Inhibition of Hedgehog Delays Liver Regeneration through Disrupting the Cell Cycle
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiment
2.2. Real-time Quantitative PCR
2.3. Western Blot Analysis
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Isolation of Primary Hepatocytes and Flow Cytometry Analysis
3. Results
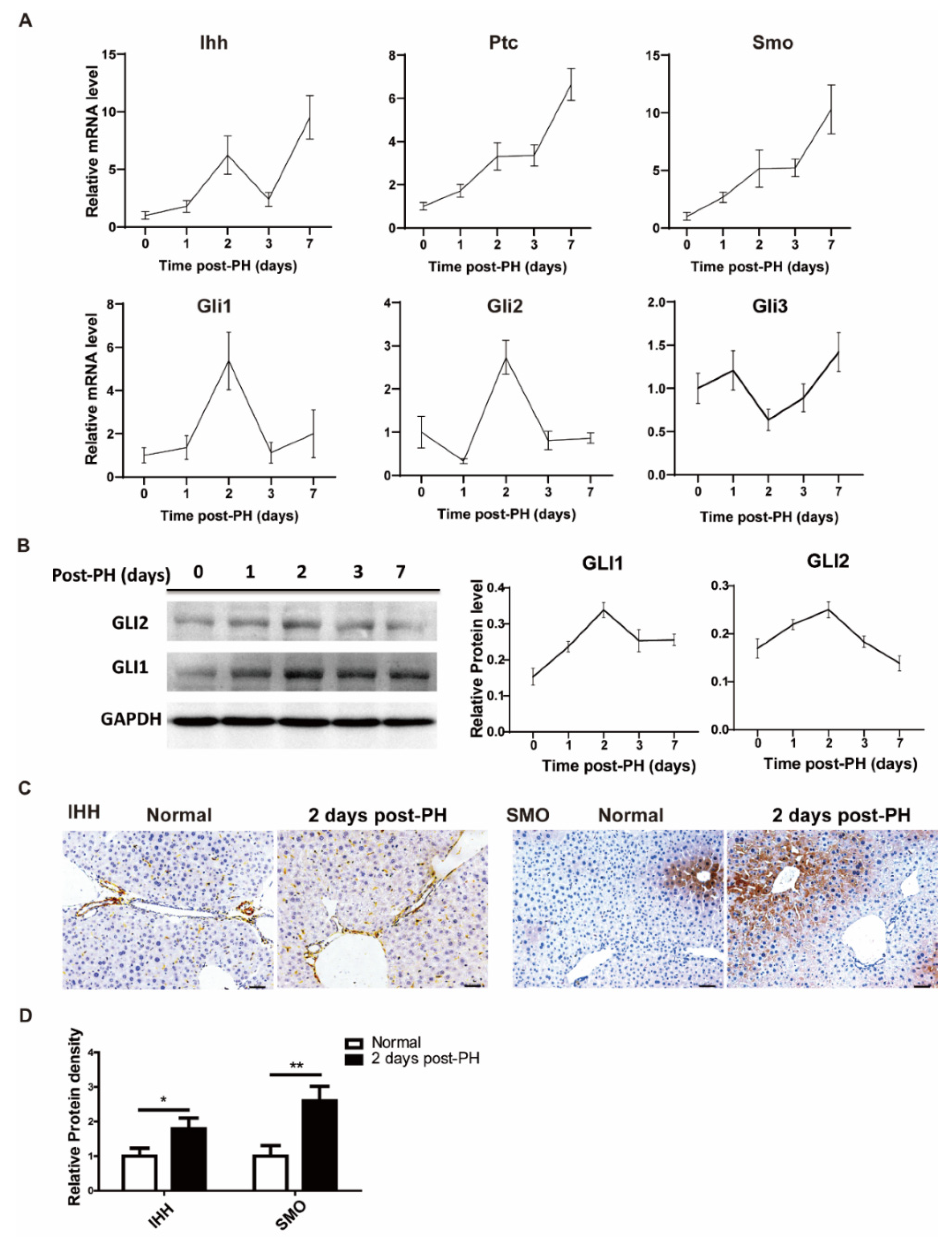
3.1. Hedgehog Signal Activated after Partial Hepatectomy
3.2. Vismodegib Suppresses the Rate of Liver Regeneration after PH
3.3. Vismodegib Inhibits the Activation of Hh Pathway after PH
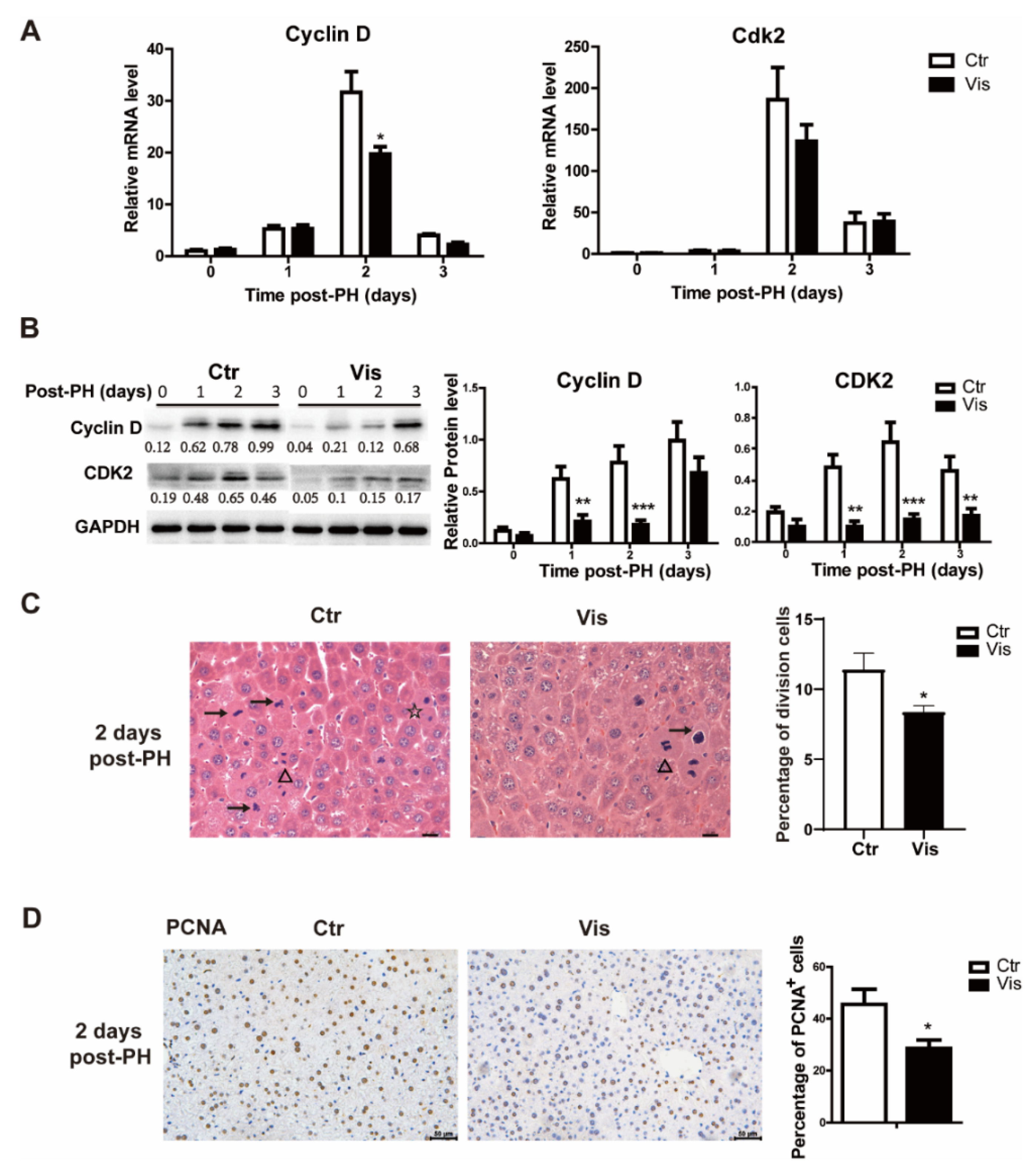
3.4. Inhibition of Hh Signal Suppressed the G1/S Phase of Cell Proliferation
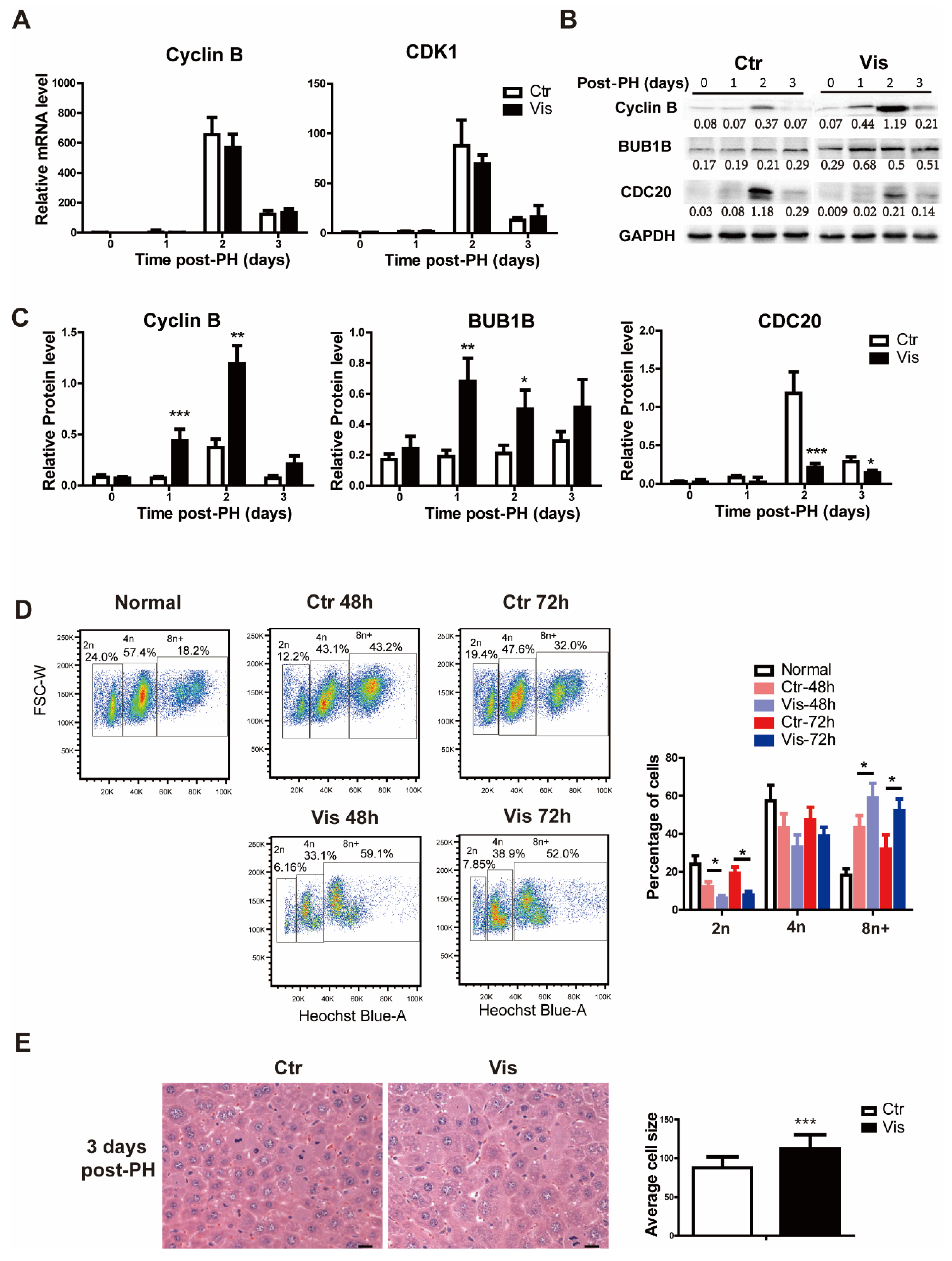
3.5. Inhibition of Hh Signaling Increased Accumulation of Polyploid Cells by Suppressing Degradation of Cyclin B
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Hh | hedgehog |
| ICR | Institute of Cancer Research |
| PH | partial hepatectomy |
| PFA | paraformaldehyde |
| HGF | hepatocyte growth factor |
| EGF | epidermal growth factor |
| TGFβ | transforming growth factor-β |
| HSC | hepatic stellate cell |
| PTC | patched |
| SMO | smoothened |
| MPF | maturation-promoting factor |
| GLI | glioma-associated oncogene |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| RIPA | Radio Immunoprecipitation Assay |
| SDS-PEGA | sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| PVDF | polyvinylidene fluoride |
| Edu | 5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine |
| IHH | Indian hedgehog |
| APC/C | anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome |
| CMC-NA | sodium carboxymethylcellulose |
References
- Michalopoulos, G.K.; Bhushan, B. Liver regeneration: Biological and pathological mechanisms and implications. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiseleva, Y.V.; Antonyan, S.Z.; Zharikova, T.S.; Tupikin, K.A.; Kalinin, D.V.; Zharikov, Y.O. Molecular pathways of liver regeneration: A comprehensive review. World J. Hepatol. 2021, 13, 270–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, S.; Hirata, M.; Miyachi, Y.; Uemoto, S. Liver Regeneration after Hepatectomy and Partial Liver Transplantation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modares, N.F.; Polz, R.; Haghighi, F.; Lamertz, L.; Behnke, K.; Zhuang, Y.; Kordes, C.; Haussinger, D.; Sorg, U.R.; Pfeffer, K.; et al. IL-6 Trans-signaling Controls Liver Regeneration After Partial Hepatectomy. Hepatology 2019, 70, 2075–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addante, A.; Roncero, C.; Lazcanoiturburu, N.; Méndez, R.; Almalé, L.; García-Álvaro, M.; Dijke, P.T.; Fabregat, I.; Herrera, B.; Sánchez, A. A