The Molecular Signature Related to Local Inflammatory and Immune Response in Canine Cutaneous Hypersensitivity Reactions: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
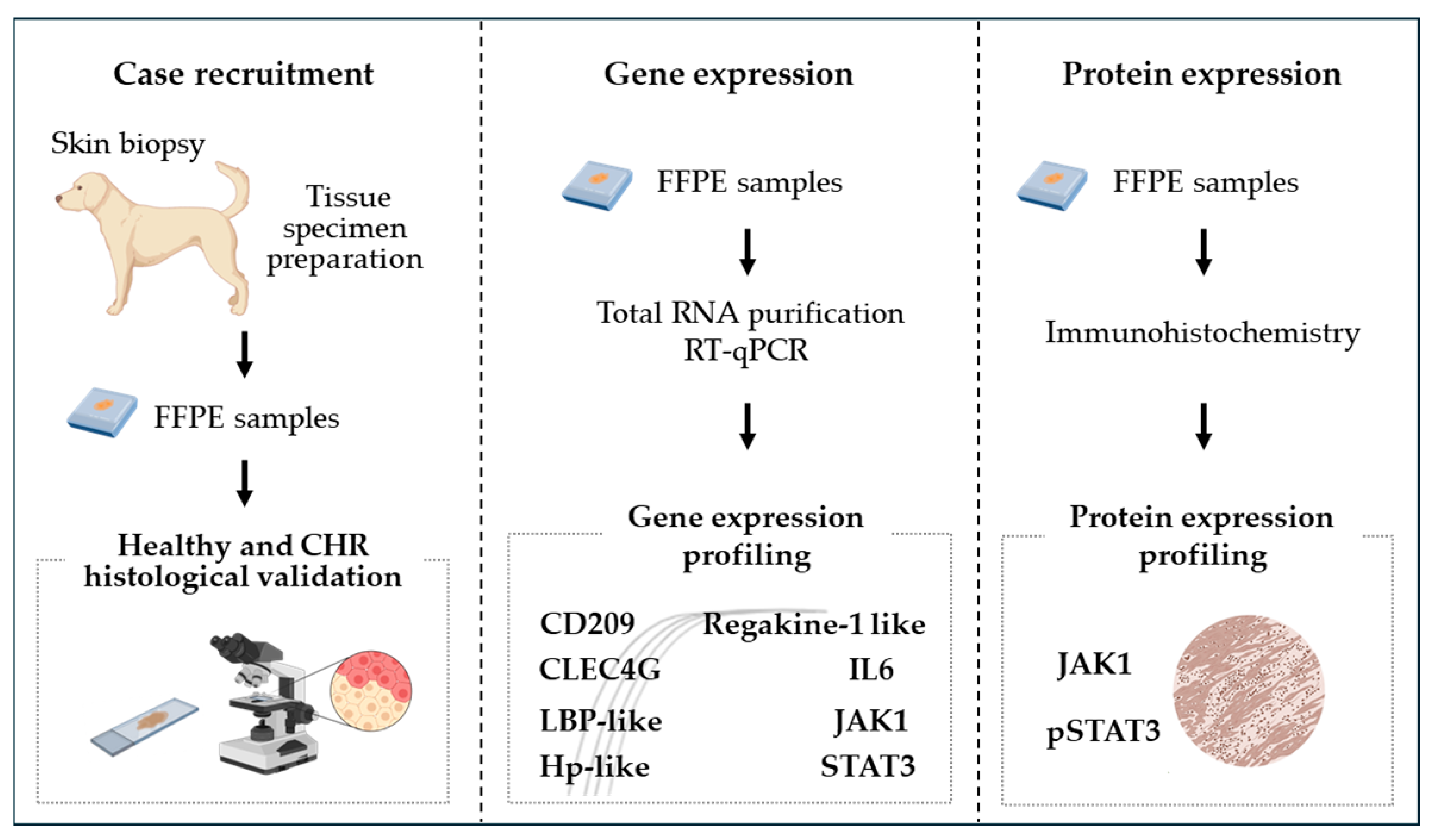
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Objectives and Targeted Gene Selection
- -
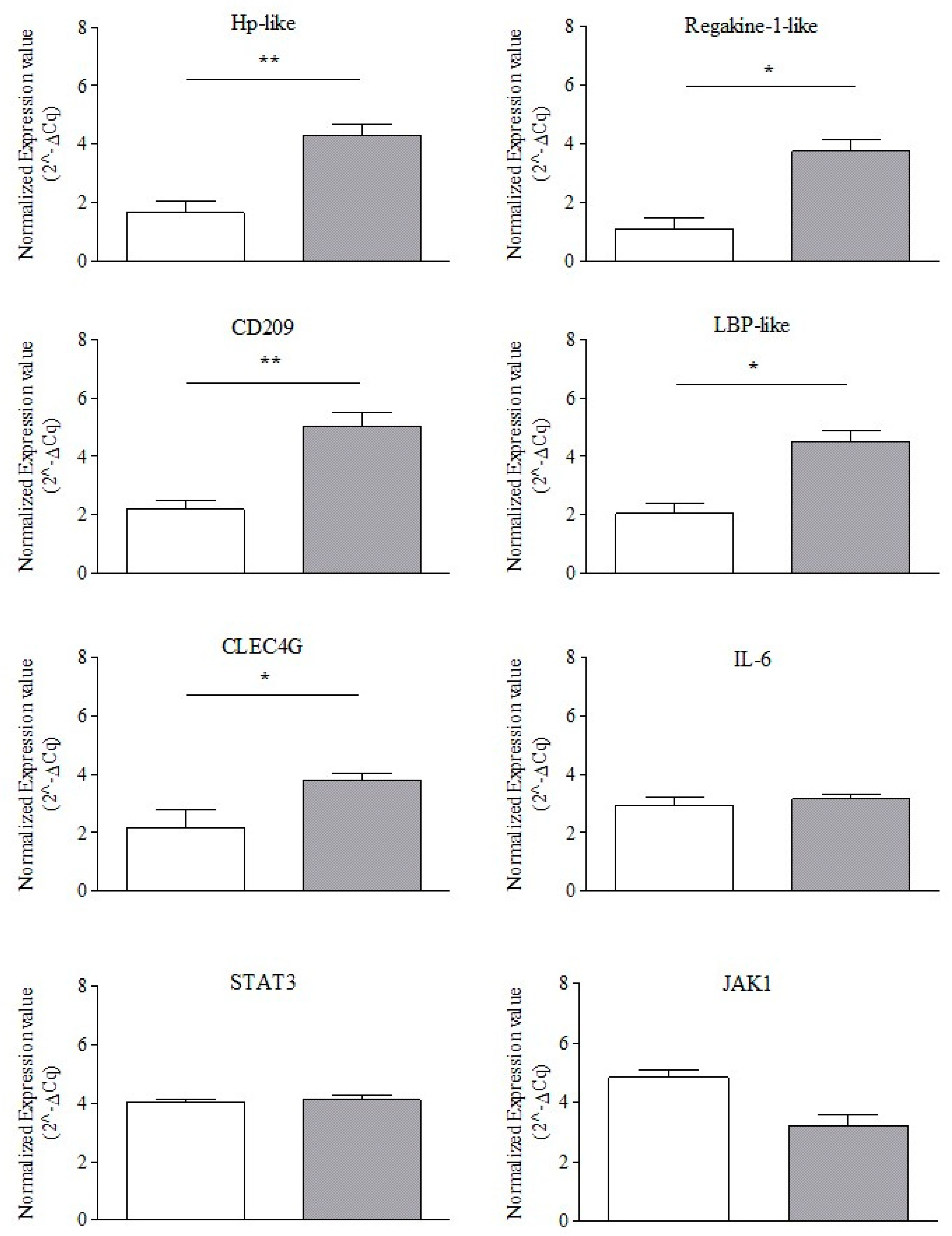
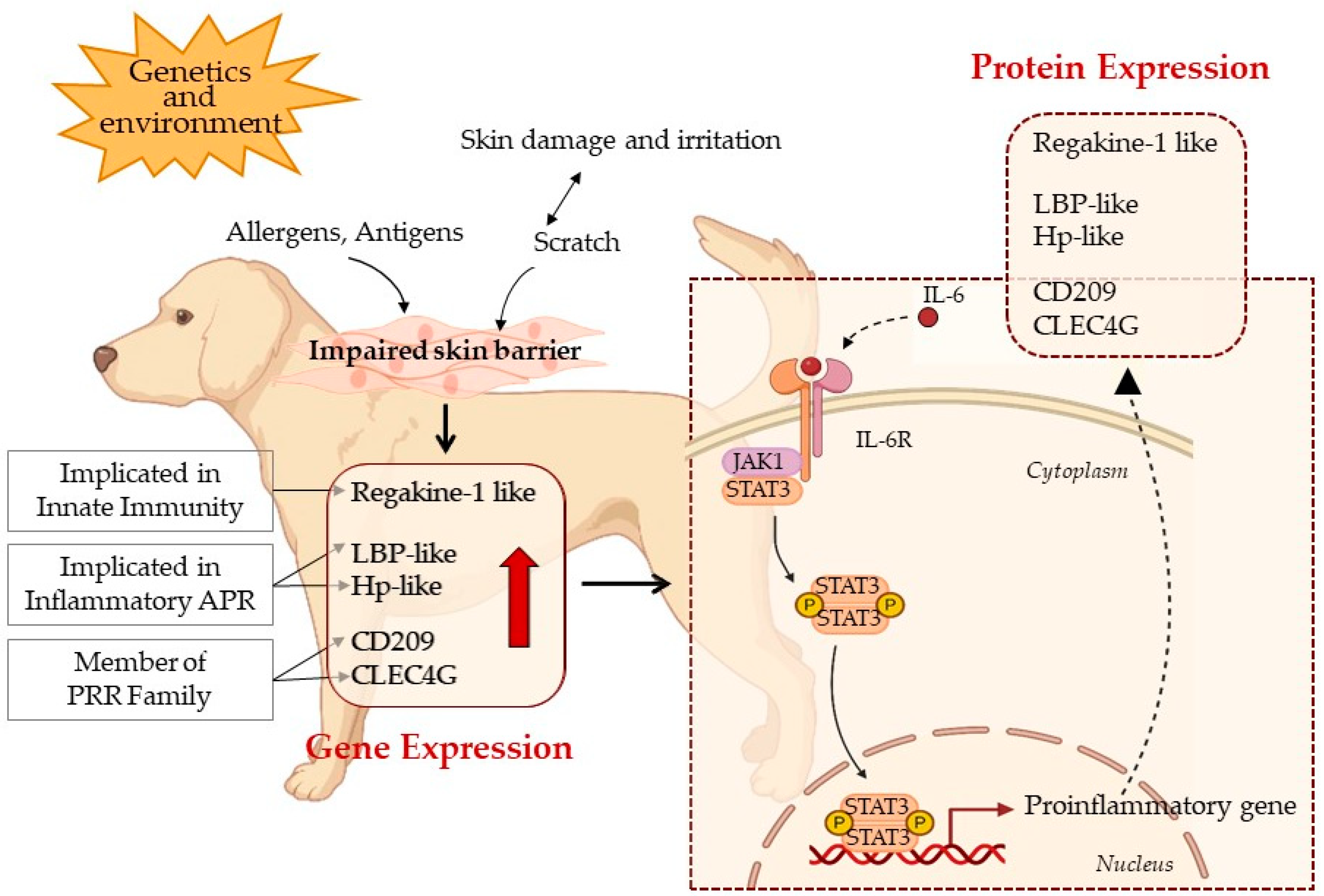
- CD209 and CLEC4G, members of the PRR family;
- -
- IL-6 and the Regakine-1-like chemokine, involved in innate immunity;
- -
- the LBP-like and Hp-like genes, implicated in inflammatory APR;
- -
- JAK1 and STAT3, involved in the signal transduction of diseases associated with immune and inflammatory responses.
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Case Selection
- -
- Tissue samples on section > 0.5 cm2;
- -
- Non-allergic dogs: no history, clinical signs, or microscopic findings suggestive of allergic dermatitis. Biopsy samples were collected from the slink of legs and face;
- -
- Allergic dogs: clinical and histological findings compatible with hypersensitivity reactions. Biopsy samples were collected from the trunk (19/20 dogs) or the skin of the face and legs (1/20 dogs).
- -
- Dogs treated with corticosteroids, antihistamines, immunosuppressive drugs, or Janus kinase inhibitors within 14 days of the biopsy.
2.4. Total RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and qPCR Amplification
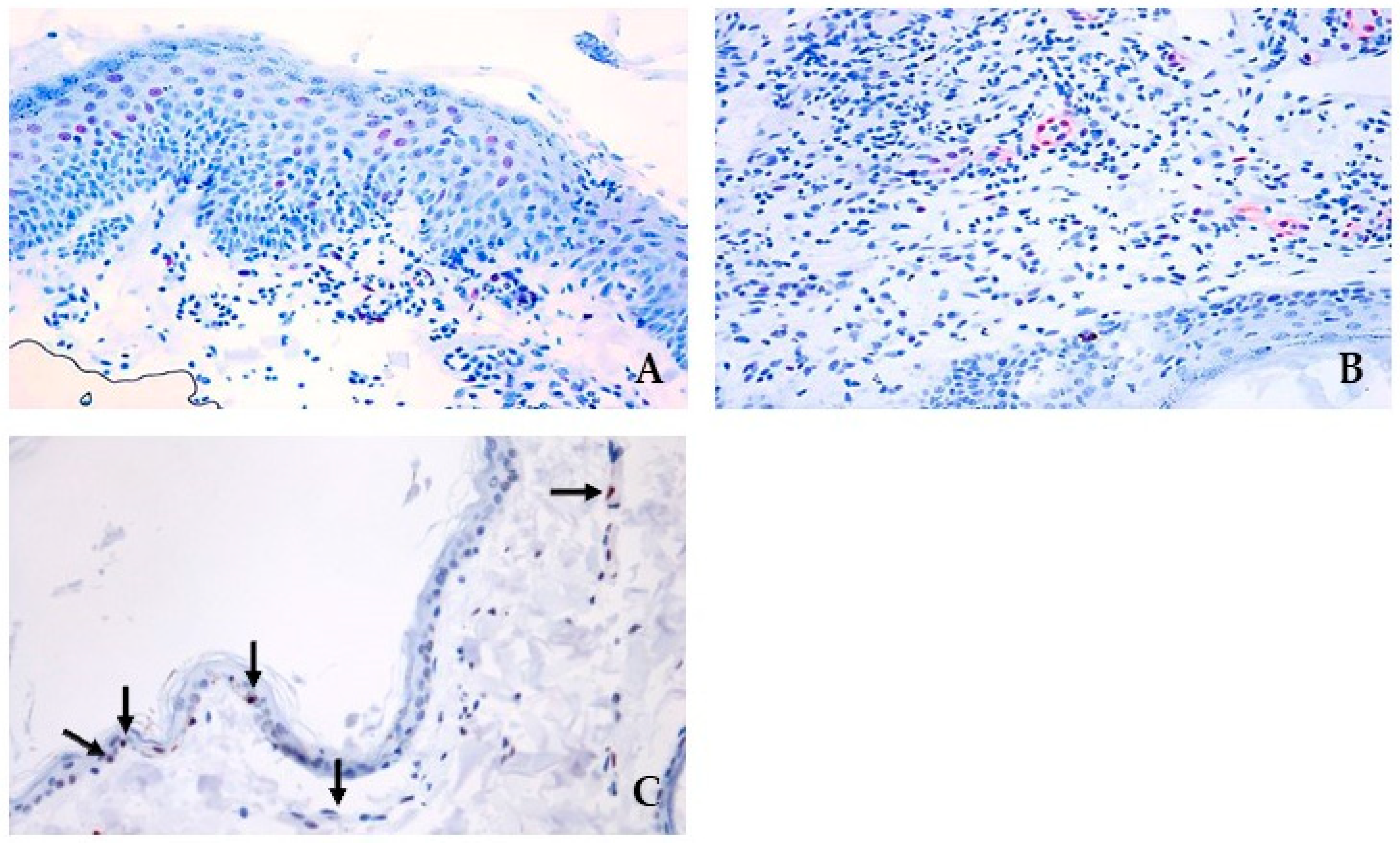
2.5. Immunohistochemical Evaluation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Histological and Clinical Evaluation
3.2. Endogenous Reference Gene Selection and Normalized Gene Expression Profiling
3.3. pSTAT3 and JAK Protein Signalling and Localization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnold, K.A.; Gao, J.; Stein, S.L. A Review of Cutaneous Hypersensitivity Reactions in Infants: From Common to Concerning. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2019, 36, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsella, R.; De Benedetto, A. Atopic Dermatitis in Animals and People: An Update and Comparative Review. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelnest, L. Canine Atopic Dermatitis: A Common, Chronic and Challenging Dermatosis. Vet. Rec. 2021, 188, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero Vega, M.T. New Aspects on Inflammation in Allergic Diseases. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2006, 34, 156–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaresma, J.A.S. Organization of the Skin Immune System and Compartmentalized Immune Responses in Infectious Diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestle, F.O.; Di Meglio, P.; Qin, J.-Z.; Nickoloff, B.J. Skin Immune Sentinels in Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcovich, S.; Maurelli, M.; Gisondi, P.; Peris, K.; Yosipovitch, G.; Girolomoni, G. Pruritus as a Distinctive Feature of Type 2 Inflammation. Vaccines 2021, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, P.M.; Wakefield, J.S. Mechanisms of Abnormal Lamellar Body Secretion and the Dysfunctional Skin Barrier in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 781–791.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hu, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Cong, L.; Wang, Q. Pathogenesis of Allergic Diseases and Implications for Therapeutic Interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.-H.; Shin, H.W.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, H.-W.; Kim, E.