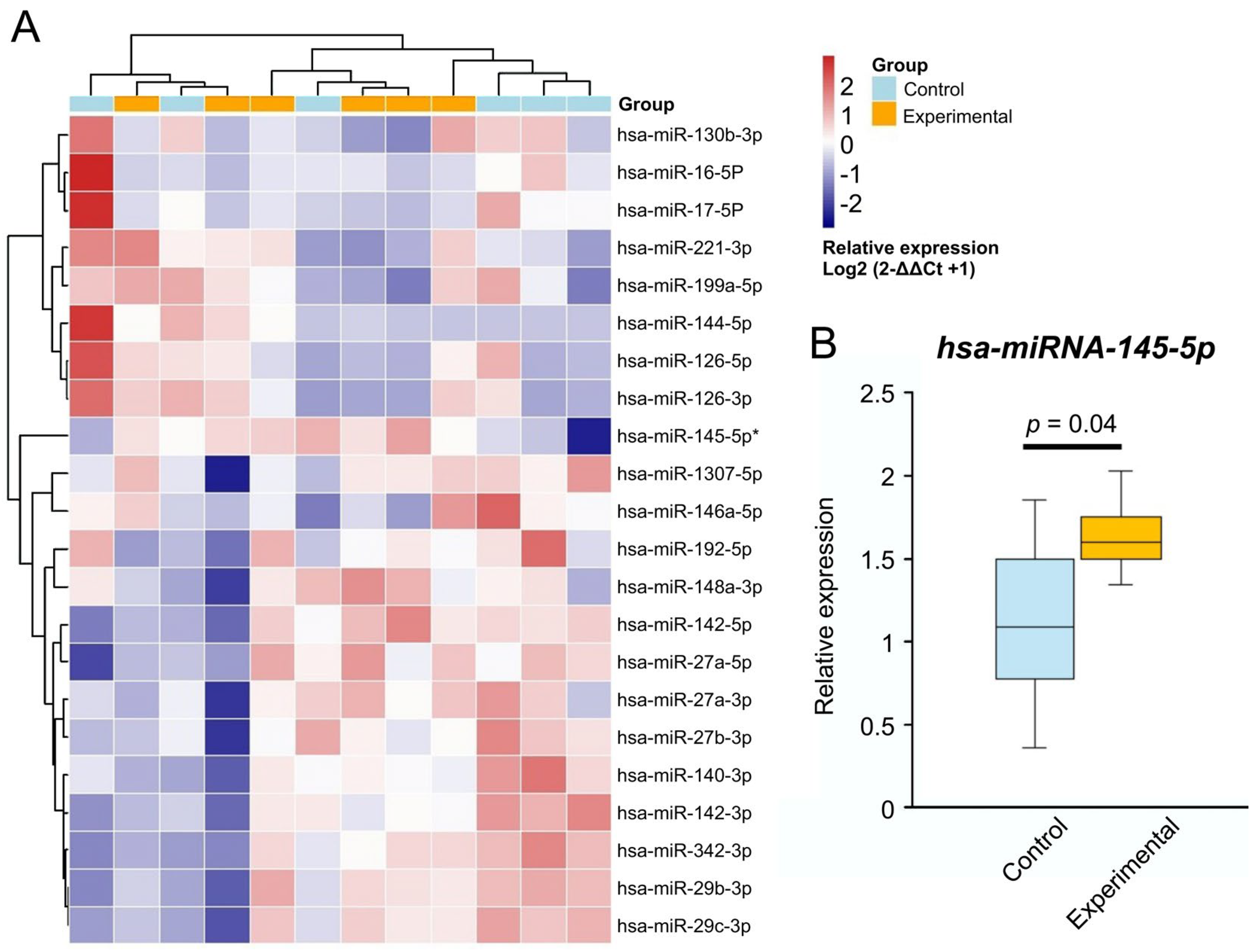
3.2. MiRNA Relative Expression Changes
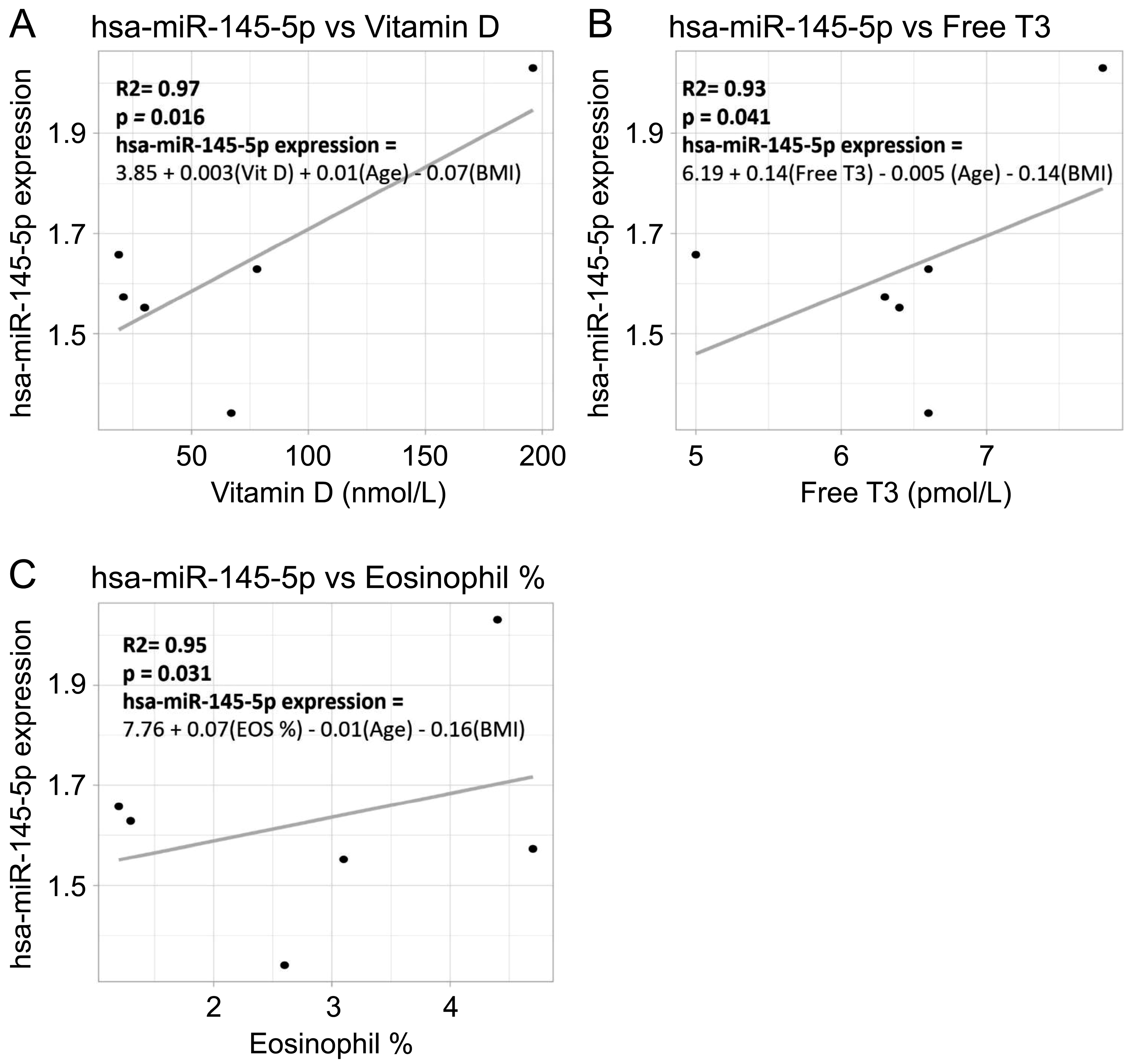
3.3. Correlation Between miRNA Expression and Clinical Parameters
3.4. Cross-Validation Using Open-Source Datasets
3.4.1. Model Reliability and Accuracy Results
3.4.2. The Regression Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| miRNAs | microRNAs |
| KSA | Kingdom of Saudi Arabia |
| BMI | body mass index |
| T2D | type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| LDL | low-density lipoprotein |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| LDH | lactate dehydrogenase |
| T3 | Triiodothyronine |
References
- Alsulami, S.; Baig, M.; Ahmad, T.; Althagafi, N.; Hazzazi, E.; Alsayed, R.; Alghamdi, M.; Almohammadi, T. Obesity prevalence, physical activity, and dietary practices among adults in Saudi Arabia. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1124051. [Google Scholar]
- Habbab, R.M.; Bhutta, Z.A. Prevalence and social determinants of overweight and obesity in adolescents in Saudi Arabia: A systematic review. Clin. Obes. 2020, 10, e12400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Rodriguez, E.; Guillen-Grima, F.; Martí, A.; Brugos-Larumbe, A. Comorbidity associated with obesity in a large population: The APNA study. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 9, 435–447. [Google Scholar]
- Rey-López, J.P.; De Rezende, L.; Pastor-Valero, M.; Tess, B.H. The prevalence of metabolically healthy obesity: A systematic review and critical evaluation of the definitions used. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, J.A.; Milagro, F.I.; Claycombe, K.J.; Schalinske, K.L. Epigenetics in adipose tissue, obesity, weight loss, and diabetes. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 71–81. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, I.; Irmler, M.; Meyer, C.; Sachs, S.; Neff, F.; Hrabě de Angelis, M.; Beckers, J.; Tschöp, M.; Hofmann, S.; Ussar, S. A history of obesity leaves an inflammatory fingerprint in liver and adipose tissue. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campion, J.; Milagro, F.; Martinez, J. Individuality and epigenetics in obesity. Obes. Rev. 2009, 10, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Maamar, M.; Sadler-Riggleman, I.; Beck, D.; McBirney, M.; Nilsson, E.; Klukovich, R.; Xie, Y.; Tang, C.; Yan, W.; Skinner, M.K. Alterations in sperm DNA methylation, non-coding RNA expression, and histone retention mediate vinclozolin-induced epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of disease. Environ. Epigenet. 