The Vasohibin Family
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Vasohibin-1 (VASH1)
| Locus | hVASH1 | mVASH1 | hVASH2 | mVASH2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hVASH1 | 14q24.3 | 100% | 91.2% | 52.5% | 51.9% |
| mVASH1 | 12D2 | 100% | 50.9% | 50.9% | |
| hVASH2 | 1q32.3 | 100% | 97.5% | ||
| mVASH2 | 1H6 | 100% |
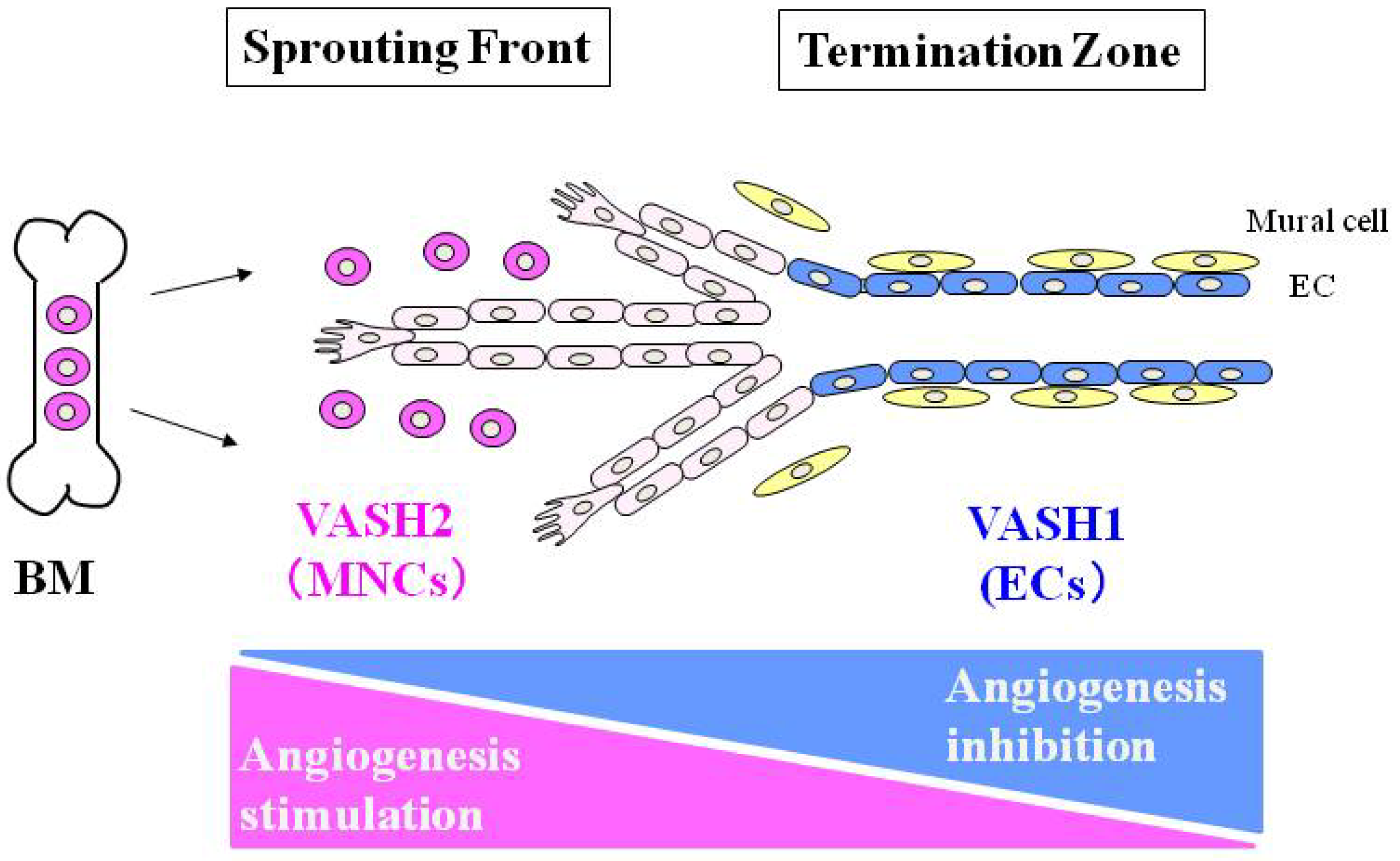
3. Vasohibin-2 (VASH2)
4. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgements
References
- Gerhardt, H.; Betsholtz, C. Endothelial-pericyte interactions in angiogenesis. Cell Tissue Res. 2003, 314, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, Y. Update on endogenous inhibitors of angiogenesis. Endothelium 2006, 13, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, M.; Sato, Y. cDNA microarray analysis of the gene expression profile of VEGF-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Angiogenesis 2001, 4, 289–298. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, K.; Hasegawa, Y.; Yamashita, H.; Shimizu, K.; Ding, Y.; Abe, M.; Ohta, H.; Imagawa, K.; Hojo, K.; Maki, H.; Sonoda, H.; Sato, Y. Vasohibin as an endothelium-derived negative feedback regulator of angiogenesis. J. Clin. Invest. 2004, 114, 898–907. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, K.; Watanabe, K.; Yamashita, H.; Abe, M.; Yoshimatsu, H.; Ohta, H.; Sonoda, H.; Sato, Y. Gene regulation of a novel angiogenesis inhibitor, vasohibin, in endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 327, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kern, J.; Bauer, M.; Rychli, K.; Wojta, J.; Ritsch, A.; Gastl, G.; Gunsilius, E.; Untergasser, G. Alternative splicing of vasohibin-1 generates an inhibitor of endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and capillary tube formation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonoda, H.; Ohta, H.; Watanabe, K.; Yamashita, H.; Kimura, H.; Sato, Y. Multiple processing forms and their biological activities of a novel angiogenesis inhibitor vasohibin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 342, 640–646. [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya, T.; Watanabe, K.; Yamashita, H.; Shimizu, K.; Miyashita, H.; Abe, M.; Moriya, T.; Ohta, H.; Sonoda, H.; Shimosegawa, T.; Tabayashi, K.; Sato, Y. Isolation and characterization of vasohibin-2 as a homologue of VEGF-inducible endothelium-derived angiogenesis inhibitor vasohibin. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar]
- Nimmagadda, S.; Geetha-Loganathan, P.; Pröls, F.; Scaal, M.; Christ, B.; Huang, R. Expression pattern of vasohibin during chick development. Dev. Dyn. 2007, 236, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar]
