Review on Advanced Cancer Modeling for a Cancer Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
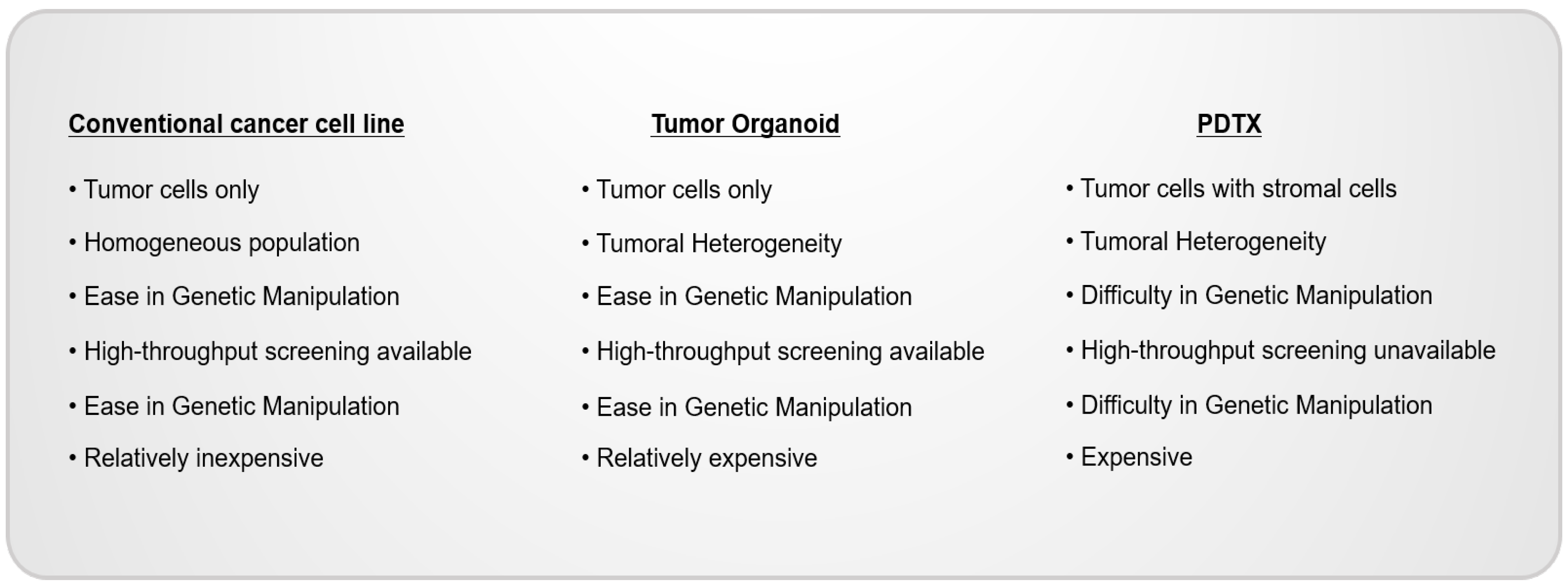
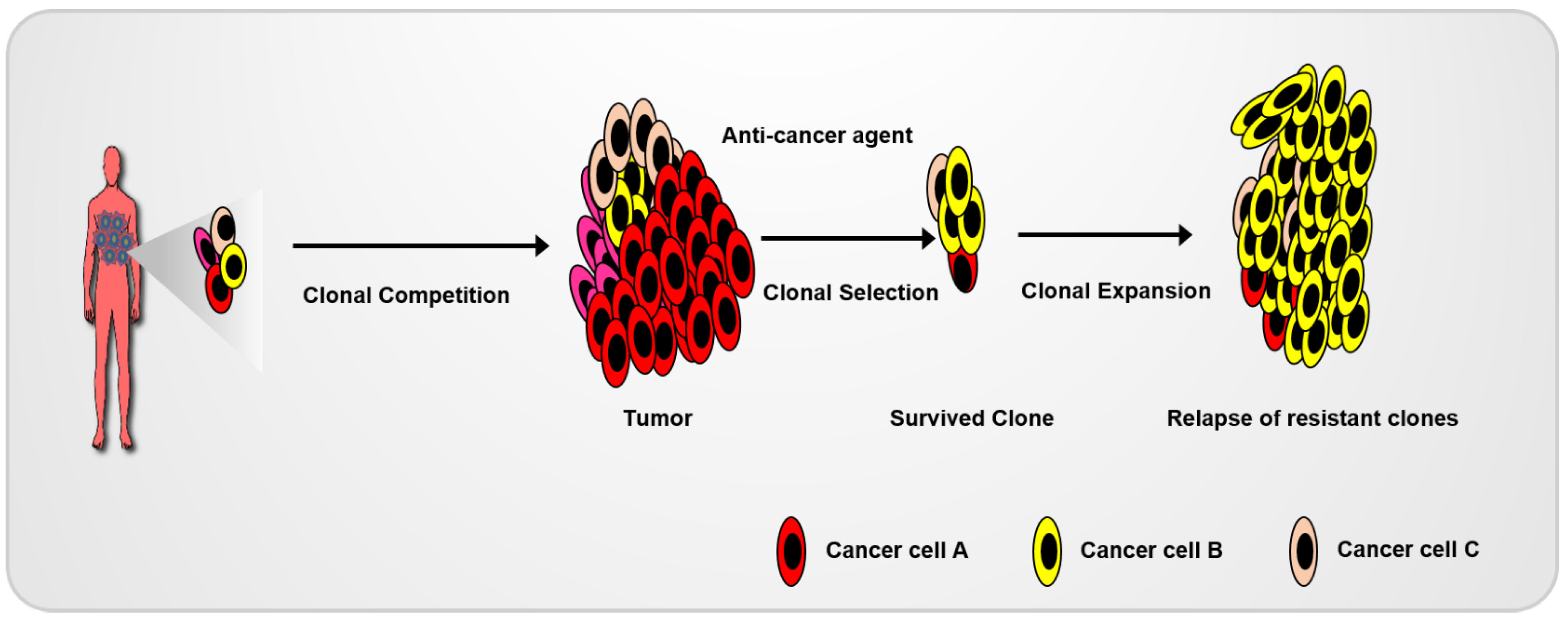
2. Limitations of Conventional Cancer Cell Lines
3. Cancer Organoid Model Systems
4. Applications for Investigating the Cancer Type Lacking Experimental Models
5. Organoid Model Systems Produced by Using a Genetic Mouse Model
6. The Limitations, at Present, of the Organoid Model System
7. Patient-Derived Tumor Xenografts (PDTXs) as a Patient’s Avatar Model
8. Drug Study
9. Co-Culture System of Organoids
10. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J. Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fearon, E.R. Vogelstein B: A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell 1990, 61, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinzler, K.W. Vogelstein B: Lessons from hereditary colorectal cancer. Cell 1996, 87, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.H.; Cha, P.H.; Kaduwal, S.; Park, J.C.; Lee, S.K.; Yoon, J.S.; Shin, W.; Kim, H.; Ro, E.J.; Koo, K.H.; et al. KY1022, a small molecule destabilizing Ras via targeting the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway, inhibits development of metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 81727–81740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.H.; Ro, E.J.; Yoon, J.S.; Mizutani, T.; Kang, D.W.; Park, J.C.; Il Kim, T.; Clevers, H.; Choi, K.Y. 5-FU promotes stemness of colorectal cancer via p53-mediated WNT/beta-catenin pathway activation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Cho, Y.H.; Kim, D.S.; Ji, W.; Choi, C.M.; Lee, J.C.; Rho, J.K.; Jeong, G.S. Establishment and Long-Term Expansion of Small Cell Lung Cancer Patient-Derived Tumor Organoids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Mun, H.; Sung, C.O.; Cho, E.J.; Jeon, H.J.; Chun, S.M.; Jung, D.J.; Shin, T.H.; Jeong, G.S.; Kim, D.K.; et al. Patient-derived lung cancer organoids as in vitro cancer models for therapeutic screening. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccelli, I.; Trumpp, A. The evolving concept of cancer and metastasis stem cells. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 198, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreso, A.; Dick, J.E. Evolution of the cancer stem cell model. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, D.; Konstantopoulos, K.; Searson, P.C. The physics of cancer: The role of physical interactions and mechanical forces in metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.X.; Yu, Q. Intra-tumor heterogeneity of cancer cells and its implications for cancer treatment. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrell, R.A.; McGranahan, N.; Bartek, J.; Swanton, C. The causes and consequences of genetic heterogeneity in cancer evolution. Nature 2013, 501, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greaves, M. Cancer stem cells: Back to Darwin? Semin. Cancer Biol. 2010, 20, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, N.; Ridgway, R.A.; van Es, J.H.; van de Wetering, M.; Begthel, H.; van den Born, M.; Danenberg, E.; Clarke, A.R.; Sansom, O.J.; Clevers, H. Crypt stem cells as the cells-of-origin of intestinal cancer. Nature 2009, 457, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Wetering, M.; Francies, H.E.; Francis, J.M.; Bounova, G.; Iorio, F.; Pronk, A.; van Houdt, W.; van Gorp, J.