Allosteric Modulation of G Protein Coupled Receptors by Cytoplasmic, Transmembrane and Extracellular Ligands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
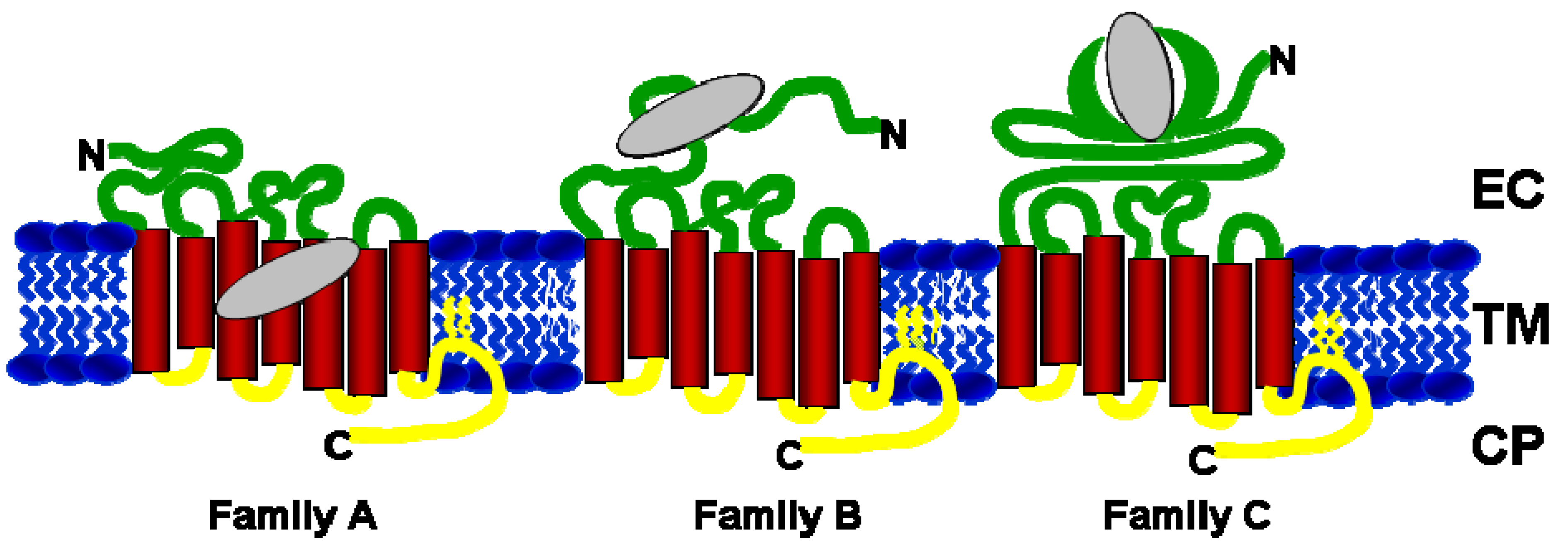
2. Orthosteric and Allosteric Ligand Binding Sites in GPCRs
| GPCR Family | Receptor Details | Endogenous ligand binding site | Allosteric Ligand binding site | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family A | Adenosine A1, A2A, A3 | TM helices 3, 5, 6 and 7 | EC domain (top of helices 6 & 7) | [19,20] |
| Adrenoreceptors α-1, -2A, -2B, -2D | TM helices 2, 3, 5, 6 and 7 | |||
| Chemokines CXCR1-4, CCR1,3,5 | EC domain | TM and CP side | [24,25] | |
| Dopamine D1, D2 | TM helices 2, 3, 5, 6 and 7 | |||
| Muscarinic M1-M5 | TM helices 3, 5, 6 and 7 | EC and CP domains | [36,37] | |
| Serotonin | TM helices 3, 5, 6 and 7 | |||
| Rhodopsin | TM helices 3, 5, 6 and 7 | CP domain | [43,44,45,46] | |
| Family B | Corticotropin Releasing Factor 1 | EC domain | TM helices 3,5 | [26,27] |
| Glucagon | EC domain | |||
| Glucagon Like Peptide-1 | EC domain | TM helices 2,3 | [28] | |
| Family C | Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors 1-5 and 7 | EC domain | TM helices 3, 5, 6 and 7 | [29,30,31,32] |
| Calcium Sensing Receptor | EC domain | TM helices 3, 5, 6, and 7 | [33,34,35] | |
| GABA-B | EC domain |
3. An Allosteric Ligand Binding Pocket in the Cytoplasmic Domain of Rhodopsin
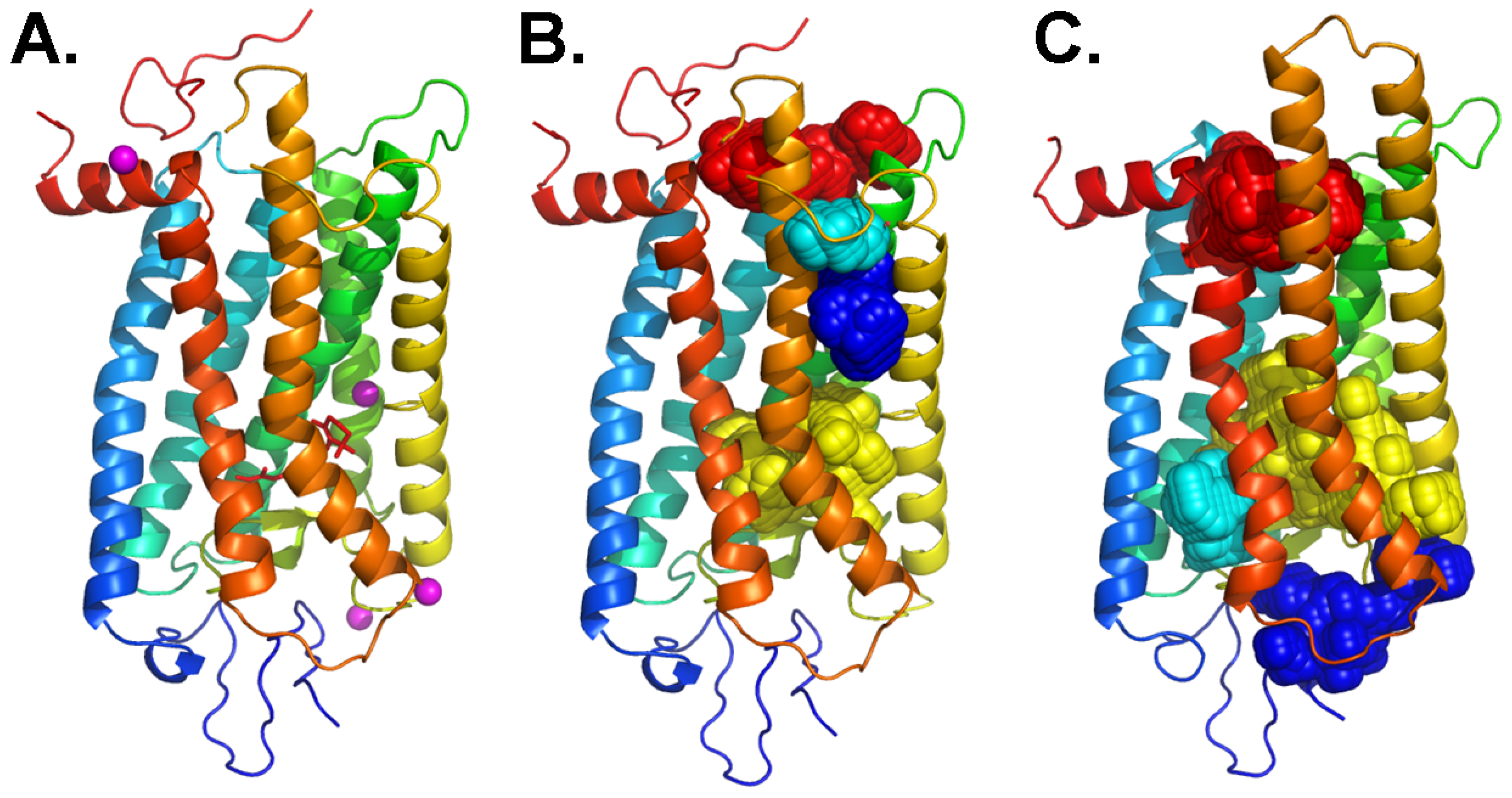
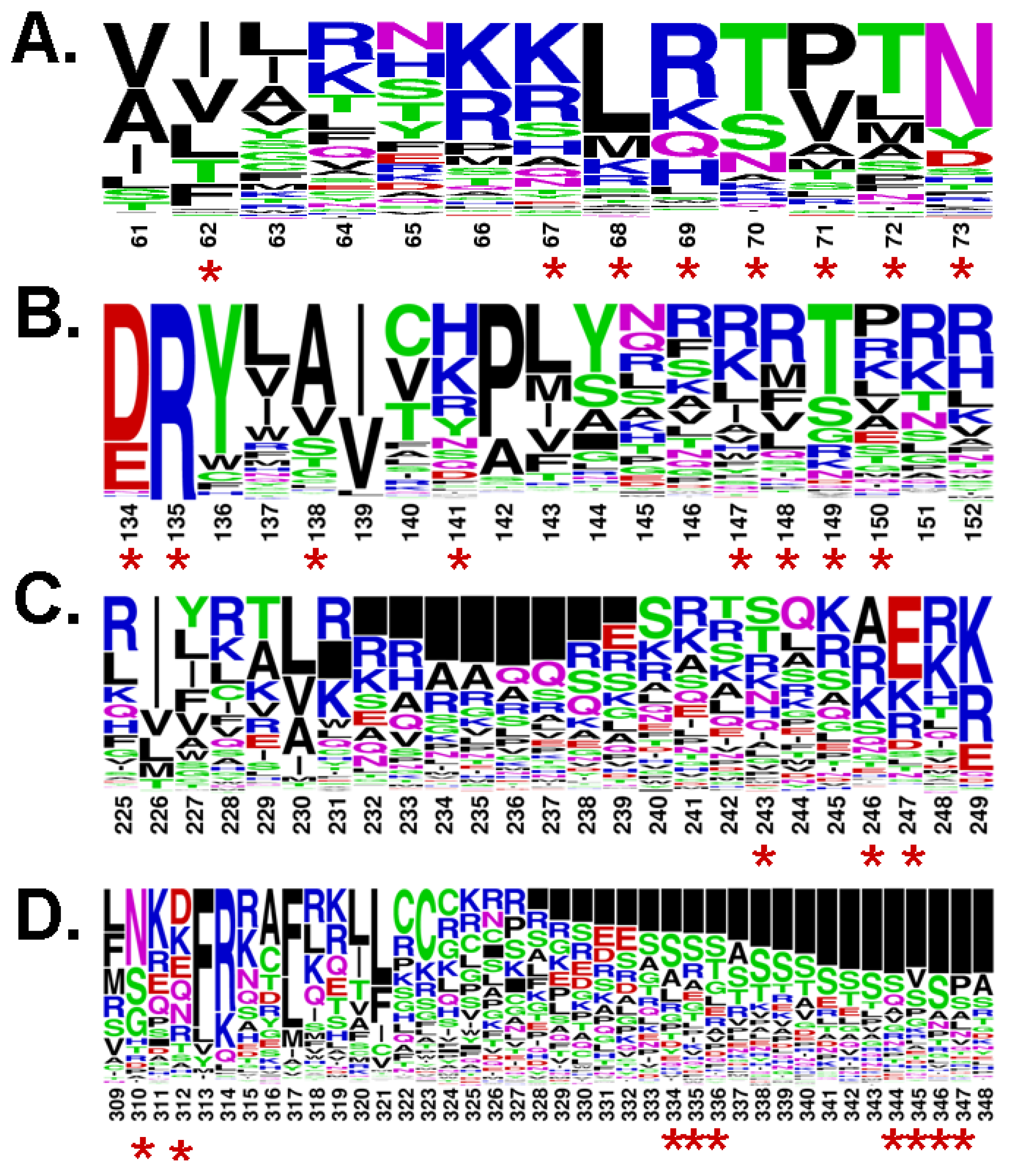
4. Analogy between the Orthosteric Transmembrane Binding Pocket in Rhodopsin and the Allosteric Binding Pocket in Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors: Insight into the Molecular Mechanisms of Allosteric Regulation
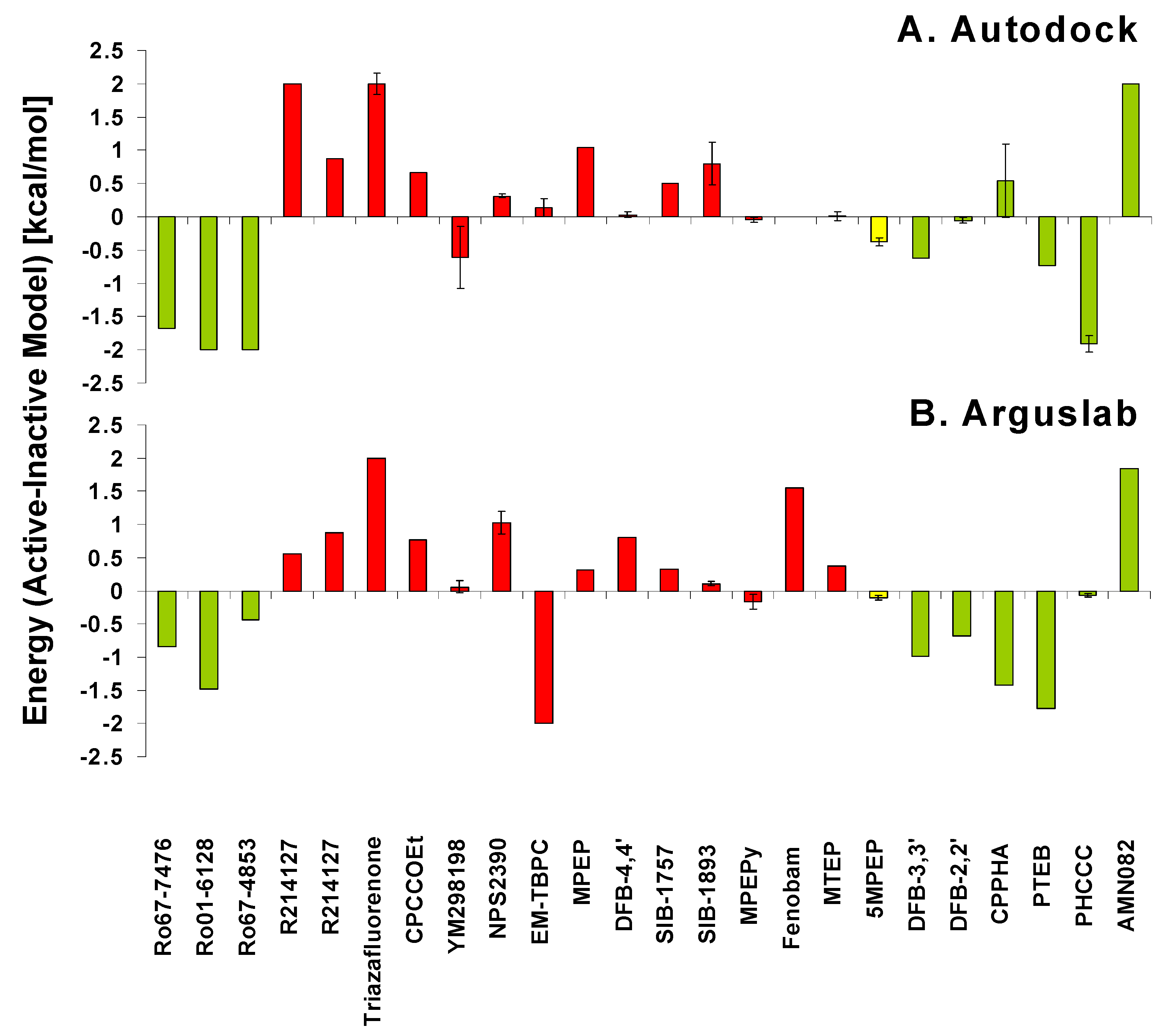
5. Pathways of Allosteric Communication
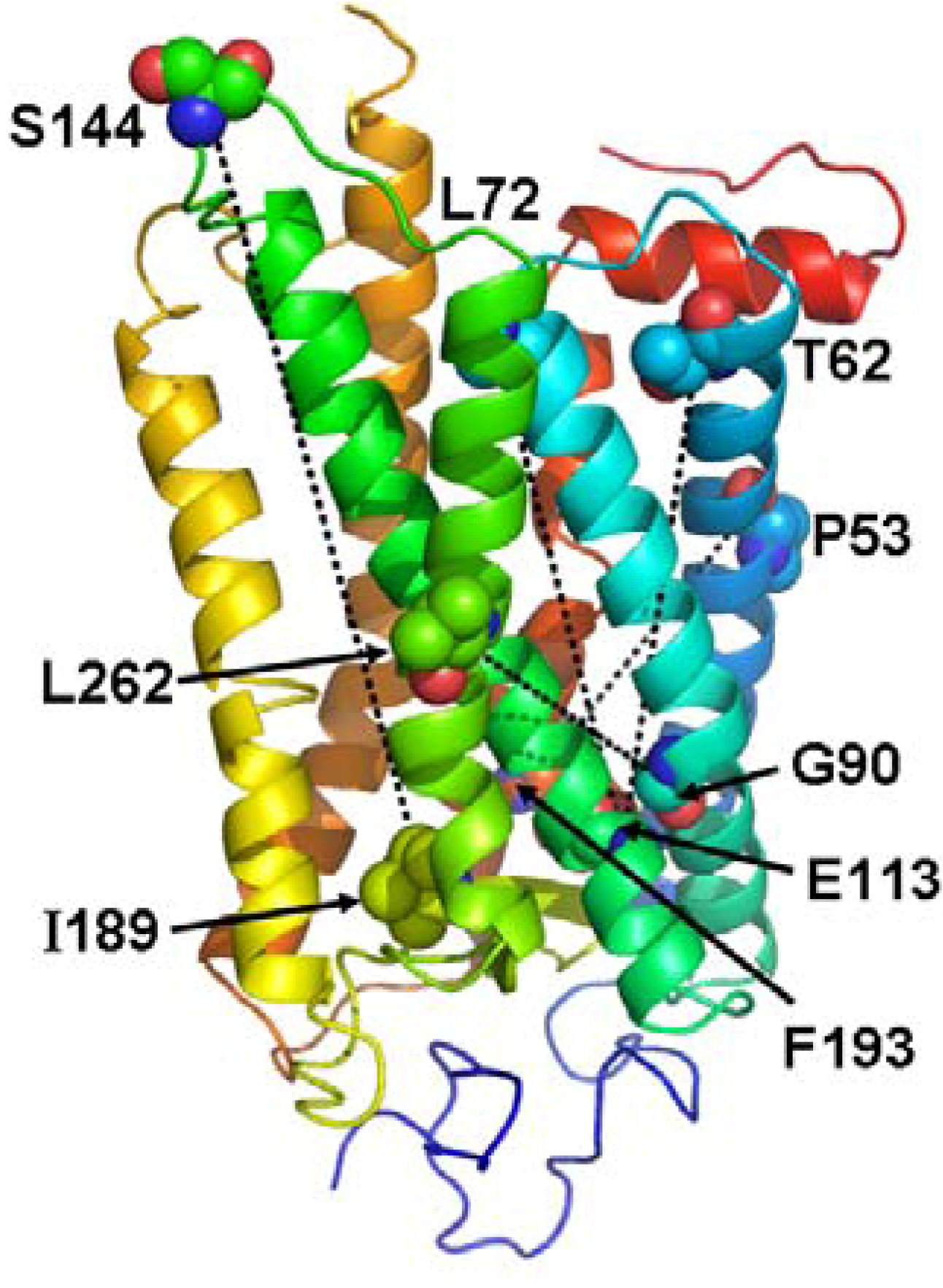
6. Conclusions
Abbreviations
| GPCRs | G protein coupled receptors |
| TM | Transmembrane |
| EC | Extracellular |
| CP | Cytoplasmic |
| C3G | Cyanidin-3-glucoside |
| DFB-3-3’ | 3,3’-difluorobenzaldazine |
| NHERF1 | Na+/H+ exchange regulatory factor 1 |
| PTH | Parathyroid hormone receptor |
| Ce6 | Chlorin e6 |
| mGluRs | Metabotropic glutamate receptors |
| ANM | Anisotropic Network Model |
| MSA | Multiple Sequence Alignment |
Acknowledgements
References
- Kolakowski, L.F., Jr. GCRDb: A G-protein-coupled receptor database. Receptors Channels 1994, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Vassilatis, D.K.; Hohmann, J.G.; Zeng, H.; Li, F.; Ranchalis, J.E.; Mortrud, M.T.; Brown, A.; Rodriguez, S.S.; Weller, J.R.; Wright, A.C.; Bergmann, J.E.; Gaitanaris, G.A. The G protein-coupled receptor repertoires of human and mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4903–4908. [Google Scholar]
- Finn, R.D.; Tate, J.; Mistry, J.; Coggill, P.C.; Sammut, S.J.; Hotz, H.R.; Ceric, G.; Forslund, K.; Eddy, S.R.; Sonnhammer, E.L.; Bateman, A. The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D281–D288. [Google Scholar]