- Naito, H.; Kidoya, H.; Sato, Y.; Takakura, N. Induction and expression of anti-angiogenic vasohibins in the hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell population. J. Biochem. 2009, 145, 653–659. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, H.; Miyashita, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Watanabe, K.; Sonoda, H.; Ohta, H.; Fujiwara, T.; Shimosegawa, T.; Sato, Y. Distinctive localization and opposed roles of vasohibin-1 and vasohibin-2 in the regulation of angiogenesis. Blood 2009, 113, 4810–4818. [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita, H.; Abe, M.; Watanabe, K.; Shimizu, K.; Moriya, T.; Sato, A.; Satomi, S.; Ohta, H.; Sonoda, H.; Sato, Y. Vasohibin prevents arterial neointimal formation through angiogenesis inhibition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 345, 919–925. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinaga, K.; Ito, K.; Moriya, T.; Nagase, S.; Takano, T.; Niikura, H.; Yaegashi, N.; Sato, Y. Expression of vasohibin as a novel endothelium-derived angiogenesis inhibitor in endometrial cancer. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 914–919. [Google Scholar]
- Wakusawa, R.; Abe, T.; Sato, H.; Yoshida, M.; Kunikata, H.; Sato, Y.; Nishida, K. Expression of vasohibin, an antiangiogenic factor, in human choroidal neovascular membranes. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 146, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamaki, K.; Moriya, T.; Sato, Y.; Ishida, T.; Maruo, Y.; Yoshinaga, K.; Ohuchi, N.; Sasano, H. Vasohibin-1 in human breast carcinoma: A potential negative feedback regulator of angiogenesis. Cancer Sci. 2008, 100, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, H.; Abe, T.; Wakusawa, R.; Asai, N.; Kunikata, H.; Ohta, H.; Sonoda, H.; Sato, Y.; Nishida, K. Vitreous levels of vasohibin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 359–361. [Google Scholar]
- Hosaka, T.; Kimura, H.; Heishi, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Miyashita, H.; Ohta, H.; Sonoda, H.; Moriya, T.; Suzuki, S.; Kondo, T.; Sato, Y. Vasohibin-1 expressed in endothelium of tumor vessels regulates angiogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 430–439. [Google Scholar]
- Miyake, K.; Nishida, K.; Kadota, Y.; Yamasaki, H.; Nasu, T.; Saitou, D.; Tanabe, K.; Sonoda, H.; Sato, Y.; Maeshima, Y.; Makino, H. Inflammatory cytokine-induced expression of vasohibin-1 by rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Acta Med. Okayama 2009, 63, 349–358. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Yang, X.; Xiao, W.H.; Hackett, S.F.; Sato, Y.; Campochiaro, P.A. Vasohibin is up-regulated by VEGF in the retina and suppresses VEGF receptor 2 and retinal neovascularization. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 723–725. [Google Scholar]
