Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the Heat-Shock Protein Gene in L. edodes and Expression Pattern Analysis under Heat Shock
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Identification of HSPs in L. edodes
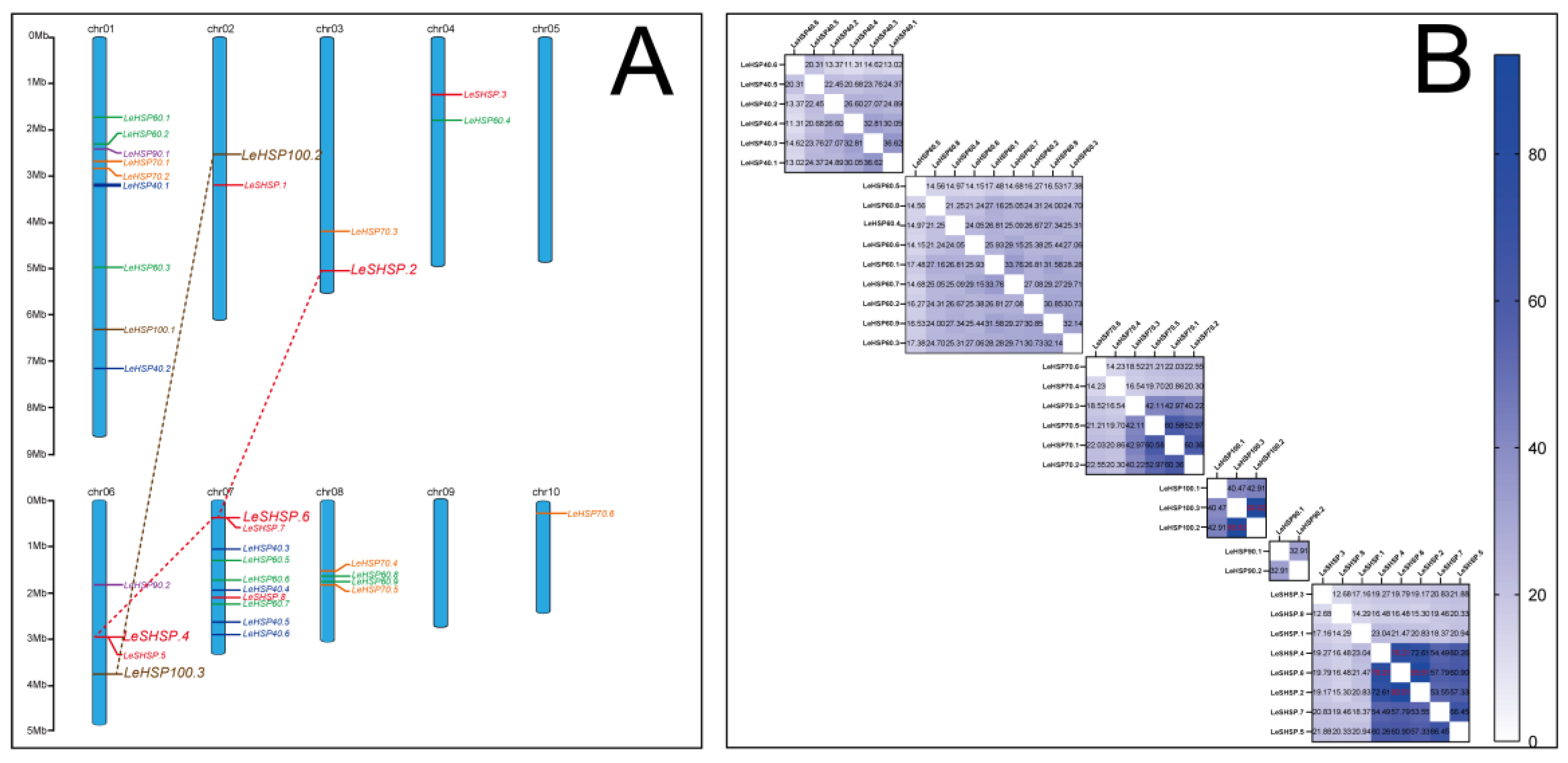
2.2. Chromosomal Localization and Gene Structure
2.3. Duplication of LeHSPs in L. edodes
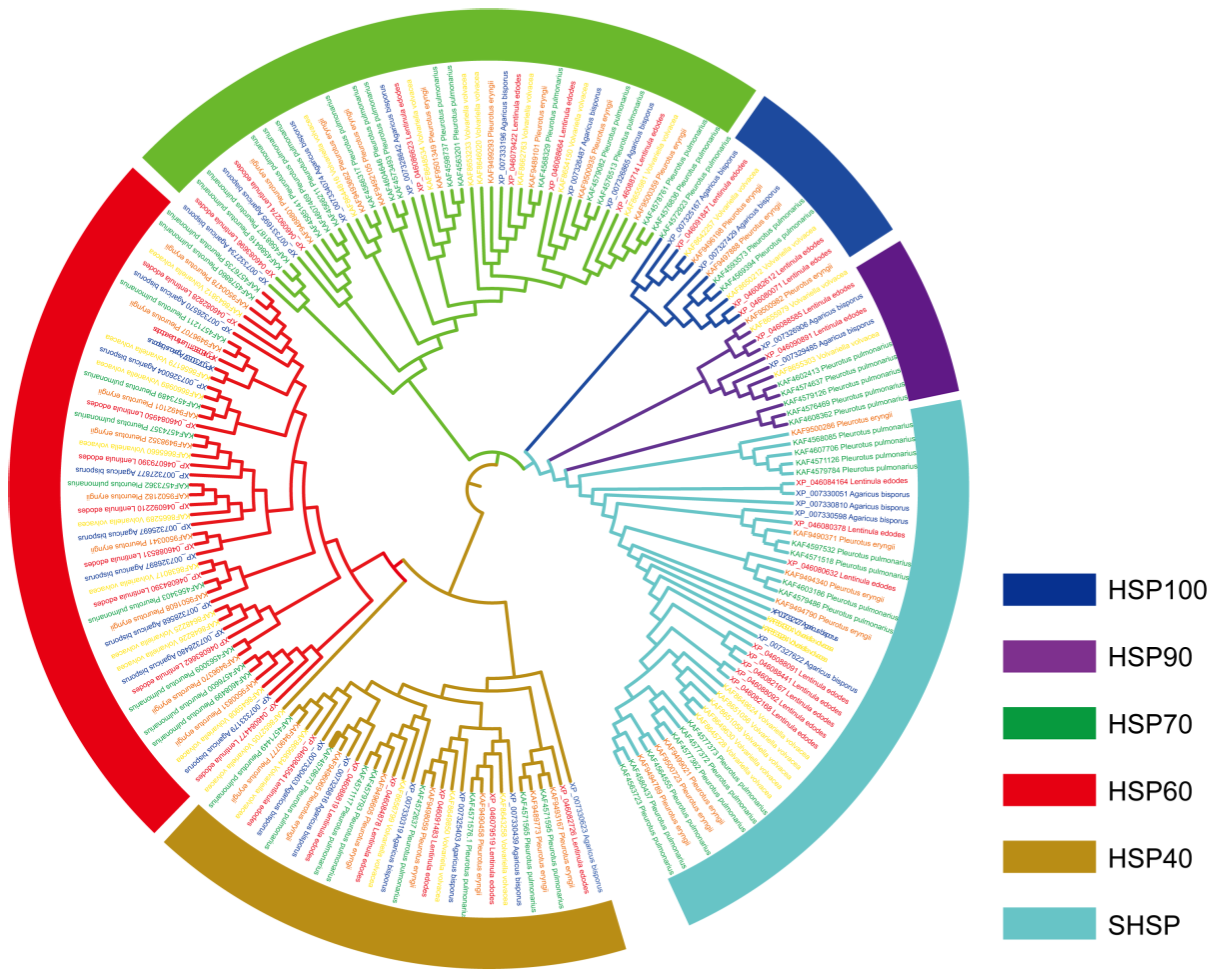
2.4. Phylogenetic Reconstruction
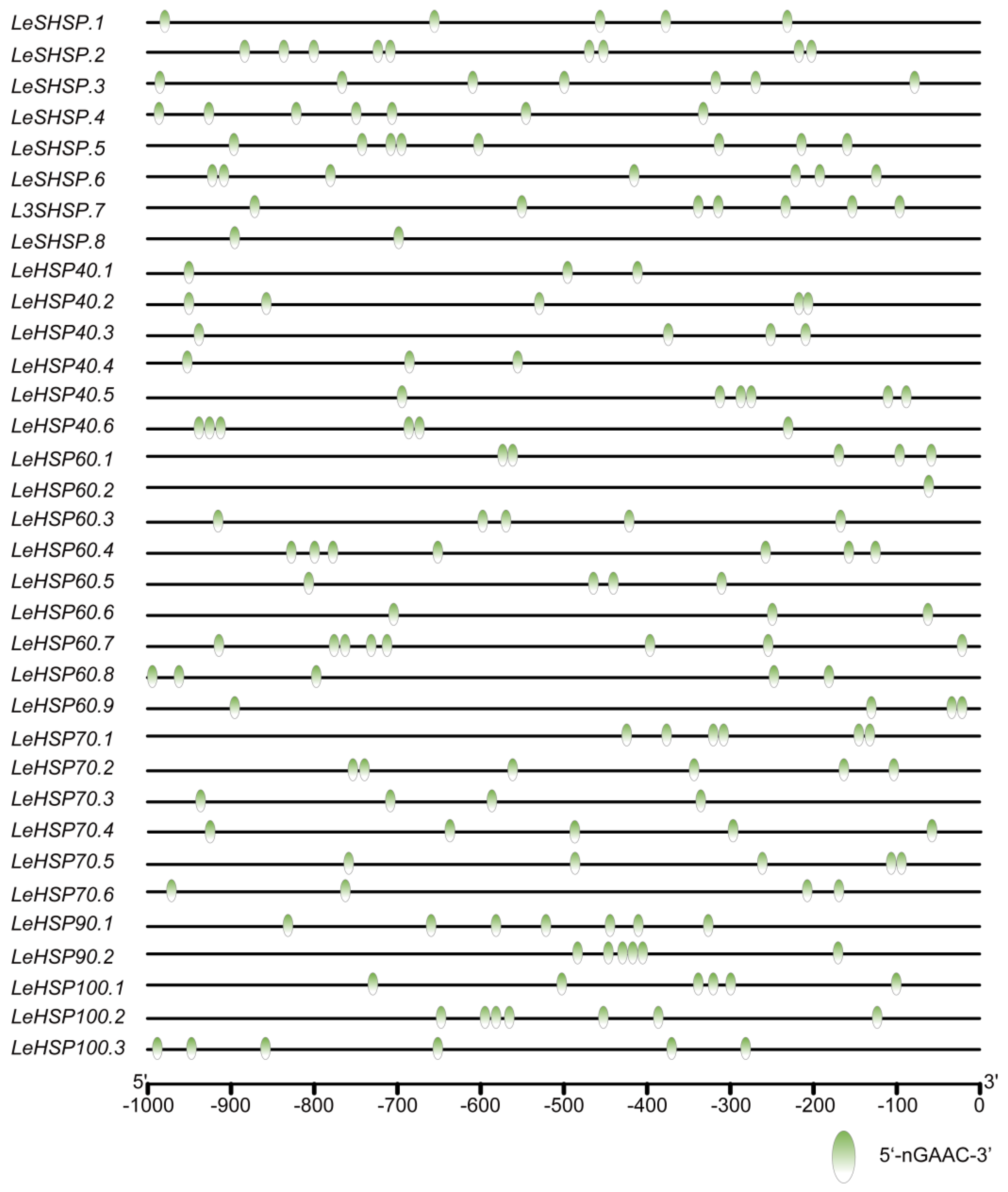
2.5. Heat Shock Element Analysis in the Promoter Regions of HSP Genes
2.6. Strain Materials and High-Temperature Treatments
2.7. Extraction and Purification of Total RNA from Mycelia
2.8. RNA-Sequencing and Analysis of HSP Genes
2.9. Gene Expression by RT-qPCR
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Analysis of HSP Genes in L. edodes
3.2. Gene Structure of HSPs
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of HSP Proteins
3.4. Chromosomal Location and Duplication of LeHSP Genes
3.5. The Binding Site of HSF in the Promoters of LeHSP Genes
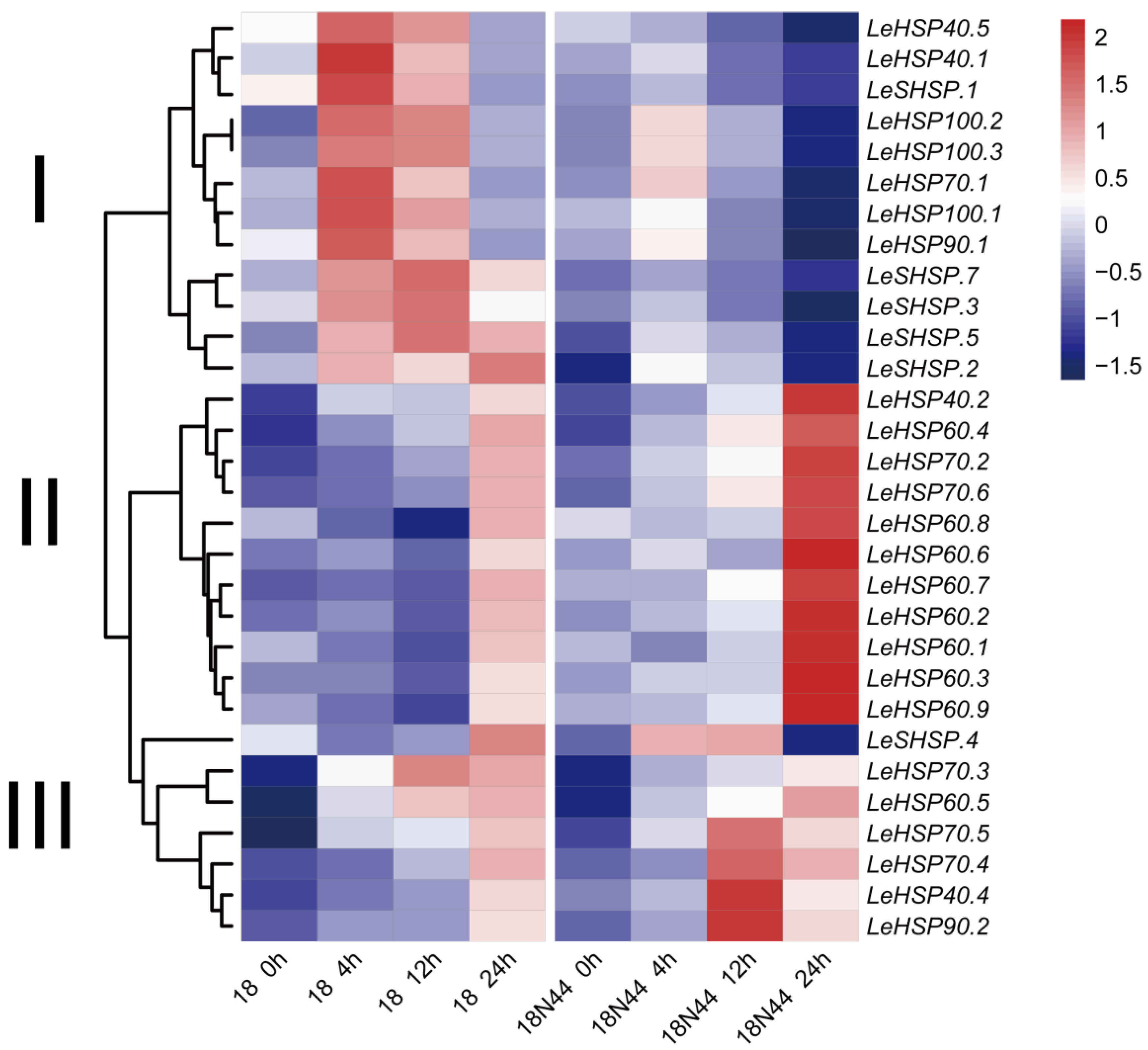
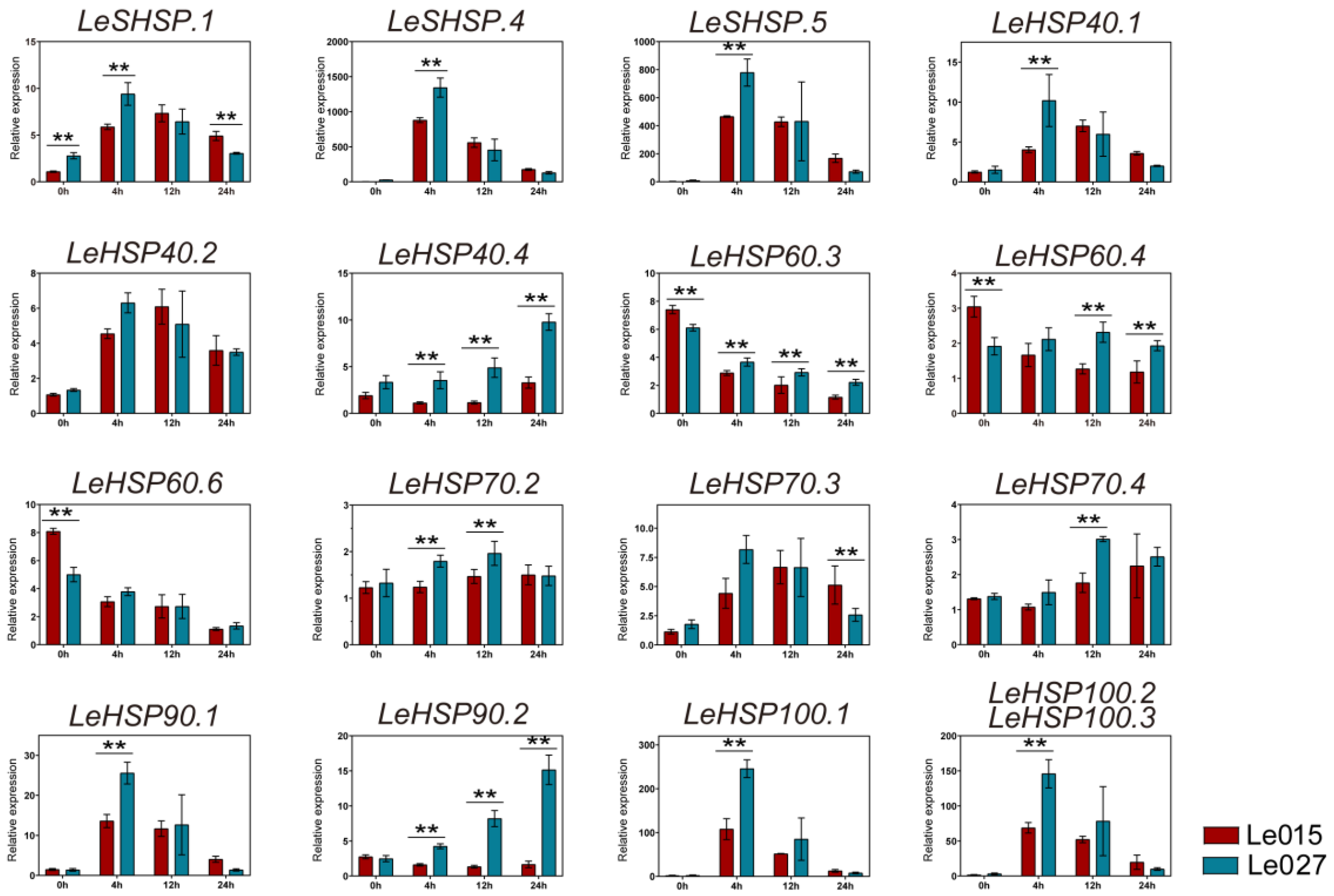
3.6. Expression Profile of LeHSP Genes in Response to Heat Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Finimundy, T.C.; Dillon, A.J.P.; Henriques, J.A.P.; Ely, M.R. A Review on General Nutritional Compounds and Pharmacological Properties of the Lentinula edodes Mushroom. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 05, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Luo, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Mou, C.; Kang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Bian, Y.; Gong, Y.H. Hsp40 Protein LeDnaJ07 Enhances the Thermotolerance of Lentinula edodes and Regulates IAA Biosynthesis by Interacting LetrpE. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotak, S.; Larkindale, J.; Lee, U.; von Koskull-Doring, P.; Vierling, E.; Scharf, K.D. Complexity of the heat stress response in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J.; Sun, X.; Ma, A. Heat stress in macrofungi: Effects and response mechanisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 7567–7576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Tamuli, R. Heat shock proteins and the calcineurin-crz1 signaling regulate stress responses in fungi. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritossa, F. A new puffing pattern induced by temperature shock and DNP in drosophila. Experientia 1962, 18, 571–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Vinocur, B.; Shoseyov, O.; Altman, A. Role of plant heat-shock proteins and molecular chaperones in the abiotic stress response. Trends Plant Sci. 2004, 9, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Long, R.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Q.; Kang, J. Research Progress on Plant Heat Shock Protein. Biotechnol. Bull. 2016, 32, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xue, C.; Xue, D.; Zhao, J.; Gai, J.; Guo, N.; Xing, H. Overexpression of GmHsp90s, a heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) gene family cloning from soybean, decrease damage of abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.C.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, Y.; Lee, M.C.; Kim, T.K.; Yim, J.H.; Lee, J.S. Genome-wide identification and structural analysis of heat shock protein gene families in the marine rotifer Brachionus spp.: Potential application in molecular ecotoxicology. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2020, 36, 100749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, A.M.; Makley, L.N.; Gestwicki, J.E.; Thiele, D.J. Genomic heat shock element sequences drive cooperative human heat shock factor 1 DNA binding and selectivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 30459–30469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Sharma, S.; Chunduri, V.; Kaur, A.; Kaur, S.; Malhotra, N.; Kumar, A.; Kapoor, P.; Kumari, A.; Kaur, J.; et al. Genome-wide Identification and Characterization of Heat Shock Protein Family Reveals Role in Development and Stress Conditions in Triticum aestivum L. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Sun, W.; Tian, J.; Wang, C. Plant Heat Shock Protein HSP100/ClpB and Its Applications in Improvement of Heat and Cold Resistances in Plants. Plant Physiol. Commun. 