- Winzell, M.S.; Ahren, B. G-protein-coupled receptors and islet function-implications for treatment of type 2 diabetes. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 116, 437–448. [Google Scholar]
- Dorsam, R.T.; Gutkind, J.S. G-protein-coupled receptors and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 79–94. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Huang, S.; Peng, S.B. Overexpression of G protein-coupled receptors in cancer cells: Involvement in tumor progression. Int. J. Oncol. 2005, 27, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Yowell, C.W.; Daaka, Y. G protein-coupled receptors provide survival signals in prostate cancer. Clin. Prostate Cancer 2002, 1, 177–181. [Google Scholar]
- Conn, P.J.; Christopoulos, A.; Lindsley, C.W. Allosteric modulators of GPCRs: A novel approach for the treatment of CNS disorders. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2009, 8, 41–54. [Google Scholar]
- Yeo, G.S.; Siddle, K. Attractin' more attention - new pieces in the obesity puzzle? Biochem. J. 2003, 376, e7–e8. [Google Scholar]
- Lomas-Neira, J.; Ayala, A. Pepducins: An effective means to inhibit GPCR signaling by neutrophils. Trends Immunol. 2005, 26, 619–621. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.M.; Insel, P.A. GPCR expression in the heart; "new" receptors in myocytes and fibroblasts. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2004, 14, 94–99. [Google Scholar]
- Fredriksson, R.; Lagerstrom, M.C.; Lundin, L.G.; Schioth, H.B. The G-protein-coupled receptors in the human genome form five main families. Phylogenetic analysis, paralogon groups, and fingerprints. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 63, 1256–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, A. Changing Face of GPCR Drug Discovery: Opportunistic Future. In Pharma Focus Asia; Ochre Media Pvt. Lts.: Hyderabad, India, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Christopoulos, A.; May, L.T.; Avlani, V.A.; Sexton, P.M. G-protein-coupled receptor allosterism: The promise and the problem(s). Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2004, 32, 873–877. [Google Scholar]
- May, L.T.; Leach, K.; Sexton, P.M.; Christopoulos, A. Allosteric modulation of G protein-coupled receptors. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007, 47, 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Raddatz, R.; Schaffhauser, H.; Marino, M.J. Allosteric approaches to the targeting of G-protein-coupled receptors for novel drug discovery: A critical assessment. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 383–391. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, A.A.; Spalding, T.A. Allosteric modulation of G-protein coupled receptors. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 21, 407–420. [Google Scholar]