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Kester, L.; et al. Prospective derivation of a living organoid biobank of colorectal cancer patients. Cell 2015, 161, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichtner, I.; Rolff, J.; Soong, R.; Hoffmann, J.; Hammer, S.; Sommer, A.; Becker, M.; Merk, J. Establishment of patient-derived non-small cell lung cancer xenografts as models for the identification of predictive biomarkers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6456–6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.C.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Huang, X.S.; Yang, X.N.; Zhong, W.Z.; Xie, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, M.; Gavine, P.; et al. Establishment of patient-derived non-small cell lung cancer xenograft models with genetic aberrations within EGFR, KRAS and FGFR1: Useful tools for preclinical studies of targeted therapies. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, T.; Kohler, D.; Pintilie, M.; Yanagawa, N.; Pham, N.A.; Li, M.; Panchal, D.; Hui, F.; Meng, F.; Shepherd, F.A.; et al. The ability to form primary tumor xenografts is predictive of increased risk of disease recurrence in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tentler, J.J.; Tan, A.C.; Weekes, C.D.; Jimeno, A.; Leong, S.; Pitts, T.M.; Arcaroli, J.J.; Messersmith, W.A.; Eckhardt, S.G. Patient-derived tumour xenografts as models for oncology drug development. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 9, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.L.; Becker, M.A.; Haluska, P.; Samimi, G. Patient-derived xenograft models to improve targeted therapy in epithelial ovarian cancer treatment. Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopetz, S.; Lemos, R.; Powis, G. The promise of patient-derived xenografts: The best laid plans of mice and men. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5160–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; van Es, J.H.; Snippert, H.J.; Stange, D.E.; Vries, R.G.; van den Born, M.; Barker, N.; Shroyer, N.F.; van de Wetering, M.; Clevers, H. Paneth cells constitute the niche for Lgr5 stem cells in intestinal crypts. Nature 2011, 469, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, N.; Huch, M.; Kujala, P.; van de Wetering, M.; Snippert, H.J.; van Es, J.H.; Sato, T.; Stange, D.E.; Begthel, H.; van den Born, M.; et al. Lgr5(+ve) stem cells drive self-renewal in the stomach and build long-lived gastric units in vitro. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 6, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clevers, H. Modeling Development and Disease with Organoids. Cell 2016, 165, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papapetrou, E.P. Patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells in cancer research and precision oncology. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1392–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siolas, D.; Hannon, G.J. Patient-derived tumor xenografts: Transforming clinical samples into mouse models. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5315–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenot, D.; Guerin, E.; Aguillon-Romain, S.; Pencreach, E.; Schneider, A.; Neuville, A.; Chenard, M.P.; Duluc, I.; Du Manoir, S.; Brigand, C.; et al. Primary tumour genetic alterations and intra-tumoral heterogeneity are maintained in xenografts of human colon cancers showing chromosome instability. J. Pathol. 