2018, 4, dvy010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, F.A.; Mall, R.; Iskandarani, A.; Ullah, E.; Samra, T.A.; Cyprian, F.; Parray, A.; Alkasem, M.; Abdalhakam, I.; Farooq, F. Characteristic MicroRNAs linked to dysregulated metabolic pathways in Qatari adult subjects with obesity and metabolic syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 937089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Maurici, J.; Ricart-Jané, D.; Viñas, A.; López-Tejero, M.D.; Eskubi-Turró, I.; Miñarro, A.; Baena-Fustegueras, J.A.; Peinado-Onsurbe, J.; Pardina, E. Circulating miRNAs as biomarkers of subclinical atherosclerosis associated with severe obesity before and after bariatric surgery. Obes. Facts 2024, 17, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandao, B.B.; Lino, M.; Kahn, C.R. Extracellular miRNAs as mediators of obesity-associated disease. J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, S.; Sabeeh, R. Impact of gestational and type 2 diabetes on fetal endothelial cell miRNA expression. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2025, 39, 109106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akman, M.; Budak, Ş.; Kendir, M. Obesity and related health problems: An adult outpatient clinical setting. Marmara Med. J. 2004, 17, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.; Zhao, D. MicroRNA regulation in renal pathophysiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 13078–13092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-Y.; Chou, C.-F.; Giovarelli, M.; Briata, P.; Gherzi, R.; Chen, C.-Y. KSRP and MicroRNA 145 are negative regulators of lipolysis in white adipose tissue. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 2339–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneghan, H.; Miller, N.; McAnena, O.; O’brien, T.; Kerin, M. Differential miRNA expression in omental adipose tissue and in the circulation of obese patients identifies novel metabolic biomarkers. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E846–E850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordes, K.R.; Sheehy, N.T.; White, M.P.; Berry, E.C.; Morton, S.U.; Muth, A.N.; Lee, T.-H.; Miano, J.M.; Ivey, K.N.; Srivastava, D. miR-145 and miR-143 regulate smooth muscle cell fate and plasticity. Nature 2009, 460, 705–710. [Google Scholar]