- Langmead, C.J.; Christopoulos, A. Allosteric agonists of 7TM receptors: Expanding the pharmacological toolbox. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 27, 475–481. [Google Scholar]
- Christopoulos, A.; Lanzafame, A.; Mitchelson, F. Allosteric interactions at muscarinic cholinoceptors. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1998, 25, 185–194. [Google Scholar]
- Christopoulos, A.; Kenakin, T. G protein-coupled receptor allosterism and complexing. Pharmacol. Rev. 2002, 54, 323–374. [Google Scholar]
- Krejci, A.; Tucek, S. Changes of cooperativity between N-methylscopolamine and allosteric modulators alcuronium and gallamine induced by mutations of external loops of muscarinic M(3) receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 60, 761–767. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.P.; Prilla, S.; Mohr, K.; Ellis, J. Critical amino acid residues of the common allosteric site on the M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor: More similarities than differences between the structurally divergent agents gallamine and bis(ammonio)alkane-type hexamethylene-bis-[dimethyl-(3-phthalimidopropyl)ammonium]dibromide. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 68, 769–778. [Google Scholar]
- Prilla, S.; Schrobang, J.; Ellis, J.; Holtje, H.D.; Mohr, K. Allosteric interactions with muscarinic acetylcholine receptors: Complex role of the conserved tryptophan M2422Trp in a critical cluster of amino acids for baseline affinity, subtype selectivity, and cooperativity. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 70, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dragic, T.; Trkola, A.; Thompson, D.A.; Cormier, E.G.; Kajumo, F.A.; Maxwell, E.; Lin, S.W.; Ying, W.; Smith, S.O.; Sakmar, T.P.; Moore, J.P. A binding pocket for a small molecule inhibitor of HIV-1 entry within the transmembrane helices of CCR5. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5639–5644. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, G.; Jones, C.; Wreggett, K.A. An intracellular allosteric site for a specific class of antagonists of the CC chemokine G protein-coupled receptors CCR4 and CCR5. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 73, 855–867. [Google Scholar]
- Liaw, C.W.; Grigoriadis, D.E.; Lorang, M.T.; De Souza, E.B.; Maki, R.A. Localization of agonist- and antagonist-binding domains of human corticotropin-releasing factor receptors. Mol. Endocrinol. 1997, 11, 2048–2053. [Google Scholar]
- Hoare, S.R.; Sullivan, S.K.; Ling, N.; Crowe, P.D.; Grigoriadis, D.E. Mechanism of corticotropin-releasing factor type I receptor regulation by nonpeptide antagonists. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 63, 751–765. [Google Scholar]
- Cascieri, M.A.; Koch, G.E.; Ber, E.; Sadowski, S.J.; Louizides, D.; de Laszlo, S.E.; Hacker, C.; Hagmann, W.K.; MacCoss, M.; Chicchi, G.G.; Vicario, P.P. Characterization of a novel, non-peptidyl antagonist of the human glucagon receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 8694–8697. [Google Scholar]