- Kern, J.; Steurer, M.; Gastl, G.; Gunsilius, E.; Untergasser, G. Vasohibin inhibits angiogenic sprouting in vitro and supports vascular maturation processes in vivo. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhou, K.; Wang, S.; Shi, Z.; Yang, Z. Recombinant adenovirus encoding vasohibin prevents tumor angiogenesis and inhibits tumor growth. Cancer Sci. 2009. (Epub ahead of print).. [Google Scholar]
- Hawighorst, T.; Oura, H.; Streit, M.; Janes, L.; Nguyen, L.; Brown, L.F.; Oliver, G.; Jackson, D.G.; Detmar, M. Thrombospondin-1 selectively inhibits early-stage carcinogenesis and angiogenesis but not tumor lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis in transgenic mice. Oncogene 2002, 21, 7945–7956. [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto, S.; Morifuji, M.; Katakura, Y.; Ohishi, M.; Nakamura, S. Endostatin inhibits lymph node metastasis by a down-regulation of the vascular endothelial growth factor C expression in tumor cells. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2005, 22, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Brideau, G.; Makinen, M.J.; Elamaa, H.; Tu, H.; Nilsson, G.; Alitalo, K.; Pihlajaniemi, T.; Heljasvaara, R. Endostatin overexpression inhibits lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis in mice. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11528–11535. [Google Scholar]
- Heishi, T.; Hosaka, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Miyashita, H.; Oike, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Nakamura, T.; Arioka, S.; Mitsuda, Y.; Takakura, T.; Hojo, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Yamauchi, C.; Ohta, H.; Sonoda, H.; Sato, Y. Endogenous angiogenesis inhibitor vasohibin1 exhibits a broad-spectrum anti-lymphangiogenic activity and suppresses lymph node metastasis. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, in press.. [Google Scholar]
- Venancio, T.M.; DeMarco, R.; Almeida, G.T.; Oliveira, K.C.; Setubal, J.C.; Verjovski-Almeida, S. Analysis of Schistosoma mansoni genes shared with Deuterostomia and with possible roles in host interactions. BMC Genomics 2007, 8, 407. [Google Scholar]
- Phng, L.K.; Gerhardt, H. Angiogenesis: A team effort coordinated by notch. Dev. Cell 2009, 16, 196–208. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Sato, Y. The Vasohibin Family. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 433-440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3020433
Sato Y. The Vasohibin Family. Pharmaceuticals. 2010; 3(2):433-440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3020433
Chicago/Turabian StyleSato, Yasufumi. 2010. "The Vasohibin Family" Pharmaceuticals 3, no. 2: 433-440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3020433
APA StyleSato, Y. (2010). The Vasohibin Family. Pharmaceuticals, 3(2), 433-440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3020433