-C.; Park, S.H. An Overview of Pathogen Recognition Receptors for Innate Immunity in Dental Pulp. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 794143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seltmann, A.; Troxell, S.A.; Schad, J.; Fritze, M.; Bailey, L.D.; Voigt, C.C.; Czirják, G.Á. Differences in Acute Phase Response to Bacterial, Fungal and Viral Antigens in Greater Mouse-Eared Bats (Myotis Myotis). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, I.; Luque, A.; Aran, J.M. Exploring the Immunomodulatory Moonlighting Activities of Acute Phase Proteins for Tolerogenic Dendritic Cell Generation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamar, P. A New Role of Acute Phase Proteins: Local Production Is an Ancient, General Stress-Response System of Mammalian Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suffredini, A.F.; Fantuzzi, G.; Badolato, R.; Oppenheim, J.J.; O’Grady, N.P. New Insights into the Biology of the Acute Phase Response. J. Clin. Immunol. 1999, 19, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarante-Mendes, G.P.; Adjemian, S.; Branco, L.M.; Zanetti, L.C.; Weinlich, R.; Bortoluci, K.R. Pattern Recognition Receptors and the Host Cell Death Molecular Machinery. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Garlanda, C. Humoral Innate Immunity and Acute-Phase Proteins. New Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturgeon, C.; Fasano, A. Zonulin, a Regulator of Epithelial and Endothelial Barrier Functions, and Its Involvement in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Tissue Barriers 2016, 4, e1251384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaronson, D.S.; Horvath, C.M. A Road Map for Those Who Don’t Know JAK-STAT. Science 2002, 296, 1653–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theilgaard-Monch, K.; Jacobsen, L.C.; Nielsen, M.J.; Rasmussen, T.; Udby, L.; Gharib, M.; Arkwright, P.D.; Gombart, A.F.; Calafat, J.; Moestrup, S.K.; et al. Haptoglobin Is Synthesized during Granulocyte Differentiation, Stored in Specific Granules, and Released by Neutrophils in Response to Activation. Blood 2006, 108, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naryzny, S.N.; Legina, O.K. Haptoglobin as a Biomarker. Biochem. Mosc. Suppl. Ser. B 2021, 15, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A. Zonulin and Its Regulation of Intestinal Barrier Function: The Biological Door to Inflammation, Autoimmunity, and Cancer. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheen, Y.H.; Jee, H.M.; Kim, D.H.; Ha, E.K.; Jeong, I.J.; Lee, S.J.; Baek, H.S.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, K.-J.; Lee, K.S.; et al. Serum Zonulin Is Associated with Presence and Severity of Atopic Dermatitis in Children, Independent of Total IgE and Eosinophil. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 1059–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, A. Zonulin, Regulation of Tight Junctions, and Autoimmune Diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1258, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruys, E.; Toussaint, M.J.M.; Niewold, T.A.; Koopmans, S.J. Acute Phase Reaction and Acute Phase Proteins. J. Zheijang Univ. Sci. B 2005, 6, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, I.-H.; Chung, W.-H.; Wu, P.-C.; Chen, C.-B. JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway in the Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis: An Updated Review. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1068260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Bian, Q.; Rong, D.; Wang, L.; Song, J.; Huang, H.-S.; Zeng, J.; Mei, J.; Wang, P.-Y. JAK/STAT Pathway: Extracellular Signals, Diseases, Immunity, and Therapeutic Regimens. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1110765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfitzner, E.; Kliem, S.; Baus, D.; Litterst, M.C. The Role of STATs in Inflammation and Inflammatory Diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 2839–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Yao, Q.; Gu, X.; Shi, Q.; Yuan, X.; Chu, Q.; Bao, Z.; Lu, J.; Li, L. Evolving Cognition of the JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway: Autoimmune Disorders and Cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, R.; Kershaw, N.J.; Babon, J.J. The Molecular Details of Cytokine Signaling via the JAK/STAT Pathway. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 1984–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damsky, W.; King, B.A. JAK Inhibitors in Dermatology: The Promise of a New Drug Class. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 76, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, L.L.; Urban, J.; King, B.A. Treatment of Recalcitrant Atopic Dermatitis with the Oral Janus Kinase Inhibitor Tofacitinib Citrate. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 73, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbert Ferreira, S.; Berbert Ferreira, R.; Scheinberg, M.A. Atopic Dermatitis: Tofacitinib, an Option for Refractory Disease. Clin. Case Rep. 2020, 8, 3243–3246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandara, M.T.; Reginato, A.; Foiani, G.; De Luca, S.; Guelfi, G. Gene Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors (TIMPs) in Meningiomas of Dogs. Vet. Intern. Medicne 2017, 31, 1816–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guelfi, G.; Casano, A.B.; Menchetti, L.; Bellicci, M.; Suvieri, C.; Moscati, L.; Carotenuto, P.; Santoro, M.M.; Diverio, S. A Cross-Talk between Blood-Cell Neuroplasticity-Related Genes and Environmental Enrichment in Working Dogs. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajik, N.; Frech, M.; Schulz, O.; Schälter, F.; Lucas, S.; Azizov, V.; Dürholz, K.; Steffen, F.; Omata, Y.; Rings, A.; et al. Targeting Zonulin and Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function to Prevent Onset of Arthritis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanghe, J.R.; Delrue, C.; Speeckaert, R.; Speeckaert, M.M. Unlocking the Link between Haptoglobin Polymorphism and Noninfectious Human Diseases: Insights and Implications. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2024, 61, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcellato, I.; Sforna, M.; Lo Giudice, A.; Bossi, I.; Musi, A.; Tognoloni, A.; Chiaradia, E.; Mechelli, L.; Brachelente, C. Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Canine Oral and Cutaneous Melanomas and Melanocytomas: Phenotypic and Prognostic Assessment. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 878949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcellato, I.; Orlandi, M.; Lo Giudice, A.; Sforna, M.; Mechelli, L.; Brachelente, C. Canine Melanocytes: Immunohistochemical Expression of Melanocytic Markers in Different Somatic Areas. Vet. Dermatol. 2023, 34, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guelfi, G.; Capaccia, C.; Santoro, M.M.; Diverio, S. Identification of Appropriate Endogenous Controls for Circulating miRNA Quantification in Working Dogs under Physiological Stress Conditions. Animals 2023, 13, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-P.; Schunck, M.; Kallen, K.