- Malherbe, P.; Kratochwil, N.; Knoflach, F.; Zenner, M.T.; Kew, J.N.; Kratzeisen, C.; Maerki, H.P.; Adam, G.; Mutel, V. Mutational analysis and molecular modeling of the allosteric binding site of a novel, selective, noncompetitive antagonist of the metabotropic glutamate 1 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 8340–8347. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malherbe, P.; Kratochwil, N.; Zenner, M.T.; Piussi, J.; Diener, C.; Kratzeisen, C.; Fischer, C.; Porter, R.H. Mutational analysis and molecular modeling of the binding pocket of the metabotropic glutamate 5 receptor negative modulator 2-methyl-6-(phenylethynyl)-pyridine. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 64, 823–832. [Google Scholar]
- Goudet, C.; Gaven, F.; Kniazeff, J.; Vol, C.; Liu, J.; Cohen-Gonsaud, M.; Acher, F.; Prezeau, L.; Pin, J.P. Heptahelical domain of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 behaves like rhodopsin-like receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 378–383. [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien, J.A.; Lemaire, W.; Chen, T.B.; Chang, R.S.; Jacobson, M.A.; Ha, S.N.; Lindsley, C.W.; Schaffhauser, H.J.; Sur, C.; Pettibone, D.J.; Conn, P.J.; Williams, D.L., Jr. A family of highly selective allosteric modulators of the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 64, 731–740. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Mora, S.; Colussi, G.; Proverbio, M.C.; Jones, K.A.; Bolzoni, L.; De Ferrari, M.E.; Civati, G.; Spiegel, A.M. Autosomal dominant hypocalcemia caused by a novel mutation in the loop 2 region of the human calcium receptor extracellular domain. J. Bone Miner Res. 2002, 17, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar]
- Miedlich, S.U.; Gama, L.; Seuwen, K.; Wolf, R.M.; Breitwieser, G.E. Homology modeling of the transmembrane domain of the human calcium sensing receptor and localization of an allosteric binding site. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 7254–7263. [Google Scholar]
- Petrel, C.; Kessler, A.; Maslah, F.; Dauban, P.; Dodd, R.H.; Rognan, D.; Ruat, M. Modeling and mutagenesis of the binding site of Calhex 231, a novel negative allosteric modulator of the extracellular Ca(2+)-sensing receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 49487–49494. [Google Scholar]
- Birdsall, N.J.; Lazareno, S. Allosterism at muscarinic receptors: Ligands and mechanisms. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2005, 5, 523–543. [Google Scholar]
- Mohr, K.; Trankle, C.; Holzgrabe, U. Structure/activity relationships of M2 muscarinic allosteric modulators. Receptors Channels 2003, 9, 229–240. [Google Scholar]