2008, 44, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; An, Y.S.; Kim, M.R.; Kim, Y.A.; Lee, J.K.; Hwang, C.S.; Chung, E.; Park, I.C.; Yi, J.Y. Heat Shock Protein 90 Regulates Subcellular Localization of Smads in Mv1Lu Cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 117, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Hu, G.; Han, B. Genome-wide survey and expression profiling of heat shock proteins and heat shock factors revealed overlapped and stress specific response under abiotic stresses in rice. Plant Sci. 2009, 176, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, D.Y.; Vierling, E.; Guy, C.L. Comprehensive expression profile analysis of the Arabidopsis Hsp70 gene family. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, S.; Song, Q.; Li, K.; Tao, H.; Huang, J.; Chen, X.; Que, S.; He, H. Genome-wide identification of heat shock proteins (Hsps) and Hsp interactors in rice: Hsp70s as a case study. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.K.; Dong, Q.L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, H.Y.; Xing, G.J.; Li, Q.Y.; Dong, Y.S. Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling under heat and drought treatments of HSP70 gene family in soybean (Glycine max L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shen, N.; Li, C.; Xiang, X.; Liu, G.; Gui, Y.; Patev, S.; Hibbett, D.S.; Barry, K.; Andreopoulos, W.; et al. Population genomics provides insights into the genetic basis of adaptive evolution in the mushroom-forming fungus Lentinula edodes. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 38, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gebali, S.; Mistry, J.; Bateman, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Luciani, A.; Potter, S.C.; Qureshi, M.; Richardson, L.J.; Salazar, G.A.; Smart, A.; et al. The Pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; R. Thomas, H.; H. Frank, M.