- Santovito, D.; Mandolini, C.; Marcantonio, P.; De Nardis, V.; Bucci, M.; Paganelli, C.; Magnacca, F.; Ucchino, S.; Mastroiacovo, D.; Desideri, G. Overexpression of microRNA-145 in atherosclerotic plaques from hypertensive patients. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2013, 17, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell, T.; Gomes, A.V. MicroRNAs in the regulation of cellular redox status and its implications in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Redox Biol. 2020, 36, 101607. [Google Scholar]
- Kermani, P.; Hempstead, B. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: A newly described mediator of angiogenesis. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2007, 17, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona-Maurici, J.; Cuello, E.; Ricart-Jané, D.; Miñarro, A.; Kissler, J.J.O.; Baena-Fustegueras, J.A.; Peinado-Onsurbe, J.; Pardina, E. Effect of bariatric surgery in the evolution of oxidative stress depending on the presence of atheroma in patients with morbid obesity. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2020, 16, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, S.D.; Krüger, M.; Willmes, D.M.; Redemann, N.; Wunderlich, F.T.; Brönneke, H.S.; Merkwirth, C.; Kashkar, H.; Olkkonen, V.M.; Böttger, T. Obesity-induced overexpression of miRNA-143 inhibits insulin-stimulated AKT activation and impairs glucose metabolism. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maria, B.; Sophia, V.; Mikhail, L.; Maria, V.; Todosenko, N.; Larisa, L. miRNA Dysregulation of AGE/RAGE Pathway in Metabolic Syndrome: A Novel Analysis Strategy Utilizing miRNA-profiling Data. Gene Expr. 2025, 24, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wu, N.; Leong, M.C.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Z.; Li, R.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Yao, X. miR-145 improves metabolic inflammatory disease through multiple pathways. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 12, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toraih, E.A.; Fawzy, M.S.; Ning, B.; Zerfaoui, M.; Errami, Y.; Ruiz, E.M.; Hussein, M.H.; Haidari, M.; Bratton, M.; Tortelote, G.G. A miRNA-based prognostic model to trace thyroid cancer recurrence. Cancers 2022, 14, 4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadkhoda, S.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. Function of miRNA-145–5p in the pathogenesis of human disorders. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2022, 231, 153780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Díazcouder, A.; Romero-Nava, R.; Del-Río-Navarro, B.E.; Sánchez-Muñoz, F.; Guzmán-Martín, C.A.; Reyes-Noriega, N.; Rodríguez-Cortés, O.; Leija-Martínez, J.J.; Vélez-Reséndiz, J.M.; Villafaña, S. The roles of microRNAs in asthma and emerging insights into the effects of vitamin D3 supplementation. Nutrients 2024, 16, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladel, A.; Khatoon, F.; Khan, M.I.; Alsheweir, A.; Almutairi, M.G.; Almutairi, S.O.; Almutairi, F.K.; Osmonaliev, K.; Beg, M.M.A. Evaluation of miRNA-143 and miRNA-145 expression and their association with Vitamin-D status among obese and non-obese Type-2 Diabetic patients. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2022, 15, 2979–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Lv, Y.; Wang, F.; Kong, X.; Di, W.; Liu, J.; Sheng, Y.; Lv, S.; Ding, G. MiR-27b-3p inhibition enhances browning of epididymal fat in high-fat diet induced obese mice. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesharwani, D.; Karolak, M.; Doucette, C.; Loomis, E.; Su, S.; Brown, A.C. Combined Deletion of miR-27a and miR-27b Enhances Protection Against Diet-Induced Obesity. bioRxiv 2025. bioRxiv:2025.07.21.666011. [Google Scholar]
- Mayr, B.; Montminy, M. Transcriptional regulation by the phosphorylation-dependent factor CREB. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliwinska, A.; Kasinska, M.A.; Drzewoski, J. MicroRNAs and metabolic disorders–where are we heading? Arch. Med. Sci. 2017, 13, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Miller, D.; Yang, Q.; Wu, B. MicroRNA Regulatory Networks as Biomarkers in Obesity: The Emerging Role. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1617, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, T.; Nishino, T.; Baba, O.; Kuwabara, Y.; Nakao, T.; Nishiga, M.; Usami, S.; Izuhara, M.; Sowa, N.; Yahagi, N.; et al. MicroRNA-33 regulates sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 expression in mice. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmas, E.; Venteclef, N.; Caer, C.; Poitou, C.; Cremer, I.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Lacroix-Desmazes, S.; Bayry, J.; Kaveri, S.V.; Clément, K.; et al. T Cell–Derived IL-22 Amplifies IL-1β–Driven Inflammation in Human Adipose Tissue: Relevance to Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2014, 63, 1966–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baelde, H.J.; Eikmans, M.; Doran, P.P.; Lappin, D.W.; de Heer, E.; Bruijn, J.A. Gene expression profiling in glomeruli from human kidneys with diabetic nephropathy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2004, 43, 636–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Deng, X.