-J.; Neumann, C.; Trautwein, C.; Rose-John, S.; Proksch, E. The Interleukin-6 Cytokine System Regulates Epidermal Permeability Barrier Homeostasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 123, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, B.Z.; Stevenson, A.W.; Prêle, C.M.; Fear, M.W.; Wood, F.M. The Role of IL-6 in Skin Fibrosis and Cutaneous Wound Healing. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, C.; Wüstefeld, T.; Assmus, U.; Roskams, T.; Rose-John, S.; Müller, M.; Manns, M.P.; Ernst, M.; Trautwein, C. The IL-6-Gp130-STAT3 Pathway in Hepatocytes Triggers Liver Protection in T Cell-Mediated Liver Injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobotta, S.; Raue, A.; Huang, X.; Vanlier, J.; Jünger, A.; Bohl, S.; Albrecht, U.; Hahnel, M.J.; Wolf, S.; Mueller, N.S.; et al. Model Based Targeting of IL-6-Induced Inflammatory Responses in Cultured Primary Hepatocytes to Improve Application of the JAK Inhibitor Ruxolitinib. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodington, D.W.; Desai, H.R.; Woo, M. JAK/STAT—Emerging Players in Metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshage, H. Cytokines and the Hepatic Acute Phase Response. J. Pathol. 1997, 181, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, S.J.; Kim, D.; Kim, E.J.; Ahn, J.-S.; Choi, E.-J.; Son, E.D.; Lee, T.R.; Choi, E.H. Psychological Stress Deteriorates Skin Barrier Function by Activating 11β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase 1 and the HPA Axis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marek-Jozefowicz, L.; Nedoszytko, B.; Grochocka, M.; Żmijewski, M.A.; Czajkowski, R.; Cubała, W.J.; Slominski, A.T. Molecular Mechanisms of Neurogenic Inflammation of the Skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tengvall, K.; Bergvall, K.; Olsson, M.; Ardesjö-Lundgren, B.; Farias, F.H.G.; Kierczak, M.; Hedhammar, Å.; Lindblad-Toh, K.; Andersson, G. Transcriptomes from German Shepherd Dogs Reveal Differences in Immune Activity between Atopic Dermatitis Affected and Control Skin. Immunogenetics 2020, 72, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, N. C-Type Lectin CD209L/L-SIGN and CD209/DC-SIGN: Cell Adhesion Molecules Turned to Pathogen Recognition Receptors. Biology 2020, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Chen, Y.; Hao, L.; Zhang, Y. DC-SIGN and Immunoregulation. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2006, 3, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in Inflammation, Immunity, and Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwa, D.N.; Pathak, A.; Agrawal, A. IL-6 Regulates Induction of C-Reactive Protein Gene Expression by Activating STAT3 Isoforms. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 146, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Rubia Ortí, J.E.; Platero, J.L.; Benlloch, M.; Franco-Martinez, L.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Escribá-Alepuz, J.; Sancho-Castillo, S. Role of Haptoglobin as a Marker of Muscular Improvement in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis after Administration of Epigallocatechin Gallate and Increase of Beta-Hydroxybutyrate in the Blood: A Pilot Study. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.-C.; Lee, C.-C.; Hsu, C.-M.; Huang, H.-B.; Su, Y.-C. IL-6 Induces Haptoglobin Expression through Activating STAT3 in Human Head and Neck Cancer. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2020, 49, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maresca, B.; Lembo, S.; Ayala, F.; Balato, N.; Di Caprio, R.; Mattii, M.; Raimondo, A.; Schiattarella, M.; Abrescia, P.; Spagnuolo, M.S.; et al. Understanding the Role of Haptoglobin in Psoriasis: Effects of Ultraviolet, B. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 41, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.E.; Schaer, D.J.; Buehler, P.W.; Wilson, M.T.; Reeder, B.J.; Silkstone, G.; Svistunenko, D.A.; Bulow, L.; Alayash, A.I. Haptoglobin Binding Stabilizes Hemoglobin Ferryl Iron and the Globin Radical on Tyrosine Β145. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2013, 18, 2264–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chance, B.; Sies, H.; Boveris, A. Hydroperoxide Metabolism in Mammalian Organs. Physiol. Rev. 1979, 59, 527–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.J.; Møller, H.J.; Moestrup, S.K. Hemoglobin and Heme Scavenger Receptors. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2010, 12, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, J.J.; Gadina, M.; Schreiber, R.D. Cytokine Signaling in 2002. Cell 2002, 109, S121–S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves De Medeiros, A.K.; Speeckaert, R.; Desmet, E.; Van Gele, M.; De Schepper, S.; Lambert, J. JAK3 as an Emerging Target for Topical Treatment of Inflammatory Skin Diseases. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, A.G.A.; Samaka, R.; Elshafey, E.N.; Shehata, W.A.; El Sherbiny, E.G.; Hammam, M.A. Immunohistochemical Study of Janus Kinase 1/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 in Psoriasis Vulgaris. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 12, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alunno, A.; Padjen, I.; Fanouriakis, A.; Boumpas, D.T. Pathogenic and Therapeutic Relevance of JAK/STAT Signaling in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Integration of Distinct Inflammatory Pathways and the Prospect of Their Inhibition with an Oral Agent. Cells 2019, 8, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsch, K.; Holstein, J.; Laurence, A.; Ghoreschi, K. Targeting JAK/STAT Signalling in Inflammatory Skin Diseases with Small Molecule Inhibitors. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 1096–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, D.E.; Darnell, J.E. STATs: Transcriptional Control and Biological Impact. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharadwaj, U.; Kasembeli, M.M.; Robinson, P.; Tweardy, D.J. Targeting Janus Kinases and Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 To Treat Inflammation, Fibrosis, and Cancer: Rationale, Progress, and Caution. Pharmacol. Rev. 2020, 72, 486–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakoli Shirazi, P.; Eadie, L.N.; Page, E.C.; Heatley, S.L.; Bruning, J.B.; White, D.L. Constitutive JAK/STAT Signaling Is the Primary Mechanism of Resistance to JAKi in TYK2-Rearranged Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Lett. 2021, 512, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, R.; Ahrens, K.; Wilkes, R.; Marsella, R. Immunolocalization and Expression of JAK1 and JAK3 in the Skin of Dust Mite-Sensitive Beagle Dogs before and after Allergen Exposure. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, M.D.; Kuo, F.I.; Smith, P.A. Targeting the Janus Kinase Family in Autoimmune Skin Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baluk, P.; Tammela, T.; Ator, E.; Lyubynska, N.; Achen, M.G.; Hicklin, D.J.; Jeltsch, M.; Petrova, T.V.; Pytowski, B.; Stacker, S.A.; et al. Pathogenesis of Persistent Lymphatic Vessel Hyperplasia in Chronic Airway Inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bainbridge, J.; Sivakumar, B.; Paleolog, E. Angiogenesis as a Therapeutic Target in Arthritis: Lessons from Oncology. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 2631–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, S.; Sans, M.; de la Motte, C.; Graziani, C.; West, G.; Phillips, M.H.; Pola, R.; Rutella, S.; Willis, J.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. Angiogenesis as a Novel Component of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Pathogenesis. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 2060–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detmar, M.; Brown, L.F.; Claffey, K.P.; Yeo, K.T.; Kocher, O.; Jackman, R.W.; Berse, B.; Dvorak, H.F. Overexpression of Vascular Permeability Factor/Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Its Receptors in Psoriasis. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, N.M. Late Phase Endothelial Cell Inflammation Is Characterized by Interferon Response Genes and Driven by JAK/STAT, Not NFκB. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2022, 146, 107090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zegeye, M.M.; Lindkvist, M.; Fälker, K.; Kumawat, A.K.; Paramel, G.; Grenegård, M.; Sirsjö, A.; Ljungberg, L.U. Activation of the JAK/STAT3 and PI3K/AKT Pathways Are Crucial for IL-6 Trans-Signaling-Mediated pro-Inflammatory Response in Human Vascular Endothelial Cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 16, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shawky, A.M.; Almalki, F.A.; Abdalla, A.N.; Abdelazeem, A.H.; Gouda, A.M. A Comprehensive Overview of Globally Approved JAK Inhibitors. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, P.R.; King, V.L.; Davis, K.R.; Cosgrove, S.B.; Stegemann, M.R. A Blinded, Randomized Clinical Trial Comparing the Efficacy and Safety of Oclacitinib and Ciclosporin for the Control of Atopic Dermatitis in Client-Owned Dogs. Vet. Dermatol. 2015, 26, 23-e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| CASE | AGE | SEX | BREED |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Control | 6 | F | Jack Russell |
| 2-Control | 3 | M | Mixed breed |
| 3-Control | 5 | M | Mixed breed |
| 4-CHR | 12 | F | Jack Russell |
| 5-CHR | 7 | F | Jack Russell |
| 6-CHR | 13 | M | Cane Corso |
| 7-CHR | 10 | M | Shar Pei |
| 8-CHR | 5 | M | Mixed breed |
| 9-CHR | 7 | M | Chow Chow |
| 10-CHR | 2 | M | Pitbull |
| 11-CHR | 4 | M | Mixed breed |
| 12-CHR | 1 | NA | Jack Russell |
| 13-CHR | 10 | F | Yorkshire terrier |
| 14-CHR | 12 | F | Mixed breed |
| 15-CHR | 16 | M | French bulldog |
| 16-CHR | 6 | F | Dachshund |
| 17-CHR | 12 | M | King Charles Cavalier Spaniel |
| 18-CHR | 9 | M | German shepherd |
| 19-CHR | 1 | M | Pitbull |
| 20-CHR | 6 | F | Maremma sheepdog |
| 21-CHR | 1.5 | F | Poodle |
| 22-CHR | 1.5 | F | Mixed breed |
| 23-CHR | 5 | F | Mixed breed |
| Target Gene | TaqMan | Exon | Amplicon |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actin Beta ACTB-NM_001195845.2 | Cf04931159_m1 | 1–2 | 52 |
| Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase GAPDH-NM_001003142.2) | Cf04419463_gH | 5–6 | 54 |
| Ribosomal Protein S18 RPS1-NM_001048082.1 | Cf02681523_g1 | 3–4 | 160 |