2006, 208, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Guan, J.; English, J.C.; Flint, J.; Yee, J.; Evans, K.; Murray, N.; Macaulay, C.; Ng, R.T.; Gout, P.W.; et al. Patient-derived first generation xenografts of non-small cell lung cancers: Promising tools for predicting drug responses for personalized chemotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1442–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamb, A. What’s wrong with our cancer models? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hajj, M.; Wicha, M.S.; Benito-Hernandez, A.; Morrison, S.J.; Clarke, M.F. Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3983–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginestier, C.; Korkaya, H.; Dontu, G.; Birnbaum, D.; Wicha, M.S.; Charafe-Jauffret, E. The cancer stem cell: The breast cancer driver. Med. Sci. 2007, 23, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.K.; Clarke, I.D.; Hide, T.; Dirks, P.B. Cancer stem cells in nervous system tumors. Oncogene 2004, 23, 7267–7273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalerba, P.; Clarke, M.F. Cancer stem cells and tumor metastasis: First steps into uncharted territory. Cell Stem Cell 2007, 1, 241–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalerba, P.; Dylla, S.J.; Park, I.K.; Liu, R.; Wang, X.; Cho, R.W.; Hoey, T.; Gurney, A.; Huang, E.H.; Simeone, D.M.; et al. Phenotypic characterization of human colorectal cancer stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10158–10163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.; Pusztai, L.; Swanton, C. Cancer heterogeneity: Implications for targeted therapeutics. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, P.J.; Yachida, S.; Mudie, L.J.; Stephens, P.J.; Pleasance, E.D.; Stebbings, L.A.; Morsberger, L.A.; Latimer, C.; McLaren, S.; Lin, M.L.; et al. The patterns and dynamics of genomic instability in metastatic pancreatic cancer. Nature 2010, 467, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yachida, S.; Jones, S.; Bozic, I.; Antal, T.; Leary, R.; Fu, B.; Kamiyama, M.; Hruban, R.H.; Eshleman, J.R.; Nowak, M.A.; et al. Distant metastasis occurs late during the genetic evolution of pancreatic cancer. Nature 2010, 467, 1114–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlinger, M.; Swanton, C. How Darwinian models inform therapeutic failure initiated by clonal heterogeneity in cancer medicine. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 1139–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonekamp, K.E.; Kretzschmar, K.; Wiener, D.J.; Asra, P.; Derakhshan, S.; Puschhof, J.; Lopez-Iglesias, C.; Peters, P.J.; Basak, O.; Clevers, H. Long-term expansion and differentiation of adult murine epidermal stem cells in 3D organoid cultures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 14630–14638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broutier, L.; Mastrogiovanni, G.; Verstegen, M.M.; Francies, H.E.; Gavarro, L.M.; Bradshaw, C.R.; Allen, G.E.; Arnes-Benito, R.; Sidorova, O.; Gaspersz, M.P.; et al. Human primary liver cancer-derived organoid cultures for disease modeling and drug screening. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankaran, A.; Prasad, K.; Chaudhari, S.; Brand, A.; Satyamoorthy, K. Advances in development and application of human organoids. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.K.; Cho, Y.H.; Cha, P.H.; Yoon, J.S.; Ro, E.J.; Jeong, W.J.; Park, J.; Kim, H.; Il Kim, T.; Min, D.S.; et al. A small molecule approach to degrade RAS with EGFR repression is a potential therapy for KRAS mutation-driven colorectal cancer resistance to cetuximab. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Vries, R.G.; Snippert, H.J.; van de Wetering, M.; Barker, N.; Stange, D.E.; van Es, J.H.; Abo, A.; Kujala, P.; Peters, P.J.; et al. Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature 2009, 459, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Stange, D.E.; Ferrante, M.; Vries, R.G.; Van Es, J.H.; Van den Brink, S.; Van Houdt, W.J.; Pronk, A.; Van Gorp, J.; Siersema, P.D.; et al. Long-term expansion of epithelial organoids from human colon, adenoma, adenocarcinoma, and Barrett’s epithelium. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1762–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkauskas, C.E.; Chung, M.I.; Fioret, B.; Gao, X.; Katsura, H.; Hogan, B.L. Lung organoids: Current uses and future promise. Development 2017, 144, 986–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S.M.; Lim, S.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, S.J.; Yang, S.D.; Yun, M.R.; Kim, C.G.; Gu, S.R.; Park, C.; et al. Modeling Clinical Responses to Targeted Therapies by Patient-Derived Organoids of Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 4397–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Qian, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, L.; Yu, L.; Liu, X.; Wu, G.; Wang, Y.; Luo, W.; Fang, F.; et al. Human Lung Adenocarcinoma-Derived Organoid Models for Drug Screening. iScience 2020, 23, 101411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Francies, H.E.; Secrier, M.; Perner, J.; Miremadi, A.; Galeano-Dalmau, N.; Barendt, W.J.; Letchford, L.; Leyden, G.M.; Goffin, E.K.; et al. Organoid cultures recapitulate esophageal adenocarcinoma heterogeneity providing a model for clonality studies and precision therapeutics. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boj, S.F.; Hwang, C.I.; Baker, L.A.; Chio, I.I.C.; Engle, D.D.; Corbo, V.; Jager, M.; Ponz-Sarvise, M.; Tiriac, H.; Spector, M.S.; et al. Organoid models of human and mouse ductal pancreatic cancer. Cell 2015, 160, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driehuis, E.; van Hoeck, A.; Moore, K.; Kolders, S.; Francies, H.E.; Gulersonmez, M.C.; Stigter, E.C.A.; Burgering, B.; Geurts, V.; Gracanin, A.; et al. Pancreatic cancer organoids recapitulate disease and allow personalized drug screening. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 26580–26590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Tang, S.; Guo, S.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, X.; Han, M.; Liu, Z.; et al. Integrated profiling of human pancreatic cancer organoids reveals chromatin accessibility features associated with drug sensitivity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Vela, I.; Sboner, A.; Iaquinta, P.J.; Karthaus, W.R.; Gopalan, A.; Dowling, C.; Wanjala, J.N.; Undvall, E.A.; Arora, V.K.; et al. Organoid cultures derived from patients with advanced prostate cancer. Cell 2014, 159, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamarthy, S.; Sabaawy, H.E. Patient derived organoids in prostate cancer: Improving therapeutic efficacy in precision medicine. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, N.; de Ligt, J.; Kopper, O.; Gogola, E.; Bounova, G.; Weeber, F.; Balgobind, A.V.; Wind, K.; Gracanin, A.; Begthel, H.; et al. A Living Biobank of Breast Cancer Organoids Captures Disease Heterogeneity. Cell 2018, 172, 373–386.e310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldhammer, N.; Kim, J.; Timmermans-Wielenga, V.; Petersen, O.W. Characterization of organoid cultured human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartfeld, S.; Bayram, T.; van de Wetering, M.; Huch, M.; Begthel, H.; Kujala, P.; Vries, R.; Peters, P.J.; Clevers, H. In vitro expansion of human gastric epithelial stem cells and their responses to bacterial infection. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 126–136.e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.H.N.; Siu, H.C.; Law, S.; Ho, S.L.; Yue, S.S.K.; Tsui, W.Y.; Chan, D.; Chan, A.S.; Ma, S.; Lam, K.O.; et al. A Comprehensive Human Gastric Cancer Organoid Biobank Captures Tumor Subtype Heterogeneity and Enables Therapeutic Screening. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 23, 882–897.e811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuciforo, S.; Fofana, I.; Matter, M.S.; Blumer, T.; Calabrese, D.; Boldanova, T.; Piscuoglio, S.; Wieland, S.; Ringnalda, F.; Schwank, G.; et al. Organoid Models of Human Liver Cancers Derived from Tumor Needle Biopsies. Cell Rep. 2018, 24, 1363–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, H.F.; Hjelmeland, M.E.; Lien, H.; Espedal, H.; Fonnes, T.; Srivastava, A.; Stokowy, T.; Strand, E.; Bozickovic, O.; Stefansson, I.M.; et al. Patient-derived organoids reflect the genetic profile of endometrial tumors and predict patient prognosis. Commun. Med. 2021, 1, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Li, J.Q.; Sulaiman, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, C.Y.; Liu, S.P.; Gao, Z.L.; Cheng, Z.P. Optimization of endometrial cancer organoids establishment by cancer-associated fibroblasts. Neoplasma 2022, 69, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y.H.; Karlsson, K.; Kuo, C.J. Applications of Organoids for Cancer Biology and Precision Medicine. Nat. Cancer 2020, 1, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiihara, M.; Furukawa, T. Application of Patient-Derived Cancer Organoids to Personalized Medicine. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhou, K.; Che, G.; Yang, M.; Su, J.; Shen, C.; Yu, P. Enhanced recovery programs in lung cancer surgery: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cancer Manag. Res. 2017, 9, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Heymach, J.V.; Lippman, S.M. Lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1367–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.R.; Yang, P.; Cassivi, S.D.; Schild, S.E.; Adjei, A.A. Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q. Emerging therapies for small cell lung cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anbazhagan, R.; Tihan, T.; Bornman, D.M.; Johnston, J.C.; Saltz, J.H.; Weigering, A.; Piantadosi, S.; Gabrielson, E. Classification of small cell lung cancer and pulmonary carcinoid by gene expression profiles. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 5119–5122. [Google Scholar]