-L.; Aleteng, Q.-Q.-G.; Li, L.; Zhu, J. Genome-Wide Transcriptome Analysis in Type 2 Diabetes Patients Treated by Sitagliptin. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2022, 15, 1761–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Civit-Urgell, A.; Peña, E.; Bejar, M.T.; Moscatiello, F.; Vilahur, G.; Badimon, L.; Arderiu, G. bFGF rescues dysfunctional properties of adipose-derived stem cells from individuals with type 2 diabetes by modulating their miRNA profile. Diabetologia 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Control | Obese | * p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender Male/Female | 5/1 | 3/3 | - | ||
| Mean | ± SD | Mean * | ± SD | ||
| Age (years) | 27.67 | 5.79 | 33.67 | 9.61 | 0.22 |
| Height (cm) | 163.33 | 12.68 | 162.17 | 9.37 | 0.86 |
| Weight (kg) | 59.17 | 10.40 | 98.33 | 12.11 | 0.00013 |
| BMI | 22.05 | 1.42 | 37.28 | 1.49 | 0.000001 |
| GLU (mmol/L) | 5.06 | 0.71 | 5.31 | 0.65 | 0.54 |
| BUN (nmol/L) | 4.0 | 0.85 | 4.09 | 0.81 | 0.85 |
| Creatinine (µmol/L) | 69 | 16 | 68.60 | 13 | 0.97 |
| Uric acid (µmol/L) | 313 | 73 | 338 | 99 | 0.64 |
| Cholesterol (mmol/L) | 5.10 | 0.79 | 5.52 | 1 | 0.46 |
| TRG (mmol/L) | 0.90 | 0.37 | 1.38 | 0.56 | 0.11 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.58 | 0.27 | 1.46 | 0.34 | 0.48 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 3.38 | 0.71 | 3.71 | 0.84 | 0.48 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 43 | 1.97 | 43.28 | 2.79 | 0.87 |
| Total protein (g/L) | 72.45 | 3.18 | 72.23 | 3.60 | 0.72 |
| LDH (U/L) | 188 | 38 | 166 | 34.60 | 0.34 |
| Amylase (U/L) | 73 | 22 | 67.30 | 19 | 0.64 |
| TSH (µmol/L) | 1.62 | 0.90 | 2.39 | 1.18 | 0.23 |
| Free T3 (pmol/L) | 6.17 | 0.76 | 6.45 | 0.89 | 0.57 |
| Free T4 (pmol/L) | 12.33 | 1.2 | 12.33 | 2 | 1 |
| Vitamin D (nmol/L) | 62.50 | 27 | 68.50 | 0.7 | 0.84 |
| WBC (109/L) | 6.48 | 1.2 | 6.68 | 2 | 0.87 |
| Platelet (109/L) | 275 | 51 | 279 | 37 | 0.88 |
| miRNA | U-Statistic | p-Value | adj_pval | Mean Control | Mean-Obesity | Fold-Change (Obesity/Control) | Direction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-145-5p | 36 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 1.11 | 1.63 | 1.5 | in Obesity |