- Kisselev, O.G.; Meyer, C.K.; Heck, M.; Ernst, O.P.; Hofmann, K.P. Signal transfer from rhodopsin to the G-protein: evidence for a two-site sequential fit mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 4898–4903. [Google Scholar]
- Arimoto, R.; Kisselev, O.G.; Makara, G.M.; Marshall, G.R. Rhodopsin-transducin interface: studies with conformationally constrained peptides. Biophys. J. 2001, 81, 3285–3293. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Yang, Y.; Abou-Samra, A.B.; Friedman, P.A. NHERF1 regulates parathyroid hormone receptor desensitization: interference with beta-arrestin binding. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 75, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon, W.B.; Syme, C.A.; Bisello, A.; Magyar, C.E.; Rochdi, M.D.; Parent, J.L.; Weinman, E.J.; Abou-Samra, A.B.; Friedman, P.A. Activation-independent parathyroid hormone receptor internalization is regulated by NHERF1 (EBP50). J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 43787–43796. [Google Scholar]
- Balem, F.; Yanamala, N.; Klein-Seetharaman, J. Additive effects of chlorin e6 and metal ion binding on the thermal stability of rhodopsin in vitro. Photochem. Photobiol. 2009, 85, 471–478. [Google Scholar]
- Tirupula, K.C.; Balem, F.; Yanamala, N.; Klein-Seetharaman, J. pH-dependent interaction of rhodopsin with cyanidin-3-glucoside. 2. Functional aspects. Photochem. Photobiol. 2009, 85, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yanamala, N.; Tirupula, K.C.; Balem, F.; Klein-Seetharaman, J. pH-dependent interaction of rhodopsin with cyanidin-3-glucoside. 1. Structural aspects. Photochem. Photobiol. 2009, 85, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taylor, C.M.; Barda, Y.; Kisselev, O.G.; Marshall, G.R. Modulating G-protein coupled receptor/G-protein signal transduction by small molecules suggested by virtual screening. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 5297–5303. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, C.M.; Rockweiler, N.B.; Liu, C.; Rikimaru, L.; Tunemalm, A.; Kisselev, O.G.; Marshall, G.R. Using Ligand-Based Virtual Screening to Allosterically Stabilize the Activated State of a GPCR. Chem. Biol. Drug Design 2010, 75, 325–332. [Google Scholar]
- Hendlich, M.; Rippmann, F.; Barnickel, G. LIGSITE: Automatic and efficient detection of potential small molecule-binding sites in proteins. J. Mol. Graph. Model 1997, 15, 359-363, 389. [Google Scholar]
- Washington, I.; Brooks, C.; Turro, N.J.; Nakanishi, K. Porphyrins as photosensitizers to enhance night vision. J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9892–9893. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Tachibanaki, S.; Kawamura, S.; Hirayama, M. Stimulatory effect of cyanidin 3-glycosides on the regeneration of rhodopsin. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 3560–3563. [Google Scholar]