| Cluster of Differentiation 209 CD209-NM_001130832.1 | Cf02638221_g1 | 7–8 | 63 |
| C-Type Lectin Domain Family 4 Member G CLEC4G-XM_005632943.3 | Cf02647953_m1 | 4–5 | 115 |
| Regakine-1-like XM_537721.5 | Cf02644954_m1 | 1–2 | 91 |
| Haptoglobin-like Hp-like-XM_845903.5 | Cf02630391_m1 | 3–4 | 71 |
| Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein-like LBP-lik-XM_017342134.1 | Oc06724131_m1 | 7–8 | 76 |
| Interleukin-6 IL-6-NM_001003301.1 | Cf02624153_m1 | 4–5 | 66 |
| Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 STAT3-XM_005624457.3 | Cf02727924_m1 | 147 |
| Antigen | Clone | Antigen Retrieval | Dilution | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JAK1 | Rabbit mAb | Tris-Edta buffer, pH 9.0 | 1:400 | Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA |
| pSTAT3 | Rabbit mAb | Tris-Edta buffer, pH 9.0 | 1:100 | Cell Signaling Technology |
| Clinical Diagnosis | Localization of Lesions | Inflammation Pattern and Cellularity | Epidermis | Additional Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Control | None | None | None | None |
| 2-Control | None | None | None | None |
| 3-Control | None | None | None | None |
| 4-CHR | Back | Perivascular mast cells, fewer eosinophils, lymphocytes and plasma cells | Moderate, irregular hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis | Moderate dermal edema |
| 5-CHR | Ventrum, Axillae | Perivascular mast cells, fewer lymphocytes and occasional eosinophils | Severe, irregular hyperplasia with spongiosis | Subepidermal edema and lymphocytic exocytosis |
| 6- CHR | Back | Perivascular mast cells, eosinophils, plasma cells and lymphocytes | Severe, irregular hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis | Multifocal moderate dermal edema |
| 7-CHR | Back | Perivascular mast cells, fewer eosinophils, lymphocytes | Moderate, irregular hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis | Diffuse dermal edema |
| 8-CHR | Ventrum, thighs | Perivascular mast cells, lymphocytes and rare eosinophils and neutrophils | Moderate, irregular hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis | Subepidermal edema |
| 9-CHR | Multifocal, predominantly back | Perivascular mast cells, lymphocytes, plasma cells rare eosinophils | Severe hyperkeratosis | Moderate dermal edema |
| 10-CHR | Multifocal, predominantly ventrum and thighs | Perivascular mast cells, lymphocytes, plasma cells rare eosinophils | Moderate and irregular hyerplasia and hyperkeratosis | Subepidermic fibrosis |
| 11-CHR | Back | Perivascular mast cells, eosinophils, lymphocytes | Moderate and irregular hyerplasia and hyperkeratosis | |
| 12-CHR | Ventrum, thighs | Perivascular to intestitial mast cells, eosinophils. Rare lymphocytes and neutrophils | Mild, regular hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis | Moderate dermal edema, ulceration and crusts |
| 13-CHR | Dorsal part of the neck and thorax | Perivascular mast cells, lymphocytes and rare eosinophils | Mild, regular hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis | Severe edema with microhemorrages |
| 14-CHR | Ventrum, thighs | Perivascular to intestitial mast cells, eosinophils. Occasional lymphocytes and plasma cells. | Severe, irregular hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis | Severe dermal edema |
| 15-CHR | Multifocal, predominantly ventral | Perivascular mast cells, lymphocytes, plasma cells rare eosinophils | Severe, irregular hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis | Epidermal spongiosis with lymphocytic exocytosis; mural folliculitis |
