Follow-Up Study of 17-β Estradiol, Prolactin and Progesterone with the Kinetics and Prevalence of T. gondii Infection in Pregnant Women
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Elimination Criteria
2.5. Questionnaire
2.6. Diagnostic Laboratorio
2.6.1. Immunoenzyme Assay (ELISA) for Anti-Toxoplasma IgG and IgM
2.6.2. Immunoenzyme Assay (ELISA) for Serum Levels of 17β-Estradiol, Prolactin and Progesterone
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Risk Factors and Sociodemographic Features
Clinical Features
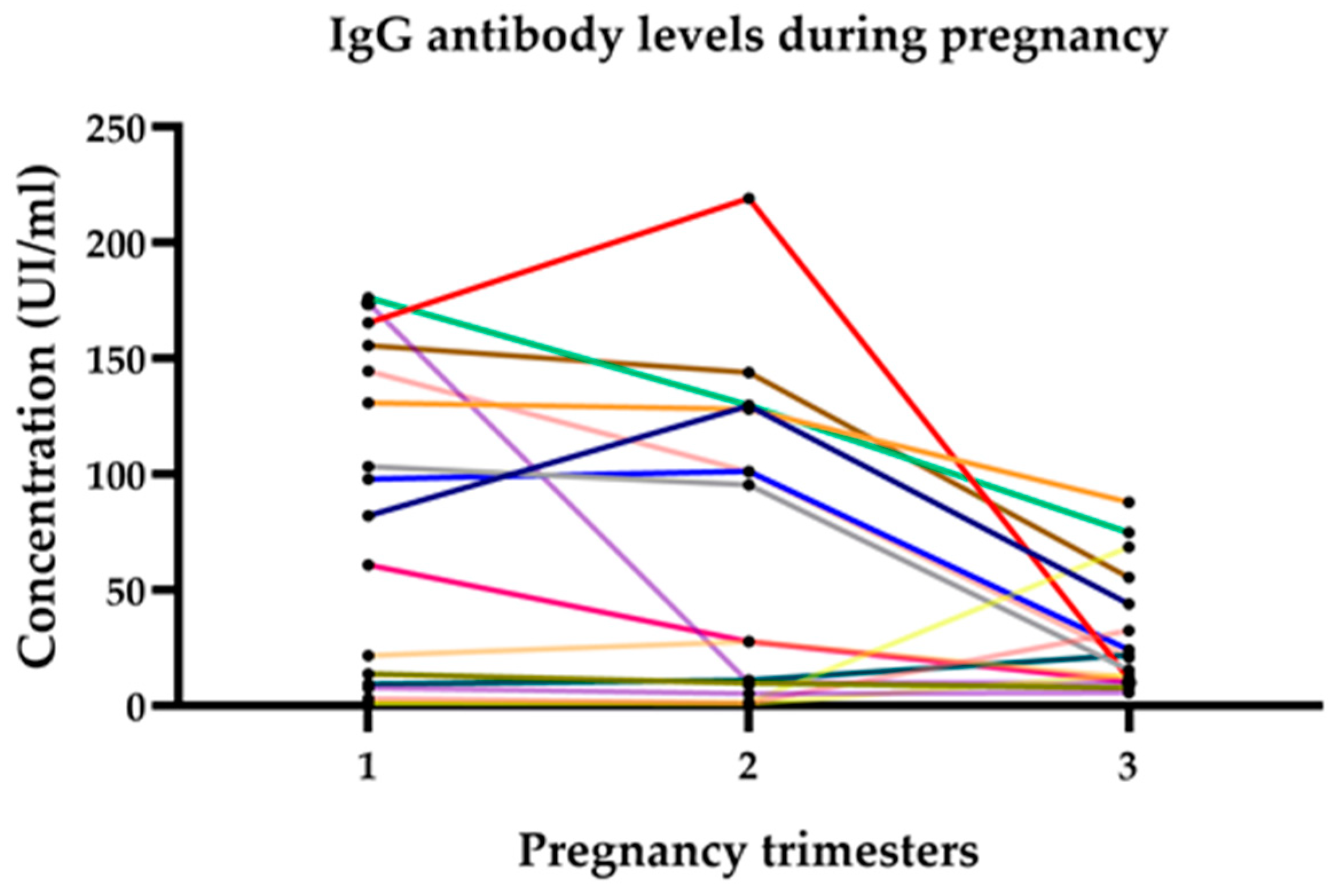
3.2. Prevalence of Anti-Toxoplasma Antibodies
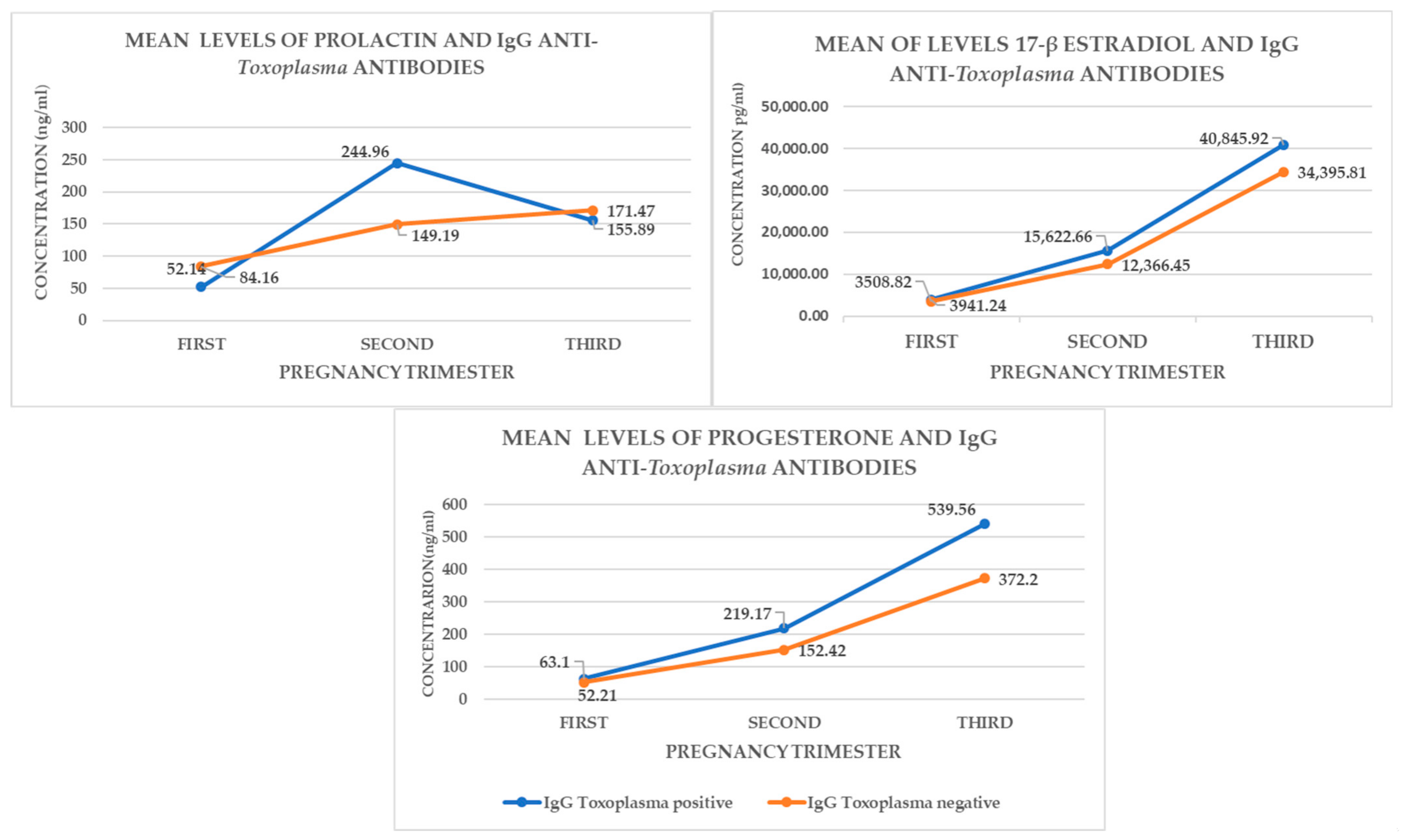
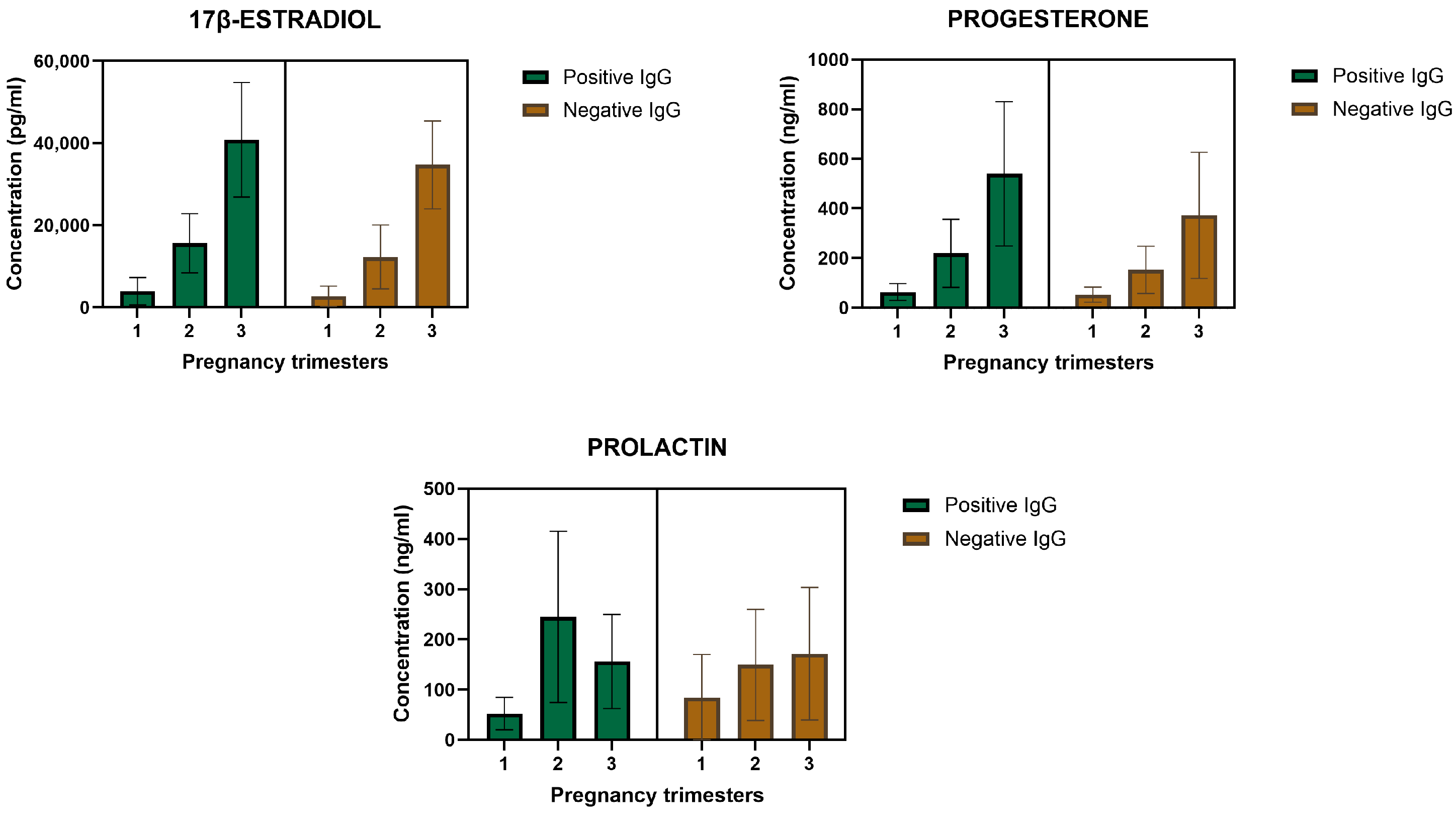
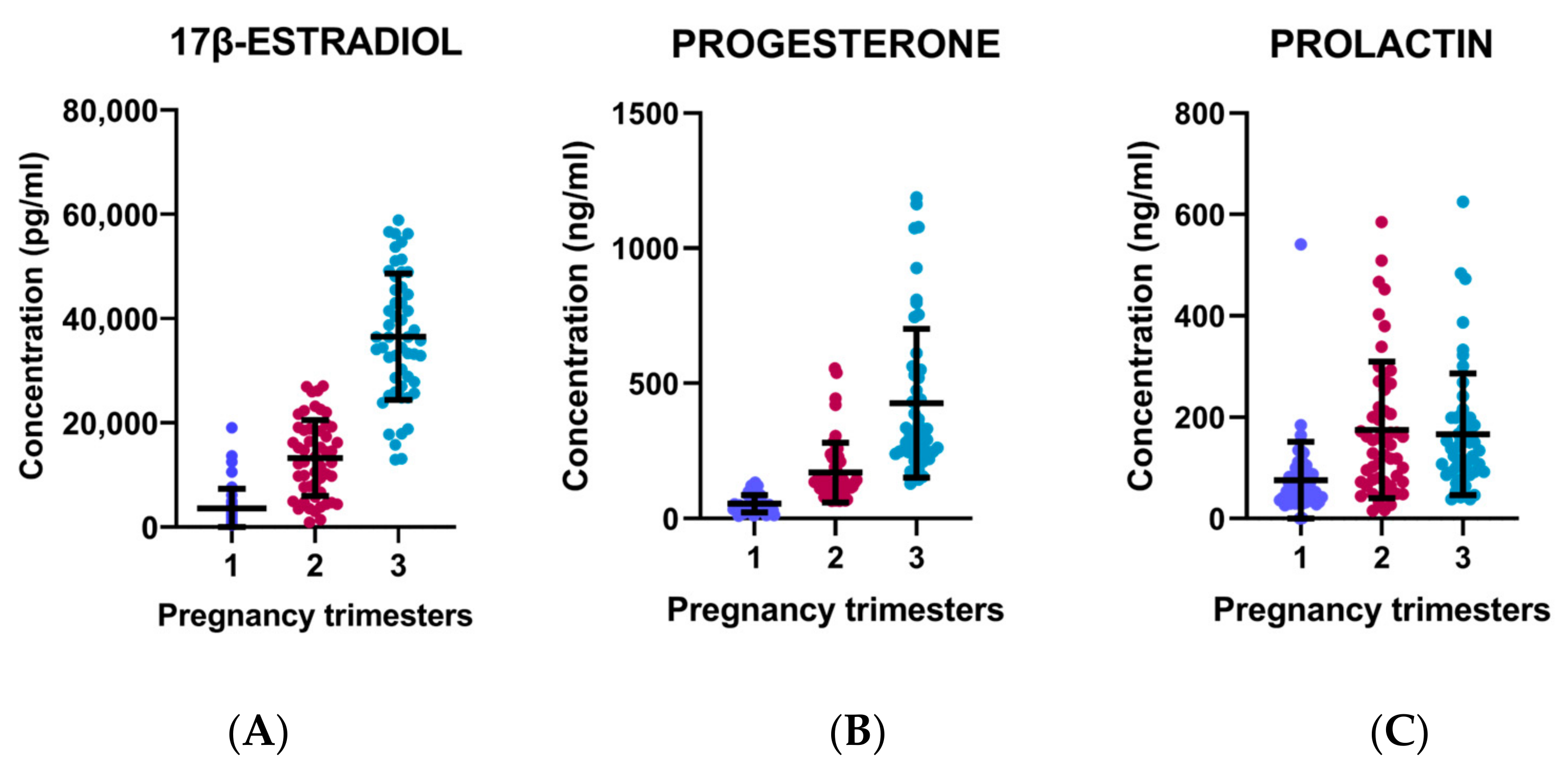
3.3. Hormonal Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galván-Ramírez, M.L.; Mondragón-Flores, R. Toxoplasmosis Humana. ECORFAN-México. 2017. Available online: https://www.ecorfan.org/libros/BOOK_TOXOPLASMOSIS.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2017).