- Douglas, R.H.; Partridge, J.C.; Dulai, K.S.; Hunt, D.M.; Mullineaux, C.W.; Hynninen, P.H. Enhanced retinal longwave sensitivity using a chlorophyll-derived photosensitiser in Malacosteus niger, a deep-sea dragon fish with far red bioluminescence. Vision Res. 1999, 39, 2817–2832. [Google Scholar]
- Isayama, T.; Alexeev, D.; Makino, C.L.; Washington, I.; Nakanishi, K.; Turro, N.J. An accessory chromophore in red vision. Nature 2006, 443, 649. [Google Scholar]
- Washington, I. Chlorophyll derivatives as visual pigments for super vision in the red. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2007, 6, 775–779. [Google Scholar]
- Holst, B.; Elling, C.E.; Schwartz, T.W. Metal ion-mediated agonism and agonist enhancement in melanocortin MC1 and MC4 receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 47662–47670. [Google Scholar]
- Holst, B.; Schwartz, T.W. Molecular mechanism of agonism and inverse agonism in the melanocortin receptors: Zn(2+) as a structural and functional probe. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 2003, 994, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan, G.J.; Holloway, D.E.; Colvin, R.A.; Campanella, G.K.; Papageorgiou, A.C.; Luster, A.D.; Acharya, K.R. Crystal structures of oligomeric forms of the IP-10/CXCL10 chemokine. Structure 2003, 11, 521–532. [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan, G.J.; Holloway, D.E.; Veluraja, K.; Acharya, K.R. Atomic resolution (0.98 A) structure of eosinophil-derived neurotoxin. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 3341–3352. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shuster, T.A.; Nagy, A.K.; Conly, D.C.; Farber, D.B. Direct zinc binding to purified rhodopsin and disc membranes. Biochem. J. 1992, 282 (Pt 1), 123–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stojanovic, A.; Stitham, J.; Hwa, J. Critical role of transmembrane segment zinc binding in the structure and function of rhodopsin. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 35932–35941. [Google Scholar]
- Gleim, S.; Stojanovic, A.; Arehart, E.; Byington, D.; Hwa, J. Conserved rhodopsin intradiscal structural motifs mediate stabilization: effects of zinc. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 1793–1800. [Google Scholar]
- Crooks, G.E.; Hon, G.; Chandonia, J.M.; Brenner, S.E. WebLogo: A sequence logo generator. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar]
- Scheerer, P.; Park, J.H.; Hildebrand, P.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Krausz, N.; Choe, H.-W.; Hofmann, K.P.; Ernst, O.P. Crystal structure of opsin in its G-protein-interacting conformation. Nature 2008, 455, 497–502. [Google Scholar]