- Demedts, I.K.; Vermaelen, K.Y.; van Meerbeeck, J.P. Treatment of extensive-stage small cell lung carcinoma: Current status and future prospects. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 35, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, J.; Inoue, M. Application of Cancer Organoid Model for Drug Screening and Personalized Therapy. Cells 2019, 8, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; Xu, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Xie, W.; et al. BMP restricts stemness of intestinal Lgr5(+) stem cells by directly suppressing their signature genes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drost, J.; Karthaus, W.R.; Gao, D.; Driehuis, E.; Sawyers, C.L.; Chen, Y.; Clevers, H. Organoid culture systems for prostate epithelial and cancer tissue. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijkstra, K.K.; Monkhorst, K.; Schipper, L.J.; Hartemink, K.J.; Smit, E.F.; Kaing, S.; de Groot, R.; Wolkers, M.C.; Clevers, H.; Cuppen, E.; et al. Challenges in Establishing Pure Lung Cancer Organoids Limit Their Utility for Personalized Medicine. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.D.; Alexandrov, A.; Kim, J.; Wala, J.; Berger, A.H.; Pedamallu, C.S.; Shukla, S.A.; Guo, G.; Brooks, A.N.; Murray, B.A.; et al. Distinct patterns of somatic genome alterations in lung adenocarcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, N.A.; Radulovich, N.; Ibrahimov, E.; Martins-Filho, S.N.; Li, Q.; Pintilie, M.; Weiss, J.; Raghavan, V.; Cabanero, M.; Denroche, R.E.; et al. Patient-derived tumor xenograft and organoid models established from resected pancreatic, duodenal and biliary cancers. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Korn, J.M.; Ferretti, S.; Monahan, J.E.; Wang, Y.; Singh, M.; Zhang, C.; Schnell, C.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Y.; et al. High-throughput screening using patient-derived tumor xenografts to predict clinical trial drug response. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendoo, D.M.A.; Denroche, R.E.; Zhang, A.; Radulovich, N.; Jang, G.H.; Lemire, M.; Fischer, S.; Chadwick, D.; Lungu, I.M.; Ibrahimov, E.; et al. Whole genomes define concordance of matched primary, xenograft, and organoid models of pancreas cancer. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattie, M.; Christensen, A.; Chang, M.S.; Yeh, W.; Said, S.; Shostak, Y.; Capo, L.; Verlinsky, A.; An, Z.; Joseph, I.; et al. Molecular characterization of patient-derived human pancreatic tumor xenograft models for preclinical and translational development of cancer therapeutics. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 1138–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jiao, D.; Liu, A.; Wu, K. Tumor organoids: Applications in cancer modeling and potentials in precision medicine. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, S.; Tang, P.; Luo, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Ma, X.; Chen, Y.; Bao, Y.; He, X.; et al. Patient-Derived Organoids from Colorectal Cancer with Paired Liver Metastasis Reveal Tumor Heterogeneity and Predict Response to Chemotherapy. Adv. Sci. 2022, e2204097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardoll, D.M. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, R.; Garon, E.B.; Goldman, J.W.; Leighl, N.B.; Hellmann, M.D.; Patnaik, A.; Gandhi, L.; Eder, J.P.; Ahn, M.J.; Horn, L.; et al. Pembrolizumab as first-line therapy for patients with PD-L1-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A phase 1 trial. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.X.; Upadhaya, S.; Tatake, R.; Barkalow, F.; Hubbard-Lucey, V.M. Cancer cell therapies: The clinical trial landscape. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 583–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, J.; Hodi, F.S.; Wolchok, J.D. Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab or Monotherapy in Untreated Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1270–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Baas, P.; Kim, D.W.; Felip, E.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Han, J.Y.; Molina, J.; Kim, J.H.; Arvis, C.D.; Ahn, M.J.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garon, E.B.; Rizvi, N.A.; Hui, R.; Leighl, N.; Balmanoukian, A.S.; Eder, J.P.; Patnaik, A.; Aggarwal, C.; Gubens, M.; Horn, L.; et al. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2018–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, K.K.; Cattaneo, C.M.; Weeber, F.; Chalabi, M.; van de Haar, J.; Fanchi, L.F.; Slagter, M.; van der Velden, D.L.; Kaing, S.; Kelderman, S.; et al. Generation of Tumor-Reactive T Cells by Co-culture of Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes and Tumor Organoids. Cell 2018, 174, 1586–1598.e1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronholm, M.; Feodoroff, M.; Antignani, G.; Martins, B.; Hamdan, F.; Cerullo, V. Patient-Derived Organoids for Precision Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 3149–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreurs, R.; Baumdick, M.E.; Drewniak, A.; Bunders, M.J. In vitro co-culture of human intestinal organoids and lamina propria-derived CD4(+) T cells. STAR Protoc. 2021, 2, 100519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, C.M.; Dijkstra, K.K.; Fanchi, L.F.; Kelderman, S.; Kaing, S.; van Rooij, N.; van den Brink, S.; Schumacher, T.N.; Voest, E.E. Tumor organoid-T-cell coculture systems. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Fan, J.; He, Y.; Xiong, A.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, F.; Li, W.; et al. Single-cell profiling of tumor heterogeneity and the microenvironment in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, Y.-H. Review on Advanced Cancer Modeling for a Cancer Study. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 5352-5362. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44110362
Cho Y-H. Review on Advanced Cancer Modeling for a Cancer Study. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2022; 44(11):5352-5362. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44110362
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Yong-Hee. 2022. "Review on Advanced Cancer Modeling for a Cancer Study" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 44, no. 11: 5352-5362. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44110362
APA StyleCho, Y.-H. (2022). Review on Advanced Cancer Modeling for a Cancer Study. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 44(11), 5352-5362. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44110362