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Williams, N.; Misleh, C.; Li, W.W. MEME: Discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panzade, K.P.; Kale, S.S.; Chavan, N.R.; Hatzade, B. Genome-wide analysis of Hsp70 and Hsp100 gene families in Ziziphus jujuba. Cell Stress Chaperones 2020, 26, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, M. Breeding thermo-tolerant strains of Lentinula edodes by UV induced protoplast mutagenesis. Microbiol. China 2014, 41, 1350–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, H.; Chen, M.; Song, X.; Yu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y. Reference Gene Selection for Quantitative Real-Time PCR of Mycelia from Lentinula edodes under High-Temperature Stress. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1670328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.; Pachter, L. Streaming fragment assignment for real-time analysis of sequencing experiments. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; van Peer, A.F.; Huang, Q.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xie, B.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xie, B. Identification of novel and robust internal control genes from Volvariella volvacea that are suitable for RT-qPCR in filamentous fungi. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glare, E.M.; Divjak, M.; Bailey, M.J.; Walters, E.H. β-Actin and GAPDH housekeeping gene expression in asthmatic airways is variable and not suitable for normalising mRNA levels. Thorax 2002, 57, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 2002–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudd, M.K.; Keene, J.; Bunke, B.; Kaminsky, E.B.; Adam, M.P.; Mulle, J.G.; Ledbetter, D.H.; Martin, C.L. Segmental duplications mediate novel, clinically relevant chromosome rearrangements. Hum. Mol. Genet 2009, 18, 2957–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antomio, D.M. Heat shock proteins: Facts, thoughts, and dreams. Shock 1999, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Z.; Ma, C.J.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, S.S.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, X.L.; Cai, Y.L.; Yu, J.J.; Bian, Y.B.; Gong, Y.H. Proteome and Transcriptome Reveal Involvement of Heat Shock Proteins and Indoleacetic Acid Metabolism Process in Lentinula Edodes Thermotolerance. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 50, 1617–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Jaishankar, J.; Muthamilarasan, M.; Shweta, S.; Dangi, A.; Prasad, M. Genome-wide analysis of heat shock proteins in C4 model, foxtail millet identifies potential candidates for crop improvement under abiotic stress. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharf, K.D.; Siddique, M.; Vierling, E. The expanding family of Arabidopsis thaliana small heat stress proteins and a new family of proteins containing alpha-crystallin domains (Acd proteins). Cell Stress Chaperones 2001, 6, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, N.; Johansson, N.; Thiele, D.J. Heat Shock Element Architecture Is an Important Determinant in the Temperature and Transactivation Domain Requirements for Heat Shock Transcription Factor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 6340–6352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Feng, K.; Ruan, M.; Ye, Q.; Wang, R.; Li, Z.; Zhou, G.; Yao, Z.; Yang, Y.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling of Tomato Hsp20 Gene Family in Response to Biotic and Abiotic Stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Liu, J.H.; Lu, J.P.; Zhai, Y.F.; Wang, H.; Gong, Z.H.; Wang, S.B.; Lu, M.H. Genome-wide analysis of the CaHsp20 gene family in pepper: Comprehensive sequence and expression profile analysis under heat stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhi, C.; Qiao, L.; Liu, C.; Pan, Y.; Cheng, Z. Genome-wide identification of small heat shock protein (HSP20) homologs in three cucurbit species and the expression profiles of CsHSP20s under several abiotic stresses. Int J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 190, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miaomiao, X. The Gene Expression and DFunction Study of Hydrophobin Heat Shock Proteins From Lentinula edodes; Nanjing Agricultural University: Nanjing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.Z.; Luo, Y.; Chen, W.; Gong, Y.H.; Zhou, Y.; Bian, Y.B. The DnaJ Gene Family in Shiitake Culinary-Medicinal Mushroom, Lentinus edodes (Agaricomycetes): Comprehensive Identification, Characterization, and Expression Profiles under Different Conditions. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2019, 21, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshameri, A.; Al-Qurainy, F.; Gaafar, A.R.; Khan, S.; Nadeem, M.; Alansi, S. Identification of Heat-Responsive Genes in Guar [Cyamopsis tetragonoloba (L.) Taub]. Int. J. Genomics 2020, 2020, 3126592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ma, Z.; Liu, S.; Yang, W.; Ma, J. Transcriptome Profiling Reveals Potential Genes and Pathways Supporting Ananas comosus L. Merr’s High Temperature Stress Tolerance. Trop. Plant Biol. 2021, 14, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopperla, R.; Singh, S.; Tomar, R.S.; Mohanty, S.; Khan, S.; Reddy, N.; Padaria, J.C.; Solanke, A.U. Isolation and allelic characterization of finger millet (Eleusine coracana L.) small heat shock protein EcHSP17.8 for stress tolerance. Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2017, 78, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wan, F.; Guo, J. Induced Thermotolerance and Expression of Three Key Hsp Genes (Hsp70, Hsp21, and sHsp21) and Their Roles in the High Temperature Tolerance of Agasicles hygrophila. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, N.; Ramakrishna, K.; Suguna, K. Characterization of rice small heat shock proteins targeted to different cellular organelles. Cell Stress Chaperones 2015, 20, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, R.I. Cells in stress: Transcriptional activation of heat shock genes. Science 1993, 259, 1409–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name | Protein ID | Exon | Intron | Location | Chr | AA | MW(kDa) | PI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HSP100 | LeHSP100.1 | XP_046091847.1 | 9 | 8 | 6279738–6282864 | 1 | 890 | 98.436 | 5.48 |
| LeHSP100.2 | XP_046082612.1 | 11 | 10 | 2522518–2526440 | 2 | 771 | 84.959 | 5.59 | |
| LeHSP100.3 | XP_046080071.1 | 11 | 10 | 3743879–3748058 | 6 | 749 | 83.108 | 5.54 | |