| hsa-miR-29b-3p | 36 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 1.19 | 1.16 | 1 | no change |
| hsa-miR-29c-3p | 36 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 1.14 | 1.11 | 1 | no change |
| hsa-miR-342-3p | 36 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 1.33 | 1.09 | 0.82 | in Obesity |
| hsa-miR-27a-5p | 36 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 1.42 | 1.9 | 1.3 | in Obesity |
| hsa-miR-142-5p | 36 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 1.15 | 1.47 | 1.3 | in Obesity |
| hsa-miR-142-3p | 36 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 1.2 | 0.91 | 0.75 | in Obesity |
| hsa-miR-1307-5p | 34 | 0.009 | 0.021 | 1.05 | 0.96 | 0.9 | no clear trend |
| hsa-miR-27b-3p | 34 | 0.009 | 0.021 | 1.03 | 0.73 | 0.71 | in Obesity |
| hsa-miR-27a-3p | 34 | 0.009 | 0.021 | 1.08 | 0.91 | 0.84 | in Obesity |
| hsa-miR-148a-3p | 33 | 0.015 | 0.030 | 1.08 | 1.06 | 1 | no change |
| hsa-miR-140-3p | 33 | 0.015 | 0.030 | 1.06 | 0.78 | 0.74 | in Obesity |
| hsa-miR-146a-5p | 32 | 0.026 | 0.045 | 1.05 | 0.99 | 0.9 | no change |
| hsa-miR-221-3p | 31 | 0.041 | 0.062 | 1.08 | 1.13 | 1 | no change |
| hsa-miR-130b-3p | 31 | 0.041 | 0.062 | 1.12 | 0.88 | 0.79 | in Obesity |
| hsa-miR-126-5p | 30 | 0.065 | 0.078 | 1.45 | 1.16 | 0.80 | in Obesity |
| hsa-miR-192-5p | 30 | 0.065 | 0.078 | 1.37 | 0.86 | 0.63 | in Obesity |
| hsa-miR-17-5P | 30 | 0.065 | 0.078 | 1.3 | 0.62 | 0.53 | in Obesity |
| hsa-miR-16-5P | 30 | 0.065 | 0.078 | 1.29 | 0.55 | 0.43 | in Obesity |
| Precision | Recall | F1-Score | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy | 0.83 | 1 | 0.91 |
| Obesity | 1 | 0.8 | 0.89 |
| miRNA | Clinical Variable | Regression Model | Adjusted R2 | p-Value | Significant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-140-3p | CHOL | hsa-miR-140-3p = 3.107 − 0.274*CHOL − 0.018*Age − 0.006*BMI | 0.700 | 0.003 | Yes |
| hsa-miR-140-3p | LDL | hsa-miR-140-3p = 2.776 − 0.340*LDL − 0.015*Age − 0.007*BMI | 0.726 | 0.002 | Yes |
| hsa-miR-142-3p | CREA | hsa-miR-142-3p = 3.806 − 0.023*CREA − 0.018*Age − 0.026*BMI | 0.595 | 0.019 | Yes |
| hsa-miR-142-3p | FREE_T3 | hsa-miR-142-3p = 4.639 − 0.356*FREE_T3 − 0.037*Age − 0.011*BMI | 0.515 | 0.043 | Yes |
| hsa-miR-142-5p | FREE_T4 | hsa-miR-142-5p = 5.042 − 0.291*FREE_T4 − 0.040*Age + 0.037*BMI | 0.579 | 0.011 | Yes |
| hsa-miR-142-5p | MONO | hsa-miR-142-5p = − 0.088 + 0.261*MONO − 0.070*Age + 0.043*BMI | 0.568 | 0.012 | Yes |
| hsa-miR-142-5p | NEUT | hsa-miR-142-5p = 4.226 − 0.040*NEUT − 0.071*Age + 0.040*BMI | 0.412 | 0.047 | Yes |