- Díaz, L.; Zambrano, B.; Chacón, G.; Rocha, A.; Díaz, S. Toxoplasmosis y embarazo. Rev. Obstet. Ginecol. Venez. 2010, 70, 190–205. [Google Scholar]
- Galván-Ramírez, M.d.L.; Troyo, R.; Roman, S.; Calvillo-Sanchez, C.; Bernal-Redondo, R. A systematic review and meta-analysis of T. gondii infection among the Mexican population. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, K.M.; Holfels, E.; Roizen, N.; Swisher, C.; Mack, D.; Remington, J.; Withers, S.; Meier, P.; McLeod, R.; Toxoplasmosis Study Group. Risk factors for T. gondii infection in mothers of infants with congenital toxoplasmosis: Implications for prenatal management and screening. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol 2005, 192, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matas Andreu, L. Toxoplasmosis: Diagnóstico serológico en las gestantes. Control Calidad SEIMC. Servicio de Microbiología. Hosp. Ger. Trias I Pujol. 2015, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Guerra-Sanches, F.; Norberg, A.N.; Covarrubias-Loayza, E.A.; Aguillar-Uriarte, M.A.; Madeira-Oliveira, J.T.; Serra-Freire, N.M. Toxoplasmosis aguda en embarazadas asintomáticas de Rio de Janeiro, Brasil. Rev. Med. Hered. 2014, 25, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Esquivel, C.; Sifuentes-Álvarez, A.; Narro-Duarte, S.G.; Estrada-Martínez, S.; Díaz-García, J.H.; Liesenfeld, O.; Martínez-García, S.A.; Canales-Molina, A. Seroepidemiology of T. gondii infection in pregnant women in a public hospital in northern Mexico. BMC Infect Dis. 2006, 6, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galván Ramírez, M.d.l.L.; Soto Mancilla, J.L.; Velasco Castrejón, O.; Pérez Medina, R. Incidence of anti-Toxoplasma antibodies in women with high-risk pregnancy and habitual abortions. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 1995, 28, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vela-Amieva, M.; Cañedo-Solares, I.; Gutierrez-Castrellon, P.; Perez-Andrade, M.; Gonzalez-Contreras, C.; Ortíz-Cortés, J.; Ortega-Velazquez, V.; Galvan-Ramirez, M.D.L.L.; Ruiz-García, M.; Saltigeral-Simentel, P.; et al. Short report: Neonatal screening pilot study of T. gondii congenital infection in Mexico. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 72, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrios, P.; Barloco, A.L.; Sayagués, B.; Giachetto, G. Infección de transmisión vertical por T. gondii: Seguimiento de los hijos de mujeres con primoinfección en una institución de asistencia médica colectiva; 2010–2015. Arch. Pediatr. Urug. 2016, 87, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J.; Zhang, R.; Xie, Y.; Wang, L.; Ge, K.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y. Estradiol Attenuates the Severity of Primary T. gondii Infection-Induced Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes through the Regulation of Tregs in a Dose-Dependent Manner. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, M.; Magalhães Silva, T.; Brito, C.; Teixeira, N.; Roberts, C.W. How does toxoplasmosis affect the maternal-foetal immune interface and pregnancy? Parasite Immunol. 2019, 41, e12606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, F.; Fenizia, C.; Introini, A.; Zavatta, A.; Scaccabarozzi, C.; Biasin, M.; Savasi, V. The pathophysiological role of estrogens in the initial stages of pregnancy: Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications for pregnancy outcome from the periconceptional period to end of the first trimester. Hum. Reprod. Update 2023, 29, 699–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galván-Ramírez, M.d.L.; Gutiérrez-Maldonado, A.F.; Verduzco-Grijalva, F.; Jiménez, J.M. The role of hormones on Toxoplasma gondii infection: A systematic review. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galván-Ramírez, M.L.; Gutiérrez-Maldonado, A.F.; Dueñas-Jiménez, J.M.; Rodríguez-Pérez, L.R.; Troyo-Sanromán, R. Effect of 17β-estradiol and progesterone on astrocytes infected with Toxoplasma. J. Adv. Parasitol. 2016, 3, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galván-Ramírez, M.L.; Ramírez De Arellano, A.; Rodríguez-Pérez, L.R.; Lopez-Pulido, E.I.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F.; Pereira-Suárez, A.L. Hormonal modulation of Toxoplasma gondii infection: Regulation of hormonal receptors and cytokine production in THP-1 cells. Exp. Parasitol. 2019, 204, 107721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira-Suárez, A.L.; Galván-Ramírez, M.L.; Rodríguez-Pérez, L.R.; López-Pulido, E.I.; Hernández-Silva, C.D.; Ramírez-López, I.G.; Morales Amaya, G.V.; Lopez Cabrera, L.D.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F.; Ramírez-de-Arellano, A. 17β-estradiol modulates the expression of hormonal receptors on THP-1 T. gondii-infected macrophages and monocytes in an AKT and ERK-dependent manner. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol 2022, 247, 111433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Han, Q.; Liu, Q. Role of an estradiol regulatory factor-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (HSD) in Toxoplasma gondii infection and pathogenicity. J. Steroid Biochem. Molec. Biol. 2017, 174, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, P.; Wang, J.; Jin, H.; Song, X.; Yan, J.; Kang, Y.; Zhao, L.; An, X.; Du, X.; Chen, X.; et al. Induction of regulatory T cells by physiological level estrogen. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 2, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Warid, H.S.; Al-Qadhi, B.N. Evaluation of progesterone and estrogen hormonal levels in pregnant women with toxoplasmosis. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2012, 91, 515–519. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, C.M.; Silva, T.M.; Castro, M.; Wyrwas, W.; Oliveira, B.M.; Fonseca, B.; Oliveira, P.W.; Roberts, C.; Teixeira, N.; Borges, M. T. gondii infection reduces serum progesterone levels and adverse effects at the maternal-fetal interface. Parasite Immunol. 2019, 42, e12690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhim, R.A.; AL-awadi, H.M. Changes in Testosterone, Progesterone, and Prolactin Levels in Pregnant Women with Chronic Toxoplasmosis. Med. J. Babylon 2013, 10, 699–708. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanain, M.A.; Elfadaly, H.A.; Abd El Wahab, W.M.; Abo El-Maaty, A.M. Comparative hormonal and immunoglobulin profiles of aborted women with or without toxoplasmosis. J. Pregnancy Reprod. 2018, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Fu, Y.; Liu, J.; Xue, Y.; Liu, Q. Progesterone Can Directly Inhibit the Life Activities of T. gondii In Vitro through the Progesterone Receptor Membrane Component (PGRMC). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadpour, A.; Keshavarz, H.; Mohebali, M.; Salimi, M.; Teimouri, A.; Shojaee, S. The relation of serum prolactin levels and Toxoplasma infection in humans. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2018, 12, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzitko, K.; Lawnicka, H.; Gatkowska, J.; Dziadek, B.; Komorowski, J.; Długońska, H. Inhibitory effect of prolactin on Toxoplasma proliferation in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with hyperprolactinemia. Parasite Immunol. 2012, 34, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J. Serum Prolactin Levels and Toxoplasma Infection: A Prospective Observational Study. Int. JPCR 2021, 13, 321–328. [Google Scholar]
- Villa, A.; Rizzi, N.; Vegeto, E.; Ciana, P.; Maggi, A. Estrogen accelerates the resolution of inflammation in macrophagic cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.J. The prolactin and growth hormone families:-specific hormones/cytokines at the maternal-fetal interface. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2004, 2, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussien, J.H.; Al-Aaraji, M.; Aljorani, R.H. Study the Effect of Acute Toxoplasmosis Infection on Some Hormones and thePhagocytic Activity of Neutrophils in Pregnant and Non-pregnant Women Before and After Treatment. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2015, 4, 459–465. [Google Scholar]
| N | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Standard Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1T Toxoplasma IgG UI/mL | 52 | 0.86830 | 176.35000 | 27.11175 | 53.25078 |
| 2T Toxoplasma IgG UI/mL | 52 | 0.83000 | 219.33000 | 23.05660 | 49.10734 |
| 3T Toxoplasma IgG UI/mL | 52 | 0.83000 | 111.67000 | 12.96396 | 24.42573 |
| 1T Toxoplasma IgM UI/mL | 52 | 0.04477 | 1.43461 | 0.16810 | 0.21263 |
| 2T Toxoplasma IgM UI/mL | 52 | 0.01684 | 0.46863 | 0.14868 | 0.09057 |
| 3T Toxoplasma IgM UI/mL | 52 | 0.05472 | 0.48979 | 0.14377 | 0.09230 |
| ESTRADIOL 1T pg/mL | 52 | 376.72512 | 19,033.90000 | 3625.24431 | 3722.97799 |
| ESTRADIOL 2T pg/mL | 52 | 938.72444 | 27,051.50000 | 13,243.12995 | 7285.86553 |
| ESTRADIOL 3T pg/mL | 52 | 12,914.73 | 58,901.15 | 36,504.5008 | 12,114.67400 |
| PROLACTIN 1T ng/mL | 52 | 0.53000 | 540.98700 | 75.54135 | 76.42632 |
| PROLACTIN 2T ng/mL | 52 | 15.38000 | 584.96000 | 174.98144 | 134.67540 |
| PROLACTIN 3T ng/mL | 52 | 38.46000 | 625.00000 | 166.37818 | 120.15226 |
| PROGESTERONE 1T ng/mL | 52 | 10.791366 | 133.20000 | 55.14779 | 31.47740 |
| PROGESTERONE 2T ng/mL | 52 | 65.10791 | 555.29000 | 170.394048 | 110.82653 |
| PROGESTERONE 3T ng/mL | 52 | 129.439252 | 1187.83783 | 426.91970 | 275.42972 |
| Hormone TOXO | IgG | N | Mean | Standard Deviation | Standard Error | CI 95% Media | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||||||
| ESTRADIOL | positive | 14 | 3941.24243 | 3326.45899 | 889.03356 | 2020.602 | 5861.882 | |
| negative | 38 | 3508.82395 | 3894.30121 | 631.73907 | 2228.798 | 4788.848 | 0.714 | |
| Total | 52 | 3625.24431 | 3722.97799 | 516.28415 | 2588.760 | 4661.728 | ||
| PROLACTIN | positive | 14 | 52.147164 | 32.48556 | 8.68213 | 33.390 | 70.903 | |
| negativo | 38 | 84.16026 | 86.00537 | 13.95191 | 55.891 | 112.429 | 0.183 | |
| Total | 52 | 75.54135 | 76.42632 | 10.59842 | 54.264 | 96.818 | ||
| PROGESTERONE | positive | 14 | 63.10866 | 33.85084 | 9.04701 | 43.563 | 82.653 | |
| negative | 38 | 52.214846 | 30.50103 | 4.94792 | 42.189 | 62.240 | 0.273 | |
| Total | 52 | 55.14779 | 31.47740 | 4.36513 | 46.384 | 63.911 | ||