| 16-CHR | Interdigital spaces, face, abdomen | Perivascular mast cells, lymphocytes, plasma cells | Moderate and irregular hyerplasia and basket-wave hyperkeratosis | Moderate edema and chronic Periadenitis |
| 17-CHR | Back, limbs, nose | Perivascular to intestitial mast cells, eosinophils, lymphocytes and rare plasma cells | Mild, regular hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis | |
| 18-CHR | Abdomen, thighs, hindlimbs | Perivascular to intestitial mast cells, eosinophils. Occasional lymphocytes, plasma cells and neutrophils | Mild, regular hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis | Lymphocytic exocytosis |
| 19-CHR | Multifocal, predominantly ventral | Perivascular mast cells, lymphocytes, plasma cells and occasional eosinophils | Mild, regular hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis | Intraepidermal pustules |
| 20-CHR | Back, thorax and abdomen | Perivascular mast cells, lymphocytes and rare eosinophils | Mild, regular hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis | Superficial edema |
| 21-CHR | Abdomen | Perivascular mast cells and lymphocytes | Mild, irregular hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis | Mild superficial edema |
| 22-CHR | Abdomen | Perivascular mast cells and lymphocytes | Mild, regular hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis | Mild superficial edema |
| 23-CHR | Ventrum, thighs | Perivascular to intestitial mast cells, eosinophils and histiocytes | Severe, irregular hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis | Severe dermal edema |
| ALGORITHMS | EC RANK | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Delta Ct | ACTB | GAPDH | RPS18 |
| BestKeeper | GAPDH | ACTB | RPS18 |
| NormFinder | ACTB | GAPDH | RPS18 |
| GeNorm | ACTB | GAPDH | RPS18 |
| RefFinder comprehensive ranking | ACTB | GAPDH | RPS18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Capaccia, C.; Ciancabilla, F.; Porcellato, I.; Brachelente, C.; Zerani, M.; Maranesi, M.; Guelfi, G. The Molecular Signature Related to Local Inflammatory and Immune Response in Canine Cutaneous Hypersensitivity Reactions: A Preliminary Study. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 9162-9178. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46080542
Capaccia C, Ciancabilla F, Porcellato I, Brachelente C, Zerani M, Maranesi M, Guelfi G. The Molecular Signature Related to Local Inflammatory and Immune Response in Canine Cutaneous Hypersensitivity Reactions: A Preliminary Study. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2024; 46(8):9162-9178. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46080542
Chicago/Turabian StyleCapaccia, Camilla, Francesco Ciancabilla, Ilaria Porcellato, Chiara Brachelente, Massimo Zerani, Margherita Maranesi, and Gabriella Guelfi. 2024. "The Molecular Signature Related to Local Inflammatory and Immune Response in Canine Cutaneous Hypersensitivity Reactions: A Preliminary Study" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 46, no. 8: 9162-9178. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46080542
APA StyleCapaccia, C., Ciancabilla, F., Porcellato, I., Brachelente, C., Zerani, M., Maranesi, M., & Guelfi, G. (2024). The Molecular Signature Related to Local Inflammatory and Immune Response in Canine Cutaneous Hypersensitivity Reactions: A Preliminary Study. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 46(8), 9162-9178. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46080542