Signaling Crosstalk between BMP9 and HGF/c-Met Regulates Mouse Adult Liver Progenitor Cell Survival. Cells 2020, 9, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiang, K.Y.; Li, Y.W.; Li, Y.H.; Huang, S.J.; Wu, C.L.; Gong, H.Y.; Wu, J.L. Progranulin A Promotes Compensatory Hepatocyte Proliferation via HGF/c-Met Signaling after Partial Hepatectomy in Zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.O.; Monga, S.P. Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling in Liver Development, Homeostasis, and Pathobiology. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. 2018, 13, 351–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inoue, Y.; Fujii, K.; Ishii, M.; Kagota, S.; Tomioka, A.; Hamamoto, H.; Osumi, W.; Tsuchimoto, Y.; Masubuchi, S.; Yamamoto, M.; et al. Volumetric and Functional Regeneration of Remnant Liver after Hepatectomy. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2019, 23, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, M.M.; McGill, M.R.; Apte, U. Mechanisms and biomarkers of liver regeneration after drug-induced liver injury. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2019, 85, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Duan, W.; Kang, L.; Mao, J.; Yu, X.; Fan, S.; Li, L.; Tao, Y. Smoothened activates breast cancer stem-like cell and promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis of breast cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2014, 68, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips, G.M.; Chan, I.; Swiderska, M.; Schroder, V.T.; Guy, C.; Karaca, G.F.; Moylan, C.; Venkatraman, T.; Feuerlein, S.; Syn, W.-K.; et al. Hedgehog Signaling Antagonist Promotes Regression of Both Liver Fibrosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in a Murine Model of Primary Liver Cancer. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, X.; Peng, Y.; Li, H. The Injury-Related Activation of Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Modulates the Repair-Associated In-flammation in Liver Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machado, M.V.; Diehl, A.M. Hedgehog signalling in liver pathophysiology. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skoda, A.M.; Simovic, D.; Karin, V.; Kardum, V.; Vranic, S.; Serman, L. The role of the Hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer: A comprehensive review. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2018, 18, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.S.; Syn, W.