- Illingworth, C.J.R.; Scott, P.D.; Parkes, K.E.B.; Snell, C.R.; Campbell, M.P.; Reynolds, C.A. Connectivity and binding-site recognition: Applications relevant to drug design. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 2677–2688. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, S.M.; Bhola, N.E.; Zhang, Q.; Contrucci, S.C.; Wentzel, A.L.; Freilino, M.L.; Gooding, W.E.; Siegfried, J.M.; Chan, D.C.; Grandis, J.R. Cross-talk between G protein-coupled receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathways contributes to growth and invasion of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11831–11839. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Bhola, N.E.; Lui, V.W.; Siwak, D.R.; Thomas, S.M.; Gubish, C.T.; Siegfried, J.M.; Mills, G.B.; Shin, D.; Grandis, J.R. Antitumor mechanisms of combined gastrin-releasing peptide receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor targeting in head and neck cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 1414–1424. [Google Scholar]
- Lui, V.W.; Thomas, S.M.; Zhang, Q.; Wentzel, A.L.; Siegfried, J.M.; Li, J.Y.; Grandis, J.R. Mitogenic effects of gastrin-releasing peptide in head and neck squamous cancer cells are mediated by activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Oncogene 2003, 22, 6183–6193. [Google Scholar]
- Gschwind, A.; Prenzel, N.; Ullrich, A. Lysophosphatidic acid-induced squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation and motility involves epidermal growth factor receptor signal transactivation. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 6329–6236. [Google Scholar]
- Acher, F.C.; Bertrand, H.O. Amino acid recognition by Venus flytrap domains is encoded in an 8-residue motif. Biopolymers 2005, 80, 357–366. [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, C.J.; Bures, M.; Johnson, M.P.; Linden, A.M.; Monn, J.A.; Schoepp, D.D. Metabotropic glutamate receptors as novel targets for anxiety and stress disorders. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 131–144. [Google Scholar]
- Kew, J.N. Positive and negative allosteric modulation of metabotropic glutamate receptors: emerging therapeutic potential. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 104, 233–244. [Google Scholar]
- Dryja, T.P.; McGee, T.L.; Berson, E.L.; Fishman, G.A.; Sandberg, M.A.; Alexander, K.R.; Derlacki, D.J.; Rajagopalan, A.S. Night blindness and abnormal cone electroretinogram ON responses in patients with mutations in the GRM6 gene encoding mGluR6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4884–4889. [Google Scholar]
- Parmentier, M.L.; Prezeau, L.; Bockaert, J.; Pin, J.P. A model for the functioning of family 3 GPCRs. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2002, 23, 268–274. [Google Scholar]
- Yanamala, N.; Tirupula, K.C.; Klein-Seetharaman, J. Preferential binding of allosteric modulators to active and inactive conformational states of metabotropic glutamate receptors. BMC Bioinformatics 2008, 9 (Suppl. 1), S16. [Google Scholar]
- Lockless, S.W.; Ranganathan, R. Evolutionarily conserved pathways of energetic connectivity in protein families. Science 1999, 286, 295–299. [Google Scholar]
- Russ, W.P.; Lowery, D.M.; Mishra, P.; Yaffe, M.B.; Ranganathan, R. Natural-like function in artificial WW domains. Nature 2005, 437, 579–583. [Google Scholar]