| Hormone TOXO | IgG | N | Mean | Standard Deviation | Standard Error | CI 95% Media | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||||||
| ESTRADIOL | positive | 14 | 15,622.66740 | 7179.86307 | 1918.89912 | 11,477.13788 | 19,768.19691 | |
| negative | 38 | 12,366.45826 | 7219.80052 | 1171.20630 | 9993.36888 | 14,739.54764 | 0.155 | |
| Total | 52 | 13,243.12995 | 7285.86553 | 1010.36776 | 11,214.73203 | 15,271.52787 | ||
| PROLACTIN | positive | 14 | 244.96568 | 170.40965 | 45.54389 | 146.57408 | 343.35728 | |
| negative | 38 | 149.19778 | 110.730559 | 17.96286 | 112.80155 | 185.59401 | 0.021 | |
| Total | 52 | 174.98144 | 134.67540 | 18.67611 | 137.48757 | 212.47532 | ||
| PROGESTERONE | positive | 14 | 219.17293 | 137.32029 | 36.70039 | 139.88656 | 298.45931 | |
| negative | 38 | 152.42287 | 95.25009 | 15.45160 | 121.11495 | 183.73080 | 0.053 | |
| Total | 52 | 170.39404 | 110.82653 | 15.36887 | 139.53974 | 201.24835 | ||
| Hormone TOXO | IgG | N | Mean | Standard Deviation | Standard Error | CI 95% Media | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||||||
| ESTRADIOL | positive | 17 | 40,845.9224 | 13,959.58813 | 3385.69743 | 33,668.5644 | 48,023.2803 | |
| negative | 35 | 34,395.8103 | 10,697.80746 | 1808.25950 | 30,720.9848 | 38,070.6357 | 0.071 | |
| Total | 52 | 36,504.5008 | 12,114.67400 | 1680.00301 | 33,131.7540 | 39,877.2475 | ||
| PROLACTIN | positive | 17 | 155.89054 | 93.587113 | 22.69820 | 107.77249 | 204.00859 | |
| negative | 35 | 171.47218 | 132.10402 | 22.329655 | 126.092862 | 216.85150 | 0.665 | |
| Total | 52 | 166.378184 | 120.152262 | 16.66212 | 132.92758 | 199.828787839996270 | ||
| PROGESTERONE | positive | 17 | 539.56442 | 290.48655 | 70.45333 | 390.21001 | 688.91882 | |
| negative | 35 | 372.20655 | 254.27726 | 42.98070 | 284.85926 | 459.55385 | 0.039 | |
| Total | 52 | 426.91970 | 275.42972 | 38.195230 | 350.23958 | 503.59983 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luna Rojas, Y.G.; Camarena Pulido, E.E.; Rodríguez-Pérez, L.R.; Galván-Ramírez, M.d.l.L. Follow-Up Study of 17-β Estradiol, Prolactin and Progesterone with the Kinetics and Prevalence of T. gondii Infection in Pregnant Women. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 5701-5711. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46060341
Luna Rojas YG, Camarena Pulido EE, Rodríguez-Pérez LR, Galván-Ramírez MdlL. Follow-Up Study of 17-β Estradiol, Prolactin and Progesterone with the Kinetics and Prevalence of T. gondii Infection in Pregnant Women. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2024; 46(6):5701-5711. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46060341
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuna Rojas, Yithzel Guadalupe, Eva Elizabet Camarena Pulido, Laura Rocío Rodríguez-Pérez, and María de la Luz Galván-Ramírez. 2024. "Follow-Up Study of 17-β Estradiol, Prolactin and Progesterone with the Kinetics and Prevalence of T. gondii Infection in Pregnant Women" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 46, no. 6: 5701-5711. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46060341
APA StyleLuna Rojas, Y. G., Camarena Pulido, E. E., Rodríguez-Pérez, L. R., & Galván-Ramírez, M. d. l. L. (2024). Follow-Up Study of 17-β Estradiol, Prolactin and Progesterone with the Kinetics and Prevalence of T. gondii Infection in Pregnant Women. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 46(6), 5701-5711. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46060341