| HSP90 | LeHSP90.1 | XP_046088585.1 | 8 | 7 | 2407716–2410082 | 1 | 706 | 80.185 | 4.62 |
| LeHSP90.2 | XP_046090891.1 | 19 | 18 | 1815650–1819056 | 5 | 817 | 91.712 | 4.29 | |
| HSP70 | LeHSP70.1 | XP_046088664.1 | 5 | 4 | 2657999–2660171 | 1 | 651 | 70.962 | 4.78 |
| LeHSP70.2 | XP_046088714.1 | 9 | 8 | 2800610–2802917 | 1 | 613 | 67 | 5.24 | |
| LeHSP70.3 | XP_046086623.1 | 11 | 10 | 4172952–4175420 | 3 | 627 | 68.046 | 5.46 | |
| LeHSP70.4 | XP_046083696.1 | 9 | 8 | 1532467–1535557 | 8 | 886 | 97.597 | 5.52 | |
| LeHSP70.5 | XP_046079422.1 | 9 | 8 | 1824230–1826698 | 8 | 678 | 73.742 | 4.74 | |
| LeHSP70.6 | XP_046090274.1 | 4 | 3 | 288215–290346 | 10 | 631 | 66.324 | 4.41 | |
| HSP60 | LeHSP60.1 | XP_046082828.1 | 9 | 8 | 1726567–1728602 | 1 | 539 | 57.88 | 7.33 |
| LeHSP60.2 | XP_046088531.1 | 8 | 7 | 2303108–2305148 | 1 | 554 | 59.722 | 6.24 | |
| LeHSP60.3 | XP_046092210.1 | 6 | 5 | 4944807–4946672 | 1 | 560 | 60.881 | 5.98 | |
| LeHSP60.4 | XP_046084390.1 | 9 | 8 | 1792382–1794487 | 4 | 550 | 59.833 | 6.63 | |
| LeHSP60.5 | XP_046084477.1 | 4 | 3 | 1298157–1300114 | 7 | 598 | 62.592 | 5.26 | |
| LeHSP60.6 | XP_046084950.1 | 8 | 7 | 1721053–1723408 | 7 | 575 | 62.377 | 5.79 | |
| LeHSP60.7 | XP_046088311.1 | 11 | 10 | 2236637–2238719 | 7 | 542 | 59.243 | 5.29 | |
| LeHSP60.8 | XP_046083662.1 | 8 | 7 | 1633717–1635690 | 8 | 561 | 60.138 | 5.91 | |
| LeHSP60.9 | XP_046079390.1 | 10 | 9 | 1750215–1752273 | 8 | 524 | 56.462 | 5.16 | |
| HSP40 | LeHSP40.1 | XP_046088819.1 | 6 | 5 | 3097898–3099296 | 1 | 398 | 43.547 | 6.44 |
| LeHSP40.2 | XP_046091483.1 | 6 | 5 | 7116980–7118740 | 1 | 493 | 52.394 | 9.53 | |
| LeHSP40.3 | XP_046084554.1 | 11 | 10 | 1053764–1055625 | 7 | 422 | 46.417 | 4.59 | |
| LeHSP40.4 | XP_046084878.1 | 12 | 11 | 1936586–1938308 | 7 | 368 | 41.501 | 6.18 | |
| LeHSP40.5 | XP_046079519.1 | 4 | 3 | 2621252–2622535 | 7 | 372 | 39.857 | 9.66 | |
| LeHSP40.6 | XP_046082726.1 | 5 | 4 | 2888022–2889557 | 7 | 429 | 48.317 | 10.02 | |
| SHSP | LeSHSP.1 | XP_046080632.1 | 4 | 3 | 3183573–3184343 | 2 | 190 | 21.261 | 10.33 |