- Socolich, M.; Lockless, S.W.; Russ, W.P.; Lee, H.; Gardner, K.H.; Ranganathan, R. Evolutionary information for specifying a protein fold. Nature 2005, 437, 512–518. [Google Scholar]
- Bateman, A.; Birney, E.; Cerruti, L.; Durbin, R.; Etwiller, L.; Eddy, S.R.; Griffiths-Jones, S.; Howe, K.L.; Marshall, M.; Sonnhammer, E.L. The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 276–280. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, J.; Ramakrishnan, N.; Bailey-Kellogg, C. Protein design by sampling an undirected graphical model of residue constraints. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2009, 6, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, S.; Kamisetty, H.; Carbonell, J.C.; Langmead, C.J. Structure Learning for Generative Models of Protein Fold Families. In Research Showcase; Technical Report; Carnegie Mellon University: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Balakrishnan, S.; Kamisetty, H.; Carbonell, J.C.; Langmead, C.J. Learning Generative Models for Protein Fold Families. In Research Showcase; Technical Report; Carnegie Mellon University: Pittsburgh, PA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Moitra, S.; Yanamala, N.; Tastan, O.; Singh, I.; Langmead, C.J.; Klein-Seetharaman, J. Analogies between Structural and Systems Biology and Systems Engineering in Dynamic Environments. In IEEE Conference on Systems of Systems Engineering; IEEE: Loughborough University, Loughborough, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Okada, T.; Fujiyoshi, Y.; Silow, M.; Navarro, J.; Landau, E.M.; Shichida, Y. Functional role of internal water molecules in rhodopsin revealed by X-ray crystallography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 5982–5987. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Yanamala, N.; Klein-Seetharaman, J. Allosteric Modulation of G Protein Coupled Receptors by Cytoplasmic, Transmembrane and Extracellular Ligands. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 3324-3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3103324
Yanamala N, Klein-Seetharaman J. Allosteric Modulation of G Protein Coupled Receptors by Cytoplasmic, Transmembrane and Extracellular Ligands. Pharmaceuticals. 2010; 3(10):3324-3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3103324
Chicago/Turabian StyleYanamala, Naveena, and Judith Klein-Seetharaman. 2010. "Allosteric Modulation of G Protein Coupled Receptors by Cytoplasmic, Transmembrane and Extracellular Ligands" Pharmaceuticals 3, no. 10: 3324-3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3103324
APA StyleYanamala, N., & Klein-Seetharaman, J. (2010). Allosteric Modulation of G Protein Coupled Receptors by Cytoplasmic, Transmembrane and Extracellular Ligands. Pharmaceuticals, 3(10), 3324-3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3103324