-K.; Karaca, G.F.; Omenetti, A.; Moylan, C.A.; Witek, R.P.; Agboola, K.M.; Jung, Y.; Michelotti, G.; Diehl, A.M. Leptin Promotes the Myofibroblastic Phenotype in Hepatic Stellate Cells by Activating the Hedgehog Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 36551–36560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, J.; Yan, J.; Wei, X.; Liu, Z.; Ni, J.; Hu, B.; Jin, L. Gant61 ameliorates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis by inhibition of Hedgehog signaling activity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 387, 114853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Hyun, J.; Premont, R.T.; Choi, S.S.; Michelotti, G.A.; Swiderska-Syn, M.; Dalton, G.D.; Thelen, E.; Rizi, B.S.; Jung, Y.; et al. Hedgehog-YAP Signaling Pathway Regulates Glutaminolysis to Control Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1465–1479.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Jung, Y.; Omenetti, A.; Witek, R.P.; Choi, S.; Vandongen, H.M.; Huang, J.; Alpini, G.D.; Diehl, A.M. Fate-Mapping Evidence That Hepatic Stellate Cells Are Epithelial Progenitors in Adult Mouse Livers. Stem Cells 2008, 26, 2104–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ingham, P.W. Hedgehog signalling. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, R238–R241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, J.H.; Siebold, C.; Rohatgi, R. Biochemical mechanisms of vertebrate hedgehog signaling. Development 2019, 146, dev166892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Yu, M.; Yang, T. Role of canonical Hedgehog signaling pathway in liver. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1636–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misawa, R.; Minami, T.; Okamoto, A.; Ikeuchi, Y. A Light-Inducible Hedgehog Signaling Activator Modulates Proliferation and Differentiation of Neural Cells. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Q.; Li, P.; Che, M.; Liu, J.; Biswas, S.; Ma, G.; He, L.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; et al. Activation of hedgehog signaling in mesenchymal stem cells induces cartilage and bone tumor formation via Wnt/beta-Catenin. eLife 2019, 8, e50208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, K.A.; Choksi, P.K.; Krup, A.L.; Mayer, W.; Santos, N.; Reiter, J.F. Hedgehog signaling drives medulloblastoma growth via CDK6. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 128, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duman-Scheel, M.; Weng, L.; Xin, S.; Du, W. Hedgehog regulates cell growth and proliferation by inducing Cyclin D and Cyclin E. Nature 2002, 417, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Wu, J.; Fan, H.; Lu, J.; Feng, J. LncRNA EGOT Promotes Tumorigenesis Via Hedgehog Pathway in Gastric Cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2017, 25, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolphe, C.; Hetherington, R.; Ellis, T.; Wainwright, B.; Thebault, S.; Flourakis, M.; Vanoverberghe, K.; Vandermoere, F.; Roudbaraki, M.; Lehen’Kyi, V.; et al. Patched1 Functions as a Gatekeeper by Promoting Cell Cycle Progression. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 2081–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnes, E.A.; Kong, M.; Ollendorff, V.; Donoghue, D.J. Patched1 interacts with cyclin B1 to regulate cell cycle progression. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 2214–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basu, S.; Roberts, E.L.; Jones, A.W.; Swaffer, M.; Snijders, A.P.; Nurse, P. The Hydrophobic Patch Directs Cyclin B to Centrosomes to Promote Global CDK Phosphorylation at Mitosis. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lara-Gonzalez, P.; Moyle, M.W.; Budrewicz, J.; Mendoza-Lopez, J.; Oegema, K.; Desai, A. The G2-to-M Transition Is Ensured by a Dual Mechanism that Protects Cyclin B from Degradation by Cdc20-Activated APC/C. Dev. Cell 2019, 51, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.Y.; Choe, M.H.; Kim, J.S.; Oh, J.S. Mis12 controls cyclin B1 stabilization via Cdc14B-mediated APC/C(Cdh1) regulation during meiotic G2/M transition in mouse oocytes. Development 2020, 147, dev185322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamano, H. APC/C: Current understanding and future perspectives. F1000Research 2019, 8, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitry-Shevah, D.; Kaisari, S.; Teichner, A.; Miniowitz-Shemtov, S.; Hershko, A. Role of ubiquitylation of components of mitotic checkpoint complex in their dissociation from anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 1777–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ochoa, B.; Syn, W.-K.; Delgado, I.; Karaca, G.F.; Jung, Y.; Wang, J.; Zubiaga, A.M.; Fresnedo, O.; Omenetti, A.; Zdanowicz, M.; et al. Hedgehog signaling is critical for normal liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in mice. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1712–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meiss, F.; Andrlova, H.; Zeiser, R. Vismodegib. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2018, 211, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frampton, J.E.; Basset-Séguin, N. Vismodegib: A Review in Advanced Basal Cell Carcinoma. Drugs 2018, 78, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsova, P.; Ibrahim, S.H.; Bronk, S.F.; Yagita, H.; Gores, G.J. Vismodegib Suppresses TRAIL-mediated Liver Injury in a Mouse Model of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pratap, A.; Singh, S.; Mundra, V.; Yang, N.; Panakanti, R.; Eason, J.D.; Mahato, R.I. Attenuation of early liver fibrosis by pharmacological inhibition of smoothened receptor signaling. J. Drug Target. 2012, 20, 770–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scales, S.J.; de Sauvage, F.J. Mechanisms of Hedgehog pathway activation in cancer and implications for therapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, G.M.; Anderson, R.M. Experimental pathology of the liver I Restoration of the liver of the white rat following partial surgical removal. Arch. Pathol. 1931, 12, 186–202. [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson, G.W. Experimental pathology of the liver—Restoration of the liver after partial hepatectomy and partial ligation of the portal vein. Arch. Pathol. 1932, 14, 484–490. [Google Scholar]
- Michalopoulos, G.K. Hepatostat: Liver regeneration and normal liver tissue maintenance. Hepatology 2017, 65, 1384–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelozzi, M.; De Charleroy, C.R.; Lefebvre, V. EdU-Based Assay of Cell Proliferation and Stem Cell Quiescence in Skeletal Tissue Sections. Springer Protoc. Handb. 2021, 2230, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, C.; Jin, H.; Sun, G.; Tian, Y.; Shi, W.; Zhang, D. Flow cytometric analysis of T lymphocyte proliferation in vivo by EdU incorporation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 41, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaoka, Y.; Ebato, K.; Kato, H.; Arakawa, S.; Shimizu, S.; Miyajima, A. Hypertrophy and Unconventional Cell Division of Hepatocytes Underlie Liver Regeneration. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 1166–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gentric, G.; Celton-Morizur, S.; Desdouets, C. Polyploidy and liver proliferation. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2012, 36, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langiewicz, M.; Schlegel, A.; Saponara, E.; Linecker, M.; Borger, P.; Graf, R.; Humar, B.; Clavien, P.A. Hedgehog pathway mediates early acceleration of liver regeneration induced by a novel two-staged hepatectomy in mice. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rennert, C.; Eplinius, F.; Hofmann, U.; Johänning, J.; Rolfs, F.; Schmidt-Heck, W.; Guthke, R.; Gebhardt, R.; Ricken, A.M.; Matz-Soja, M. Conditional loss of hepatocellular Hedgehog signaling in female mice leads to the persistence of hepatic steroidogenesis, androgenization and infertility. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 3677–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matz-Soja, M.; Aleithe, S.; Marbach, E.; Böttger, J.; Arnold, K.; Schmidt-Heck, W.; Kratzsch, J.; Gebhardt, R. Hepatic Hedgehog signaling contributes to the regulation of IGF1 and IGFBP1 serum levels. Cell Commun. Signal. 2014, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Hyun, J.; Wang, S.; Lee, C.; Jung, Y. MicroRNA-378 is involved in hedgehog-driven epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocytes of regenerating liver. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, E. HEDGEHOG Signal in hepatocytes mediates macrophage recruitment: A new mechanism and potential therapeutic target for fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2015, 63, 1071–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwon, H.; Song, K.; Han, C.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Dash, S.; Lim, K.; Wu, T. Inhibition of hedgehog signaling ameliorates hepatic inflammation in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2015, 63, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Machado, M.V.; Diehl, A.M. The hedgehog pathway in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 53, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Wei, R.; Getachew, A.; Pan, T.; Yang, F.; Li, Y. Inhibition of Hedgehog Delays Liver Regeneration through Disrupting the Cell Cycle. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 470-482. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44020032
Tao J, Chen Y, Zhuang Y, Wei R, Getachew A, Pan T, Yang F, Li Y. Inhibition of Hedgehog Delays Liver Regeneration through Disrupting the Cell Cycle. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2022; 44(2):470-482. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44020032
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Jiawang, Yan Chen, Yuanqi Zhuang, Ruzhi Wei, Anteneh Getachew, Tingcai Pan, Fan Yang, and Yinxiong Li. 2022. "Inhibition of Hedgehog Delays Liver Regeneration through Disrupting the Cell Cycle" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 44, no. 2: 470-482. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44020032
APA StyleTao, J., Chen, Y., Zhuang, Y., Wei, R., Getachew, A., Pan, T., Yang, F., & Li, Y. (2022). Inhibition of Hedgehog Delays Liver Regeneration through Disrupting the Cell Cycle. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 44(2), 470-482. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44020032