| hsa-miR-192-5p | CHOL | hsa-miR-192-5p = 3.991 − 0.479*CHOL − 0.010*Age − 0.004*BMI | 0.555 | 0.005 | Yes |
| hsa-miR-192-5p | LDL | hsa-miR-192-5p = 3.345 − 0.567*LDL − 0.004*Age − 0.007*BMI | 0.519 | 0.008 | Yes |
| hsa-miR-27a-3p | CHOL | hsa-miR-27a-3p = 2.651 − 0.252*CHOL − 0.019*Age + 0.008*BMI | 0.527 | 0.011 | Yes |
| hsa-miR-27a-3p | LDL | hsa-miR-27a-3p = 2.321 − 0.303*LDL − 0.015*Age + 0.007*BMI | 0.513 | 0.012 | Yes |
| hsa-miR-27a-5p | CHOL | hsa-miR-27a-5p = 4.415 − 0.676*CHOL − 0.030*Age + 0.058*BMI | 0.315 | 0.037 | Yes |
| hsa-miR-27a-5p | FREE_T3 | hsa-miR-27a-5p = 6.079 − 0.799*FREE_T3 − 0.038*Age + 0.060*BMI | 0.348 | 0.030 | Yes |
| hsa-miR-27a-5p | LDL | hsa-miR-27a-5p = 3.466 − 0.788*LDL − 0.021*Age + 0.054*BMI | 0.274 | 0.048 | Yes |
| hsa-miR-27a-5p | TSH | hsa-miR-27a-5p = 1.125 + 0.673*TSH − 0.035*Age + 0.009*BMI | 0.438 | 0.016 | Yes |
| hsa-miR-27b-3p | LDL | hsa-miR-27b-3p = 2.292 − 0.211*LDL − 0.013*Age − 0.009*BMI | 0.528 | 0.035 | Yes |
| hsa-miR-342-3p | CHOL | hsa-miR-342-3p = 4.916 − 0.487*CHOL − 0.053*Age + 0.017*BMI | 0.515 | 0.023 | Yes |
| hsa-miR-342-3p | LDL | hsa-miR-342-3p = 4.305 − 0.594*LDL − 0.046*Age + 0.014*BMI | 0.520 | 0.022 | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sultan, S.; Maashi, M. Obesity Alters the microRNA Expression Profile Related to Metabolic Disorders in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells: Preliminary Results. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100799
Sultan S, Maashi M. Obesity Alters the microRNA Expression Profile Related to Metabolic Disorders in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells: Preliminary Results. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(10):799. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100799
Chicago/Turabian StyleSultan, Samar, and Marwah Maashi. 2025. "Obesity Alters the microRNA Expression Profile Related to Metabolic Disorders in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells: Preliminary Results" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 10: 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100799
APA StyleSultan, S., & Maashi, M. (2025). Obesity Alters the microRNA Expression Profile Related to Metabolic Disorders in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells: Preliminary Results. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(10), 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100799


_Kim.png)