| LeSHSP.2 | XP_046088441.1 | 3 | 2 | 5037923–5037741 | 3 | 154 | 17.671 | 6.54 | |
| LeSHSP.3 | XP_046084164.1 | 2 | 1 | 1241615–1242240 | 4 | 188 | 20.37 | 4.83 | |
| LeSHSP.4 | XP_046088091.1 | 3 | 2 | 2943783–2944370 | 6 | 156 | 17.666 | 5.65 | |
| LeSHSP.5 | XP_046088092.1 | 3 | 2 | 2944818–2945400 | 6 | 155 | 17.409 | 5.45 | |
| LeSHSP.6 | XP_046082167.1 | 3 | 2 | 382364–382938 | 7 | 153 | 17.491 | 5.57 | |
| LeSHSP.7 | XP_046082168.1 | 4 | 3 | 383366–383941 | 7 | 162 | 18.492 | 6.45 | |
| LeSHSP.8 | XP_046080378.1 | 3 | 2 | 2094217–2095081 | 7 | 254 | 29.054 | 5.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Yin, K.; Feng, R.; Miao, R.; Lin, J.; Cao, L.; Ni, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, Q. Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the Heat-Shock Protein Gene in L. edodes and Expression Pattern Analysis under Heat Shock. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 614-627. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45010041
Zhao X, Yin K, Feng R, Miao R, Lin J, Cao L, Ni Y, Li W, Zhang Q. Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the Heat-Shock Protein Gene in L. edodes and Expression Pattern Analysis under Heat Shock. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2023; 45(1):614-627. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45010041
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xu, Kaiyong Yin, Rencai Feng, Renyun Miao, Junbin Lin, Luping Cao, Yanqing Ni, Wensheng Li, and Qin Zhang. 2023. "Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the Heat-Shock Protein Gene in L. edodes and Expression Pattern Analysis under Heat Shock" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 45, no. 1: 614-627. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45010041
APA StyleZhao, X., Yin, K., Feng, R., Miao, R., Lin, J., Cao, L., Ni, Y., Li, W., & Zhang, Q. (2023). Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the Heat-Shock Protein Gene in L. edodes and Expression Pattern Analysis under Heat Shock. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 45(1), 614-627. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45010041





